Abstract
A study of the unconfined Continental Terminal aquifer in Abidjan District, located in a coastal sedimentary basin in Southern Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa), is conducted. This aquifer is the principal source of drinking water for the city of Abidjan. The water quality of the aquifer is affected by anthropogenic sources of pollution, such as scattered deposits of solid and liquid waste of all kinds. Additionally, the proliferation of gas stations, including potential tank leakage, must be considered in the event of an accident. To ensure the effective protection and management of the Abidjan groundwater, this work assesses the groundwater contamination risk of the Abidjan aquifer by hydrocarbons such as benzene. To achieve this objective, a numerical groundwater model that included the geological and hydrogeological data of the Abidjan aquifer was constructed with FEFLOW 7.1. A predictive simulation of groundwater flow coupled with the transport of dissolved benzene deposited on the soil surface at the N’Dotré and Anador gas stations was performed. The initial concentrations of dissolved benzene were 43.12 mg/L and 14.17 mg/L at the N’Dotré and Anador sites, respectively. The results revealed that a threshold concentration of 0.001 mg/L was reached after 44 years and two months at borehole ZE11, which is located four kilometers downgradient from the source. The maximum peak concentration of 0.011 mg/L was reached at this point after 47 years and two months. In this region, 14 other boreholes could be threatened by dissolved benzene pollution based on the simulation.
1. Introduction
Groundwater is the largest reserve of continental freshwater [1], and is also an important source of drinking water in many parts of the world, especially in areas with limited or polluted surface water [2,3]. According to Morris et al. [4], approximately two billion people worldwide depend directly on groundwater. The continued growth of the global population is leading to increased water and groundwater requirements [5,6]. Groundwater, which has been long regarded as an inexhaustible and high-quality natural resource, is currently threatened by pollution, mainly from anthropogenic activities [7]. Therefore, many international organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), have expressed their concern regarding this issue. For example, the third World Water Forum in Kyoto, Shiga and Osaka, Japan, focused on groundwater development and management by recommending the implementation of more effective governance methods in developing countries [8]. Several groundwater studies of cities around the world have indicated the prevalence of pollutants such as nitrate, pesticide, sodium chloride, ammonium ion, nitrites, sulfates, chlorides, mercury, cadmium, and arsenic [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. This groundwater is the main source of drinking water, exposing these citizens to many waterborne illnesses and diseases, such as diarrhea, cholera, and typhoid fever, which are major causes of morbidity around the world and, specifically, in Africa [17,18,19].
Abidjan, similar to other large African cities, is also experiencing significant and uncontrolled population growth according to the National Institute of Statistics [20]. This rapid growth of the population has increased the demand for drinking water. Notably, the city of Abidjan is currently supplied by drinking water from the Continental Terminal aquifer, which is also called “Abidjan groundwater” according to the Directorate of Human Hydraulics [21]. The Abidjan District, with an area of 1160 km2, has 13 main boreholes catchment areas [22]. The groundwater, which is collected from various boreholes at depths between 60–130 m, is unequally distributed in the municipalities of Abobo, Adjamé, Attécoubé, Cocody, Yopougon, Anguédédou, Songon, and Bingerville.
The District of Abidjan has been affected by various pollution issues, such as garbage dumping throughout the city, especially in neighborhoods with low standards of living. Other pollution sources include the dumping of used oils from garages onto unpaved roadways, the discharge of domestic and industrial wastewater, and automobile workshops that do not comply with safety criteria. The Akouédo open-air dump and the dumping of approximately 400,000 L of toxic waste from the “Probo Koala” ship in August 2006 are also important pollutant sources. The dumped toxic waste contained high doses of organochlorine compounds, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfide, causing the death of more than 17 people, with 69 hospitalizations and 102,806 medical consultations [23]. The Abidjan aquifer, which is mainly composed of sandy formations, is unconfined throughout its entire domain [24,25]. However, according to Gilli et al. [26], the majority of the recharge of the unconfined aquifer comes from the infiltration of surface water, including rainwater. This water flowing to the aquifer can carry some contaminants.
Therefore, the Abidjan aquifer has been the subject of several studies, including [19,27,28,29], which reported the potential overexploitation and pollution. High nitrate concentrations of up to 120 mg/L have been found in some boreholes [30]. Some boreholes used to supply drinking water in the Southern Abidjan District have been abandoned due to high nitrate concentrations [27,31]. To understand and assess the evolution of pollution, groundwater flow models have been coupled with the transport of pollutants such as nitrates and perchloroethylene (PCE) [12,28]. Deh [12] showed that 79% of the groundwater in the District of Abidjan has uncertain hydrogeological protection, and 12% is vulnerable.
This potential threat of the pollution of the Continental Terminal aquifer could also come from economic enterprises such as gas stations, which have become abundant in the different municipalities of the district of Abidjan [32]. Therefore, it is necessary to study cases regarding the contaminant plumes of fuels such as benzene originating from leaky tanks as they become obsolete, break, or rupture during accidents.
To ensure the protection and efficient management of the Abidjan aquifer, it is necessary to conduct studies relating to oil pollution, specifically benzene pollution, which is an essential component of gasoline with well-known properties that are considered dangerous and carcinogenic [33]. Based on the complexity of the geological formations of the Continental Terminal aquifer, hydrogeological numerical models are effective tools for investigating the underground environment and predicting the fate of pollutants in the subsurface.
2. Description of the Study Area
2.1. Location
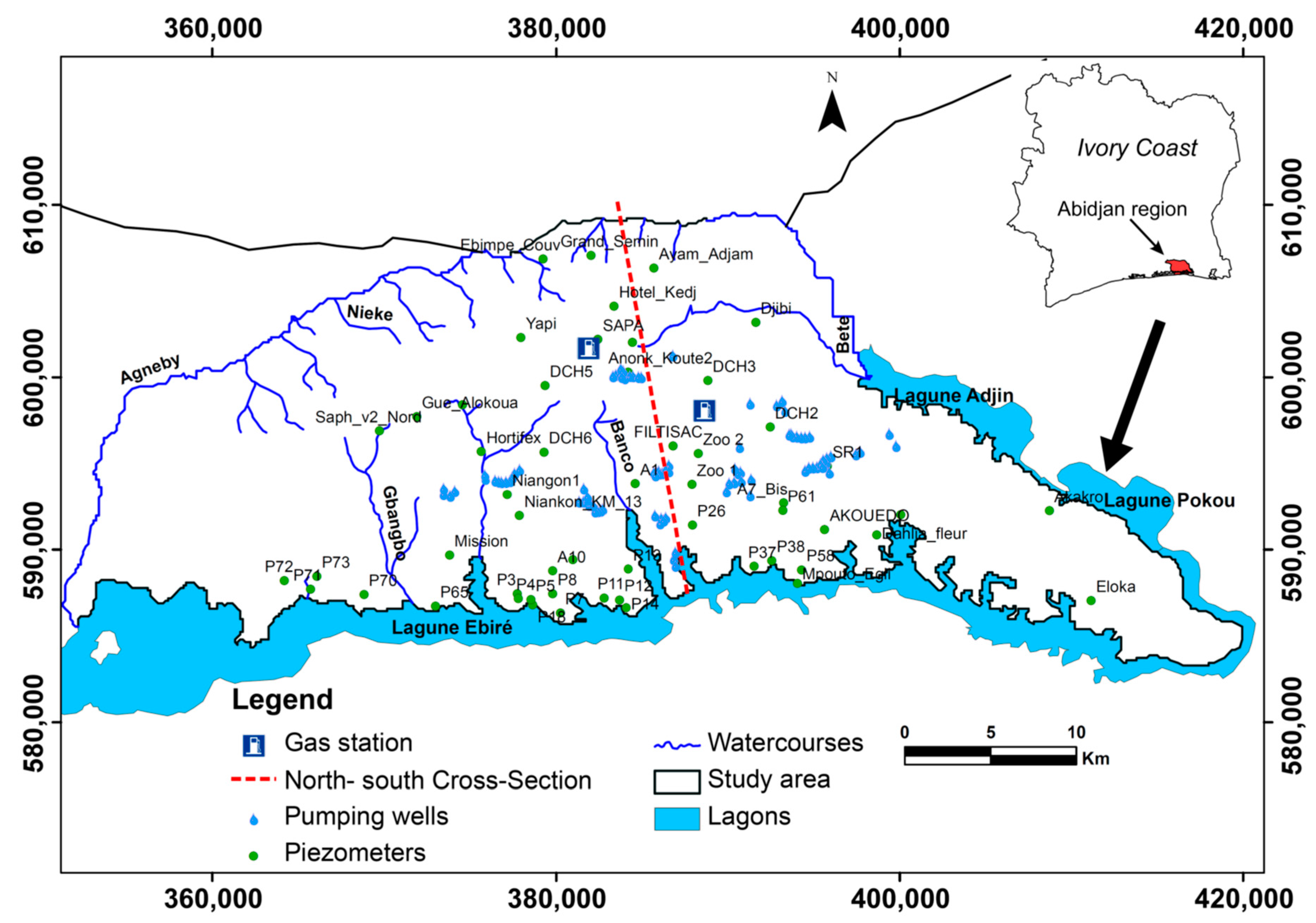
The District of Abidjan, which is located in southern Côte d’Ivoire, is a recent legal creation of the Ivorian state (Figure 1). It is composed of the city of Abidjan, which includes 10 municipalities (Abobo, Adjamé, Attécoubé, Cocody, Koumassi, Marcory, Plateau, Port-Bouët, Treichville, and Yopougon), and the municipalities of Anyama in the north, Bingerville to the east, and Songon to the west. With an area of 1160 km2, the District of Abidjan population was estimated at approximately three million inhabitants in 1998 according to the National Institute of Statistics [34]. This population reached 4.7 million inhabitants in 2014 [20]. The modeled portion of the Abidjan District covers an area of 986 km2 with a perimeter of 266 km, or 85% of the total area of the District.
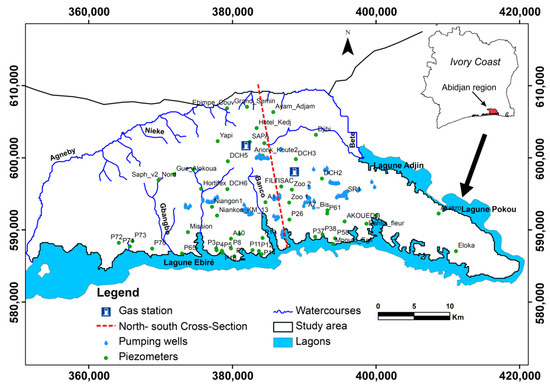
Figure 1.
Location of Abidjan District.
2.2. Geology
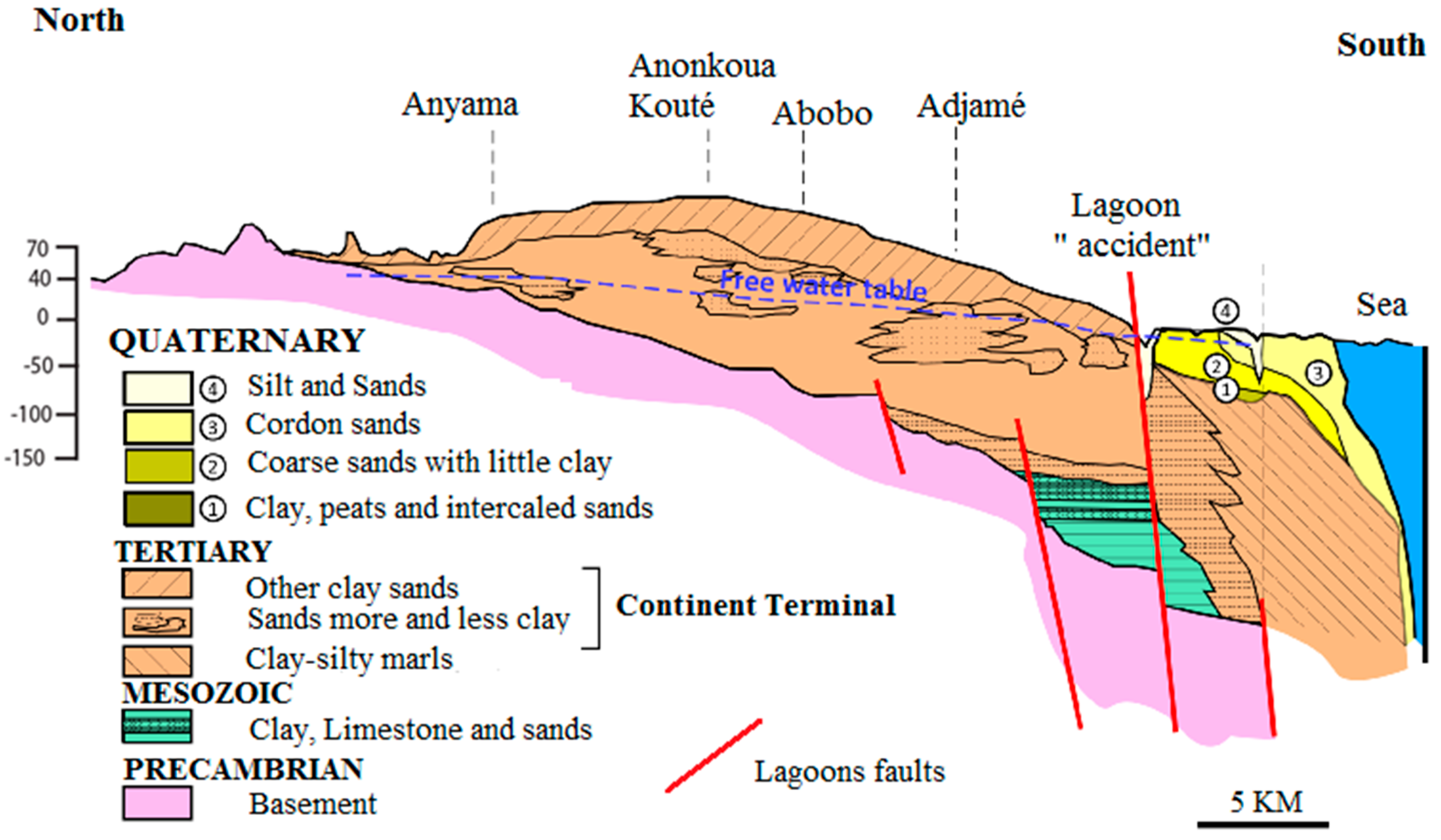
From a geological perspective, the Early Cretaceous to Quaternary sedimentary basin was characterized by three episodes of transgression [35,36], which are the Albian–Aptian, Maastrichtian–Eocene, and Lower Miocene episodes (Figure 2). Two stratigraphic gaps are observed, namely, the Precambrian Cretaceous and Oligocene end gaps. According to Aghui and Biemi [37], Precambrian Terminal and Early Secondary formations are absent throughout the sedimentary basin. The coastal Ivorian sedimentary basin is crescent-shaped with little curvature, and the tips of the crescent point toward the sea [24,38,39]. The basin extends from the Fresco region in the west to the city of Axim in Ghana to the east, between latitudes 5° 00’ and 5° 30’ N and between longitudes 3° 00’ and 6° 00’ W [40]. This basin is 350 to 400 km long and 40 to 50 km wide.
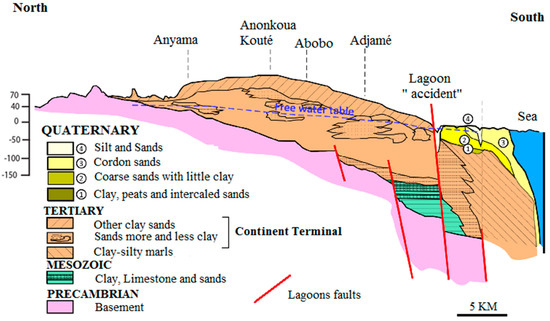
Figure 2.
Geological formations of the coastal sedimentary basin in Abidjan (based on [24]).
The aquifer in the basin is of Mio–Pliocene age, and is composed of sand, silt, and sandy clay with a few levels of mottled clays.
2.3. Hydrogeology
The coastal sedimentary basin in Abidjan is composed of three aquifers: the Quaternary aquifer, the Continental Terminal aquifer, and the Maastrichtian aquifer. The Continental Terminal aquifer covers the entire surface of the coastal sedimentary basin in the form of high plateaus, with the exception of the Quaternary littoral area [40]. This aquifer is unconfined, and includes four levels from top to bottom. The formations encountered are discontinuous lateritic cuirass and locally sandy clays or clayey sands, coarse fluvial sands, mixed clayey sand and black clay, and gravelly sands; however, most formations are clayey sands interspersed with variegated clay [36,37,40]. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show that the different layers of the sedimentary basin at the study scale are not homogeneous over their extent. The Continental Terminal aquifer, which is also known as the Abidjan aquifer, is the main source of drinking water for the district of Abidjan. The water supply system is operated by the Water Distribution Company of the Ivory Coast (SODECI). The waters of the Continental Terminal are drained by the Ebrié Lagoon [37] and feed the Maastrichtian aquifer when there are no ferruginous sandstone clays separating the two aquifers [40]. The reserves in the Continental Terminal aquifer are renewed by direct infiltration or percolation through Quaternary formations [31]. According to Kouame [28], the Abidjan aquifer recharges from one to four months after the long rainy season.
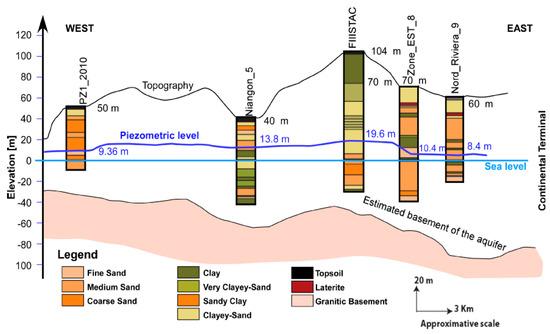
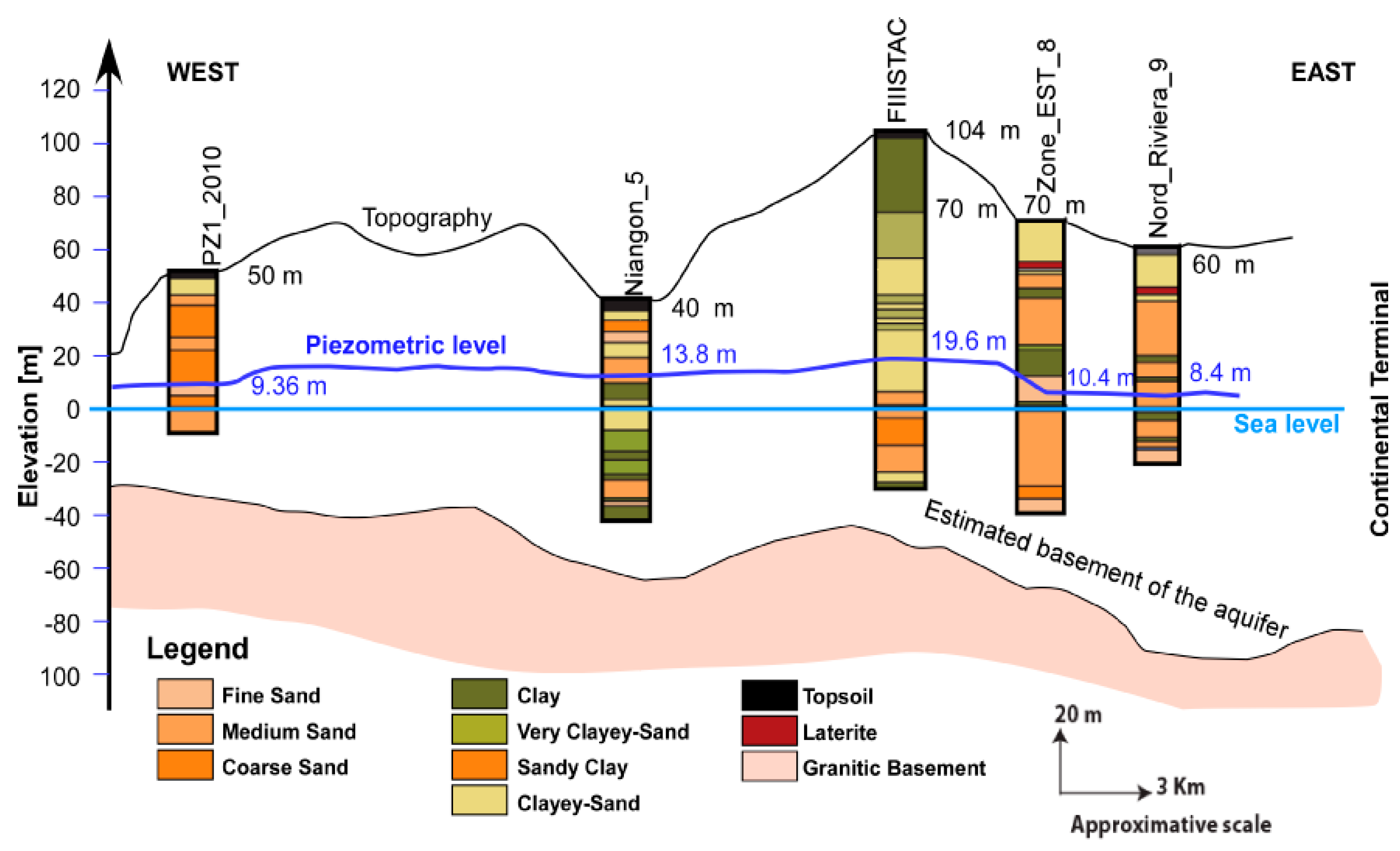
Figure 3.
West–east approximate cross-section of the coastal sedimentary basin in Abidjan from boreholes on 11 December 1992.
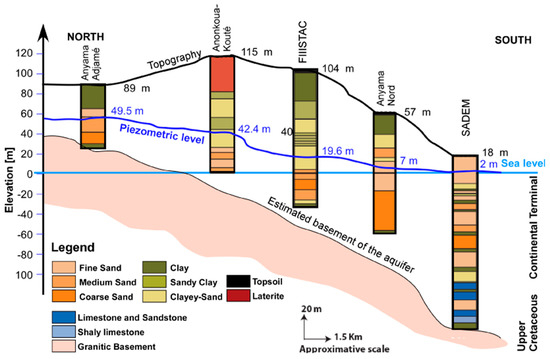
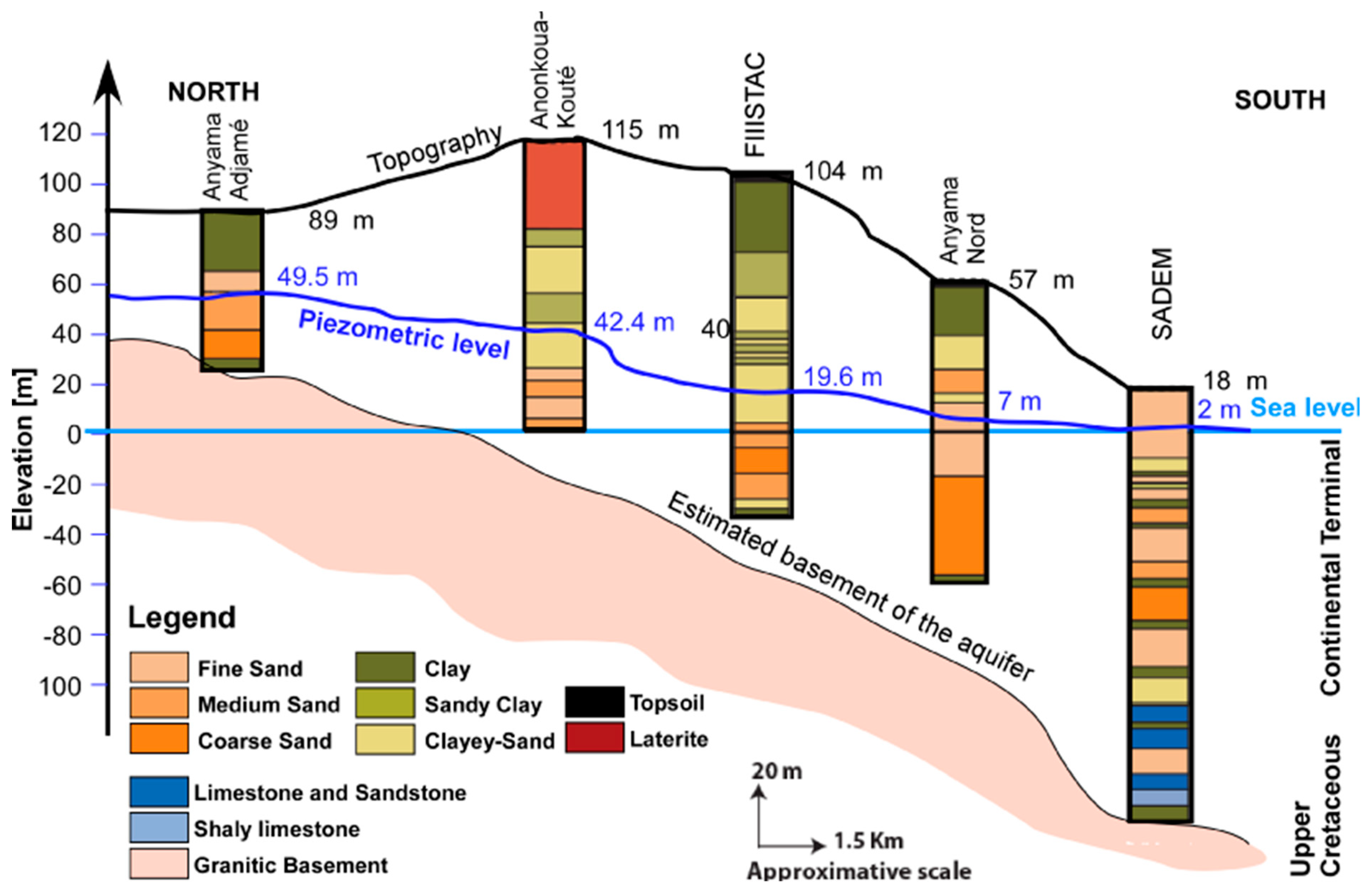
Figure 4.
North–south approximate cross-section of the coastal sedimentary basin in Abidjan from boreholes on 11 December 1992.
Figure 3 and Figure 4, which are based on a few drill logs, illustrate the approximate patterns of the west–east and north–south cross-sections of the study area considering the topography and aquifer base piezometric level on 11 December 1992. According to both cross-sections, there is a large variation in the lithological facies; some are recurrent, such as clayey sands, sandy clays and sands, and others, such as laterite, are observed in only one well. Some clay lenses are included in the various layers.
3. Materials and Methods
Numerical modeling can provide approximate solutions to the partial differential equations that describe flow in porous media [41]. According to Thangarajan and Rajan [42], in general in numerical modeling, little attention is given to obtaining an exact solution; instead, the focus is on obtaining a reasonable approximate solution. The general equation of groundwater flow can be written according to Hiscock and Bense [43] and Yeh et al. [44] as following:
where Kx,y,z [L·T−1] is the hydraulic conductivity along the x, y, and z axes; Ss [L−1] is the specific storage coefficient; h [L] is the hydraulic head; and t [T] is time.
The implementation of the numerical model FEFLOW 7.1 requires several steps. The main steps include the development of the conceptual model, the choice of numerical codes, the digitization of the model, the calibration and validation of the model, sensitivity analysis, and predictive analysis [45]. In the implementation of different models, a certain number of assumptions are established according to the characteristics of the representative elementary volume (REV), as defined by Bear [46], such as assuming that the aquifer is porous, unconfined, and continuous. In this case, the Abidjan aquifer is not hydraulically connected to the Quaternary and Maastrichtian aquifers. Recharge is constant and uniform in time and space. The 1978 piezometric data (year zero of the model) is representative of the average annual steady-state piezometric level under basic operating conditions. The transport of benzene is monophasic in its gaseous state, and it completely dissolves in the infiltration water. General mass transport equation is according to Ingebristen et al. [47] and Fitts [48]:
where [L2·T−1] is the hydrodynamic dispersion tensor; C [M·L−3] is the solute concentration; Qs [M·L−3·T−1] is the source term relating to the reaction of the solute, which can be a contribution or a loss; v [L·T−1] is the average linear speed; ne [-] is the effective porosity; ρ [M·L−3] is the fluid density; and t [T] is time.
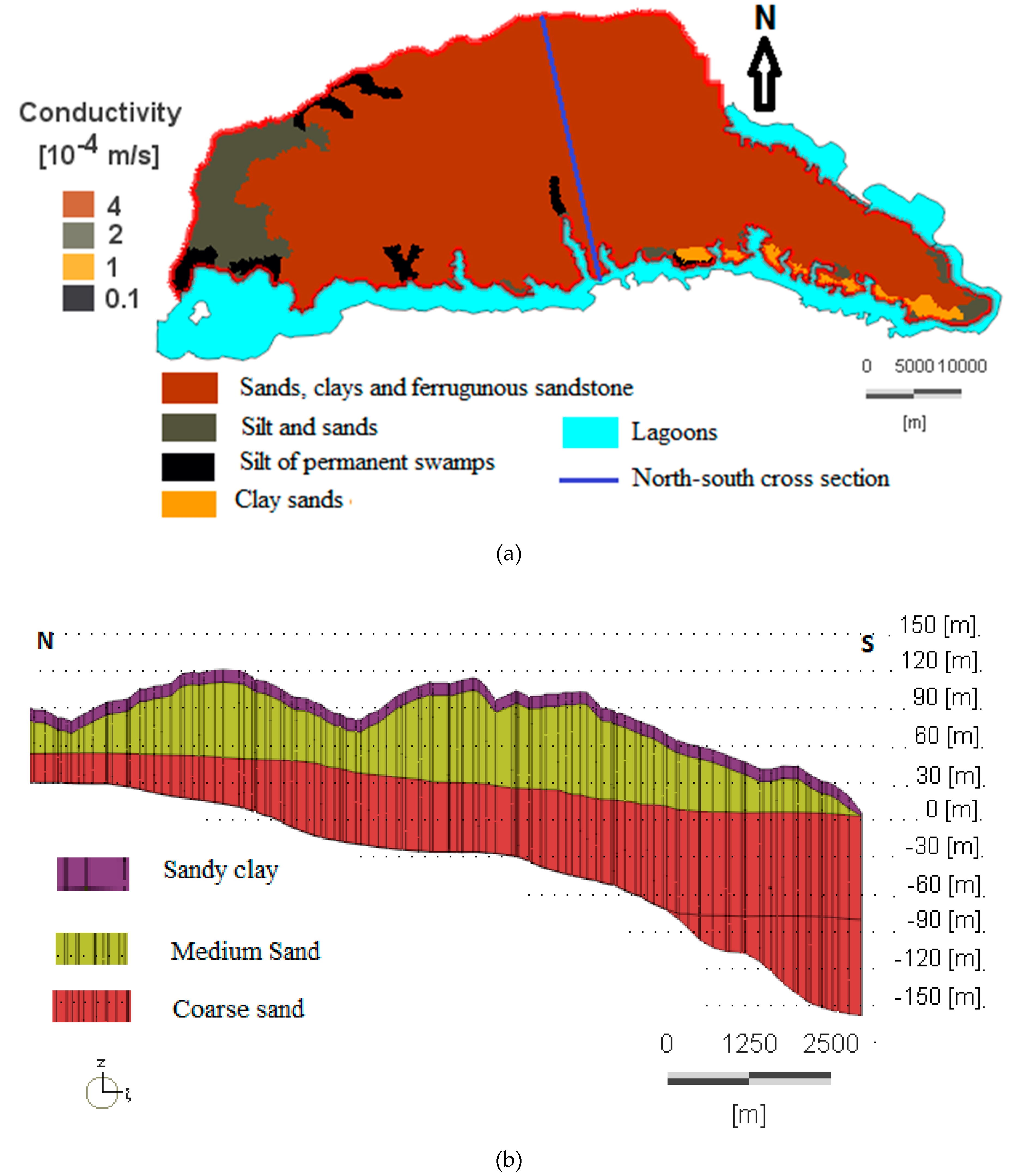
3.1. Layer Properties
The 3D model is composed of three main layers (Figure 5). The surface layer is clayey sand and has an average thickness of 10 m. The second layer is medium sand and has a thickness of 60 m. The third layer consists of coarse sand, and has an average thickness of 90 m. The hydraulic conductivities assigned to the domain range from 0.1 to 4 × 10−4 m/s [24,37] according to the geological formations of Abidjan. Figure 5a indicates the surface geology with four hydraulic conductivities. In view of the complexity of the geological formations and the heterogeneity of the lithological units of the Continental Terminal aquifer, and in order to simplify the reality, not all of the observed layers in the various drilling logs have been integrated in the model. Therefore, average properties are used, and the lithological units were regrouped (Figure 5b). Porosities ranged from 0.18 to 0.25 according to Jourda [24], Aghui and Biémi [37]. The porosity is 0.18 for sandy clay, 0.2 for medium sand, and 0.25 for coarse sand. Since the aquifer is unconfined and porous, the specific yield, which is equal to the porosity, is taken into account directly by the Finite Element subsurface FLOW system (FEFLOW). FEFLOW also requires a molecular diffusion coefficient as an input parameter, and the software calculates the dispersion. No value on the dispersion coefficient (FEFLOW user manual reference) was put. Specifically, the number of elements per layer was increased from 64,764 to 224,667. The average area for each element depends on the refinement (the benzene source and the boreholes areas), which ranges between 10,000–30,000 m2. Time steps of 365 days were attributed with the value of 14 for validation model and 52 for the prediction model. The lower limit is 1978, and the upper limits are 1992 (14 time steps) for the calibration model and 2030 for the predictive simulation (52 time steps).
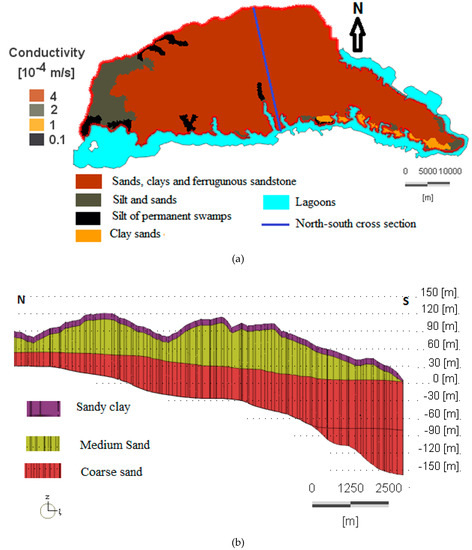
Figure 5.
Model characteristics: (a) map of the superficial geological formations of the model and the corresponding hydraulic conductivities, and (b) north–south profile of the model layers.
3.2. Boundaries of the Model
The solution of the subsurface flow equation is typically in a one, two, or three-dimensional domain, and includes its Euclidean space boundaries [49]. The unique and appropriate solution sought is that which corresponds to the particular boundary conditions of the elaborate conceptual system [48]. Therefore, if possible, the boundary and initial conditions of the model ought to be defined using natural hydrogeological boundaries as advocated by Anderson et al. [45].
3.2.1. Geographic Boundaries of the Model
The geographic coordinates of the modeled area are given in the WGS 1984 UTM Zone 30 North reference frame between 350,000–421,000 m on the x-axis, and 581,000 and 609,000 m on the y-axis. This area covers a domain of 986.8 km2 with a perimeter of 266.68 km. The modeling zone is limited to the north by contact with the crystalline basement and the Bété and Nieké Rivers, to the south by the northern edge of the Ebrié Lagoon, to the east by the Adjin and Potou Lagoons, and to the Bété River and the West by the Agnéby and Niéké rivers (Figure 1).
3.2.2. Boundary Conditions and Recharge of the Model
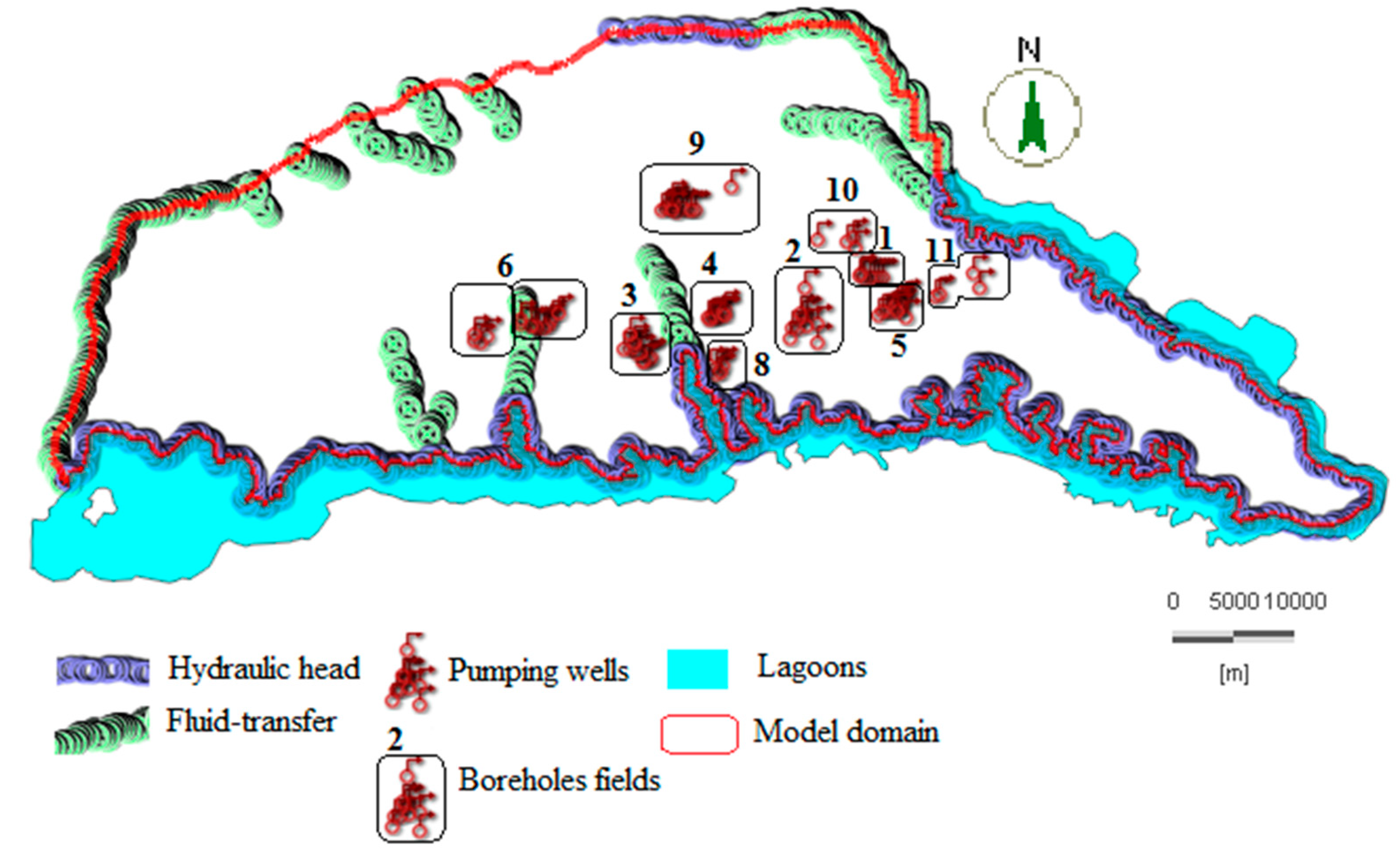
The different types of flow boundary conditions used in this work include imposed head, fluid transfer, and flow boundaries (Figure 6). Appendix A Table A1 gives the numbers and names of the pumping wells used in FEFLOW.
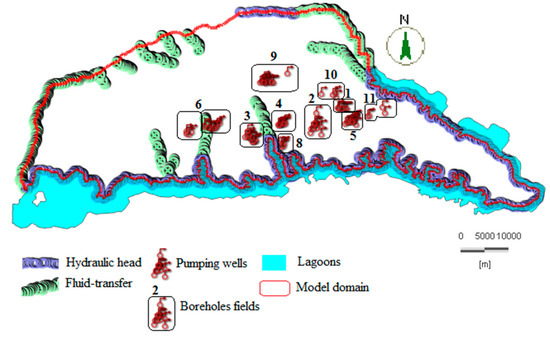
Figure 6.
Boundary conditions of the model. Hydraulic heads (58 m for the north, and 0.2 m for the south). Fluid transfer boundaries ranging from 0 m to 57 m according to the elevation. Borehole fields: 1 (Riviera Center), 2 (Zone Est), 3 (Zone Ouest), 4 (Zone Nord), 5 (Nord Riviera), 6 (Niangon), 8 (Adjamé Nord), 9 (Anoukoua Kouté), 10 (Djibi), and 11 (Abatar-Akandje).
Constant hydraulic head boundary conditions of 58 m (mean piezometric level) and 0.2 m (relative to the Ebrié Lagoon elevation) were imposed at the northern and southern boundaries of the model domain, respectively, to simulate equipotential curves. These heads represent the level of the water table. The choice of these imposed heads is justified because the model does not represent all of the sand formations, which essentially constitutes the aquifer of Continental Terminal. Therefore, they impose a head flow regime based on equipotential curves located upstream and downstream of the modeled aquifer zone. The fluid transfer values range from 0.2 to 57 m, according to the elevation. The vertical recharge rates assigned to the model range from 250 to 200 mm/year [19], resulting from the infiltration of precipitation and representing a so-called “volumetric fluid source” applied uniformly to the different zones in the model domain. In terms of boreholes, water withdrawals from the area were assigned in the form of constant pumping rates over time ranging from 0 to 7488 m3/day. These rates were distributed over 93 boreholes in the nine fields in the area.
3.2.3. Initial Conditions of Underground Flow
The initial conditions were based on data from 54 piezometers collected in 1978. These data are representative of the average annual piezometric level of the Abidjan aquifer in 1978, which was the reference year in which the pumping rate was very low, with 30 boreholes in service (Table 1).

Table 1.
Pumping rate in 1978.
4. Results
4.1. Groundwater Flow Model
The numerical flow models carried out with the FEFLOW 7.1 software made it possible to understand the behavior of the Abidjan aquifer according to the assumptions made, and thus to predict its evolution in the future. To achieve this, the various implemented models were calibrated and validated by real measurements such as the piezometric levels of 1978 and 1992. The flow models were made in two dimensions and in a saturated zone. It is assumed that the aquifer is porous, unconfined, and continuous. Steady-state calibration consisted of manually adjusting the hydrodynamic parameters of hydraulic conductivity and porosity by “trial and error”, as well as the boundary conditions that were imposed on the model. The year 1978 is the reference year for the simulation, because according to Kouamé [19], there would have been less pumping in the aquifer.
4.1.1. Model Calibration and Validation
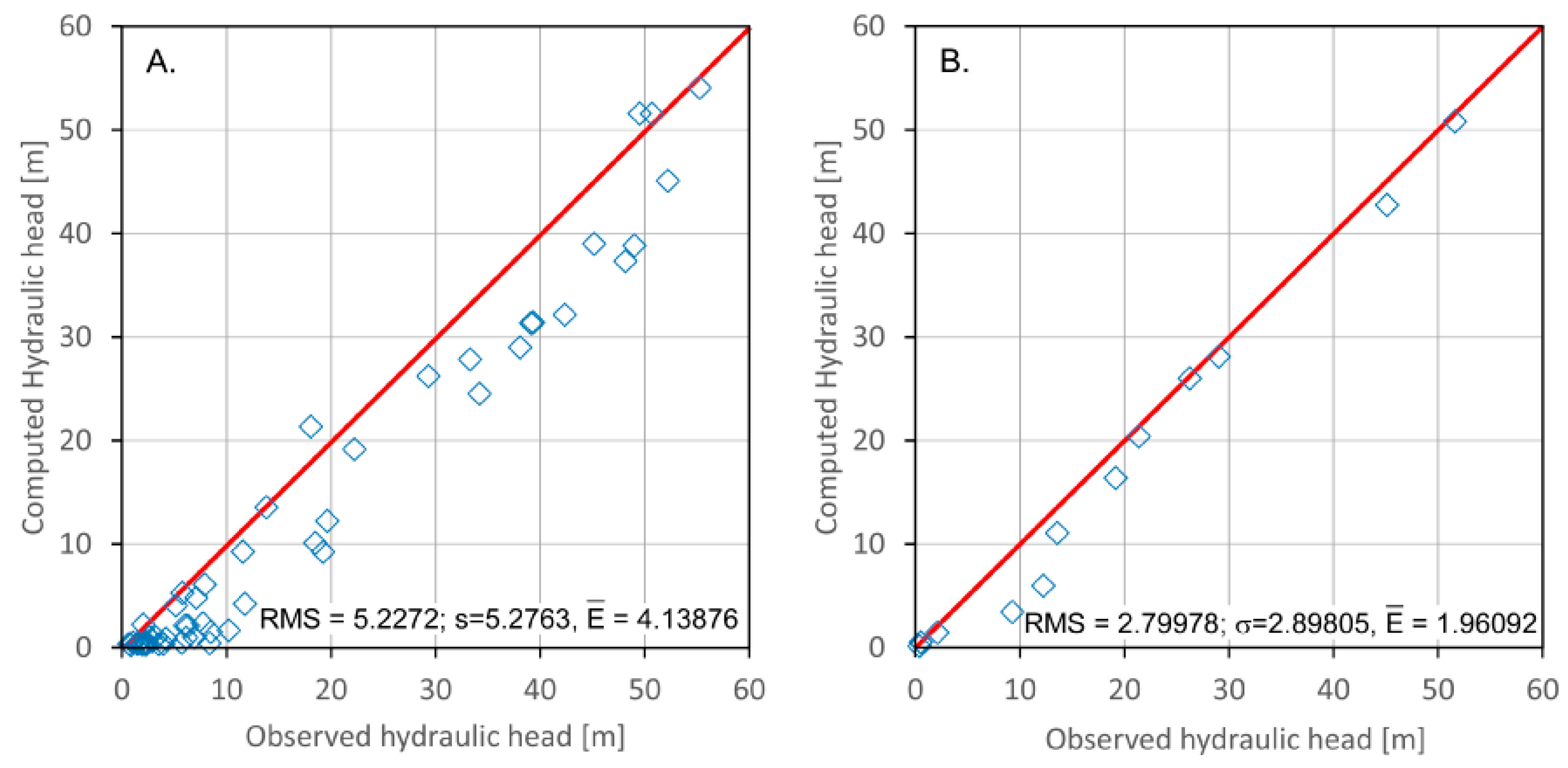
The model calibration and validation results were satisfactory. The Root Mean Square error (RMS) was 5.22% for the steady-state condition and 2.79% for the transient state (Figure 7).
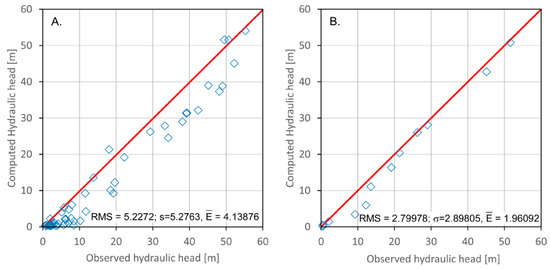
Figure 7.
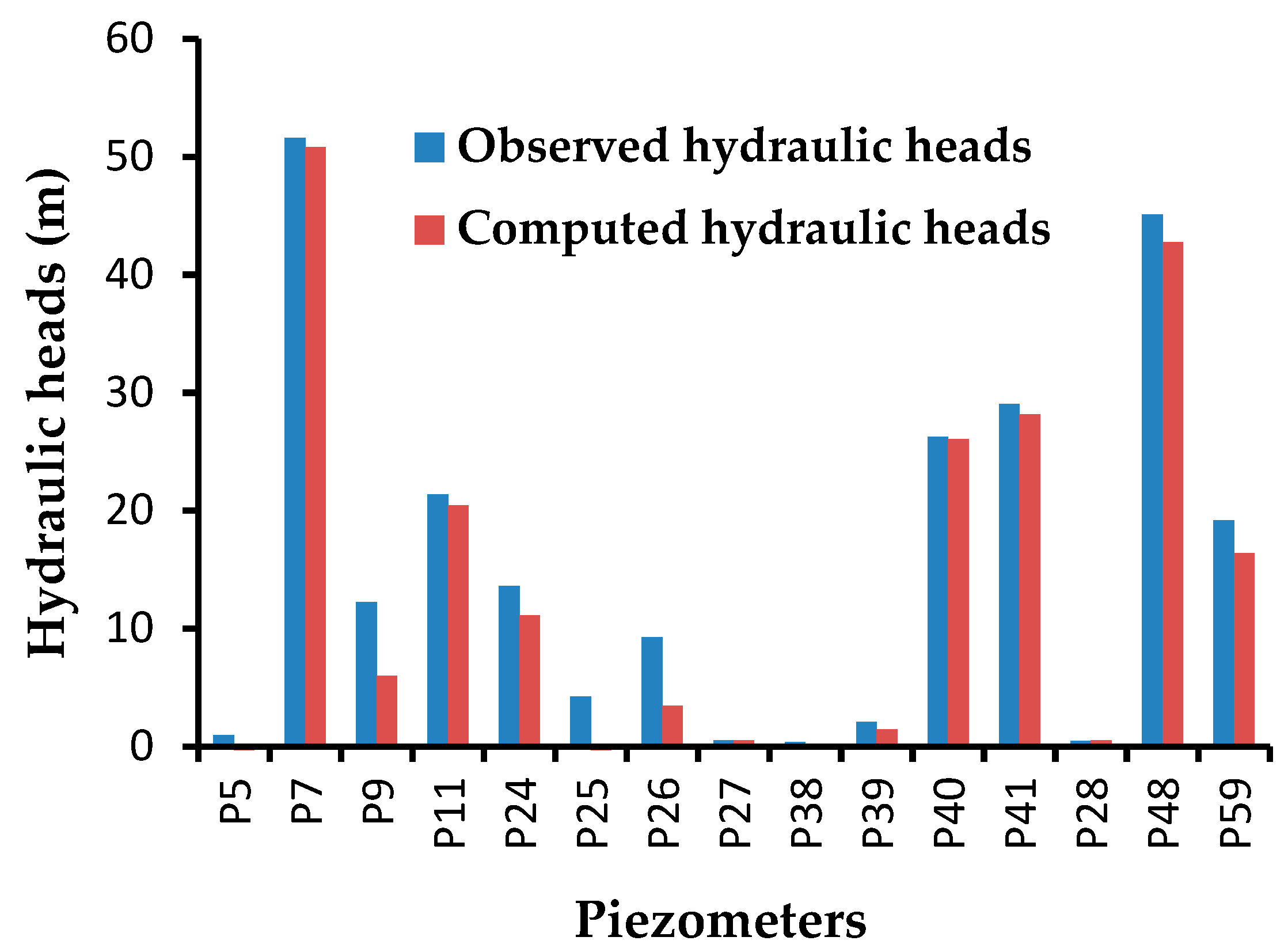
Diagram of the computed and observed hydraulic heads based on the simulation: (A) calibration and (B) validation. (m): Average of the absolute deviations, RMS (m): Root Mean Square error, σ (m): error standard deviation.
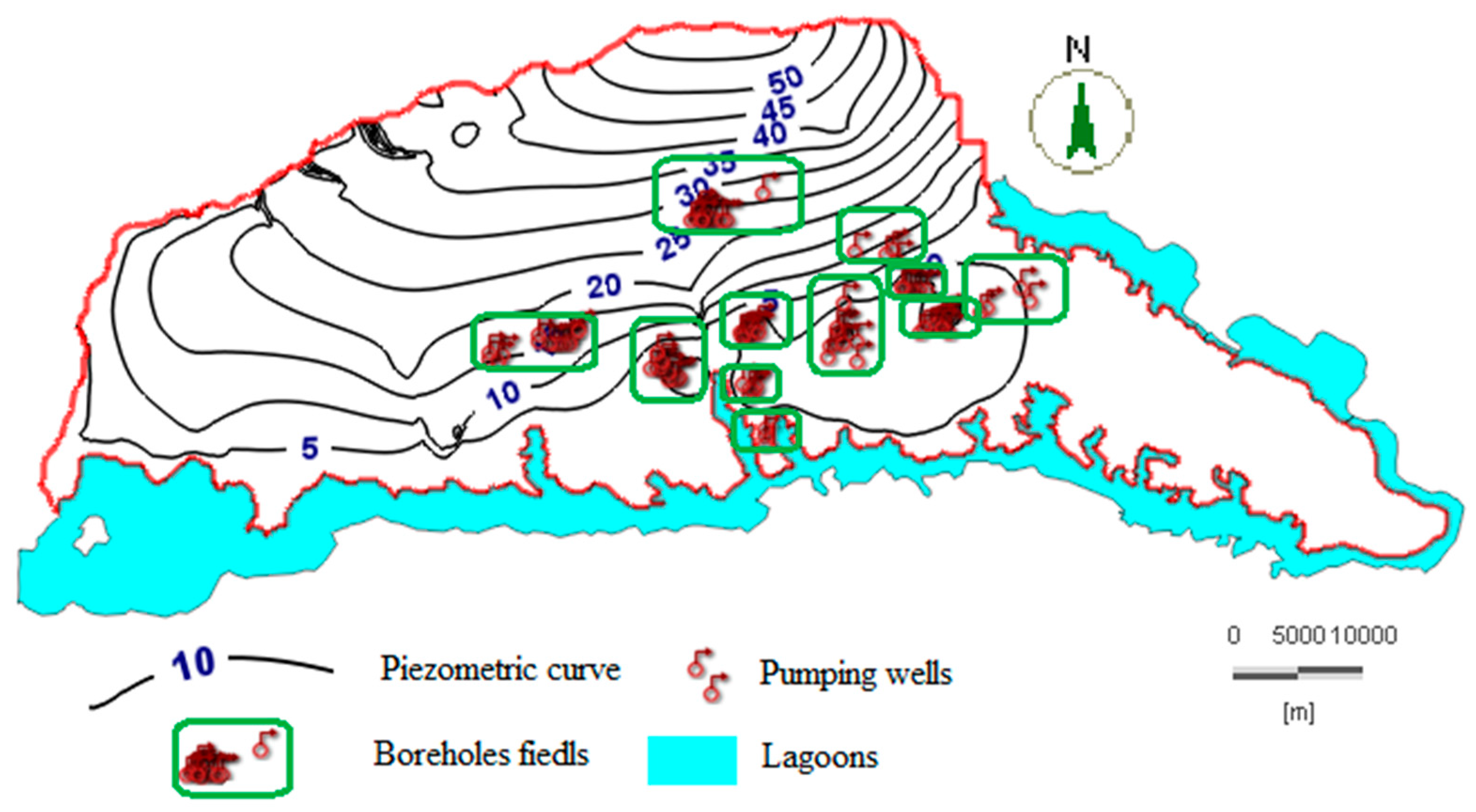
In the calibration of the groundwater flow model, the piezometric map from 1978 with a pumping rate of 177,504 m3/day was used. This rate was from 30 boreholes in service that were distributed unequally over the study area. Figure 8 shows the piezometric isolines in meters. The direction of underground flow is from north to south, as indicated by the decrease in the piezometric level from north (55 m) to south (five meters).
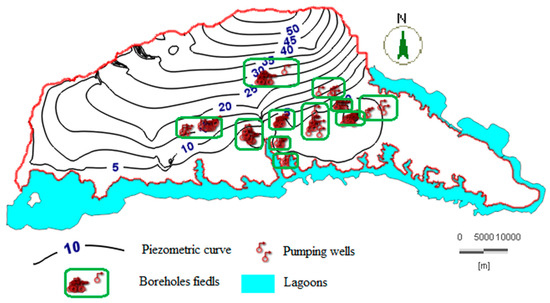
Figure 8.
Piezometric map simulated under steady-state conditions in the reference year (1978).
To validate the transient model, two years were chosen: 1978, the reference year, and 1992, year for comparison, with 14 time steps over a year. Notably, the actual piezometric levels that were observed in 1992 were compared with those simulated from 1978 to 1992 by the model. In this comparison, 15 piezometers that were active in 1978 and still functional in 1992 were used. After 5110 days, i.e., from 1978 to 1992, the number of pumping wells increased, and the flow rate increased from 177,504 m3/day in 1978 to 355,761 m3/day in 1992. The model remains valid despite the maximum deviation value of more than five meters that was observed at P26 (Zoo 1). In addition, in the calculated correlation coefficient between the observed and computed hydraulic heads, R2 is 0.96. Appendix A Table A2 gives the difference between the observed and computed hydraulic heads in 1978. Moreover, the water imbalance in the model (the difference between recharge and consumption) is 1.67 m3/day (Table 2).

Table 2.
Imbalance of the contributions calculated in 1992.
Based on the various scenarios that were done as a “trial and error”, various parameters were estimated for the calibration of the model: first in a steady-state, and then in transitory state. The estimated parameters are boundary conditions such as the hydraulic conductivity H, fluid-transfer rate, or i source/sink, such as the vertical recharge rates resulting from the infiltration of precipitation and finally the attribution of the pumping rate. Estimations are based on geological, hydrological, and hydrogeological realities. While calibrating, on one side, we compared the computed and observed head counts using the criteria of the RMS and, on the other side, we looked at the Imbalance from the “Rate Budget” panel in the FEFLOW software that sums the rate of the different estimated parameters of the model domain. Figure 9 illustrates the performance of the validation, and shows the differences between the observed and computed hydraulic heads for the transient state model.
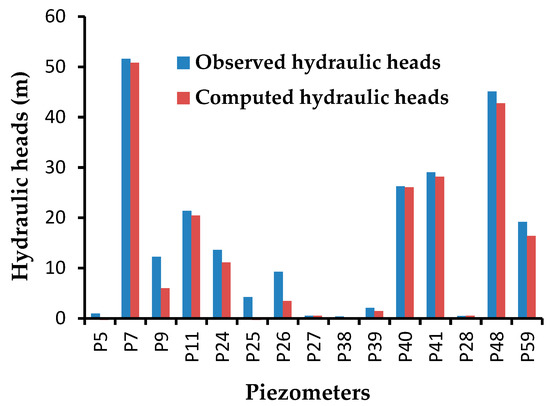
Figure 9.
Comparison of observed and computed hydraulic heads in the transient state after the transient state simulation for 1995. P5 (AKOUEDO), P7 (Ayam_Adjam), P9 (Filtisac), P11 (Hortifix), P24 (Niangon1), P25 (Zoo 1), P26 (Zoo 2), P27 (Akakro), P38 (Dahlia_Fleur), P39 (yop_pz_a8), P40 (Saph_v2_Nord), P28 (Eloka), P48 (Hotel_Kedj), and P59 (DCH6)
4.1.2. Simulation of the Piezometric Level of the Abidjan Aquifer
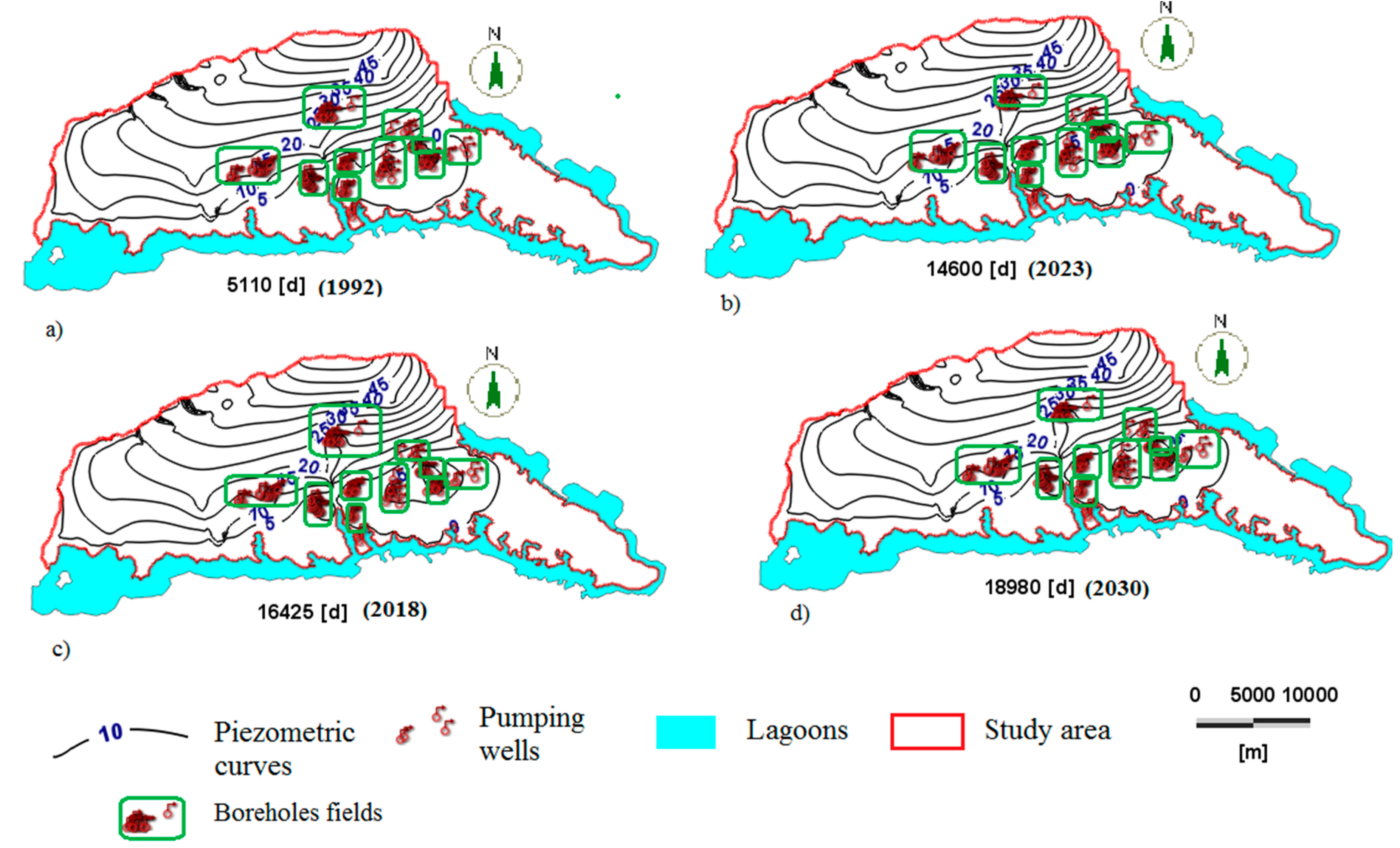
The flow model calibrated under steady-state conditions and validated based on a transient state was used for the predictive simulation of the piezometric level from 1978 to 2030. The pumping rate that was taken was only used for boreholes for the drinking water supply; those that were used for agriculture were not. Current evaporation and runoff have been taken into account in the recharge calculation. This value varies from 150 to 422 mm/a according to recent studies of Deh [12] and Kouame [19]. Here, the climate change effect has not been considered because, even if the impact can be strong [50], the resolution of forecast models and the urbanization scenario are beyond the scope of this paper. In addition, such study is in itself a larger question that will be the subject of further research in the next step. Appendix B Table A3 shows the different exploitation rates of the boreholes from 1978 to 2030. It should be noted that from 1978 to 2030, the flow consumption forecasts are from the SODECI, which is a drinking water distribution company in Côte d’Ivoire. Figure 10 shows the evolution of the simulated piezometric level as a function of time.
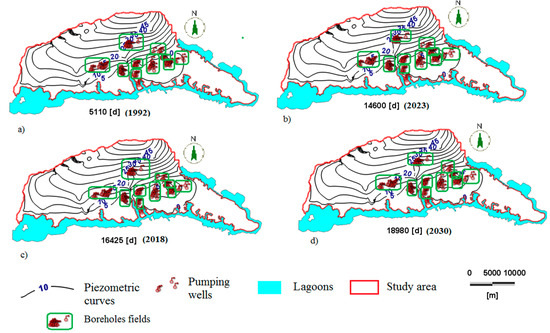
Figure 10.
Simulated piezometric isolines (five-meter interval) (a) 1992, (b) 2018, (c) 2023, and (d) 2030.
The analysis of these isolines over time shows a local change in the groundwater flow direction. A cone of depression is observed between piezometric isolines, especially at the pumping wells. These cones expand from 5110 to 18,980 days in the simulation. The different watercourses in the model provide a draining function toward the water table of the Abidjan aquifer. This draining process has been observed in previous studies [51,52]. Table 3 shows the values of the drawdown of the water table between 1978–2030. These values range from 0.0 (Eloka) m to 10.13 m (Filtisac).

Table 3.
Simulated drawdowns of the water table level from 1978 to 2030 at piezometer locations.
4.2. Benzene Transport Simulation
The transport model was simulated in three dimensions (3D) with FEFLOW 7.1 for the unsaturated zone and 2D for the saturated zone in the transient state. The input data are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Transport model input data.
The calibration of the model was done by trial and error. Referring to the geological formations of the region, the deposits are known to be subhorizontal. Also, after our on-site observations, it was obvious to see a very strong anisotropy of those deposits. Therefore, vertical hydraulic permeability is proportional to lateral hydraulic permeabilities. Several models were tried by dividing Kxx by two to nine, and the most suitable value is the number seven.
4.2.1. Unsaturated Zone
In the unsaturated zone, initial concentrations of 43.12 mg/L and 14.37 mg/L of benzene are injected at the N’Dotré and Anador gas stations respectively, which are the contaminant sources, under drilling conditions and without delay. The proportion of benzene in gasoline is 1% of the volume. Thus, 30,000 L of gasoline (volume of each tank) equals 300 L of benzene per tank. Knowing that the density of benzene is equal to 0.876 kg/L, or 876 kg/m3, the mass of benzene is 263 kg. The elevations at N’Dotré and Anador are 106.8 m and 114 m, respectively. The areas of the two sites are 6100 m2 and 18,298 m2, respectively. Assuming a maximum thickness of two meters from the soil surface, based on the aquifer volumes at both sites, the initial concentration at N’Dotré is 263/6,100 = 0.0431147 g/L = 43.12 mg/L, and that at Anador is 263/18,297.51 = 0.01437 g/L = 14.37 mg/L.
The Northern Abidjan District, which is mainly the Abobo municipality, is considered the main recharge area [52]. In addition, the volumes of the tanks of at the N’Dotré and Anador gas stations are known. The global pumping rate ranges from 177,000 m3/d to 470,000 m3/d at the beginning and end of the simulation, respectively. In this extreme case without any pollutant attenuation, only hydrodynamic dispersion and the infiltration of water contribute to decreasing the concentration of dissolved benzene from the ground surface to the water table. Figure 11 shows the north–south cross-section of the area to illustrate the vertical migration of benzene.
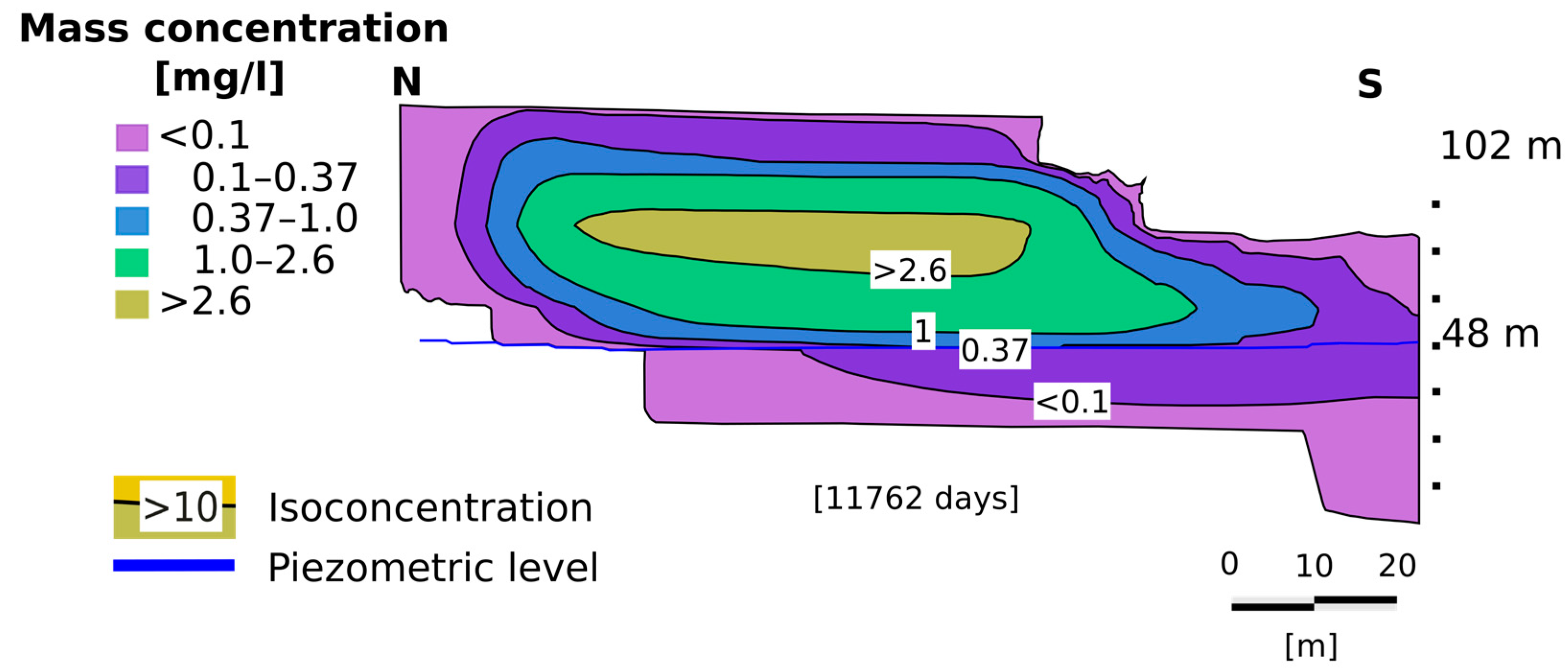
Figure 11.
North–south cross-section of the area.
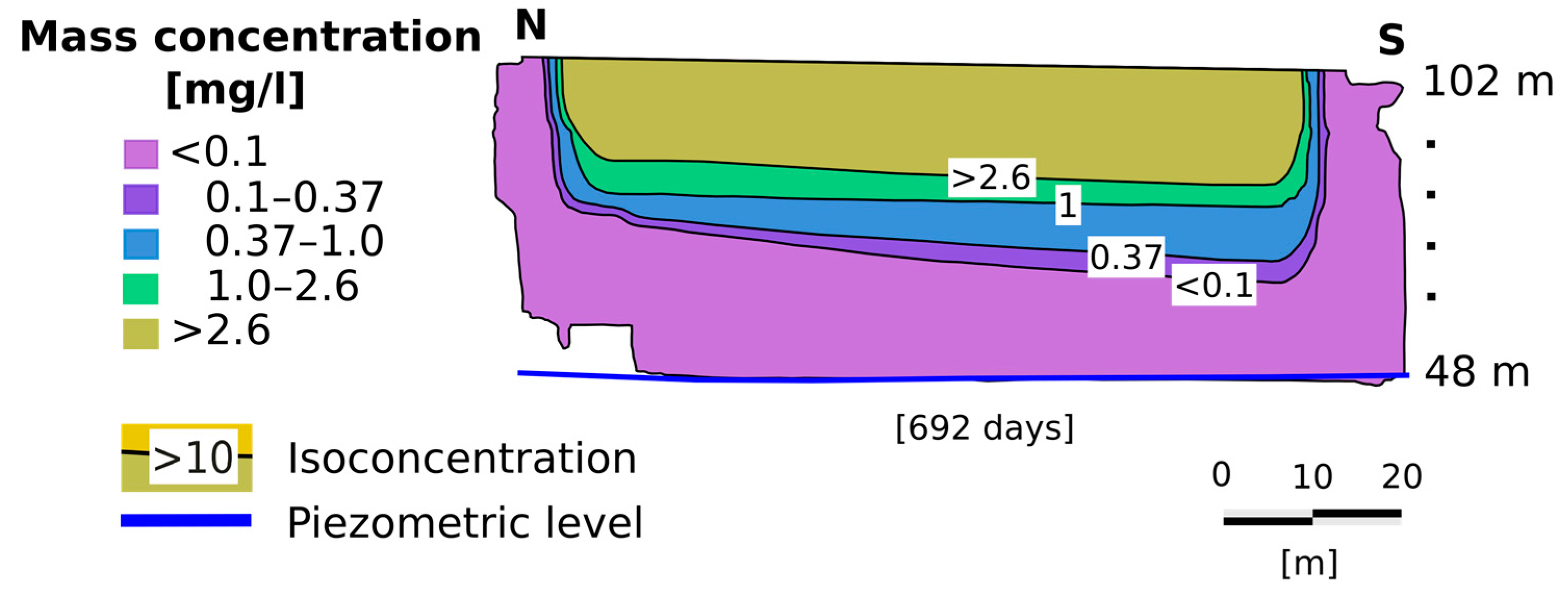
After 692 days (one year and 10 months), dissolved benzene was detected (Figure 12). The allowable levels of benzene in water are 0.001 mg/L and 0.01 mg/L, respectively, according to the European Union and WHO. The aquifer was contaminated after 1132 days according to the European standard, and after 1962 days according to WHO.
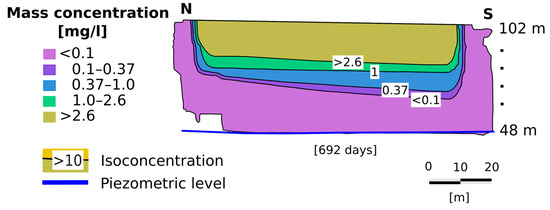
Figure 12.
Concentration of 8 × 10−5 mg/L of dissolved benzene detected on the water table at 692 days.
The maximum concentration of 0.37 mg/L of dissolved benzene (Figure 13) was reached after 11,762 days (32 years and two months). At Anador, dissolved benzene was detected after 1542 days, or approximately four years and two months. The water table was polluted in this zone at 2692 days (seven years and four months). The maximum concentration of 0.04 mg/L was reached in 33 years, and this concentration remained until the end of the simulation at 18,980 days (52 years).
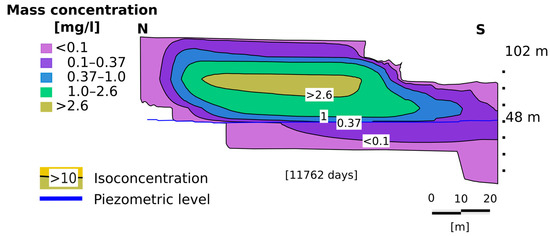
Figure 13.
Maximum concentration of 0.37 mg/L of dissolved benzene detected on the water table at 11762 days (32 years and two months).
4.2.2. Saturated Zone
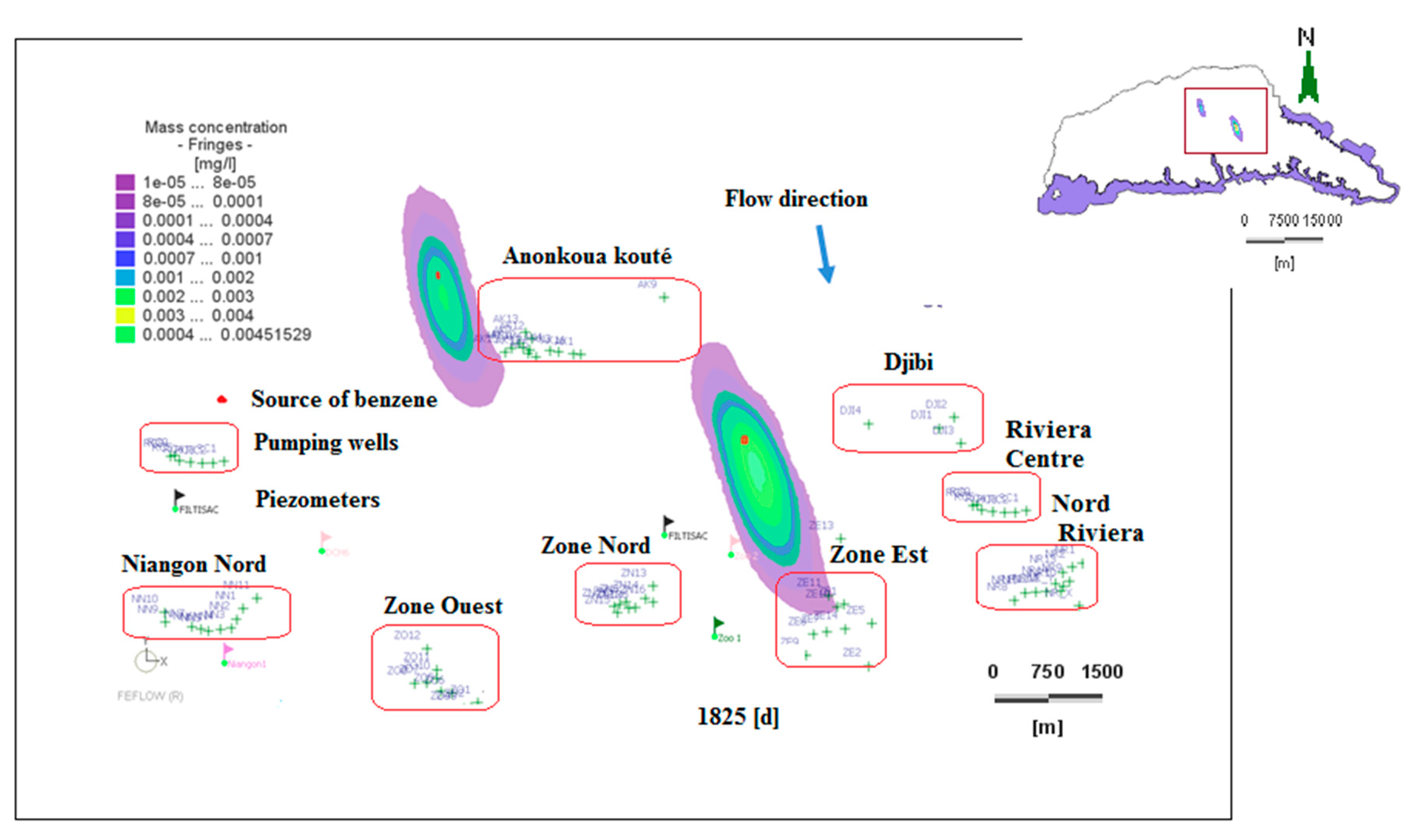
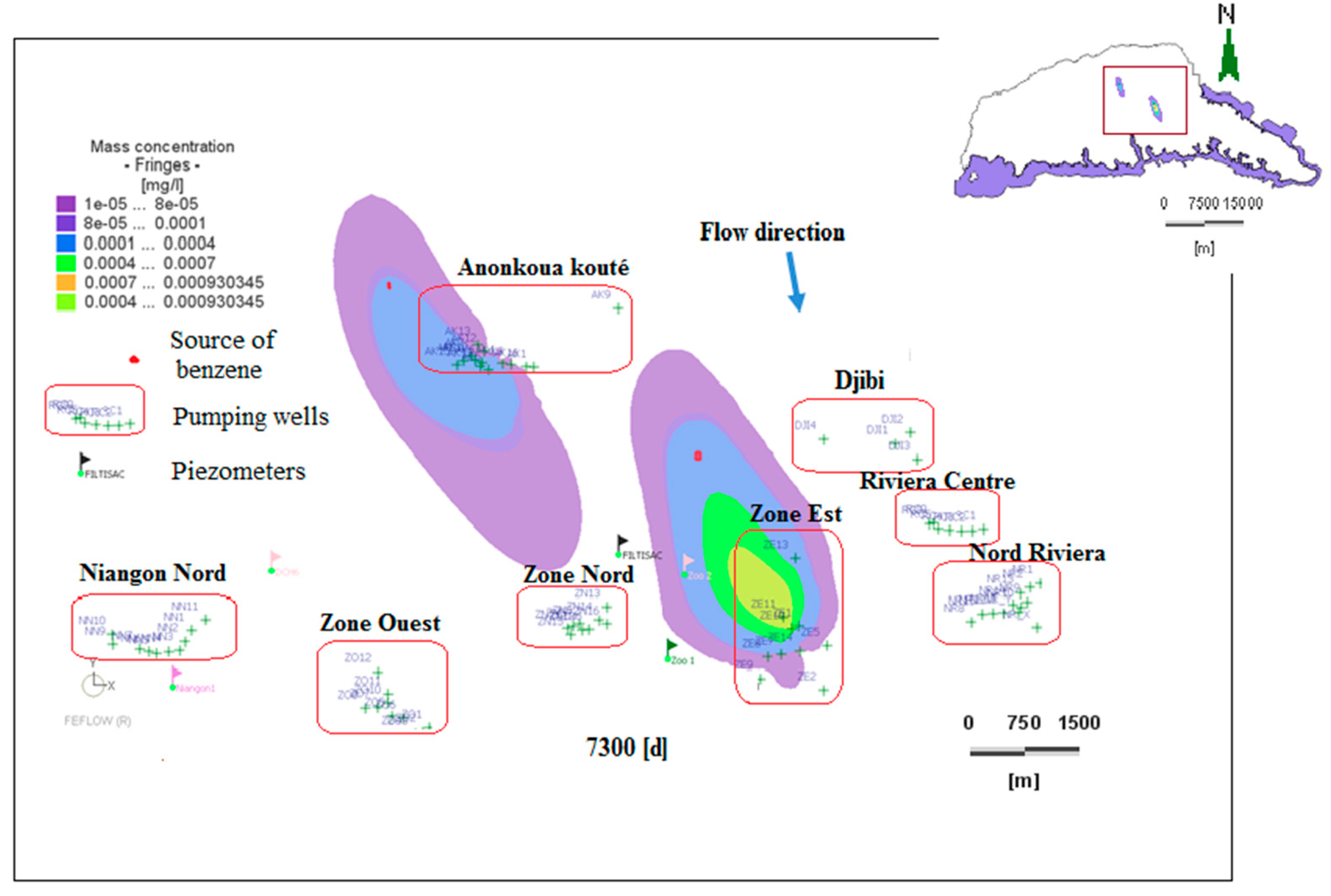
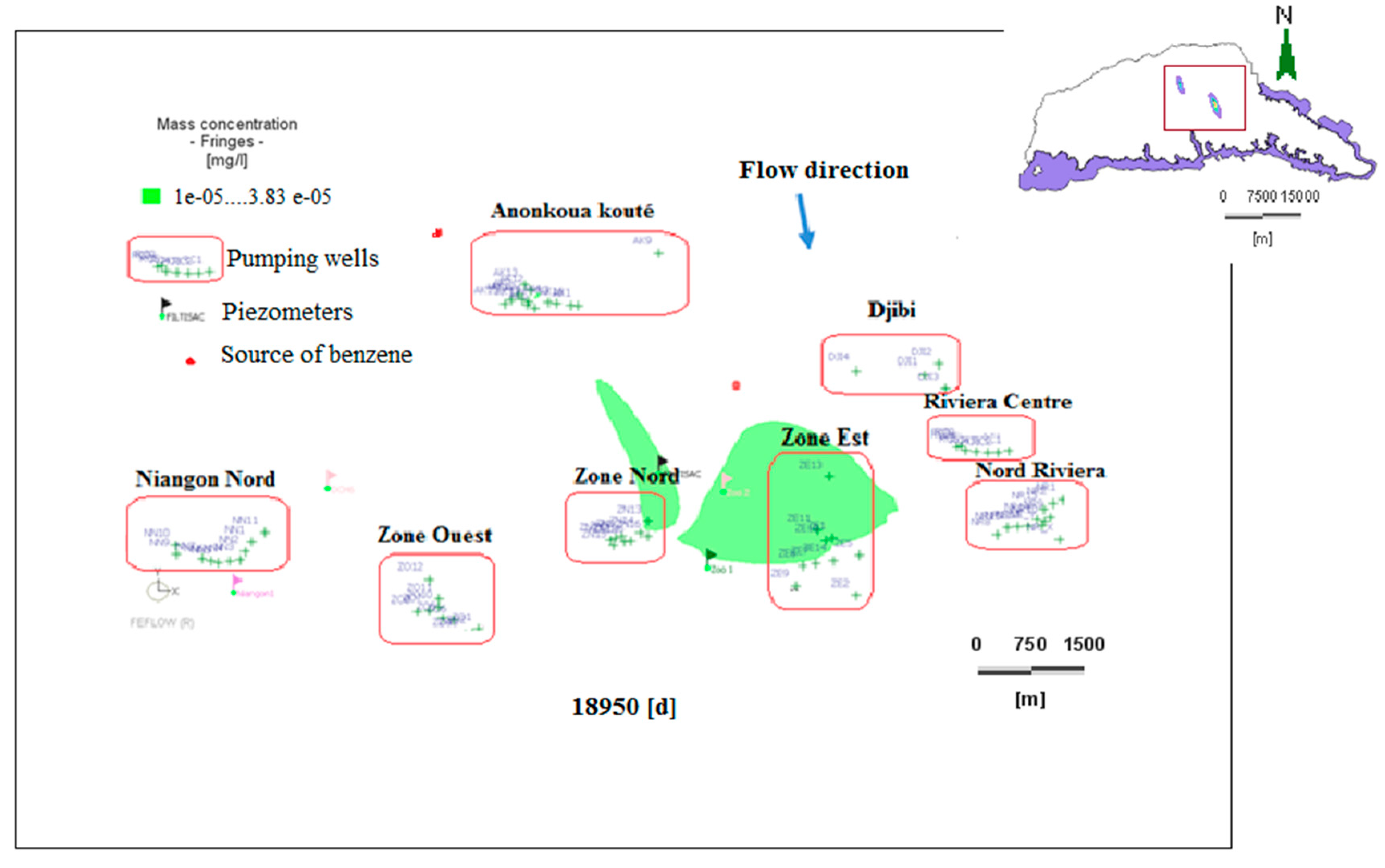
In this analysis, the maximum concentration of 0.37 mg/L from the unsaturated zone simulation was injected into the saturated zone at the N’Dotré and Anador sites. Figure 14, Figure 15 and Figure 16 show the dissolved benzene plume in two dimensions (2D) at five, 20, and 52 years without delay. All these pollution plumes evolve in a north–south direction. These plumes of pollutants extend considerably and reach some of the surrounding boreholes.
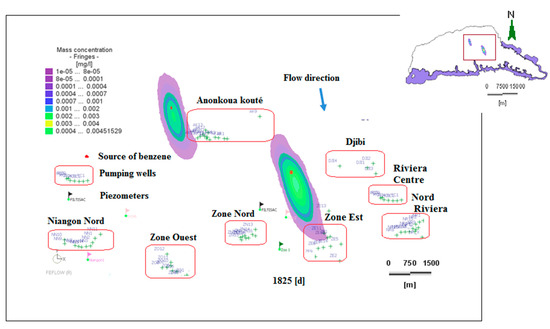
Figure 14.
Dissolved benzene plume dispersion at 1825 days (1983).
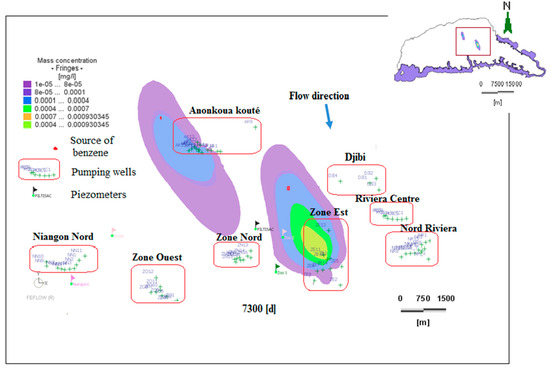
Figure 15.
Dissolved benzene plume dispersion at 7300 days (1998).
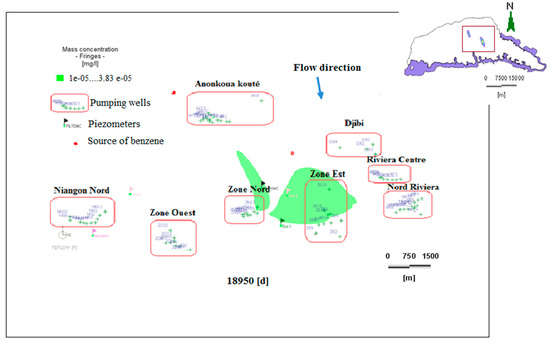
Figure 16.
Dissolved benzene plume dispersion at 18,980 days (2030).
Table 5 shows the concentrations recorded in the boreholes over time. These contaminant detection times at a concentration of 8 × 10−5 mg/L are between 2190 days and approximately six years in borehole ZE11 and 4015 days (11 years) in ZE7 at the Anador site. The ZE11 borehole of the East Zone capture field is polluted after 4380 days of simulation (12 years), and has a maximum concentration of 0.0011 mg/L at 5475 days (15 years). A maximum concentration of 0.0008 mg/L in 5110 days (14 years) was detected in borehole ZE10. Although this concentration does not reach the limiting value of 0.001 mg/L, the concentration remains significant. Therefore, dissolved benzene was detected in five boreholes in the East Zone capture field. Additionally, the southern part of the plume at Anador spatially expands (Figure 16). A concentration of 8 × 10−5 mg/L of dissolved benzene was recorded in some boreholes between 2400–5475 days. These boreholes are AK15, AK8, AK17, AK5, AK6, AK10, AK7, and AK4, which are close to the N’Dotré site.

Table 5.
Time of appearance of dissolved benzene in boreholes close to the Anador site.
4.3. Overall Time and Boreholes Threatened by Pollution
The overall transport time of dissolved benzene is calculated by adding the vertical transfer time and the horizontal time. The vertical time is the time that the pollutant takes to travel from the ground surface to the water table. The horizontal time expresses the duration of contaminant transport from the source at the water table of the aquifer to the nearest boreholes. Table 6 shows these different overall times. The results in this table indicate that the overall transport time of dissolved benzene from the soil surface to some boreholes ranges from 38 to 47 years. Considering the assumptions made at the start of the simulations, only the ZE11 borehole in the East Zone becomes polluted after 44 years and two months because the threshold concentration of 0.001 mg/L, according to the WHO, was reached. The ZE11 borehole is four km from the Anador site. In addition, some boreholes in the “East Zone” and “Anonkoua Kouté” areas would be threatened if an accident were to occur or if the tanks at the N’Dotré and Anador gas stations ruptured. These boreholes include ZE1, ZE7, ZE8, ZE10, ZE13, and ZE14 for the Anador site, and AK15 AK5, AK6, AK7, AK8, AK10, AK4, and AK17 for the N’Dotré site. The most exposed boreholes remain ZE11 and ZE10.

Table 6.
Overall time of transport of dissolved benzene.
5. Discussion
5.1. Groundwater Flow Model
The Continental Terminal aquifer in the region of Abidjan is the major source of drinking water for the local population. To manage, predict, and protect the supply through determining its fluctuations and quality over time, numerical groundwater flow models have been constructed by FEFLOW 7.1.
The model was implemented under steady-state conditions and calibrated based on hydraulic head data from 1978 collected by 54 piezometers. Based on the agreement between calculations and the measurements at pumping wells in the region of Abidjan [37,27], hydraulic conductivities ranging from 0.1 to 4 × 10−4 m/s were imposed on the model domain. The model converged, and the RMS was 5.22% with a distribution coefficient of 0.96, which reflects a good fit. Despite this good calibration result, large differences were observed between some of the measured and computed hydraulic heads. Such is the case for the Plantation-Sabo piezometer, where a head of 48.15 m was observed in the field, but the modeled value was 37.35 m, which is a difference of more than 10 m. However, this difference between the hydraulic heads can be explained by the groundwater table not being in static reality, but rather in perpetual fluctuation. Additionally, the geological formations of the Continental Terminal aquifer in the region of Abidjan are extremely complex. It should be noted that the pumping boreholes and wells remained in operation during the 1978 piezometric surveys. The 1978 simulated piezometric map shows that groundwater circulates from north to south and from north to east, which confirms the findings of Deh [12] and Kouame [19].
After the model has been calibrated, it was validated in a transient state to observe the water table fluctuations over time. Fifteen of the 54 piezometers in 1978 were still operating in 1992, and were selected for model validation from the steady state 1978 model to the transient 1992 model. The RMS of the calibrated transient model was 2.79%. Thus, the piezometric level was effectively simulated from 1978 to 2030. The variations in the isolines over time can be explained by the increase in the pumping rate due to the higher water demand of the city of Abidjan, which has led to an increase in withdraws from 117,505 m3/d to 468,415 m3/d. A maximum drawdown of over nine meters was observed at Filtisac and Zoo 2. This area of the model domain is also the zone with the largest fluctuations. Additionally, the Niangon region experienced a drawdown of more than three meters. This change can be explained by the implantation of new boreholes with pumping, which affects the water level. Conversely, the western and northeastern parts of the Abidjan region did not observe significant drawdowns and remain favorable areas for new drilling, as was clearly stated in Kouame [19]. The widening of the drawdown cone around the boreholes implies that the water withdrawals exceed the imposed recharge. This simulation made it possible to observe the behavior of the Abidjan aquifer, and the numerical groundwater flow model is a good management tool for the Abidjan aquifer that can be used by the authorities to make decisions concerning the Continental Terminal aquifer.
5.2. Simulation of Transport of Dissolved Benzene in the Unsaturated Zone
The initial concentrations of dissolved benzene of 43.12 mg/L and 14.37 mg/L were injected at the Shell gas stations in N’Dotré and Anador respectively in order to track the vertical path of contaminant transport from the ground surface to the water table. Dissolved benzene is observed at the top of the aquifer after one year at the N’Dotré site and after four years at the Anador site. The pollutant will reach the water table after three years at N’Dotré and seven years and four months at Anador. At these two sites, Kouamé [19] estimated that under the same flow conditions and an average infiltration rate, the pollutant would be detected after four years at the surface of the water table at N’Dotré, but not detected at Anador. This difference in results may be due to the greater depth of the aquifer at Anador.
5.3. Simulation of the Transport of Dissolved Benzene in the Saturated Zone
In the saturated zone, the source area of contamination and the surrounding borehole areas have been numerically refined because according to Matti and Tacher [57], refinement makes it possible to improve the accuracy of calculations and measurements. Specifically, the number of elements per layer was increased from 64,764 to 224,667. As the area of the contaminant plume increases during transport, the concentration decreases. According to Wiedemeier et al. [58], this change is due to the dispersive effect of the pollutant flow in the aquifer, which results in the displacement of dissolved benzene in different directions. At both sites, the concentration plume moves toward the boreholes due to pumping. In fact, any pollutant will eventually reach the surrounding pumping wells [59]. Pumping wells represent a type of convergence point that reduces the dispersion of the contaminant. At the end of the simulation (52 years of simulation), the maximum concentration remained very low, at 1 × 10−8 mg/L of dissolved benzene. The contamination plume also spatially expands from north to south in the direction of groundwater flow. A previous study of Gomez and Alvarez [60] regarding the presence of ethanol in gasoline also observed the extension of a benzene plume. The contaminant will reach boreholes in the “East Zone” and “Anonkoua Kouté” fields. Additionally, the horizontal transport time varies between six and 15 years for the transient state model.
5.4. Overall Transport Time of Dissolved Benzene
Adding the vertical and horizontal transport time results yields a global transport time ranging from 38 to 47 years for dissolved benzene. At these two sites (N’Dotré and Anador), Deh [12] obtained a global transport time for PCE between 36–60 years. The difference between these times could be explained by the characteristics of hydrocarbon contaminants being different, and among other differences, each having distinct viscosity and density traits. This overall transport time of dissolved benzene could be shorter if the pollutant flow path includes channels with high hydraulic conductivity.
5.5. Polluted and Threatened Boreholes
Based on the above findings, ZE11 in the “East Zone” area, which is four kilometers from the Anador gas station, would become polluted after 44 years and two months if benzene were released. Six boreholes in the same zone namely, ZE1, ZE7, ZE8, ZE10, ZE13, and ZE14 and eight in the “Anonkoua Kouté” area namely, AK15 AK5, AK6, AK7, AK8, AK10 AK4, and AK17 would be threatened by contamination, although the concentration of 0.001 mg/L was not reached. It should be noted that the borehole ZE10 recorded a level of 0.0008 mg/L, or almost 0.001 mg/L, after 46 years. This time scale could be important, but because dissolved benzene is lighter than water, it could infiltrate air pockets and form pools of contamination. Adams and Reddy [61] revealed that this type of light hydrocarbon can float on the surface of the water table and form pools, and when the water table level fluctuates, these areas can be saturated, which contributes to the trapping of the contaminant in the pores of the soil, which is often called residual contamination. Therefore, special attention should be paid to these sites in cases of disasters or major accidents. For soils containing immiscible pollutants, these dissolved contaminants can be released for years before concentrations significantly decrease [62]. It should also be noted that dissolved benzene could migrate 10 to 100 times faster in coarse grains than in fine grains. Although the results of these different simulations are based on calibrated and validated models, it is important to note that due to a lack of basic data, several assumptions have been made. Additionally, it was necessary to use data from the literature and archives, such as the piezometric data from 1978. These same data were used to model the water table of the Abidjan aquifer in previous studies [12,19,51]. Consequently, the proposed numerical prediction models can serve as predictive tools for the management and protection of the Abidjan aquifer. However, numerical modeling calculations are theoretical, and must therefore be used to guide field investigations [62].
5.6. Pollution Issues and Perspectives
Based on the available data, the present model is very innovative in the way that it has used a compilation of study done on the Abidjan District aquifer [12,19,24,28,52] by many authors. Although, for example Kouamé [28] only modeled the zone of the Landfill of Akouédo, Jourda [24] did not do a numerical modeling of the Abidjan District, and Kouassi [52] modeled the geometry of the aquifer. The present study is innovative in the way that it is complete, as the model has been calibrated at steady state with a set of data of 54 piezometers from 1978, and it was then refined in a transient state with a set of 15 piezometers. The model includes the unsaturated zone, allowing the simulation of the presence of a contaminant from ground to the piezometric surface, and the saturated zone allowing the simulation of the presence of a contaminant from the surface of the piezometric level to the surrounding boreholes. Although no previous studies had simulated the contaminant benzene, that is part of oil.
In future research, the transfer of the other main components of gasoline will be simulated. Additionally, the specific vulnerability of hydrocarbons at the level of the municipalities of the district of Abidjan will be mapped, and the saline intrusion in the Abidjan region with the proposed model will be also simulated.
6. Conclusions
The groundwater flow patterns in the Abidjan aquifer simulated with the FEFLOW 7.1 code indicate that the water in this aquifer flows from north to south. The predictive piezometric simulation of the water table from 1978 to 2030 shows a drawdown ranging from zero to 10 m at all of the piezometers, especially at Akakro and Filtisac. These large differences are mainly explained by the pumping rate and data limitations. The western and northeastern parts of the region have not experienced drawdown variations, and remain areas that are favorable for the construction of new boreholes. These results must be refined by applying different climate change scenarios [50], potentially impacting strongly the recharge as well as land cover use practice in the future. Nevertheless, the management of the Abidjan groundwater will be challenging tasks, which needs further studies, including the climate and land use changes.
A permissible concentration of 0.001 mg/L for benzene according to the European Union was reached after 44 years of simulation in borehole ZE11. Fourteen boreholes are threatened by pollution, and possible air pockets can form contamination pools. Therefore, special attention must be paid to this site in the case of disasters or major accidents. It should also be noted that dissolved benzene can migrate 10 to 100 times faster in high-permeability channels (coarse sand), which would greatly reduce the overall transport time. The over contaminant transport scenario is alarming, but considerable uncertainties related to the heterogeneity of the material and the future recharge due to urbanization and climate change remain. The operating conditions must be carefully considered for the future of the Abidjan aquifer. This work provides decision support tools for the management of groundwater resources in the event of a disaster, but also provide a good basis for future research studies.
Author Contributions
A.A.K. created and ran the models, performed the literature review, and wrote the original draft. A.G. Bi Tie, M.H.D., and M.J. supervised the paper. A.A.K., J.K.K., and M.J. conceived the subject of the paper; A.A.K., J.K.K., and C.M. implemented models; and A.A.K., M.J., C.M and M.H.D, made most of the corrections during the reviewing process of the paper.
Funding
This research received external funding from the Foundation Herbette of the University of Lausanne (6,713 CHF) and the Swiss Center for Scientific Research in Côte d’Ivoire (3,300,300 FCFA).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the DHI WASY GmbH Group in Berlin for giving us a free academic license for the FEFLOW code. We also thank the Foundation Herbette and the Swiss Center for Scientific Research, who financed the field work. In addition, we are thankful to the Institute of Earth Sciences of the Faculty of Geosciences and the Environment of the University of Lausanne (Switzerland) and the Laboratory of Geosciences and the Environment of Nangui-Abrogoua University (Côte d’Ivoire), who financially supported this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Numbers and the names of the boreholes used in FEFLOW 7.1.
Table A1.
Numbers and the names of the boreholes used in FEFLOW 7.1.
| Boreholes Fields | Designation | Number of Boreholes | Boreholes Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone Nord | ZN | 9 | ZN5, ZN6, ZN8, ZN11, ZN12, ZN13, ZN14, ZN15, ZN16 |
| Anonkoua Kouté | AK | 14 | AK1, AK3, AK4, AK5, AK6, AK7, AK8, AK9, AK10, AK12, AK13, AK15, AK16, AK17 |
| Niangon Nord | NN | 10 | NN1, NN2, NN3, NN4, NN5, NN6, NN7, NN9, NN10, NN11 |
| Zone Ouest | ZO | 11 | ZO1, ZO2, ZO3, ZO4, ZO5, ZO6, ZO7, ZO8, ZO10, ZO11, ZO12 |
| Adjamé Nord | AN | 5 | AN1, AN2, AN7, AN8, AN9 |
| Zone Est | ZE | 11 | ZE1, ZE2, ZE5, ZE7, ZE8, ZE9, ZE10, ZE10, ZE11, ZE13, ZE14 |
| Nord Riviera | NR | 12 | NR1, NR2, NR8, NR9, NR10, NR11, NR12, NR13, NR14, NR16, NR_X, NR_Y |
| Riviera center | RC | 7 | RC1, RC2, RC3, RC4, RC5, RC9, RC8 |
| Plateau | Plateau | 3 | C4, C5, IFAN |
| Djibi | DJI | 4 | DJI1, DJI2, DJI3, DJ4 |
| Niangon2 | N2 | 4 | N2F5, N2F6, N2F7, N2F9 |
| Abata | ABA | 2 | AB1, ABA2, |
| Akandje | AKA | 2 | AKA1, AKA2 |
| Total | 13 | 93 |

Table A2.
Difference between the observed and computed hydraulic heads in 1978.
Table A2.
Difference between the observed and computed hydraulic heads in 1978.
| Piezometers | Observed hydraulic heads (m) | Computed hydraulic heads (m) | Difference (m) | Piezometers | Observed hydraulic heads (m) | Computed hydraulic heads (m) | Difference (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.89 | 6.08 | 1.81 | P14 | 0.84 | 0.23 | 0.61 |
| A10 | 6.04 | 2.14 | 3.90 | P18 | 1.92 | 0.32 | 1.60 |
| A7_Bis | 10.19 | 1.67 | 8.52 | P4 | 2.91 | 0.65 | 2.26 |
| AKOUEDO | 6.13 | 0.98 | 5.15 | P5 | 2.27 | 0.61 | 1.66 |
| Anonk_Koute2 | 42.36 | 32.15 | 10.21 | P65 | 1.05 | 0.50 | 0.55 |
| Ayam_Adjam | 49.52 | 51.60 | −2.08 | P7 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.30 |
| Ebimpe_Couv | 50.69 | 51.57 | -0.88 | P70 | 2.01 | 2.24 | -0.23 |
| Filtisac | 19.62 | 12.23 | 7.39 | P72 | 5.16 | 4.09 | 1.07 |
| Grand_Semin | 55.25 | 54.07 | 1.18 | Dahlia_fleur | 3.95 | 0.39 | 3.56 |
| Hortifex | 18.06 | 21.36 | −3.30 | yop_pz_a8 | 6.32 | 2.11 | 4.21 |
| Mission | 5.77 | 5.30 | 0.47 | Saph_v2_Nord | 29.3 | 26.24 | 3.06 |
| Niankon_KM_13 | 11.56 | 9.28 | 2.28 | vp_sodepalm | 38.07 | 29.01 | 9.06 |
| P13 | 1.61 | 0.43 | 1.18 | DCH2 | 18.47 | 10.12 | 8.35 |
| P26 | 6.92 | 1.00 | 5.92 | DCH3 | 34.21 | 24.52 | 9.69 |
| P3 | 4.19 | 0.89 | 3.30 | Djibi | 39.12 | 31.35 | 7.77 |
| P37 | 2.04 | 0.36 | 1.68 | Hotel_Kedj | 52.2 | 45.10 | 7.10 |
| P38 | 1.07 | 0.49 | 0.58 | P71 | 7.73 | 2.36 | 5.37 |
| P58 | 2.61 | 1.04 | 1.57 | P73 | 7.09 | 4.84 | 2.25 |
| P61 | 8.5 | 1.52 | 6.98 | Yapi | 45.16 | 39.02 | 6.14 |
| P8 | 3.26 | 1.01 | 2.25 | SAPA | 49 | 38.85 | 10.15 |
| SR1 | 8.38 | 0.43 | 7.95 | P12 | 2.31 | 0.31 | 2.00 |
| Niangon1 | 13.8 | 13.57 | 0.23 | Mais_Jardin | 5.7 | 0.49 | 5.21 |
| Zoo 1 | 11.75 | 4.24 | 7.51 | Gue_Alokoua | 33.3 | 27.84 | 5.46 |
| Zoo 2 | 19.23 | 9.25 | 9.98 | Mpouto_Egli | 1.42 | 0.37 | 1.05 |
| Akakro | 2.34 | 0.52 | 1.82 | Plantation_Sabo | 48.15 | 37.35 | 10.80 |
| Eloka | 2.2 | 0.50 | 1.70 | DCH5 | 39.33 | 31.41 | 7.92 |
| P11 | 3.51 | 0.36 | 3.15 | DCH6 | 22.22 | 19.16 | 3.06 |
Appendix B

Table A3.
Pumping rates (m3/day) from 1978 to 2030.
Table A3.
Pumping rates (m3/day) from 1978 to 2030.
| Years | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boreholes fields | Boreholes name | 1978 | 1978–1980 | 19801–985 | 1985–1992 | 1992–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2012 | 2012–2015 | 2015–2020 | 2020–2030 | |
| Zone Nord | ZN | Pumping rate (m3/day) | 24000 | 24000 | 30000 | 25824 | 25824 | 32592 | 34992 | 37000 | 37000 | 37000 | 37000 | 37000 |
| Anonkoua Kouté | AK | - | - | 28296 | 21960 | 21960 | 31440 | 38000 | 43000 | 43000 | 43000 | 43000 | 43000 | |
| Niangon Nord | NN | - | - | 28800 | 33000 | 33000 | 40608 | 37000 | 48000 | 48000 | 48000 | 48000 | 48000 | |
| Zone Ouest | ZO | 49200 | 25200 | 31200 | 37488 | 37488 | 37920 | 48000 | 50000 | 50000 | 50000 | 50000 | 50000 | |
| Adjamé Nord | AN | 37680 | 37680 | 31680 | 13848 | 13848 | 20880 | 9300 | 27480 | 27480 | 27480 | 27480 | 27480 | |
| Zone Est | ZE | 29040 | 38304 | 26784 | 28776 | 28776 | 32304 | 33000 | 43992 | 43992 | 43992 | 43992 | 43992 | |
| Nord Riviera | NR | - | - | 36000 | 32496 | 32496 | 33062 | 38000 | 43992 | 43992 | 52790 | 52790 | 52790 | |
| Riviera Center | RC | - | - | 9984 | 16704 | 16704 | 19992 | 20000 | 21288 | 21288 | 21288 | 21288 | 21288 | |
| Plateau | Plateau | 1800 | 30000 | 24000 | 1800 | 1800 | 1368 | 194 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Djibi | DJI | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24000 | 24000 | 24000 | 24000 | |
| Niangon2 | N2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24000 | 24000 | 24000 | |
| Abatar | ABA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12000 | 12000 | 12000 | |
| Akandje | AKA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12000 | 12000 | 12000 | |
Note: “-”denotes that drilling not in use.
References
- Bosca, C. Groundwater law and administration of sustainable development. Medit. Mag. Sci. Train. Technol. 2002, 2, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Brassington, R. Field Hydrogeology, 3rd ed.; The Geological Field Guide Series; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2007; 264p. [Google Scholar]
- Hallam, F.; Acoubi-Khebiza, M.Y.; Oufdou, K.; Oulanouar, M.B. Qualité des eaux souterraines dans une région aride du Maroc: Impact des pollutions sur la biodiversité et relations crustacés—Bactéries d’intérêt sanitaire. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, B.L.; Lawrence, A.R.; Chilton, P.J.C.; Adams, B.; Calow, R.C.; Klinck, B.A. A Global Assessment of Problem and Options for Management; United Nations Environment Program Groundwater: Nairobi, Kenya, 2003; 140p. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Zeid, I. La modélisation Stochastique des Étiages et de Leurs Durées en vue de L’analyse du Risque. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Québec, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Water, U.N. Water in a Changing World: United Nations World Water Development Report 3; World Water Assessment Programme: Paris, France, 2009; Volume 429. [Google Scholar]
- Castany, G. Principes et Méthodes de L’hydrogéologie; Dunod Université: Paris, France, 1982; 238p. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations World Water Assessment Program. WWAP: The 3rd World Water Forum Final Report; United Nations World Water Assessment Program: Kyoto, Japan, 2003; 273p. [Google Scholar]
- Tandia, A.A.; Gaye, C.B.; Faye, A. Origine des teneurs élevées en nitrates dans la nappe phréatique des sables quaternaires de la région de Dakar. Sécheresse 1997, 8, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Adelena, S.M. Nitrate pollution of groundwater in Nigeria. In Groundwater Pollution in Africa; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Takem, G.E.; Chandrasekharam, D.; Ayonghe, P.; Thambidurai, P. Pollution characteristics of alluvial groundwater from springs and bore wells in semi-urban informal settlements of Douala, Cameroon, Western Africa. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deh, S.K. Contributions de L’évaluation de la Vulnérabilité Spécifique aux Nitrates et d’un Modèle de Transport des Organochlorés à la Protection des Eaux Souterraines du District d’Abidjan (sud de la Côte d’Ivoire). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Félix Houphouet-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2013; 230p. [Google Scholar]
- Sieczka, A.; Bujakowski, F.; Falkowski, T.; Koda, E. Morphogenesis of a Floodplain as a Criterion for Assessing the Susceptibility to Water Pollution in an Agriculturally Rich Valley of a Lowland River. Water 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugan, R.; Tredoux, G.; Jovanovic, N.; Israel, S. Pollution Plume Development in the Primary Aquifer at the Atlantis Historical Solid Waste Disposal Site, South Africa. Geosciences 2018, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, E.; Sieczka, A.; Osinski, P. Ammonium Concentration and Migration in Groundwater in the Vicinity of Waste Management Site Located in the Neighborhood of Protected Areas of Warsaw, Poland. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Václavík, V.; Ondrašiková, I.; Dvorský, T.; Černochová, K. Leachate from Municipal Waste Landfill and Its Natural Degradation—A Case Study of Zubří, Zlín Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.; Bartram, J.; Pedley, S.; Schmoll, O.; Chorus, I.; Berger, P. Chapter 1: Groundwater and public health. In Protecting Groundwater for Health: Managing the Quality of Drinking-Water Sources; London IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2006; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Usher, B.H. Issues of groundwater pollution in Africa. In Groundwater pollution in Africa; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kouamé, K.J. Contribution à la Gestion Intégrée des Ressources en Eaux (GIRE) du District d’Abidjan (Sud de la Côte d’Ivoire): Outils d’aide à la Décision pour la Prévention et la Protection des Eaux Souterraines Contre la Pollution. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2007; 229p. [Google Scholar]
- Institut National de la Statistique (INS). Recensement Général de la Population et de l’Habitation (RGPH). Données Socio-Démographiques et Économiques des Localités, Résultats Définitifs par Localités, Région des Lagunes; INS: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2014; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Direction de l’Hydraulique Humaine en Côte d’Ivoire; Ministère des Infrastructures Economiques: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2001; 66p.
- Société de Distribution d’Eau en Côte d’Ivoire (SODECI). Etude de la Gestion et de la Protection de la Nappe d’Abidjan; Actualisation des études hydrogéologiques SOGREHAH de 1997; SODECI: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2015; 78p. [Google Scholar]
- Dongo, K.; Tiembre, I.; Kone, B.A.; Zurbrugg, C.; Odrematt, P.; Tanner, M.; Zinsstag, J.; Cissé, G. Exposure to toxic waste containing high concentrations of hydrogen sulphide illegally dumped in Abidjan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Resour. 2012, 10, 3192–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourda, J.P. Contribution à L’étude Géologique et Hydrogéologique de la Région du Grand Abidjan (Côte D’Ivoire). Ph.D. Thesis, Université Scientifique, Technique et Médicale de Grenoble, Grenoble, France, 1987; 319p. [Google Scholar]
- Adiaffi, B. Apport de la Géochimie Isotopique, de L’hydrochimie et de la Télédétection à la Connaissance des Aquifères de la Zone de Contact « Socle-Bassin Sédimentaire » du Sud-Est de la Côte d’Ivoire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Sud, Orsay, France, 2008; 196p. [Google Scholar]
- Gilli, E.; Mangan, C.; Mudry, J. Hydrogéologie: Objets, Méthodes, Applications, 3rd ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 2012; 340p. [Google Scholar]
- Jourda, J.P.; Kouamé, K.J.; Saley, M.B.; Kouadio, B.H.; Oga, Y.S. Contamination of the Abidjan aquifer by sewage: An assessment of extent and strategies for protection. In Groundwater Pollution in Africa; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Kouamé, K.I. Pollution Physico-Chimique des Eaux dans la Zone de la Décharge d’Akouédo et Analyse du Risque de Contamination de la Nappe d’Abidjan par un Modèle de Simulation des Écoulements et du Transport des Polluants, Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Abobo-Adjamé, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2007; 206p. [Google Scholar]
- Dongo, K.; Kouamé, K.F.; Koné, B. Analyse de la situation de l’environnement sanitaire des quartiers défavorisés dans le tissu urbain de Yopougon à Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. Vertigo-Rev. Electron. Sci. Environ. 2008, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, N.; Ouattara, L.; Dongo, K.; Kouadio, K.E.; Ahoussi, K.E.; Soro, G.; Oga, M.S.; Savané, I.; Biémi, J. Déchets municipaux dans le District d’Abidjan en Côte d’Ivoire sources potentielles de pollution des eaux souterraines. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2010, 4, 364–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiraud, R. L’hydrogéologie de l’Afrique. J. Afr. Sci. 1988, 7, 519–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soro, N.C. Géolocalisation des Stations D’essences dans la Commune D’Abobo. Master’s Thesis, Université Félix Houphouët-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fiche de Données Toxicologiques et Environnementales des Substances Chimiques. Available online: https://substances.ineris.fr/fr/page/21 (accessed on 26 January 2019).
- Institut National de Statistiques. Recensement Général de la Population et de l’Habitation de la Côte d’Ivoire (RGPH). Données Socio-Démographiques et Économiques des Localités, Résultats Définitifs par Localités, Région des Lagunes; Institut National de Statistiques: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2001; Volume 3, p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L. Morphologie, Sédimentologie et Paléogéographie au Quaternaire récent du Plateau Continental Ivoirien. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Paris VI, Paris, France, 1973; 340p. [Google Scholar]
- Tastet, J.P. Environnements Sédimentaires et Structuraux Quaternaires du Littoral du Golfe de Guinée (Côte d’Ivoire, Togo, Bénin). Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bordeaux 1, Bordeaux, France, 1979; 181p. [Google Scholar]
- Aghui, N.; Biemi, J. Géologie et hydrogéologie des nappes de la région d’Abidjan et risques de contamination. Ann. l’Université Natl. Côte d’Ivoire 1984, 20, 331–347. [Google Scholar]
- Delor, C.; Diaby, I.; Siméon, Y.; Yao, B.; Tastet, J.P.; Vidal, M.; Chiron, J.P.; Dommang, A. Notice Explicative de la Carte Géologique de la Côte d’Ivoire à 1/200000; Mémoire de la Direction de la Géologie de Côte d’Ivoire, n 3: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1992a; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Delor, C.; Diaby, I.; Siméon, Y.; Yao, B.; Tastet, J.P.; Vidal, M.; Chiron, J.P.; Dommang, A. Notice Explicative de la Carte Géologique de la Côte d’Ivoire à 1/200000; Mémoire de la Direction de la Géologie de Côte d’Ivoire, n 4: Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 1992b; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Loroux, B.F.E. Contribution à L’étude Hydrogéologique du Bassin Sédimentaire de Côte d’Ivoire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bordeaux I, Bordeaux, France, 1978; 93p. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.; Ahmad, Z. Regional groundwater flow modelling of Upper Chaj Doab of Indus Basin, Pakistan using finite element model (Feflow) and geoinformatics. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, M.; Rajan, T. Regional Groundwater Modeling; Capital Publishing Company: New Delhi, India, 2004; Volume 340. [Google Scholar]
- Hiscock, K.M.; Bense, V.F. Hydrogeology: Principes and Practice, 2nd ed.; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; 519p. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, T.-C.J.; Khaleel, R.; Carroll, K.C. Flow through Heterogeneous Geologic Media; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; 243p. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W.; Hunt, R.J. Applied Groundwater Modelling: Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; 564p. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1972; 764p. [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen, S.; Sanford, W.; Neuzil, C. Groundwater in Geologic Processes, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; 536p. [Google Scholar]
- Fitts, C.R. Groundwater Sciences, 2nd ed.; Elsevier, Academy press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; 672p. [Google Scholar]
- Diersch, H.-J.G. Feflow, Finite element Modelling of Flow, Mass and Heat Transport in Porous and Fractured Media; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2014; 996p. [Google Scholar]
- Sylla, M.B.; Pal, J.S.; Faye, A.; Dimobe, K.; Kuntsmann, H. Climate change to severely impact West African basin scale irrigation in 2 °C and 1.5 °C global warming scenarios. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Société Grenobloise d’Etudes et d’Applications Hydrauliques (SOGREAH). Etude de la Gestion et de la Protection de la Nappe Assurant la Production en eau Potable d’Abidjan. Etude sur Modèle Mathématique. Rapport Rapport de Phase 2; Présentation du modèle mathématique et des résultats du calage; Ministère des Infrastructures Economiques, Direction et Contrôles des Grands Travaux (DCGTX); Société Grenobloise d’Etudes et d’Applications Hydrauliques (SOGREAH): Lyon, France, 1996; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi, K.A. Modélisation en Milieu Poreux Saturé par Approche Inverse via une Paramétrisation Multi-Échelle: Cas de L’aquifère du Continental Terminal. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Nangui-Abrogoua, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire, 2013; 268p. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductvity of Unsaturated soils. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippisch, O.; Vogel, H.J.; Bastian, P. Validity limits for the van Genuchten–Mualem model and implications for parameter estimation and numerical simulation. Adv. Water. Resour. 2006, 29, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, A.B.; Liaghat, A.; Huang, G.-H.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Estimation of the van Genuchten Soil Water Retention Properties from Soil Textural Data. Soil Sci. Soc. China 2010, 20, 456–465. [Google Scholar]
- Mobile Geochemistry Incorporation. Available online: http://www.handpmg.com/articles/lustline29-oh-henry.html (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Matti, B.; Tacher, L. Modèles couplés hydraulique/thermique de la nappe alluviale de la plaine du Rhône et modélisation de l’implantation d’un système de refroidissement eau-eau à l’hôpital cantonal de Sion (VS, Suisse). Swiss Bull. Angew. Geol. 2009, 14, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemeieir, T.H.; Swanson, M.A.; Wilson, J.T.; Kampell, D.H.; Miller, R.N.; Hansen, J.E. Approximation of biodegradation rate constants for monoaromatic hydrocarbons (BTEX) in ground water. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 1996, 16, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, H.; Rouleau, A. Guide de Détermination D’aires d’alimentation et de Protection de Captage D’eaux Souterraines. Centre D’étude sur les Ressources Minérales, Université de Québec à Chicoutimi. Contrat du Ministère de L’environnement du Québec 2003. Available online: https://www.agrireseau.net/agroenvironnement/documents/guide.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Gomez, D.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Modeling the natural attenuation of benzene in groundwater impacted by ethanol-blended fuels: Effect of ethanol content on the lifespan and maximum length of benzene plumes. Water Resour. 2009, 45, W03409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.A.; Reddy, K.A. Removal of dissolved- and free-phase benzene pools from ground water using in situ air sparging. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, Y. Prédiction de l’effet du décapage d’une mine à ciel ouvert sur l’hydrogéologie locale à l’aide de la modélisation numérique systèmes geost. Int. Laval Qué. 1999, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).