The Impact of Clinical Pilates Exercises on Tension-Type Headaches: A Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
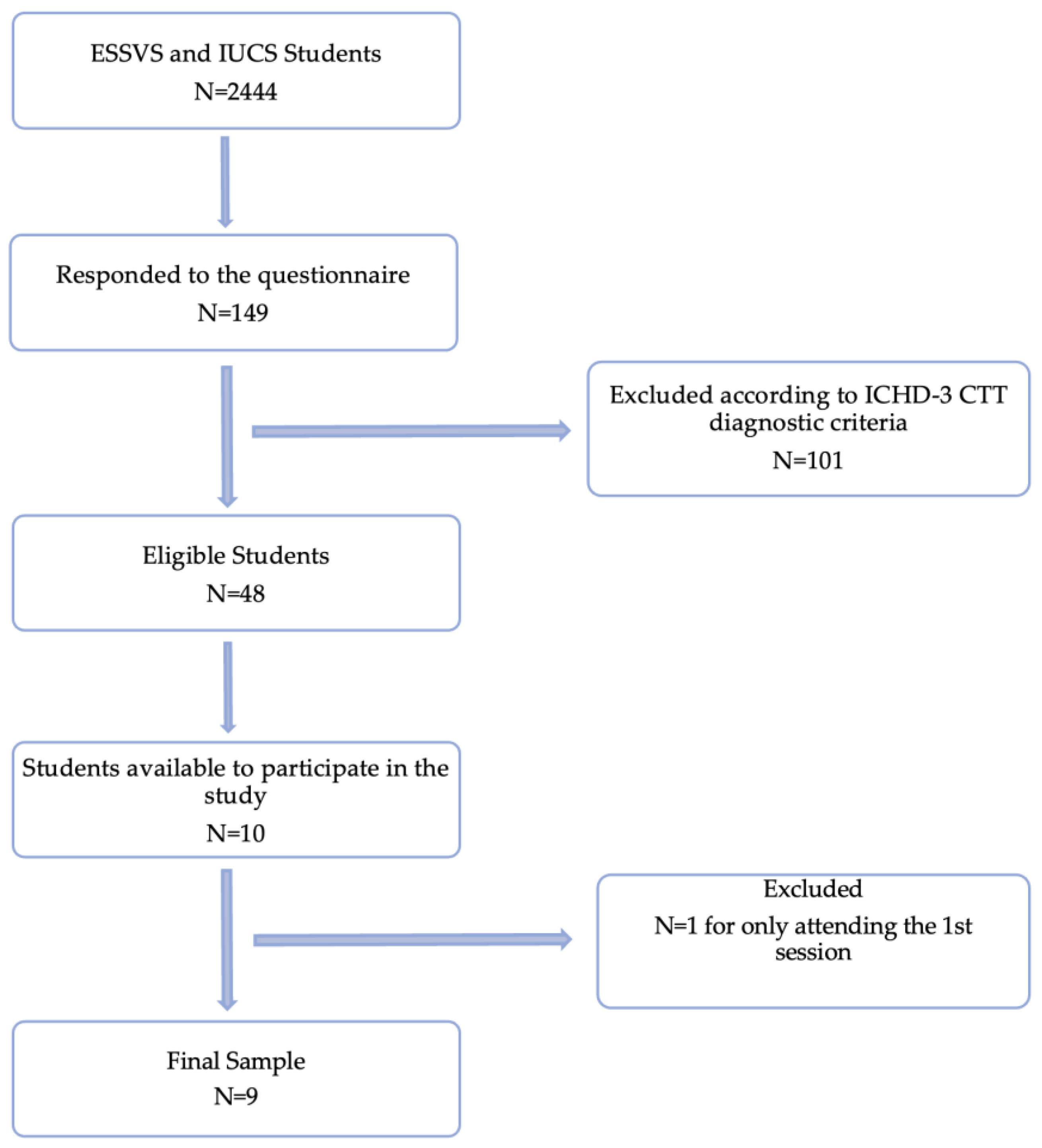
2.2. Sample Recruitment and Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Sociodemographic Questionnaire
2.3.2. Data Collection
2.3.3. Intervention
2.3.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Outcomes
3.2.1. Numerical Rating Scale (NRS)
3.2.2. Headache Impact Test (HIT-6)
3.2.3. Neck Disability Index (NDI)
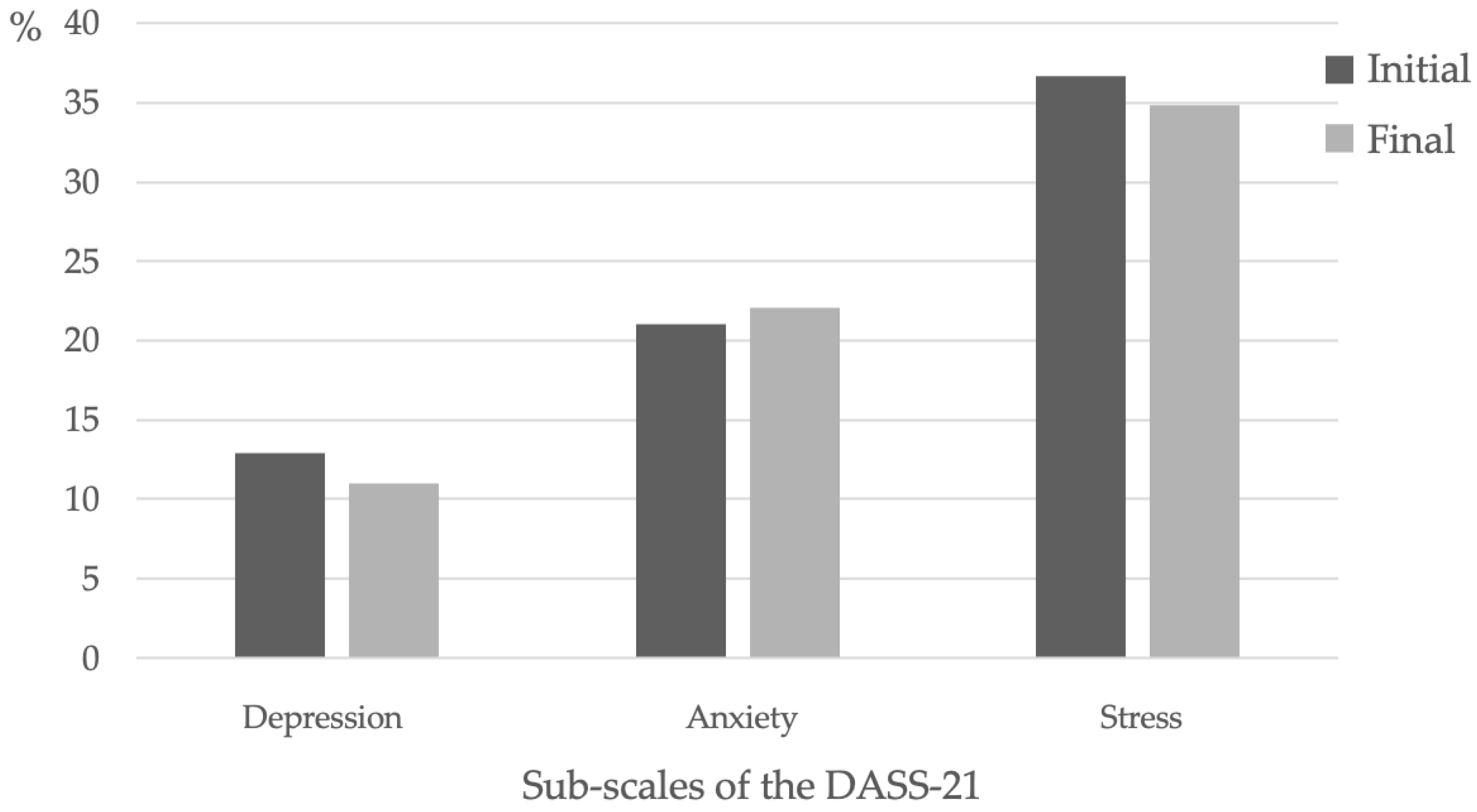
3.2.4. Depression, Anxiety, Stress Scales (DASS-21)
3.2.5. Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index—Portuguese Version (PSQI-PT)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sociedade Portuguesa de Neurologia. Classificação Internacional de Cefaleias (CIC-3)—3ª edição. Sinapse 2018, 18. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Headache Disorders. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/headache-disorders (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Parreira, E. Recomendações Terapêuticas para Cefaleias da Sociedade Portuguesa de Cefaleias—2021. Sinapse 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, R.W.; Dhadwal, S. Primary Headaches. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovner, L.J.; Andree, C. Prevalence of headache in Europe: A review for the Eurolight project. J. Headache Pain 2010, 11, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, S.J.; Robertson, C.E.; Whealy, M.A. Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Approach to Tension-Type Headache. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmadi, M.; Mohseni-Bandpei, M.A.; Keshtkar, A.; Koes, B.W.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C.; Dommerholt, J.; Bahramian, M. Effectiveness of dry needling for improving pain and disability in adults with tension-type, cervicogenic, or migraine headaches: Protocol for a systematic review. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2019, 27, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildir, S.; Tuzun, E.H.; Eroglu, G.; Eker, L. A randomized trial of trigger point dry needling versus sham needling for chronic tension-type headache. Medicine 2019, 98, e14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjão, F.M.; Jorge, J.H.; Nepelenbroek, K.H.; Alencar Júnior, F.G.P. Cefaleia, Tipo Tensional. Rev. Saúde Pesqui. 2008, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, G.; Smith, J.M. Remedial Massage Therapy Interventions Including and Excluding Sternocleidomastoid, Scalene, Temporalis, and Masseter Muscles for Chronic Tension Type Headaches: A Case Series. Int. J. Ther. Massage Bodyw. 2020, 13, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart, S.; Winefield, A.H.; Lushington, K.; Rolan, P. Stress and tension-type headache mechanisms. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1250–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, J.C.; Davis, R.E.; Smitherman, T.A. Tension-type headache and sleep. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.C.; Cruz, L.C.; Cruz, M.C.C.; Camargo, R.P. Cefaleia do tipo tensional: Revisão de literatura. Arch. Health Investig. 2017, 6, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigal, M.E.; Bigal, J.M.; Betti, M.; Bordini, C.A.; Speciali, J.G. Evaluation of the impact of migraine and episodic tension-type headache on the quality of life and performance of a university student population. Headache 2001, 41, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C. Céphalées de tension. Rev. Rhum. Monogr. 2021, 88, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varangot-Reille, C.; Suso-Marti, L.; Romero-Palau, M.; Suarez-Pastor, P.; Cuenca-Martinez, F. Effects of Different Therapeutic Exercise Modalities on Migraine or Tension-Type Headache: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Replicability Analysis. J. Pain 2022, 23, 1099–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.F.C.; Melo, L.G.; Rezende, A.A.B.; Herrera, S.D.S.C.; Ueda, T.K. Intervenção fisioterapêutica na melhoria da qualidade de vida de paciente portador de cefaleia do tipo tensional crônica. Amaz. Sci. Health 2013, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tolnai, N.; Szabo, Z.; Koteles, F.; Szabo, A. Physical and psychological benefits of once-a-week Pilates exercises in young sedentary women: A 10-week longitudinal study. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 163, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.; Liberali, R.; Cruz, T.; Netto, M. The Pilates method in the rehabilitation of musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review. Fisioter. Mov. 2016, 29, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute, T.A.P.P. Pilates Therapy. Available online: https://www.pilates-therapy.com/ (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Latey, P. The Pilates method: History and philosophy. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2001, 5, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.E. Pilates: What is it? Should it be used in rehabilitation? Sports Health 2011, 3, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, P.; Jensen, R.; Olesen, J. Physiotherapy for tension-type headache: A controlled study. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak Key, F.N.; Donmez, S.; Tuzun, U. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics with psychosocial aspects of tension-type headache in Turkish college students. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, L.K. Epidemiology and impact of primary headache disorders. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 85, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertel, M.; Bakar, Y.; Simsek, T.T. The Effect of Body Awareness Therapy and Aerobic Exercises on Pain and Quality of Life in the Patients with Tension Type Headache. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifar, M.; Bazghandi, R.; Azimi, Z.; Bohlouli, B.K. Effectiveness of Neck Myofascial Release Techniques and Exercise Therapy on Pain Intensity and Disability in Patients with Chronic Tension-Type Headache. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2016, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricton, J.; Velly, A.; Ouyang, W.; Look, J.O. Does exercise therapy improve headache? a systematic review with meta-analysis. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2009, 13, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corum, M.; Aydin, T.; Medin Ceylan, C.; Kesiktas, F.N. The comparative effects of spinal manipulation, myofascial release and exercise in tension-type headache patients with neck pain: A randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, G.; Murphy, S. The effectiveness of a 6-week Pilates programme on outcome measures in a population of chronic neck pain patients: A pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.C.P.; Martins, I.B.; Menezes, R.A.; Leão, A.D.G.; Valadares, Y.D.i. The effects of the Pilates method on the mental health of patients with depression and anxiety disorder: A literature review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e5911729368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhiya, M.; Selvam, P.S.; Sundaram, M.S.; Banu, B.F. Effect of Yoga and Pilates on academic stress among college students. Int. J. Physiother. Res. 2020, 8, 3563–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, F.; Livanelioglu, A. Impact of the clinical Pilates exercises and verbal education on exercise beliefs and psychosocial factors in healthy women. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.M.; Herring, M.P. The effects of pilates on mental health outcomes: A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 37, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix Vilella, S.; León Zarceño, E.; Serrano Rosa, M. Evidencias de la práctica Pilates sobre la salud mental de personas sanas. Univ. Salud 2017, 19, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshhal, K.I.; Khairy, G.A.; Guraya, S.Y.; Guraya, S.S. Exam anxiety in the undergraduate medical students of Taibah University. Med. Teach. 2017, 39, S22–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ye, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, W.; He, T.; Xu, X. Effect of Pilates on Sleep Quality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, K.; Harrison, M.; Adams, M.; Triplett, N.T. Effect of Pilates and taiji quan training on self-efficacy, sleep quality, mood, and physical performance of college students. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2009, 13, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldino, A.A.; Avelar, N.C.; Passos, G.B., Jr.; Santana, N.A., Jr.; Teixeira, V.P., Jr.; de Lima, V.P.; de Melo Vitorino, D.F. Effect of Pilates on sleep quality and quality of life of sedentary population. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins Filho, O.L.; Queiroz, G.K.F.; Santos, J.F.J.; Santos, M.A.M.; Oliveira, L.M.F.T.; Farah, B.Q. Efeitos do Pilates na qualidade do sono em adultos e idosos: Uma revisão sistemática. Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fís. Saúde 2019, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.S.; El Kablawy, M.A.; Abd El Azeim, A.S.S. Effect of Pilates Mat Exercise on Myoelectric activity of cervical Muscles in Patient with Chronic Mechanical Neck Pain: Randomized Clinical Trial. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-de-las-Penas, C.; Falla, D.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Farina, D. Cervical muscle co-activation in isometric contractions is enhanced in chronic tension-type headache patients. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.T.; Faria, L.M.; Wittmann, J.I.; Teixeira, W.; Nogueira, L.A. The influence of Pilates method in quality of life of practitioners. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Session Number | Condition of the Session | Exercises |
|---|---|---|
| Session 1 | Learning the 5 key elements | - Hundred level 1 |
| Session 2 | Closed kinetic chain exercises | - Hundred level 1 - Hundred level 2 - Overhead Reach level 1 with variation - Swan Dive level 1 - Breath Stroke Preparation level 1 with variation |
| Session 3 | Open kinetic chain exercises | - Hundred level 1 - Hundred level 3 - Overhead Reach level 1 - Swan Dive level 3 - Breath Stroke Preparation level 2 |
| Session 4 | Mobility Exercises | - Hundred level 3 - Arm Openings level 1 - Arm Openings level 2 - Spine Twist level 1 |
| Criterion A (Presence of the Headache) | Criterion B (Presence of the Causative Disorder) | Criterion C * (Evidence of Causation) | Criterion D (Other Symptoms during Headache) | TTH Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual A | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.2. Frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual B | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 4 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | Photophobia and phonophobia ** | 2.4.2 Probable frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual C | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts less than 30 min ** | It has 4 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.4.2 Probable frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual D | At least 10 episodes of headaches occurring on <1 day per month on average | The headache lasts less than 30 min ** | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.4.1 Probable infrequent episodic TTH |
| Individual E | At least 10 episodes of headaches occurring on <1 day per month on average | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.1 Infrequent episodic TTH |
| Individual F | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts less than 30 min ** | It has 4 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.4.2 Probable frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual G | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 4 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | Photophobia | 2.2. Frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual H | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.2. Frequent episodic TTH |
| Individual I | At least 10 episodes of headaches occurring on <1 day per month on average | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.1 Infrequent episodic TTH |
| Individual J | At least 10 headache episodes occurring on 1 to 14 days on average for more than 3 months | The headache lasts from 30 min to 72 h | It has 3 of the 4 characteristics of criterion C | No associated | 2.2. Frequent episodic TTH |
| % Variation in NRS | % Variation in HIT-6 | % Variation in NDI | % Variation in DASS-21 | % Variation in PSQI-PT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual A | −10 | −2.56 | −6 | +6,35 | −4.76 |
| Individual B | 0 | −6.41 | −8 | −4.76 | −9.52 |
| Individual C | 0 | −16.67 | −6 | −6.35 | −9.52 |
| Individual D | 0 | −7.69 | 0 | +4.76 | +9.52 |
| Individual E | 0 | −23.08 | −12 | −7.94 | −14.29 |
| Individual F | 0 | −2.56 | −18 | −3.17 | −14.29 |
| Individual G | −10 | −1.28 | −2 | +15.87 | −4.76 |
| Individual H | 0 | −1.28 | −12 | −9.52 | −61.90 |
| Individual I | 0 | −3.84 | −6 | −1.59 | −14.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leite, A.; Matignon, A.; Marlot, L.; Coelho, A.; Lopes, S.; Brochado, G. The Impact of Clinical Pilates Exercises on Tension-Type Headaches: A Case Series. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13020105
Leite A, Matignon A, Marlot L, Coelho A, Lopes S, Brochado G. The Impact of Clinical Pilates Exercises on Tension-Type Headaches: A Case Series. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13020105
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeite, Agathe, Antoine Matignon, Léa Marlot, Ana Coelho, Sofia Lopes, and Gabriela Brochado. 2023. "The Impact of Clinical Pilates Exercises on Tension-Type Headaches: A Case Series" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 2: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13020105
APA StyleLeite, A., Matignon, A., Marlot, L., Coelho, A., Lopes, S., & Brochado, G. (2023). The Impact of Clinical Pilates Exercises on Tension-Type Headaches: A Case Series. Behavioral Sciences, 13(2), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13020105





