Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenesis Approaches: Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
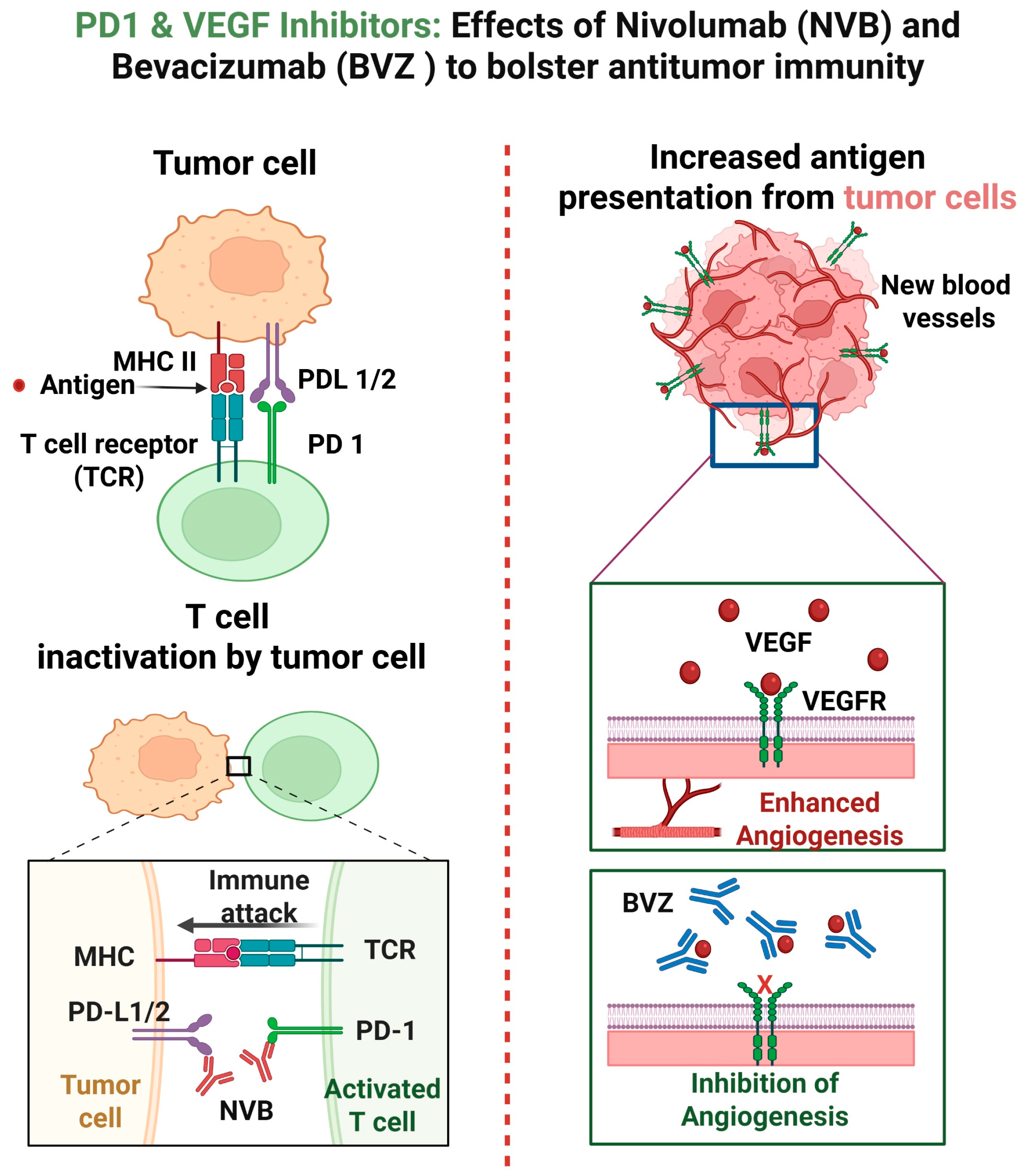
2. Mechanisms of Action of Nivolumab and Bevacizumab
3. Mechanism of Resistance and Adverse Reactions of Nivolumab and Bevacizumab
4. Studies of Nivolumab and Bevacizumab Combination with or Without Other Agents
5. Potential of Other ICIs and Anti-Angiogenic Therapies for NSCLC
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| PFS | Progression free survival |
| OS | Overall survival |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| ROS1 | ROS proto-oncogene 1 |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PD-L1 | PD-ligand 1 |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| APC | Antigen presenting cells |
| Tregs | Regulatory T cells |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressive cells |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| imDC | Immature dendritic cells |
| RET | Rearranged during transfection |
| TMB | Tumor mutation burden |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha |
| IRRC | Independent Regulatory Review |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, A.; Maji, A.; Potdar, P.D.; Singh, N.; Parikh, P.; Bisht, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Paul, M.K. Lung cancer immunotherapy: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, S.S.; Paliogiannis, P.; Zinellu, A.; Fois, A.G.; Cossu, A.; Palmieri, G. Molecular Epidemiology of the Main Druggable Genetic Alterations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basumallik, N.; Agarwal, M. Small Cell Lung Cancer. StatPearls, 10 July 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482458/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Zhu, J.; Li, R.; Tiselius, E.; Roudi, R.; Teghararian, O.; Suo, C.; Song, H. Immunotherapy (excluding checkpoint inhibitors) for stage I to III non-small cell lung cancer treated with surgery or radiotherapy with curative intent. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD011300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Xia, Y. Management of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: State of the art and future directions. Cancer Commun. 2024, 44, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafni, U.; Tsourti, Z.; Vervita, K.; Peters, S. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, alone or in combination with chemotherapy, as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2019, 134, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, B.; Patil, P.D.; Pennell, N.A. Perioperative Systemic Therapy for Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.; West, H.J. Perioperative Therapy for Resectable Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Weighing Options for the Present and Future. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Wang, X.; Alessi, J.V.; Rizvi, H.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Polio, A.; Lindsay, J.; Umeton, R.; Sinha, R.; et al. Association of High Tumor Mutation Burden in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancers with Increased Immune Infiltration and Improved Clinical Outcomes of PD-L1 Blockade Across PD-L1 Expression Levels. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yi, M.; Qin, S.; Chu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Wu, K. The efficacy and safety of combination of PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvetyanon, T.; Gray, J.E.; Antonia, S.J. PD-1 checkpoint blockade alone or combined PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade as immunotherapy for lung cancer? Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Kang, K.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y. Dual blockade immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions. Oncologist 2019, 24 (Suppl. 1), S31–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, W.; Jiang, M.; Wu, L. Research Progress of Anti-angiogenic Agents Combined with Immunotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021, 24, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, J. Review on the combination strategy of anti-angiogenic agents and other anti-tumor agents in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Lung Cancer 2021, 24, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Xiong, X.; You, H.; Shen, J.; Zhou, P. The Combination of Immune Checkpoint Blockade and Angiogenesis Inhibitors in the Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, A.; Rayi, A. Nivolumab. StatPearls, 28 February 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567801/ (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B. Nivolumab as Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) Inhibitor for Targeted Immunotherapy in Tumor. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assoun, S.; Brosseau, S.; Steinmetz, C.; Gounant, V.; Zalcman, G. Bevacizumab in advanced lung cancer: State of the art. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 2515–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar, R.B.; de Moraes, J.Z. Exploring the immunological mechanisms underlying the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor activity in tumors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Sugawara, S.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; Inui, N.; Hida, T.; Lee, K.H.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, H.; Yang, C.; et al. First-line nivolumab, paclitaxel, carboplatin, and bevacizumab for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: Updated survival analysis of the ONO-4538-52/TASUKI-52 randomized controlled trial. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 17061–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Inui, N.; Hida, T.; Lee, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, H.; Yang, C.-T.; et al. Nivolumab with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, S.; Ohe, Y.; Goto, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Tamura, T. Five-year safety and efficacy data from a phase Ib study of nivolumab and chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Mechanism of acquired resistance to nivolumab in lung squamous cell carcinoma: Case report and review of the literature. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Opdivo-Highlights of Prescribing Information. 2022. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/medwatch (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Barrios, D.M.; Do, M.H.; Phillips, G.S.; Postow, M.A.; Akaike, T.; Nghiem, P.; Lacouture, M.E. CME Part I: Immune checkpoint inhibitors to treat cutaneous malignancies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Kang, K.; Chen, P.; Zeng, Z.; Li, G.; Xiong, W.; Yi, M.; Xiang, B. Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Avastin-Highlights of Prescribing Information. 2014. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/medwatch (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Haibe, Y.; Kreidieh, M.; El Hajj, H.; Khalifeh, I.; Mukherji, D.; Temraz, S.; Shamseddine, A. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-angiogenic Therapies in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakai, Y. Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancer—Alterations to Anti-VEGF Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Nathanson, T.; Rizvi, H.; Creelan, B.C.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Ahuja, A.; Ni, A.; Novik, J.B.; Mangarin, L.M.; Abu-Akeel, M.; et al. Genomic Features of Response to Combination Immunotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, J.; Ishino, T.; Togashi, Y. Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vokes, N.I.; Pan, K.; Le, X. Efficacy of immunotherapy in oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2023, 15, 17588359231161408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, S.; Deng, J.; Shen, J.; Du, F.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; et al. VEGF/VEGFR-Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3845–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melosky, B.; Juergens, R.; Hirsh, V.; McLeod, D.; Leighl, N.; Tsao, M.-S.; Card, P.B.; Chu, Q. Amplifying Outcomes: Checkpoint Inhibitor Combinations in First-Line Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Tabata, K.; Kimura, T.; Yachie-Kinoshita, A.; Ozawa, Y.; Yamada, K.; Ito, J.; Tachino, S.; Hori, Y.; Matsuki, M.; et al. Lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody combination treatment activates CD8+ T cells through reduction of tumor-associated macrophage and activation of the interferon pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Arkenau, H.T.; Bendell, J.; Arrowsmith, E.; Wermke, M.; Soriano, A.; Penel, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Bischoff, H.; Chau, I.; et al. Phase 1 Expansion Cohort of Ramucirumab Plus Pembrolizumab in Advanced Treatment-Naive NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient Population | Study Design | Intervention | Control | Primary Endpoint | Key Results | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment- naïve stage HIB/IV NSCLC | Randomized 1:1 trial | Nivolumab with bevacizumab + platinum- based chemo | Placebo + chemo | OS | OS: 30.8 vs. 24.7 months (HR 0.74) CI: 0.58–0.94 | [24] |
| Treatment- naïve stage IIIB/IV NSCLC | Randomized, double- blind, 1:1 trial | Nivolumab with bevacizumab, paclitaxel + platinum-based chemo | Placebo + chemo | PFS | PFS: 12.1 vs. 8.1 months (HR 0.56) CI: 0.43–0.71 | [25] |
| Japanese patients with NSCLC | Phase Ib | Nivolumab with bevacizumab, paclitaxel + platinum-based chemo | None | PFS and OS | PFS: 40.7 months, OS: 28.5 months CI: not reported | [26] |
| Advanced NSCLC | Meta- analysis of phase III clinical trials | Nivolumab + ipilimumab with bevacizumab | Chemo alone | OS | Improved OS in EGFR/ ALK mutated patients CI: not reported | [38] |
| Patient Population | Study Design | Intervention | Control | Primary Endpoint | Key Results | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic non-squamous NSCLC | Phase III clinical trial | Bevacizumab + Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab + Carboplatin + Paclitaxel | PFS and OS | Median PFS: 8.3 months (Intervention) vs. 6.8 months (Control) (HR: 0.59, p < 0.0001); Median OS: 19.2 months (Intervention) vs. 14.7 months (Control) (HR: 0.78, p = 0.02) | [18] |
| Metastatic NSCLC | Preclinical and clinical studies | Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib | Not specified | Modulation of TME | Lenvatinib may decrease TAMs and Tregs, improving ICI efficacy (p < 0.01) | [39] |
| Metastatic NSCLC | Open-label phase la/b trial | Pembrolizumab + Ramucirumab | Not specified | PFS and OS | Median PFS: 9.3 months; 12-month and 18-month PFS: 45%; 12-month and 18-month OS: 73% and 64% Respectively (p value not reported) | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barney, T.; Thyagarajan, A.; Sahu, R.P. Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenesis Approaches: Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030143
Barney T, Thyagarajan A, Sahu RP. Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenesis Approaches: Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Medical Sciences. 2025; 13(3):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030143
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarney, Tate, Anita Thyagarajan, and Ravi P. Sahu. 2025. "Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenesis Approaches: Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Medical Sciences 13, no. 3: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030143
APA StyleBarney, T., Thyagarajan, A., & Sahu, R. P. (2025). Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenesis Approaches: Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Medical Sciences, 13(3), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030143







