Effects of Physical Exercise on Cerebral Blood Velocity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta−Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Eligibility
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Screening
2.4. Data Extraction and Coding
2.5. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.6. Certainty Assessment
2.7. Data Synthesis
3. Results
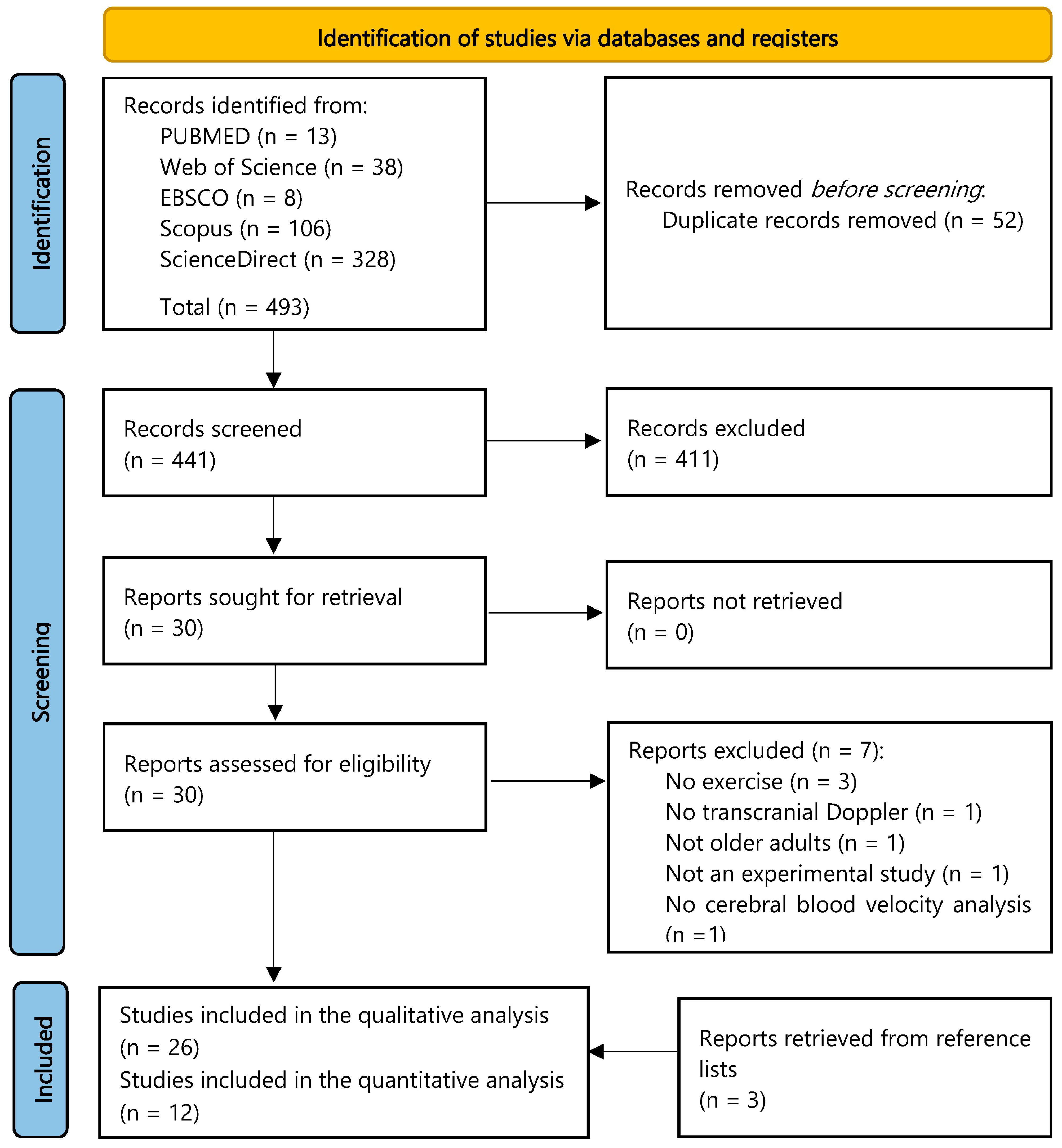
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
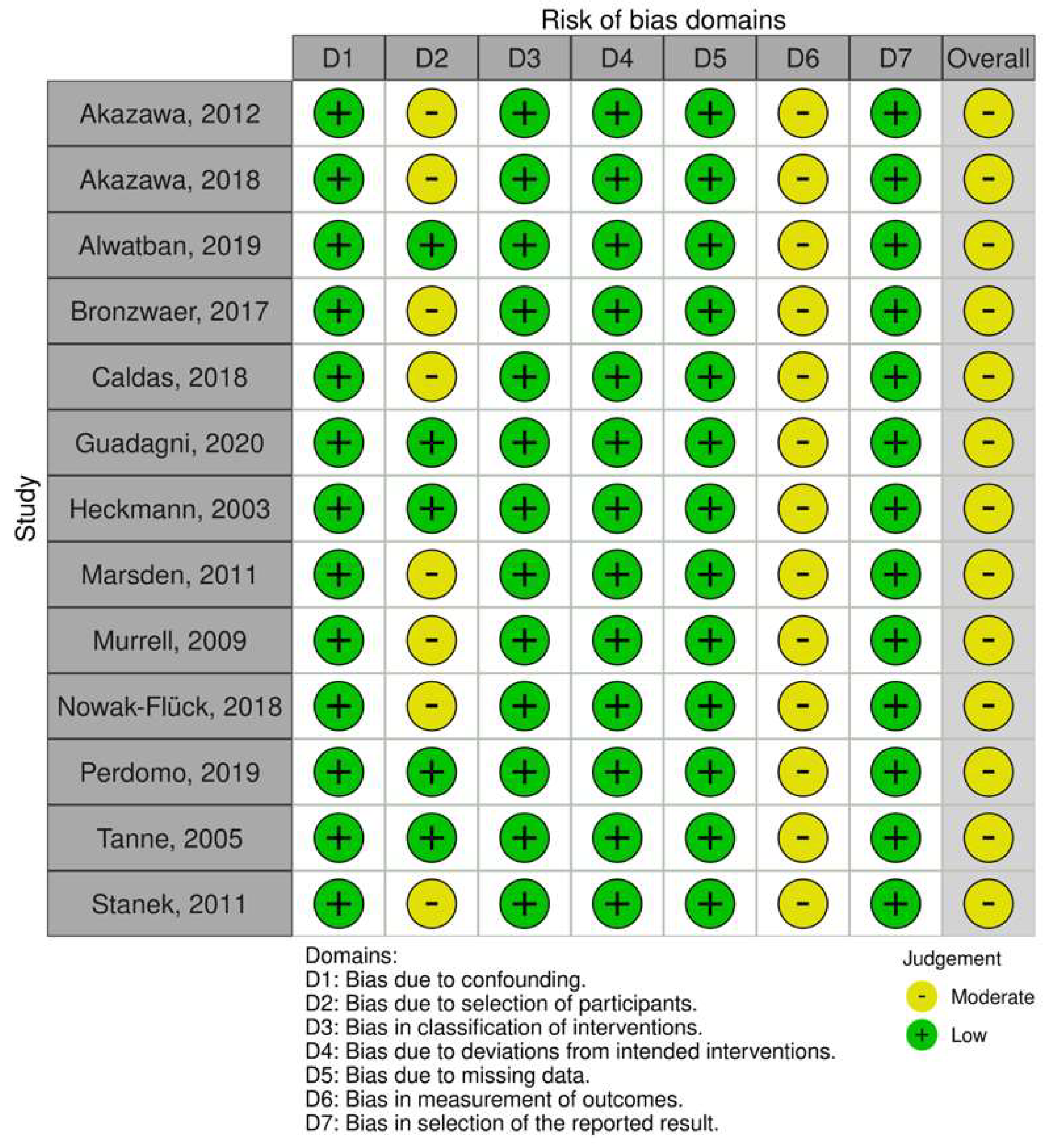
3.3. Risk of Bias within Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Certainty Assessment
3.6. Synthesis of Results

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.-J. Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 931536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates: Life Expectancy and Leading Causes of Death and Disability; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Kisler, K.; Montagne, A.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. The Role of Brain Vasculature in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.R.; Pan, P.L.; Sheng, L.Q.; Dai, Z.Y.; Di Wang, G.; Luo, R.; Chen, J.H.; Xiao, P.R.; Zhong, J.G.; Shi, H.C. Aberrant Pattern of Regional Cerebral Blood Flow in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Voxel-Wise Meta-Analysis of Arterial Spin Labeling MR Imaging Studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93196–93208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeuwis, A.E.; Benedictus, M.R.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; Binnewijzend, M.A.A.; Hooghiemstra, A.M.; Verfaillie, S.C.J.; Koene, T.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Prins, N.D.; et al. Lower Cerebral Blood Flow Is Associated with Impairment in Multiple Cognitive Domains in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Min, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Di, Q.; Ma, X. The Effect of Exercise on Cerebral Blood Flow and Executive Function among Young Adults: A Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, H.N.P.; Oliveira, G.M.; Oliva, I.O.; Cassilhas, R.C.; De Paula, A.M.B.; Monteiro-Junior, R.S. Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Velocity and Cognitive Function After High- and Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Exercise Sessions. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 817, 137511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, H.N.P.; Monteiro-Junior, R.S.; Oliva, I.O.; Powers, A.R. Effects of Exercise Intervention on Psychotic Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis and Hypothetical Model of Neurobiological Mechanisms. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 125, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Oliva, H.N.; Mansur Machado, F.S.; Rodrigues, V.D.; Leão, L.L.; Monteiro-Júnior, R.S. The Effect of Dual-Task Training on Cognition of People with Different Clinical Conditions: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. IBRO Rep. 2020, 9, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Junior, R.S.; David, I.R.; Mendes, I.H.R.; Coutinho, L.A.; Júnior, B.J.M.; Oliva, H.N.P. Cortical Brain Response to Acute Bouts of Exercise in Patients with Severe Psychiatric Disorders: Report of Three Cases. In Exploratory Research and Hypothesis in Medicine (ERHM); Xia & He Publishing Inc.: Sugar Land, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Physical Activity and Health: A Report of the Surgeon General. 1996. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/sgr/pdf/execsumm.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Moraine, J.J.; Lamotte, M.; Berré, J.; Niset, G.; Leduc, A.; Naeijel, R. Relationship of Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow Velocity to Intensity during Dynamic Exercise in Normal Subjects. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 67, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, S.R.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Schroeder, E.C.; Lefferts, W.K.; Lima, N.S.; Grigoriadis, G.; Baynard, T. No Sex Differences in Cerebral Blood Velocity Responses During Resistance Exercise. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, E.; Allie, K.N.; Salvador, P.M.; Schoech, L.; Martinez, M. Sex Difference in Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity during Exercise Hyperthermia. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 94, 102741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteis, M.; Troisi, E.; Monaldo, B.C.; Caltagirone, C.; Silvestrini, M. Age and Sex Differences in Cerebral Hemodynamics. Stroke 1998, 29, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniela, M.; Catalina, L.; Ilie, O.; Paula, M.; Daniel-Andrei, I.; Ioana, B. Effects of Exercise Training on the Autonomic Nervous System with a Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidants Effects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Ainslie, P.N. Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism during Exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 1356–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, J.N. Exercise, Cognitive Function, and Aging. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2015, 39, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fico, B.G.; Miller, K.B.; Rivera-Rivera, L.A.; Corkery, A.T.; Pearson, A.G.; Loggie, N.A.; Howery, A.J.; Rowley, H.A.; Johnson, K.M.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. Cerebral Hemodynamics Comparison Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound and 4D Flow MRI. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1198615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, F.M.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Brazzelli, M.; Best, J.J. Doppler Ultrasound, CT Angiography, MR Angiography, and Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography versus Intra-Arterial Angiography for Moderate and Severe Carotid Stenosis in Symptomatic Patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD007423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Wong, K.S.; Alexandrov, A.V. Transcranial Doppler. In Intracranial Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 124–140. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.D.; McMorris, C.A.; Longman, R.S.; Leigh, R.; Hill, M.D.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Poulin, M.J. Effects of Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Cerebral Blood Flow on Cognitive Outcomes in Older Women. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, N.; Tanahashi, K.; Kosaki, K.; Ra, S.-G.; Matsubara, T.; Choi, Y.; Zempo-Miyaki, A.; Maeda, S. Aerobic Exercise Training Enhances Cerebrovascular Pulsatility Response to Acute Aerobic Exercise in Older Adults. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagni, V.; Drogos, L.L.; Tyndall, A.V.; Davenport, M.H.; Anderson, T.J.; Eskes, G.A.; Longman, R.S.; Hill, M.D.; Hogan, D.B.; Poulin, M.J. Aerobic Exercise Improves Cognition and Cerebrovascular Regulation in Older Adults. Neurology 2020, 94, e2245–e2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinloog, J.P.D.; Nijssen, K.M.R.; Mensink, R.P.; Joris, P.J. Effects of Physical Exercise Training on Cerebral Blood Flow Measurements: A Systematic Review of Human Intervention Studies. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2023, 33, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, C.; Cotter, J.D.; George, K.; Shave, R.; Wilson, L.; Thomas, K.; Williams, M.J.A.; Lowe, T.; Ainslie, P.N. Influence of Age on Syncope Following Prolonged Exercise: Differential Responses but Similar Orthostatic Intolerance. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5959–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, J.; Tarumi, T.; Xing, C.; Liu, J.; Tomoto, T.; Pasha, E.P.; Zhang, R. Aerobic Exercise Training Reduces Cerebrovascular Impedance in Older Adults: A 1-Year Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 133, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanne, D.; Freimark, D.; Poreh, A.; Merzeliak, O.; Bruck, B.; Schwammenthal, Y.; Schwammenthal, E.; Motro, M.; Adler, Y. Cognitive Functions in Severe Congestive Heart Failure before and after an Exercise Training Program. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 103, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Roh, H.-T. Taekwondo Enhances Cognitive Function as a Result of Increased Neurotrophic Growth Factors in Elderly Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renke, M.B.; Marcinkowska, A.B.; Kujach, S.; Winklewski, P.J. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Physical Exercise-Induced Increased Resting Cerebral Blood Flow on Cognitive Functions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 803332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmagarmid, A.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Hammady, H.; Ilyas, I.; Khabsa, M.; Ouzzani, M. Rayyan: A Systematic Reviews Web App for Exploring and Filtering Searches for Eligible Studies for Cochrane Reviews. In Proceedings of the Evidence-Informed Publich Health: Opportunities and Challenges, Abstracts of the 22nd Cochrane Colloquium, Hyderabad, India, 21–25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Vist, G.E.; Glasziou, P.; Akl, E.A.; Skoetz, N.; Guyatt, G.H. Completing ‘Summary of Findings’ Tables and Grading the Certainty of the Evidence. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 375–402. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 1483276481. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.; Thomas, J.; Higgins, J.P.T. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119536628. [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick, P.; Marston, L. How to Read a Funnel Plot in a Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2015, 351, h4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager. RevMan, version 5.4; Cochrane: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Northey, J.M.; Pumpa, K.L.; Quinlan, C.; Ikin, A.; Toohey, K.; Smee, D.J.; Rattray, B. Cognition in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study of Interval and Continuous Exercise. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2019, 22, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Ye, Y.; Wan, M.; Qiu, P.; Xia, R.; Zheng, G. Effect of Baduanjin Exercise on Cerebral Blood Flow and Cognitive Frailty in the Community Older Adults with Cognitive Frailty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2023, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronzwaer, A.-S.G.T.; Verbree, J.; Stok, W.J.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; van Buchem, M.A.; van Osch, M.J.P.; van Lieshout, J.J. Aging Modifies the Effect of Cardiac Output on Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow Velocity. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, J.R.; Panerai, R.B.; Salinet, A.M.; Seng-Shu, E.; Ferreira, G.S.R.; Camara, L.; Passos, R.H.; Galas, F.R.B.G.; Almeida, J.P.; Nogueira, R.C.; et al. Dynamic Cerebral Autoregulation Is Impaired during Submaximal Isometric Handgrip in Patients with Heart Failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H254–H261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, N.; Choi, Y.; Miyaki, A.; Sugawara, J.; Ajisaka, R.; Maeda, S. Aerobic Exercise Training Increases Cerebral Blood Flow in Postmenopausal Women. Artery Res. 2012, 6, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwatban, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Perdomo, S.J.; Ward, J.L.; Vidoni, E.D.; Burns, J.M.; Billinger, S.A. TCD Cerebral Hemodynamic Changes during Moderate-Intensity Exercise in Older Adults. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Smith, K.; Maslen, B.A.; Cox, K.L.; Lautenschlager, N.T.; Pestell, C.F.; Naylor, L.H.; Ainslie, P.N.; Carter, H.H. The Impact of 6-Month Land versus Water Walking on Cerebrovascular Function in the Aging Brain. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, J.G.; Brown, C.M.; Cheregi, M.; Hilz, M.J.; Neundörfer, B. Delayed Cerebrovascular Autoregulatory Response to Ergometer Exercise in Normotensive Elderly Humans. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 16, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, F.M.; Ryan, A.S.; Hafer-Macko, C.E.; Macko, R.F. Improved Cerebral Vasomotor Reactivity After Exercise Training in Hemiparetic Stroke Survivors. Stroke 2011, 42, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maasakkers, C.M.; Melis, R.J.F.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Gardiner, P.A.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M.; Thijssen, D.H.J.; Claassen, J.A.H.R. The Short-Term Effects of Sedentary Behaviour on Cerebral Hemodynamics and Cognitive Performance in Older Adults: A Cross-over Design on the Potential Impact of Mental and/or Physical Activity. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, K.R.; Haykowsky, M.J.; Smirl, J.D.; Jones, H.; Nelson, M.D.; Altamirano-Diaz, L.A.; Gelinas, J.C.; Tzeng, Y.C.; Smith, K.J.; Willie, C.K.; et al. Aging Blunts Hyperventilation-Induced Hypocapnia and Reduction in Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity during Maximal Exercise. Age 2012, 34, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.; Gaitán, J.M.; Pewowaruk, R.J.; Gepner, A.D.; Hess, T.; Wilbrand, S.M.; Dempsey, R.J.; Dougherty, R.J.; Cook, D.B.; Okonkwo, O. Transcranial Color-Coded Doppler Cerebral Hemodynamics Following Aerobic Exercise Training: Outcomes From a Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Vasc. Ultrasound 2022, 46, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Flück, D.; Ainslie, P.N.; Bain, A.R.; Ahmed, A.; Wildfong, K.W.; Morris, L.E.; Phillips, A.A.; Fisher, J.P. Effect of Healthy Aging on Cerebral Blood Flow, CO 2 Reactivity, and Neurovascular Coupling during Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 125, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, S.J.; Ward, J.; Liu, Y.; Vidoni, E.D.; Sisante, J.F.; Kirkendoll, K.; Burns, J.M.; Billinger, S.A. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Is Associated With Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow Velocity in Older Adults. Cardiopulm. Phys. Ther. J. 2020, 31, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, K.M.; Gunstad, J.; Spitznagel, M.B.; Waechter, D.; Hughes, J.W.; Luyster, F.; Josephson, R.; Rosneck, J. Improvements in Cognitive Function Following Cardiac Rehabilitation for Older Adults with Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Neurosci. 2011, 121, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoto, T.; Tarumi, T.; Chen, J.N.; Hynan, L.S.; Cullum, C.M.; Zhang, R. One-Year Aerobic Exercise Altered Cerebral Vasomotor Reactivity in Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoto, T.; Liu, J.; Tseng, B.Y.; Pasha, E.P.; Cardim, D.; Tarumi, T.; Hynan, L.S.; Munro Cullum, C.; Zhang, R. One-Year Aerobic Exercise Reduced Carotid Arterial Stiffness and Increased Cerebral Blood Flow in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 80, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoto, T.; Verma, A.; Kostroske, K.; Tarumi, T.; Patel, N.R.; Pasha, E.P.; Riley, J.; Tinajero, C.D.; Hynan, L.S.; Rodrigue, K.M.; et al. One-Year Aerobic Exercise Increases Cerebral Blood Flow in Cognitively Normal Older Adults. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Campos, D.; Mora, J.; Castro-Piñero, J.; González-Montesinos, J.L.; Conde-Caveda, J.; Chicharro, J.L. Impact of a Physical Activity Program on Cerebral Vasoreactivity in Sedentary Elderly People. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2012, 52, 537–544. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, M.J.; Dunstan, D.W.; Smith, B.; Smith, K.J.; Scheer, A.; Lewis, J.; Naylor, L.H.; Heinonen, I.; Ellis, K.A.; Cerin, E.; et al. Morning Exercise Mitigates the Impact of Prolonged Sitting on Cerebral Blood Flow in Older Adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Takano, D.; Maeda, T.; Fujimaki, Y.; Nakase, T.; Sato, Y. Cerebral Circulation in Aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 30, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Russell, D.; Nyberg-Hansen, R.; Rootwelt, K. A Comparison of Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow Velocities: Simultaneous Measurements in Healthy Subjects. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1992, 12, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, C.L.; Shields, K.L.; Broxterman, R.M.; Hydren, J.R.; Park, S.H.; Gifford, J.R.; Richardson, R.S. Imaging Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound to Measure Middle Cerebral Artery Blood Flow: The Importance of Measuring Vessel Diameter. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 319, R33–R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.-H.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Rafols, J.; Clark, J.; Ding, Y. Cerebral Angiogenesis and Expression of Angiogenic Factors in Aging Rats after Exercise. Curr. Neurovasc Res. 2006, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, T.; Rolland, Y.; de Souto Barreto, P. Protective Effects of Physical Exercise in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsenik, A.; Podbregar, M.; Fabjan, A. Cerebral Blood Flow Impairment and Cognitive Decline in Heart Failure. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-R.; Han, S.-B.; Kim, D.-H.; Song, J.-M.; Kang, D.-H.; Song, J.-K.; Park, S.-W.; Park, S.-J.; et al. Cerebral Blood Flow as a Marker for Recovery of Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in Patients With Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J. Card. Fail. 2012, 18, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-R.; Kim, J.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Park, K.-M.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Hong, M.-K.; Song, J.-K.; Park, S.-W.; Park, S.-J.; et al. Factors Associated with Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow in Congestive Heart Failure Secondary to Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, A.A.; Alwatban, M.; Freemyer, A.; Perales-Puchalt, J.; Billinger, S.A. Effects of High Intensity Interval Exercise on Cerebrovascular Function: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batacan, R.B.; Duncan, M.J.; Dalbo, V.J.; Tucker, P.S.; Fenning, A.S. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Cardiometabolic Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Intervention Studies. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicine, I.; Board, F.N.; Research, S.C.M.N.; Applications, C.M.M.M.F. Monitoring Metabolic Status: Predicting Decrements in Physiological and Cognitive Performance; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780309091596. [Google Scholar]
- Brain Perfusion: Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Techniques. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Masdeu, J.C.; Gonzalez, R.G. (Eds.) Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 135, pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, J.C.; Suzuki, W.A. The Effects of Acute Exercise on Mood, Cognition, Neurophysiology, and Neurochemical Pathways: A Review. Brain Plast. 2017, 2, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y. Acute Effects of Different Exercise Forms on Executive Function and the Mechanism of Cerebral Hemodynamics in Hospitalized T2DM Patients: A within-Subject Study. Front. Public. Health 2023, 11, 1165892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Ba, X.; Liu, Z. Exercise Sustains Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence from 109 Randomized Controlled Trials on over 4600 Patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1071803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papalia, G.F.; Papalia, R.; Diaz Balzani, L.A.; Torre, G.; Zampogna, B.; Vasta, S.; Fossati, C.; Alifano, A.M.; Denaro, V. The Effects of Physical Exercise on Balance and Prevention of Falls in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, P.d.S.; Lima, N.d.S.; Venturini, G.R.d.O.; da Silva, E.B. The Chronic Effects of Muscle-Resistance Training in Arterial Pressure of Hypertensive Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Fisioter. Em Mov. 2019, 32, e003205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author, Year | Design | N | Age of Participants (Mean, SD) | Previous Status | Exercise Type | Minutes/Week | Exercise Duration (Total) | Cerebral Blood Velocity Finding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akazawa, 2012 [45] | QE | 20 | Control: 61 ± 2 Exp: 60 ± 2 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 90–360 | 8 weeks | ↑ |
| Akazawa, 2018 [23] | QE | 10 | 62 ± 4 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 140–270 | 12 weeks | — |
| Alwatban, 2019 [46] | QE | 104 | 70.39 ± 4.78 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | Single time | 8 min | — |
| Bronzwaer, 2017 [43] | QE | 11 | 72 ± 3 | NR | LBNP or dynamic HG | Single time | 15 min | ↑ |
| Caldas, 2018 [44] | QE | 63 | Control: 62.8 ± 8.6 Exp: 62.9 ± 8.7 | NR | Isometric HG | Single time | 3 min | ↑ |
| Cho, 2019 [29] | RCT | 37 | Control: 69.00 ± 4.41 Exp: 68.89 ± 4.16 | Sedentary | Taekwondo | 300 | 16 weeks | — |
| Green, 2021 [47] | RCT | 63 | Control: 60.9 ± 6.1 Land: 63.9 ± 7.7 Water: 61.8 ± 5.8 | Sedentary/Low-active | Aerobic exercise (land and water) | 45–180 | 24 weeks | Land: — Water: — |
| Guadagni, 2020 [24] | QE | 206 | 65.9 ± 6.4 | Low-active | Aerobic exercise | 60–120 | 6 months | ↑ |
| Heckmann, 2003 [48] | QE | 18 | 66.5 ± 5.8 | NR | Aerobic exercise | Single time | 3 min | ↑ |
| Ivey, 2011 [49] | RCT | 38 | Control: 61 ± 8 Exp: 62 ± 10 | NR | Aerobic exercise | 120 | 6 months | ↑ |
| Lin, 2023 [42] | RCT | 102 | Control: 65.35 ± 5.15 Exp: 67.68 ± 5.19 | Sedentary | Baduanjin training | 180 | 24 weeks | ↑ |
| Maasakkers, 2020 [50] | RCOT | 22 | 78 ± 5.3 | Sedentary | 4 conditions | 1 condition/week | 4 weeks | — |
| Marsden, 2011 [51] | QE | 14 | 71 ± 10 | Active | Aerobic exercise | Single time | Variable | ↑ |
| Mitchell, 2022 [52] | RCT | 20 | 64.95 (7.77) (Median, IQR) | Sedentary/Low-active | Aerobic exercise | 150 | 26 weeks | |
| Murrell, 2009 [26] | QE | 12 | 65 ± 5 | Active | Aerobic exercise | Single time | 4 h | ↑ |
| Northey, 2018 [41] | RCT | 17 | Control: 61.5 ± 7.8 MOD: 60.3 ± 8.1 HIIT: 67.8 ± 7.0 | Sedentary/Low-active | Aerobic exercise (MOD and HIIT) | 60–90 | 12 weeks | MOD: — HIIT: ↑ |
| Nowak-Flück, 2018 [53] | QE | 9 | 65.5 ± 2.8 | Active | Aerobic exercise | Single time | Variable | |
| Perdomo, 2019 [54] | QE | 72 | 70.1 ± 4.7 | NR | Aerobic exercise | Single time | ~10 min | ↑ |
| Stanek, 2011 [55] | QE | 42 | 68.17 ± 9.03 | NR | Aerobic exercise | 90 | 12 weeks | — |
| Sugawara, 2022 [27] | RCT | 73 | Control: 68 ± 5 Exp: 69 ± 6 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 75–200 | 12 months | ↑ |
| Tanne, 2005 [28] | QE | 23 | 63 ± 13 | NR | Aerobic exercise | 100 | 18 weeks | — |
| Tomoto, 2021A [56] | RCT | 37 | Control: 64.8 ± 6.6 Exp: 64.6 ± 5.9 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 75–200 | 12 months | — |
| Tomoto, 2021B [57] | RCT | 48 | Control: 66.1 ± 6.8 Exp: 64.8 ± 6.4 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 75–200 | 12 months | ↑ |
| Tomoto, 2022 [58] | RCT | 43 | Control: 67.8 ± 4.9 Exp: 68.2 ± 5.3 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 75–200 | 12 months | ↑ |
| Vicente-Campos, 2012 [59] | RCT | 43 | Control: 64 ± 5 Exp: 64 ± 4 | Sedentary | Aerobic exercise | 150–200 | 7 months | ↑ |
| Wheeler, 2019 [60] | RCOT | 12 | 70 ± 7 | Sedentary/Low-active | 4 conditions | 1 condition/week | 4 weeks | ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paiva Prudente, T.; Oliva, H.N.P.; Oliva, I.O.; Mezaiko, E.; Monteiro-Junior, R.S. Effects of Physical Exercise on Cerebral Blood Velocity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta−Analysis. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100847
Paiva Prudente T, Oliva HNP, Oliva IO, Mezaiko E, Monteiro-Junior RS. Effects of Physical Exercise on Cerebral Blood Velocity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta−Analysis. Behavioral Sciences. 2023; 13(10):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100847
Chicago/Turabian StylePaiva Prudente, Tiago, Henrique Nunes Pereira Oliva, Isabela Oliveira Oliva, Eleazar Mezaiko, and Renato Sobral Monteiro-Junior. 2023. "Effects of Physical Exercise on Cerebral Blood Velocity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta−Analysis" Behavioral Sciences 13, no. 10: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100847
APA StylePaiva Prudente, T., Oliva, H. N. P., Oliva, I. O., Mezaiko, E., & Monteiro-Junior, R. S. (2023). Effects of Physical Exercise on Cerebral Blood Velocity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta−Analysis. Behavioral Sciences, 13(10), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13100847






