Prompting Strategy Use and Beyond: Examining the Relationships between Elaboration, Quantity, and Diversity of Learning Strategies on Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The SOI Model of Generative Learning
1.2. Effectiveness of Prompting Elaboration Strategy Use on Learning Outcomes
1.3. What Additional Strategies Are Learners Using When Unprompted?
1.4. Effectiveness of Quantity and Diversity of Learning Strategy Use on Learning Outcomes
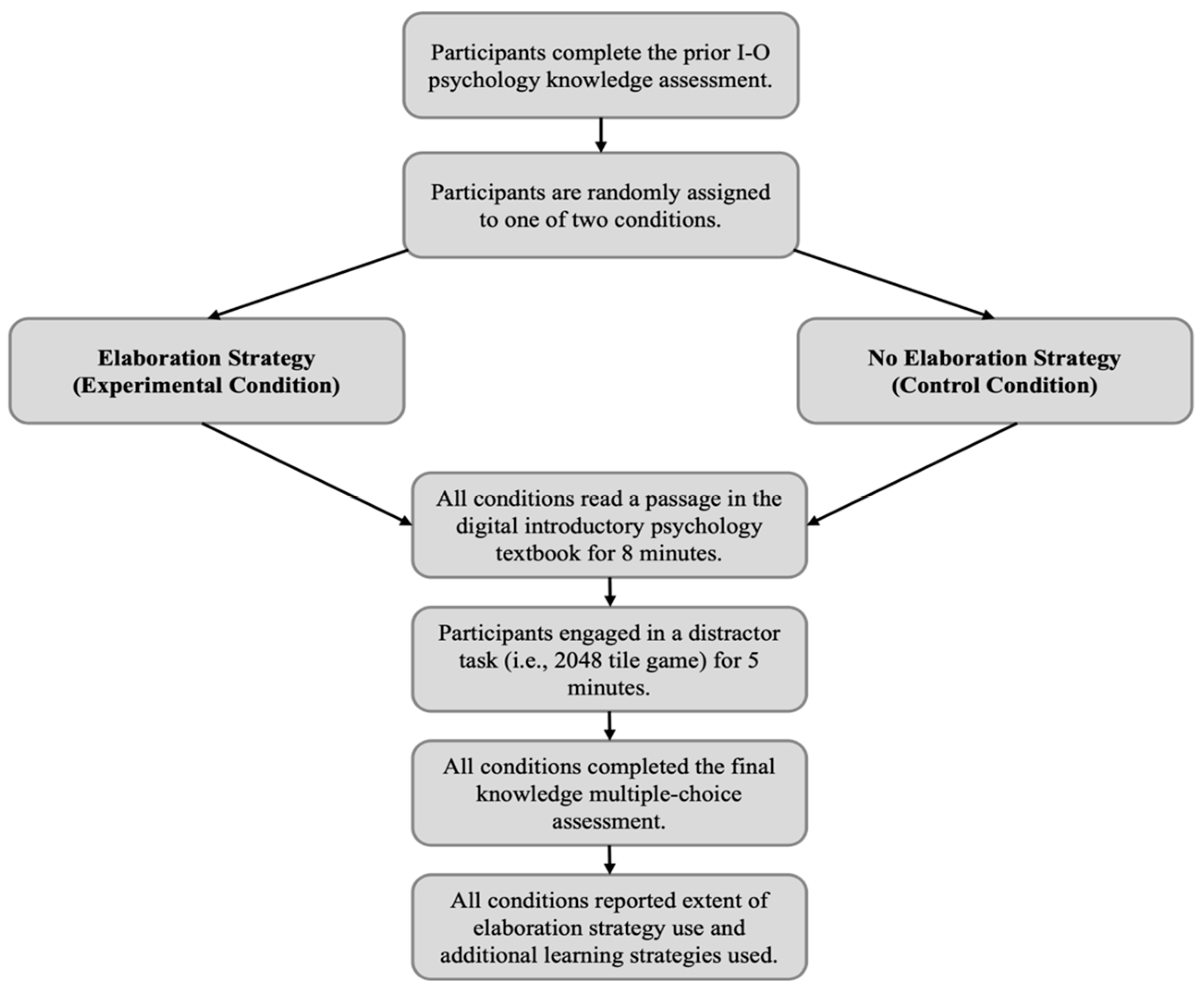
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Measures
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exploratory Analyses
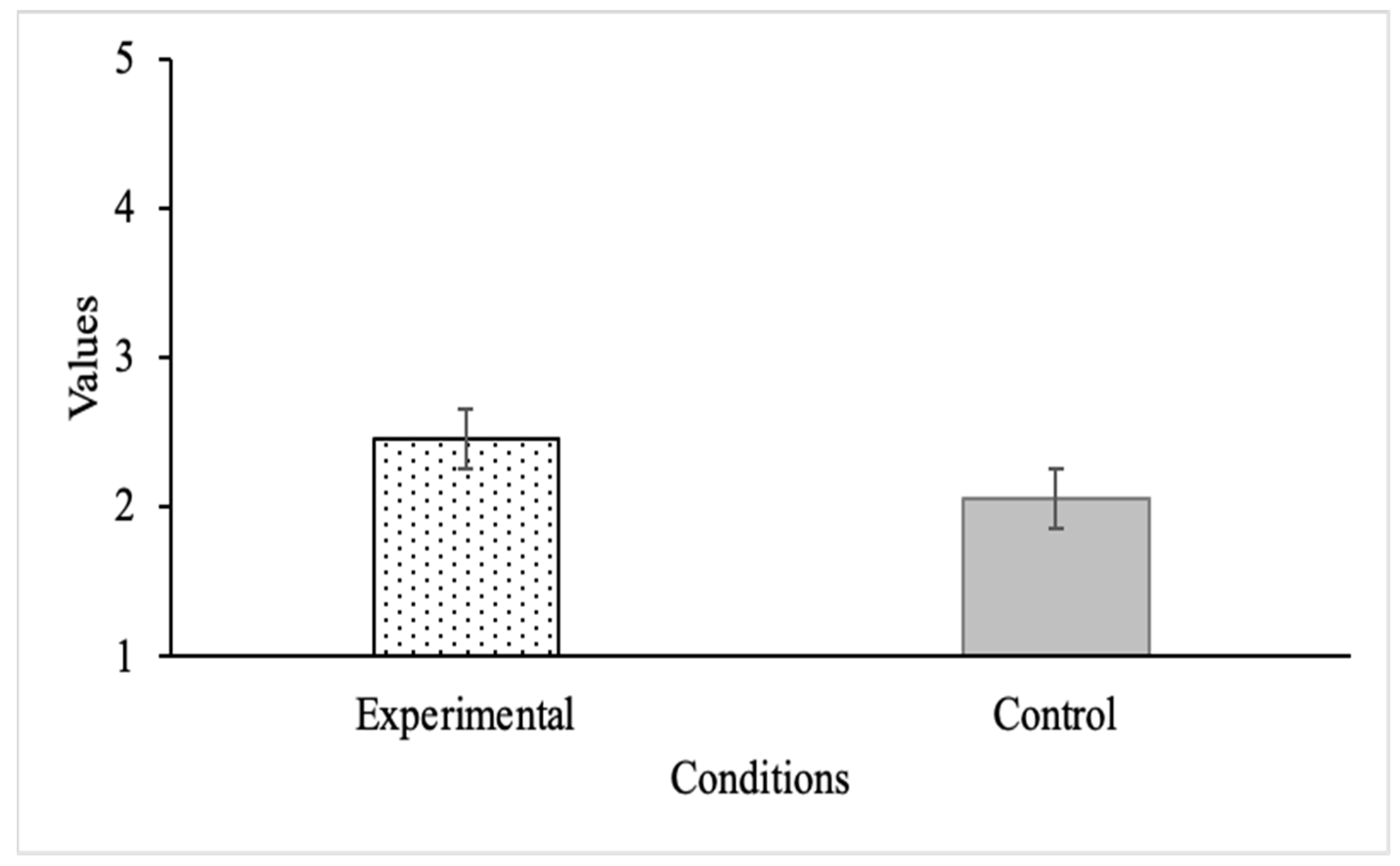
3.1.1. Extent of Elaboration Strategy Use
3.1.2. Relationship between Extent of Elaboration Strategy Use and Knowledge Test Performance
3.1.3. What Learning Strategies Do Learners Report Using When Reading Expository Text?
- Antecedents of generative learning strategy use;
- Reported strategies aligned with generative learning strategies, per the SOI model;
- Ineffective learning strategy use.
Antecedents of Generative Learning Strategy Use
Generative Learning Strategy Use
Ineffective Learning Strategy Use
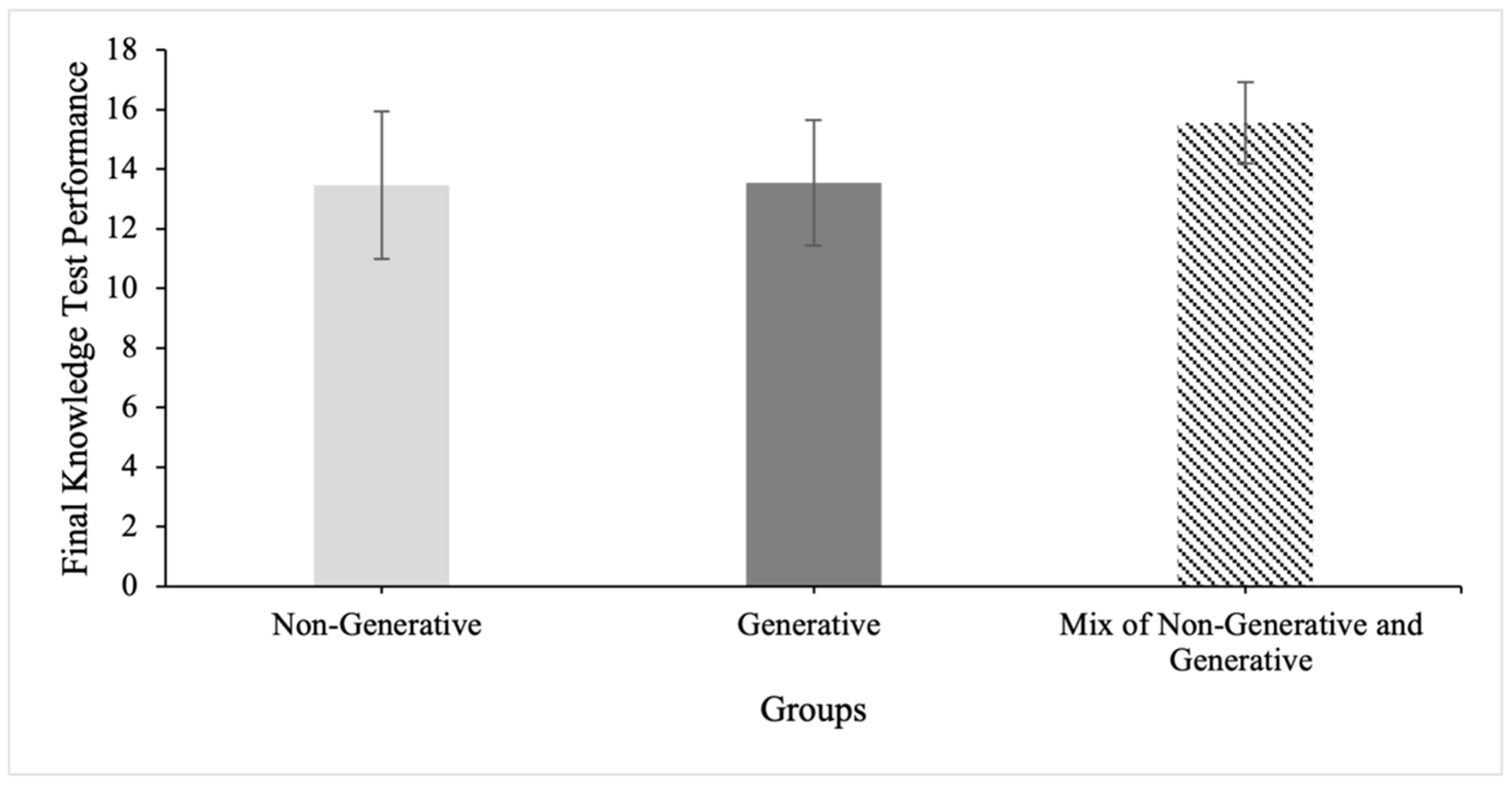
3.1.4. Does the Quantity of Learning Strategies Used Influence Performance?
3.1.5. Does a Mix of Generative and Non-Generative Learning Strategies Improve Performance?
4. Discussion
4.1. Theoretical and Practical Implications
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merriam, S.B.; Caffarella, R.S.; Baumgartner, L.M. Learning in Adulthood: A Comprehensive Guide, 3rd ed.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rea, S.D.; Wang, L.; Muenks, K.; Yan, V.X. Students can (mostly) recognize effective learning, so why do they not do it? J. Intell. 2022, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornell, N.; Bjork, R.A. The promise and perils of self-regulated study. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2007, 14, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorella, L. Making sense of generative learning. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2023, 35, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittrock, M.C. Generative processes of comprehension. Educ. Psychol. 1989, 24, 345–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, L.; Mayer, R.E. Learning as a Generative Activity: Eight Learning Strategies That Promote Understanding; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlett, F.C. Remembering: A Study in Experimental and Social Psychology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Wittrock, M.C. Learning as a generative process. Educ. Psychol. 1974, 11, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, U. Generative learning. In Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning; Seel, N.M., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorella, L.; Mayer, R.E. Eight ways to promote generative learning. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 28, 717–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brod, G. Which strategies for what age? Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 33, 1295–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reder, L.M.; Charney, D.H.; Morgan, K.I. The role of elaborations in learning a skill from an instructional text. Mem. Cogn. 1986, 14, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, P.; Allan, C. Learning strategies and occupational training. In Personnel Psychology and HRM: A Reader for Students and Practitioners; Robertson, I., Cooper, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 89–228. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, C.E.; Mayer, R.E. The teaching of learning strategies. Innov. Abstr. 1983, 5, n32. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlosky, J.; Rawson, K.A.; Marsh, E.J.; Nathan, M.J.; Willingham, D.T. Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2013, 14, 4–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthold, K.; Nückles, M.; Renkl, A. Do learning protocols support learning strategies and outcomes? The role of cognitive and metacognitive prompts. Learn Instr. 2007, 17, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A. Comparison of self-questioning, summarizing, and notetaking-review as strategies for learning from lectures. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1992, 29, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, B. Differential-associative processing or example elaboration: Which strategy is best for learning the definitions of related and unrelated concepts? Learn. Instr. 2012, 22, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, A.; Babel, F.; Hock, P.; Baumann, M.; Seufert, T. Prompting in-depth learning in immersive virtual reality: Impact of an elaboration prompt on developing a mental model. Comput. Educ. 2021, 171, 104235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsey, A.; Morrison, G.R.; Ross, S.M. Using elaboration strategies training in computer-based instruction to promote generative learning. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 1992, 17, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, T.; Carpenter, S.; Martin, A.; Renkl, A. Enhancing learning by retrieval: Enriching free recall with elaborative prompting. Learn. Instr. 2017, 49, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, R.A.; Dunlosky, J.; Kornell, N. Self-regulated learning: Beliefs, techniques, and illusions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 417–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, A.; Balaban, J. Learning strategies of successful and unsuccessful students. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2010, 1, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walck-Shannon, E.M.; Rowell, S.F.; Frey, R.F. To what extent do study habits relate to performance? CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2021, 20, ar6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogger, I.; Schwonke, R.; Holzäpfel, L.; Nückles, M.; Renkl, A. Learning strategies assessed by journal writing: Prediction of learning outcomes by quantity, quality, and combinations of learning strategies. J. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 104, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winne, P.H.; Perry, N.E. Measuring self-regulated learning. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Boekaerts, M., Pintrich, P., Zeidner, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 531–566. [Google Scholar]
- Nückles, M.; Hübner, S.; Renkl, A. Enhancing self-regulated learning by writing learning protocols. Learn. Instr. 2009, 19, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielman, R.M.; Jenkins, W.J.; Lovett, M.D. Psychology 2e; OpenStax: Houston, TX, USA, 2020; Available online: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/13-introduction (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology. Available online: https://www.apa.org/ed/graduate/specialize/industrial#:~:text=The%20specialty%20of%20industrial%2Dorganizational,organizations%20and%20the%20work%20place (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Occupational Outlook Handbook: Psychologists. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/psychologists.htm#tab-6 (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- 2048 Tile Game, version 2.4.34; Game Software. Available online: https://github.com/gabrielecirulli/2048 (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- McGartland Rubio, D. Alpha reliability. In Encyclopedia of Social Measurement; Kempf-Leonard, K., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Distractor Analysis for Test Items. Available online: https://assess.com/distractor-analysis-test-items/ (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- snowIRT: Item Response Theory for Jamovi, version 4.8.8; Jamovi Module. Available online: https://github.com/hyunsooseol/snowIRT (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Miles, M.B.; Huberman, A.M.; Saldana, J. Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Maanen, J. The fact of fiction in organizational ethnography. Adm. Sci. Q 1979, 24, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, A.S.; DelSignore, L.; Marcus, C.; Chiel, L.; Freiman, E.; Stafford, D.; Newman, L. Applying cognitive learning strategies to enhance learning and retention in clinical teaching settings. J. Teach. Learn. Resour. 2019, 15, 10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, D.; Nakaya, M.; Koizumi, R. Effects of metacognitive strategies on the self-regulated learning process: The mediating effects of self-efficacy. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavell, J.H. Metacognition and cognitive monitoring: A new area of cognitive—Developmental inquiry. Am. Psychol. 1979, 34, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzmann, T.; Ely, K. A meta-analysis of self-regulated learning in work-related training and educational attainment: What we know and where we need to go. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpicke, J.D.; Butler, A.C.; Roediger III, H.L. Metacognitive strategies in student learning: Do students practice retrieval when they study on their own? Memory 2009, 17, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, L.E.; Bernacki, M.L.; Bernacki, L.E. How do digital textbook platforms promote active learning in undergraduate biology courses? J. Res. Sci. Teach. 2023, 60, 1579–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L. Essentials of Psychological Testing; Hapercollins College Division: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hoenig, J.M.; Heisey, D.M. The abuse of power: The pervasive fallacy of power calculations for data analysis. Am. Stat. 2001, 55, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hedo, R.; Rivera, A.; Rull, R.; Richardson, S.; Tu, X.M. Post hoc power analysis: Is it an informative and meaningful analysis? Gen. Psychiatry 2019, 32, e100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, N.E.; Yang, K.; Chen, R.; Tu, J.; Xu, M.; Tu, X.M.; Zhang, X. Post-hoc power analysis: A conceptually valid approach for power based on observed study data. Gen. Psychiatry 2022, 35, e100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, S.R.; Thompson, K.L.; McKenzie, M.; Rosenbaum, A. Psychological research in the internet age: The quality of web-based data. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 58, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, D.S. Strategies to read and learn: Overcoming learning by consumption. Med. Educ. 2010, 44, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scale Range | Elaboration Prompt | No Elaboration Prompt | Cohen’s d | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | |||||
| Prior I-O Psychology Knowledge | Likert Scale (1–5) | 1.53 (0.64) | 1.68 (0.73) | 0.21 | 0.126 |
| Knowledge Test Performance | Multiple Choice (0–18) | 13.88 (2.20) | 13.67 (2.43) | 0.09 | 0.509 |
| Extent of Elaboration Learning Strategy Use | Likert Scale (1–5) | 2.45 (0.89) | 2.05 (1.08) | 0.40 | 0.005 ** |
| Variable | 1. | 2. | 3. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Prior I-O Psychology Knowledge | (0.96) | ||
| 2. Knowledge Test Performance | 0.02 [−0.12, 0.16] | (0.60) | |
| 3. Extent of Elaboration Learning Strategy Use | 0.11 [−0.02, 0.25] | 0.17 * [0.04, 0.30] | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruffin, M.A.; Tudor, R.N.; Beier, M.E. Prompting Strategy Use and Beyond: Examining the Relationships between Elaboration, Quantity, and Diversity of Learning Strategies on Performance. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090764
Ruffin MA, Tudor RN, Beier ME. Prompting Strategy Use and Beyond: Examining the Relationships between Elaboration, Quantity, and Diversity of Learning Strategies on Performance. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(9):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090764
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuffin, Makai A., Ryann N. Tudor, and Margaret E. Beier. 2024. "Prompting Strategy Use and Beyond: Examining the Relationships between Elaboration, Quantity, and Diversity of Learning Strategies on Performance" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 9: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090764
APA StyleRuffin, M. A., Tudor, R. N., & Beier, M. E. (2024). Prompting Strategy Use and Beyond: Examining the Relationships between Elaboration, Quantity, and Diversity of Learning Strategies on Performance. Behavioral Sciences, 14(9), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14090764






