Automated Detection and Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Images via Efficient Attention Transformer Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- EAT-Net directly processes raw H&E-stained slides without complex preprocessing and achieves a robust performance across RCC grades 1 to 4. Its dual-stream design, enhanced by SE modules, adaptively emphasizes key features, supporting precise and reliable classification.
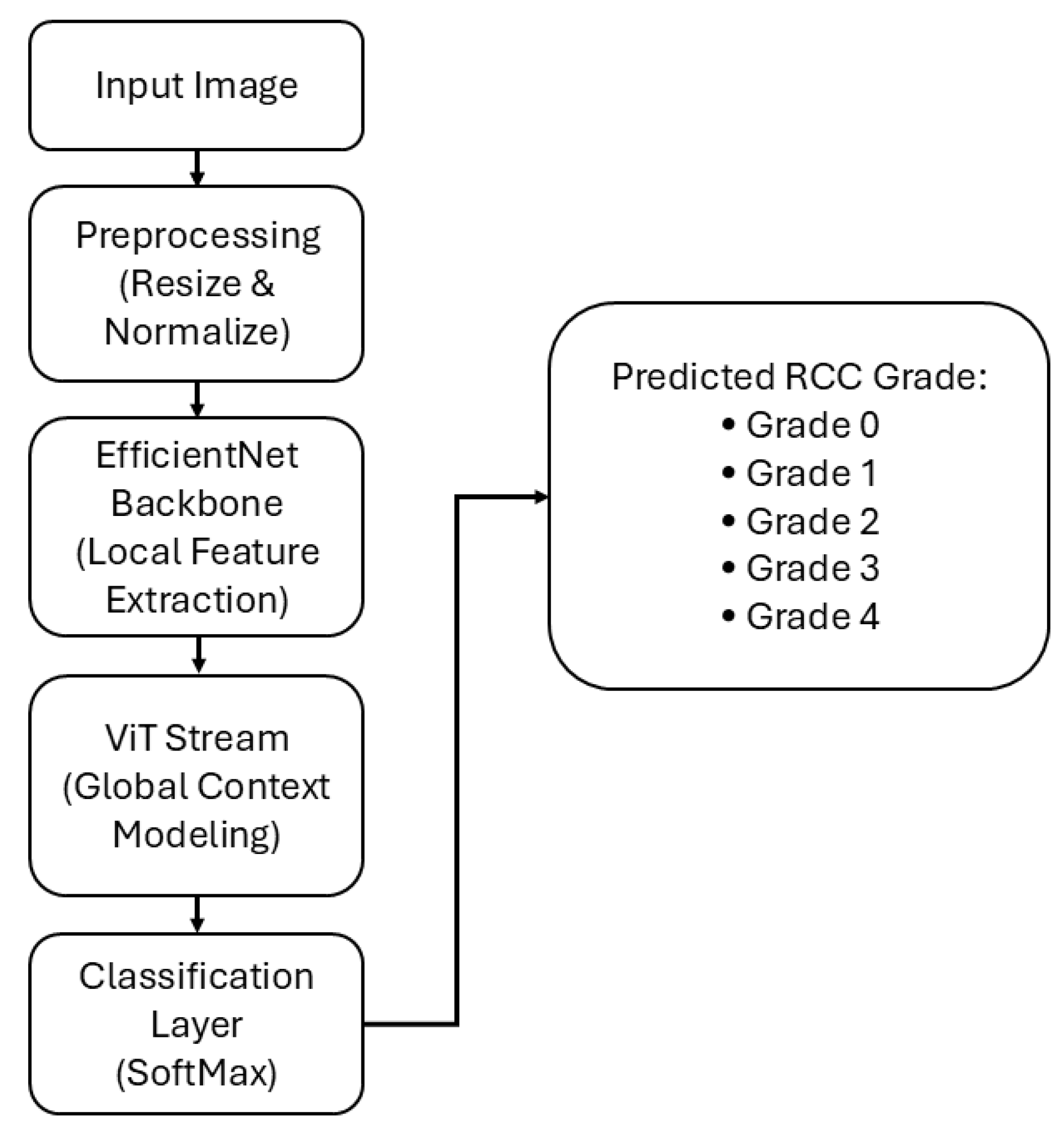
2. Proposed Methodology
2.1. Proposed Methods Overview
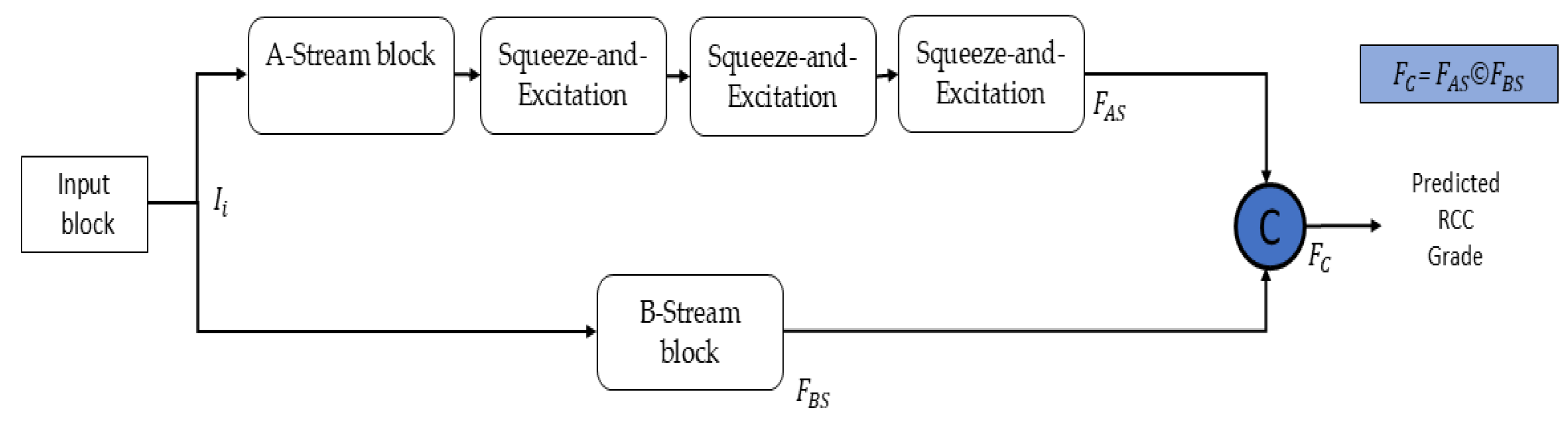
2.2. Design Principles and Architecture of EAT-Net
3. Experimental Environment and Results
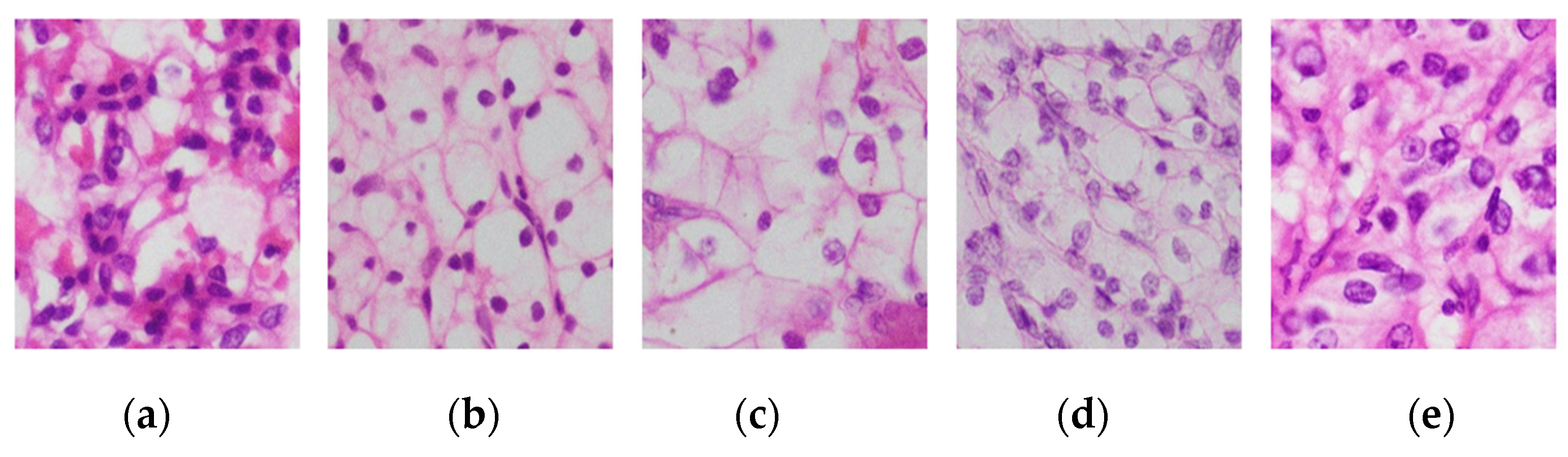
3.1. Renal Cell Carcinoma Image Dataset
3.2. EAT-Net: Training Procedures and Experimental Framework
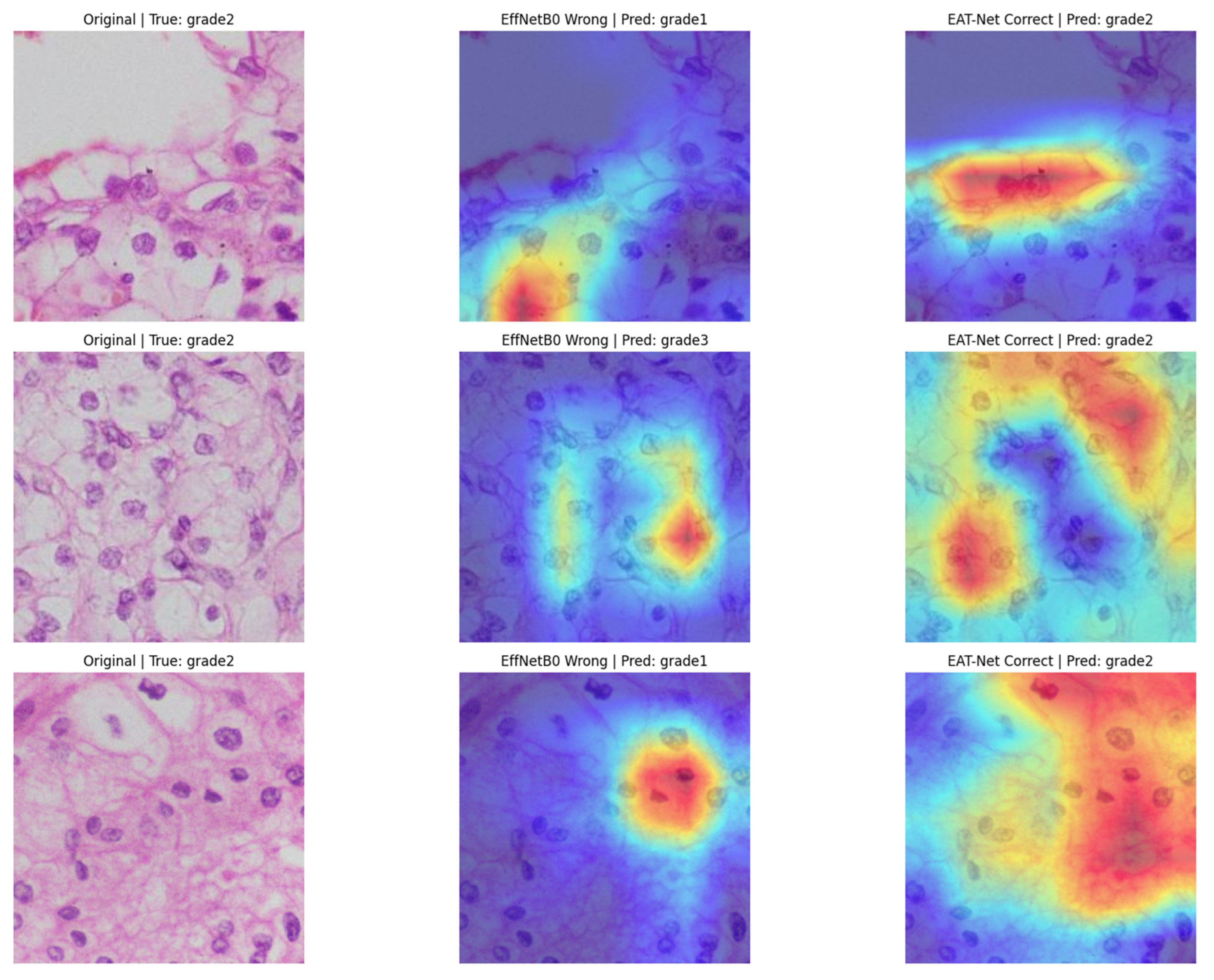
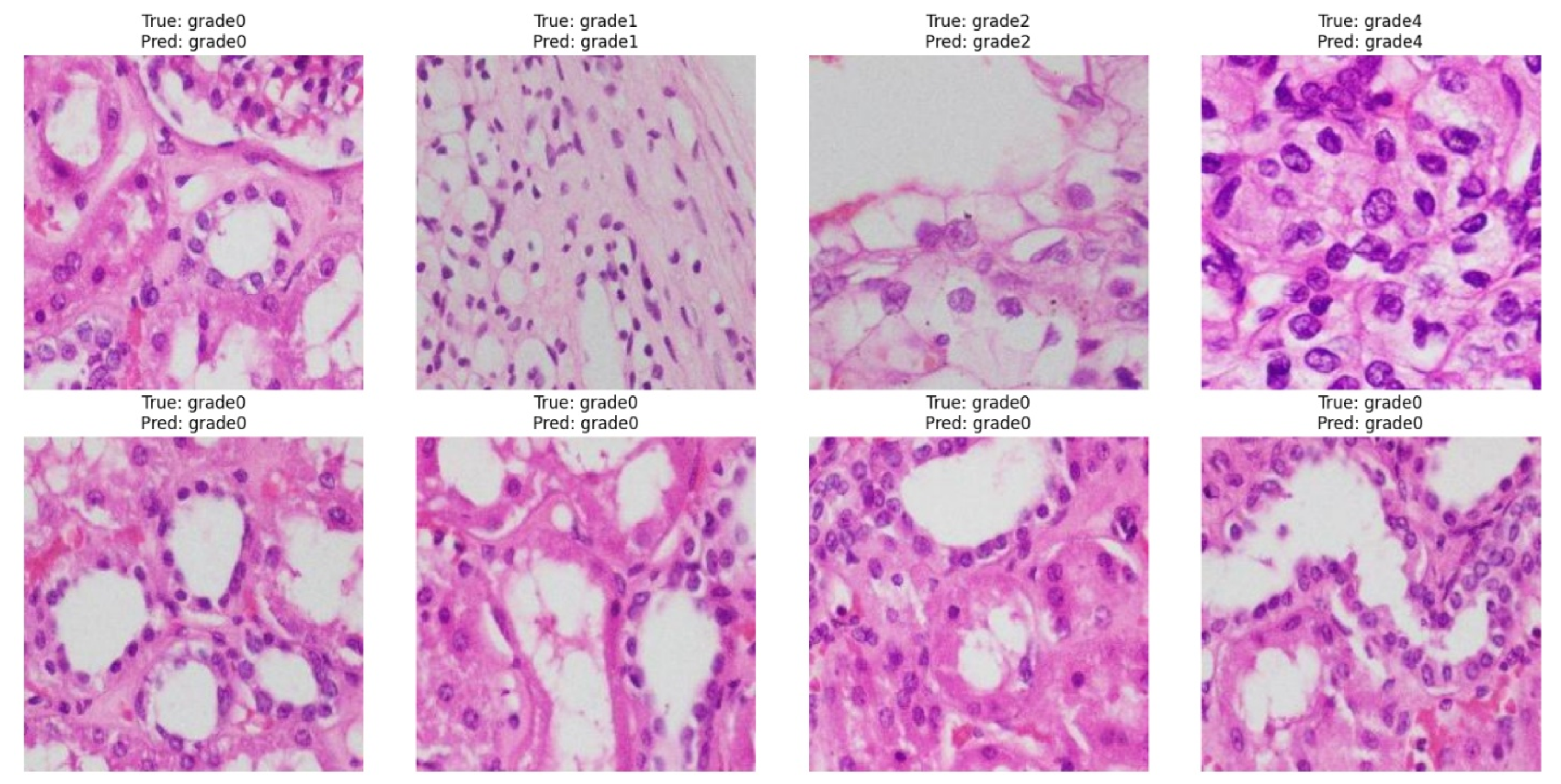
3.3. Performance Evaluation of EAT-Net
3.4. Ablation Study for Proposed EAT-Net
3.5. EAT-Net Comparison with Existing SOTA Approaches
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rose, T.L.; Kim, W.Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review. JAMA 2024, 332, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.S.; Goggins, W.B.; Yip, B.H.K.; Fung, F.D.H.; Leung, C.; Fang, Y.; Wong, S.Y.S.; Ng, C.F. Incidence and Mortality of Kidney Cancer: Temporal Patterns and Global Trends in 39 Countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Devesa, S.S.; Fraumeni, J.F.J.; Chow, W.-H. Global Increases in Kidney Cancer Incidence, 1973–1992. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2002, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. Epidemiology and Prevention of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.; Jackson-Spence, F.; Beltran, L.; Day, E.; Suarez, C.; Bex, A.; Powles, T.; Szabados, B. Renal Cell Carcinoma. Lancet 2024, 404, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Brinkmann, O.A.; Bergmann, L.; Heinzer, H.; Steiner, T.; Ringsdorf, M.; Römer, A.; Roigas, J. The Role of Cytokine Therapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2007, 6, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Teng, J.; Fang, C.; Chen, S.; et al. Rationale for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors plus Targeted Therapy for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Mills, S.E. KIT and RCC Are Useful in Distinguishing Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma From the Granular Variant of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleeb, R.M.; Brimo, F.; Farag, M.; Rompré-Brodeur, A.; Rotondo, F.; Beharry, V.; Wala, S.; Plant, P.; Downes, M.R.; Pace, K.; et al. Toward Biological Subtyping of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma With Clinical Implications Through Histologic, Immunohistochemical, and Molecular Analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, A.Y.; Harrison, D. WHO/ISUP Classification, Grading and Pathological Staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Standards and Controversies. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercken, K.; Berkel, B.V.; Wever, L.D. Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer (HLRCC) Syndrome. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2024, 39, e00548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Bonert, M.; Naqvi, A.; Zbuk, K.; Kapoor, A. SDH-Deficient Renal Cell Carcinoma—Clinical, Pathologic and Genetic Correlates: A Case Report. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, L.A.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Witkowski, T.; Joy, C.; McEvoy, C.R.; Hanegbi, U.; Aga, A. ALK-Rearranged Renal Cell Carcinoma with TPM3::ALK Gene Fusion and Review of the Literature. Virchows Arch. 2023, 482, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, R.; Takemura, K.; Urasaki, T.; Fujiwara, R.; Numao, N.; Yonese, J.; Miura, Y.; Yuasa, T. Prevailing Challenges in Personalized Treatment for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Review. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2025, 25, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khene, Z.-E.; Kammerer-Jacquet, S.-F.; Bigot, P.; Rabilloud, N.; Albiges, L.; Margulis, V.; De Crevoisier, R.; Acosta, O.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Lotan, Y.; et al. Clinical Application of Digital and Computational Pathology in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2024, 7, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, B.G.; MacLennan, G.T. Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review of Its Histopathology, Genetics, and Differential Diagnosis. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2025, 33, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, L.; Tauziède-Espariat, A.; Guillemot, D.; Pierron, G.; Gigant, P.; Mehdi, L.; Berthaud, C.; Pucelle, N.; Lacombe, J.; Hasty, L.; et al. BCOR Immunohistochemistry, but Not SATB2 Immunohistochemistry, Is a Sensitive and Specific Diagnostic Biomarker for Central Nervous System Tumours with BCOR Internal Tandem Duplication. Histopathology 2021, 79, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Hu, W.; Wu, G.; Wu, D.; Zhu, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, P. Grading Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Grade Using Diffusion Relaxation Correlated MR Spectroscopic Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 59, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ren, B.; Richards, R.; Suriawinata, M.; Tomita, N.; Hassanpour, S. Development and Evaluation of a Deep Neural Network for Histologic Classification of Renal Cell Carcinoma on Biopsy and Surgical Resection Slides. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibu, S.; Vinod, P.K.; Jawahar, C.V. Pan-Renal Cell Carcinoma Classification and Survival Prediction from Histopathology Images Using Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.; Kather, J.N. A Systematic Analysis of Deep Learning in Genomics and Histopathology for Precision Oncology. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Ye, X.; Lu, H.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y. Dense Convolutional Network and Its Application in Medical Image Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2384830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, W.; Han, X. TransPath: Transformer-Based Self-Supervised Learning for Histopathological Image Classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021; de Bruijne, M., Cattin, P.C., Cotin, S., Padoy, N., Speidel, S., Zheng, Y., Essert, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.; Wahid, A.; Hong, J.S.; Kim, S.G.; Park, K.R. A Novel Convolution Transformer-Based Network for Histopathology-Image Classification Using Adaptive Convolution and Dynamic Attention. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 135, 108824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gorriz, J.M.; Wang, S. Deep Learning and Vision Transformer for Medical Image Analysis. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.A.; Saeed, F.; Yun, S.; Park, J.-H.; Paul, A.; Kang, J.-M. A Robust Approach for Brain Tumor Detection in Magnetic Resonance Images Using Finetuned EfficientNet. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 65426–65438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Brar, T.P.S.; Kaur, C.; Singh, C. A Comprehensive Study of Deep Learning Methods for Kidney Tumor, Cyst, and Stone Diagnostics and Detection Using CT Images. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 4163–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, S.; Demircioglu, P.; Bogrekci, I. Enhancing Melanoma Diagnosis with Advanced Deep Learning Models Focusing on Vision Transformer, Swin Transformer, and ConvNeXt. Dermatopathology 2024, 11, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpofu, J.B.; Li, C.; Gao, X.; Su, X. Optimizing Motion Detection Performance: Harnessing the Power of Squeeze and Excitation Modules. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Wan, X.; Liu, M. Squeeze-and-Excitation Self-Attention Mechanism Enhanced Digital Audio Source Recognition Based on Transfer Learning. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 2025, 44, 480–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.R.; Singh, S.K.; Chaudhuri, B.B. Activation Functions in Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Survey and Benchmark. Neurocomputing 2022, 503, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadpour, S.; Warner, T.A.; Maxwell, A.E. Selecting and Interpreting Multiclass Loss and Accuracy Assessment Metrics for Classifications with Class Imbalance: Guidance and Best Practices. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KMC-RENAL. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/shreyan983/kmc-renal (accessed on 31 October 2025).
- Chanchal, A.K.; Lal, S.; Kumar, R.; Kwak, J.T.; Kini, J. A Novel Dataset and Efficient Deep Learning Framework for Automated Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma from Kidney Histopathology Images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiq, M.; Gu, Z. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning Transferable Architectures for Scalable Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, X. Breast Cancer Histopathological Image Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks with Small SE-ResNet Module. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toğaçar, M.; Özkurt, K.B.; Ergen, B.; Cömert, Z. BreastNet: A Novel Convolutional Neural Network Model through Histopathological Images for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 545, 123592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatresh, A.A.; Alabhya, K.; Lal, S.; Kini, J.; Saxena, P.P. LiverNet: Efficient and Robust Deep Learning Model for Automatic Diagnosis of Sub-Types of Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cancer from H&E Stained Liver Histopathology Images. Int. J. CARS 2021, 16, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, F.; Wang, Z.; Ali, M.M.; Qiu, B.; Mahmood, T.; Sarwar, R. An Efficient Enhanced Feature Framework for Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma Using Histopathological Images. Appl. Intell. 2024, 55, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchal, A.K.; Lal, S.; Suresh, S. Development and Evaluation of Deep Neural Networks for the Classification of Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma from Kidney Histopathology Images. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Stream | Name (Layer) | K | Stride | F | O/P Size | Param. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficient Stream | Conv2d (3 → 32) | 3 × 3 | 1 | 32 | 224 × 224 × 32 | 896 |
| BatchNorm | - | - | 32 | 224 × 224 × 32 | 128 | |
| SiLU Activation | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MBConv1-GAP (AvgPool) | - | - | - | 1 × 1 × 16 | - | |
| MBConv1-FC1 | 1 × 1 | - | 256 | 1 × 1 × 256 | 256 | |
| MBConv1-ReLU | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MBConv1-FC2 | 1 × 1 | - | 16 | 1 × 1 × 16 | 256 | |
| MBConv1-Sigmoid * | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Conv2d (32 → 16) * | 3 × 3 | 1 | 16 | 224 × 224 × 16 | 4608 | |
| MBConv6–GAP (AvgPool) | - | - | - | 1 × 1 × 40 | - | |
| Conv2d (24 → 40) * | 3 × 3 | 1 | 40 | 112 × 112 × 40 | 21,600 | |
| Flatten | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ViT Stream | Conv2d (3 → 256) * (Patch Embed) | 16 × 16 | 16 | 256 | 14 × 14 × 256 | 18432 |
| Flatten | - | - | - | 1 × 196 × 256 | - | |
| Transpose | - | - | - | 196 × 256 | - | |
| Transformer Encoder ×5 | - | - | 256 (per head) | 196 × 256 | ≈786,000 | |
| LayerNorm + FC | - | - | 256 → Num_classes | 1 × 256 | 65,792 | |
| Final | Fusion-Concatenate | - | - | 512 (256 + 256) | 1 × 512 | - |
| Predicted Output (Logits) | - | - | Num_classes | Num_classes | - |
| Method | Parameters (Millions) | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetB0 only | 4 | 92.96 | 91.57 | 91.56 | 91.57 |
| EfficientNetB1 only | 7.8 | 91.55 | 90.12 | 90.05 | 90.08 |
| EfficientNetB2 only | 9.2 | 90.14 | 88.48 | 88.30 | 88.39 |
| EfficientNetB1 + ViT Stream | 15.9 | 92.25 | 91.46 | 91.15 | 91.30 |
| EfficientNetB2 + ViT Stream | 17.3 | 90.85 | 90.95 | 90.83 | 90.89 |
| EAT-Net (EfficientNetB0 + ViT Stream) | 12.1 | 92.25 | 92.15 | 92.12 | 92.25 |
| Method | Parameters (Million) | GFLOPS | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet [37] | 23.60 | 7.75 | 74.64 | 73.60 | 70.97 | 70.93 |
| IncResV2 [38] | 54.34 | 13 | 71.83 | 71.85 | 68.64 | 68.69 |
| NASNet [39] | 4.27 | 1.15 | 80.28 | 79.69 | 77.99 | 77.09 |
| ShuffleNet [40] | 23.83 | 6.69 | 83.80 | 83.15 | 81.75 | 81.86 |
| BHCNet [41] | 0.30 | 4.46 | 86.61 | 85.08 | 84.62 | 84.34 |
| BreastNet [42] | 0.61 | 5.68 | 85.91 | 86.88 | 85.47 | 85.41 |
| LiverNet [43] | 0.57 | 3.72 | 86.62 | 85.52 | 84.69 | 84.93 |
| ViT [24] | 86.00 | 33.03 | 82.39 | 81.60 | 80.88 | 80.38 |
| RCCGNet [36] | 0.36 | 4.48 | 90.14 | 89.78 | 89.60 | 89.06 |
| RCG-Net [26] | 2.38 | 1.68 | 90.62 | 91.23 | 90.63 | 90.92 |
| EFF-Net [44] | - | - | 91.90 | 91.42 | 91.84 | 91.90 |
| EAT-Net (Proposed) | 12.1 | 1.99 | 92.25 | 92.15 | 92.12 | 92.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-kuwari, H.; Alshami, B.; Al-Khinji, A.; Haider, A.; Arsalan, M. Automated Detection and Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Images via Efficient Attention Transformer Network. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040257
Al-kuwari H, Alshami B, Al-Khinji A, Haider A, Arsalan M. Automated Detection and Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Images via Efficient Attention Transformer Network. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(4):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040257
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-kuwari, Hissa, Belqes Alshami, Aisha Al-Khinji, Adnan Haider, and Muhammad Arsalan. 2025. "Automated Detection and Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Images via Efficient Attention Transformer Network" Medical Sciences 13, no. 4: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040257
APA StyleAl-kuwari, H., Alshami, B., Al-Khinji, A., Haider, A., & Arsalan, M. (2025). Automated Detection and Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Histopathological Images via Efficient Attention Transformer Network. Medical Sciences, 13(4), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13040257






