A Rasch Analysis of Students’ Academic Motivation toward Mathematics in an Adaptive Learning System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Motivation
2.1. Self-Determination Theory (SDT)
2.2. Measuring Motivation in Learning Mathematics
2.3. Rasch Measurement Theory (RMT)
3. Method
3.1. Stage 1
3.2. Stage 2
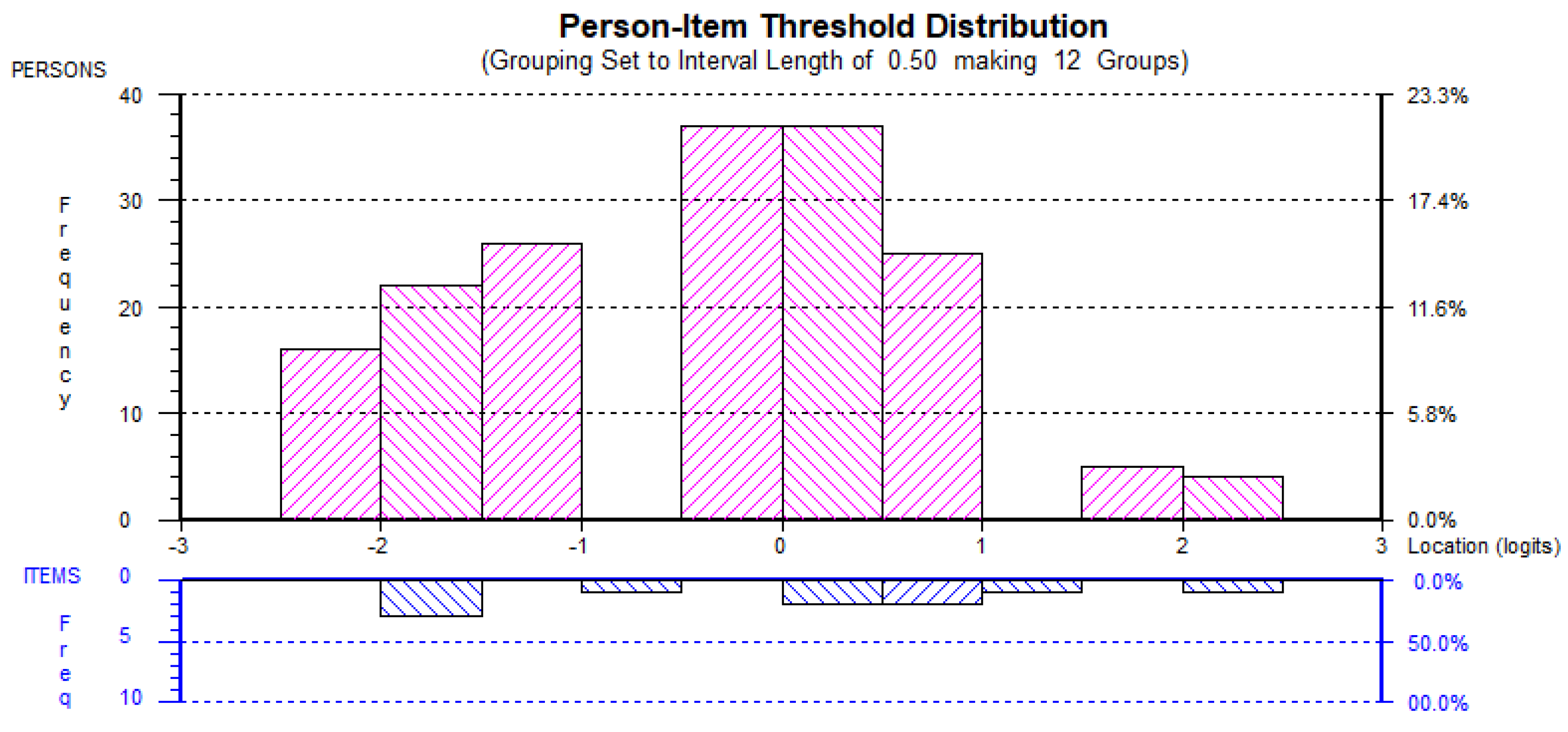
4. Results
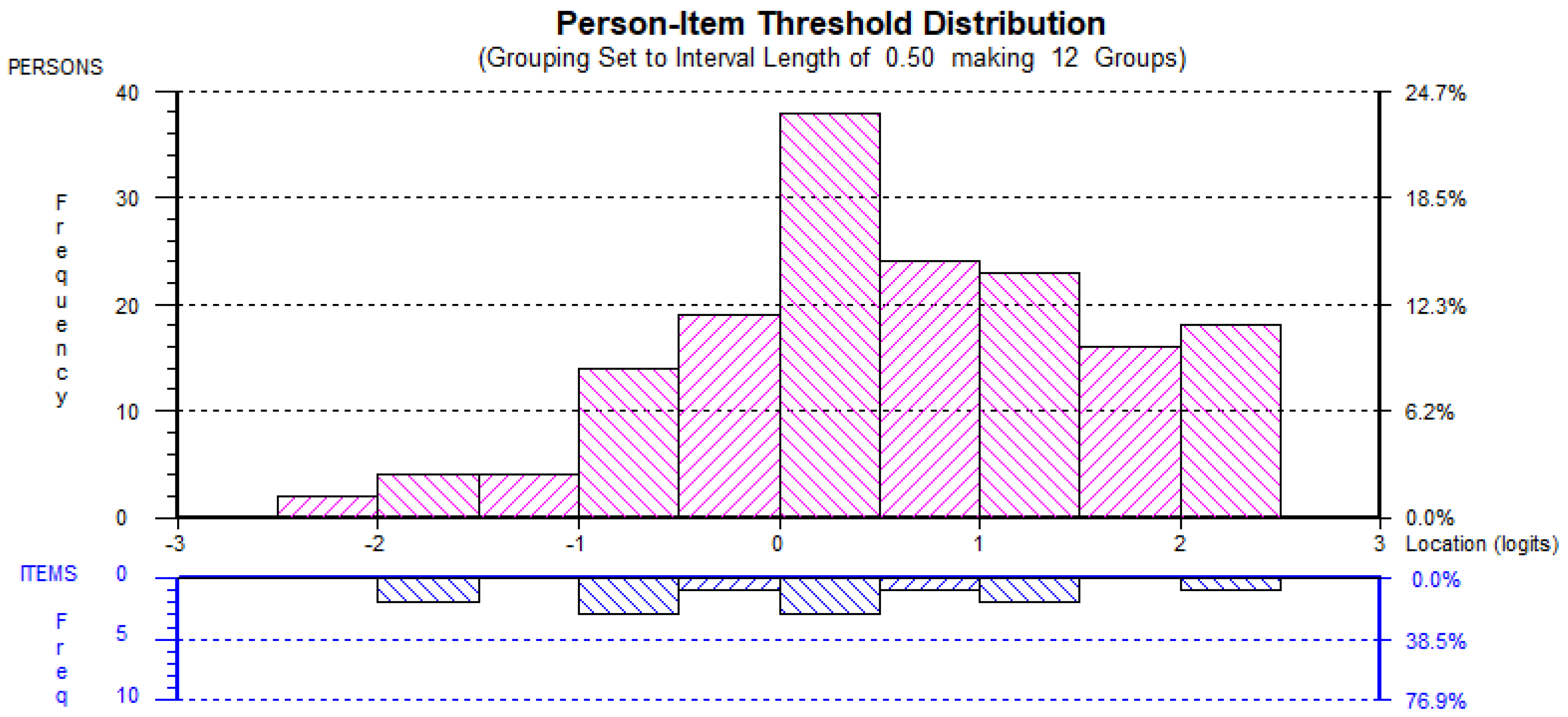
4.1. AMTMS
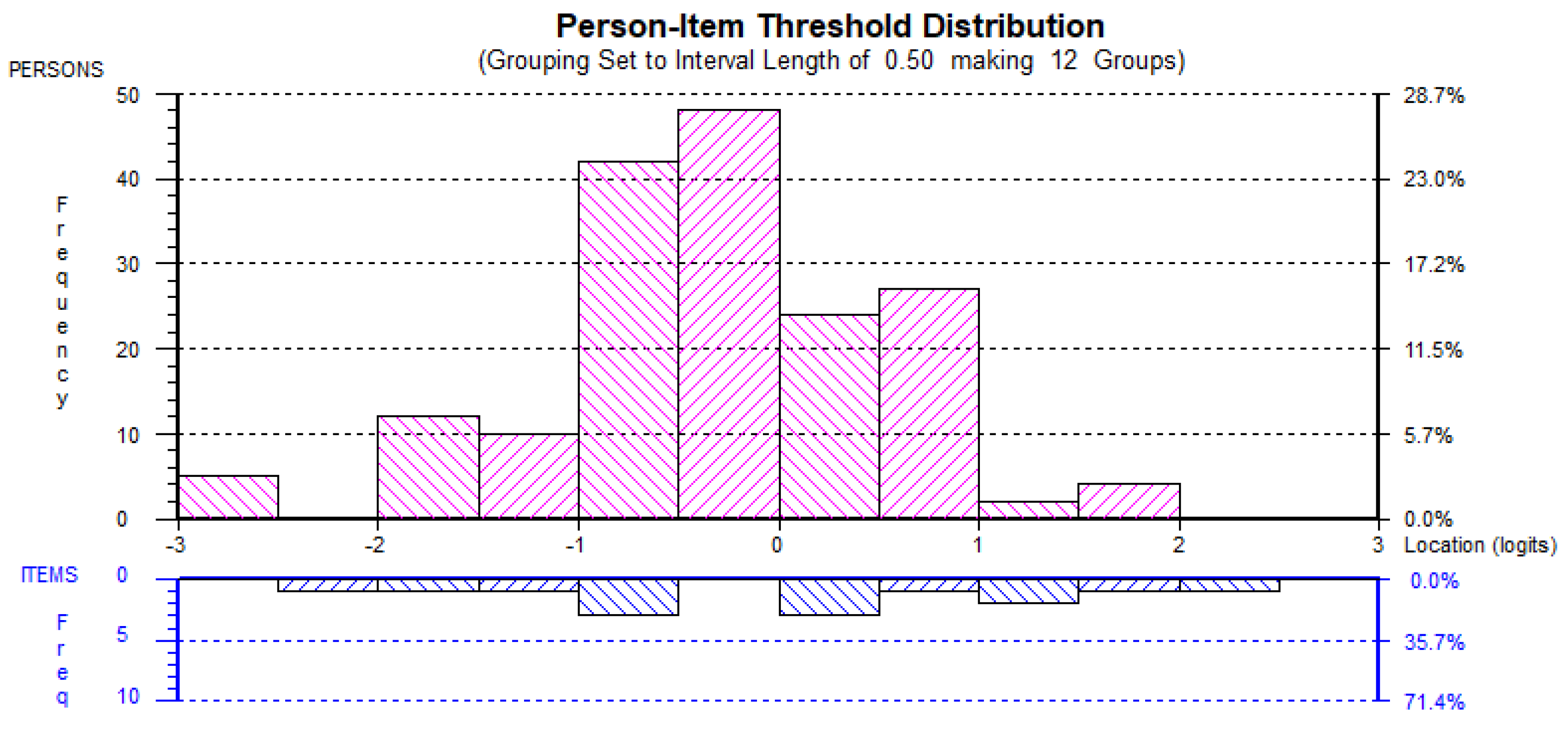
4.2. AMTMS Re-Scored (AMTMSrs)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Academic Motivation toward Mathematics Scale (5 Point Likert Scale: 1, Does Not Correspond at All; 2, Corresponds a Little; 3, Corresponds Moderately; 4, Corresponds a Lot; 5, Corresponds Exactly)
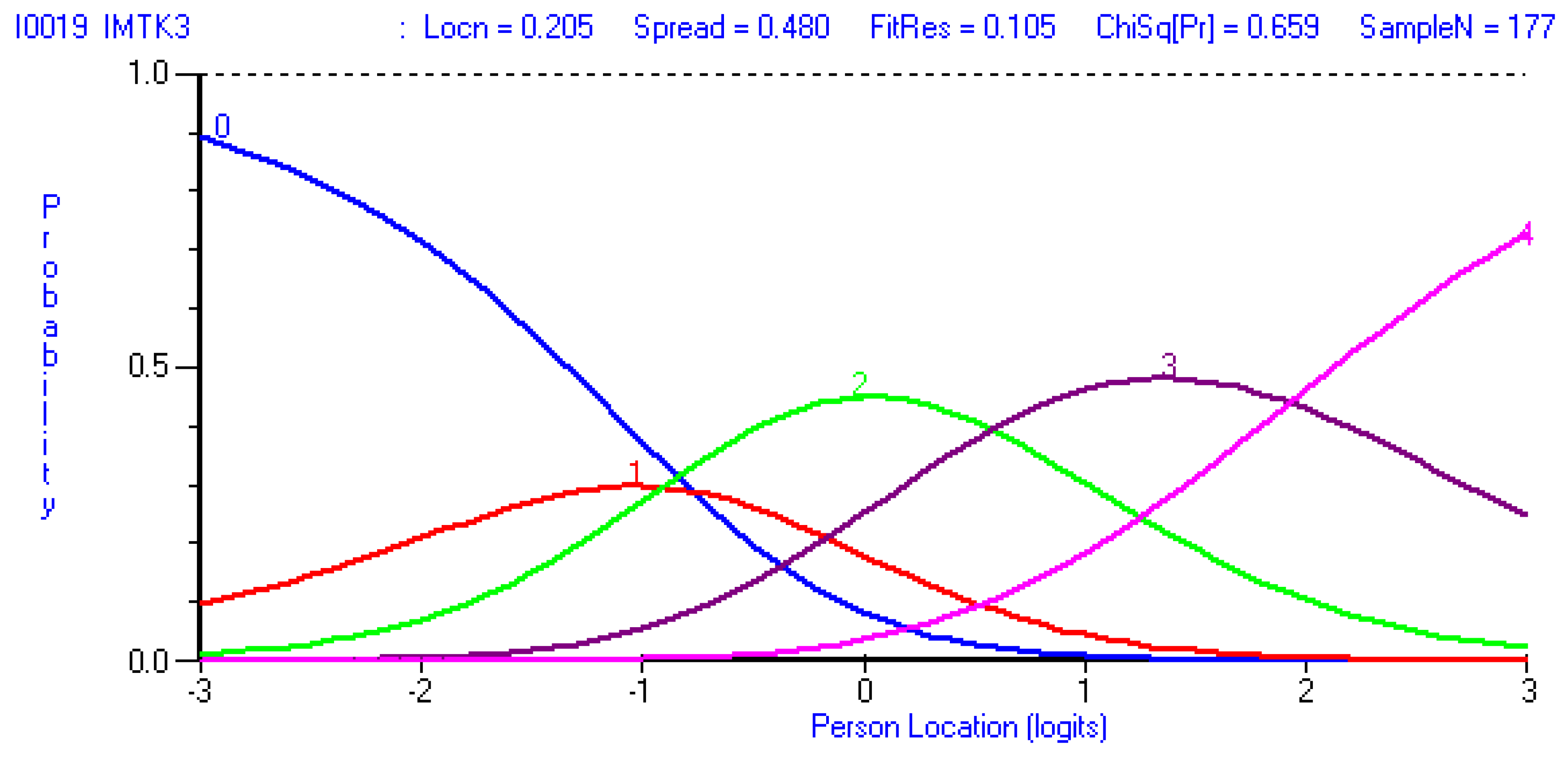
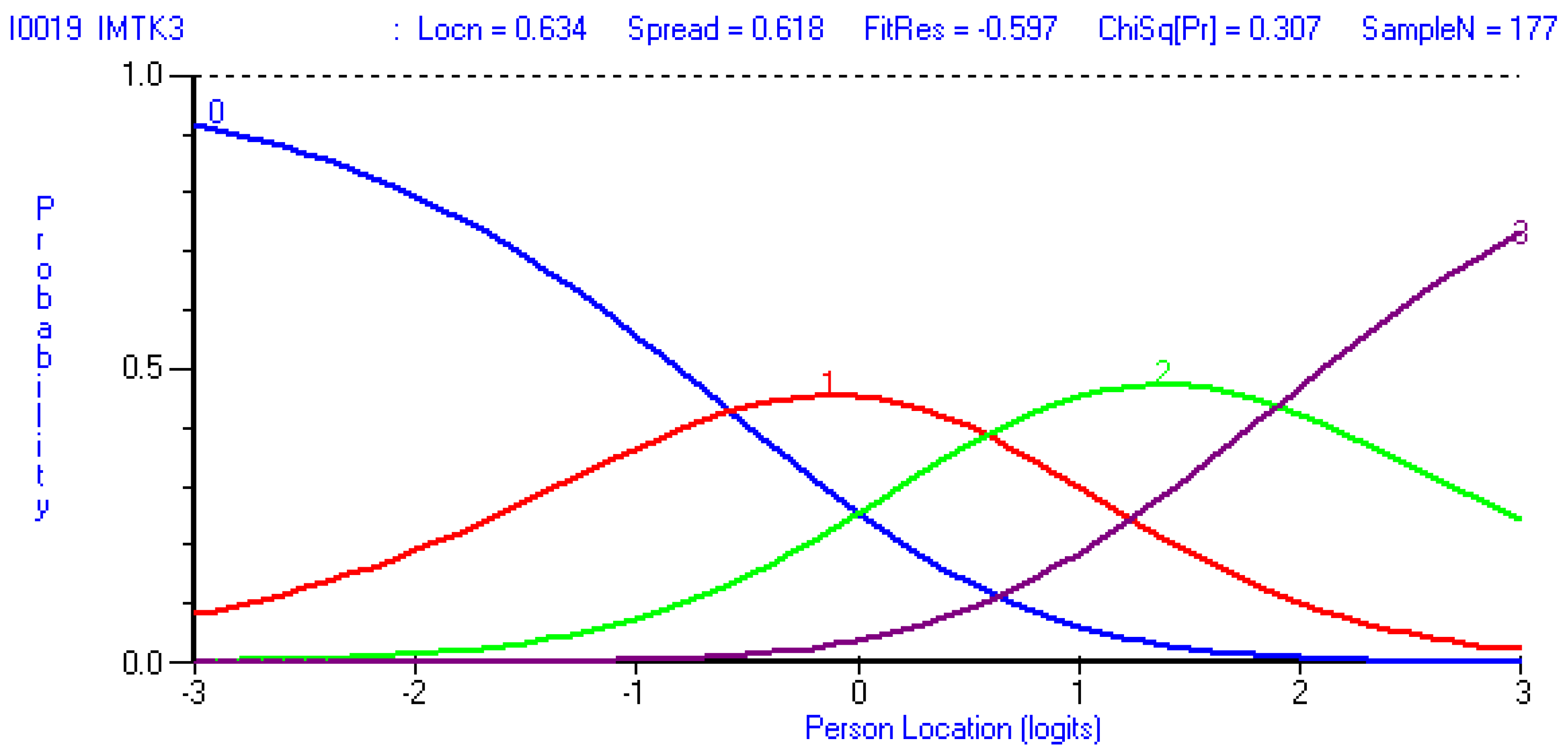
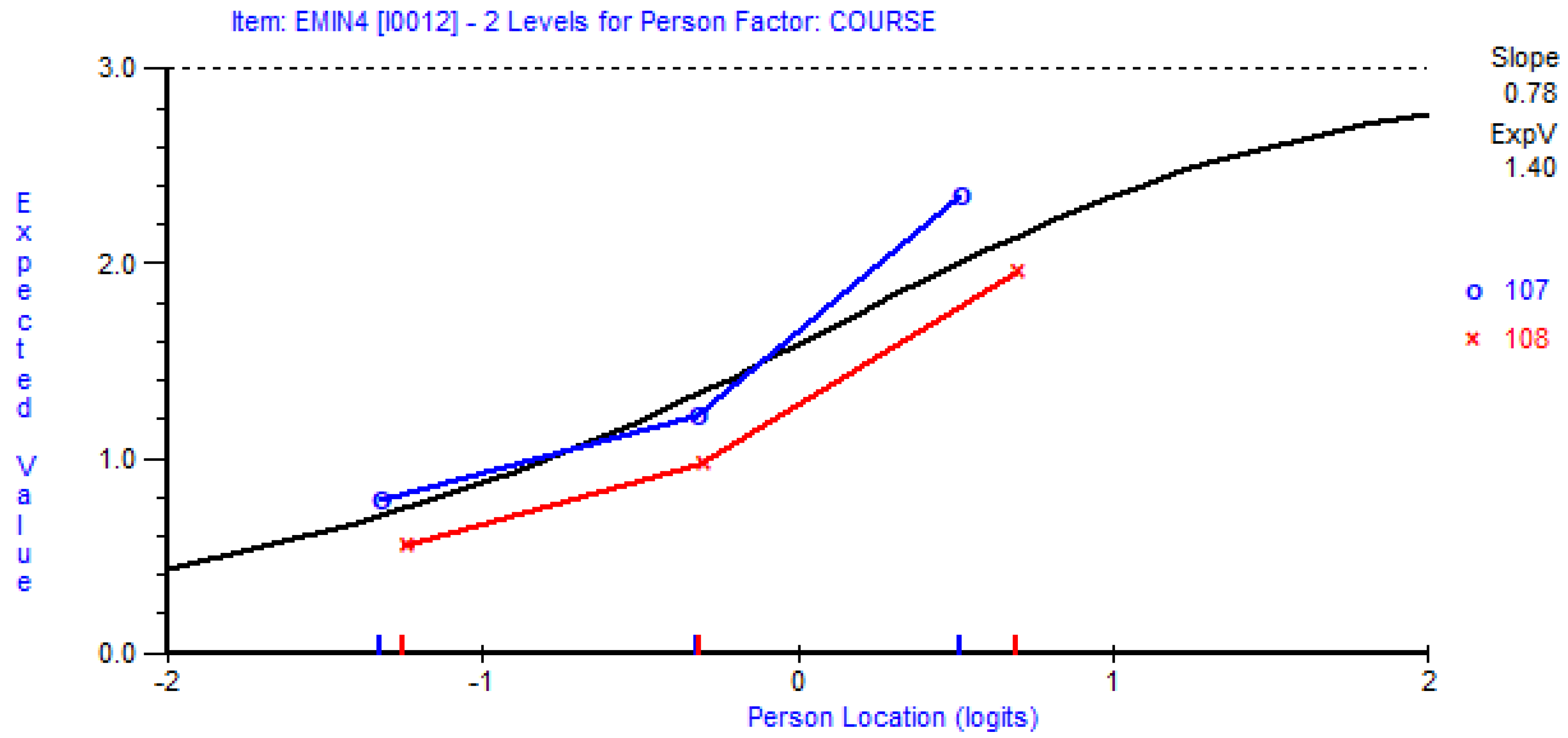
Appendix B. Example Item with Disordered Thresholds
References
- Yarnall, L.; Means, B.; Wetzel, T. Lessons Learned from Early Implementations of Adaptive Courseware; SRI International: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, C.; Cheluvappa, R.; Bellinson, Z.; Maguire, D.; Zimitat, C.; Abraham, J.; Eri, R. Empirical evaluation of a virtual laboratory approach to teach lactate dehydrogenase enzyme kinetics. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 8, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, M.; Weiser, C.; Maur, A. How feedback provided by voluntary electronic quizzes affects learning outcomes of university students in large classes. Comput. Educ. 2018, 121, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; McKelroy, E.; Corliss, S.B.; Carrigan, J. Investigating the effect of an adaptive learning intervention on students’ learning. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2017, 65, 1605–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Govaerts, S.; Verbert, K.; Duval, E. Goal-oriented visualizations of activity tracking: A case study with engineering students. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29 April–2 May 2012; pp. 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Demski, J. This time it’s personal. Technol. Horiz. Educ. 2012, 39, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, L.; Adams Becker, S.; Cummins, M.; Estrada, V.; Freeman, A.; Hall, C. NMC Horizon Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/p/171478/ (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Garrick, B.; Pendergast, D.; Geelan, D. (Eds.) Austin, Texas: The New Media Consortium. Introduction to the philosophical arguments underpinning personalised education. In Theorising Personalised Education; Higher Education Edition; Springer: Berlin/Hailderberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wolper, J. Student-driven personalized learning is trending in higher education. Talent Dev. 2016, 70, 64–65. [Google Scholar]
- Felt, L.J.; Robb, M.B. Technology Addiction: Concern, Controversy, and Finding Balance; Common Sense Media: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Male, T.; Burden, K. Access denied? Twenty-first-century technology in schools. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2014, 23, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Chapman, E. Adapting the academic motivation scale for use in pre-tertiary mathematics classrooms. Math. Educ. Res. J. 2015, 27, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory: Basic Psychological Needs in Motivation Development and Wellness; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pintrich, P. A motivational science perspective on the role of student motivation in learning and teaching contexts. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 95, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, C.S. From needs to goals and representations: Foundations for a unified theory of motivation, personality, and development. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 124, 689–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H.; Usher, E.L. Social cognitive theory and motivation. In The Oxford Handbook of Human Motivation; Ryan, R.M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pantziara, M.; Philippou, G.N. Students’ motivation in the mathematics classroom revealing causes and consequences. Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 2015, 13, 385–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.J.; Oh, E.; Kim, S.M. Motivation, instructional design, flow, and academic achievement at a Korean online university: A structural equation modeling study. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2015, 27, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, D.C.; Bonde, C. Flipping the classroom: Embedding self-regulated learning prompts in videos. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2016, 21, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Park, S.W.; Cozart, J. Affective and motivational factors of learning in online mathematics courses. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2014, 45, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artino, A.R. Motivational beliefs and perceptions of instructional quality: Predicting satisfaction with online training. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2008, 24, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.M. First principles of motivation to learn and e3-learning. Distance Educ. 2008, 29, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation from a self-determination theory perspective: Definitions, theory, practices, and future directions. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 61, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Self-determination theory: A macrotheory of human motivation, development, and health. Can. Psychol. 2008, 49, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, R.F.; Leary, M.R. The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychol. Bull. 1995, 117, 497–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCharms, R. Personal Causation: The Internal Affective Determinants of Behavior; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand, R.J. Toward a hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Zanna, M.P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 29, pp. 271–360. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, K.L. Motivation for Mathematics: The Development and Initial Validation of an Abbreviated Instrument. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand, R.J.; Pelletier, L.G.; Blais, M.R.; Brire, N.M.; Sencal, C.; Vallires, E.F. The academic motivation scale: A measure of intrinsic, extrinsic, and amotivation in education. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1992, 52, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, G. Turkish version of the Academic Motivation Scale. Psychol. Rep. Employ. Psychol. Mark. 2015, 116, 388–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staribratov, I.; Babakova, L. Development and validation of a Math-specific version of the Academic Motivation Scale (AMS-Mathematics) among first-year university students in Bulgaria. TEM J. 2019, 8, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Yerdelen, S.; Yalmanci, G.S.; Göksu, V. Academic Motivation Scale for learning Biology: A scale development study. Educ. Sci. 2014, 39, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.H.; Alsawaie, O.; Alsartawi, A.; Alghazo, I.; Tibi, S. Developing Mathematics Motivation Scale for the United Arab Emirates. J. Educ. Psychol. Stud. 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrich, D.; Marais, I. A Course in Rasch Measurement Theory: Measuring in the Educational, Social and Health Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Hailderberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, L. Validation of the Moral Reasoning Questionnaire against Rasch measurement theory. J. Pac. Rim Psychol. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lim, L.; Chapman, E.; Houghton, S. Validation of the Mental Health Changes Indicators Scale against Rasch measurement theory. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2022, 50, e11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Educational Research Association; American Psychological Association; National Council on Measurement in Education. Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing; American Educational Research Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, B. The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linacre, J.M. Sample size and item calibration stability. Rasch Meas. Trans. 1994, 7, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, A.; Conaghan, P.G. The Rasch measurement model in rheumatology: What is it and why use it? When should it be applied, and what should one look for in a Rasch paper? Arthritis Care Res. 2007, 57, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.Y.; Lim, L. Targeting student learning needs: The development and preliminary validation of the Learning Needs Questionnaire for a diverse university student population. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2021, 40, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslau, J.; Javaras, K.N.; Blacker, D.; Murphy, J.M.; Normand, S.T. Differential item functioning between ethnic groups in the epidemiological assessment of depression. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2008, 196, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Yu, X. A Rasch analysis of emerging adults’ health motivation questionnaire in higher education context. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrich, D. Components of variance of scales with a bifactor subscale structure from two calculations of α. Educ. Meas. Issues Pract. 2016, 35, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Reise, S.P.; Haviland, M.G. Evaluating bifactor models: Calculating and interpreting statistical indices. Psychol. Methods 2016, 21, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Amotivation (AMOT): Nonself-Determined | Extrinsic Motivation * (EMOT): Least Self-Determined | Intrinsic Motivation (IMOT): Most Self-Determined |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of motivation | 1. External regulation (EMER) (lower): reward or punishment (non-autonomous) | Perform a task due to enjoyment, interest, or satisfaction |
| Absence of both intrinsic and extrinsic motivations | 2. Introjected regulation (EMIN): social approval or guilt (non-autonomous) | Presence of high-quality learning |
| 3. Identified regulation (EMID): self-endorsement of goals (autonomous) | ||
| 4. Integrated regulation (EMIR) (higher): congruence (autonomous) |
| Course/Semester/Year | Number of Enrolled Students * | Number of Students Who Completed the AMTMS |
|---|---|---|
| MTH107/2/2021 | 130 | 42 |
| MTH107/1/2022 | 160 | 80 |
| MTH108/2/2021 | 74 | 41 |
| MTH108/1/2022 | 96 | 33 |
| Factor | Number of Items | χ2 Value/p | PSI | Cronbach’s Alpha | Unidimensionality (%) | Item Residual (M/SD) | Person Residual (M/SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMOT | 4 | 15.28/0.05 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 2.04 | 0.37/1.48 | −0.49/1.19 |
| EMER | 4 | 23.47/0.003 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 5.10 | 0.47/1.54 | −0.64/1.44 |
| EMIN | 4 | 53.04/0.000 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 3.06 | 0.66/1.86 | −0.405/1.41 |
| EMID | 4 | 55.59/0.000 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 1.53 | 0.77/2.45 | −0.46/1.32 |
| IMT | 5 | 4.48/0.92 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 5.10 | 0.25/0.48 | −0.74/1.64 |
| AMTMS | 21 | 200.42/0.000 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 26.53 | 0.77/2.38 | −0.47/2.24 |
| Item | Original Scoring | Adjusted Scoring |
|---|---|---|
| AMOT1 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 4-3-2-1-0 |
| AMOT2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 2-2-1-0-0 |
| AMOT3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 3-2-1-0-0 |
| AMOT4 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 4-3-2-1-0 |
| EMER1 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| EMER2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| EMER3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMER4 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMIN1 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMIN2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMIN3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| EMIN4 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMID1 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMID2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| EMID3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-1-2-3 |
| EMID4 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| IMTA4 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| IMTK2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| IMTK3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-0-1-2-3 |
| IMTS2 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| IMTS3 | 0-1-2-3-4 | 0-1-2-3-4 |
| Factor | Number of items | χ2 Value/p | PSI | Cronbach’s Alpha | Unidimensionality (%) | Item Residual (M/SD) | Person Residual (M/SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMOTrs | 4 | 14.07/0.08 | 0.66 | 0.77 | 2.04 | 0.20/0.99 | −0.43/1.14 |
| EMERrs | 4 | 20.88/0.007 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 5.10 | 0.51/1.20 | −0.65/1.41 |
| EMINrs | 3 | 12.72/0.05 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 2.55 | 0.46/0.72 | −0.50/1.05 |
| EMIDrs | 3 | 7.09/0.31 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 4.08 | 0.39/0.56 | −0.70/1.32 |
| IMTrs | 5 | 5.52/0.85 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 5.10 | 0.29/0.63 | −0.71/1.63 |
| AMTMSrs | 19 | 239.64/0.000 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 25.51 | 0.71/3.22 | −0.56/2.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, L.; Lim, S.H.; Lim, W.Y.R. A Rasch Analysis of Students’ Academic Motivation toward Mathematics in an Adaptive Learning System. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12070244
Lim L, Lim SH, Lim WYR. A Rasch Analysis of Students’ Academic Motivation toward Mathematics in an Adaptive Learning System. Behavioral Sciences. 2022; 12(7):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12070244
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Lyndon, Seo Hong Lim, and Wei Ying Rebekah Lim. 2022. "A Rasch Analysis of Students’ Academic Motivation toward Mathematics in an Adaptive Learning System" Behavioral Sciences 12, no. 7: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12070244
APA StyleLim, L., Lim, S. H., & Lim, W. Y. R. (2022). A Rasch Analysis of Students’ Academic Motivation toward Mathematics in an Adaptive Learning System. Behavioral Sciences, 12(7), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12070244







