Manual Abilities and Cognition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Do Fine Motor Skills Impact Cognition as Measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant Development?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Manual Ability Classification System (MACS)
2.3.2. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development—Third Edition (Bayley-III)
2.4. Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Item Number | Fine Motor Dependent | Item Number | Fine Motor Independent |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | Explores Object | 1 | Calms When Picked Up |
| 17 | Carries Object to Mouth | 2 | Responds to surroundings Series: Inspects |
| 21 | Persistent Reach | 3 | Regards Object for 3 s |
| 23 | Plays With String | 4 | Habituates to Rattle |
| 24 | Bangs in Play | 5 | Discriminates Between Objects |
| 26 | Bell Series: Manipulates | 6 | Recognizes Caregiver |
| 27 | Picks Up Block Series: Reaches for Second Block | 7 | Becomes Excited in Anticipation |
| 28 | Pulls Cloth to Obtain Object | 8 | Regards Object for 5 s |
| 29 | Pulls String Adaptively | 9 | Reacts to Disappearance of Face |
| 30 | Retains Both Blocks | 10 | Shifts Attention |
| 31 | Bell Series: Rings Purposely | 11 | Shows Visual Preference |
| 33 | Picks Up Block Series: Retains 2 or 3 Blocks | 12 | Habituates to Object |
| 35 | Takes Blocks out of Cup | 13 | Prefers Novel Object |
| 36 | Block Series: 1 Block | 14 | Habituates to Picture (Balloons) |
| 37 | Picks Up Block Series: 3 Blocks | 15 | Prefers Novel Picture (Ball) |
| 38 | Explores Holes in Pegboard | 18 | Inspects Own Hand |
| 39 | Pushes Car | 19 | Mirror Image Series: Approaches |
| 40 | Finds Hidden Object | 20 | Responds to Surroundings Series: Awareness of Novelty |
| 41 | Suspends Ring | 22 | Mirror Image Series: Responds Positively |
| 42 | Removes Pellet | 25 | Searches for Fallen Object |
| 43 | Clear Box: Front | 32 | Looks at Pictures |
| 44 | Squeezes Object | 34 | Searches for Missing Objects |
| 45 | Finds Hidden Object (Reversed) | 59 | Attends to Story |
| 46 | Removes Lid from Bottle | 64 | Matches Pictures |
| 47 | Pegboard Series: 2 Holes | 68 | Matches 3 Colors |
| 48 | Relational Play Series: Self | 72 | Concept Grouping: Color |
| 49 | Pink Board Series: 1 Piece | 73 | Concept Grouping: Size |
| 50 | Finds Hidden Object (Visible Displacement) | 75 | Matches size |
| 51 | Blue Board Series: 1 Piece | 76 | Discriminates Pictures |
| 52 | Clear Box: Slides | 77 | Simple Pattern |
| 53 | Relational Play Series: Others | 79 | Counts (One-to-One Correspondence) |
| 54 | Block Series: 9 Blocks | 80 | Discriminates Sizes |
| 55 | Pegboard Series: 6 Pegs | 81 | Identifies 3 Incomplete Pictures |
| 56 | Pink Board Series: Completes | 83 | Discriminates Patterns |
| 57 | Uses Pencil to Obtain Object | 85 | Counts (Cardinality) |
| 58 | Blue Board Series: 4 Pieces | 86 | Number Constancy |
| 60 | Rotated Pink Board | 88 | Classifies Objects |
| 61 | Object Assembly (Ball) | 89 | Understands Concept of More |
| 62 | Completes Pegboard: 25 s | 90 | Repeats Number Sequences |
| 63 | Object Assembly (Ice Cream Cone) | ||
| 65 | Representational Play | ||
| 66 | Blue Board Series: Completes (75 s) | ||
| 67 | Imitates a Two-Step Action | ||
| 69 | Imaginary Play | ||
| 70 | Understands Concept of One | ||
| 71 | Multischeme Combination Play | ||
| 74 | Compares Masses | ||
| 78 | Sorts Pegs by Color | ||
| 82 | Object Assembly (Dog) | ||
| 84 | Spatial Memory | ||
| 87 | Laces Card | ||
| 91 | Completes Patterns |
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A Report: The Definition and Classification of Cerebral Palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.S.; Wingate, M.S.; Braun, K.V.N.; Doernberg, N.S.; Arneson, C.L.; Benedict, R.E.; Mulvihill, B.; Durkin, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Maenner, M.J.; et al. Prevalence and Functioning of Children with Cerebral Palsy in Four Areas of the United States in 2006: A Report from the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonmukayakul, U.; Shih, S.T.F.; Bourke-Taylor, H.; Imms, C.; Reddihough, D.; Cox, L.; Carter, R. Systematic Review of the Economic Impact of Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 80, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, C.A.; Boulet, S.; Schieve, L.A.; Cohen, R.A.; Blumberg, S.J.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Visser, S.; Kogan, M.D. Trends in the Prevalence of Developmental Disabilities in US Children, 1997–2008. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.O.; Tian, L.H.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Dowling, N.F.; Christensen, D.L. Prevalence of Cerebral Palsy, Intellectual Disability, Hearing Loss, and Blindness, National Health Interview Survey, 2009–2016. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.L.; Malouin, F. Cerebral Palsy: Definition, Assessment and Rehabilitation. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 111, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Walter, S.; Russell, D.; Wood, E.; Galuppi, B. GMFCS–E & R Gross Motor Function Classification System Expanded and Revised. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1997, 39, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson, A.C.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Rösblad, B.; Beckung, E.; Arner, M.; Öhrvall, A.M.; Rosenbaum, P. The Manual Ability Classification System (MACS) for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Scale Development and Evidence of Validity and Reliability. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, H.; Hay, K.; Nelin, M.A.; Sowers, B.; Lewandowski, D.J.; Moore-Clingenpeel, M.; Maitre, N.L. Caregiver Perception of Hand Function in Infants with Cerebral Palsy: Psychometric Properties of the Infant Motor Activity Log. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, E. Grounded in the World: Developmental Origins of the Embodied Mind. Dev. Perspect. Embodiment Conscious. 2012, 1, 99–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, E.; Schöner, G.; Scheier, C.; Smith, L.B. The Dynamics of Embodiment: A Field Theory of Infant Perseverative Reaching. Behav. Brain Sci. 2001, 24, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd ed.; PsychCorp: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dusing, S.C.; Harbourne, R.T.; Lobo, M.A.; Westcott-Mccoy, S.; Bovaird, J.A.; Kane, A.E.; Syed, G.; Marcinowski, E.C.; Koziol, N.A.; Brown, S.E. A Physical Therapy Intervention to Advance Cognitive and Motor Skills: A Single Subject Study of a Young Child with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Valencia, E.; Torres-Sánchez, L.; López-Carrillo, L.; Rothenberg, S.J.; Schnaas, L. Early Motor Development and Cognitive Abilities among Mexican Preschoolers. Child Neuropsychol. 2018, 24, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, S.L.C.; Santos, R.; Jones, R.A.; Sousa-Sá, E.; Okely, A.D. Associations between Gross Motor Skills and Cognitive Development in Toddlers. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 132, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.; Ruiter, S.A.J.; Van Der Meulen, B.F.; Ruijssenaars, W.A.J.J.M.; Timmerman, M.E. Accommodating the Bayley-III for Motor and/or Visual Impairment: A Comparative Pilot Study. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2014, 26, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, L.; Ruiter, S.A.J.; Van der Meulen, B.F.; Ruijssenaars, W.A.J.J.M.; Timmerman, M.E. Validity and Suitability of the Bayley-III Low Motor/Vision Version: A Comparative Study among Young Children with and without Motor and/or Visual Impairments. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporta-Hoyos, O.; Panek, K.; Pagnozzi, A.M. Cognitive, Academic, Executive and Psychological Functioning in Children with Spastic Motor Type Cerebral Palsy: Influence of Extent, Location, and Laterality of Brain Lesions. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2022, 38, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nemr, A.; Abdelazeim, F. Relationship of Cognitive Functions and Gross Motor Abilities in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2018, 7, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluca, S.C.; Echols, K.; Law, C.R.; Ramey, S.L. Intensive Pediatric Constraint-Induced Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryalls, B.O.; Harbourne, R.; Kelly-Vance, L.; Wickstrom, J.; Stergiou, N.; Kyvelidou, A. A Perceptual Motor Intervention Improves Play Behavior in Children with Moderate to Severe Cerebral Palsy. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning Disability and Health: Children & Youth Version; ICF-CY: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, I.; Hines, M.; Goldsmith, S.; Barclay, R. Clinical Prognostic Messages from a Systematic Review on Cerebral Palsy. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1285–e1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.; Honan, I.; Allsop, A.; Novak, I.; Badawi, N. Psychometric Properties of Assessments of Cognition in Infants with Cerebral Palsy or Motor Impairment: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2019, 44, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudgenoeg-Paz, O.; Mulder, H.; Jongmans, M.J.; van der Ham, I.J.M.; Van der Stigchel, S. The Link between Motor and Cognitive Development in Children Born Preterm and/or with Low Birth Weight: A Review of Current Evidence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, K.E.; Hoch, J.E. Motor Development: Embodied, Embedded, Enculturated, and Enabling. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinini, R.M.; Koziol, N.A.; Marcinowski, E.C.; Hsu, L.Y.; Tripathi, T.; Harbourne, R.T.; McCoy, S.W.; Lobo, M.A.; Bovaird, J.A.; Dusing, S.C. Early Motor Skills Predict the Developmental Trajectory of Problem Solving in Young Children with Motor Delays. Dev. Psychobiol. 2021, 63, e22123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, P.; Honan, I.; Warschausky, S.; Kaufman, J.N.; Henry, G.; Stephenson, C.; Webb, A.; McEwan, A.; Badawi, N. A Validation and Acceptability Study of Cognitive Testing Using Switch and Eye-Gaze Control Technologies for Children with Motor and Speech Impairments: A Protocol Paper. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 991000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, P.K.; Mani, S. Current Profile of Physical Impairments in Children with Cerebral Palsy in Inclusive Education Settings: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2022, 13, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester-Plané, J.; Laporta-Hoyos, O.; Macaya, A.; Póo, P.; Meléndez-Plumed, M.; Toro-Tamargo, E.; Gimeno, F.; Narberhaus, A.; Segarra, D.; Pueyo, R. Cognitive Functioning in Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy: Its Relation to Motor Function, Communication and Epilepsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, M.A.; Harbourne, R.T.; Dusing, S.C.; McCoy, S.W. Grounding Early Intervention: Physical Therapy Cannot Just Be about Motor Skills Anymore. Phys. Ther. 2013, 93, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwell, S.; Reid, S.M.; Reddihough, D.S.; Wrennall, J.; Ong, B.; Stargatt, S. Measuring Intellectual Ability in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Can We Do Better? Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Overall (n = 61) |
|---|---|
| Gestational Age (weeks) | 37.0 (27.1, 39.0) |
| Birth Weight (kg) | 2.48 (0.93, 3.41) |
| Birth Length (in) | 18.0 (13.0, 20.0) |
| APGAR 1 | 6.00 (2.00, 8.00) |
| APGAR 5 | 6.00 (5.00, 9.00) |
| Total Hospital Length of Stay (days) | 28.50 (0.00, 134.75) |
| Type of CP | |
| Hypotonic | 10 (16.39%) |
| Hypertonic Spastic | 45 (73.77%) |
| Ataxic | 5 (8.20%) |
| Unspecified | 1 (1.64%) |
| CP distribution | |
| Left hemiplegia | 9 (15.52%) |
| Right hemiplegia | 2 (3.45%) |
| Diplegia | 9 (15.52%) |
| Quadriplegia | 37 (63.79%) |
| Triplegia | 1 (1.72%) |
| Not reported | 3 |
| GMFCS | |
| Level I | 14 (23.33%) |
| Level II | 8 (13.33%) |
| Level III | 5 (8.33%) |
| Level IV | 21 (35.00%) |
| Level V | 12 (20.00%) |
| Age at enrollment (years) | 3.50 (2.58, 4.75) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 37 (60.66%) |
| Female | 24 (39.34%) |
| Race | |
| White | 43 (70.49%) |
| Black or African American | 12 (19.67%) |
| More than One Race | 4 (6.56%) |
| Asian | 2 (3.28%) |
| Hispanic | 1 (1.64%) |
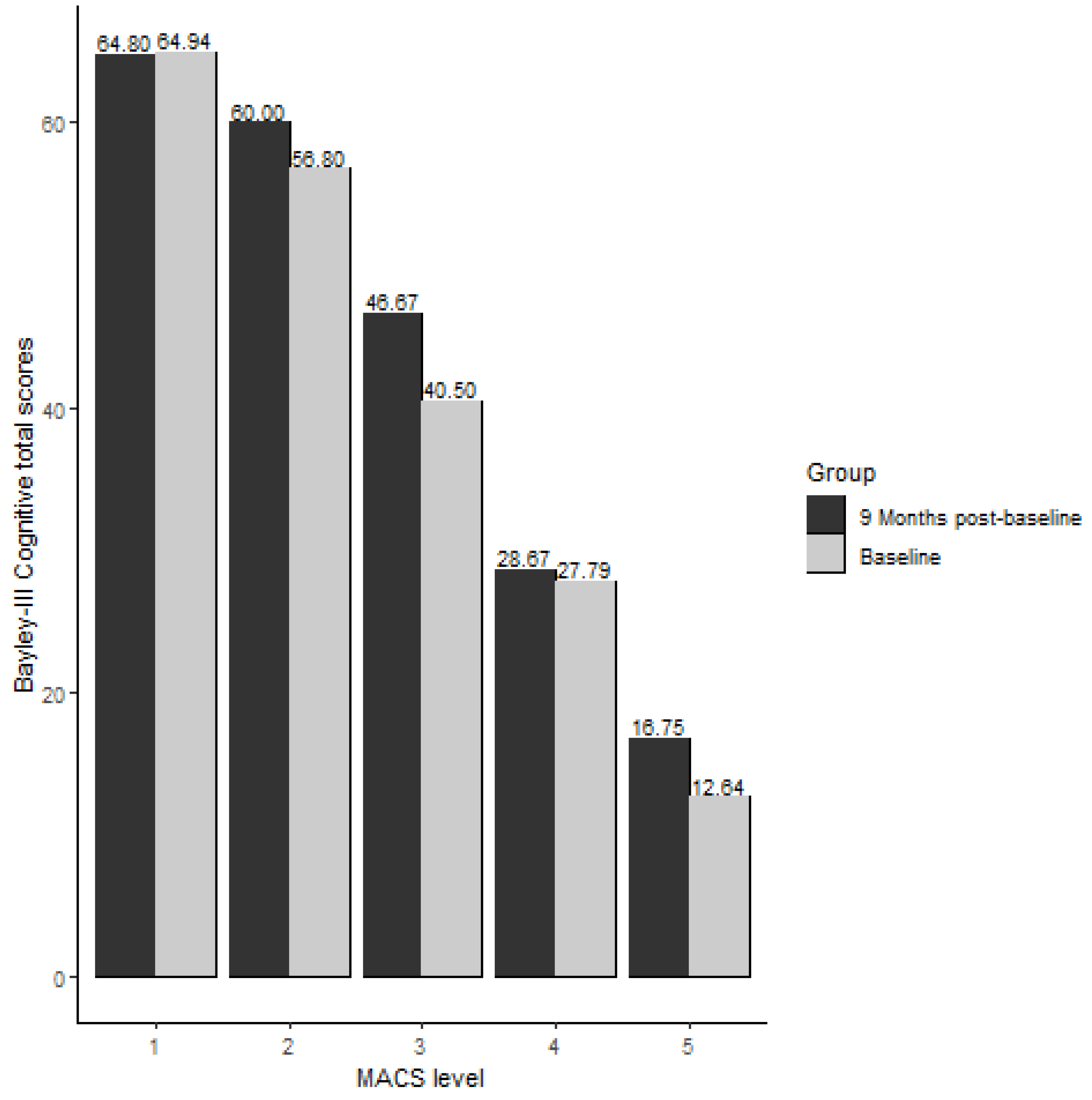
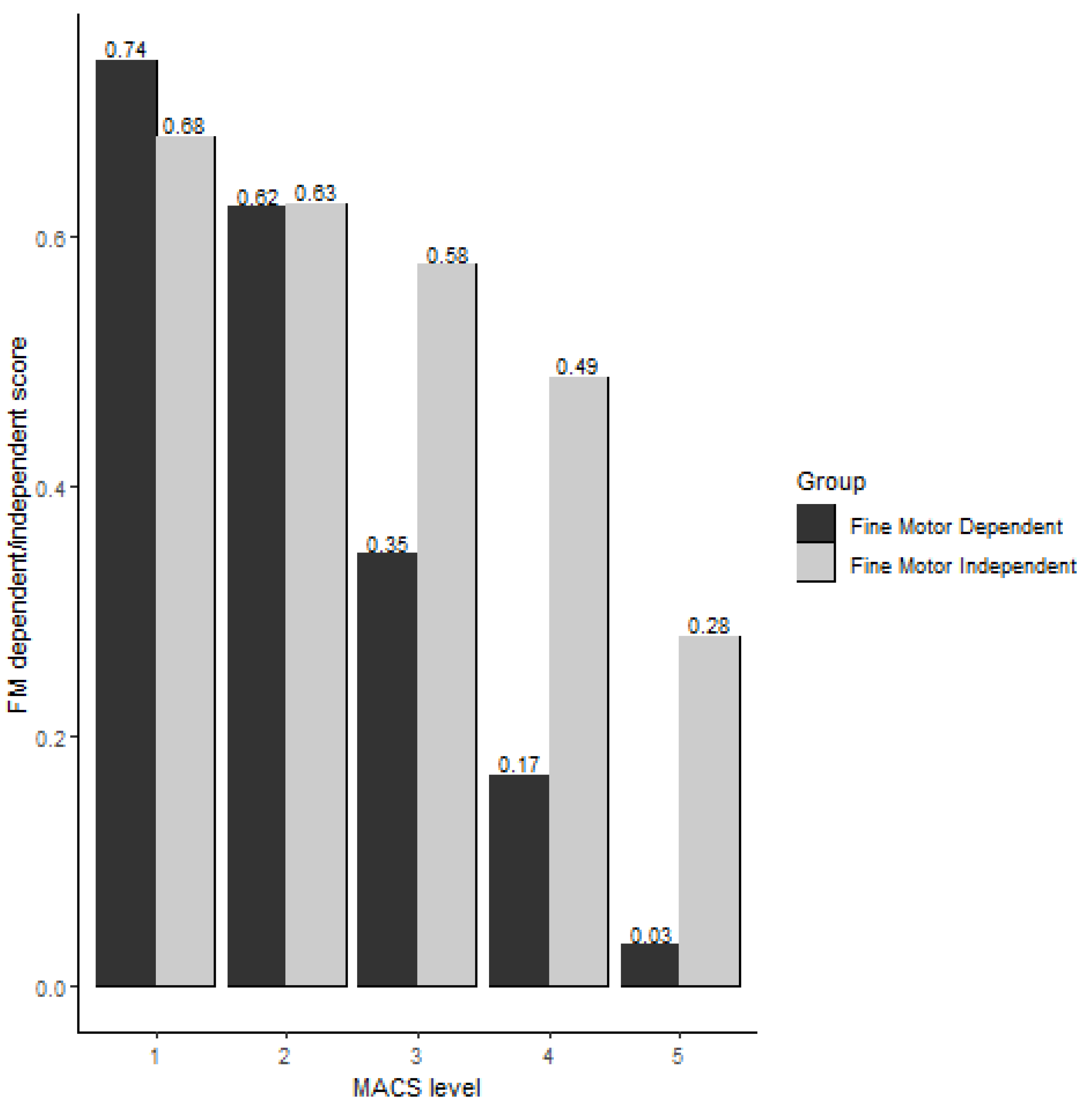
| MACS Level | Baseline (n = 61) | 9-Month Post-Baseline (n = 28) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | FMD Score * | FMI Score ** | Total | FMD Score * | FMI Score ** | |
| 1 | 64.94 (14.10) | 0.74 (0.20) | 0.68 (0.10) | 64.80 (15.28) | 0.73 (0.21) | 0.68 (0.11) |
| 2 | 56.80 (16.40) | 0.62 (0.24) | 0.63 (0.11) | 60.00 (12.88) | 0.68 (0.17) | 0.63 (0.10) |
| 3 | 40.50 (14.20) | 0.35 (0.23) | 0.58 (0.06) | 46.67 (21.36) | 0.44 (0.33) | 0.61 (0.10) |
| 4 | 27.79 (8.14) | 0.17 (0.09) | 0.49 (0.10) | 28.67 (10.03) | 0.17 (0.14) | 0.50 (0.07) |
| 5 | 12.64 (8.82) | 0.03 (0.07) | 0.28 (0.15) | 16.75 (13.30) | 0.07 (0.10) | 0.34 (0.23) |
| Cerebral Palsy Distribution | GMFCS Level | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemiplegia (n = 11) | Diplegia (n = 9) | Quadriplegia and Triplegia (n = 38) | p-Value | I | II | III | IV | V | p-Value | |
| MACS Level | <0.001 | NA 1 | ||||||||
| 1 | 6 (55%) | 6 (67%) | 3 (7.9%) | 11 (79%) | 3 (38%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (4.8%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| 2 | 4 (36%) | 2 (22%) | 8 (21%) | 3 (21%) | 4 (50%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (24%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| 3 | 0 (0%) | 1 (11%) | 3 (7.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (14%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| 4 | 1 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 13 (34%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 11 (52%) | 2 (17%) | ||
| 5 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 11 (29%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.8%) | 10 (83%) | ||
| Cognitive total raw score | 55 (44, 68) | 70 (49, 75) | 32 (16, 43) | <0.001 | 73 (62, 75) | 55 (48, 64) | 43 (36, 44) | 34 (30, 39) | 12 (8, 16) | <0.001 |
| Fine Motor Dependent | 32 (22, 42) | 42 (26, 48) | 10 (2, 21) | <0.001 | 0.87 (0.74, 0.90) | 0.63 (0.49, 0.71) | 0.40 (0.29, 0.42) | 0.23 (0.17, 0.33) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.04) | <0.001 |
| Fine Motor Independent | 23 (22, 26) | 27 (23, 29) | 21 (15, 22) | 0.002 | 0.69 (0.61, 0.76) | 0.58 (0.56, 0.69) | 0.56 (0.54, 0.56) | 0.54 (0.51, 0.56) | 0.31 (0.20, 0.36) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Invencao Cabral, T.; Pan, X.; Tripathi, T.; Ma, J.; Heathcock, J.C. Manual Abilities and Cognition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Do Fine Motor Skills Impact Cognition as Measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant Development? Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070542
Invencao Cabral T, Pan X, Tripathi T, Ma J, Heathcock JC. Manual Abilities and Cognition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Do Fine Motor Skills Impact Cognition as Measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant Development? Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(7):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070542
Chicago/Turabian StyleInvencao Cabral, Thais, Xueliang Pan, Tanya Tripathi, Jianing Ma, and Jill C. Heathcock. 2023. "Manual Abilities and Cognition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Do Fine Motor Skills Impact Cognition as Measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant Development?" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 7: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070542
APA StyleInvencao Cabral, T., Pan, X., Tripathi, T., Ma, J., & Heathcock, J. C. (2023). Manual Abilities and Cognition in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Do Fine Motor Skills Impact Cognition as Measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant Development? Behavioral Sciences, 13(7), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13070542






