Predicting Alcohol-Related Memory Problems in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Study with Multi-Domain Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Recent Telephone Interview
2.3. EEG Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.4. EEG Functional Connectivity Analysis Using eLORETA
2.5. Functional Connectivity across the Default Mode Network
2.6. Assessment of Temperament, Personality, and Alcohol Experience
2.7. Genomic Data and Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS)
2.8. Feature selection of EEG Functional Connectivity Variables
2.9. Random Forests Classification Model and Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Feature Selection of EEG Functional Connectivity Variables
3.2. Random Forests Classification Accuracy
3.3. Top Significant Features Contributed to the Classification
3.3.1. EEG Source Functional Connectivity of the Default Mode Network
3.3.2. Recent Alcohol Consumption and Health Outcomes
3.3.3. Measures of Personality, Behavior, and Life Experiences
3.3.4. Polygenic Risk Scores
3.4. Correlations across Significant Predictors
4. Discussion
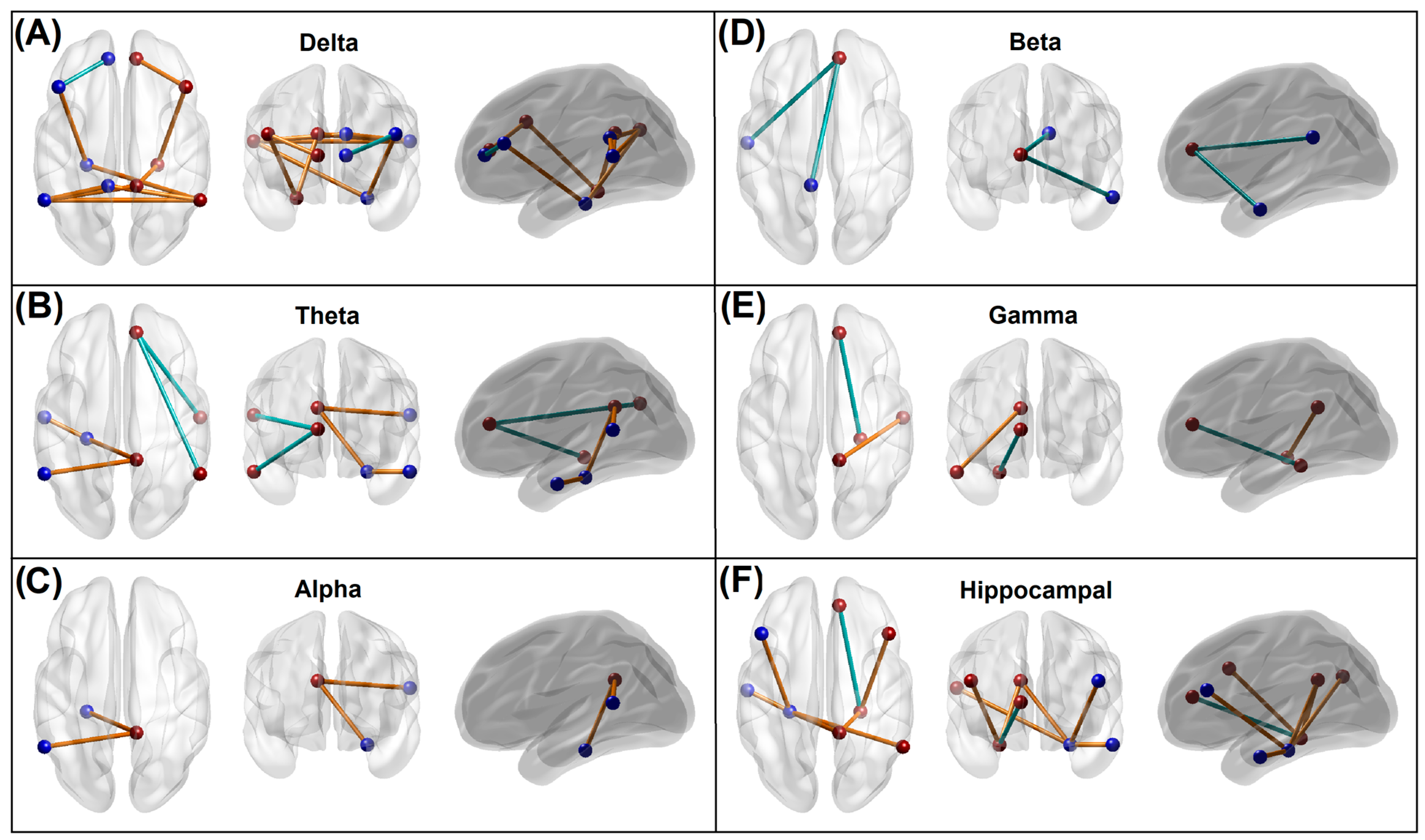
4.1. Altered Functional Connectivity in the Memory Group
4.1.1. Predominant Hyperconnectivity of Low-Frequency Oscillations in the Memory Group
4.1.2. Hyperconnectivity across the Hippocampal–Cortical Networks in the Memory Group
4.1.3. Hypoconnectivity across the Anterior Cingulate Hub Networks in the Memory Group
4.2. Alcohol Consumption and Health Problems in the Memory Group
4.3. Personality Features in the Memory Group
4.4. Genomic Risk in the Memory Group
4.5. Correlations among the Significant Features
4.6. Limitations and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, C.P.; McLellan, A.T. Myths about the treatment of addiction. Lancet 1996, 347, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. Neurocircuitry of alcohol addiction: Synthesis from animal models. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscar-Berman, M. Neuropsychological vulnerabilities in chronic alcoholism. In Review of NIAAA’s Neuroscience and Behavioral Research Portfolio National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) Research Monograph No 34; Noronha, A., Eckardt, M.J., Warren, K., Eds.; NIAAA: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2000; pp. 437–471. [Google Scholar]
- Pitel, A.L.; Beaunieux, H.; Witkowski, T.; Vabret, F.; Guillery-Girard, B.; Quinette, P.; Desgranges, B.; Eustache, F. Genuine episodic memory deficits and executive dysfunctions in alcoholic subjects early in abstinence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, X.; Van der Linden, M.; Brevers, D.; Campanella, S.; Hanak, C.; Kornreich, C.; Verbanck, P. The contribution of executive functions deficits to impaired episodic memory in individuals with alcoholism. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 198, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscar-Berman, M.; Valmas, M.M.; Sawyer, K.S.; Ruiz, S.M.; Luhar, R.B.; Gravitz, Z.R. Profiles of impaired, spared, and recovered neuropsychologic processes in alcoholism. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Berre, A.P.; Fama, R.; Sullivan, E.V. Executive Functions, Memory, and Social Cognitive Deficits and Recovery in Chronic Alcoholism: A Critical Review to Inform Future Research. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoch, M.A. Genetic and environmental influences on the development of alcoholism: Resilience vs. risk. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1094, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porjesz, B.; Rangaswamy, M.; Kamarajan, C.; Jones, K.A.; Padmanabhapillai, A.; Begleiter, H. The utility of neurophysiological markers in the study of alcoholism. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 993–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Fagan, P. Alcoholism: A polygenic, multifactorial disease. Compr. Ther. 1985, 11, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donner, T.H.; Siegel, M. A framework for local cortical oscillation patterns. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzel, E.; Penny, W.D.; Burgess, N. Brain oscillations and memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G.; Moser, E.I. Memory, navigation and theta rhythm in the hippocampal-entorhinal system. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimesch, W. Memory processes, brain oscillations and EEG synchronization. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1996, 24, 61–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanslmayr, S.; Staudigl, T. How brain oscillations form memories—A processing based perspective on oscillatory subsequent memory effects. Neuroimage 2014, 85 Pt 2, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahana, M.J. The cognitive correlates of human brain oscillations. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herweg, N.A.; Solomon, E.A.; Kahana, M.J. Theta Oscillations in Human Memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2020, 24, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgin, L.L. Oscillations and hippocampal-prefrontal synchrony. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgin, L.L. Mechanisms and functions of theta rhythms. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 36, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgin, L.L. Theta-gamma coupling in the entorhinal-hippocampal system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 31, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canolty, R.T.; Knight, R.T. The functional role of cross-frequency coupling. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Lehmann, D.; Koukkou, M.; Kochi, K.; Anderer, P.; Saletu, B.; Tanaka, H.; Hirata, K.; John, E.R.; Prichep, L.; et al. Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 3768–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuet, L.; Ishii, R.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Iwase, M.; Kurimoto, R.; Aoki, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Takahashi, H.; Nakahachi, T.; Takeda, M. Resting-state EEG source localization and functional connectivity in schizophrenia-like psychosis of epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, S.M. Coherence a measure of the brain networks: Past and present. Neuropsychiatr. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, G.; Bai, O.; Wheaton, L.; Mari, Z.; Vorbach, S.; Hallett, M. Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 2292–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, S.; Trankner, A.; Chittka, T.; Hegerl, U.; Schonknecht, P. Functional connectivity in major depression: Increased phase synchronization between frontal cortical EEG-source estimates. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 222, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, M.; Kazui, H.; Tanaka, T.; Ishii, R.; Canuet, L.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Aoki, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Kanemoto, H.; Yoshiyama, K.; et al. Functional connectivity assessed by resting state EEG correlates with cognitive decline of Alzheimer’s disease—An eLORETA study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperatori, C.; Della Marca, G.; Brunetti, R.; Carbone, G.A.; Massullo, C.; Valenti, E.M.; Amoroso, N.; Maestoso, G.; Contardi, A.; Farina, B. Default Mode Network alterations in alexithymia: An EEG power spectra and connectivity study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, A.E.; Deccy, S.; Ironside, M.L.; Kumar, P.; Beltzer, M.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Electroencephalography Source Functional Connectivity Reveals Abnormal High-Frequency Communication among Large-Scale Functional Networks in Depression. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mohan, A.; De Ridder, D.; Sunaert, S.; Vanneste, S. The neural correlates of the unified percept of alcohol-related craving: A fMRI and EEG study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, W.; Pennartz, C.M.; Cabeza, R.; Daselaar, S.M. The hippocampus is coupled with the default network during memory retrieval but not during memory encoding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlye, E.T.; Lundervold, A.; Rootwelt, H.; Lundervold, A.J.; Westlye, L.T. Increased hippocampal default mode synchronization during rest in middle-aged and elderly APOE epsilon4 carriers: Relationships with memory performance. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7775–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.M.; Schultz, A.P.; Huijbers, W.; Van Dijk, K.R.; Hedden, T.; Sperling, R.A. The parahippocampal gyrus links the default-mode cortical network with the medial temporal lobe memory system. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 35, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, L.; Li, R.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J. The Default Mode Network Supports Episodic Memory in Cognitively Unimpaired Elderly Individuals: Different Contributions to Immediate Recall and Delayed Recall. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Wang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Lai, D.; Wetherill, L.; Edenberg, H.J.; Aliev, F.; Plawecki, M.H.; Chorlian, D.; Chan, G.; et al. High Polygenic Risk Scores Are associated with Early Age of Onset of Alcohol Use Disorder in Adolescents and Young Adults at Risk. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2022, 2, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinreich, S.; McCutcheon, V.V.; Aliev, F.; Meyers, J.L.; Kamarajan, C.; Pandey, A.K.; Chorlian, D.B.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, W.; Pandey, G.; et al. Predicting alcohol use disorder remission: A longitudinal multimodal multi-featured machine learning approach. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Savage, J.E.; Kendler, K.S.; Hickman, M.; Mahedy, L.; Macleod, J.; Kaprio, J.; Rose, R.J.; Dick, D.M. Polygenic Risk, Personality Dimensions, and Adolescent Alcohol Use Problems: A Longitudinal Study. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2017, 78, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, A.; Kato, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Ono, Y.; Kitamura, T. Examination of the tridimensional personality hypothesis of alcoholism using empirically multivariate typology. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1994, 18, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, A.; Struglia, F.; Spaziani, D.; Pacifico, R.; Stratta, P.; Rossi, A. Decision making, impulsivity, and personality traits in alcohol-dependent subjects. Am. J. Addict. 2012, 21, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, A.K.; Sher, K.J. The Multiple, Distinct Ways that Personality Contributes to Alcohol Use Disorders. Soc. Pers. Psychol. Compass 2010, 4, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstrom, T.; Torvik, F.A.; Ystrom, E.; Czajkowski, N.O.; Gillespie, N.A.; Aggen, S.H.; Krueger, R.F.; Kendler, K.S.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T. Prediction of alcohol use disorder using personality disorder traits: A twin study. Addiction 2018, 113, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creed, M. Current and emerging neuromodulation therapies for addiction: Insight from pre-clinical studies. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 49, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, R.M.G.; Nguyen, J.A. Working memory revived in older adults by synchronizing rhythmic brain circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Smith, T.L.; Danko, G.; Kramer, J.; Bucholz, K.K.; McCutcheon, V.; Chan, G.; Kuperman, S.; Hesselbrock, V.; Dick, D.M.; et al. A 22-Year Follow-Up (Range 16 to 23) of Original Subjects with Baseline Alcohol Use Disorders from the Collaborative Study on Genetics of Alcoholism. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Kramer, J.R.; Schuckit, M.A.; Hesselbrock, V.; Bucholz, K.K.; Edenberg, H.J.; Acion, L.; Langbehn, D.; McCutcheon, V.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; et al. A Pilot Follow-Up Study of Older Alcohol-Dependent COGA Adults. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begleiter, H.; Reich, T.; Hesselbrock, V.; Porjesz, B.; Li, T.-K.; Schuckit, M.A.; Edenberg, H.J.; Rice, J.P. The Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism. Alcohol Health Res. World 1995, 19, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Bucholz, K.K.; McCutcheon, V.V.; Agrawal, A.; Dick, D.M.; Hesselbrock, V.M.; Kramer, J.R.; Kuperman, S.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Salvatore, J.E.; Schuckit, M.A.; et al. Comparison of Parent, Peer, Psychiatric, and Cannabis Use Influences Across Stages of Offspring Alcohol Involvement: Evidence from the COGA Prospective Study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Wetherill, L.; Bertelsen, S.; Carey, C.E.; Kamarajan, C.; Kapoor, M.; Meyers, J.L.; Anokhin, A.P.; Bennett, D.A.; Bucholz, K.K.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of alcohol dependence, DSM-IV criterion count and individual criteria. Genes Brain Behav. 2019, 18, e12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucholz, K.K.; Cadoret, R.; Cloninger, C.R.; Dinwiddie, S.H.; Hesselbrock, V.M.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Reich, T.; Schmidt, I.; Schuckit, M.A. A new, semi-structured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: A report on the reliability of the SSAGA. J. Stud. Alcohol 1994, 55, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselbrock, M.; Easton, C.; Bucholz, K.K.; Schuckit, M.; Hesselbrock, V. A validity study of the SSAGA-A comparison with the SCAN. Addiction 1999, 94, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap consortium: Building an international community of software platform partners. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaswamy, M.; Porjesz, B.; Chorlian, D.B.; Wang, K.; Jones, K.A.; Bauer, L.O.; Rohrbaugh, J.; O’Connor, S.J.; Kuperman, S.; Reich, T.; et al. Beta power in the EEG of alcoholics. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 52, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorlian, D.B.; Rangaswamy, M.; Porjesz, B. EEG coherence: Topography and frequency structure. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Discrete, 3D distributed, linear imaging methods of electric neuronal activity. Part 1: Exact, zero error localization. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0710.3341. [Google Scholar]
- Buckner, R.L.; Andrews-Hanna, J.R.; Schacter, D.L. The brain’s default network: Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1124, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, R.W.; North, D.M.; Biver, C.J. LORETA EEG phase reset of the default mode network. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, C.; Ardekani, B.A.; Pandey, A.K.; Chorlian, D.B.; Kinreich, S.; Pandey, G.; Meyers, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, W.; Stimus, A.T.; et al. Random Forest Classification of Alcohol Use Disorder Using EEG Source Functional Connectivity, Neuropsychological Functioning, and Impulsivity Measures. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, C.; Ardekani, B.A.; Pandey, A.K.; Kinreich, S.; Pandey, G.; Chorlian, D.B.; Meyers, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Bermudez, E.; Stimus, A.T.; et al. Random Forest Classification of Alcohol Use Disorder Using fMRI Functional Connectivity, Neuropsychological Functioning, and Impulsivity Measures. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzler, H.R.; Zhou, H.; Kember, R.L.; Vickers Smith, R.; Justice, A.C.; Damrauer, S.; Tsao, P.S.; Klarin, D.; Baras, A.; Reid, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and use disorder in 274,424 individuals from multiple populations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelernter, J.; Sun, N.; Polimanti, R.; Pietrzak, R.H.; Levey, D.F.; Lu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, B.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Aslan, M.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study of Maximum Habitual Alcohol Intake in >140,000 U.S. European and African American Veterans Yields Novel Risk Loci. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.K.; Polimanti, R.; Johnson, E.C.; McClintick, J.N.; Adams, M.J.; Adkins, A.E.; Aliev, F.; Bacanu, S.A.; Batzler, A.; Bertelsen, S.; et al. Transancestral GWAS of alcohol dependence reveals common genetic underpinnings with psychiatric disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1656–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Chen, C.Y.; Ni, Y.; Feng, Y.A.; Smoller, J.W. Polygenic prediction via Bayesian regression and continuous shrinkage priors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Feng, Y.-C.A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lam, M.; Guo, Z.; He, L.; Sawa, A.; Martin, A.R.; Qin, S.; et al. Improving Polygenic Prediction in Ancestrally Diverse Populations. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.B.; Ksinan, A.; Su, J.; Johnson, E.C.; Meyers, J.L.; Wetherill, L.; Latvala, A.; Aliev, F.; Chan, G.; Kuperman, S.; et al. Using polygenic scores for identifying individuals at increased risk of substance use disorders in clinical and population samples. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Abreu, M.; Chan, G.; Hesselbrock, V.; Kamarajan, C.; Liu, Y.; Meyers, J.L.; Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Plawecki, M.H.; et al. Gene-based polygenic risk scores analysis of alcohol use disorder in African Americans. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, D.; Johnson, E.C.; Colbert, S.; Pandey, G.; Chan, G.; Bauer, L.; Francis, M.W.; Hesselbrock, V.; Kamarajan, C.; Kramer, J.; et al. Evaluating risk for alcohol use disorder: Polygenic risk scores and family history. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, T.; Irvin, M.R.; Patki, A.; Srinivasasainagendra, V.; Lin, Y.F.; Tiwari, H.K.; Armstrong, N.D.; Benoit, B.; Chen, C.Y.; Choi, K.W.; et al. Development and validation of a trans-ancestry polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes in diverse populations. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarajan, C.; Ardekani, B.A.; Pandey, A.K.; Kinreich, S.; Pandey, G.; Chorlian, D.B.; Meyers, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Bermudez, E.; Kuang, W.; et al. Differentiating Individuals with and without Alcohol Use Disorder Using Resting-State fMRI Functional Connectivity of Reward Network, Neuropsychological Performance, and Impulsivity Measures. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Wang, Y.; Nguyen, H.N. Random forest classifier combined with feature selection for breast cancer diagnosis and prognostic. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2013, 6, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, G.; Sahin, F. A survey on feature selection methods. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2014, 40, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Luo, J.W.; Wang, S.L.; Yang, S. Feature selection in machine learning: A new perspective. Neurocomputing 2018, 300, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala, R.F.; Thangaiah, P.R.J. A Novel Two-Stage Selection of Feature Subsets in Machine Learning. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 4169–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Sarkar, S.; Pradhan, C. Feature Selection and Random Forest Classification for Breast Cancer Disease. In Data Analytics in Bioinformatics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Package ’randomForest’: Breiman and Cutler’s Random Forests for Classification and Regression. R Development Core Team 2014, 4, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; Wing, J.; Weston, S.; Williams, A.; Keefer, C.; Engelhardt, A.; Cooper, T.; Mayer, Z.; Kenkel, B.; Benesty, M.; et al. Classification and Regression Training; R Package Version 6.0-84. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/caret (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Paluszynska, A.; Biecek, P.; Jiang, Y. randomForestExplainer: Explaining and Visualizing Random Forests in Terms of Variable Importance; R Package Version 0.10.0. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/randomForestExplainer (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Semon, R. The Mneme; G. Allen & Unwin Limited: London, UK, 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Hebb, D.O. The Organization of Behavior: A Neuropsychological Theory; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, L.; Moretti, D.; Benussi, A.; Ferri, L.; Russo, M.; Carrarini, C.; Barbone, F.; Arnaldi, D.; Falasca, N.W.; Koch, G.; et al. Hyperconnectivity in Dementia Is Early and Focal and Wanes with Progression. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Daverio, A.; Ferrentino, F.; Santarnecchi, E.; Ciabattini, F.; Monaco, L.; Lisi, G.; Barone, Y.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Niolu, C.; et al. Altered resting-state EEG source functional connectivity in schizophrenia: The effect of illness duration. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuchter, A.F.; Cook, I.A.; Hunter, A.M.; Cai, C.; Horvath, S. Resting-state quantitative electroencephalography reveals increased neurophysiologic connectivity in depression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, L. Increased EEG coherence in long-distance and short-distance connectivity in children with autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arns, M.; Peters, S.; Breteler, R.; Verhoeven, L. Different brain activation patterns in dyslexic children: Evidence from EEG power and coherence patterns for the double-deficit theory of dyslexia. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2007, 6, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahou, E.L.; Thurm, F.; Kolassa, I.T.; Schlee, W. Resting-state slow wave power, healthy aging and cognitive performance. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, H.; Kumarnsit, E.; Chatpun, S. Age-Related Alterations in EEG Network Connectivity in Healthy Aging. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar-Eroglu, C.; Basar, E.; Demiralp, T.; Schurmann, M. P300-response: Possible psychophysiological correlates in delta and theta frequency channels. A review. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1992, 13, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Kamarajan, C.; Rangaswamy, M.; Porjesz, B. Event-Related Oscillations in Alcoholism Research: A Review. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2012, Suppl 7, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, B.; Boha, R.; Posfai, M.; Gaal, Z.A.; Konya, A.; Stam, C.J.; Molnar, M. EEG synchronization characteristics of functional connectivity and complex network properties of memory maintenance in the delta and theta frequency bands. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 83, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, J. Core Concept: How synaptic pruning shapes neural wiring during development and, possibly, in disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16096–16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pievani, M.; de Haan, W.; Wu, T.; Seeley, W.W.; Frisoni, G.B. Functional network disruption in the degenerative dementias. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinger, D.M.; Roberto, M. Synaptic effects induced by alcohol. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 13, 31–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahao, K.P.; Salinas, A.G.; Lovinger, D.M. Alcohol and the Brain: Neuronal Molecular Targets, Synapses, and Circuits. Neuron 2017, 96, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, M.J.; Rivera, P.D.; Bilbo, S.D. Glial and Neuroimmune Mechanisms as Critical Modulators of Drug Use and Abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socodato, R.; Henriques, J.F.; Portugal, C.C.; Almeida, T.O.; Tedim-Moreira, J.; Alves, R.L.; Canedo, T.; Silva, C.; Magalhaes, A.; Summavielle, T.; et al. Daily alcohol intake triggers aberrant synaptic pruning leading to synapse loss and anxiety-like behavior. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaba5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormann, F.; Osterhage, H.; Andrzejak, R.G.; Weber, B.; Fernandez, G.; Fell, J.; Elger, C.E.; Lehnertz, K. Independent delta/theta rhythms in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2008, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inhoff, M.C.; Ranganath, C. Dynamic Cortico-hippocampal Networks Underlying Memory and Cognition: The PMAT Framework. In The Hippocampus from Cells to Systems; Hannula, D.E., Duff, M.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 559–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.; Pudas, S.; Nyberg, L. Elevated hippocampal resting-state connectivity underlies deficient neurocognitive function in aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17654–17659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedlbauer, A.M.; Copara, M.S.; Watrous, A.J.; Ekstrom, A.D. Multiple interacting brain areas underlie successful spatiotemporal memory retrieval in humans. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaefer, K.; Stella, F.; McNaughton, B.L.; Battaglia, F.P. Replay, the default mode network and the cascaded memory systems model. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 23, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernbach, J.M.; Yeo, B.T.T.; Smallwood, J.; Margulies, D.S.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Walter, H.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Holmes, A.J.; Gramfort, A.; Varoquaux, G.; et al. Subspecialization within default mode nodes characterized in 10,000 UK Biobank participants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.D.; Jadhav, S.P. Multiple modes of hippocampal-prefrontal interactions in memory-guided behavior. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2016, 40, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucewicz, M.T.; Berry, B.M.; Miller, L.R.; Khadjevand, F.; Ezzyat, Y.; Stein, J.M.; Kremen, V.; Brinkmann, B.H.; Wanda, P.; Sperling, M.R.; et al. Evidence for verbal memory enhancement with electrical brain stimulation in the lateral temporal cortex. Brain 2018, 141, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, C.; Protzner, A.B.; Barnett, A.J.; Cohn, M.; Valiante, T.A.; McAndrews, M.P. Linking DMN connectivity to episodic memory capacity: What can we learn from patients with medial temporal lobe damage? Neuroimage Clin. 2014, 5, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, B.; Sala-Padro, J.; Cucurell, D.; Santurino, M.; Falip, M.; Fuentemilla, L. Theta rhythm supports hippocampus-dependent integrative encoding in schematic/semantic memory networks. Neuroimage 2021, 226, 117558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuet, L.; Tellado, I.; Couceiro, V.; Fraile, C.; Fernandez-Novoa, L.; Ishii, R.; Takeda, M.; Cacabelos, R. Resting-state network disruption and APOE genotype in Alzheimer’s disease: A lagged functional connectivity study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Hou, J.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Cai, P.; Lii, H. Disrupted functional connectivity of the hippocampus in patients with hyperthyroidism: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, N.; King, T.Z.; Shin, J.; Srivastava, A.; Brewster, R.C.; Jovanovic, T.; Bradley, B.; Ressler, K.J. Structural and Functional Connectivity in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Associations with Fkbp5. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez de la Plata, C.D.; Garces, J.; Shokri Kojori, E.; Grinnan, J.; Krishnan, K.; Pidikiti, R.; Spence, J.; Devous, M.D., Sr.; Moore, C.; McColl, R.; et al. Deficits in functional connectivity of hippocampal and frontal lobe circuits after traumatic axonal injury. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Ardekani, B.A.; Kamarajan, C.; Zhang, J.; Chorlian, D.B.; Byrne, K.N.; Pandey, G.; Meyers, J.L.; Kinreich, S.; Stimus, A.; et al. Lower Prefrontal and Hippocampal Volume and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Differences Reflect Structural and Functional Abnormalities in Abstinent Individuals with Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, M.; Klawonn, A.M.; Zahr, N.M. Neuroimaging in alcohol use disorder: From mouse to man. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 100, 1140–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Im, S.J.; Lee, S.G.; Stadlin, A.; Son, J.W.; Shin, C.J.; Ju, G.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, S. Volume of hippocampal subfields in patients with alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2016, 258, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Pereira, M.C.; Santana, L.N.; Fernandes, R.M.; Teixeira, F.B.; Oliveira, G.B.; Fernandes, L.M.; Fontes-Junior, E.A.; Prediger, R.D.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; et al. Chronic ethanol exposure during adolescence through early adulthood in female rats induces emotional and memory deficits associated with morphological and molecular alterations in hippocampus. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, M.C.; Mandyam, C.D. Thinking after Drinking: Impaired Hippocampal-Dependent Cognition in Human Alcoholics and Animal Models of Alcohol Dependence. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akam, T.; Rodrigues-Vaz, I.; Marcelo, I.; Zhang, X.; Pereira, M.; Oliveira, R.F.; Dayan, P.; Costa, R.M. The Anterior Cingulate Cortex Predicts Future States to Mediate Model-Based Action Selection. Neuron 2021, 109, 149–163.e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, A.T.; Tennyson, S.S.; deBettencourt, C.A.; Gaye, F.; Roesch, M.R. Anterior cingulate cortex is necessary for adaptation of action plans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6196–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, P.L.; Wittmann, M.K. Ventral anterior cingulate cortex and social decision-making. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 92, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushworth, M.F.; Walton, M.E.; Kennerley, S.W.; Bannerman, D.M. Action sets and decisions in the medial frontal cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennerley, S.W.; Walton, M.E.; Behrens, T.E.; Buckley, M.J.; Rushworth, M.F. Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.E.; Croxson, P.L.; Behrens, T.E.; Kennerley, S.W.; Rushworth, M.F. Adaptive decision making and value in the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroimage 2007, 36 (Suppl. 2), T142–T154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Cohen, J.D.; Carter, C.S. Conflict monitoring and anterior cingulate cortex: An update. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.S.; Braver, T.S.; Barch, D.M.; Botvinick, M.M.; Noll, D.; Cohen, J.D. Anterior cingulate cortex, error detection, and the online monitoring of performance. Science 1998, 280, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veen, V.; Carter, C.S. The anterior cingulate as a conflict monitor: fMRI and ERP studies. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 77, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W.J.; Willoughby, A.R. The medial frontal cortex and the rapid processing of monetary gains and losses. Science 2002, 295, 2279–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.F.; Xu, H.S.; Fu, X.M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D.R. Addiction related alteration in resting-state brain connectivity. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojemann, G.A.; Creutzfeldt, O.; Lettich, E.; Haglund, M.M. Neuronal activity in human lateral temporal cortex related to short-term verbal memory, naming and reading. Brain 1988, 111 Pt 6, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojemann, G.A.; Schoenfield-McNeill, J.; Corina, D. The roles of human lateral temporal cortical neuronal activity in recent verbal memory encoding. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kable, J.W.; Kan, I.P.; Wilson, A.; Thompson-Schill, S.L.; Chatterjee, A. Conceptual representations of action in the lateral temporal cortex. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelen, M.V.; Romagno, D.; Caramazza, A. Independent representations of verbs and actions in left lateral temporal cortex. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 24, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.S. Functional clustering of the human inferior parietal lobule by whole-brain connectivity mapping of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging signals. Brain Connect. 2014, 4, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, O.A.; Nixon, S.J. Neurobehavioral sequelae of alcoholism. Neurol. Clin. 1993, 11, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Topiwala, A. Alcohol use disorders and the brain. Addiction 2020, 115, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giancola, P.R.; Moss, H.B. Executive cognitive functioning in alcohol use disorders. Recent Dev. Alcohol. 1998, 14, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evert, D.L.; Oscar-Berman, M. Alcohol-Related Cognitive Impairments: An Overview of How Alcoholism May Affect the Workings of the Brain. Alcohol Health Res. World 1995, 19, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Oscar-Berman, M.; Shagrin, B.; Evert, D.L.; Epstein, C. Impairments of brain and behavior: The neurological effects of alcohol. Alcohol Health Res. World 1997, 21, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fama, R.; Le Berre, A.P.; Hardcastle, C.; Sassoon, S.A.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Sullivan, E.V.; Zahr, N.M. Neurological, nutritional and alcohol consumption factors underlie cognitive and motor deficits in chronic alcoholism. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.O.; Kivlahan, D.; Walker, R.D. Cloninger’s tridimensional theory of personality and psychopathology: Applications to substance use disorders. J. Stud. Alcohol 1997, 58, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, K.P.; Compton, W.; Stinson, F.S.; Grant, B.F. Lifetime comorbidity of DSM-IV mood and anxiety disorders and specific drug use disorders: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2006, 67, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, M.G.; Wall, M.M.; Krueger, R.F.; Sher, K.J.; Maurer, E.; Thuras, P.; Lee, S. Alcohol dependence is related to overall internalizing psychopathology load rather than to particular internalizing disorders: Evidence from a national sample. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Yang, Z.; Zang, Y.; Acion, L.; Bierut, L.; Bucholz, K.; Chan, G.; Dick, D.M.; Edenberg, H.J.; Kramer, J.; et al. Development of Alcohol Use Disorder as a Function of Age, Severity, and Comorbidity with Externalizing and Internalizing Disorders in a Young Adult Cohort. J. Psychiatr. Brain Sci. 2019, 4, e190016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meque, I.; Dachew, B.A.; Maravilla, J.C.; Salom, C.; Alati, R. Externalizing and internalizing symptoms in childhood and adolescence and the risk of alcohol use disorders in young adulthood: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2019, 53, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussong, A.M.; Jones, D.J.; Stein, G.L.; Baucom, D.H.; Boeding, S. An internalizing pathway to alcohol use and disorder. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2011, 25, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.D.; Griffin, M.L.; Mirin, S.M. Drug abuse as self-medication for depression: An empirical study. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 1992, 18, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D. The reality of comorbidity: Depression and drug abuse. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottlender, M.; Soyka, M. Impact of different personality dimensions (NEO Five-Factor Inventory) on the outcome of alcohol-dependent patients 6 and 12 months after treatment. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 136, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribadier, A.; Varescon, I. Anxiety and depression in alcohol use disorder individuals: The role of personality and coping strategies. Subst. Use Misuse 2019, 54, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.F.; Fede, S.J.; Diazgranados, N.; Momenan, R. Addiction neurocircuitry and negative affect: A role for neuroticism in understanding amygdala connectivity and alcohol use disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 722, 134773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, J.W.; Zinbarg, R.E.; Craske, M.G.; Mineka, S.; Rose, R.D.; Waters, A.M.; Sutton, J.M. Neuroticism as a common dimension in the internalizing disorders. Psychol. Med. 2010, 40, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.D.; Coyne, J.C.; Schaefer, C.; Lazarus, R.S. Comparison of two modes of stress measurement: Daily hassles and uplifts versus major life events. J. Behav. Med. 1981, 4, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, M.; Windle, R.C. A prospective study of stressful events, coping motives for drinking, and alcohol use among middle-aged adults. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2015, 76, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettis, A.H.; Forehand, R.; McKee, L.; Dunbar, J.P.; Watson, K.H.; Compas, B.E. Testing Specificity: Associations of Stress and Coping with Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression in Youth. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2016, 25, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffge-Krenke, I. Causal links between stressful events, coping style, and adolescent symptomatology. J. Adolesc. 2000, 23, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edenberg, H.J.; Foroud, T. Genetics and alcoholism. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhulst, B.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S. The heritability of alcohol use disorders: A meta-analysis of twin and adoption studies. Psychol. Med. 2015, 45, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, E.; Kaminski, J.; Ripke, S. Heritability of Alcohol Use Disorder: Evidence from Twin Studies and Genome-Wide Association Studies. In Textbook of Addiction Treatment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.C.; Sanchez-Roige, S.; Acion, L.; Adams, M.J.; Bucholz, K.K.; Chan, G.; Chao, M.J.; Chorlian, D.B.; Dick, D.M.; Edenberg, H.J.; et al. Polygenic contributions to alcohol use and alcohol use disorders across population-based and clinically ascertained samples. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.L.; Chorlian, D.B.; Johnson, E.C.; Pandey, A.K.; Kamarajan, C.; Salvatore, J.E.; Aliev, F.; Subbie-Saenz de Viteri, S.; Zhang, J.; Chao, M.; et al. Association of Polygenic Liability for Alcohol Dependence and EEG Connectivity in Adolescence and Young Adulthood. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, T.K.; Smith, A.H.; Gelernter, J.; Kranzler, H.R.; Farrer, L.A.; Hall, L.S.; Fernandez-Pujals, A.M.; MacIntyre, D.J.; Smith, B.H.; Hocking, L.J.; et al. Polygenic risk for alcohol dependence associates with alcohol consumption, cognitive function and social deprivation in a population-based cohort. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, A.S.; Johnson, E.C.; Baranger, D.A.A.; Paul, S.E.; Agrawal, A.; Bogdan, R. Polygenic risk scores for alcohol involvement relate to brain structure in substance-naive children: Results from the ABCD study. Genes Brain Behav. 2021, 20, e12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Svensson, F.P.; Mazeh, A.; Kocsis, B. Prefrontal-hippocampal coupling by theta rhythm and by 2–5 Hz oscillation in the delta band: The role of the nucleus reuniens of the thalamus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketz, N.A.; Jensen, O.; O’Reilly, R.C. Thalamic pathways underlying prefrontal cortex-medial temporal lobe oscillatory interactions. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kubota, S.; Shimizu, F.A.; Hirano-Iwata, A.; Niwano, M. Effective Subnetwork Topology for Synchronizing Interconnected Networks of Coupled Phase Oscillators. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babapoor-Farrokhran, S.; Vinck, M.; Womelsdorf, T.; Everling, S. Theta and beta synchrony coordinate frontal eye fields and anterior cingulate cortex during sensorimotor mapping. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axmacher, N.; Henseler, M.M.; Jensen, O.; Weinreich, I.; Elger, C.E.; Fell, J. Cross-frequency coupling supports multi-item working memory in the human hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3228–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincat, S.L.; Donoghue, J.A.; Mahnke, M.K.; Kornblith, S.; Lundqvist, M.; Miller, E.K. Interhemispheric transfer of working memories. Neuron 2021, 109, 1055–1066.e1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.; Bernards, S.; Knibbe, R.; Kairouz, S.; Kuntsche, S.; Wilsnack, S.C.; Greenfield, T.K.; Dietze, P.; Obot, I.; Gmel, G. Alcohol-related negative consequences among drinkers around the world. Addiction 2011, 106, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.C.; Fiellin, D.A.; O’Connor, P.G. Hazardous and harmful alcohol consumption in primary care. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, L. Neurobiological Correlates of Personality Traits: A Study on Harm Avoidance and Neuroticism; University of Turku: Turku, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jasper, H.H. Report of the committee on methods of clinical examination in electroencephalography. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1958, 10, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Electroencephalographic Society. Guideline thirteen: Guidelines for standard electrode position nomenclature. American Electroencephalographic Society. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 11, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuwer, M.R.; Comi, G.; Emerson, R.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Guerit, J.M.; Hinrichs, H.; Ikeda, A.; Luccas, F.J.; Rappelsburger, P. IFCN standards for digital recording of clinical EEG. International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperman, S.; Porjesz, B.; Arndt, S.; Bauer, L.; Begleiter, H.; Cizadlo, T.; O’Connor, S.; Rohrbaugh, J. Multi-center N400 ERP consistency using a primed and unprimed word paradigm. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1995, 94, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansereau, C.; Benhajali, Y.; Risterucci, C.; Pich, E.M.; Orban, P.; Arnold, D.; Bellec, P. Statistical power and prediction accuracy in multisite resting-state fMRI connectivity. Neuroimage 2017, 149, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerman, M. Behavioral Expressions and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cloninger, C.R.; Przybeck, T.R.; Svrakic, D.M.; Wetzel, R.D. The Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI): A Guide to Its Development and Use; Washington University: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- DeLongis, A.; Folkman, S.; Lazarus, R.S. The impact of daily stress on health and mood: Psychological and social resources as mediators. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.T., Jr.; McCrae, R.R. Cross-sectional studies of personality in a national sample: 1. Development and validation of survey measures. Psychol. Aging 1986, 1, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procidano, M.E.; Heller, K. Measures of perceived social support from friends and from family: Three validation studies. Am. J. Community Psychol. 1983, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.; Christiansen, B.A.; Goldman, M.S. The Alcohol Expectancy Questionnaire: An instrument for the assessment of adolescent and adult alcohol expectancies. J. Stud. Alcohol 1987, 48, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuckit, M.A.; Tipp, J.E.; Smith, T.L.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Kalmijn, J. The relationship between Self-Rating of the Effects of alcohol and alcohol challenge results in ninety-eight young men. J. Stud. Alcohol 1997, 58, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenberg, H.J.; Koller, D.L.; Xuei, X.; Wetherill, L.; McClintick, J.N.; Almasy, L.; Bierut, L.J.; Bucholz, K.K.; Goate, A.; Aliev, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates a region on chromosome 11. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Foroud, T.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Le, N.X.; Bertelsen, S.; Budde, J.P.; Harari, O.; Koller, D.L.; Wetherill, L.; Agrawal, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study of alcohol-dependence symptom counts in extended pedigrees identifies C15orf53. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baurley, J.W.; Edlund, C.K.; Pardamean, C.I.; Conti, D.V.; Bergen, A.W. Smokescreen: A targeted genotyping array for addiction research. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaneau, O.; Howie, B.; Cox, A.J.; Zagury, J.F.; Marchini, J. Haplotype estimation using sequencing reads. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schonherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.C.; Su, J.; Kuo, S.I.; Kapoor, M.; Wetherill, L.; Bertelsen, S.; Lai, D.; Salvatore, J.E.; et al. An endophenotype approach to the genetics of alcohol dependence: A genome wide association study of fast beta EEG in families of African ancestry. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherill, L.; Agrawal, A.; Kapoor, M.; Bertelsen, S.; Bierut, L.J.; Brooks, A.; Dick, D.; Hesselbrock, M.; Hesselbrock, V.; Koller, D.L.; et al. Association of substance dependence phenotypes in the COGA sample. Addict. Biol. 2015, 20, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonti, V.; Belitser, E. Feature Selection Using LASSO. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/David-Booth-7/post/Regression-of-pairwise-trait-similarity-on-similarity-in-personal-attributes/attachment/5b18368d4cde260d15e3a4e3/AS%3A634606906785793%401528313485788/download/werkstuk-fonti_tcm235-836234.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y. Random Forest for Bioinformatics. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Zhang, C., Ma, Y., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 307–323. [Google Scholar]
- Couronne, R.; Probst, P.; Boulesteix, A.L. Random forest versus logistic regression: A large-scale benchmark experiment. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobl, C.; Malley, J.; Tutz, G. An introduction to recursive partitioning: Rationale, application, and characteristics of classification and regression trees, bagging, and random forests. Psychol. Methods 2009, 14, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L.; Cutler, A. Random Forest. Available online: https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/RandomForests/cc_home.htm#ooberr (accessed on 1 June 2019).

| Variable | Measure/Category | Parameter | Study Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory (N = 94) | Control (N = 94) | |||
| Age during assessment | EEG * | Min–Max | 29.21–60.71 | 28.17–62.19 |
| Mean (SD) | 39.42 (6.18) | 40.11 (6.74) | ||
| Follow-up interview | Min–Max | 50.55–81.86 | 50.34–81.49 | |
| Mean (SD) | 57.84 (5.77) | 58.75 (6.07) | ||
| Sex | Male | N (%) | 52 (55.30) | 52 (55.30) |
| Female | N (%) | 42 (44.70) | 42 (44.70) | |
| Self-reported race | White | N (%) | 67 (71.30) | 67 (71.30) |
| Black | N (%) | 24 (25.50) | 24 (25.5) | |
| Other | N (%) | 3 (3.20) | 3 (3.20) | |
| Genetic ancestry | European | N (%) | 63 (50.40) | 62 (49.60) |
| African | N (%) | 23 (47.92) | 25 (52.08) | |
| Other | N (%) | 8 (53.33) | 7 (46.67) | |
| Alcohol use pattern during the latest SSAGA interview * | AUD diagnosis | N (%) | 68 (72.30) | 68 (72.30) |
| Low-risk drinking | N (%) | 9 (9.60) | 9 (9.60) | |
| Abstinence | N (%) | 17 (18.10) | 17 (18.10) | |
| Time lag ** | Years | Mean (SD) | 18.42 (3.84) | 18.63 (3.90) |
| Domain | Question | Memory-Related Response * |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol-related memory problems | Compared to most people your age, is your memory currently better, about the same, or worse than theirs? | Worse |
| ** There are several other health problems that can result from heavy drinking. In the last 5 years did drinking: (check all that apply) | Impair your memory even when you were not drinking (not including blackouts)? | |
| ** There are several other health problems that can result from heavy drinking. In the last 10 years did drinking: (check all that apply) | Impair your memory even when you were not drinking (not including blackouts)? |
| ROI | Region Name | Region Code | BA | MNI (X) | MNI (Y) | MNI (Z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Left posterior cingulate cortex | L.PCC | 23 | −10 | −45 | 25 |
| 2 | Right posterior cingulate cortex | R.PCC | 23 | 10 | −45 | 25 |
| 3 | Left anterior cingulate cortex | L.ACC | 32 | −10 | 45 | 10 |
| 4 | Right anterior cingulate cortex | R.ACC | 32 | 10 | 45 | 10 |
| 5 | Left inferior parietal lobule | L.IPL | 40 | −55 | −55 | 20 |
| 6 | Right inferior parietal lobule | R.IPL | 40 | 55 | −55 | 20 |
| 7 | Left prefrontal cortex | L.PFC | 46 | −45 | 25 | 25 |
| 8 | Right prefrontal cortex | R.PFC | 46 | 45 | 25 | 25 |
| 9 | Left lateral temporal cortex | L.LTC | 21 | −55 | −15 | −20 |
| 10 | Right lateral temporal cortex | R.LTC | 21 | 55 | −15 | −20 |
| 11 | Left parahippocampal gyrus | L.PHG | 36 | −25 | −30 | −20 |
| 12 | Right parahippocampal gyrus | R.PHG | 36 | 25 | −30 | −20 |
| Phenotype | Discovery Sample/Consortium | Sample Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EA | AA | ||
| AUD diagnosis (ICD-9/ICD-10) | MVP [60] | 202,004 | 56,648 |
| AUDIT-C symptoms | MVP [60] | 200,680 | 56,495 |
| Max alcohol intake | MVP [61] | 126,936 | 17,029 |
| Alcohol dependence (DSM-IV) | PGC [62] | 46,568 | 6280 |
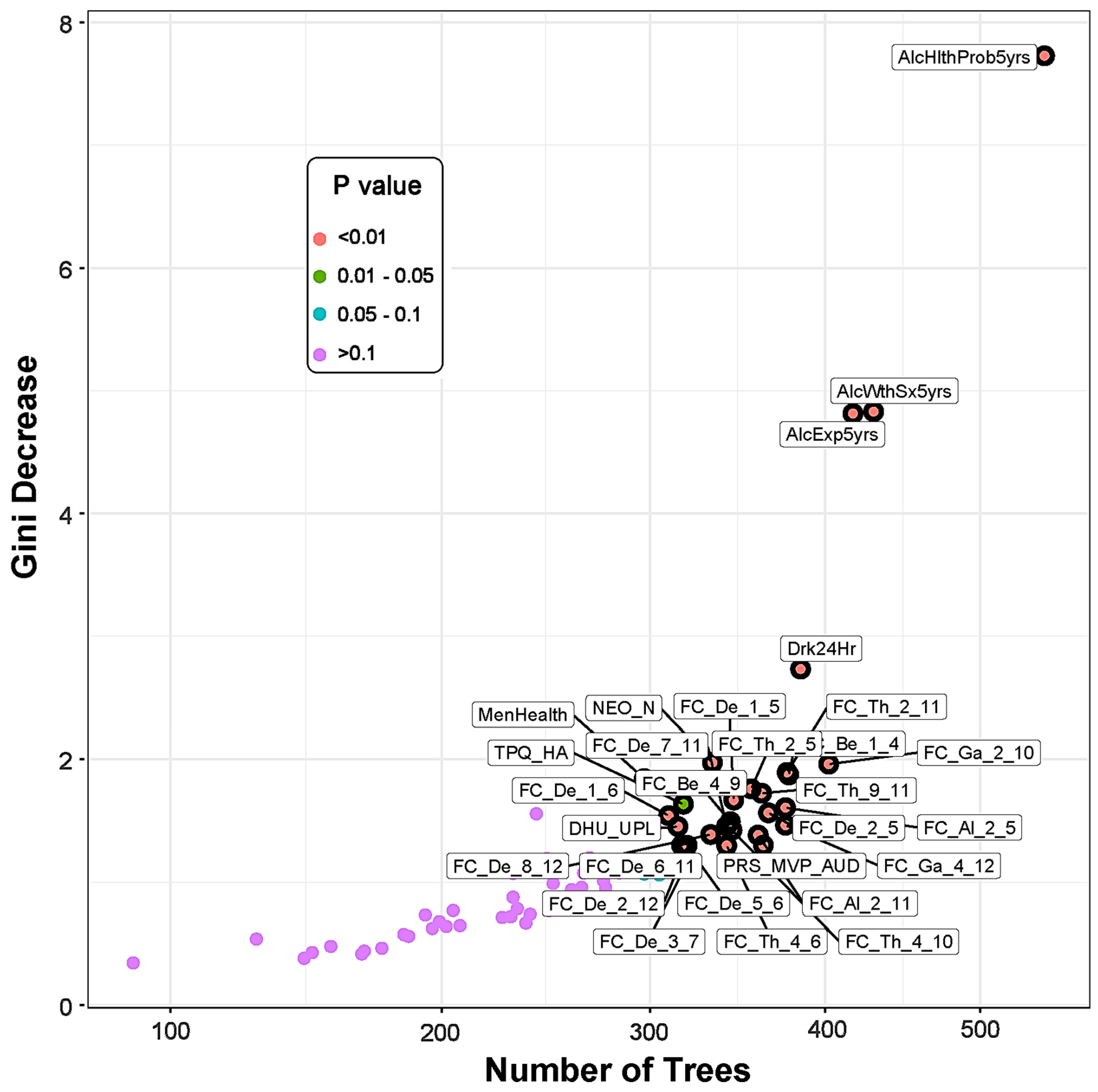
| Feature | Measure/Source | Gini Decrease | Accuracy Decrease | # Trees | # Nodes | Times a Root | Min. Depth | p Value | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlcHlthProb5yrs | FU Interview | 7.7281 | 0.0449 | 545 | 610 | 111 | 2.3303 | 8.26 × 10−47 | MEM > CTL |
| AlcWthSx5yrs | FU Interview | 4.8291 | 0.0196 | 430 | 459 | 109 | 3.8230 | 4.09 × 10−13 | MEM > CTL |
| AlcExp5yrs | FU Interview | 4.8134 | 0.0176 | 417 | 468 | 95 | 4.0144 | 1.42 × 10−14 | MEM > CTL |
| Drk24Hr | FU Interview | 2.7318 | 0.0097 | 385 | 440 | 70 | 5.0280 | 2.75 × 10−10 | MEM > CTL |
| *NEO_N | Questionnaire | 1.9701 | 0.0029 | 334 | 382 | 47 | 5.6475 | 6.84 × 10−4 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Ga_2_10 | R.PCC–R.LTC | 1.9574 | 0.0019 | 402 | 486 | 5 | 5.5047 | 1.02 × 10−17 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Th_2_11 | R.PCC–L.PHG | 1.8902 | 0.0020 | 377 | 463 | 11 | 5.7415 | 9.38 × 10−14 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Be_1_4 | L.PCC–R.ACC | 1.8699 | 0.0030 | 378 | 463 | 6 | 5.8232 | 9.38 × 10−14 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_Th_2_5 | R.PCC–L.IPL | 1.7564 | 0.0039 | 356 | 424 | 16 | 5.8446 | 3.53 × 10−8 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Th_9_11 | L.LTC–L.PHG | 1.7206 | 0.0010 | 362 | 437 | 17 | 5.8282 | 7.15 × 10-10 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_1_5 | L.PCC–L.IPL | 1.6655 | 0.0011 | 346 | 412 | 12 | 6.0057 | 9.11 × 10−7 | MEM > CTL |
| *TPQ_HA | Questionnaire | 1.6312 | 0.0026 | 318 | 363 | 37 | 6.1333 | 1.44 × 10-02 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Al_2_5 | R.PCC–L.IPL | 1.6034 | 0.0013 | 376 | 455 | 9 | 5.9314 | 1.72 × 10−12 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_2_5 | R.PCC–L.IPL | 1.5614 | 0.0004 | 366 | 437 | 18 | 5.8339 | 7.15 × 10−10 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_1_6 | L.PCC–R.IPL | 1.5384 | 0.0009 | 310 | 383 | 27 | 6.2101 | 5.68 × 10−4 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Be_4_9 | R.ACC–L.LTC | 1.4901 | 0.0009 | 344 | 402 | 12 | 6.2038 | 1.05 × 10−5 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_Ga_4_12 | R.ACC–R.PHG | 1.4605 | 0.0016 | 376 | 451 | 3 | 5.6709 | 6.99 × 10−12 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_De_7_11 | L.PFC–L.PHG | 1.4543 | 0.0019 | 342 | 407 | 13 | 6.1891 | 3.19 × 10−6 | MEM > CTL |
| *DHU_UPL | Questionnaire | 1.4497 | 0.0021 | 315 | 368 | 15 | 6.4736 | 7.06 × 10−3 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_Th_4_10 | R.ACC–R.LTC | 1.4211 | 0.0006 | 345 | 422 | 8 | 6.2084 | 6.21 × 10−8 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_De_8_12 | R.PFC–R.PHG | 1.3844 | 0.0010 | 333 | 394 | 15 | 6.0851 | 6.29 × 10−5 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Al_2_11 | R.PCC–L.PHG | 1.3805 | 0.0006 | 360 | 443 | 3 | 6.2337 | 1.04 × 10−10 | MEM > CTL |
| PRS_MVP_AUD | PRS | 1.2987 | 0.0002 | 363 | 432 | 1 | 6.2696 | 3.35 × 10−9 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_De_5_6 | L.IPL–R.IPL | 1.2964 | 0.0009 | 320 | 378 | 11 | 6.4012 | 1.40 × 10−3 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_6_11 | R.IPL–L.PHG | 1.2959 | −0.0001 | 317 | 381 | 10 | 6.3433 | 8.21 × 10−4 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_Th_4_6 | R.ACC–R.IPL | 1.2955 | 0.0002 | 342 | 404 | 2 | 6.3120 | 6.59 × 10−6 | CTL > MEM |
| FC_De_2_12 | R.PCC–R.PHG | 1.2581 | 0.0007 | 319 | 380 | 9 | 6.4407 | 9.83 × 10−4 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_4_8 | R.ACC–R.PFC | 1.1741 | 0.0015 | 315 | 364 | 6 | 6.5837 | 1.26 × 10−2 | MEM > CTL |
| FC_De_3_7 | L.ACC–L.PFC | 1.1278 | 0.0000 | 319 | 391 | 6 | 6.7618 | 1.18 × 10−4 | CTL > MEM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamarajan, C.; Pandey, A.K.; Chorlian, D.B.; Meyers, J.L.; Kinreich, S.; Pandey, G.; Subbie-Saenz de Viteri, S.; Zhang, J.; Kuang, W.; Barr, P.B.; et al. Predicting Alcohol-Related Memory Problems in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Study with Multi-Domain Features. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050427
Kamarajan C, Pandey AK, Chorlian DB, Meyers JL, Kinreich S, Pandey G, Subbie-Saenz de Viteri S, Zhang J, Kuang W, Barr PB, et al. Predicting Alcohol-Related Memory Problems in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Study with Multi-Domain Features. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(5):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050427
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamarajan, Chella, Ashwini K. Pandey, David B. Chorlian, Jacquelyn L. Meyers, Sivan Kinreich, Gayathri Pandey, Stacey Subbie-Saenz de Viteri, Jian Zhang, Weipeng Kuang, Peter B. Barr, and et al. 2023. "Predicting Alcohol-Related Memory Problems in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Study with Multi-Domain Features" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 5: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050427
APA StyleKamarajan, C., Pandey, A. K., Chorlian, D. B., Meyers, J. L., Kinreich, S., Pandey, G., Subbie-Saenz de Viteri, S., Zhang, J., Kuang, W., Barr, P. B., Aliev, F., Anokhin, A. P., Plawecki, M. H., Kuperman, S., Almasy, L., Merikangas, A., Brislin, S. J., Bauer, L., Hesselbrock, V., ... Porjesz, B. (2023). Predicting Alcohol-Related Memory Problems in Older Adults: A Machine Learning Study with Multi-Domain Features. Behavioral Sciences, 13(5), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13050427








