Abstract
The city of Ivanec is located between valley of the Bednja River and Mt. Ivanščica and this area can be prone to significant seismic site amplification due to local site characteristics. This study presents the first assessment of seismic site amplification for the city of Ivanec by the microtremor horizontal-to-vertical-spectral-ratio (HVSR) method and the equivalent-linear (EQL) site response analysis. Based on microtremor measurements and HVSR analysis, fundamental soil frequency and HVSR peak amplitude maps indicate potentially seismic danger zones. The 1-D EQL site response analysis was performed using multiple suites of earthquake ground motions scaled to the 95- and 475-year return periods of peak ground accelerations. Site amplification maps at the predominant peak frequency and ground surface indicate two microzones, one with high amplification in the central part of the city due to soft soil characteristics, and the other with small amplification in the transitional zone from alluvial basin towards the foothills of Mt. Ivanščica. HVSR peak amplitudes and site response peak amplifications showed similar spatial distributions with similar predominant peak frequencies but with different amplitude levels. Site amplification maps provided significant information about potential resonance effects for structures of certain heights that can be correlated with the local ground shaking characteristics.
1. Introduction
The city of Ivanec (46.224° N, 16.124° E) is located in northwestern Croatia and is part of the County of Varaždin with a population of approx. 14,000 inhabitants. It is a leading industrial, cultural and tourist centre in this part of Croatia due to its natural resources and history [1]. The area of the city of Ivanec belongs to the Varaždin-Ivanščica-Kozjansko epicentral area where moderate to strong earthquake events have occurred [2]. In the last 50 years, the proximate area of Ivanec (extending some 20 kilometres) has experienced more than ten ML ≥ 3.5 earthquakes and reported small to moderate damage to some buildings in different parts of the city area. The city of Ivanec is situated in a transitional zone between the Bednja River alluvial and coarse-grained clastic sediments toward carbonate rocks of Mount Ivanščica (Figure 1a). According to the spatial master plan of the city of Ivanec dated from 2012 [3] and amendments from 2016, the maximum allowed construction height of the buildings is 12–15 m (four or five floors) in the urban residential area in the central part of the city (Figure 1b, shadow grey area) and a maximum permitted height of 8 m for industrial buildings in the industrial area (Figure 1b, shadow red area).
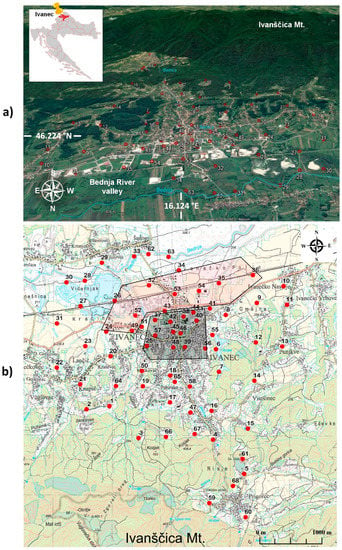
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the City of Ivanec between Bednja River valley and Mt. Ivanščica. Figure is oriented to South direction to better perceive topographic terrain of the studied area and transition from Bednja River valley towards foothills of the Mt. Ivanščica. (b) Topographic map of the City of Ivanec. Red circles indicate microtremor measurement locations. Shadow areas mark industrial zone (red) and residential city central area (grey).
In recent earthquakes (e.g., Mexico City 1985), it was observed that recorded ground motions on soft soil sites (e.g., alluvial basins, soft sediments) were significantly larger than those recorded on nearby rock outcrops [4,5,6,7]. One of the challenges in earthquake engineering practice is to evaluate the local ground response in order to predict site amplification of surface ground motions based on specific geological site characteristics, geometrical features of soil deposits and surface topography [6,8,9]. In practice, the effects of local soil conditions were evaluated using the amplification factor: the ratio of ground motion at the free surface and ground motion at a nearby rock site [5,6,9,10]. The microtremor horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (HVSR) methodology expressed by the natural/fundamental soil frequency and HVSR spectral peak amplitude, introduced by Nogoshi and Igarashi [11] and extensively revised by Nakamura [12], has been used in numerous studies for estimating local seismic ground response, particularly in Slovenia, Italy, and Croatia [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The estimated HVSR site frequency and peak amplitude provides only an indication of the initial soil site frequency and amplification without earthquake activity [21,22,23,24]. One-dimensional (1-D) equivalent-linear (EQL) site response analysis estimates the effects of local soil conditions on ground shaking, based on one-dimensional wave propagation theory [5]. Local soil profiles used in site response analysis are usually determined from boreholes, in-situ tests, or geophysical survey methods (spectral analysis of surface waves—SASW; multichannel analysis of surface waves—MASW; seismic refraction—RF; refraction microtremor—ReMI, and down-hole) [25].
The main objective of this paper is to determine local seismic hazard damage zones of the study area (city of Ivanec) at peak amplification frequencies (or periods) and ground surface amplifications for different earthquake scenarios. Estimation of seismic site amplification is based on a combination of microtremor and geophysical data incorporated into the H/V forward modelling routine [26,27] and 1-D EQL site response analysis for different peak ground accelerations corresponding to 95- and 475-year return periods, according to the seismic hazard map for the Republic of Croatia [28]. Comprehensive seismic microzonation maps incorporating seismic site amplification data provide input data for earthquake-resistant designs as well as the construction and reconstruction of important buildings, and are also useful for urban planning that utilises spatial master plans [29].
2. Seismological and Geological Characteristics of the Study Area
2.1. Seismicity of the Wider Ivanec Area
In the northwestern part of Croatia, the most seismically active area is the hinterland region, which is particularly important for the city of Ivanec, extending from Mt. Ivanščica to the Bednja River valley and finally Mt. Kalnik [30,31]. Based on data from the Croatian Earthquake Catalogue (updated version of the catalogue described in [32]), most of the epicentres stretch along the Kalnik, Ivanščica, Medvednica and Žumberak mountains (Figure 2) [30,31]. The most important seismogenic fault areas in close vicinity to Ivanec include the Drava River fault extending from Slovenia in the west towards Varaždin and Čakovec (undermined fault), including Mt. Ivanščica and Mt. Kalnik North faults (reverse and strike slip) stretching along the mountain chains and Bednja River [33]. The most notable historical earthquakes in terms of intensity in this area occurred as follows: on 20 May 1459 with its epicentre near Varaždin (Io = IX °MCS), 30 April 1738 near Štrigova and Čakovec (Io = VIII °MCS), 8 November 1778 near Koprivnica (Io = IX °MCS), 12 November 1836 (Io = VII–VIII °MCS) where the event caused heavy damage in the village of Zajezda, a few kilometres from the city of Ivanec. Also, it is worth to mention earthquakes that were largely felt in the wider area of city of Ivanec: on 9 November 1880 (the great Zagreb earthquake, Io = IX °MCS), on 20 December 1883 near Mt. Kalnik (Io = VII °MCS) and 29 May 1905 near Budinšćina (Io = V–VI °MCS) on the southern part of Mt. Ivanščica.
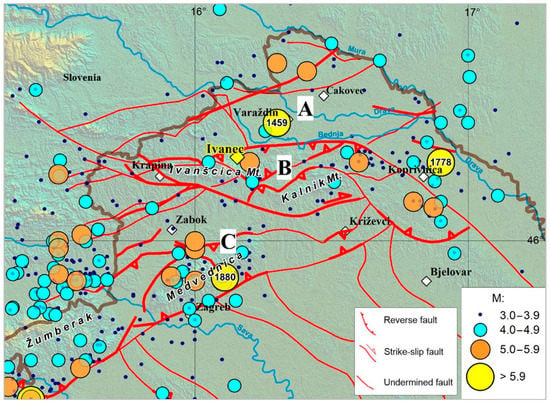
Figure 2.
Epicentres of all earthquakes with ML ≥ 3.0 based on Croatian Earthquake Catalogue (373 BC to 2018) in the circle of approx. 50 km around the City of Ivanec (city location marked with yellow square). Most important seismogenic faults are shown with red lines are: (A) Drava fault, (B) Mt. Ivanščica and Mt. Kalnik North fault, (C) Medvednica fault [31,32].
Except for these mentioned earthquakes, and especially the 1836 earthquake that heavily damaged the village of Zajezda, moderate damage and long strong motion duration in the city of Ivanec and wider area resulted from an earthquake that occurred on 27 March 1938, ML = 5.6 with its epicentre near the Koprivnica. Most notable earthquake damage in the city of Ivanec was observed after a series of earthquakes of 11 June 1973 with the epicentre near Varaždin, ML = 4.0 and on 16 March 1982, ML = 4.5 with the epicentre below Mt. Ivanščica (Figure 2). As noted in city records [1], the central city area experienced significant damage including a heavily damaged primary school (collapsed roof with cracked walls) (point 42 in Figure 1), the city hall (point 48 in Figure 1) and a few residential buildings in central part of the city with up to five storeys were slightly damaged (broken windows, cracked walls and falling plasters). Towards Mt. Ivanščica, houses and vineyard cottages were also slightly damaged, mostly due to poor construction. What is worth mentioning is the fact that the earthquake triggered a landslide at Pahinsko school (location between points 65 and 18 in the Figure 1b) as well as in some vineyards located on steep hills. It should also be mentioned that historical Trakošćan Castle suffered serious damage in the 1982 earthquake (approx. 20 km in northwest towards Slovenia) due to topographic effects from pronounced polarization and directionality of ground motion stemming from the alluvial basin of Bednja River to the hilltop where the Castle is situated [8,34].
According to the Croatian Seismic Hazard Map for the 95- and 475-year return periods (accepted as a part of the National Annex to Eurocode 8 [35]), city of Ivanec is located in a relatively moderate seismic hazard zone: 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g (475yrp) peak ground accelerations.
2.2. Geological Characteristics of the City of Ivanec Area
Geological characteristics of the city of Ivanec area [36] are somewhat complex (Figure 3). In terms of tectonics, the strongest tectonic phase occurred during the Middle Miocene when Lower Miocene sediments were overthrusted by Upper Paleozoic and Mesozoic rocks. Final uplifting of Mt. Ivanščica and formation between the present mountain relief and the valley of Bednja River was caused by earlier tectonic movements in the Upper Pliocene and Quaternary [33]. The city of Ivanec is located on the Holocene alluvial basin (silts, sands and gravels) in the valley of Bednja River. In the central section, Holocene proluvium sands, including Upper Pliocene gravels and sands, are most prevalent. Towards Mt. Ivanščica, the presence of Upper and Lower Miocene coarse-grained clastic sediments such as limestones, marls, sandstones, and gravel conglomerates exchange intermittently. On the foothills of Mt. Ivanščica, Lower Miocene sandstones, marls and tuffs are also present, and exhibit toward the uphill a gradual transition into Lower Triassic clastic deposits such as limestones. Isolated outcrops are mostly Upper Paleozoic metamorfits of coarse-grained clastic sediments such as sandstones. Middle and Upper Triassic limestones and dolomites are also widespread on Mt. Ivanščica [36,37,38]. The whole area is intersected with several faults. The main fault zone in the area runs along the valley of Bednja River and also extends along Mt. Ivanščica, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, and is known as the Mt. Ivanščica reverse to strike-slip faults [30,31,33,36]. On the surface, other fault zones are visible, and their direction coincides mainly with the topography of the entire area [36].
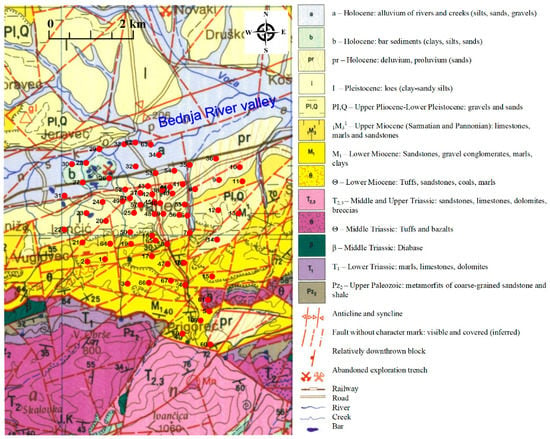
Figure 3.
Geological map of the City of Ivanec area between Bednja River valley and Mt. Ivanščica (highest point Ivanščica at 1060 m elevation). Red circles indicate microtremor measurement locations [36].
Amplification of ground motions may result from near-surface impedance contrast which in turn is due to surficial soft deposits (e.g., alluvium) or highly fractured material overlying more intact materials (e.g., landslide-prone slopes) [39]. Also, the focusing of seismic ground motions due to surface morphology can lead to topographic amplification near topographic ridges. Furthermore, polarization due to the shape and orientation of geological structures may affect amplified ground motion in a particular direction. [8].
As the local geological and topographic characteristics of the city of Ivanec area are complex (Figure 1 and Figure 3), and particularly with the experienced earthquake damage in the past, the local site effects on weak and strong ground motions had and could potentially have an effect for the city of Ivanec in terms of structural damage and financial loss.
3. Application of the Microtremor HVSR Method in the City of Ivanec
Since its introduction over the last three decades [11,12], the non-destructive microtremor HVSR method has become a popular tool by many authors for doing studies on local seismic responses and performing vulnerability response analyses (latest comprehensive state of the art of microtremor HVSR method is provided in [40]). Advantages of the HVSR method, as opposed to other geophysical methods (e.g., spectral analysis of surface waves—SASW; multichannel analysis of surface waves—MASW; seismic refraction—RF, and refraction microtremor—ReMI) are its simple and fast non-invasive measurements and straight-forward estimation of seismic site effects, e.g., fundamental natural frequency and HVSR peak amplitude, and identifying potentially dangerous seismic zones in the city at reasonable costs [25,41]. Geophysical investigation requires obtaining a distance profile (often several tens of meters) and is a big problem at some sites (historical monument sites, slopes, hills, cities, etc.) due to the lack of space, but microtremor measurements can overcome these problems. Geophysical methods (e.g., MASW) rarely estimate profile depths below 30 m [25,41]. The limitations of the microtremor HVSR method are that it does not directly provide 1-D or 2-D shear wave velocity (VS) soil profiles in the form of geophysical methods. Therefore, VS profiles and deeper bedrock depths can be estimated by inverting the observed HVSR curve to identify a synthetic HVSR curve that matches a known soil profile [26,27,41,42,43].
3.1. Microtremor Measurements and HVSR Analysis
Free-field microtremor measurements were performed in the city of Ivanec area (approx. 12 km2, 68 measurements in total, approx. 6 measurements/km2) all done with a Tromino Engy 3G (Micromed, Italy). The Tromino was set on natural ground outside paved areas to achieve good ground coupling and obtain longer spikes. The instrument was precisely levelled and oriented with Geographic North. Measurement locations were selected so that the recorded free-field microtremors avoided the influence on traffic or industrial noise, trees or buildings, and any other high transient noise source that is able to affect measurements [44]. Most of the microtremor measurements were performed in the central city area at intervals of 100–300 m whereas other measurement locations were chosen to cover typical geological and topographical areas (marked in Figure 1 with red circles).
HVSR analyses of the free-field microtremor recordings were done by adhering to SESAME guidelines for criteria in obtaining reliable measurements and clear peaks [44]. Figure 4 shows an example of the analysed HVSR curve at measurement location 42 (primary school) in the area of composed of thick soft delluvium and proluvium sands (Figure 3) with observed peak frequency around 1.5 Hz. The difference between stratigraphic origin and anthropogenic origin for the H/V peak can be determined by investigating single component amplitude spectra exhibiting a typical “eye-shaped” pattern when the three components are plotted together (Figure 4b) [26,40]. The H/V time history plot (Figure 4c) shows stability of the H/V amplitude during a 20-minute recording. Noisy windows (transient and stationary near-white noise) were removed from the analysis to obtain best results (indicated by the black windows). The directional HVSR plots (Figure 4d) represents the projection of HVSR along different directions, from 0° (N) to 180° (S) in a clockwise direction (from 180° to 360°, the results are symmetric). The results of these analyses indicate that the average HVSR receives more contribution from one of two horizontal components, and the direction in which it operates. Several studies [9,45] have shown that microseismic noise and seismic signals in fault zones are polarized across a horizontal plane with a preferred orientation that is comparable with the directions of fault zones near these locations.
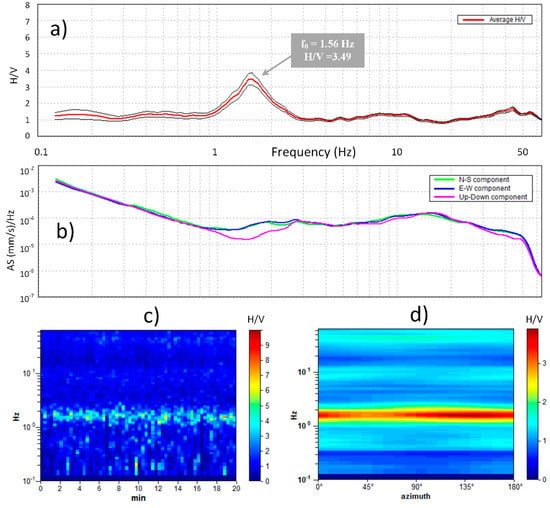
Figure 4.
(a) Example of HVSR curve at measurement location 42. The x-axis represents frequency (Hz). The y-axis represents HVSR amplitude. The average HVSR plot is represented by a thick red line. Black thin lines indicate the 95% confidence interval of the HVSR. (b) Single component amplitude spectra. The x-axis represents frequency (Hz). The y-axis represents amplitude of single component spectra. The spectral signature of the H/V peaks is found to be ’eye-shaped’ within the horizontal to vertical spectra. (c) H/V frequency-time history plot. (d) Directional HVSR plot. The HVSR function (represented on the z-axis by the colour scale) shows a peak around the fundamental frequency (y-axis) and azimuth (x-axis).
The HVSR peak resonance frequency of the local site correlates strongly with local geological conditions, i.e., the average shear wave velocity and thickness of sediments found on bedrock [40,46]. Figure 5 shows a few selected examples of typical HVSR plots showing clear, broad and multiple peaks with examples of plateauing HVSR curves that may indicate reference rock sites [44]. Considered HVSR peaks were carefully examined and checked if clearer peaks are observed in the vicinity of each measurement site and if their related frequencies lie within the frequency range of the broad peak so that significant variation from nearby measurement sites are minimized. In extensive literature on HVSR [9,20,40,43,46], the widely accepted opinion is that higher HVSR spectral peak frequencies correspond to shallower sedimentary structures above bedrock. The opposite is also true where lower HVSR frequencies indicate deeper soft sediments above bedrock. By observing a geological map of city of Ivanec area (Figure 3) and comparing with corresponding HVSR examples (Figure 5), a good correlation exists between estimated frequencies and local site characteristics. This will be discussed in more detail in subsequent chapters.
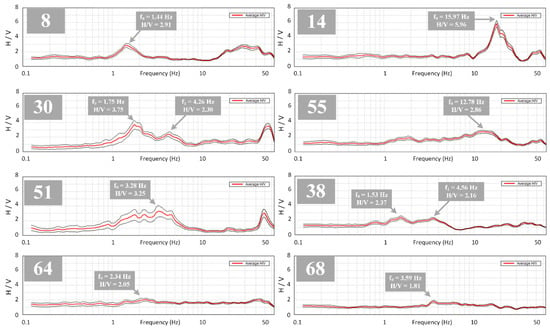
Figure 5.
Selected examples of HVSR curves showing clear (8, 14), broad (51, 55) and multiple peaks (30, 38) with examples of flat HVSR curves that show small peak (64, 68). The average HVSR plot is represented by a thick red line and fundamental frequencies are marked with grey arrow. Black thin lines indicate the 95 % confidence interval of the HVSR.
3.2. Fundamental Soil Frequency Map for the City of Ivanec
Based on individual microtremor measurements and HVSR analyses (Figure 5), a map of fundamental soil frequencies for the city of Ivanec was obtained using the natural neighbour interpolation algorithm (Figure 6). Based on the respective frequency map by directly comparing to the topography map (Figure 1b) and local geological map (Figure 3), a strong correlation between fundamental soil frequencies and local site characteristics (alluvial basin area and topographic area) can be distinguished, where the lowest frequencies (<4 Hz) are observed in soft sedimentary alluvial in the Bednja River zone (thicker sediments above bedrock) with increasing frequencies (>4 Hz) towards the foothills of Mt. Ivanščica and characteristic topographical areas (relatively thin and well compacted sediments above bedrock). The fundamental soil frequency map for the city of Ivanec provides valuable information for assessing soil-structure resonance in potential danger zones using the relationship between fundamental building frequency and the height of RC (reinforced concrete) structures [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,47].
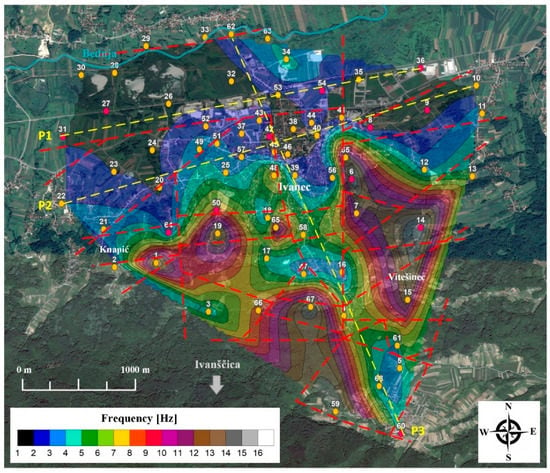
Figure 6.
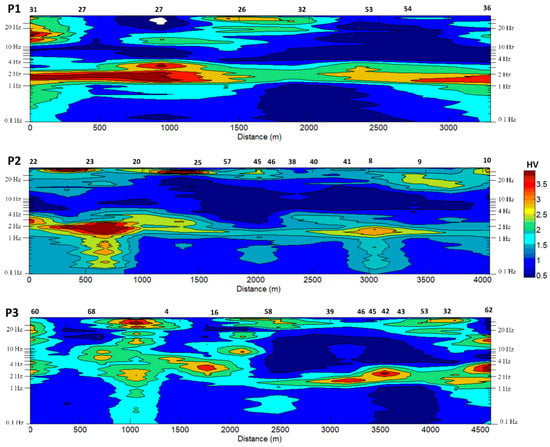
Map of the fundamental HVSR soil frequencies obtained for the City of Ivanec with marked faults (red dashed lines) based on geological map (Figure 3). Yellow circles indicate microtremor measurements and red geophysical measurements. Extrapolated HVSR amplitude-frequency contours vs. distance profiles marked with yellow dashed lines will be shown in Figure 10.
3.3. Geophysical Measurements
Based on estimated HVSR frequencies (Figure 5) and the map (Figure 6) created using individually analysed microtremor measurements, a few typical locations were chosen (marked with red circles in Figure 6) for detailed geophysical investigations in order to determine soil profiles and validate HVSR results.
Shear wave velocity profiles were measured using the MASW geophysical survey method [25,48,49]. The principle behind the MASW method is as follows: a) data acquisition with 24 multichannel geophones (4.5 Hz) in a linear array (69 m spread length, 3 m spacing and 6 m offset on each side of the array), generation of surface Rayleigh waves using a sledgehammer impact source of 10 kg on a metal plate, b) dispersion analysis to obtain the most appropriate dispersive phase velocity versus frequency curve of generated waves, and c) calculation of shear wave velocity profile for the site using the inversion technique provided in the SeisImager software (for more detailed and comprehensive description look in [25,49,50,51,52,53]). The maximum investigated depth of the analysed VS profile is usually 10–30 m, but may vary from site to site, and the resolution depends on geophone spacing. If the soil is consisted of layers with a very low velocity (e.g., clays or sands), reaching depths of more than 20 m is difficult given that the signal is filtered and attenuated by the soil [48,49,53].
Figure 7 shows 1-D MASW shear wave profiles estimated at 12 locations in the studied area (marked with red circles in Figure 6) on the same locations as microtremors. For each example, the estimated values of the site parameter VS30 [35,41] are shown. The maximum investigated depth in estimated geophysical VS profiles is the main disadvantage when deeper subsurface structure levels are needed. Measured shear wave velocity profiles may be extended up to bedrock depths using the H/V forward modelling routine as is required for site response analysis. Also, the low density of MASW sites prevents the derivation of a map of VS30 for the entire city area, and H/V forward modelling makes estimating VS30 values for each microtremor measurement location [26,27] possible, as well as the presentation of a detailed VS30 map for the city of Ivanec.
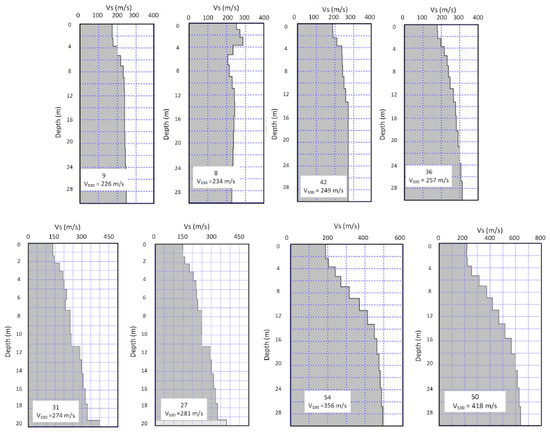
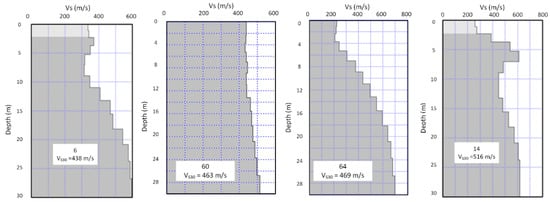
Figure 7.
1-D shear wave velocity profiles derived from MASW measurements with estimated values of VS30. Note that profiles for sites 27 and 31 didn’t reach depth of 30 m as other sites due to very low surface shear wave velocity.
3.4. Estimation of Bedrock Depth for the City of Ivanec Using the H/V Forward Modelling Routine
The determination of bedrock depth is crucial for EQL site response analysis [4,5,6,7] given that input rock motions are propagated from the bedrock level through the soil profile. Geophysical methods can provide depths of up to 20–30 m [25]. By combining microtremor and geophysical data in the H/V forward modelling routine, deeper bedrock depths can be estimated. The limitation of the modelled H/V shear-wave velocity profile compared to multi-layered geophysical profile, is in fact that simple soil models are used and are based on an observed number of HVSR peaks [26,27].
Figure 8 shows three examples of an interpolation of known geophysical soil models reaching to different bedrock depths using the H/V forward modelling routine. Here, a simplified procedure is described (for more details look in [26,27]. The input soil model is based on the number of clear HVSR peaks (for N peaks, N+1 layers in the soil model are used). Initial soil model parameters for each layer are provided by the user: shear wave velocity, thickness, Poisson’s ratio and density. The first step includes identifying a clear HVSR curve peak. If only one clear peak exists (location 42), a two-layer soil model above bedrock (defined as 800 m/s) is sufficient to reproduce the theoretical HVSR curve matching the observed HVSR curve. If more clear H/V peaks are present (location 30), then the modelling incorporates N+1 discrete layers. The first order of the VS estimate for each layer generally follows a simple relation h = VS,avg/4f0 within a known layer thickness and observed HVSR peak frequency. This step is iterated with random perturbation until the input soil model and selected VS reproduces a theoretical HVSR curve that is comparable to the observed HVSR curve. If the synthetic HVSR peak curve is too high or too low, VS values are modified, often leading to deviations in the order of 10–15% between VS30 values from H/V forward modelling and geophysical measurements [26]. Values of Poisson’s ratio and soil layers densities can also be corrected, while supported by physically realistic values [26,42,43]. Generally speaking, VS increases linearly with depth across all soil profiles from the depth of the geophysical profile to the first rock layer defined as VS = 800 m/s [41]. For profiles that did not reach a depth of 30 m (in the geophysical survey and H/V modelling), the VS30 was estimated from an empirical correlation as proposed by Boore [54].
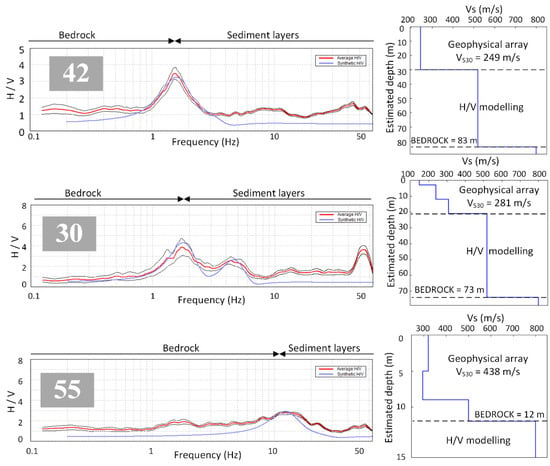
Figure 8.
Examples of H/V forward modelling routine: Left: Observed H/V spectra (red) fitted with theoretical HVSR curve for representative soil model shown in right figures. Right: Values of VS30 estimated from geophysical data and H/V forward modelling.
Using known soil profiles from geophysical measurements, bedrock depths were extracted for all observed microtremor HVSR curves using H/V forward modelling, where the map depicting sediment thickness cover above bedrock was derived using the spatial natural neighbour interpolation (Figure 9). Interestingly, the layers exhibiting velocities of 500 m/s probably act as a first rock refractor in HVSR shallow bedrock estimation (location 55) and the same effect can be observed for locations 6, 14, 50, 60, 64 if HVSR peak frequencies and geophysical measurements (Figure 5 and Figure 7) are compared with estimated depths shown in Figure 9. A good correlation is noticeable between the estimated bedrock depths (Figure 9) as well as topographical (Figure 1b) and local geological characteristics (Figure 3), the distribution of fundamental soil frequency (Figure 6), and geophysical profiles (Figure 7).
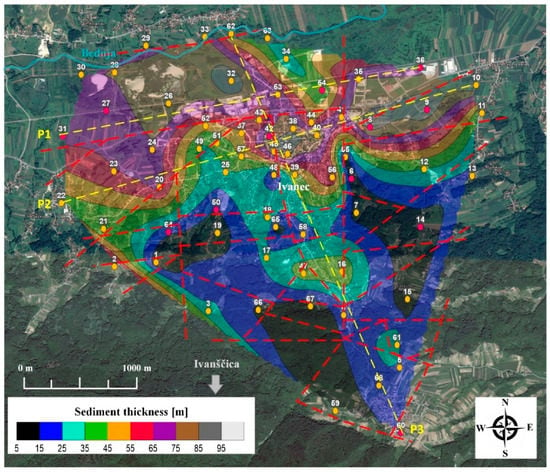
Figure 9.
Map of sediment thickness cover above bedrock for the City of Ivanec with marked faults (red dashed lines) from geological map (Figure 3). Red circles indicate location of geophysical measurements and yellow microtremor measurements.
The presented maps of fundamental frequencies and estimated bedrock depths show that distributions roughly follow surface fault directions in geographical terms (Figure 3). A better representation of these effects is given by extrapolated HVSR amplitude-frequency contours plotted against distance profiles as shown in Figure 10, and which provided the basis for evaluating resonance characteristics [55] of the chosen 2-D profiles. A clear distinction between a change from lower to higher frequencies and higher to lower HVSR amplitudes in the alluvial basin (profiles P1 and P2) with respect to topographical areas (P3) is noticeable. A change to the fundamental resonant frequency and first overtone are clearly linked to the estimated sediment thicknesses between locations (Figure 6, Figure 9 and Figure 10), and exhibit a relationship with a change in local site characteristics, e.g., typology of sediments, lithological and thickness variations of soft sediments up to bedrock depths, alluvial basin and topographical variations (Figure 1) and surface faults orientation (Figure 3). Discrepancies between the 2-D spectral HVSR model (Figure 10) and estimated bedrock map (Figure 9) are more likely due to insufficient knowledge of a realistic bedrock model, and are more likely due to the uncertainty in the correct sediment thicknesses using fundamental frequency and first overtones [55] and the lack of proper geotechnical boreholes. Therefore, the microtremor HVSR method combined with detailed geotechnical borehole drilling and geophysical surveys is the recommended approach for future tasks in engineering-geological mapping of bedrock for the city of Ivanec area (Figure 3).
3.5. VS30 Map for the City of Ivanec
A comparative test between active and passive MASW and microtremor H/V shear wave velocity profiles indicated that microtremor data can provides a good estimate of the one-dimensional shear wave velocity profile [56]. Figure 11 shows the estimated map of average shear wave velocity distribution in the upper 30 m, where VS30 is estimated based on a combination of geophysical MASW measurements and H/V forward modelling (Figure 7 and Figure 8). A comparison of the respective VS30 map (Figure 11) with estimated bedrock depths (Figure 9), topographical (Figure 1b) and local geological characteristics (Figure 3), and fundamental soil frequencies (Figure 6), provides a clear distinction between deeper and softer alluvial Bednja River basin zone (lower VS30 values, Eurocode 8 category C, 180–360 m/s) and transitional topographical zone (higher VS30 values, Eurocode 8 category B, 360–800 m/s) towards Mt. Ivanščica. These observations are important as they indicate effects on weak and strong ground motion amplification towards the local site—this will be analysed and discussed in more detail in subsequent chapters.
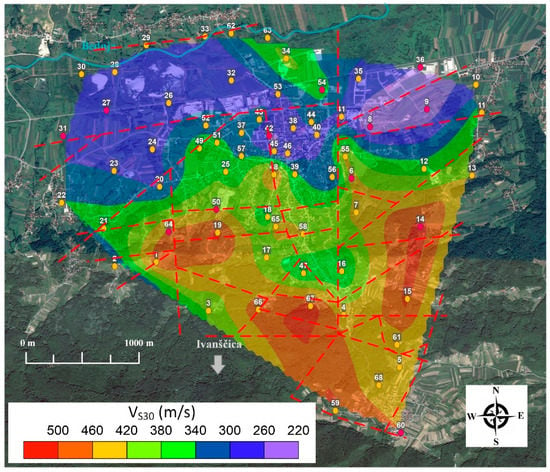
Figure 11.
Map of VS30 distribution for the City of Ivanec. Red circles indicate location of geophysical measurements and yellow microtremor measurements. According to Eurocode 8 soil classification [30], city area can be divided into soil classes B (360–800 m/s) and C (180–360 m/s).
4. Analysis of the 1-D Equivalent-Linear Site Response for the City of Ivanec
Soil undergoes inelastic deformation after a certain intensity of ground shaking. Hence, the non-linear behaviour of soil should be taken into account when performing ground response analysis [4,5]. The 1-D EQL site response analysis is based on the assumption that superficial soil layers extend horizontally on elastic rock and that vertically propagating horizontally-polarized waves (SH waves) dominate the earthquake ground motion wavefield [5]. Some of the well-known programs used are SHAKE [7], SHAKE 91 [57], DEEPSOIL [58] and STRATA [59]. The EQL site response analysis procedure consists of four steps: (1) definition of the local shear wave velocity profile, (2) selection of appropriate dynamic soil properties: shear modulus reduction G/GMAX and damping ξ curves, (3) specification of the input rock ground motions, and (4) propagation of the input rock motion through soil profiles in order to estimate ground motions at the surface and the effect of local soil conditions on ground shaking [2].
4.1. Soil Profiles Used in Site Response Analysis
Soil profiles used in the 1-D EQL site response analysis are based on the combination of geophysical measurements and the H/V forward modelling routine (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Typical soil profiles utilized in the 1-D EQL analysis are characterised by horizontal multi-layered damped soil layers (based on detailed layered geophysical profiles, Figure 7) on elastic bedrock (estimated using H/V forward modelling, Figure 9) extending to an infinite depth. The collected soil profiles are entered into the DEEPSOIL software [58]. For each profile, soil layers are defined by their corresponding soil properties; shear wave velocity; unit weights and dynamic soil properties. Provided that GMAX is known from geophysical measurements (GMAX = ρVS2), shear response at various levels of strain is estimated using soil modulus reduction curves G/GMAX to represent nonlinear soil behaviour of soils under specific levels of strain from induced ground motions (in this study 0.09 g to 0.19 g). Soil profiles extracted from geophysical measurements does not contain any information about soil density or soil classification. Drilled boreholes and laboratory sampling tests are necessary in order to characterize soil layers in terms of soil type and density. Since borehole and laboratory data are not available, soil layer types are approximated using the published relation between soil density and shear wave velocity [60]. Due to local geology characteristics for the city of Ivanec (Figure 3), simple soil profile models were based on selected strain-compatible shear modulus reduction G/GMAX and damping ξ curves for the sands and gravels [61], clays [62] and stiff and rock formation soil layers [63]. In the EQL site response analysis, the equivalent-linear approximation of the non-linear soil behaviour is represented by an iterative procedure: G/GMAX and ξ are varied with induced strain in each layer and the EQL approach is the first-order approximation of the effects of non-linear and inelastic soil behaviour under cycling conditions (e.g., earthquake) in which stiffness G decreases and damping ξ increases as induced shear strain increases [5,58,61].
4.2. Input Rock Motions Used in Site Response Analysis
In the site response analysis incident seismic ground motion propagates from elastic bedrock to ground surface through horizontal soil layers. Input rock motions in the EQL site response analysis are defined using previously recorded, or simulated rock acceleration motions in a time series approach (TS-approach). In seismically active regions, a strong motion database is relatively straightforward, because observed records exist to physically constrain and validate the estimation of future earthquakes. In regions of moderate seismicity such as the area of northwestern Croatia and especially the area around the city of Ivanec (extending approx. 30 km outwards), there are little or no records of strong motion earthquake events, particularly those of interest to engineers. Therefore, input ground motions for the TS-approach were selected from previously recorded rock motions at stations with VS30 >800 m/s provided by NGA-West 2 database from Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center (PEER). To model the uncertainty introduced by the record selection procedure [64], 22 ground motions were utilized in the analyses (Table 1) for the near-source distances (epicentral distances < 30 km). Usually, a stable median of the target input motion levels is obtained by implementing five to ten different input rock time series that fit the target acceleration response spectrum [64,65]. Selected ground motions were scaled to input ground motion levels PGAROCK = 0.09 g and 0.19 g in order to cover peak ground accelerations scenarios for the 95- and 475- year return periods. In the last few years, 1-D EQL site response analysis based on random vibration theory (RVT) has grown popular among the geotechnical earthquake engineering community, mainly because it does not require strong motion records and the input motion is defined solely by the Fourier amplitude spectrum [10,65].

Table 1.
Ground motions (horizontal components) from PEER database used in 1-D EQL site response analysis. Source: (http://ngawest2.berkeley.edu/).
4.3. Results of 1-D Equivalent-Linear Site Response Analysis
Using the DEEPSOIL software, 1-D EQL analysis was performed [58]. First, multi-layered soil profiles were defined using respective soil properties (shear wave velocity, unit weight, strain-compatible shear modulus reduction G/GMAX and damping ξ curves). Selected ground motions (Table 1) were scaled to PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g and (475yrp) and entered into the DEEPSOIL software. Figure 12 shows an example how the site amplification factor for location 42 is estimated. Figure 12a shows an input median 5% damped response spectra at the bedrock level defined from previously recorded rock acceleration time series (Table 1) scaled to PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g and (475yrp). Target PGAROCK values in the input response spectra are defined by spectral acceleration at the high frequency (or the zero period). Figure 12b shows 5% damped median response spectra at the surface from each individual analysis using scaled ground motion records (Table 1). The value of peak ground acceleration (PGA) at the surface is represented by spectral acceleration at high frequency (or the zero period) [9,26,64,65]. The site amplification factor (AF) is calculated as the ratio of surface response spectrum to rock (input) response spectrum (at 5% critical damping): AF(T) = SaSURF/SaROCK [9,65]. Figure 12c shows the estimated frequency-dependent site amplification factor where AF@PGA designates the amplification at the surface of the soil model and AF@PF designates the amplification factor at predominant spectral peak frequency [9,65]. Figure 12d shows the propagation of input ground motion from the bedrock level to the surface using a multi-layered soil column model. The main amplification effects are observed at the top soft surface soil layers [10,22,29,65]. The bedrock layer is defined as an elastic-half space with a unit weight of 24 kN/m3, 2% damping and VS = 800 m/s [41].
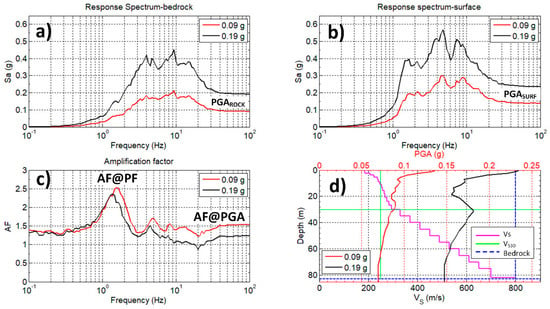
Figure 12.
Example of the 1-D EQL site response analysis result for location 42. a) Input median response spectrum at the bedrock from the suite of previously recorded rock acceleration time series for PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g (475yrp). b) Median response spectrum at the surface. c) Amplification factor AF is calculated as the ratio of the surface response spectrum to the rock (bedrock) response spectrum at 5% of critical damping. AF@PGA marks AF at the top of the soil model (ground surface) and AF@PF marks amplification factor at predominant spectral peak frequency. d) Variation of the input ground motion PGAROCK from the bedrock depth through shear wave velocity Vs model to the surface represented by peak ground acceleration - PGA.
Under low-intensity input ground motions (0.09 g), soil responds more within the linear range, thus significantly reducing stiffness degradation and consequently resulting in greater bedrock-to-surface acceleration amplification at surface soil layers and the predominant peak frequency [5,10,64,65]. Amplification decreases rapidly when input ground motion acceleration is increased (0.19 g), and nonlinear behaviour of soils is expected for a PGAROCK larger than 0.1 g and 0.2 g, given that induced large strains significantly reduce stiffness and increase hysteretic damping, thus reducing the ability of soil to transmit force to the surface and structure above [65,66]. At low-to-mid frequencies, nonlinear soil response means that more amplification occurs for larger input intensities because the induced strain is increased, and shear modulus (stiffness) is reduced which consequently shortens the predominant peak frequency. At higher frequencies, less amplification occurs for larger input intensities due to increased levels of induced strain and increased soil damping [64,67,68]. Based on the presented example in Figure 12, site amplification factors for all 68 locations were estimated in the same way and will be discussed in more detail with reference to the presented site response amplification maps.
5. Assessment of the Seismic Site Amplification Map for the City of Ivanec
The seismic site amplification map for the city of Ivanec was derived from individual HVSR and site response analyses using a spatial interpolation method as applied for maps of fundamental frequencies (Figure 6), sediment thickness (Figure 9) and VS30 (Figure 11). Since the HVSR peak amplitude is only an indication of amplification in natural state and is related to impedance contrast between sediments and bedrock, the question remains as to the qualitative validity of HVSR peak amplitudes and differences between whole spectral HVSR amplitudes and seismic site response (amplification) for the local site when subjected to earthquake influence [21,22,23,24]. For these reasons, all three maps in Figure 13, i.e., the map of HVSR peak amplitude and maps of site response peak amplification for PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g (475yrp) are shown together to better perceive differences between HVSR peak amplitude and seismic site response (amplification). First, maps of HVSR peak amplitudes and site response peak amplifications will be discussed separately in the context of why they are important for the city of Ivanec. This is followed by a qualitative discussion and treatment of the differences between the HVSR peak amplitude and seismic site response amplifications.
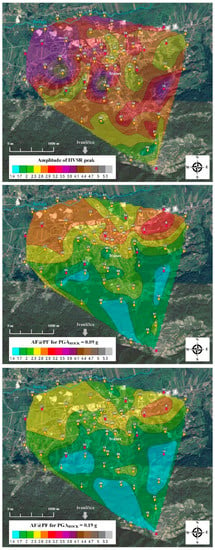
Figure 13.
Up: Map of the amplitude of HVSR peak at fundamental HVSR frequency. Middle: Map of site response amplification factor at predominant frequency for input PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp). Bottom: Map of site response amplification factor at predominant frequency for input PGAROCK = 0.19 g (475yrp). The same colour scale for the amplification is used in all three cases.
5.1. Site Peak HVSR Amplitude Map for the City of Ivanec
The map of peak HVSR amplitudes at fundamental HVSR frequencies for the city of Ivanec is shown in Figure 13 (upper figure). HVSR peak values above 2.0 indicate the presence of site amplification due to soft sediment cover above bedrock, whereas values below 2.0 - flat HVSR curves [44] indicate a potentially small or no amplification. It has become widely accepted that a flat HVSR curve—i.e., with HVSR amplitudes below 2.0 or closer to unity—is often associated with rock reference sites (soil category A in Eurocode 8 [35]). A comparison of the presented HVSR peak amplitude map (Figure 13) with the local geology map (Figure 3) leads to the observation that the highest HVSR peaks above 3.0 are related to the alluvial basin of Bednja River. For locations 14 and 18, HVSR peaks are above 4.0 and are the result of a sharp impedance contrast between high-frequency, thin-soft sediment cover above bedrock (Figure 5 and Figure 7) and topographic effects (this location lies in the isolated elevated peak area). Lower amplitude HVSR peaks relate to a low impedance contrast between surface soil layers (sands and gravels) and the underlying bedrock, whereas higher amplitude HVSR peaks relate to a high impedance contrast of soft sediments with the bedrock or stiff sediments (cemented sands or gravels) [14,18,40,44,46].
A similar correlation between the distribution of HVSR peak amplitudes and geological faults (Figure 3) is noticeable, although not so expressed as within fundamental soil frequency distribution (Figure 6) for the entire area. Fundamental soil frequency is directly correlated with the local geology [46] and bedrock depth (Figure 9), which in turn is reflected with geological faults, whereas the HVSR peak amplitude results from the impedance contrast between soft soil cover and stiff sediment layers or bedrock [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. The isolated area in the northwestern region (around measurement locations 30-28-26-24-20-23-31-30) exhibits the lowest fundamental frequency (Figure 6) and highest HVSR peak amplitudes (Figure 13). This may possibly be associated with abandoned mining trenches (known and unknown, see Figure 3) probably covered with soil (clays and sands). This specific area needs to be further investigated using the geoelectrical tomography or seismic reflection methods in order to detect buried mining shafts that may collapse during strong earthquakes.
Maps of the fundamental soil frequency (Figure 6) and HVSR peak amplitude (Figure 13) for the city of Ivanec can help to distinguish potentially highly amplified seismic zones in the city in terms of soil-structure (building) resonance at fundamental soil frequencies, something that is important for urban and earthquake resistant planning, or the retrofitting of the existing buildings [14,29,69]. Fundamental soil frequencies and the derived empirical relationship between height-period (frequency): T = 0.016·H for typical RC (Reinforced Concrete) buildings [47], future planning sites subject to maximum permitted heights for construction of future 8–10 storey residential buildings in the city of Ivanec can now be determined. A high HVSR peak amplitude above 3.0 (Figure 13) at frequencies of around 1.5–3.0 Hz (Figure 6) corresponding to buildings with approximate 5–8 storeys [47] was observed in the central part of the city. This is particularly important as it indicates that the central part of the city with the highest residential density and taller buildings (see Figure 1b) may be prone to higher seismic amplification and soil-building resonance due to soft sediments and in case of an earthquake [2]. Therefore, particular care needs to be taken with maximum permitted construction heights of newly planned buildings. Towards the foothill of Mt. Ivanščica, HVSR peak amplitudes are lower than those in the alluvial zone with some isolated sites that showing higher HVSR peak amplitudes due to a sharp impedance contrast and soft surface layers on shallow bedrock in elevated topographical areas [70]. This area also exhibits a higher fundamental soil frequency (Figure 6) which may possibly correlate with reported damages from earthquakes in 1973 and 1982 (1–2 floor houses and vineyard cottages) [1].
5.2. Site Response Amplification Map for the City of Ivanec
Maps of site response peak amplification for PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp) and 0.19 g (475yrp) are shown in Figure 13 (middle and bottom figures). These maps clearly distinguish two major seismic microzones: the highest site response peak amplifications that occurs in the alluvial basin of Bednja River (also covering the central city area) where soft soils such as sands and gravels are dominant (designated as soil category C based on EC8 VS30 classification), and the zone exhibiting a smaller site response peak amplification in an area mostly dominated by coarse-grained clastic sediments (soil category B based on EC8) and which could possibly be prone to topographic site effects. Clearly, site response peak amplifications are correlate better with VS30 (Figure 11) and input seismic ground motions (0.09 g and 0.19 g) than HVSR peak amplitudes, although similar distribution may be observed when the three maps are compared to each other [22,23]. Soft soil can play a very important role in the amplification (or de-amplification) of ground motion when propagated from bedrock to the surface (Figure 12d). Figure 14 shows maps of the site response amplification factor at the surface (amplification of the peak ground acceleration-PGA) for input PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95-yrp) and 0.19 g (475yrp). The main observation is that the soft soil alluvial basin shows nonlinear behaviour when higher input ground motion (0.19 g) is induced, that is to say, amplification factors decrease significantly [66,67].
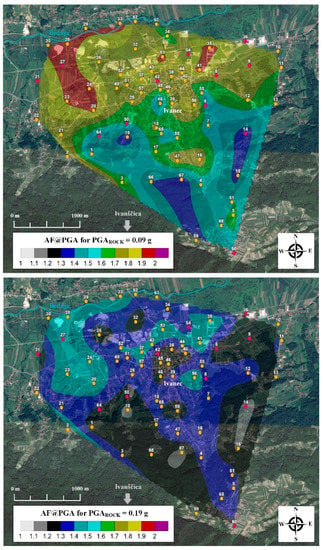
Figure 14.
Up: Map of site response amplification factor at surface peak ground acceleration PGA for input PGAROCK = 0.09 g (95yrp). Bottom: Map of site response amplification factor at surface peak ground acceleration PGA for input PGAROCK = 0.19 g (475 yrp).
The findings from the 1-D EQL site response analysis for all 68 local soil profiles (Figure 11) based on the example in Figure 12 and site response amplification maps in Figure 13 and Figure 14 can be summarized as follows: 1) for PGAROCK = 0.09 g, the input motion is significantly amplified at the top layers of the soil profile; 2) AF is most prominent at a predominant peak frequency, particularly for softer soils with lower VS30 and thicker alluvium layers overlying bedrock; 3) at higher input motion levels PGAROCK = 0.19 g, in softer soils with lower values of VS30, reduction observed at the surface PGA relative to PGAROCK in soft soil sites is attributed to the non-linearity of the soil [66,67,71] which in turn is due to the degradation of the shear modulus subject to large deformations, the AF@PGA decreases at a higher spectral frequency, and the predominant spectral frequency shifts to lower frequencies with decreasing AF@PF [67,68]; 5) for stiffer soil and soft rocks with higher values of VS30, site amplification factors generally show small to no amplification, whereas in some cases significant amplification can be observed (for example location 64, Figure 7) in the presence of upper weaker soil materials (lower VS values) and very shallow bedrock (mainly in topographical areas) [72]. Local site amplifications can be correlated with the seismic ground motion polarization and directionality in both approaches, ambient noise vibrations and earthquake recordings at sites with pronounced topographies [70].
Site response amplification maps (Figure 13 and Figure 14) indicate areas that are prone to the significant amplification of ground motion for a predominant site frequency and at ground surface, as well as indicating a potential danger of soil-building resonance (Figure 6) subject to the permitted construction heights for planned, new multi-rise buildings that may show a correlation with the behaviour of local underground layers during an earthquake. For different ranges of input ground motion, site amplification factors vary significantly depending on the chosen spectral frequency (predominant peak, Figure 13 or at the ground surface, Figure 14) and are subject to different site characteristics (Figure 11). If these variations are evaluated and known, new structures on particular local soft sites (as is the case here for the central city area) may be constructed so as to avoid potential resonance at the natural soil frequency by taking into account nonlinear effects at higher spectral frequencies and significant amplification at the predominant soil frequency for different earthquake scenarios. Also, the results are important as they can be used in terms of aseismic reinforcement in order to improve seismic resistance of existing structures which are prone to resonance failure [69].
5.3. Discussion on the Differences between HVSR Peak Amplitudes and Seismic Site Response Amplifications
The microtremor HVSR method is used to observe variations of fundamental soil frequency and rapid estimation of HVSR peak amplitude as an indication of local site amplification [40,42]. The main questions is whether the estimated HVSR peak amplitudes represent qualitatively an indication of local site amplification? The underlying principle of the HVSR methodology is that ambient noise measurements are performed without an earthquake influence [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]; therefore, the fundamental soil frequency and HVSR peak amplitude only represent a site response in the natural state and not within ground motion amplification [21,22,24,73]. Otherwise, site response analysis provides site response amplification for given ground motion propagated from the bedrock level through the local soil profile [5].
The change from site response of natural state (HVSR) and the site response of the local soil when subject to an earthquake influence (PGAROCK=0.09 g and 0.19 g) is clearly observed in terms of site amplification changes, particularly in the alluvial basin where AF decreases under a higher input of ground motion levels (Figure 13 and Figure 14). Site response analysis enables evaluation of local site amplification subject to seismic ground motion at the surface (AF@PGA), at the predominant peak frequency (AF@PF), or at any spectral frequency [5,20,65]. HVSR amplitudes are only typical at the HVSR peak frequency [21,22], therefore a change to local site amplification under the influence of ground motion was not observed within HVSR spectra. In this study, the HVSR method proved to be a reliable and fast method in free-field for estimating HVSR peak amplitudes at fundamental frequencies that matched the spatial distribution of EQL estimated site amplifications at similar predominant peak frequencies [22,24,73]; however, amplitude levels are not the same (Figure 13). In some cases, amplitude levels are matched, but generally, these two approaches cannot be matched in terms of site amplification amplitude levels [24], and their relationship needs to be further studied before only HVSR peak amplitudes are applied to local site responses in relation to earthquake ground motion amplification. Another open question regarding validation of HVSR peak amplitudes or simply full spectral HVSR amplitudes at any frequency is whether microtremor HVSR spectra show potential nonlinear site effects as do EQL site response analysis spectra? Clearly, HVSR spectra are limited to detecting nonlinear behaviour of soft soils as observed in this study. This may possibly be addressed if ambient noise vibrations are measured for a stronger earthquake, but this approach is beyond the scope of this study.
In general, the microtremor HVSR method is a good and fast, economically feasible method to estimate local free-field amplification. We have observed that HVSR peak amplitudes showed similar spatial distributions with much the same predominant peak frequencies as the site response peak amplitudes under different earthquake scenarios, but with different amplitude levels [24,73]. Site response analysis can evaluate site amplification factors as a function of local site characteristics, VS30 (Figure 11), and ois subject to the influence of different seismic ground motions [20,65,67]. Therefore, for a detailed assessment of linear and nonlinear site amplification behaviour under different input levels of seismic ground motions, the EQL site response analysis should be used. Moreover, some of the current building codes require the performance of site response analysis under specific conditions.
6. Conclusions
This study is the first stage towards a comprehensive seismic microzonation map of the city of Ivanec based on the estimation of seismic site amplification using microtremor measurements and HVSR analysis combined with 1-D equivalent-linear site response analysis for different peak ground accelerations [29,74,75,76,77,78]. Site amplification maps at the predominant peak frequency and ground surface indicated two potentially dangerous seismic microzones: one with a high amplification in the central city area due to soft soil characteristics in the alluvial basin of Bednja River, and the other with a small amplification in the transitional zone from the alluvial basin towards the foothills of Mt. Ivanščica, which may be prone to topographic site effects.
Differences between the HVSR peak amplitudes and seismic site response amplifications were addressed in this study. Microtremor HVSR methods have been proven to be a good and fast, economically feasible method in free field to estimate local site amplification in terms of HVSR peak amplitude with a similar predominant peak frequency, but at a different site amplification level to the site response analysis. Site response analysis enables the evaluation of site amplification factors as a function of local site characteristics VS30, as well as covering the seismic response of the local site under the influence of different seismic ground motions.
This study provides support for earthquake resistant building designs or the retrofitting of existing buildings, protection of industrial buildings and structures, planning of civil emergency protection, and the preservation of cultural heritage in the city of Ivanec. Moreover, it is crucial for the city of Ivanec that this study continue with detailed geotechnical drilling leading to bedrock depths (or at least 30 m), in-situ test investigation, and denser geophysical investigations in order to fully support microtremor measurements. Accordingly, the local seismic hazard index [78] should be evaluated for a certain intensity of input ground motion at the bedrock level, local site amplifications, liquefaction potential, predominate frequency of the earthquake motion at the surface, local soil effects, and potential landslides for certain parts of the city area. Given that the city has rapidly grown in recent times, and with future plans for expansion, a full and comprehensive seismic microzonation map [74,75,76,77,78] should be developed to include new and updated spatial master planning documents of the city of Ivanec, especially as the area has experienced moderate earthquakes in the past around Mt. Ivanščica.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.S. and S.M.; methodology, D.S. and S.M.; software, D.S. and M.G.; validation, D.S., S.M. and M.G.; formal analysis, D.S., V.S. and I.S.; investigation, V.S., and I.S.; resources, M.G, I.I.; data curation, D.S., S.M., I.I., writing—original draft preparation, D.S., V.S., I.S.; writing—review and editing, D.S., S.M,; visualization, D.S., I.I.; supervision, S.M. and M.G.; project administration, M.G.; funding acquisition, M.G.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported partially by the University of Zagreb through internal project “Analysis of the local site effects on the amplification of seismic ground motion in Croatia” in the period 2016–2018. The authors wish to thank to the University of Zagreb, Faculty of Geotechnical Engineering for the administrative and technical support for geophysical surveys. The support is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also thank to the Department of Geophysics, Faculty of Science University of Zagreb, which put them on disposal the earthquake database for the Nortwestern Croatia. Finally, we acknowledge City of Ivanec for support to perform microtremor and geophysical measurements in the city area.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Krznar, S.; Poljak, S.; Jagić, S.; Miljan, Z.; Pehard, I. Ivanec Kroz Stoljeća 1396–2016 (Ivanec through Centuries 1396–2016); Monography: Ivanec, Croatia, 2017; p. 257. [Google Scholar]
- Herak, D.; Herak, M.; Tomljenović, B. Seismicity and earthquake focal mechanisms in North-Western Croatia. Tectonophysics 2009, 465, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatial Master Planning of the City of Ivanec with Amendments. 2012 & 2016. Available online: http://www.ivanec.hr/46-prostorni-planovi (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Idriss, I.M.; Seed, H.B. Seismic Response of Horizontal Soil Layers. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1968, 94, 1003–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, S.L. Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering, 1st ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, Bergen County, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 654. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, L. Earthquake Hazard. Analysis: Issues and Insights; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 254. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, P.B.; Lysmer, J.; Seed, H.B. SHAKE: A Computer Program for Earthquake Response Analysis of Horizontally Layered Sites; UCB/EERC-72/12; Earthquake Engineering Research Center: Oakland, CA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, P.; Hovius, N.; Haines, J.A. Topographic site effects and the location of earthquake induced landslides. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 275, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzera, F.; Lombardo, G.; D’Amico, S.; Galea, P. Speedy Techniques to Evaluate Seismic Site Effects in Particular Geomorphologic Conditions: Faults, Cavities, Landslides and Topographic Irregularities. In Engineering Seismology, Geotechnical and Structural Earthquake Engineering, 1st ed.; D’Amico, S., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2013; Chapter 5; pp. 102–138. [Google Scholar]
- Stanko, D.; Gülerce, Z.; Markušić, S.; Šalić, R. Evaluation of the site amplification factors estimated by equivalent linear site response analysis using time series and random vibration theory based approaches. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 117, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogoshi, M.; Igarashi, T. On the Propagation Characteristics of Microtremor. J. Seismol. Soc. Jpn. 1970, 23, 264–280. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y. Method for Dynamic Characteristics Estimation of Subsurface using Microtremor on the Ground Surface. Railw. Tech. Res. Inst. Q. Rep. 1989, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gosar, A. Microtremor HVSR study for assessing site effects in the Bovec basin (NW Slovenia) related to 1998 Mw5.6 and 2004 Mw5.2 earthquakes. Eng. Geol. 2007, 91, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, A. Study on the applicability of the microtremor HVSR method to support seismic microzonation in the town of Idrija (W Slovenia). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucciarelli, M.; Gallipoli, M.R. A critical review of 10 years of microtremor HVSR technique. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2001, 42, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giacomo, D.; Gallipoli, M.R.; Mucciarelli, M.; Parolai, S.; Richwalski, S.M. Analysis and modeling of HVSR in the presence of a velocity inversion: The case of Venosa, Italy. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2005, 95, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, V.; Picozzi, M.; Baliva, F.; Albarello, D. Ambient noise measurements for preliminary site-effects characterization in the urban area of Florence, Italy. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2008, 98, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monaco, F.; Tallini, M.; De Rose, C.; Durante, F. HVNSR survey in historical downtown L’Aquila (central Italy): Site resonance properties vs. subsoil model. Eng. Geol. 2013, 158, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herak, M.; Allegretti, I.; Herak, D.; Kuk, K.; Kuk, V.; Marić, K.; Markušić, S.; Stipčević, J. HVSR of ambient noise in Ston (Croatia): Comparison with theoretical spectra and with the damage distribution after the 1996 Ston-Slano earthquake. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 8, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, D.; Markušić, S.; Strelec, S.; Gazdek, M. HVSR analysis of seismic site effects and soil-structure resonance in Varaždin city (North Croatia). Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 92, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucciarelli, M. Reliability and applicability of Nakamura’s technique using microtremors: An experimental approach. J. Earthq. Eng. 1998, 2, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imposa, S.; Lombardo, G.; Panzera, F.; Grassi, S. Ambient Vibrations Measurements and 1D Site Response Modelling as a Tool for Soil and Building Properties Investigation. Geosciences 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, V.; Wasowski, J.; Muscillo, S. New developments in ambient noise analysis to characterise the seismic response of landslide-prone slopes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Fu, L.-Y.; Wang, Z.; LI, X.; Carpenter, N.S.; Woolery, N.S.; Lyu, Y. On the Amplitude Discrepancy of HVSR and Site Amplification from Strong-Motion Observations. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2017, 170, 2873–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, S.; Parolai, S.; Albarello, D.; Picozzi, M. Application of Surface-Wave Methods for Seismic Site Characterization. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 777–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellaro, S.; Mulargia, F. VS30 Estimates Using Constrained H/V Measurements. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellaro, S. The complementarity of H/V and dispersion curves. Geophysics 2016, 81, T323–T338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herak, M.; Allegretti, I.; Herak, D.; Ivančić, I.; Kuk, V.; Marić, K.; Markušić, S.; Sović, I. Seismic Hazard Map of Croatia for a 475-Year Return Period. 2011. Available online: http://seizkarta.gfz.hr/ (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Anbazhagan, P.; Sitharam, T.G. Seismic microzonation of Bangalore, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 117, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivančić, I.; Herak, D.; Markušić, S.; Sović, I.; Herak, M. Seismicity of Croatia in the period 2002–2005. Geofizika 2006, 23, 87–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ivančić, I.; Herak, D.; Herak, M.; Allegretti, I.; Fiket, T.; Kuk, K.; Markušić, S.; Prevolnik, S.; Sović, I.; Dasović, I.; et al. Seismicity of Croatia in the period 2006–2015. Geofizika 2018, 35, 69–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herak, M.; Herak, D.; Markušić, S. Revision of the earthquake catalogue and seismicity of Croatia, 1908–1992. Terra Nova 1996, 8, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomljenović, B.; Csontos, L. Neogene-quaternary structures in the border zone between Alps, Dinarides and Pannonian Basin (Hrvatsko zgorje and Karlovac basins, Croatia). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 90, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, D.; Markušić, S.; Strelec, S.; Gazdek, M. Seismic response and vulnerability of historical Trakošćan Castle using HVSR method. Environ. Earth Sci 2016, 75, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Normalization. Eurocode: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance—Part 1: General Rules, Seismic Actions and Rules for Buildings (EN 1998-1: 2004); European Committee for Normalization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Šimunić, A.; Pikija, M.; Hećimović, I. Basic Geological Map of Croatia, Sheet Varaždin, M 1: 100000; Croatian Geological Survey: Zagreb, Croatia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Šimunić, A. Geology of the Lepoglava area (Northwestern Croatia). Radovi Zavoda za Znanstveni rad Varaždin 1986, 1, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Šimunić, A. Geological Basis of Mineral Deposits in Ivanec Area; Zbornik 600 Godina Ivanca; HAZU: Varaždin, Croatia, 1997; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, A.E.; Holden, C.; Massey, C.I. Site amplification, polarity and topographic effects in the Port Hills during the Canterbury earthquake sequence. GNS Sci. Consult. Rep. 2014, 121, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, S.; Cassidy, J.F.; Castellaro, S.; Cornou, C.; Crow, H.; Hunter, J.A.; Matsushima, S.; Sánchez-Sesma, F.J.; Yong, A. Application of Microtremor Horizontal-toVertical Spectral Ratio (MHVSR) Analysis for Site Characterization: State of the Art. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 613–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, L.; Puglia, R.; Pacor, F.; Gallipoli, M.R.; Bindi, D.; Mucciarelli, M. Proposal for a soil classification based on parameters alternative or complementary to Vs,30. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 9, 1877–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignardi, S.; Mantovani, A.; Zeid, N.A. OpenHVSR: Imaging the subsurface 2D/3D elastic properties through multiple HVSR modeling and inversion. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 93, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; McBride, J. Application of HVSR to estimating thickness of laterite weathering profiles in basalt. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, P.; Duval, A.; Koehler, A.; Rao, S. Guidelines for the Implementation of the H/V Spectral Ratio Technique on Ambient Vibrations Measurements, Processing and Interpretation. SESAME H/V User Guidelines. 2004, pp. 1–62. Available online: http://sesame.geopsy.org/SES_Reports.htm (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Pischiutta, M.; Rovelli, A.; Salvini, F.; Di Giulio, G.; Ben-Zion, Y. Directional resonance variations across the pernicana fault, Mt Etna, in relation to brittle deformation fields. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 193, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leyton, F.; Ruiz, S.; Sepúlveda, S.A.; Contreras, J.P.; Rebolledo, S.; Astroza, M. Microtremors’ HVSR and its correlation with surface geology and damage observed after the 2010 Maule earthquake (Mw 8.8) at Talca and Curico, Central Chile. Eng. Geol. 2013, 161, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, M.R.; Mucciarelli, M.; Šket-Motnikar, B.; Zupanćić, P.; Gosar, A.; Prevolnik, S.; Herak, M.; Stipčević, J.; Herak, D.; Milutinović, Z.; et al. Empirical estimates of dynamic parameters on a large set of European buildings. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 8, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Miller, R.D.; Xia, J. Multichannel analysis of surface waves. Geophysics 1999, 64, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Miller, R.D.; Park, C.B. Estimation of near-surface shear-wave velocity by inversion of Rayleigh waves. Geophysics 1999, 64, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Heljeson, M.A.; Ivanov, J.; Brohammer, M. Surfseis User’s Manual v 2.0; Kansas Geological Survey: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2007; p. 74. Available online: http://www.kgs.ku.edu/software/surfseis/SurfSeisMan.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Sheehan, J.R.; Doll, W.E.; Mandell, W.A. An Evaluation of Methods and Available Software for Seismic Refraction Tomography Analysis. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2006, 10, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegah, E.; Liu, H. Application of near-surface seismic refraction tomography and multichannel analysis of surface waves for geotechnical site characterizations: A case study. Eng. Geol. 2016, 208, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.A.; Stephenson, W.J.; Odum, J.K.; Worley, D.M. Comparison of P- and S-wave velocity profiles from surface seismic refraction/reflection and downhole dana. Tectonophysics 2003, 368, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, D.M. Estimating Vs (30) (or NEHRP site classes) from shallow velocity models (depths <30 m). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2004, 94, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Poggi, V.; Ermert, L.; Burjanek, J.; Michel, C.; Fah, D. Modal analysis of 2-D sedimentary basin from frequency domain decomposition of ambient vibration array recordings. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 200, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, A.; Stopar, R.; Rošer, J. Comparative test of active and passive multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) methods and microtremor HVSR method. RMZ Mater. Geoenviron. 2008, 55, 41–66. [Google Scholar]
- Idriss, I.M.; Sun, J.I. User’s Manual for SHAKE91: A Computer Program for Conducting Equivalent Linear Seismic Response Analyses of Horizontally Layered Soil Deposits. 1993. Available online: http://www.soilquake.net/shake91_input/ (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- Hashash, Y.M.A.; Groholski, D.R.; Phillips, C.A.; Park, D.; Musgrove, M. DEEPSOIL 5.0, User Manual and Tutorial; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kottke, A.R.; Rathje, E.M. Technical Manual for Strata; PEER Report 2008/10; Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center College of Engineering University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009; p. 100. [Google Scholar]
- Boore, D.M. Determining generic velocity and density models for crustal amplification calculations, with an update of the Boore and Joyner (1997) generic site amplification for Vs(Z) = 760 m/s. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2016, 106, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Wong, R.T.; Idriss, I.M.; Tokimatsu, K. Moduli and Damping Factors for Dynamic Analyses of Cohesionless Soils. J. Geotech. Eng. 1986, 112, 1016–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučetić, M.; Dobry, R. Effect of Soil Plasticity on Cyclic Response. J. Geotech. Eng. 1991, 117, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, P.B. Effects of Local Geology and Distance from Source on Earthquake Ground Motions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Rathje, E.M.; Kottke, A.R.; Trent, W.L. Influence of Input Motion and Site Property Variabilities on Seismic Site Response Analysis. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottke, A.R.; Rathje, E.M. Comparison of time series and random-vibration theory site-response methods. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2013, 103, 2111–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresnev, I.; Wen, K. Nonlinear Soil Response-A Reality? Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1996, 86, 1964–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bolisetti, C.; Whittaker, A.S.; Mason, H.B.; Almufti, I.; Willford, M. Equivalent linear and nonlinear site response analysis for design and risk assessment of safety-related nuclear structures. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2014, 275, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.P.; Lin, S.L.; Loye, A.K.; Evans, S.J. Seismic design spectra for different soil classes. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 46, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Elnashai, A.S.; Di Sarno, L. Fundamentals of Earthquake Engineering; Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008; p. 347. [Google Scholar]
- Burjanek, J.; Edwards, B.; Fäh, D. Empirical evidence of local seismic effects at sites with pronounced topography: A systematic approach. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 197, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Muraka, R.; Lysmer, J.; Idriss, I.M. Relationships of maximum acceleration, maximum velocity, distance from source, and local site conditions for moderately strong earthquakes. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1323–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Anbazhagan, P.; Neaz Sheikh, M.; Parihar, A. Influence of rock depth on seismic site classification for shallow bedrock regions. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2013, 14, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, L.F.; Steidl, J.H.; Gariel, J.C.; Archuleta, R.J. Borehole response studies at the Garner Valley Downhole Array, southern California. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2002, 92, 3165–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belavauxm, M.; Meza-Fajardo, K.; Abad, J.; Bertil, D.; Roulle, A.; Munoz, S.; Prepetit, C. Combined Geophysical and Geotechnical Approaches for Microzonation Studies in Hispaniola Island. Geosciences 2018, 8, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Grasso, S.; Maugeri, M. The seismic microzonation of the city of Catania (Italy) for the Etna scenario earthquake (M = 6.2) od 20 February 1818. Earthq. Spectra 2012, 28, 573–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Sahu, R.B. Site specific ground motion simulation and seismic response analysis for microzonation of Kolkata. Geomech. Eng. 2012, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzo, G.; Silvestri, F.; Costanzo, A.; d’Onofrio, A.; Martelli, L.; Pagliaroli, A.; Sica, S.; Simonelli, A. Site response studies and seismic microzoning in the middle Aterno valley (L’Aquila, Central Italy). Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 9, 1417–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.; Sitharam, T.G.; Padmanabhan, G.; Pillai, C.S. Seismic microzonation of a nuclear power plant site with detailed geotechnical, geophysical and site effect studies. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 419–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).