Experimental Study on the Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on the Swelling Pressure Expansion Attributes of Silica Fume Stabilized Clayey Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Properties
2.1. Expansive Soil
2.2. Polypropylene Fiber
2.3. Silica Fume
3. Experimental Investigation
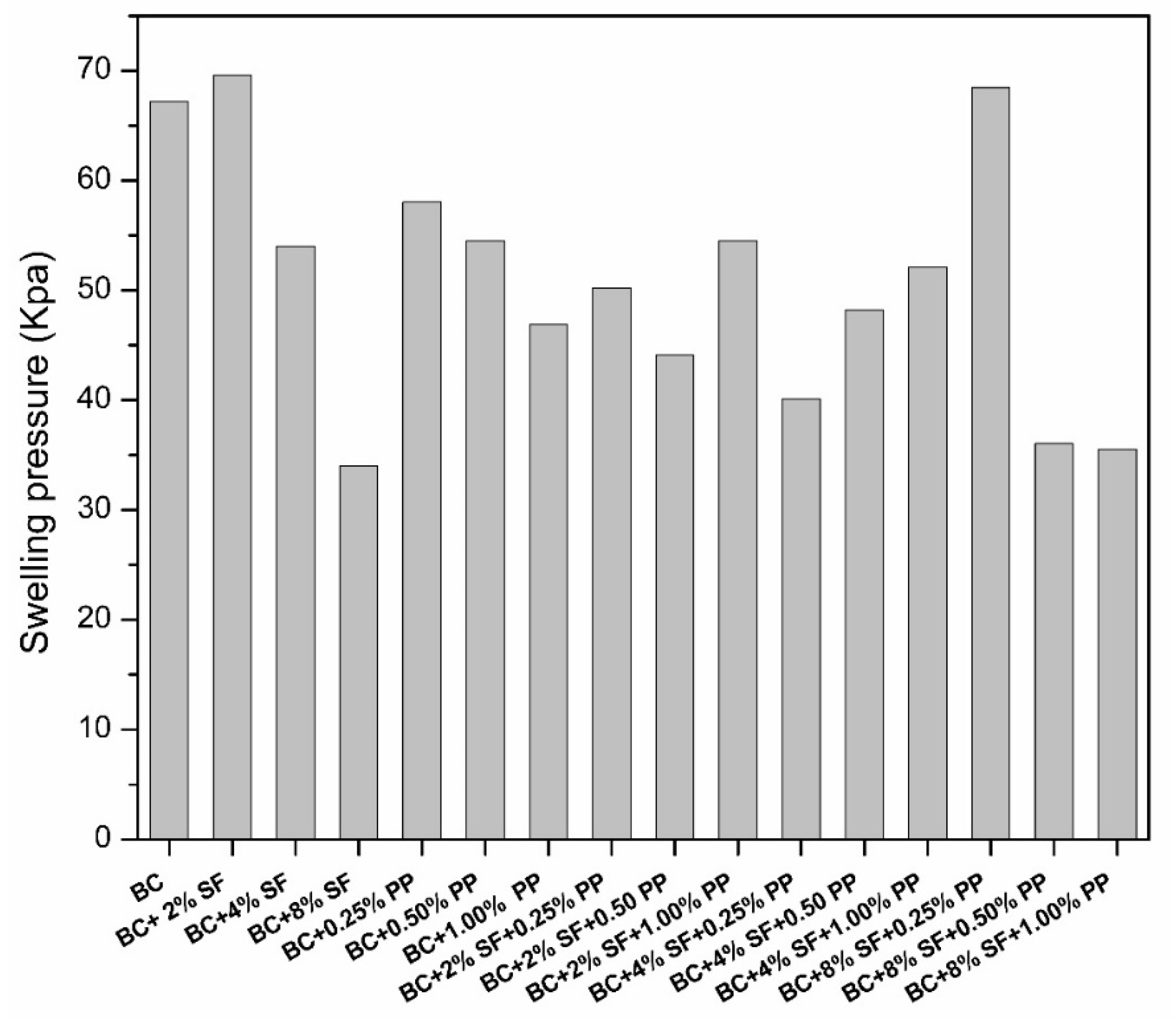
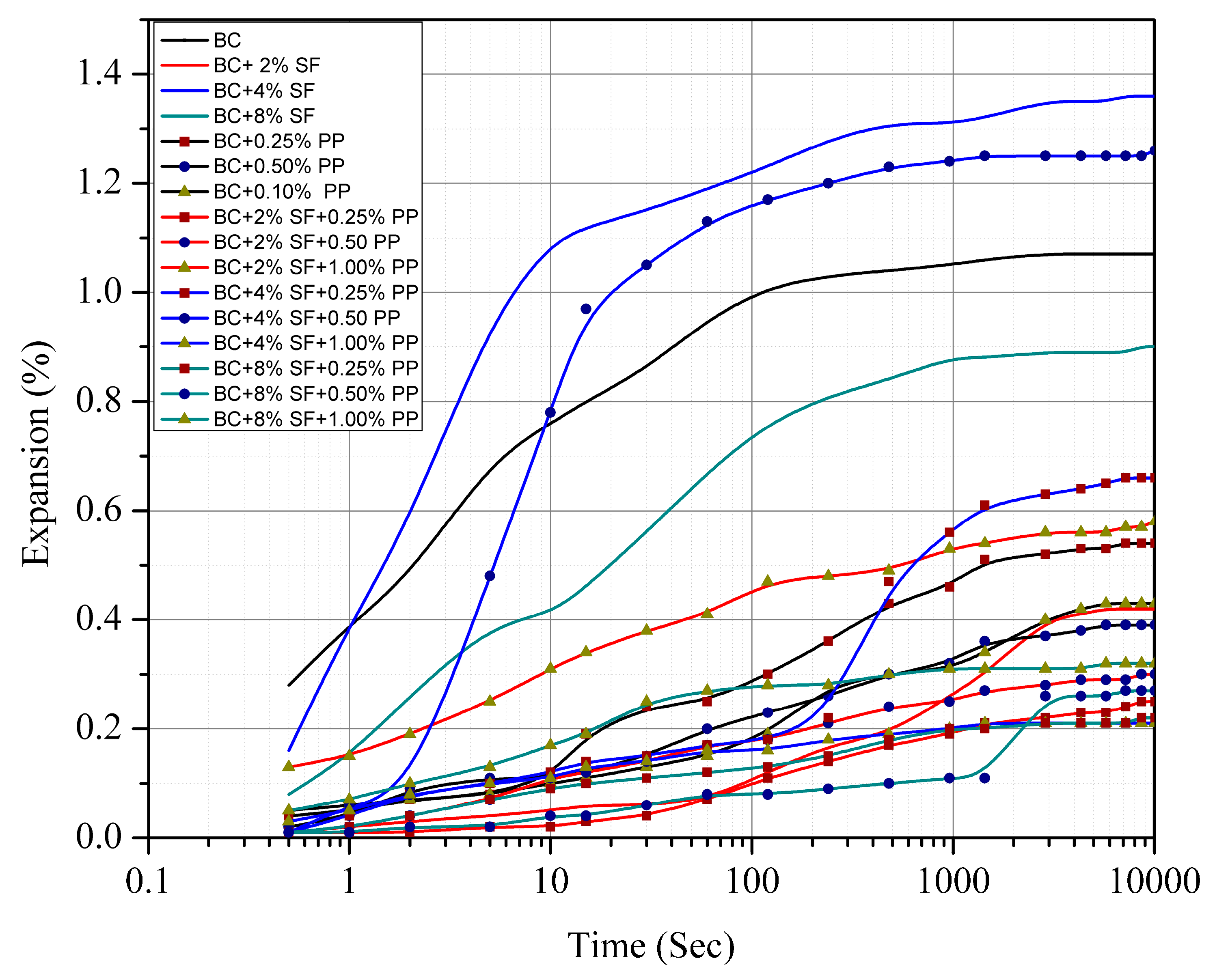
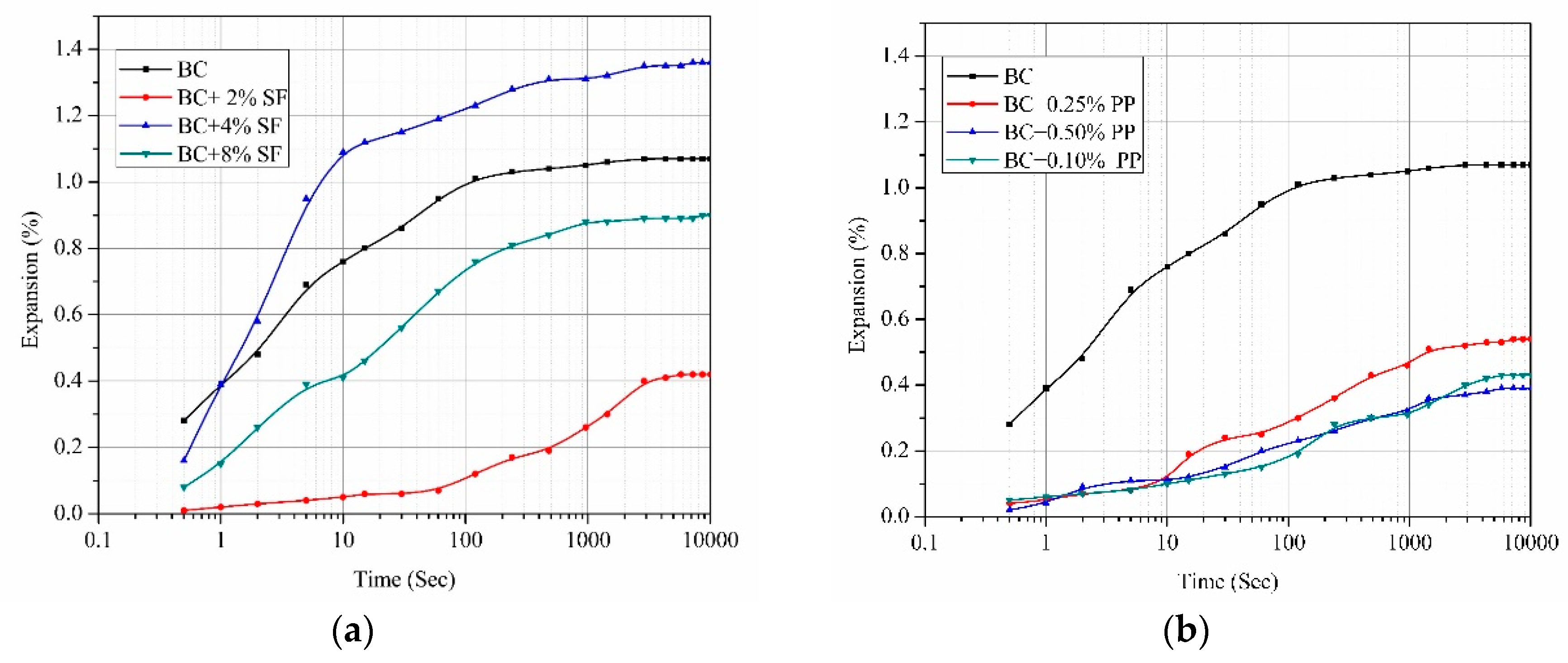
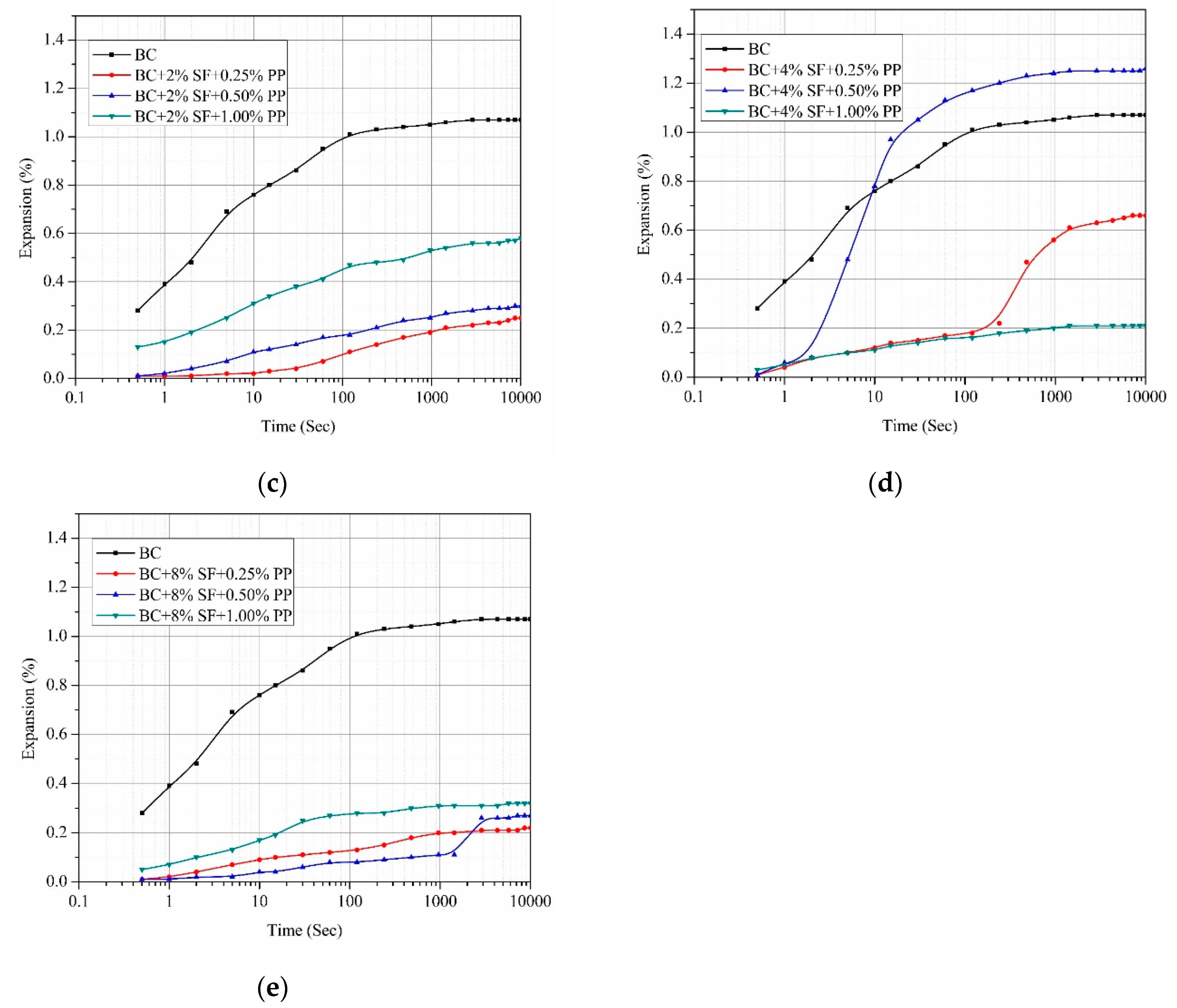
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.H. Foundations on Expansive Soils; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.D.; Miller, D.J. Expansive Soils: Problems and Practice in Foundation and Pavement Engineering; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, M.L. Geomembranes and the Control of Expansive Soils in Construction; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulut, S.; Arasan, S.; Kalkan, E. Modification of clayey soils using scrap tire rubber and synthetic fibers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 38, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Liu, S.; Du, Y.; Cui, K. Behavior of expansive soils stabilized with fly ash. Nat. Hazards 2008, 47, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzababaei, M.; Yasrobi, S.; Al-Rawas, A. Effect of polymers on swelling potential of expansive soils. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. - Gr. Improv. 2009, 162, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawas, A.A.; Hago, A.W.; Al-Sarmi, H. Effect of lime, cement and Sarooj (artificial pozzolan) on the swelling potential of an expansive soil from Oman. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdandoust, F.; Yasrobi, S.S. Effect of cyclic wetting and drying on swelling behavior of polymer-stabilized expansive clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabragh, A.R.; Rafatjo, H.; Javadi, A.A. Treatment of an expansive soil by mechanical and chemical techniques. Geosynth. Int. 2014, 21, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuoka, F.; Correia, A.G. Importance of controlling the degree of saturation in soil compaction. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, A.; Khosrowshahi, S.K.; Yildirim, H. Improvement of expansive soils using fiber materials. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering (ACE 2014), Istanbul, Turkey, 21–25 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Phanikumar, B.R.; Singla, R. Swell-consolidation characteristics of fibre-reinforced expansive soils. Soils Found. 2016, 56, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, J.K.; Patro, S.K. Properties of fresh and hardened concrete using agro-waste as partial replacement of coarse aggregate - A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 82, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar Babu, G.L.; Vasudevan, A.K.; Haldar, S. Numerical simulation of fiber-reinforced sand behavior. Geotext. Geomembranes 2008, 26, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.H.; Asce, A.M.; Al-Refeai, T. Behavior of fabric-versus fiber-reinforced sand. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 112, 804–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.H.; Woods, R.D. Dynamic response of sand reinforced with randomly sistributed fibers. J. Geotech. Eng. 2008, 116, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Loehr, J.E. Undrained and drained triaxial tests of fiber-reinforced sand. In Geosynthetics in Civil and Environmental Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesouky, H.M.; Morsy, M.M.; Mansour, M.F. Fiber-reinforced sand strength and dilation characteristics. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2016, 7, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, G.; Vasan, R.M.; Charan, H.D. Behaviour of plastic-fibre-reinforced sand. Geotext. Geomembranes 1994, 13, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diambra, A.; Ibraim, E.; Muir Wood, D.; Russell, A.R. Fibre reinforced sands: Experiments and modelling. Geotext. Geomembranes 2010, 28, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naithani, A.; Project, H.; Himalaya, S. Engineering geological investigations of Dik Chhu Hydroelectric Project, Sikkim Himalaya, India. J. Nepal Geol. Socity 2011, 43, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Harikumar, M.; Sankar, N.; Chandrakaran, S. Response of sand reinforced with multi-oriented plastic hexa-pods. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2015, 52, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Kamai, T.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Shi, B. Static liquefaction behavior of saturated fiber-reinforced sand in undrained ring-shear tests. Geotext. Geomembr. 2011, 29, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Bilsel, H. Swell and compressibility of fiber reinforced expansive soils. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Civ. Eng. 2012, 1, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Knopp, J.; Moormann, C. Ettringite swelling in the treatment of sulfate-containing soils used as subgrade for road constructions. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Effect of cement additives on unconfined compressive strength of warm and ice-rich frozen soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, E. Impact of wetting-drying cycles on swelling behavior of clayey soils modified by silica fume. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 52, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, E.; Akbulut, S. The positive effects of silica fume on the permeability, swelling pressure and compressive strength of natural clay liners. Eng. Geol. 2004, 73, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayano, K.; Yamauchi, H.; Wakuri, N.; Tomiyoshi, S. A new granulation method with the process of crumbling partially-cemented liquid muds and its application to a motocross track. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.W.; Wilson, K.; Hassan, S.A. Prediction of performance and evaluation of flexible pavement rehabilitation strategies. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2017, 4, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharief, A.M.; Zumrawi, M.M.E.; Salam, A.M. Experimental study of some factors affecting swelling pressure. Univ. Khartoum Eng. J. 2014, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkan, E. Effects of silica fume on the geotechnical properties of fine-grained soils exposed to freeze and thaw. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2009, 58, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific gravity | 2.78 |
| Liquid limit (%) | 89 |
| Plastic limit (%) | 47 |
| Plasticity index (%) | 42 |
| Shrinkage limit (%) | 11 |
| USCS soil classification | CH |
| Grain size distribution Clay (%) Silt (%) Sand (%) | 71.5 24.5 4.0 |
| Free swell index (%) | 120 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific gravity | 0.91 |
| Tensile strength (kN/mm2) | 0.67 |
| Young’s modulus (kN/mm2) | 4.0 |
| Melting point (°C) | 165 |
| Ignition point (°C) | 600 |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 910 |
| Loose density (kg/m3) | 250–430 |
| Fiber cut length (mm) | 6 mm |
| Dispersion | Excellent |
| Acid and salt Resistance | Chemical Proof |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density (Mg/m3) | 92.25 |
| Silt (2–75 μm) | 0.67 |
| Clay (<2 μm) | 4.0 |
| SiO2 | 99.39% |
| Al2O3 | 0.08% |
| Fe2O3 | 0.02% |
| K2O | 0.08% |
| CaO | 0.43% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiwari, N.; Satyam, N. Experimental Study on the Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on the Swelling Pressure Expansion Attributes of Silica Fume Stabilized Clayey Soil. Geosciences 2019, 9, 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090377
Tiwari N, Satyam N. Experimental Study on the Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on the Swelling Pressure Expansion Attributes of Silica Fume Stabilized Clayey Soil. Geosciences. 2019; 9(9):377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090377
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiwari, Nitin, and Neelima Satyam. 2019. "Experimental Study on the Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on the Swelling Pressure Expansion Attributes of Silica Fume Stabilized Clayey Soil" Geosciences 9, no. 9: 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090377
APA StyleTiwari, N., & Satyam, N. (2019). Experimental Study on the Influence of Polypropylene Fiber on the Swelling Pressure Expansion Attributes of Silica Fume Stabilized Clayey Soil. Geosciences, 9(9), 377. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9090377






