The Influence of Gaming Behavior on School Adjustment among Korean Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Self-Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Gaming Culture and Issues among Korean Adolescents
1.2. Negative and Positive Functions of Gaming Behavior
1.3. Gaming Behavior and School Adjustment
1.4. Gaming Behavior and Self-Regulation
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instrument
2.3.1. Gaming Behavior
2.3.2. Self-Regulation
2.3.3. School Adjustment
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistical Office. Youth Statistics; 2020; Ministry of Gender Equality and Family: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020; p. 26.
- Kim, Y.E. The Rise of a New Generation, the Game Generation; Communication Books: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Creative Content Agency. 2019 Comprehensive Survey on Excessive Immersion in Games; Korea Creative Content Agency: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.W. Relationship between pre- and post-COVID-19 leisure changes in college students and leisure motivation and health beliefs. J. Korean Soc. Leis. Recreat. 2020, 44, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S. The Internet and the Transformation of Youth’s Daily Culture: Focusing on Youth Online Game Culture. Youth Cult. Forum 2012, 30, 84–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.S.; Han, Y.J. Mediating effects of real and cyber self-identity in adolescents’ relationship between Internet game immersion and family relationships and school life adjustment. J. Hum. Dev. 2008, 15, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Creative Content Agency. 2022 Comprehensive Survey of Child and Adolescent Gaming Behavior; Korea Creative Content Agency: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; p. 355. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.S.; Jun, S.H. Exploring Explanatory Factors across the Types of Internet Addiction. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2006, 13, 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.B.; Lee, S.H. Adolescents’ Self-control and Big Five Personality Types Affecting Maladaptive and Adaptive Computer Game Use State. J. Korea Ind. Inf. Syst. Soc. 2019, 24, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.M. Game Usage Behavior of Children and Adolescent Game Users: Focusing on Adaptive-use and Over-immersion of Games. J. Learn.-Centered Curric. Instr. 2020, 20, 1473–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.O. Influence of Youth Internet Game Addiction on ADHD and Academic Achievement—Focusing on Elementary School Students in Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi Region. Youth Facil. Environ. 2014, 12, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, K.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.M. Relationships between the Attitudes toward Life, Internet Game Addiction and Health in Adolescence. Korean J. Psychol. Health 2014, 19, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, M.K. The Effect of Game Addiction on Subjective Health Status of Out-of-School Youths: The Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem and Social Stigma. J. Korean Soc. Wellness 2020, 15, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Yu, H.J. A Study on the Influence of Game Behavior on Life Satisfaction—Focusing on the Adjustment Effect of Social Support. Health Commun. Res. 2019, 18, 51–101. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, N.Y.; Kim, S.J. Internet Game Addiction and Health Habits in Korean Adolescents. Korean J. Stress Res. 2010, 18, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.W.; Baik, J.S. A Study on School Life Adjustment according to the Level of Internet Game Addiction among Middle School Students. Youth Facil. Environ. 2011, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.K.; Chae, K.M. Relations of Computer Game Addiction and Social Relationship, Adjustment of Adolescent. Korean J. Clin. Psychol. 2006, 25, 711–726. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S. The Impact on the Academic Achievement and Friendships with Children’s Computer Game Addiction. Master’s Thesis, Kyungwoon University, Gyeongbuk, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.A. Differences in Learning Strategy and Academic Achievement According to the Levels of Computer Game Addiction. Master’s Thesis, Keimyung University, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Han, J.S. A Study on the Effect of Game Addiction on the School Refusal: A Mediating Effect of Depression. Korean J. Youth Welf. 2012, 14, 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, Y.H. A Exploratory Research of the Antecedents and Consequences of Internet Addiction Tendency. Stud. Korean Youth 2004, 15, 305–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, H.R.; Jeong, E.J. The Effect of Game Players Personality, Social Capital and Adaptive Game Use on Life Satisfaction. J. Korean Soc. Comput. Game 2015, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.A.; Kim, H.I.; Ryu, S.H. An Exploratory Study on the Social Capital and Subjective Well-Being in Social Network Games. J. Korea Game Soc. 2011, 11, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Jeong, E.J. Psychological Needs of Game Addiction: An Exploratory Study Focusing on Therapeutic Catharsis Seeking and Game Self-Efficacy. J. Korea Game Soc. 2015, 15, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.R.; Choi, J.M.; Seo, S.B. An Analysis on the Relationship between Game and Happiness. J. Korea Game Soc. 2017, 17, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.R. A study on the effect of juvenile game play on future happiness—Focus on the mediating role of trusting others. J. Korea Game Soc. 2019, 19, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J. Study on the Juvenile Culture of Community within the Online Game. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2006, 13, 386–409. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, M.C.; Jeong, E.J. The Effect of adolescent game players Game using pattern, psychology factor on Leadership. J. Korean Soc. Comput. Game 2016, 29, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.K. Influence of Health Promoting Lifestyle and School Adjustment on Learning Flow among Adolescents. Master’s Thesis, Sahmyook University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.S. The Influence of Consciousness of Human Rights on School Adjustment among Adolescents: Focusing on the Moderating Effects of Self-Esteem, Parents’ Abuse, School Violence Victimization. J. Sch. Soc. Work 2021, 54, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.K.; Lee, Y.S. Effects of Adolescents’ Smart Phone Addiction on their School Adjustment: Mediating Effects of Self-Efficacy. Korean J. Youth Welf. 2016, 18, 217–241. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.M.; Lee, S. The Effect of Communication with Parent-Adolescence and Self-Efficacy on School Adjustment. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2008, 19, 641–658. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.Y. Relationship between Adjustment to School Life and Stress Coping Style in Adolescents. J. Korean Soc. Sch. Health 2013, 26, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, H.M. The Mediating Effects of Self-Esteem on Family Communication and School Adjustment of Middle School Students. J. Sch. Soc. Work 2017, 39, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J. The Mediating Effect of Career Identity and the Moderating Effect of Delinquency on the Relationship between Perceived Parenting Attitudes and Adolescents’ Adjustment to School. J. Sch. Soc. Work 2017, 39, 177–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, H.J. Behaviors and Ego-Resilience on Adolescents’ School Adjustment. Master’s Thesis, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, M.S. A Study on the Effects of Parenting Attitudes, Teacher Relationship, and Peer Relationship on School Adjustment in Middle School Students—Mediating Effects of a Sense of Community. Ph.D. Dissertation, Honam University, Gwangju, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.R. Effect of Parenting Attitudes on School Adjustment of Adolescents. Master’s Thesis, Konkuk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.S.; Jeong, G.C. Difference of Collaboration · Empathy Skill and Adaptation of School Life according to School Bullying Types. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2016, 16, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H. Effects of Family Functioning & Adolescents’ Self-Regulation on Online Game Overflow and School Adjustment. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2011, 18, 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Han, E.J. The Mediated Effects of Reality Ego-Identity and Cyber Ego-Identity upon Family Relationship and School Life Adjustment as determined by the Degree of Indulgence of Adolescent’s Internet Gaming. Korean J. Hum. Dev. 2008, 15, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, K.Y. Internet Game Addiction and Stress Response, Subjective Well-Being and Motivation and Expectations for Life in Male High School Students. J. Adolesc. Stud. 2013, 20, 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H. Psychological, Behavioral Characteristics and Human Relationship of Adolescent Addicted to Smartphone, Internet and Games. Ph.D. Dissertation, Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.Y.; Seo, K.H. Phone Addiction and Internet Game Addiction and Stress Response in High School Students: Focusing on the Mediating Effects of Sleep Deprivation. J. Korean Psychol. Assoc. Health 2012, 17, 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J. Research on the factors influencing the subjective sense of well-being of adolescents: Focusing on demographic and sociological characteristic factors, health factors, and deviant behavior factors. Stress 2013, 21, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.J. The problems and challenges for self-regulation studies. J. Res. Educ. 2011, 39, 161–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H. Addiction and Self-Regulation: A Cognitive Neuroscience Approach. Korean J. Psychol. Health 2006, 11, 63–105. [Google Scholar]
- Derryberry, D.; Rothbart, M.K. Arousal, affect, and attention as components of temperament. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 55, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, R.F.; Vohs, K.D. Self-Regulation, ego depletion, and motivation. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 2007, 1, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, R.F.; DeWall, C.N.; Ciarocco, N.J.; Twenge, J.M. Social exclusion impairs self-regulation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 88, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L. The Mediating Effects of Parent-adolescent Communication and School Life Adjustment in Relationship between Adolescent’s Self-control and Smartphone Overdependence. Korean J. Hum. Ecol. 2018, 27, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.M.; Choi, W.S.; Park, I.J. The Effects of Children’s Self-Regulation on their Friendships and School Adjustment. J. Fam. Better Life 2009, 27, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.M. The Influence of Middle School Students’ Perceived Social Support and Self-Control Ability on Their Perceived School Stress and School Adjustment. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2005, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.S. The Moderate Effects of Self-Esteem on the Relationship between Personality Strength of Adolescent and School Adjustment. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2021, 28, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Song, K.B.; Lee, W.Y. A study on effects of adolescent’s social skill and self-control ability on internet addiction. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2013, 20, 335–365. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B.W. Etiologic Factors of Internet Addiction. J. Ethics 2013, 88, 77–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, G.C. Relationships among Mental Health, Internet Addiction, and Smartphone Addiction in University Students. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2016, 16, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S. A study on the effect of teenagers’ use of a cellular phone on sex delinquencies. Korean Assoc. Addict. Crime 2011, 1, 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- So, S.H. Impact of Adolescents’ Internet Addiction on Social Adaptation—Focused on the Moderating Effects of Psycho-Social Factors. Ph.D. Dissertation, Seoul Christian University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, I.H.; Han, S.C. Moderating Effect of Conflict Negotiation Strategies on the Relationships between Peer Conformity, Self-Control and Bullying with Adolescents. J. Future Oriented Youth Soc. 2020, 17, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Creative Content Agency. A Study on the Development of a Comprehensive Scale for Game Use; Korea Creative Content Agency: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2020; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Moilanen, K. The Adolescent Self-Regulatory Inventory: The Development and Validation of a Questionnaire of Short-Term and Long-Term Self-Regulation. J. Youth Adolesc. 2007, 36, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, U.Y. Translation and Validity of the Korean Version of the Adolescent Self-Regulatory Inventory (ASRI). Master’s Thesis, Seoul University of Buddhism, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.Y. Development of Standardized Student Motivation Scales. J. Educ. Educ. 2002, 15, 157–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.Y.; Yi, S.H. Children’s and Adolescents’ Achievement Level in Online Game, Sense of Self-efficacy, School Adjustment and Life Satisfaction. J. Korea Game Soc. 2011, 11, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Creative Content Agency. 2018 A Comprehensive Survey of Game Over-Immersion; Korea Creative Content Agency: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, D.B. Mediating Effects of Self-Control on the Relationship between Smartphone Use and School Adjustment in Middle School Students. Korean J. Youth Stud. 2016, 23, 133–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Baik, J.S. Effects of Smartphone Addiction Level on Adolescent School Adjustment. Youth Facil. Environ. 2015, 13, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y. Effect of Smart-phone addiction on school resilience in elementary school students. Trans. Anal. Couns. Res. 2013, 3, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.Y. The Relationship between Internet Addiction, Emotional Intelligence and School Life Adjustment in Elementary School Students. Master’s Thesis, Dankook University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, U.S. A Study of Relations between the Internet-Addiction and School Life Adjustment among Middle School Students. Master’s Thesis, Kwandong University, Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, C.W.; Jeong, G.C. Development and Effectiveness Verification of Smartphone Game Addiction Prevention Program for Adolescents. Korean J. Addict. Psychol. 2016, 1, 67–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, B.Y. Effectiveness of Internet Game Addiction Prevention Program Based on Life Skill Training. J. Korean Data Anal. Soc. 2013, 15, 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H. The Moderating Effect of Resilience between Smartphone Addiction and Interpersonal Relation Problems, School Adjustment of Adolescents. J. Child Welf. Dev. 2020, 18, 39–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.A. Smart-phone Addiction of Adolescents and Its Related Variables. Korean Soc. Study Sociol. Educ. Acad. Conf. Mater. 2016, 1, 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, W.H.; Jo, M.J. Relationships between Ego-Resilience and Smartphone Addiction among Nursing Students. J. Korea Contents Assoc. 2016, 16, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Kim, N.M.; Joh, H.S. The Effects of Elementary School Students’ Smartphone Addiction on Their Adaptation to School Life: Mediating Effects of Positive Psychological Capital and Self-control. Alcohol Health Behav. Res. 2019, 20, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.R. Structural Analysis of Factors and Related Variables of Self-Regulation in Young Children. Ph.D. Dissertation, Duksung Women’s University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boo, J.M. Ecological Variables Affecting the Online-Game Flow and Addiction of the Youth. Ph.D. Dissertation, Sookmyung Women’s University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Hwang, S.H. Effects of Adolescents’ Game Addiction on Depression: Moderating Effect of Self-control. J. Korea Converg. Soc. 2020, 11, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.K.; Kwon, J. A Study on the Self-control and Game-overindulgence among Adolescents: Moderating effect of game-efficacy. Korean J. Youth Welf. 2021, 23, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H. Role of Self-Regulation in the Relations among Media Use, Emotional-Behavioral Problems, and School Adjustment for Middle School Students. Korean J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 28, 691–710. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, M.J.; Yi, J.H. The Self-regulation Program Development for Youth and Verification of its Effects. Korean J. Sch. Psychol. 2009, 6, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Son, S.A.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.K. The Study on Psychological Factors Affecting the Self-regulation in Adolescence. Stud. Korean Youth 2006, 17, 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.M. The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Group Activities program for Improving Self-regulation Ability and Optimism and Psychological Stability in adolescents. J. Soc. Work. Couns. 2021, 5, 25–50. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | Maladaptive Use of Games | Self-Regulation | School Adjustment | M ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive use of games | 0.40 *** | 0.15 ** | 0.23 *** | 32.05 ± 14.84 |
| Maladaptive use of games | 1.00 | −0.31 *** | −0.20 *** | 12.15 ± 12.62 |
| Self-regulation | 1.00 | 0.54 *** | 55.06 ± 9.12 | |
| School adjustment | 1.00 | 88.44 ± 14.80 |
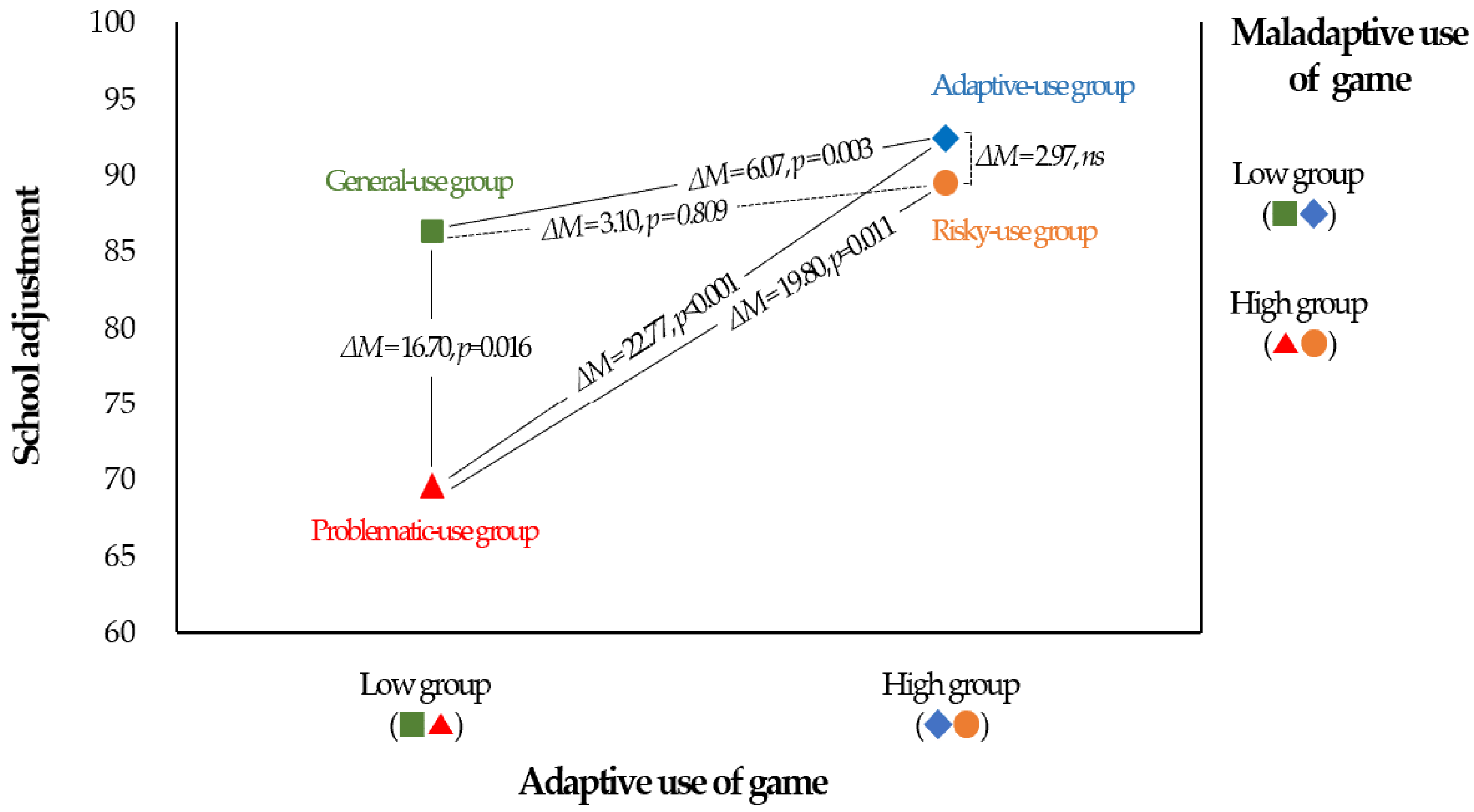
| Gaming Behavior Group | Self-Regulation | School Adjustment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | F (p) | M ± SD | F (p) | |
| Adaptive-use group (a) | 57.22 ± 9.09 | 8.75 (<0.001) | 92.40 ± 15.01 | 9.50 (<0.001) |
| General-use group (b) | 54.38 ± 8.97 | a > b > d | 86.33 ± 13.78 | a > b > d |
| Risky-use group (c) | 52.04 ± 5.19 | a > c | 89.43 ± 13.94 | c > d |
| Problematic-use group (d) | 43.25 ± 9.42 | 69.63 ± 15.51 | ||
| Variables (Reference) | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | t (p) | B | t (p) | B | t (p) | |
| Gender (male) | 2.25 | 1.42 (0.157) | 2.06 | 1.51 (0.132) | 2.34 | 1.72 (0.087) |
| Age | −0.40 | −0.57 (0.556) | −0.13 | −0.22 (0.830) | −0.24 | −0.41 (0.682) |
| Adaptive use of games (low group) (a) | 7.40 | 4.59 (<0.001) | 4.74 | 3.37 (0.001) | 4.40 | 3.12 (0.002) |
| Maladaptive use of games (low group) (b) | −6.54 | −2.36 (0.019) | −0.81 | −0.33 (0.741) | 2.78 | 0.95 (0.343) |
| Self-regulation (c) | 0.83 | 11.19 (<0.001) | 0.72 | 7.38 (<0.001) | ||
| Interaction 1 (a×c) | 0.17 | 1.16 (0.247) | ||||
| Interaction 2 (b×c) | 0.67 | 2.12 (0.035) | ||||
| R2 (F, p) | 0.068 (F = 6.42, p < 0.001) | 0.312 (F = 31.99, p < 0.001) | 0.322 (F = 23.85, p < 0.001) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Jeong, G.-C. The Influence of Gaming Behavior on School Adjustment among Korean Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Self-Regulation. Behav. Sci. 2024, 14, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030259
Lee J, Jeong G-C. The Influence of Gaming Behavior on School Adjustment among Korean Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Self-Regulation. Behavioral Sciences. 2024; 14(3):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030259
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jisue, and Goo-Churl Jeong. 2024. "The Influence of Gaming Behavior on School Adjustment among Korean Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Self-Regulation" Behavioral Sciences 14, no. 3: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030259
APA StyleLee, J., & Jeong, G.-C. (2024). The Influence of Gaming Behavior on School Adjustment among Korean Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Self-Regulation. Behavioral Sciences, 14(3), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14030259





