Self-Rated Depressive Symptoms in Children and Youth with and without Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Depressive Symptoms
2.2.2. Behavioral Assessment
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Group Comparisons of DSRS-C and SDQ
3.2. Correlation Analysis between Depressive Symptoms and Behavioral Features
3.3. Hierarchical Regressions Analysis to Identify the Factors Contributing to Depressive Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindsay, S. Child and youth experiences and perspectives of cerebral palsy: A qualitative systematic review. Child Care Health Dev. 2016, 42, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Brossard-Racine, M.; Hall, N.; Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.I.; Law, M.; Poulin, C.; Rosenbaum, P. Behavioural problems in school age children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, J.; White-Koning, M.; Dickinson, H.O.; Thyen, U.; Arnaud, C.; Beckung, E.; Fauconnier, J.; Marcelli, M.; McManus, V.; Michelsen, S.I.; et al. Psychological problems in children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional European study. J. Child Psychol. 2008, 49, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Brinbaum, R.; Chilingaryan, G.; Rosenbaum, P.; Poulin, C. Participation and enjoyment of leisure activities in school-aged children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser-Cram, P. Mastery motivation in toddlers with developmental disabilities. Child Dev. 1996, 67, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, K.D.; Connors, R.E.; Stegman, C.E. Does a physical handicap alter the development of mastery motivation during the preschool years? J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. 1988, 27, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, E. Dynamic systems theory and the complexity of change. Psychoanal. Dialogues 2005, 15, 255–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majnemer, A.; Shevell, M.; Law, M.; Poulin, C.; Rosenbaum, P. Level of motivation in mastering challenging tasks in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryanton, C.; Bosse, J.; Brien, M.; Mclean, J.; McCormick, A.; Sveistrup, H. Feasibility, motivation, and selective motor control: Virtual reality compared to conventional home exercise in children with cerebral palsy. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atun-Einy, O.; Berger, S.E.; Scher, A. Assessing motivation to move and its relationship to motor development in infancy. Infant Behav. Dev. 2013, 36, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liptak, G.S.; O’Donnell, M.; Conaway, M.; Chumlea, W.C.; Worley, G.; Henderson, R.C.; Fung, E.; Stallings, V.A.; Samson-Fang, L.; Calvert, R.; et al. Health status of children with moderate to severe cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2001, 43, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Rigoli, D.; Piek, J. Developmental coordination disorder and internalizing problems in children: The environmental stress hypothesis elaborated. Dev. Rev. 2013, 33, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Hay, J.; Faught, B.; Mandigo, J.; Flouris, A. Developmental coordination disorder, self-efficacy toward physical activity, and play: Does gender matter? Adapt. Phys. Activ. Q. 2005, 22, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, H.O.; Parkinson, K.N.; Ravens-Sieberer, U.; Schirripa, G.; Thyen, U.; Arnaud, C.; Beckung, E.; Fauconnier, J.; McManus, V.; Michelsen, S.I.; et al. Self-reported quality of life of 8–12-year-old children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional European study. Lancet 2007, 369, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, K.F.; Belza, B.; Kartin, D.; Logsdon, R.G.; McLaughlin, J. Self-reported health status and quality of life in youth with cerebral palsy and typically developing youth. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colver, A.; Rapp, M.; Eisemann, N.; Ehlinger, V.; Thyen, U.; Dickinson, H.O.; Parkes, J.; Parkinson, K.; Nystrand, M.; Fauconnier, J.; et al. Self-reported quality of life of adolescents with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, P.; Otsuka, N.; Sanders, J.; McGee-Brown, J. Functioning and health-related quality of life of adolescents with cerebral palsy: Self versus parent perspectives. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, J.; Blackmore, A.M.; Epstein, A.; Skoss, R.; Langdon, K.; Jacoby, P.; Whitehouse, A.J.O.; Leonard, H.; Rowe, P.W.; Glasson, E.J.; et al. The prevalence of mental health disorders and symptoms in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna, R.J.; Holub, A.; Turk, M.A.; Meccarello, J.; Davidson, P.W. Health conditions, functional status and health care utilization in adults with cerebral palsy. Fam. Pract. 2018, 35, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienko, S.E. An exploratory study investigating the multidimensional factors impacting the health and well-being of young adults with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Slot, W.M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, C.; van den Berg-Emons, R.J.; Bergen, M.P.; Hilberink, S.R.; Stam, H.J.; Roebroeck, M.E. Chronic pain, fatigue, and depressive symptoms in adults with spastic bilateral cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.J.; Peterson, M.D.; O’Connell, N.E.; Victor, C.; Liverani, S.; Anokye, N.; Ryan, J.M. Risk of depression and anxiety in adults with cerebral palsy. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, D.G.; Warschausky, S.A.; Peterson, M.D. Mental health disorders and physical risk factors in children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, D.G.; Peterson, M.D.; Warschausky, S.A. Mental health disorders, participation, and bullying in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birleson, P. The validity of depressive disorder in childhood and the development of a self-rating scale: A research report. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1981, 22, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T. Childhood depressive state in the school situation. Consideration from the Birleson’s Scale. Jpn. J. Psychiatry 1996, 1, 131–138. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, S. Investigation of the factor structure model and normative data for Depression Self-Rating Scale for Children (DSRS) among junior high-school students. Jpn. J. Res. Emot. 2008, 16, 133–140. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Denda, K.; Kako, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Ito, K.; Kitagawa, N.; Koyama, T. Depressive Symptoms in a School Sample of Children and Adolescents; Using the Birleson Depression Self-Rating Scale for Children (DSRS-C). Jpn. J. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 424–436. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, R. The Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire: A research note. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1997, 38, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuishi, T.; Nagano, M.; Araki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Nagamitsu, S.; Iizuka, C.; Ohya, T.; Shibuya, K.; et al. Scale properties of the Japanese version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ): A study of infant and school children in community samples. Brain Dev. 2008, 30, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, A.; Kamio, Y. Normative data and psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire among Japanese school-aged children. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2014, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi. (Version 0.9). Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2020).
- Chiarello, L.A.; Palisano, R.J.; McCoy, S.W.; Bartlett, D.J.; Wood, A.; Chang, H.J.; Kang, L.J.; Avery, L. Child engagement in daily life: A measure of participation for young children with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelsen, S.I.; Flachs, E.M.; Damsgaard, M.T.; Parkes, J.; Parkinson, K.; Rapp, M.; Arnaud, C.; Nystrand, M.; Colver, A.; Fauconnier, J.; et al. European study of frequency of participation of adolescents with and without cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2014, 18, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.P.; Hetrick, S.E.; Rosenbaum, S.; Purcell, R.; Parker, A.G. Treating depression with physical activity in adolescents and young adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, L.P.; Vanderloo, L.; Moore, S.; Faulkner, G. Physical activity and depression, anxiety, and self-esteem in children and youth: An umbrella systematic review. Ment. Health Phys. Activ. 2019, 16, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczak, D.J.; Madigan, S.; Colasanto, M. Children’s physical activity and depression: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20162266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, F.B.; Vancampfort, D.; Richards, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B.; Stubbs, B. Exercise as a treatment for depression: A meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 77, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Estévez-López, F.; Muñoz, N.E.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Migueles, J.H.; Molina-García, P.; Henriksson, H.; Mena-Molina, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; et al. Role of physical activity and sedentary behavior in the mental health of preschoolers, children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1383–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, J.M.; Pierce, S.; Mohan, M.; Skorup, J.; Paremski, A.; Bochnak, M.; Prosser, L. Physical activity in non-ambulatory toddlers with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 90, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denda, K.; Kako, Y.; Kitagawa, N.; Koyama, T. Assessment of depressive symptoms in Japanese school children and adolescents using the Birleson Depression Self-Rating Scale. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2006, 36, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, C.J.; Hinkley, K. Social-cognitive processing and depressive symptoms in children: A comparison of measures. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 1989, 17, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, T.; Gillberg, C.; Arvidsson, T.; Broberg, A.G. The Youth Self-Report (YSR) and the Depression Self-Rating Scale (DSRS) as measures of depression and suicidality among adolescents. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2002, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, K.L.; Katz, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Hammen, C.; Brennan, P.A.; Najman, J.M. The association of ADHD and depression: Mediation by peer problems and parent–child difficulties in two complementary samples. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2013, 122, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, Y.; Inoue, Y. The direct/indirect association of ADHD/ODD symptoms with self-esteem, self-perception, and depression in early adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, K.; Fiss, A.; Avery, L.; Wentz, E.; Kerfeld, C.; Cicirello, N.; Hanna, S.E. Longitudinal trajectories of physical activity and walking performance by gross motor function classification system level for children with cerebral palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, C.S.; Pedersen, N.S.A.; Thomasen, A.; Mechlenburg, I.; Nordbye-Nielsen, K. Pain is frequent in children with cerebral palsy and negatively affects physical activity and participation. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K.L.; Schmidt, L.A.; Missiuna, C.; Saigal, S.; Boyle, M.H.; van Lieshout, R.J. Motor coordination and mental health in extremely low birth weight survivors during the first four decades of life. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 43, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.C.; Wade, T.J.; Veldhuizen, S.; Missiuna, C.; Timmons, B.; Cairney, J. Emotional and Behavioral Problems in 4-and 5-year old children with and without motor delays. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piek, J.P.; Barrett, N.C.; Smith, L.M.; Rigoli, D.; Gasson, N. Do motor skills in infancy and early childhood predict anxious and depressive symptomatology at school age? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2010, 29, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | CP Group (n = 24) | TD Group (n = 33) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age (year) | 12.2 | 4.0 | 12.2 | 3.3 | p = 0.90 |
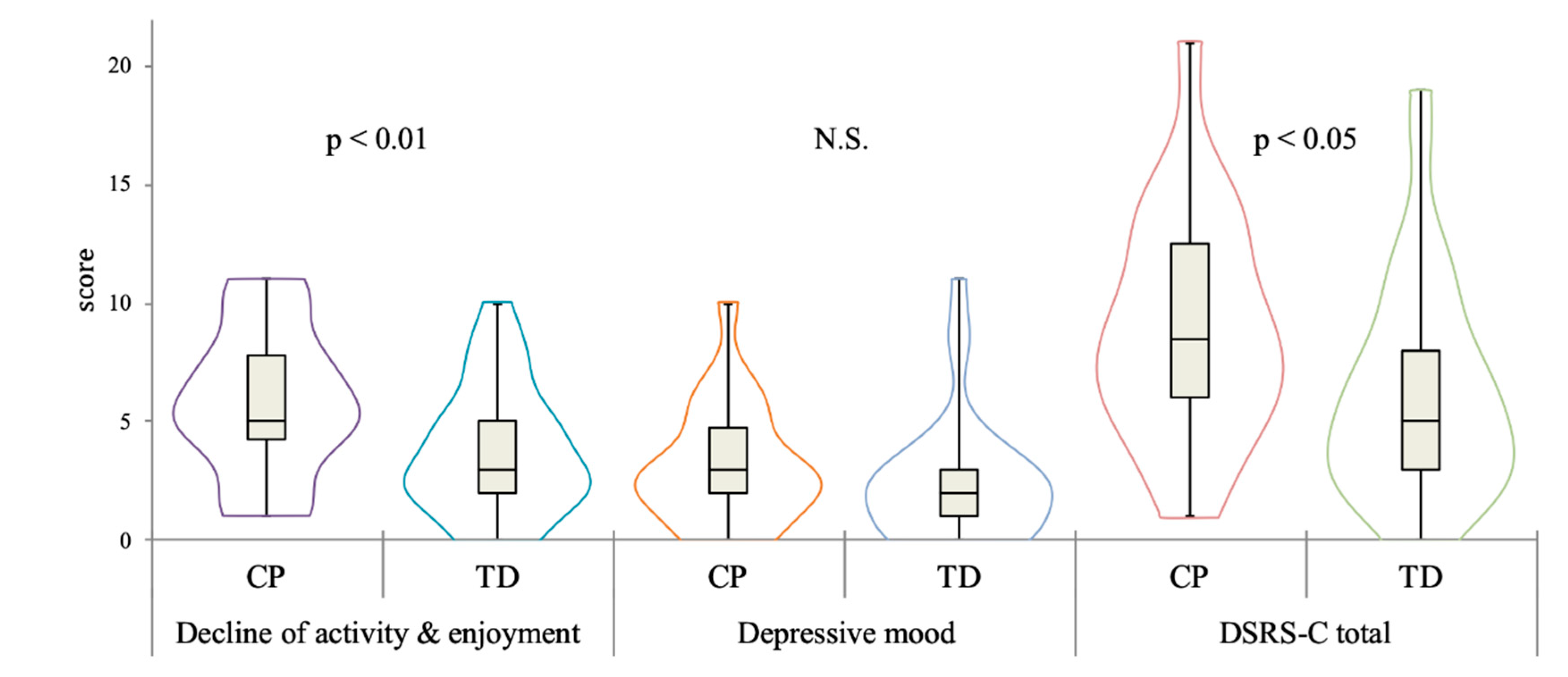
| DSRS-C | |||||
| Decline of activity & enjoyment | 5.71 | 2.99 | 3.76 | 2.67 | p = 0.005 |
| Depressive mood | 3.17 | 2.46 | 2.52 | 2.62 | p = 0.20 |
| total score | 8.88 | 4.71 | 6.27 | 4.51 | p = 0.02 |
| SDQ | |||||
| Conduct problems | 2.67 | 2.20 | 1.33 | 1.34 | p = 0.02 |
| Hyperactivity/Inattention | 3.88 | 2.71 | 2.18 | 2.19 | p = 0.01 |
| Emotional symptoms | 2.01 | 1.91 | 0.67 | 0.85 | p = 0.01 |
| Peer problems | 3.29 | 2.10 | 1.06 | 1.30 | p < 0.01 |
| Pro-social behavior | 6.75 | 2.29 | 7.24 | 1.86 | p = 0.56 |
| TDS | 11.91 | 6.19 | 5.24 | 3.91 | p < 0.01 |
| Participants with CP | Age | DSRS-C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decline of Activity and Enjoyment | Depressive Mood | DSRS-C Total Score | ||
| Age | - | 0.02 | −0.32 | −0.13 |
| GMFCS level | - | −0.23 | −0.17 | −0.22 |
| Conduct problems | −0.51 * | −0.06 | 0.20 | 0.07 |
| Hyperactivity/Inattention | −0.50 * | −0.55 ** | −0.03 | −0.37 |
| Emotional symptoms | −0.13 | 0.13 | −0.03 | 0.10 |
| Peer problems | −0.01 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Pro-social behavior | 0.40 | 0.39 | −0.12 | 0.18 |
| TDS | −0.47 * | −0.15 | 0.12 | −0.02 |
| Participants with TD | Age | DSRS-C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decline of Activity and Enjoyment | Depressive Mood | DSRS-C Total Score | ||
| Age | - | 0.52 ** | 0.22 | 0.42 * |
| Conduct problem | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.22 |
| Hyperactivity/Inattention | −0.37 * | −0.34 | −0.21 | −0.29 |
| Emotional symptoms | −0.13 | 0.17 | 0.39 * | 0.34 |
| Peer problem | −0.05 | 0.41 * | 0.33 | 0.48 ** |
| Pro-social behavior | −0.10 | −0.11 | 0.21 | −0.03 |
| TDS | −0.19 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| Decline of Activity and Enjoyment | B | SE | β | t | p | R2 | ⊿R2 | F |
| Step 1 | 0.21 | - | 4.72 | |||||
| Age | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 2.27 | 0.03 * | |||
| Gender (Female-Male) | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.13 | 1.01 | 0.32 | |||
| Group (CP-TD) | 2.06 | 0.73 | 0.35 | 2.81 | 0.01 ** | |||
| Step 2 | 0.48 | 0.27 ** | 5.56 | |||||
| Age | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 1.52 | 0.14 | |||
| Gender | 0.22 | 0.66 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.74 | |||
| Group | 1.01 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 1.25 | 0.22 | |||
| Conduct problem | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 0.30 | |||
| Hyperactivity/inattention | −0.58 | 0.16 | −0.50 | −3.60 | <0.01 ** | |||
| Emotional symptoms | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 1.29 | 0.20 | |||
| Peer problem | 0.57 | 0.21 | 0.38 | 2.65 | 0.01 ** | |||
| Pro-social behavior | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 0.55 | |||
| DSRS-C Total Score | B | SE | β | t | p | R2 | ⊿R2 | F |
| Step 1 | 0.12 | - | 2.43 | |||||
| Age | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 1.27 | 0.21 | |||
| Gender (Female-Male) | 1.12 | 1.24 | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.37 | |||
| Group (CP-TD) | 2.78 | 1.24 | 0.29 | 2.24 | 0.03 * | |||
| Step 2 | 0.40 | 0.28 ** | 4.00 | |||||
| Age | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.36 | |||
| Gender | 0.30 | 1.14 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.79 | |||
| Group | 0.63 | 1.40 | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.66 | |||
| Conduct problem | 0.72 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 1.93 | 0.06 | |||
| Hyperactivity/inattention | −0.83 | 0.28 | −0.44 | −2.98 | 0.01 ** | |||
| Emotional symptoms | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0.80 | 0.43 | |||
| Peer problem | 0.95 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 2.58 | 0.01 ** | |||
| Pro-social behavior | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.82 | 0.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asano, D.; Takeda, M.; Nobusako, S.; Morioka, S. Self-Rated Depressive Symptoms in Children and Youth with and without Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10110167
Asano D, Takeda M, Nobusako S, Morioka S. Self-Rated Depressive Symptoms in Children and Youth with and without Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study. Behavioral Sciences. 2020; 10(11):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10110167
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsano, Daiki, Masaki Takeda, Satoshi Nobusako, and Shu Morioka. 2020. "Self-Rated Depressive Symptoms in Children and Youth with and without Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study" Behavioral Sciences 10, no. 11: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10110167
APA StyleAsano, D., Takeda, M., Nobusako, S., & Morioka, S. (2020). Self-Rated Depressive Symptoms in Children and Youth with and without Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study. Behavioral Sciences, 10(11), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10110167





