Avoiding Academic Burnout: Academic Factors That Enhance University Student Engagement
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1: To what extent do students feel connected and engaged in university studies?
- RQ2: Do students’ perceived engagements differ according to subject areas?
- RQ3: Is there a relationship between the classroom variables studied and the level of engagement perceived by students?
- RQ4: What are the specific classroom variables that most influence the engagement of university students?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Internal Structure of the Instrument
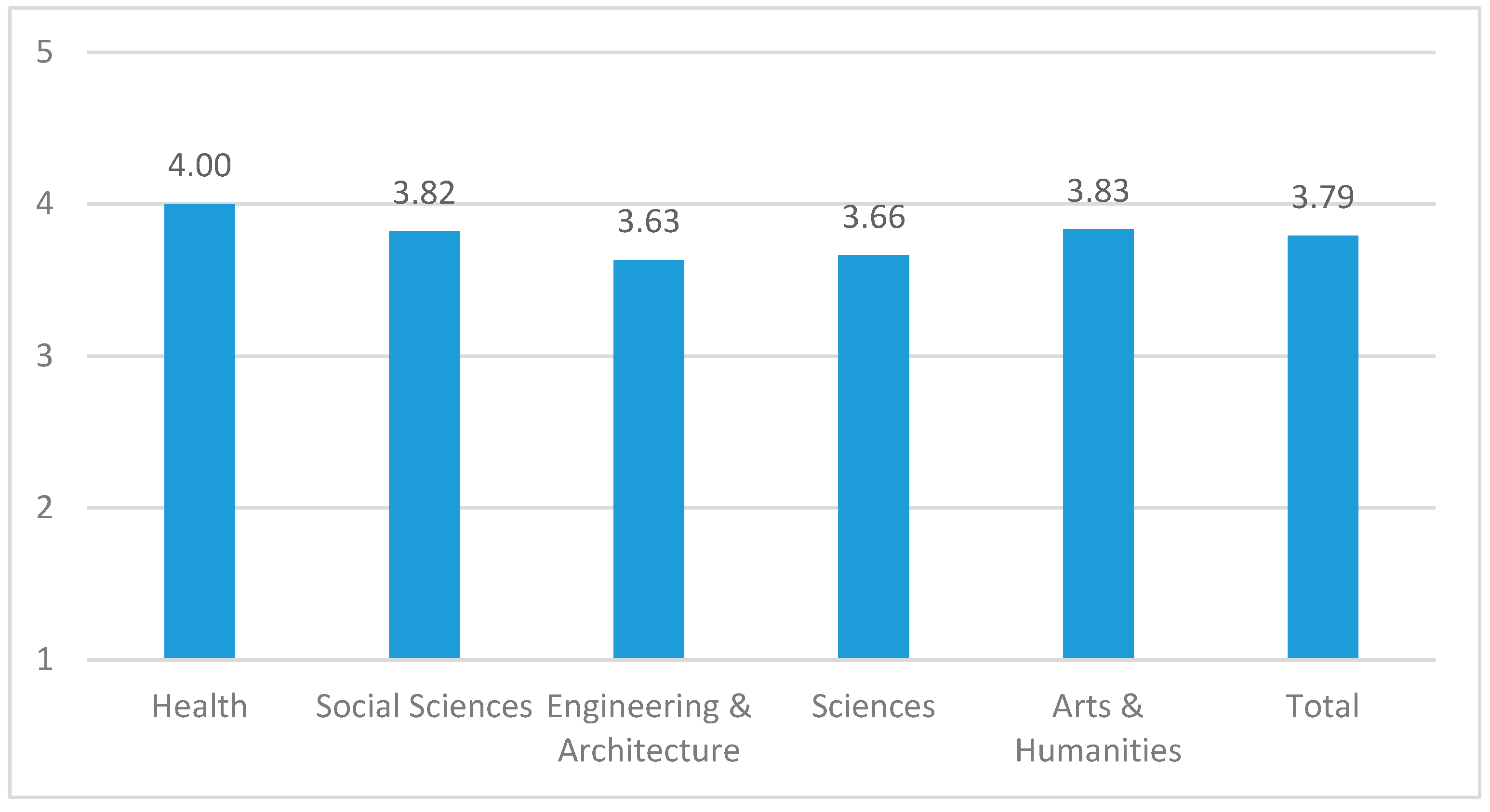
3.3. Level of Engagement Perceived by University Students
3.4. Relationship between the Level of Engagement and Classroom Variables
3.5. Classroom Factors Associated with Improved Engagement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahu, E.R.; Nelson, K. Student engagement in the educational interface: Understanding the mechanisms of student success. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2018, 37, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odlin, D.; Benson-Rea, M.; Sullivan-Taylor, B. Student internships and work placements: Approaches to risk management in higher education. High. Educ. 2022, 83, 1409–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, M.A.; Lashari, A.A.; Abbas, S. Analysis of sustainable academic performance through interactive learning environment in higher education. Glob. Econ. Rev. 2023, 8, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. “Education and Training in the EU: Where Do We Stand?”. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/education/sites/default/files/document-library-docs/education-and-training-monitor-2020-eu-factsheet_en.pdf (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Ministerio de Educación y Formación Profesional. Panorama de la Educación. 2022. Indicadores de la OCDE. Informe Español. Available online: https://sede.educacion.gob.es/publiventa/d/26339/19/00 (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Al-Sowygh, Z.H. Academic distress, perceived stress and coping strategies among dental students in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 25, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xu, H.; Feng, J.; Ye, J.; Lu, Z.; Gan, Y. The global prevalence of burnout among general practitioners: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Fam. Pract. 2021, 39, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrbye, L.N.; Satele, D.; West, C.P. Association of Characteristics of the Learning Environment and US Medical Student Burnout, Empathy, and Career Regret. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 2, e2119110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu Alves, S.; Sinval, J.; Lucas Neto, L.; Marôco, J.; Gonçalves Ferreira, A.; Oliveira, P. Burnout and dropout intention in medical students: The protective role of academic engagement. BMC Med. Educ. 2022, 22, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, M.J.Q.; de Almeida, L.P.B.M.; da Silva, L.F.R.; Cremer, E.; Scholze, A.R.; Martins, J.T.; Haddad, M.d.C.F.L. Burnout among nursing students: A mixed method study. Investig. Educ. Enferm. 2020, 38, e07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodics, B.; Szabó, É. Student burnout in higher education: A demand-resource model approach. Trends Psychol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopmeijer, J.M.; Schutgens, C.A.; Kappe, F.R.; Gubbels, N.; Visscher, T.L.; Jongen, E.M.; Bovens, R.H.; De Jonge, J.M.; Bos, A.E.; Wiers, R.W. The role of performance pressure, loneliness and sense of belonging in predicting burnout symptoms in students in higher education. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Largani, M. Analysis of student’s academic burnout in Iran’s public higher education system: Identification of determinants and strategies. Q. J. Res. Plan. High. Educ. 2023, 23, 43–69. [Google Scholar]
- Turhan, D.; Scheunemann, A.; Schnettler, T.; Bäulke, L.; Thies, D.O.; Dresel, M.; Fries, S.; Leutner, D.; Wirth, J.; Grunschel, C. Psychometric Properties of the German Short Version of the Maslach Burnout Inventory—Student Survey. Eur. J. Health Psychol. 2021, 28, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.; Oberhoffer-Fritz, R.; Reiner, B.; Schulz, T. Study related factors associated with study engagement and student burnout among German university students. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1168264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norez, D. Academic Burnout In College Students: The Impact of Personality Characteristics and Academic Term on Burnout. Master’s Thesis, Fort Hays State University, Hays, KS, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltojević, V.D.; Krstić, I.L.I.; Orlić, A.N. Burnout Among Students of Technical Faculties in Serbia—A Case Study. Int. J. Cogn. Res. Sci. Eng. Educ. 2022, 10, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilli, C.; De Stasio, S.; Di Chiacchio, C.; Pepe, A.; Salmela-Aro, K. School burnout, depressive symptoms and engagement: Their combined effect on student achievement. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 84, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.T.; Abbasi, E.; Khoshnodifar, Z. Students’ academic burnout in Iranian agricultural higher education system: The mediating role of achievement motivation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas-Atencia, C.; Bravo-Cunza, J.; Nolberto-Quispe, L.; Iraola-Real, I. Burnout in University Students of the Initial Education Career. In Proceedings of the IEEE World Conference on Engineering Education (EDUNINE), Bogota, Colombia, 15–18 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, D.J.; Curran, T. Does burnout affect academic achievement? A meta-analysis of over 100,000 students. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 33, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.; Kadhum, M.; Farrell, S.M.; Ventriglio, A.; Molodynski, A. A descriptive study of mental health and wellbeing among medical students in Portugal. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2019, 31, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmacbi, B.; Zare Bahramabadi, M.; Izadi, M.; Abdolhoseini, H. The Causal Relationship of Job Stressors, Job Calling and Job Burnout in Non-academic Staff of Faculties of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. Iran. J. Ergon. 2020, 7, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y. Research Progress of College Students’ Learning Burnout. Rev. Educ. Theory 2021, 4, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, I.C.; Martínez, S.T. La satisfacción en el desempeño profesional de los docentes de educación infantil y educación primaria. Un estudio de caso. Profesorado. Rev. Currículum Form. Profr. 2017, 21, 279–292. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11162/152011 (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- Ortiz-Reyes, M.; Williams-Tejeda, D.; Delgado, M.; López, J.; Negrón, N. La tercera misión de las universidades: Enfoques, indicadores principales y descriptores de un grupo selecto de instituciones de educación superior en Puerto Rico. Cuad. Investig. Educ. 2018, 32, 30–50. Available online: https://revistas.upr.edu/index.php/educacion/article/view/13922 (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Veluvali, P.; Surisetti, J. Learning management system for greater learner engagement in higher education—A review. High. Educ. Future 2022, 9, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.A.; Ward, E.; Longo, N.V.; Saltmarsh, J. (Eds.) Publicly Engaged Scholars: Next-Generation Engagement and the Future of Higher Education; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Bajpai, L. Linking conservation of resource perspective to personal growth initiative and intention to leave: Role of mediating variables. Pers. Rev. 2021, 50, 686–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmela-Aro, K.; Upadyaya, K.; Ronkainen, I.; Hietajärvi, L. Study burnout and engagement during COVID-19 among university students: The role of demands, resources, and psychological needs. J. Happiness Stud. 2022, 23, 2685–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önder, İ.; Önder, A.N.; Güven Yıldırım, E. Burnout and engagement in university students: Relationships with morningness-eveningness preferences, average sleep length and social jetlag. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2023, 54, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhoc, K.C.H.; Webster, B.J.; King, R.B.; Li, J.C.H.; Chung, T.S.H. Higher Education Student Engagement Scale (HESES): Development and Psychometric Evidence. Res. High. Educ. 2019, 60, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poort, I.; Jansen, E.; Hofman, A. Promoting University Students’ Engagement in Intercultural Group Work: The Importance of Expectancy, Value, and Cost. Res. High. Educ. 2023, 64, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hyland, K. Student engagement with teacher and automated feedback on L2 writing. Assess. Writ. 2018, 36, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhen, R.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Xu, L. Teacher support and math engagement: Roles of academic self-efficacy and positive emotions. Educ. Psychol. 2018, 38, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkmann, M.; Salandra, R.; Tartari, V.; McKelvey, M.; Hughes, A. Academic engagement: A review of the literature 2011–2019. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, C.; Paskewich, B.S.; Leff, S.S.; Waasdorp, T.E. Relational peer victimization as a predictor of academic engagement. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2023, 32, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashidi, O.; Phan, H.P.; Ngu, B.H. Academic engagement: An overview of its definitions, dimensions, and major conceptualizations. Int. Educ. Stud. 2016, 9, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.; McColskey, W.; Meli, J.; Mordica, J.; Montrosse, B.; Mooney, K. Measuring Student Engagement in Upper Elementary through High School: A Description of 21 Instruments. Issues & Answers. REL 2011-No. 098; Regional Educational Laboratory Southeast: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fredricks, J.; Blumenfeld, P.; Paris, A. School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 2004, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, P.; Abawi, L.; Brown, A.; Henderson, R.; Heffernan, A. An online engagement framework for higher education. Online Learn. J. 2018, 22, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groccia, J.E. What is student engagement? New Dir. Teach. Learn. 2018, 154, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Tapia, J.; Merino-Tejedor, E.; Huertas, J.A. Academic engagement: Assessment, conditions, and effects—A study in higher education from the perspective of the person-situation interaction. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2023, 38, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colás-Bravo, P.; Reyes-de-Cózar, S.; Conde-Jiménez, J. Validación de la escala multifactorial mixta de engagement educativo (EMMEE). An. Psicol. Ann. Psychol. 2021, 37, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, R.; Egan, A.; Hyland, P.; Maguire, P. Engaging students emotionally: The role of emotional intelligence in predicting cognitive and affective engagement in higher education. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2017, 36, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namaziandost, E.; Heydarnejad, T.; Azizi, Z. The impacts of reflective teaching and emotion regulation on work engagement: Into the prospect of effective teaching in higher education. Teach. Engl. Lang. 2023, 17, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Borges, A.; Peñalver, J.; Martínez, I.M.; Salanova, M. Engagement académico en estudiantes universitarios. El rol mediador del Capital Psicológico como recurso personal. Educ. XX1 2023, 26, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrick, G.E.; Chen, P.Y.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Larivière, V.; Sugimoto, C.R. The relationship between parenting engagement and academic performance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, Q. The Influence of Academic Self-Efficacy on University Students’ Academic Performance: The Mediating Effect of Academic Engagement. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, A.P. Student engagement and academic performance of students of Partido State University. Asian J. Univ. Educ. 2019, 15, n1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokye Effah, N.A.; Nkwantabisa, A.O. The influence of academic engagement on academic performance of university accounting students in Ghana. S. Afr. J. Account. Res. 2022, 36, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctoroff, G.; Arnold, D. Doing homework together: The relation between parenting strategies, child engagement, and achievement. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2017, 48, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbark, K.; Peters, M.L.; Richardson, T. Effectiveness of the student success course on persistence, retention, academic achievement, and student engagement. Community Coll. J. Res. Pract. 2017, 41, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beymer, P.N.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Schmidt, J.A.; Naftzger, N.J. Examining Relationships among Choice, Affect, and Engagement in Summer STEM Programs. J. Youth Adolesc. 2018, 47, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekwa, A.J.; Reddy, L.A.; Shernoff, E.S. Measuring teacher practices and student academic engagement: A convergent validity study. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 34, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokabi Rahman, E.; Taghvaei, D.; Pirani, Z. The Effectiveness of Teaching Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies on Academic Motivation and Academic Engagement of Students with Specific Learning Disorders in Hamaden City. Islam. Life J. 2023, 7, 54–62. Available online: http://islamiclifej.com/article-1-1857-en.html (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Windham, C. Father Google & Mother IM: Confessions of a Net Gen Learner. Educ. Rev. 2005, 40, 42–59. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/p/99185/ (accessed on 7 September 2023).
- Niemi, H.; Multisilta, J. Digital storytelling promoting twenty-first century skills and student engagement. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2016, 25, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.N. Improving student engagement in higher education through mobile-based interactive teaching model using socrative. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Athens, Greece, 25–28 April 2017; pp. 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, F.; Tan, C.Y.; Chen, G. Student engagement and mathematics achievement: Unraveling main and interactive effects. Psychol. Sch. 2018, 55, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedler, M.; Hudson, S.; Yeigh, T. The teachers’ role in student engagement: A review. Aust. J. Teach. Educ. 2020, 45, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngussa, B.M.; Fitriyah, F.K.; Diningrat, S.W.M. Correlation between Facebook use, mental health and learning engagement: A case of universities in Surabaya City, Indonesia. Turk. Online J. Distance Educ. 2021, 22, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Menor, I. El enganche y sentido de pertenencia escolar en Educación Secundaria: Conceptos, procesos y líneas de actuación. Rev. Investig. Educ. 2023, 21, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaysha, J.R.; Shriedeh, F.B.; In’airat, M. Impact of classroom environment, teacher competency, information and communication technology resources, and university facilities on student engagement and academic performance. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.; Bakker, A. Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (UWES) Preliminary Manual; Países Bajos: Occupational Health Psychology Unit, Utrecht University, ND: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Available online: https://goo.gl/nqu9zE (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Wang, M.; Willett, J.; Eccles, J. The assessment of school engagement: Examining dimensionality and measurement invariance by gender and race/ethnicity. J. Sch. Psychol. 2011, 49, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shernoff, D.; Tonks, S.; Anderson, B.G. The impact of the learning environment on student engagement in high school classrooms. In Engaging Youth in Schools: Evidence-Based Models to Guide Future Innovations; NSSE Yearbooks; Teachers College Record: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yazzie-Mintz, E. Charting the Path from Engagement to Achievement: A Report on the 2009 High School Survey of Student Engagement; High School Survey of Student Engagement: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2010; Available online: http://hub.mspnet.org/index.cfm/20806 (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Freitas, F.; Almeida, V.M.C.D. Theoretical model of engagement in the context of brand communities. BBR. Braz. Bus. Rev. 2017, 14, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, A.M.; Capraro, R.M. Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics project-based learning: Merging rigor and relevance to increase student engagement. Electron. Int. J. Educ. Arts Sci. 2017, 3, 140–158. Available online: https://www.researchgate.com/publication/335474310 (accessed on 9 September 2023).
- Hasni, A.; Bousadra, F.; Belletête, V.; Benabdallah, A.; Nicole, M.C.; Dumais, N. Trends in research on project-based science and technology teaching and learning at K–12 levels: A systematic review. Stud. Sci. Educ. 2016, 52, 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynard, J. Advising for language learner autonomy: Theory, practice, and future directions. In Autonomy in Language Education; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2020; pp. 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Intraboonsom, C.; Darasawang, P.; Reinders, H. Teacher’s Practices in Fostering Learner Autonomy in a Thai University Context. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2020, 11, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterall, S. The pedagogy of learner autonomy: Lessons from the classroom. Stud. Self Access Learn. J. 2017, 8, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejas, M.T.; Tan, D.A. Student Academic Performance and Engagement in Mathematics through Flipped Classroom in a Synchronous Learning Environment. Am. J. Educ. Res. 2023, 11, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Schunn, C.D. Passive, active, and constructive engagement with peer feedback: A revised model of learning from peer feedback. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2023, 73, 102160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvert-Bruce, Z.; Neill, J.T.; Sjöblom, M.; Hamari, J. Social motivations of live-streaming viewer engagement on Twitch. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 84, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, B.; Hayward, C.; Niemer, R. Improve student engagement with gameful learning. In Teaching in the Game-Based Classroom: Practical Strategies for Grades 6–12; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M.S.; Van der Wal, Z.; Van den Berg, C. Comparative studies in public administration: Intellectual challenges and alternative perspectives. Public Adm. Rev. 2021, 81, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussaid, Y. Evaluation and Adaptation of Materials: The Use of BackPack 1 Textbook in Chinese Schools. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Invent. 2022, 9, 7086–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dago-oc, N.C.; Tagadiad, C.L. The Mediating Effect of Teachers Engagement on the Relationship Between Students Intellectual Stimulation and Their Engagement. United Int. J. Res. Technol. 2023, 4, 63–78. Available online: https://uijrt.com/articles/v4/i10/UIJRTV4I100008.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Nguyen, T.D.; Cannata, M.; Miller, J. Understanding student behavioral engagement: Importance of student interaction with peers and teachers. J. Educ. Res. 2018, 111, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanelopoulos, J.; Papanikolaou, K.A.; Zalimidis, P. Flipping The Classroom to Increase Students’ Engagement and Interaction in a Mechanical Engineering Course on Machine Design. Int. J. Eng. Pedagog. 2017, 7, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.; McDonough, K. Effect of proficiency on Vietnamese EFL learners’ engagement in peer interaction. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2018, 88, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygotsky, L. Interaction between learning and development. In Readings on the Development of Children; Gauvain, C., Ed.; Scientific American Books: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, P. Effect of interaction strategy instruction on learner engagement in peer interaction. System 2020, 91, 102–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilford, J. Psychometric Methods; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, J.W.; Heslin, R.; Jones, J.E. Instrumentation in Human Relations Training; University Associates: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1976; Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1130282270346816512 (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Stăiculescu, C.; Elena Ramona, R.N. University dropout: Causes and solution. Ment. Health Glob. Chall. J. 2019, 1, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatpour, P.; Chehrzad, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Sadat-Ebrahimi, S.R. Academic burnout as an educational complication and promotion barrier among undergraduate students: A cross-sectional study. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2019, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Naranjo, A. Deserción y estrategias de retención: Un análisis desde la universidad particular. 593 Digit. Publ. CEIT 2020, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, N.; Österman, K.; Björkqvist, K. School burnout and its psychological concomitants among students from three school types in Pakistan. Eurasian J. Med. Investig. 2020, 4, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, P.C.F.; Oliveira, Í.M.; Noronha-Sousa, D.; Noronha, A.; Mateus, C.C.; Vázquez-Justo, E.; Costa-Lobo, C. Dropout factors in higher education: A literature review. Psicol. Esc. Educ. 2022, 26, e228736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abangwu, C.A.; Fatudimu, M.B.; Hamzat, T.K. Prevalence of Burnout Among Clinical Undergraduates in the University of Ibadan. Egypt. J. Phys. Ther. 2021, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viloria, A.; Naveda, A.S.; Palma, H.H.; Núñez, W.N.; Núñez, L.N. Using big data to determine potential dropouts in higher education. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1432, 012077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarzaie, H.; Nastiezaie, N.; Jenaabadi, H. 2017. The relationship of academic burnout and academic stress with academic self-efficacy among graduate students. New Educ. Rev. 2017, 49, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoo, S.; Mutua, J. Social Support and Academic Burnout Among Secondary School Students in Kenya. Int. J. Innov. Res. Adv. Stud. 2019, 6, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Arlinkasari, F.; Akmal, S.Z.; Rauf, N.W. Should students engage to their study? (Academic burnout and school-engagement among students). GUIDENA J. Ilmu Pendidik. Psikol. Bimbing. Dan Konseling 2017, 7, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, N.; Kappe, R. Stress and Engagement in HBO Students: Infographic; Hogeschool Inholland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiyue, C. The relationship between engagement and burnout among student in Universiti Malaysia Sabah (ums). Malays. J. Bus. Econ. 2022, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherinos, M. Margaret Kettle, International student engagement in higher education: Transforming practices, pedagogies and participation. Aust. Rev. Appl. Linguist. 2019, 42, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman-Van Deventer, E. Student engagement: More than bells and whistles. Obiter 2019, 40, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.K. Engagements with Students and Sustainable Development; SSRN: Rochester, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, C.M.; Rodríguez-Álvarez, M.; Viñuela-Hernández, M.P. University students and their perception of teaching effectiveness. Effects on students’ engagement. Rev. Psicodidáctica 2021, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearamae, R.; Nammungkhun, W. Understanding an active learning of Pre service Teachers in Southern of Thailand. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Educational Research, Khon Kaen, Thailand, 25–27 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, F.; Marto, H.; Pereira, R. Work-in-Progress: Analysis of engineering students’ preparation for active learning considering the study methods. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Porto, Portugal, 27–30 April 2020; pp. 1512–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelSattar, A.; Labib, W. Active learning in engineering education: Teaching strategies and methods of overcoming challenges. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Educational and Information Technology, Cambridge, UK, 2–4 March 2019; pp. 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, B.S. An Implementation of Active Learning Strategies for Effective Use of In-class Hour to Achieve Complete Knowledge Transfer in an Engineering Course. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2022, 13, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, A.; Yahia, M.W.; Mushtaha, E.S.; Maksoud, A.M.; Nasif, O.M.; Melahifci, O. The Effect of Active Teaching on Quality Learning: Students’ Perspective in an Architectural Science Course at the University of Sharjah. In Proceedings of the Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 February 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Muro, J.P.; Arbulú Pérez Vargas, C.G.; Montenegro Camacho, L. La metacognición como factor de desarrollo de competencias en la educación peruana. Rev. Educ. 2022, 46, 528–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munna, A.S.; Kalam, M.A. Impact of Active Learning Strategy on the Student Engagement. GNOSI Interdiscip. J. Hum. Theory Prax. 2021, 4, 96–114. Available online: http://gnosijournal.com/index.php/gnosi/article/view/96 (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Gosavi, C.S.; Arora, S. Active Learning Strategies for Engaging Students in Higher Education. J. Eng. Educ. Transform. 2022, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheat, C.A.; Sun, Y.; Wedgworth, J.C.; Hocutt, M.M. Active University Teaching and Engaged Student Learning: A Mixed Methods Approach. J. Scholarsh. Teach. Learn. 2018, 18, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aji, C.A.; Khan, M.J. The impact of active learning on students’ academic performance. Open J. Soc. Sci. 2019, 7, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmara, R.; Kusumaningrum, W.R. Pendampingan penulisan karya ilmiah remaja berstandar LKIR LIPI bagi guru dan siswa SMA islam terpadu Ihsanul Fikri kabupaten Magelang. Widya Laksana 2020, 9, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Tomás, J.M.; Alberola, S. Apoyo docente, compromiso académico y satisfacción del alumnado universitario. Estud. Sobre Educ. 2018, 35, 535–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patall, E.A.; Steingut, R.R.; Vasquez, A.C.; Trimble, S.S.; Pituch, K.A.; Freeman, J.L. Daily autonomy supporting or thwarting and students’ motivation and engagement in the high school science classroom. J. Educ. Psychol. 2018, 110, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenijević, J.; Nikolić, M.; Belousova, A. Notes from experience in application of interactive teaching methods in university settings. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 210, 22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Discussing the application of interactive teaching in classroom. In International Seminar on Education Research and Social Science (ISERSS); Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.A.; Stallings, L.; Pierce, R.L.; Largent, D. Classroom Interaction Redefined: Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Moving beyond Traditional Classroom Spaces to Promote Student Engagement. J. Learn. Spaces 2018, 7, 45–61. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1195242 (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Vracheva, V.P.; Moussetis, R.; Abu-Rahma, A. The mediational role of engagement in the relationship between curiosity and student development: A preliminary study. J. Happiness Stud. 2020, 21, 1529–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmin, A.I. Observing the Intellectual Curiosity of English Education Students in the Class. IDEAS J. Engl. Lang. Teach. Learn. Linguist. Lit. 2020, 8, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, J. Exploratory implementation of a blended format escape room in a large enrollment pharmacy management class. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2019, 11, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, D.Y.; Riccetti, A.E.; Siracusa, M.; Paoloni, P. Tres experiencias sobre clases invertidas para promover el compromiso por el aprendizaje. Percepciones de estudiantes universitarios. Páginas Educ. 2019, 12, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.C.; Namli, N.A. Öğretmen Adaylarinin Eğitimde Teknoloji Kullanma Tutumlarinin İncelenmesi. Türkiye Sos. Araştırmalar Derg. 2019, 23, 95–112. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/tsadergisi/issue/44605/432280 (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Adlet, K.; Zhanagul, S.; Tolkin, Y.; Olga, F.; Nazymgul, A.; Kadir, N. Interactive Educational Technologies as a Factor in the Development of the Subjectivity of University Students. World J. Educ. Technol. Curr. Issues 2022, 14, 533–543. Available online: https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1049236 (accessed on 17 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Rose, T.M.; Gundrum, D.A.; McMorris, T.E.; Klausner, E.A.; Lang, L.A.; Shan, G. Evaluating the effects of a mindfulness mobile application on student pharmacists’ stress, burnout, and mindfulness. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganin, G.; Apolinário-Hagen, J.; Simbula, S. Introducing mobile apps to promote the well-being of German and Italian university students. A cross-national application of the Technology Acceptance Model. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 42, 27562–27573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.; Pintrich, P.R. Regulating motivation and cognition in the classroom: The role of self-schemas and self-regulatory strategies. In Self-Regulation of Learning and Performance; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2023; pp. 127–153. [Google Scholar]
- Knoster, K.C.; Goodboy, A.K. Making content relevant: A teaching and learning experiment with replication. Commun. Educ. 2021, 70, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolian, T.L.; Jach, E.A. Engagement in college and university applied learning experiences and students’ academic motivation. J. Exp. Educ. 2020, 43, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.W. Improving engagement in a lecture course by increasing relevance to student needs and interests. Contemp. Issues Educ. Res. 2019, 12, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; Paganin, G.; Guglielmi, D.; Mazzetti, G. Motivation is not enough: How career planning and effort regulation predict academic achievement. Curr. Psychol. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yao-Ping, M.; Rong-Sheng, W.; Feng-Chi, L.; Sheng-Hwa, T. Multi-engagement. learning approach and student learning outcomes: Evidence from Taiwanese private university. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 5, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyklová, E.; Aleja, M. Research on Teacher Engagement or on Typology of (Un) Engaged Teachers in Contemporary Education. In Educational Challenges in Central Europe, Olomouc. 2018. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Research-on-Teacher-Engagement-or-on-Typology-of-in-Nyklov%C3%A1-Kaleja/882a4eaae662a2e2b8fdf04481555790ea253619 (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Holliman, A.J.; Martin, A.J.; Collie, R.J. Adaptability, engagement, and degree completion: A longitudinal investigation of university students. Educ. Psychol. 2018, 38, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n = 764 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Percentage (%) | ||
| Course | First | 20.4 |
| Second | 20.4 | |
| Third | 20.9 | |
| Fourth | 20.4 | |
| Master’s/Postgraduate | 17.9 | |
| Areas of knowledge | Science | 17.8 |
| Social Sciences | 20.9 | |
| Health | 19.9 | |
| Engineering and Architecture | 20.7 | |
| Arts and Humanities | 20.7 |
| PCA | Reliability | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | No. of Items | % Variance | Cronbach’s α |
| Relevance | 6 | 32.625 | 0.847 |
| Exploration | 4 | 12.997 | 0.793 |
| Intellectual challenges | 4 | 9.516 | 0.815 |
| Interaction | 3 | 7.447 | 0.759 |
| Summary (n = 764) | 17 | 62.585 | 0.865 |
| Variables | Engagement | |
|---|---|---|
| Coef. | Sig. | |
| Relevance | 0.133 ** | 0.010 |
| Exploration | 0.137 ** | 0.008 |
| Intellectual challenges | 0.140 ** | 0.007 |
| Interaction | 0.209 ** | 0.000 |
| I Am More Involved in My Studies When…/I Have More Engagement in My Studies When… | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Item | Min. | Max. | s | s2 | |
| Interaction | I feel integrated and part of a work team | 3.99 | 1 | 5 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| I can express my opinions and discuss them | 3.86 | 1 | 5 | 1.01 | 1.03 | |
| I have fluent interpersonal communication with colleagues and teachers | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.93 | 0.87 | |
| Total | 3.95 | 1 | 5 | 0.76 | 0.57 | |
| 1 = Not at all. 2 = A little. 3 = Some. 4 = Quite a lot. 5 = A lot. | ||||||
| I Am More Involved in My Studies When…/I Have More Engagement in My Studies When… | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Item | Min. | Max. | s | s2 | |
| Exploration | I find the teachers’ explanations easy to understand and connected to my interests | 3.70 | 1 | 5 | 1.08 | 1.18 |
| I find the teachers’ explanations stimulating | 3.91 | 1 | 5 | 1.11 | 1.24 | |
| In the classes, questions arise that provoke curiosity or the desire to inquire about them | 3.88 | 1 | 5 | 0.98 | 0.96 | |
| I find a positive attitude on the part of my tutors and professors to attend to my needs | 3.94 | 1 | 5 | 1.02 | 1.04 | |
| Total | 3.85 | 1 | 5 | 0.84 | 0.70 | |
| 1 = Not at all. 2 = A little. 3 = Some. 4 = Quite a lot. 5 = A lot. | ||||||
| I Am More Involved in My Studies When…/I Have More Engagement in My Studies When… | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Item | Min. | Max. | s | s2 | |
| Intellectual Challenges | In class I use all the possibilities of new technologies | 3.22 | 1 | 5 | 1.14 | 1.30 |
| The professors propose the subjects with activities that require autonomy (research work, voluntary, open topic, etc.) | 3.44 | 1 | 5 | 1.10 | 1.22 | |
| The teachers facilitate the use of different sources or technological resources (audiovisual media, internet, blogs, etc.) for the development of the subjects | 3.48 | 1 | 5 | 1.08 | 1.17 | |
| The activities demand the maximum from me to overcome them | 3.51 | 1 | 5 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |
| Total | 3.41 | 1 | 5 | 0.76 | 0.58 | |
| 1 = Not at all. 2 = A little. 3 = Some. 4 = Quite a lot. 5 = A lot. | ||||||
| I Am More Involved in My Studies When…/I Have More Engagement in My Studies When… | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Item | Min. | Max. | s | s2 | |
| Relevance | The teachers use the doubts I raise in class to expand the content of the subjects | 3.14 | 1 | 5 | 1.19 | 1.41 |
| Teachers find meaning in the subject matter that I consider useful in other contexts | 3.28 | 1 | 5 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| The review of exams and evaluation tests helps me to clarify and learn about my mistakes | 3.38 | 1 | 5 | 1.12 | 1.26 | |
| In the classroom I work on activities related to possible work problems | 3.23 | 1 | 5 | 1.19 | 1.43 | |
| The doubts I raise in class are satisfactorily resolved | 3.68 | 1 | 5 | 1.04 | 1.09 | |
| My professors invite professionals from the working world to the classes | 3 | 1 | 5 | 1.14 | 1.30 | |
| Total | 3.28 | 1 | 5 | 0.79 | 0.63 | |
| 1 = Not at all. 2 = A little. 3 = Some. 4 = Quite a lot. 5 = A lot. | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes-de-Cózar, S.; Merino-Cajaraville, A.; Salguero-Pazos, M.R. Avoiding Academic Burnout: Academic Factors That Enhance University Student Engagement. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120989
Reyes-de-Cózar S, Merino-Cajaraville A, Salguero-Pazos MR. Avoiding Academic Burnout: Academic Factors That Enhance University Student Engagement. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(12):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120989
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes-de-Cózar, Salvador, Alba Merino-Cajaraville, and María Rosa Salguero-Pazos. 2023. "Avoiding Academic Burnout: Academic Factors That Enhance University Student Engagement" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 12: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120989
APA StyleReyes-de-Cózar, S., Merino-Cajaraville, A., & Salguero-Pazos, M. R. (2023). Avoiding Academic Burnout: Academic Factors That Enhance University Student Engagement. Behavioral Sciences, 13(12), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13120989







