Variables and Mechanisms Affecting Response to Language Treatment in Multilingual People with Aphasia
Abstract
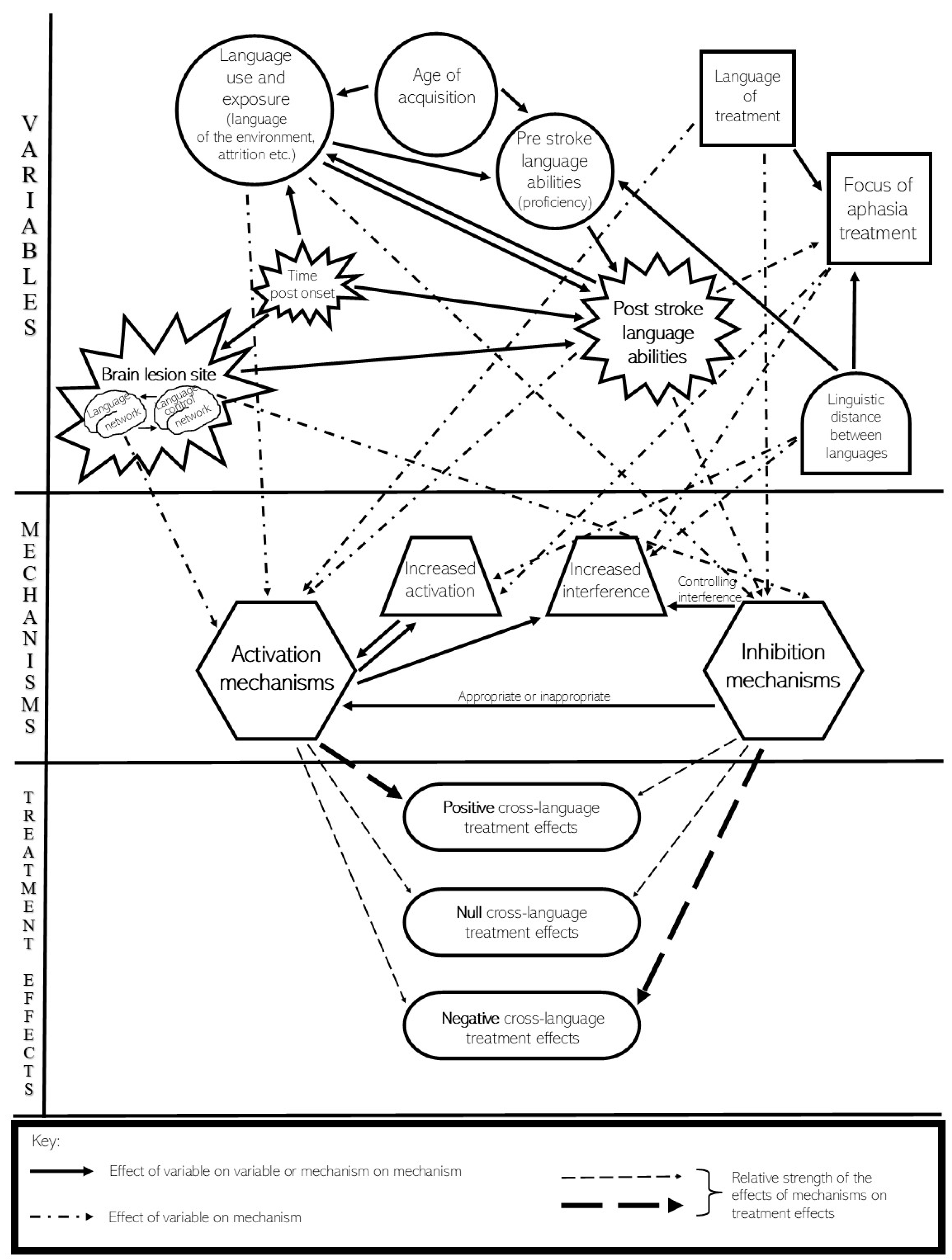
1. Introduction
2. Multilingualism-Related Variables Affecting Response to Treatment in Multilingual PWA
2.1. Age of Language Acquisition
2.2. Language Use and Exposure
2.3. Language Proficiency
2.4. Post-Stroke Language Abilities
3. Stroke-Related Variables Affecting Response to Treatment in Multilingual PWA
3.1. Lesion Site
3.2. Time Post-Onset
4. Treatment
4.1. Treatment Focus
4.2. Language of Treatment
5. Mechanisms Accounting for Observed Response to Treatment in Multilingual PWA
5.1. Activation
5.2. Inhibition
5.3. Interactions of Activation and Inhibition and the Variables that Affect Them
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallowell, B.; Chapey, R. Introduction to language intervention strategies in adult aphasia. In Language Intervention Strategies in Aphasia and Related Neurogenic Communication Disorders, 4th ed.; Chapey, R., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean, F. Bilingualism: A short introduction. In The Psycholinguistics of Bilingualism; Grosjean, F., Li, P., Eds.; Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, M.L.; Obler, L.K. The Bilingual Brain: Neuropsychological and Neurolinguistic Aspects of Bilingualism; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, M. Bilingualism and aphasia. Stud. Neuroling. 1977, 3, 65–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, M. A Neurolinguistic Theory of Bilingualism; John Benjamins: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, M. Readings on Aphasia in Bilinguals and Polyglots; Didier: Montréal, QU, Canada, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Centeno, J.G.; Ghazi-Saidi, L.; Ansaldo, A.I. Aphasia in multilingual populations. In Aphasia and Related Neurogenic Communication Disorders, 2nd ed.; Papathanasiou, I., Coppens, P., Potagas, C., Eds.; Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 331–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmina, E.; Goral, M.; Norvik, M.I.; Weekes, B. What influences language impairment in bilingual aphasia? A meta-analytic review. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, A.; Goral, M.; Obler, L.K. The complex relationship between pre-stroke and post-stroke language abilities in multilingual individuals with aphasia. Aphasiology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, L.R.; Robey, R.R. Aphasia treatment: Recovery, prognosis and clinical effectiveness. In Language Intervention Strategies in Aphasia and Related Neurogenic Communication Disorders, 4th ed.; Chapey, R., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Raymer, A.; Beeson, P.; Holland, A.; Kendall, D.; Maher, L.; Martin, N.; Murray, L.; Rose, M.; Thompson, C.K.; Turkstra, L.; et al. Translational research in aphasia: From neuroscience to neurorehabilitation. J. Speech Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S259–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza, C.; Grasemann, U.; Dekhtyar, M.; Miikkulainen, R.; Kiran, S. BiLex: A computational approach to the effects of age of acquisition and language exposure on bilingual lexical access. Brain Lang. 2019, 195, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaldo, A.I.; Saidi, L.G. Aphasia therapy in the age of globalization: Cross-linguistic therapy effects in bilingual aphasia. Behav. Neurol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faroqi-Shah, Y.; Frymark, T.; Mullen, R.; Wang, B. Effect of treatment for bilingual individuals with aphasia: A systematic review of the evidence. J. Neurolinguist. 2010, 23, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, S. Bilingual aphasia: Explanations in population encoding. J. Neurolinguist. 2019, 49, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.; Jones, T. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: Implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J. Speech Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saur, D.; Lange, R.; Baumgaertner, A.; Schraknepper, V.; Willmes, K.; Rijntjes, M.; Weiller, C. Dynamics of language reorganization after stroke. Brain 2006, 129, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwigsen, G.; Stockert, A.; Charpentier, L.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Klingbeil, J.; Wrede, K.; Obrig, H.; Saur, D. Short-term modulation of the lesioned language network. eLife 2020, 9, e54277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockert, A.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Klingbeil, J.; Wrede, K.; Kümmerer, D.; Hartwigsen, G.; Kaller, C.P.; Weiller, C.; Saur, D. Dynamics of language reorganization after left temporo-parietal and frontal stroke. Brain 2020, 143, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giussani, C.; Roux, F.E.; Lubrano, V.; Gaini, S.M.; Bello, L. Review of language organisation in bilingual patients: What can we learn from direct brain mapping? Acta Neurochir. 2007, 149, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingerhoets, G.; Van Borsel, J.; Tesink, C.; Van Den Noort, M.; Deblaere, K.; Seurinck, R.; Vandemaele, P.; Achten, E. Multilingualism: An FMRI Study. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 2181–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutalebi, J.; Cappa, S.F.; Perani, D. The bilingual brain as revealed by functional neuroimaging. Biling.-Lang. Cogn. 2001, 4, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartenburger, I.; Heekeren, H.R.; Abutalebi, J.; Cappa, S.F.; Villringer, A.; Perani, D. Early Setting of Grammatical Processing in the Bilingual Brain. Neuron 2003, 37, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutalebi, J.; Green, D. Bilingual language production: The neurocognition of language representation and control. J. Neurolinguist. 2007, 20, 242–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W.; Abutalebi, J. Language control in bilinguals: The adaptive control hypothesis. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2013, 25, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Houwer, A.; Ortega, L. The Cambridge Handbook of Bilingualism; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Milroy, L.; Muysken, P. One Speaker, Two Languages: Cross-Disciplinary Perspectives on Code-Switching; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Finkbeiner, M.; Gollan, T.; Caramazza, A. Bilingual lexical access: What’s the (hard) problem? Biling.-Lang. Cogn. 2006, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, M.; Guo, T.; Bobb, S.C.; Kroll, J.F. When bilinguals choose a single word to speak: Electrophysiological evidence for inhibition of the native language. J. Mem. Lang. 2012, 67, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W.; Abutalebi, J. Understanding the link between bilingual aphasia and language control. J. Neurolinguist. 2008, 21, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, M.T. The declarative/procedural model: A Neurobiologically Motivated Theory of First and Second Language. In Theories in Second Language Acquisition: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Van Patten, P., William, J., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 135–158. [Google Scholar]
- Goral, M.; Naghibolhosseini, M.; Conner, P.S. Asymmetric inhibitory treatment effects in multilingual aphasia. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2013, 30, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goral, M.; Levy, E.S.; Kastl, R. Cross-language treatment generalisation: A case of trilingual aphasia. Aphasiology 2010, 24, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miertsch, B.; Meisel, J.M.; Isel, F. Non-treated languages in aphasia therapy of polyglots benefit from improvement in the treated language. J. Neurolinguist. 2009, 22, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, M.; Libben, G. The Assessment of Bilingual Aphasia; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.S.; Köpke, B. L1 attrition and the mental lexicon. In The Bilingual Mental Lexicon: Interdisciplinary Approaches; Pavlenko, A., Ed.; Multilingual Matters: Clevedon, UK, 2009; pp. 209–238. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, M.S.; Jarvis, S. Lexical access and lexical diversity in first language attrition. Biling.-Lang. Cogn. 2014, 17, 729–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpke, B. First language attrition: From bilingual to monolingual proficiency. In The Cambridge Handbook of Bilingualism; De Houwer, A., Ortega, L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 349–365. [Google Scholar]
- Altenberg, E.P. Assessing first language vulnerability to attrition. In First Language Attrition; Seliger, H.W., Vago, R.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrick, H.P. Semantic memory content in permastore: Fifty years of memory for Spanish learned in school. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 1984, 113, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardovi-Harlig, K.; Stringer, D. Variables in second language attrition: Advancing the state of the art. Stud. Second Lang. Acquis. 2010, 32, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoph, M.I.N.; Lind, M.; Simonsen, H.G. Semantic feature analysis targeting verbs in a quadrilingual speaker with aphasia. Aphasiology 2015, 29, 1473–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goral, M.; Rosas, J.; Conner, P.S.; Maul, K.K.; Obler, L.K. Effects of language proficiency and language of the environment on aphasia therapy in a multilingual. J. Neurolinguist. 2012, 25, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.P.-H.; Whiteside, J. Early recovery of a multi-lingual speaker with aphasia using Cantonese and English. Speech Lang. Hear. 2015, 18, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, M.; Grunden, N.; Serra, M.; García-Sánchez, C.; Costa, A. Semantic processing in bilingual aphasia: Evidence of language dependency. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollan, T.H.; Weissberger, G.H.; Runnqvist, E.; Montoya, R.I.; Cera, C.M. Self-ratings of spoken language dominance: A Multilingual Naming Test (MINT) and preliminary norms for young and aging Spanish–English bilinguals. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2012, 15, 594–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoschuk, B.; Ferreira, V.; Gollan, T. When a seven is not a seven: Self-ratings of bilingual language proficiency differ between and within language populations. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2019, 22, 516–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoph, M.I.K. Language intervention in Arabic–English bilingual aphasia: A case study. Aphasiology 2013, 27, 1440–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, P.S.; Goral, M.; Anema, I.; Borodkin, K.; Haendler, Y.; Knoph, M.; Mustelier, C.; Paluska, E.; Melnikova, Y.; Moeyaert, M. The role of language proficiency and linguistic distance in cross-linguistic treatment effects in aphasia. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2018, 32, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, L.A.; Kiran, S. Effect of semantic naming treatment on crosslinguistic generalization in bilingual aphasia. J. Speech Hear. Res. 2006, 49, 729–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Roberts, P.M. Semantic feature analysis treatment in Spanish-English and French-English bilingual aphasia. Aphasiology 2010, 24, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallowell, B. Aphasia and Other Acquired Neurogenic Language Disorders: A Guide for Clinical Excellence; Plural Publishing Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hickok, G.; Poeppel, D. The cortical organization of speech processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yourganov, G.; Smith, K.G.; Fridriksson, J.; Rorden, C. Predicting aphasia type from brain damage measured with structural MRI. Cortex 2015, 73, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutalebi, J.; Rosa, P.A.D.; Tettamanti, M.; Green, D.W.; Cappa, S.F. Bilingual aphasia and language control: A follow-up fMRI and intrinsic connectivity study. Brain Lang. 2009, 109, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, A.; Goral, M.; Edmonds, L.A.; Obler, L.K. Activation and Inhibition Processes Underlying Aphasia Treatment Effects in Multilingual People. Biling. Lang. Cogn. (under review).
- Radman, N.; Mouthon, M.; Di Pietro, M.; Gaytanidis, C.; Leemann, B.; Abutalebi, J.; Annoni, J.M. The role of the cognitive control system in recovery from bilingual aphasia: A multiple single-case fMRI study. Neural Plast. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, R.M.; Minzer, B.; Antoniello, D.; Festa, J.R.; Krakauer, J.W.; Marshall, R.S. Improvement in aphasia scores after stroke is well predicted by initial severity. Stroke 2010, 41, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.; Goral, M. Nonparallel recovery in bilingual aphasia: Effects of language choice, language proficiency, and treatment. Int. J. Biling. 2004, 8, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletta, E.; Goral, M.; Conner, P. Aphasia rehabilitation. In Stroke Rehabilitation; Wilson, R., Raghavan, P., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bhogal, S.K.; Teasell, R.W.; Foley, N.C.; Speechley, M.R. Rehabilitation of aphasia: More is better. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2013, 10, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, L.R. Aphasia treatment: Intensity, dose parameters, and script training. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2012, 14, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E. Optimal intervention intensity. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2012, 14, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Sandberg, C.; Gray, T.; Ascenso, E.; Kester, E. Rehabilitation in bilingual aphasia: Evidence for within- and between-language generalization. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2013, 22, S298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.F.; Van Hell, J.G.; Tokowicz, N.; Green, D.W. The Revised Hierarchical Model: A critical review and assessment. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2010, 13, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, T.; Van Heuven, W.J.B. The BIA model and bilingual word recognition. In Localist Connectionist Approaches to Human Cognition; Grainger, J., Jacobs, A.M., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 189–225. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, T.; Van Heuven, W.J.B. The architecture of the bilingual word recognition system: From identification to decision. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2002, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnert, K. Cognitive and cognate-based treatments for bilingual aphasia: A case study. Brain Lang. 2004, 91, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.M.; Deslauriers, L. Picture naming of cognate and non-cognate nouns in bilingual aphasia. J. Commun. Dis. 1999, 32, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, J.; Falcon, M. Effects of cognate status and language of therapy during intensive semantic naming treatment in a case of severe nonfluent bilingual aphasia. Clin. Linguist. Phon. 2011, 25, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejazi, Z.; Nieves, Y.; Dilone, R.; Saldivia, P.; Velasco, K.; Goral, M. Language Treatment in Bilingual and Multilingual Individuals with Aphasia; American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Convention: Orlando, FL, USA, November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Marangolo, P.; Rizzi, C.; Peran, P.; Piras, F.; Sabatini, U. Parallel recovery in a bilingual aphasic: A neurolinguistic and fMRI study. Neuropsychology 2019, 23, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Code, C.F.S. Significant landmarks in the history of aphasia and its therapy. In Aphasia and Related Neurogenic Communication Disorders, 2nd ed.; Papathanasiou, I., Coppens, P., Potagas, C., Eds.; Jones and Bartlett: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, R.A.; Kartsounis, L.D. Wobbly words: Refractory anomia with preserved semantics. Neurocase 2000, 6, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftus, E.F. Activation of semantic memory. Am. J. Psychol. 1973, 86, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.M.; Loftus, E.F. A spreading-activation theory of semantic processing. Psychol. Rev. 1975, 82, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamoura, A.; Williams, J.N. Processing verb argument structure across languages: Evidence for shared representations in the bilingual lexicon. Appl. Psycholing. 2007, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoph, M.I.N.; Simonsen, H.G.; Lind, M. Cross-linguistic transfer effects of verb-production therapy in two cases of multilingual aphasia. Aphasiology 2017, 31, 1482–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, L.A. A review of Verb Network Strengthening Treatment: Theory, methods, results, and clinical implications. Top. Lang. Disord. 2016, 36, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W. Mental control of the bilingual lexico-semantic system. Biling.-Lang. Cogn. 1998, 1, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szöllősi, I.; Marton, K. Interference control in aphasia. Psychol. Hung. IV 2016, 1, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lerman, A.; Goral, M.; Obler, L.K. Rehabilitating an Attrited Language in a Bilingual Person with Aphasia. Biling.-Lang. Cogn. (under review).
- Friederici, A.D.; Gierhan, S.M. The language network. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, A. Direct and Indirect Treatment Effects in Multilingual People with Aphasia. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Graduate Center, City University of New York, New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goral, M.; Lerman, A. Variables and Mechanisms Affecting Response to Language Treatment in Multilingual People with Aphasia. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10090144
Goral M, Lerman A. Variables and Mechanisms Affecting Response to Language Treatment in Multilingual People with Aphasia. Behavioral Sciences. 2020; 10(9):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10090144
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoral, Mira, and Aviva Lerman. 2020. "Variables and Mechanisms Affecting Response to Language Treatment in Multilingual People with Aphasia" Behavioral Sciences 10, no. 9: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10090144
APA StyleGoral, M., & Lerman, A. (2020). Variables and Mechanisms Affecting Response to Language Treatment in Multilingual People with Aphasia. Behavioral Sciences, 10(9), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10090144



