Multi-Wavelength High-Resolution Spectroscopy for Exoplanet Detection: Motivation, Instrumentation and First Results
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Path toward Multi-Wavelength Observations
2.1. The VIS Regime
2.2. The Role of the NIR
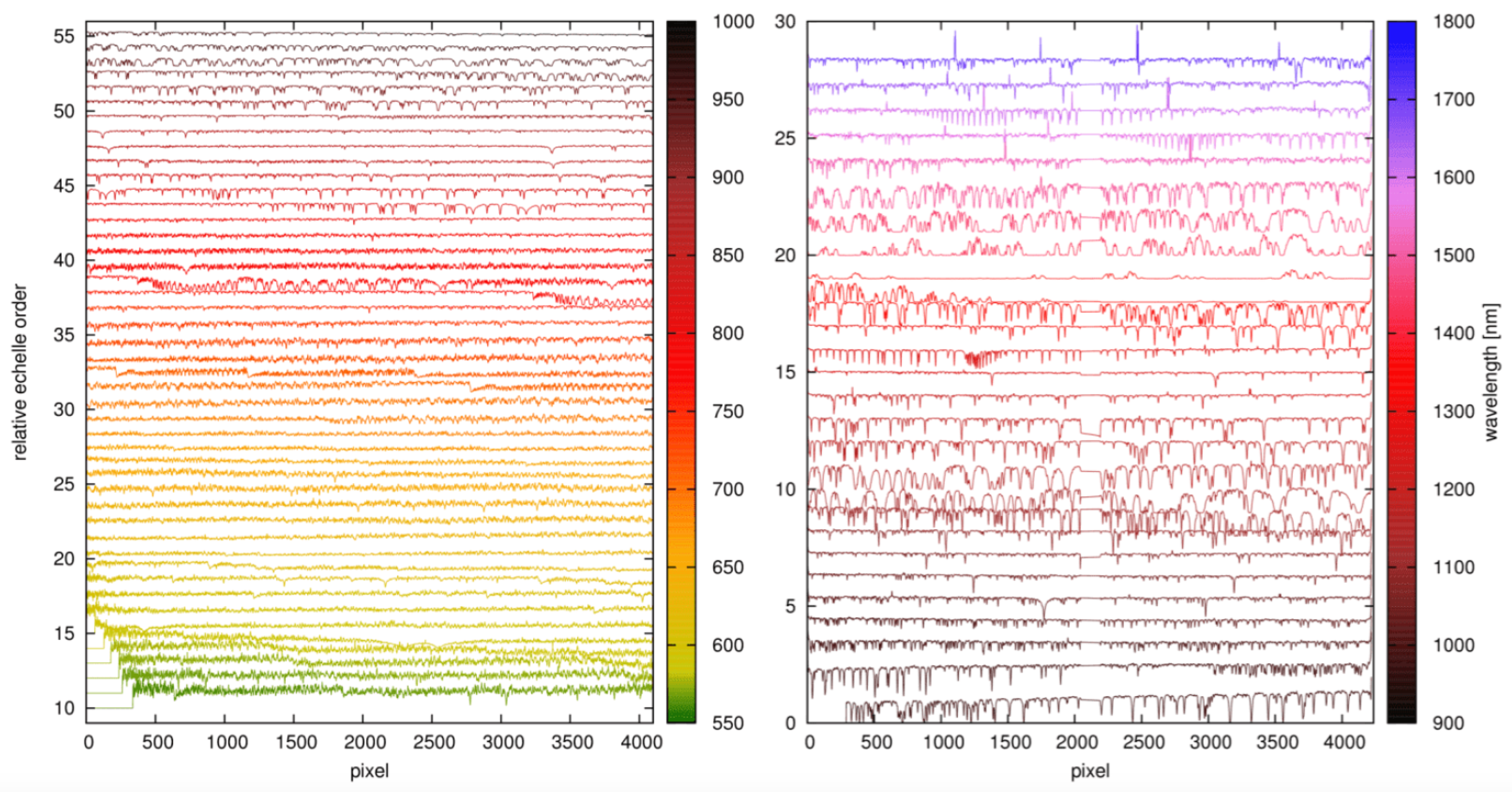
Spectrographs for the NIR Spectral Domain
2.3. First Multi-Wavelength Investigations
2.4. The Goal of the Simultaneity
3. New Breakthrough Facilities
3.1. CARMENES at the 3.5-m Telescope at Calar Alto
3.2. GIARPS at TNG
3.3. Work in Progress: NIRPS + HARPS at ESO
3.4. Future Instrumentation
3.4.1. G-CLEF and GMTNIRS at the GMT
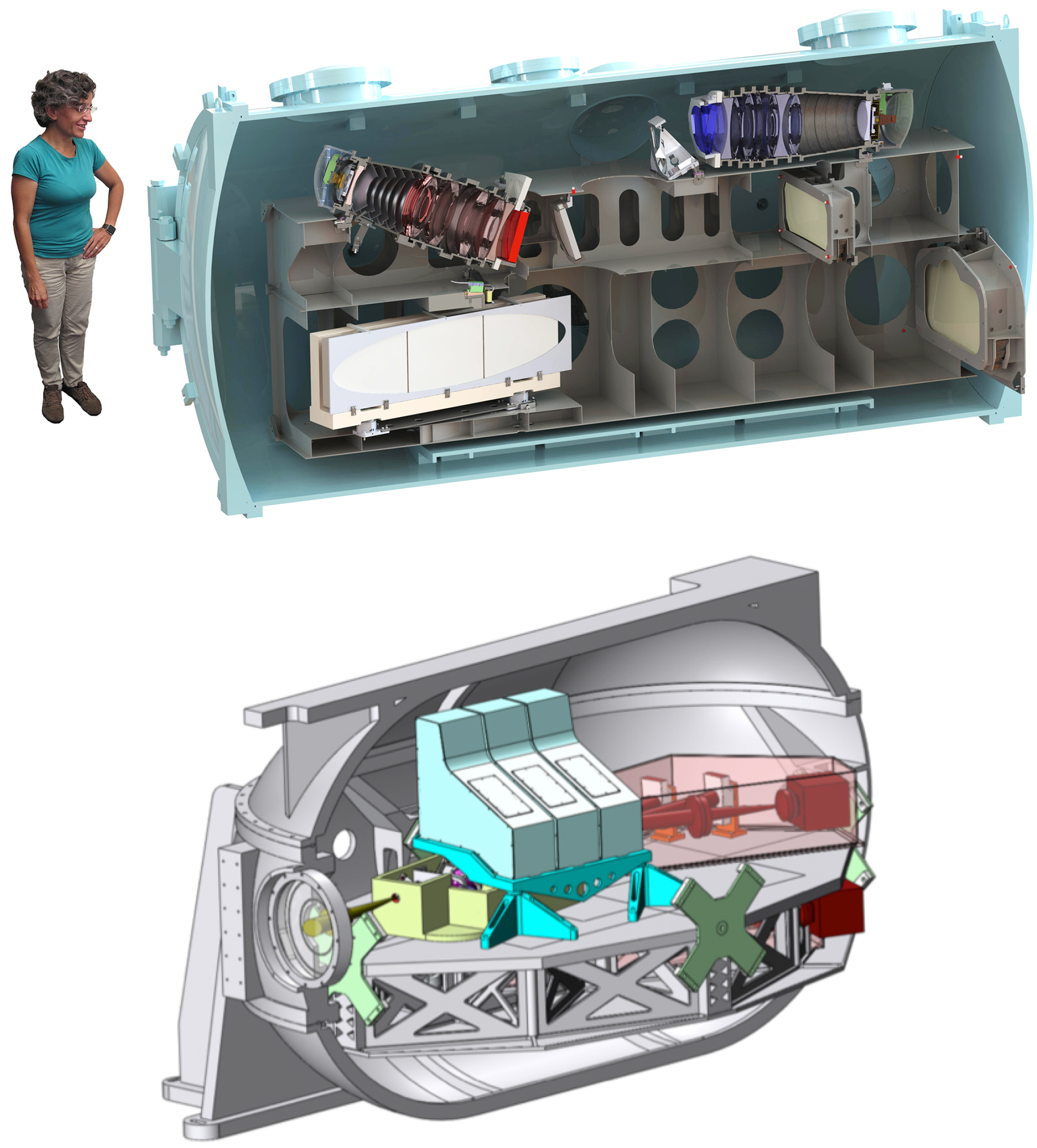
- G-CLEF is a fiber-fed, cross-dispersed echelle spectrograph built for general purposes, but designed to provide also high precision RVs (up to 10 cm s [130]). The wavelength range covered by G-CLEF spans between 0.35 and 1 m to satisfy the requirements of the main science cases. The bluer part is included to perform studies on very metal-poor stars since the iron content is evaluated through very faint features between 3500 and 3900 Å, undetectable from the existing facilities in terms of high resolution and telescope aperture. The wavelength coverage is pushed up to 1 μm to exploit the spectral information of the M dwarfs and obtain precise RVs for these stars. Among the other exoplanet science cases, it is noteworthy to mention the search for biomarkers (in particular, the features of molecular oxygen between 7600 and 7700 Å in the atmospheres of the exoplanets) and the follow-up of the planet candidates detected by the TESS satellite.The spectral resolution can be chosen according to the science program. G-CLEF offers both high-resolution modes (R ∼ 105,000), available with or without an image scrambler that enhances the RV precision and medium resolution modes (35,000 and 19,000). As for GMTNIRS, particular attention is paid to providing the maximum performance in terms of throughput, to exploit the benefit of the huge telescope collecting area. To optimize the incoming stellar flux, the light beam will be split through a dichroic in two channels, red and blue (see Figure 11, upper panel), each one equipped with specific detectors and coatings.
- GMTNIRS will cover the wavelength range between 1.15 and 5.3 m making use of five spectrograph units (see Figure 11, lower panel), each one dedicated to a specific atmospheric window: J, H, K, L and M bands. The light that feeds the instrument will be subdivided into the five channels thanks to a series of dichroic elements. The spectral resolution is expected to be ∼60,000 in the JHK bands and ∼85,000 in the L and M bands. In order to test the innovative technical elements planned to equip GMTNIRS, the University of Texas and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) joined to build a sort of forerunner instrument, the cross-dispersed NIR spectrograph IGRINS (Immersion Grating Infrared Spectrometer, see http://www.as.utexas.edu/mcdonald/facilities/2.7m/igrins.html) [131]. IGRINS, which has operated since 2014, has been installed alternatively at the Harlan J. Smith 2.7-m telescope (McDonald Observatory, USA), at the 4.3-m Discovery Channel Telescope (Lowell Observatory, USA) and at the 8.1-m Gemini South Telescope. It covers the H and K windows, from 1.45–2.5 m in a single acquisition with a resolving power of R = 45,000. The design of this instrument was particularly focused to optimize the throughput rather than to reach extreme precision in RV, and the same concept will be adopted for GMTNIRS, as well.The instrumental design originally proposed for GMTNIRS [132] is currently evolving [133,134], aiming to match the requirements of the main scientific driver emerging through the years, i.e., the observation of exoplanetary atmospheres, as for HIRES (see the discussion in Section 3.4.2). Being part of a large and international project as the GMT, the GMTNIRS spectrograph will not be focused on exoplanet science alone; it will provide a significant contribution to the study of young stellar objects, debris disks, protoplanetary systems, stellar evolution, interstellar medium and the star formation history of the Galaxy.
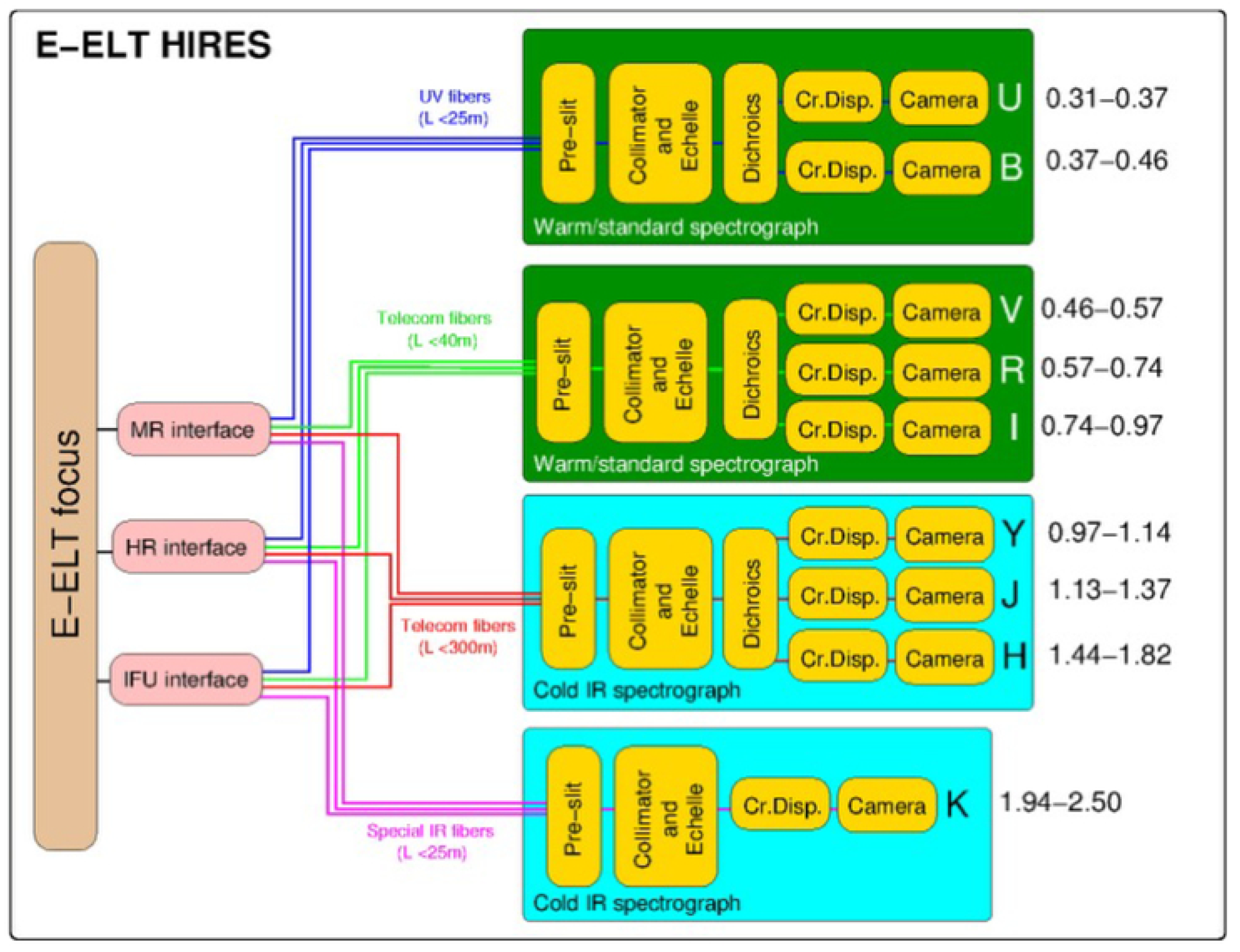
3.4.2. HIRES at E-ELT
4. First Results
4.1. The CARMENES M Dwarf Survey
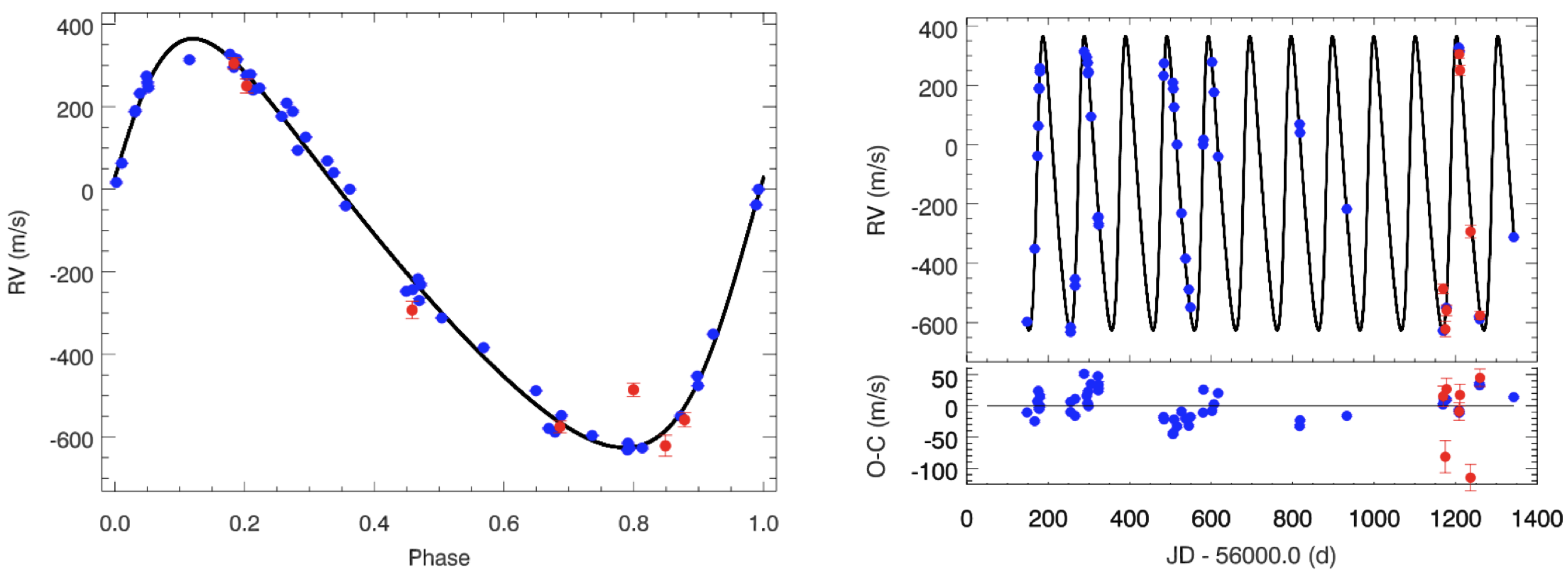
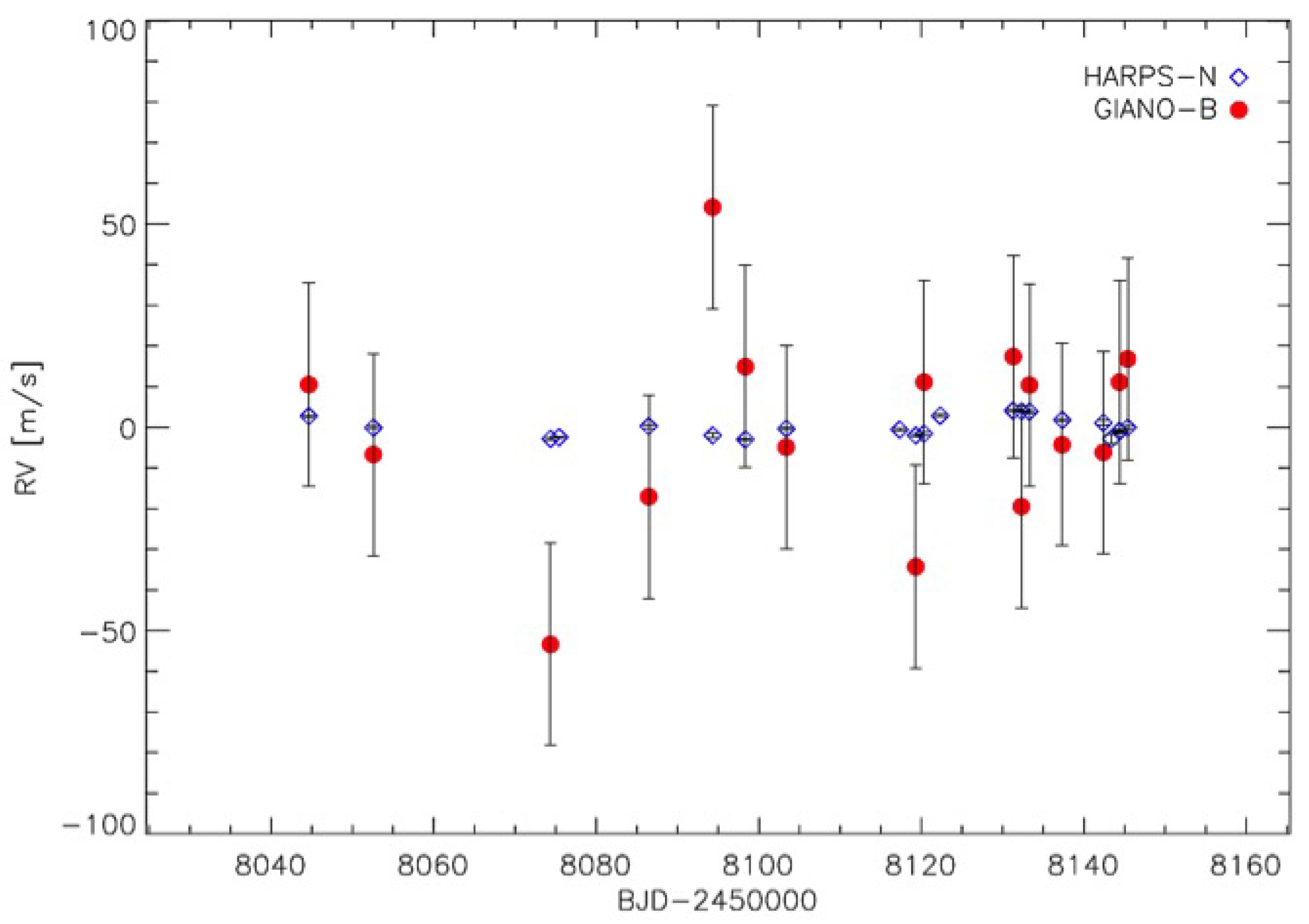
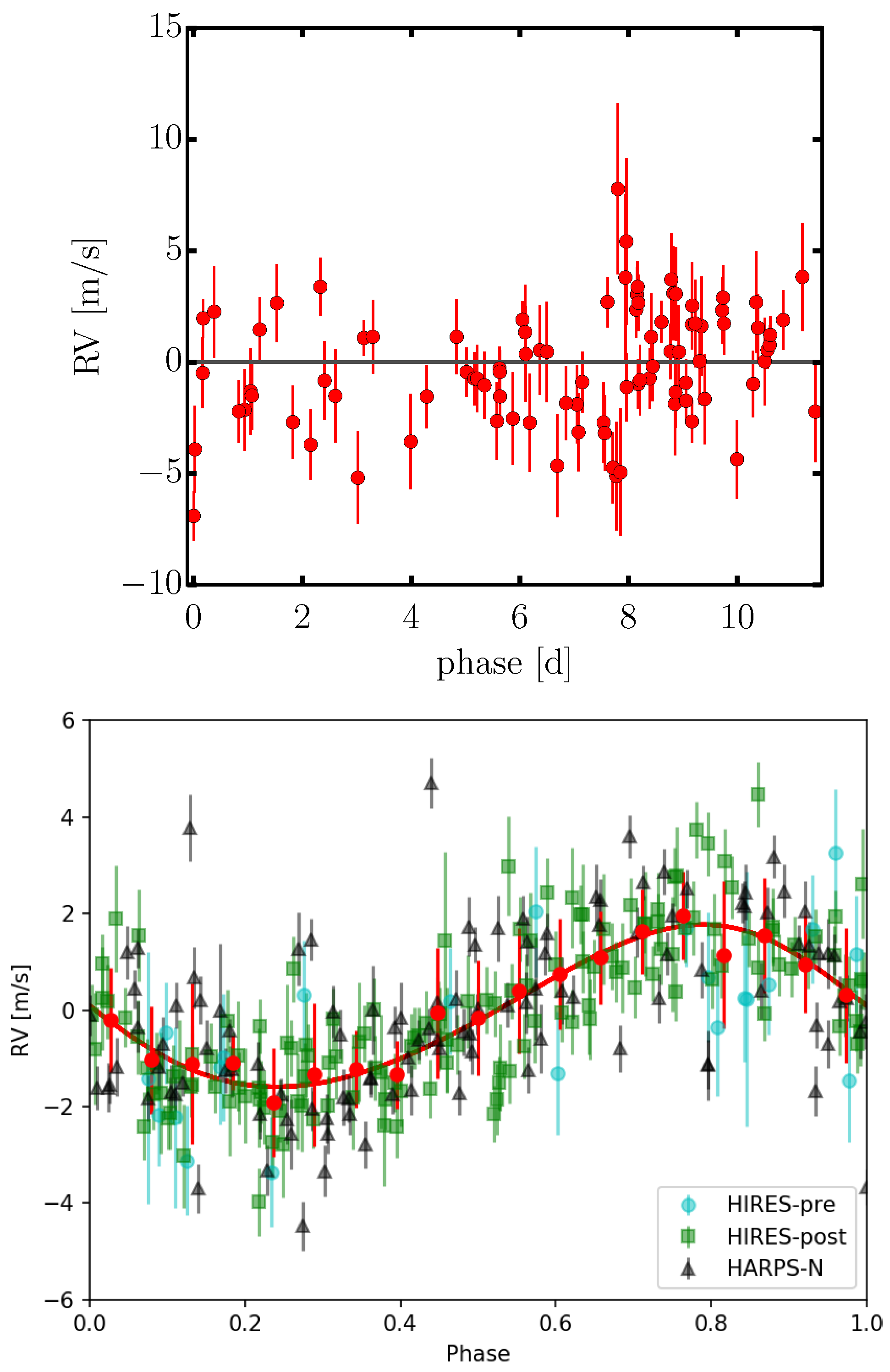
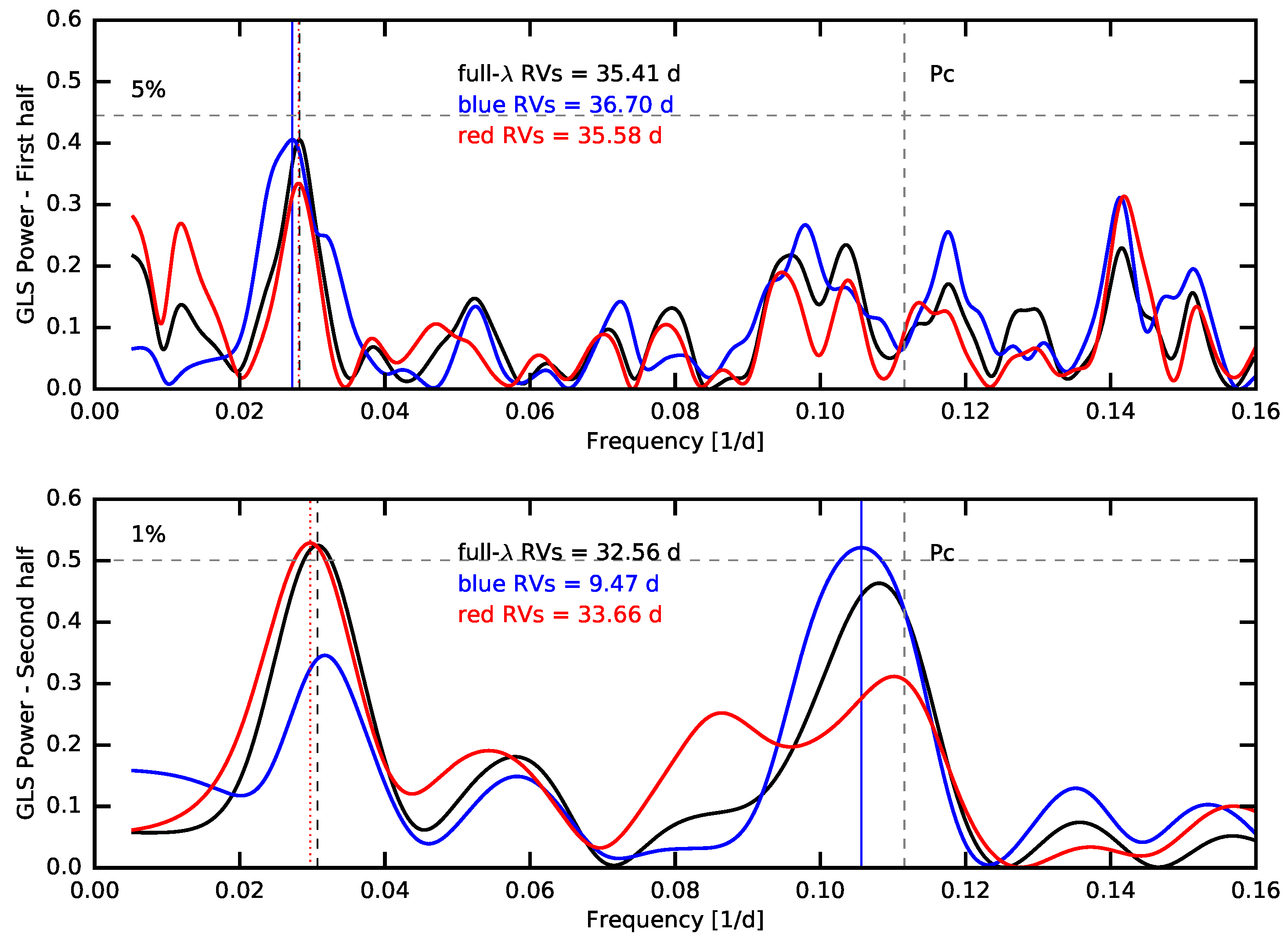
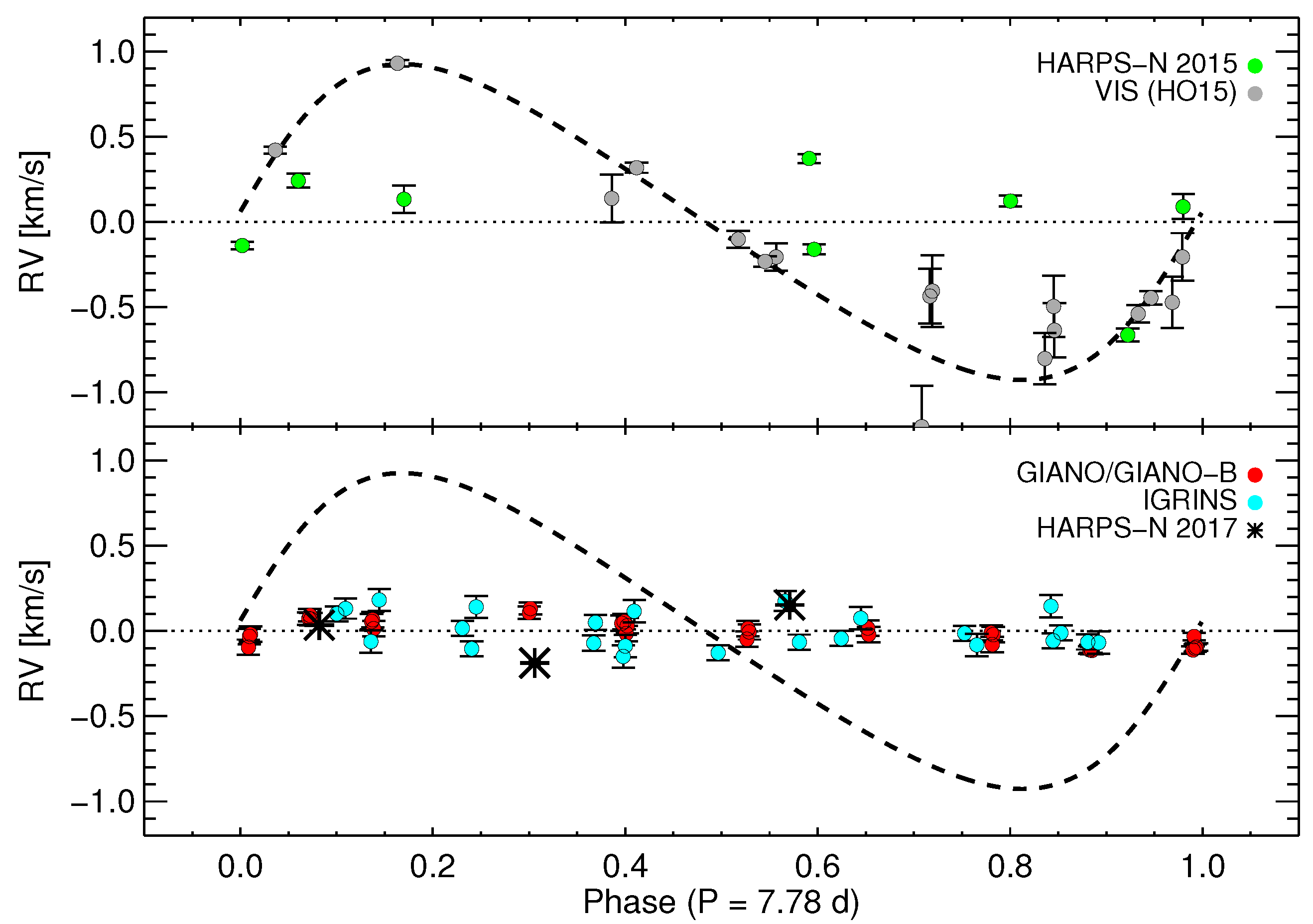
4.2. Retreat of the Debated Hot Jupiter BD+20 1790 b
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AO | Adaptive Optic |
| CARMENES | Calar Alto high-Resolution search for M dwarfs with Exo-Earths with Near-infrared and optical Échelle Spectrographs |
| CRIRES | Cryogenic high-resolution infrared echelle spectrograph |
| E-ELT | European Extremely Large Telescope |
| ELT | Extremely Large Telescope |
| ESO | European Southern Observatory |
| FP | Fabry–Perot |
| G-CLEF | GMT Consortium Large Earth Finder |
| GLS | Generalized Lomb–Scargle |
| GMT | Giant Magellan Telescope |
| GMTNIRS | GMT Near-IR spectrograph |
| HARPS | High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher |
| HIRES | High Resolution Spectrograph |
| HZ | habitable zone |
| IGRINS | Immersion Grating Infrared Spectrometer |
| JWST | James Webb Space Telescope |
| INAF | (Italian) National Institute for Astrophysics |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NIRPS | Near Infra Red Planet Searcher |
| RV | radial velocity |
| TNG | Telescopio Nazionale Galileo |
| VIS | visible |
| VLT | Very Large Telescope |
Appendix A. Other VIS and NIR Facilities
| Spectrograph | Telescope and Site | Expected Availability | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visible: | |||
| ESPRESSO | VLT (4 × 8-m, Paranal, Chile) | 2018 | https://www.eso.org/sci/facilities/paranal/instruments/espresso.html |
| PEPSI | LBT (8.4-m, Mt. Graham, USA) | 2018 | https://pepsi.aip.de/ |
| HRS-2 | HET (10-m, McDonald, USA) | 2020 | https://hydra.as.utexas.edu/?a=help&h=93 |
| MAROON-X | Gemini N. (8.1-m, Maunakea, USA) | 2019 | https://www.gemini.edu/sciops/instruments/maroon-x |
| NEID | WIYN (3.5-m, Kitt Peak, USA) | 2019 | http://neid.psu.edu/ |
| Veloce | AAT (4-m, Siding Spring, UAS) | 2020 * | https://www.aao.gov.au/science/instruments/current/veloce/overview |
| HARPS3 | INT (2.5-m, La Palma, Spain) | 2020 | http://www.terrahunting.org/harps3.html |
| KPF | Keck I (10-m, Maunakea, USA) | 2020 | [158], https://www2.keck.hawaii.edu/inst/kpf/ |
| Near Infrared: | |||
| iSHELL | IRTF (3-m, Maunakea, USA) | 2016 | http://irtfweb.ifa.hawaii.edu/~ishell/ |
| HPF | HET (10-m, McDonald, USA) | 2018 | https://hpf.psu.edu/ |
| IRD | Subaru (8.2-m, Maunakea, USA) | 2018 | http://ird.mtk.nao.ac.jp/IRDpub/index_tmp.html |
| PARVI | Hale (5.1-m, Mt. Palomar, USA) | 2019 | https://techport.nasa.gov/view/92844 |
| SPIRou | CFHT (3.6-m, Maunakea, USA) | 2019 | http://www.cfht.hawaii.edu/en/projects/SPIRou/ |
References
- Mayor, M.; Queloz, D. A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star. Nature, 1995; 378, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, K.; Agol, E. Analytic Light Curves for Planetary Transit Searches. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 580, L171–L175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, J.N. Transits and Occultations. arXiv, 2010; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1001.2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.T.; Gaudi, B.S. Exoplanet Detection Methods. Planets, Stars and Stellar Systems. Volume 3: Solar and Stellar Planetary Systems; Oswalt, T.D., French, L.M., Kalas, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Lovis, C.; Fischer, D. Radial Velocity Techniques for Exoplanets. In Exoplanets; Seager, S., Ed.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2010; pp. 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Borucki, W.J.; Koch, D.; Basri, G.; Batalha, N.; Brown, T.; Caldwell, D.; Caldwell, J.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Cochran, W.D.; DeVore, E.; et al. Kepler Planet-Detection Mission: Introduction and First Results. Science 2010, 327, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borucki, W.J. KEPLER Mission: Development and overview. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 036901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, M.; Marmier, M.; Lovis, C.; Udry, S.; Ségransan, D.; Pepe, F.; Benz, W.; Bertaux, J.; Bouchy, F.; Dumusque, X.; et al. The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets XXXIV. Occurrence, mass distribution and orbital properties of super-Earths and Neptune-mass planets. arXiv, 2011; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1109.2497. [Google Scholar]
- Baranne, A.; Queloz, D.; Mayor, M.; Adrianzyk, G.; Knispel, G.; Kohler, D.; Lacroix, D.; Meunier, J.P.; Rimbaud, G.; Vin, A. ELODIE: A spectrograph for accurate radial velocity measurements. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1996, 119, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, R.P.; Marcy, G.W.; Williams, E.; McCarthy, C.; Dosanjh, P.; Vogt, S.S. Attaining Doppler Precision of 3 m s−1. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1996, 108, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R.P.; Vogt, S.S.; Laughlin, G.; Burt, J.A.; Rivera, E.J.; Tuomi, M.; Teske, J.; Arriagada, P.; Diaz, M.; Holden, B.; et al. The LCES HiRES/Keck Precision Radial Velocity Exoplanet Survey. Astron. J. 2017, 153, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, F.; Mayor, M.; Delabre, B.; Kohler, D.; Lacroix, D.; Queloz, D.; Udry, S.; Benz, W.; Bertaux, J.L.; Sivan, J.P. HARPS: A new high-resolution spectrograph for the search of extrasolar planets. In Optical and IR Telescope Instrumentation and Detectors; Iye, M., Moorwood, A.F., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 4008, pp. 582–592. [Google Scholar]
- Wildi, F.; Pepe, F.; Chazelas, B.; Lo Curto, G.; Lovis, C. The performance of the new Fabry-Perot calibration system of the radial velocity spectrograph HARPS. In Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 8151. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Curto, G.; Manescau, A.; Avila, G.; Pasquini, L.; Wilken, T.; Steinmetz, T.; Holzwarth, R.; Probst, R.; Udem, T.; Hänsch, T.W.; et al. Achieving a few cm/sec calibration repeatability for high resolution spectrographs: The laser frequency comb on HARPS. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy IV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8446, p. 84461W. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, R.A.; Lo Curto, G.; Avila, G.; Canto Martins, B.L.; de Medeiros, J.R.; Esposito, M.; González Hernández, J.I.; Hänsch, T.W.; Holzwarth, R.; Kerber, F.; et al. A laser frequency comb featuring sub-cm/s precision for routine operation on HARPS. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 91471C. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, F.; Lovis, C.; Ségransan, D.; Benz, W.; Bouchy, F.; Dumusque, X.; Mayor, M.; Queloz, D.; Santos, N.C.; Udry, S. The HARPS search for Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. I. Very low-mass planets around HD 20794, HD 85512, and HD 192310. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 534, A58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfils, X.; Delfosse, X.; Udry, S.; Forveille, T.; Mayor, M.; Perrier, C.; Bouchy, F.; Gillon, M.; Lovis, C.; Pepe, F.; et al. The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets. XXXI. The M-dwarf sample. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 549, A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.C.; Mortier, A.; Faria, J.P.; Dumusque, X.; Adibekyan, V.Z.; Delgado-Mena, E.; Figueira, P.; Benamati, L.; Boisse, I.; Cunha, D.; et al. The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets. XXXV. The interesting case of HD 41248: Stellar activity, no planets? Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 566, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Hernández, J.I.; Pepe, F.; Molaro, P.; Santos, N. ESPRESSO on VLT: An Instrument for Exoplanet Research. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:astro-ph.IM/1711.05250. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, D.A.; Anglada-Escude, G.; Arriagada, P.; Baluev, R.V.; Bean, J.L.; Bouchy, F.; Buchhave, L.A.; Carroll, T.; Chakraborty, A.; Crepp, J.R.; et al. State of the Field: Extreme Precision Radial Velocities. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2016, 128, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumming, A.; Butler, R.P.; Marcy, G.W.; Vogt, S.S.; Wright, J.T.; Fischer, D.A. The Keck Planet Search: Detectability and the Minimum Mass and Orbital Period Distribution of Extrasolar Planets. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2008, 120, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenmyer, R.A.; Butler, R.P.; Tinney, C.G.; Horner, J.; Carter, B.D.; Wright, D.J.; Jones, H.R.A.; Bailey, J.; O’Toole, S.J. The Anglo-Australian Planet Search XXIV: The Frequency of Jupiter Analogs. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saar, S.H.; Donahue, R.A. Activity-Related Radial Velocity Variation in Cool Stars. Astrophys. J. 1997, 485, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.T. Radial Velocity Jitter in Stars from the California and Carnegie Planet Search at Keck Observatory. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2005, 117, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haywood, R.D. Stellar Activity as a Source of Radial-Velocity Variability. In Radial-Velocity Searches for Planets Around Active Stars; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 13–44. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Fiorenzano, A.F.; Gratton, R.G.; Desidera, S.; Cosentino, R.; Endl, M. Line bisectors and radial velocity jitter from SARG spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Queloz, D.; Henry, G.W.; Sivan, J.P.; Baliunas, S.L.; Beuzit, J.L.; Donahue, R.A.; Mayor, M.; Naef, D.; Perrier, C.; Udry, S. No planet for HD 166435. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 379, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toner, C.G.; Gray, D.F. The starpatch on the G8 dwarf XI Bootis A. Astrophys. J. 1988, 334, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, P.; Santos, N.C.; Pepe, F.; Lovis, C.; Nardetto, N. Line-profile variations in radial-velocity measurements. Two alternative indicators for planetary searches. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 557, A93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, A.F.; Malavolta, L.; Benatti, S.; Desidera, S.; Bignamini, A.; Bonomo, A.S.; Esposito, M.; Figueira, P.; Gratton, R.; Scandariato, G.; et al. The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG XVII. Line profile indicators and kernel regression as diagnostics of radial-velocity variations due to stellar activity in solar-like stars. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1804.07039. [Google Scholar]
- Noyes, R.W.; Hartmann, L.W.; Baliunas, S.L.; Duncan, D.K.; Vaughan, A.H. Rotation, convection, and magnetic activity in lower main-sequence stars. Astrophys. J. 1984, 279, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, H.; Fischer, D. Chromospheric Activity and Jitter Measurements for 2630 Stars on the California Planet Search. Astrophys. J. 2010, 725, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti, S.; Desidera, S.; Damasso, M.; Malavolta, L.; Lanza, A.F.; Biazzo, K.; Bonomo, A.S.; Claudi, R.U.; Marzari, F.; Poretti, E.; et al. The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG. XII. Characterization of the planetary system around HD 108874. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 599, A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desort, M.; Lagrange, A.M.; Galland, F.; Udry, S.; Mayor, M. Search for exoplanets with the radial-velocity technique: Quantitative diagnostics of stellar activity. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, R.D.; Collier Cameron, A.; Queloz, D.; Barros, S.C.C.; Deleuil, M.; Fares, R.; Gillon, M.; Lanza, A.F.; Lovis, C.; Moutou, C.; et al. Planets and stellar activity: Hide and seek in the CoRoT-7 system. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Morales, M.; Haywood, R.D.; Coughlin, J.L.; Zeng, L.; Buchhave, L.A.; Giles, H.A.C.; Affer, L.; Bonomo, A.S.; Charbonneau, D.; Collier Cameron, A.; et al. Kepler-21b: A Rocky Planet Around a V = 8.25 Magnitude Star. Astron. J. 2016, 152, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasso, M.; Bonomo, A.S.; Astudillo-Defru, N.; Bonfils, X.; Malavolta, L.; Sozzetti, A.; Lopez, E.; Zeng, L.; Haywood, R.D.; Irwin, J.M.; et al. Eyes on K2-3: A system of three likely sub-Neptunes characterized with HARPS-N and HARPS. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1802.08320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
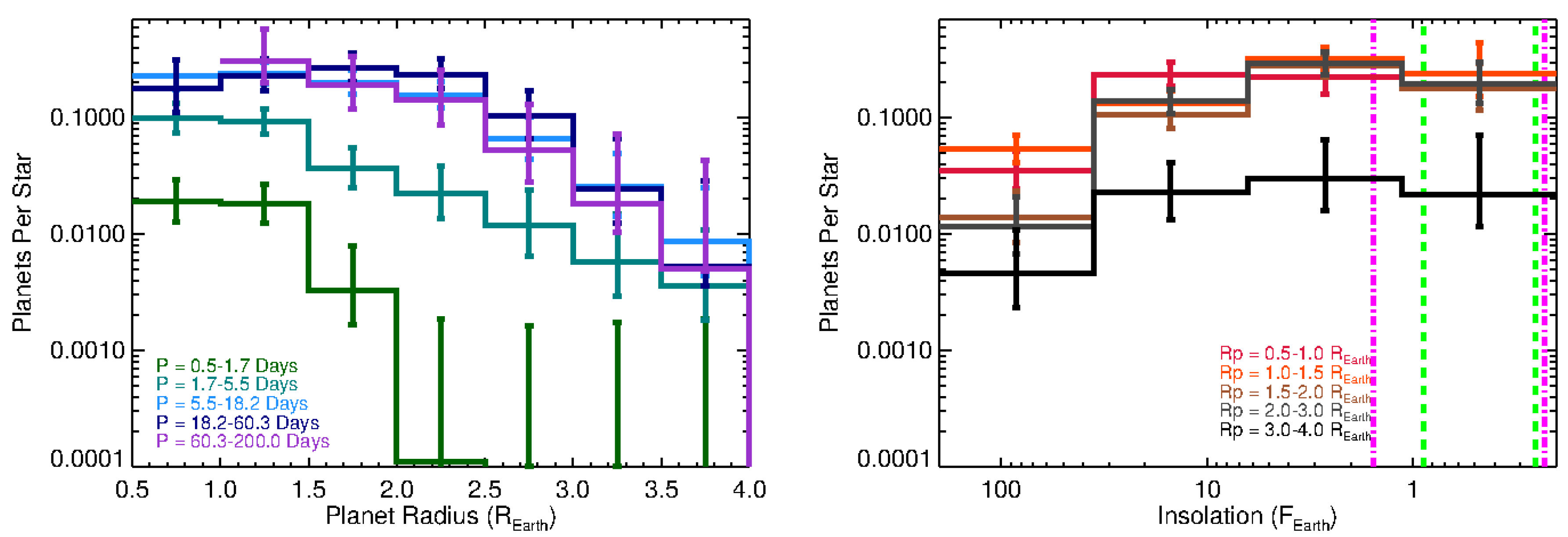
- Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W.; Bryson, S.T.; Jenkins, J.M.; Rowe, J.F.; Batalha, N.M.; Borucki, W.J.; Koch, D.G.; Dunham, E.W.; Gautier, T.N., III; et al. Planet Occurrence within 0.25 AU of Solar-type Stars from Kepler. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2012, 201, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressing, C.D.; Charbonneau, D. The Occurrence Rate of Small Planets around Small Stars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressing, C.D.; Charbonneau, D. The Occurrence of Potentially Habitable Planets Orbiting M Dwarfs Estimated from the Full Kepler Dataset and an Empirical Measurement of the Detection Sensitivity. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopparapu, R.K.; Ramirez, R.; Kasting, J.F.; Eymet, V.; Robinson, T.D.; Mahadevan, S.; Terrien, R.C.; Domagal-Goldman, S.; Meadows, V.; Deshpande, R. Habitable Zones around Main-sequence Stars: New Estimates. Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, A.L.; Ballard, S.; Johnson, J.A. The habitability of planets orbiting M-dwarf stars. Phys. Rep. 2016, 663, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winters, J.G.; Henry, T.J.; Lurie, J.C.; Hambly, N.C.; Jao, W.C.; Bartlett, J.L.; Boyd, M.R.; Dieterich, S.B.; Finch, C.T.; Hosey, A.D.; et al. The Solar Neighborhood. XXXV. Distances to 1404 m Dwarf Systems Within 25 pc in the Southern Sky. Astron. J. 2015, 149, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, A.; Bean, J.L.; Huber, K.F.; Dreizler, S.; Seifahrt, A.; Czesla, S. Detecting Planets Around Very Low Mass Stars with the Radial Velocity Method. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchwinski, R.C.; Mahadevan, S.; Robertson, P.; Ramsey, L.; Harder, J. Toward Understanding Stellar Radial Velocity Jitter as a Function of Wavelength: The Sun as a Proxy. Astrophys. J. 2015, 798, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, J.; Bertout, C. Spots on T Tauri stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 211, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, J.R.; Jeffers, S.V.; Jones, H.R.A. The effect of M dwarf starspot activity on low-mass planet detection thresholds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 412, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ford, E.B.; Matsumura, S.; Rasio, F.A. Dynamical Outcomes of Planet-Planet Scattering. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, 580–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruteau, C.; Crida, A.; Paardekooper, S.J.; Masset, F.; Guilet, J.; Bitsch, B.; Nelson, R.; Kley, W.; Papaloizou, J. Planet-Disk Interactions and Early Evolution of Planetary Systems. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1312.4293. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Batygin, K.; Bodenheimer, P.H.; Laughlin, G.P. In Situ Formation and Dynamical Evolution of Hot Jupiter Systems. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, J.F.; Moutou, C.; Malo, L.; Baruteau, C.; Yu, L.; Hébrard, E.; Hussain, G.; Alencar, S.; Ménard, F.; Bouvier, J.; et al. A hot Jupiter orbiting a 2-million-year-old solar-mass T Tauri star. Nature 2016, 534, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Donati, J.F.; Hébrard, E.M.; Moutou, C.; Malo, L.; Grankin, K.; Hussain, G.; Collier Cameron, A.; Vidotto, A.A.; Baruteau, C.; et al. A hot Jupiter around the very active weak-line T Tauri star TAP 26. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 1342–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakos, T.; Königl, A. On the Origin of the Sub-Jovian Desert in the Orbital-period-Planetary-mass Plane. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 820, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeh, T.; Holczer, T.; Faigler, S. Dearth of short-period Neptunian exoplanets: A desert in period-mass and period-radius planes. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 589, A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzes, A.P.; Cochran, W.D. The radial velocity variability of the K giant Beta Ophiuchi. 1: The detection of low-amplitude, short-period pulsations. Astrophys. J. 1994, 432, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saio, H.; Wood, P.R.; Takayama, M.; Ita, Y. Oscillatory convective modes in red giants: A possible explanation of the long secondary periods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 3863–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, W.J.; Miglio, A. Asteroseismology of Solar-Type and Red-Giant Stars. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 353–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatzes, A.P.; Endl, M.; Cochran, W.D.; MacQueen, P.J.; Han, I.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, K.M.; Mkrtichian, D.; Döllinger, M.; Hartmann, M.; et al. The Radial Velocity Variability of the K-giant γ Draconis: Stellar Variability Masquerading as a Planet. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percy, J.R.; Wilson, J.B.; Henry, G.W. Long-Term VRI Photometry of Small-Amplitude Red Variables. I. Light Curves and Periods. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2001, 113, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudi, R. Exoplanets: Possible Biosignatures. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.05829. [Google Scholar]
- Tessenyi, M.; Tinetti, G.; Savini, G.; Pascale, E. Molecular detectability in exoplanetary emission spectra. Icarus 2013, 226, 1654–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellen, I.A.G.; de Kok, R.J.; de Mooij, E.J.W.; Albrecht, S. The orbital motion, absolute mass and high-altitude winds of exoplanet HD209458b. Nature 2010, 465, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodler, F.; Kürster, M.; Barnes, J.R. Detection of CO absorption in the atmosphere of the hot Jupiter HD 189733b. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogi, M.; Giacobbe, P.; Guilluy, G.; de Kok, R.J.; Sozzetti, A.; Mancini, L.; Bonomo, A.S. Exoplanet atmospheres with GIANO. I. Water in the transmission spectrum of HD 189733b. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1801.09569. [Google Scholar]
- Rodler, F.; Lopez-Morales, M.; Ribas, I. Weighing the Non-transiting Hot Jupiter τ Boo b. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 753, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.H.C.; Santos, N.C.; Figueira, P.; Faria, J.P.; Montalto, M.; Boisse, I.; Ehrenreich, D.; Lovis, C.; Mayor, M.; Melo, C.; et al. Evidence for a spectroscopic direct detection of reflected light from 51 Pegasi b. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 576, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piskorz, D.; Benneke, B.; Crockett, N.R.; Lockwood, A.C.; Blake, G.A.; Barman, T.S.; Bender, C.F.; Carr, J.S.; Johnson, J.A. Detection of Water Vapor in the Thermal Spectrum of the Non-transiting Hot Jupiter Upsilon Andromedae b. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seager, S.; Deming, D. Exoplanet Atmospheres. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 48, 631–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crossfield, I.J.M.; Petigura, E.; Schlieder, J.E.; Howard, A.W.; Fulton, B.J.; Aller, K.M.; Ciardi, D.R.; Lépine, S.; Barclay, T.; de Pater, I.; et al. A Nearby M Star with Three Transiting Super-Earths Discovered by K2. Astrophys. J. 2015, 804, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, S.; Ge, J. The Use of Absorption Cells as a Wavelength Reference for Precision Radial Velocity Measurements in the Near-Infrared. Astrophys. J. 2009, 692, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Benedick, A.J.; Fendel, P.; Glenday, A.G.; Kärtner, F.X.; Phillips, D.F.; Sasselov, D.; Szentgyorgyi, A.; Walsworth, R.L. A laser frequency comb that enables radial velocity measurements with a precision of 1 cm s−1. Nature 2008, 452, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, T.; Wilken, T.; Araujo-Hauck, C.; Holzwarth, R.; Hänsch, T.W.; Pasquini, L.; Manescau, A.; D’Odorico, S.; Murphy, M.T.; Kentischer, T.; et al. Laser Frequency Combs for Astronomical Observations. Science 2008, 321, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tozzi, A.; Oliva, E.; Iuzzolino, M.; Fini, L.; Puglisi, A.; Sozzi, M.; Falcini, G.; Carbonaro, L.; Ghedina, A.; Mercatelli, L.; et al. GIANO and HARPS-N together: Towards an Earth-mass detection instrument. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9908, p. 99086C. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchy, F.; Doyon, R.; Artigau, É.; Melo, C.; Hernandez, O.; Wildi, F.; Delfosse, X.; Lovis, C.; Figueira, P.; Canto Martins, B.L.; et al. Near-InfraRed Planet Searcher to Join HARPS on the ESO 3.6-metre Telescope. Messenger 2017, 169, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Seifahrt, A.; Käufl, H.U. High precision radial velocity measurements in the infrared. A first assessment of the RV stability of CRIRES. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 491, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
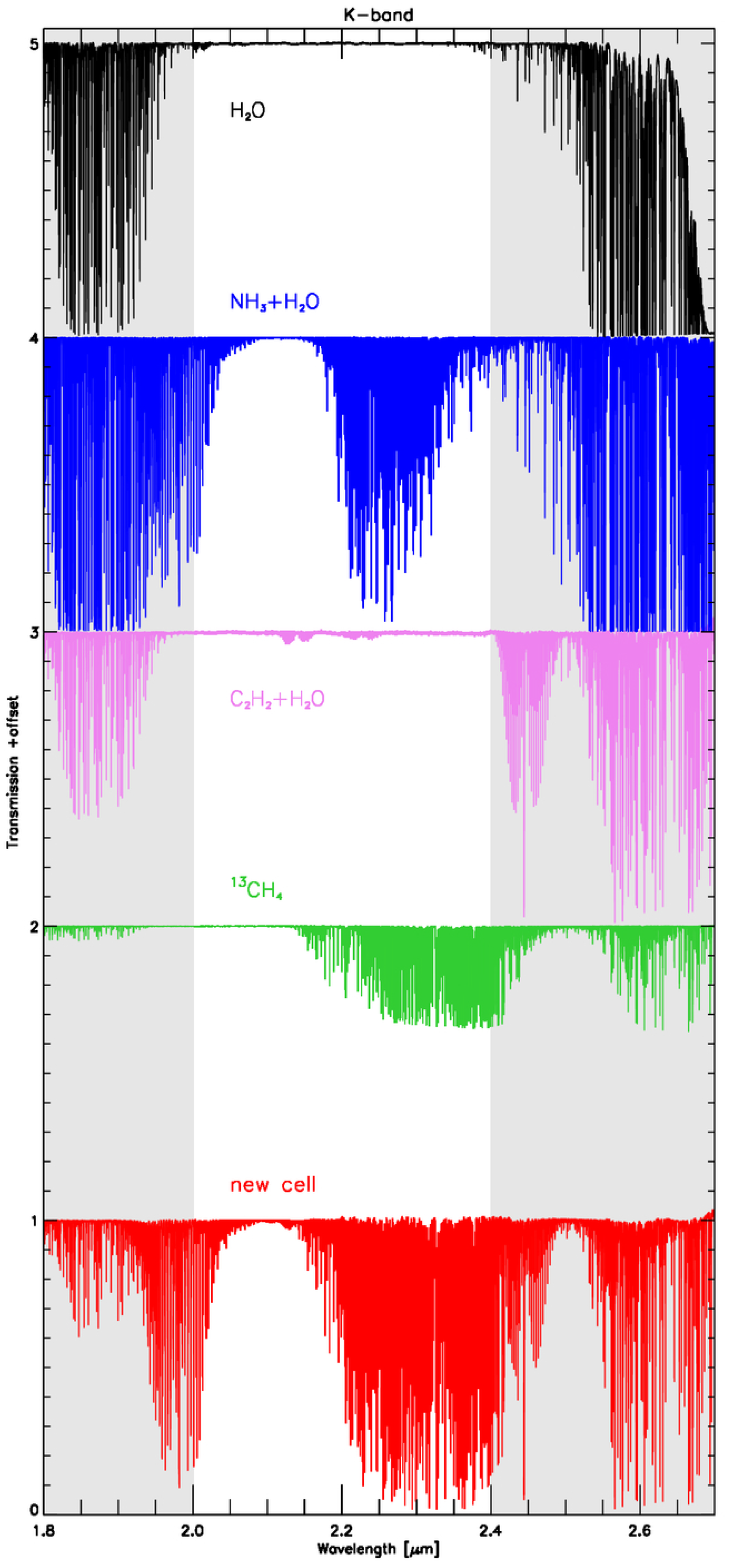
- Bean, J.L.; Seifahrt, A.; Hartman, H.; Nilsson, H.; Wiedemann, G.; Reiners, A.; Dreizler, S.; Henry, T.J. The CRIRES Search for Planets Around the Lowest-mass Stars. I. High-precision Near-infrared Radial Velocities with an Ammonia Gas Cell. Astrophys. J. 2010, 713, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglada-Escudé, G.; Plavchan, P.; Mills, S.; Gao, P.; García-Berríos, E.; Lewis, N.S.; Sung, K.; Ciardi, D.; Beichman, C.; Brinkworth, C.; et al. Design and Construction of Absorption Cells for Precision Radial Velocities in the K Band Using Methane Isotopologues. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2012, 124, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, U.; Anglada-Escude, G.; Baade, D.; Bristow, P.; Dorn, R.J.; Follert, R.; Gojak, D.; Grunhut, J.; Hatzes, A.P.; Heiter, U.; et al. Wavelength calibration from 1–5 μm for the CRIRES+ high-resolution spectrograph at the VLT. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 91475G. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, R.; Griffin, R. Accurate wavelengths of stellar and telluric absorption lines near lambda 7000 Angstroms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1973, 162, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, P.; Pepe, F.; Melo, C.H.F.; Santos, N.C.; Lovis, C.; Mayor, M.; Queloz, D.; Smette, A.; Udry, S. Radial velocities with CRIRES. Pushing precision down to 5-10 m/s. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 511, A55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, G.; Sommer, S.; Rapp, M.; Latteck, R. Investigation of gravity waves using horizontally resolved radial velocity measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alcalá, J.M.; Natta, A.; Manara, C.F.; Spezzi, L.; Stelzer, B.; Frasca, A.; Biazzo, K.; Covino, E.; Randich, S.; Rigliaco, E.; et al. X-shooter spectroscopy of young stellar objects. IV. Accretion in low- mass stars and substellar objects in Lupus. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 561, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
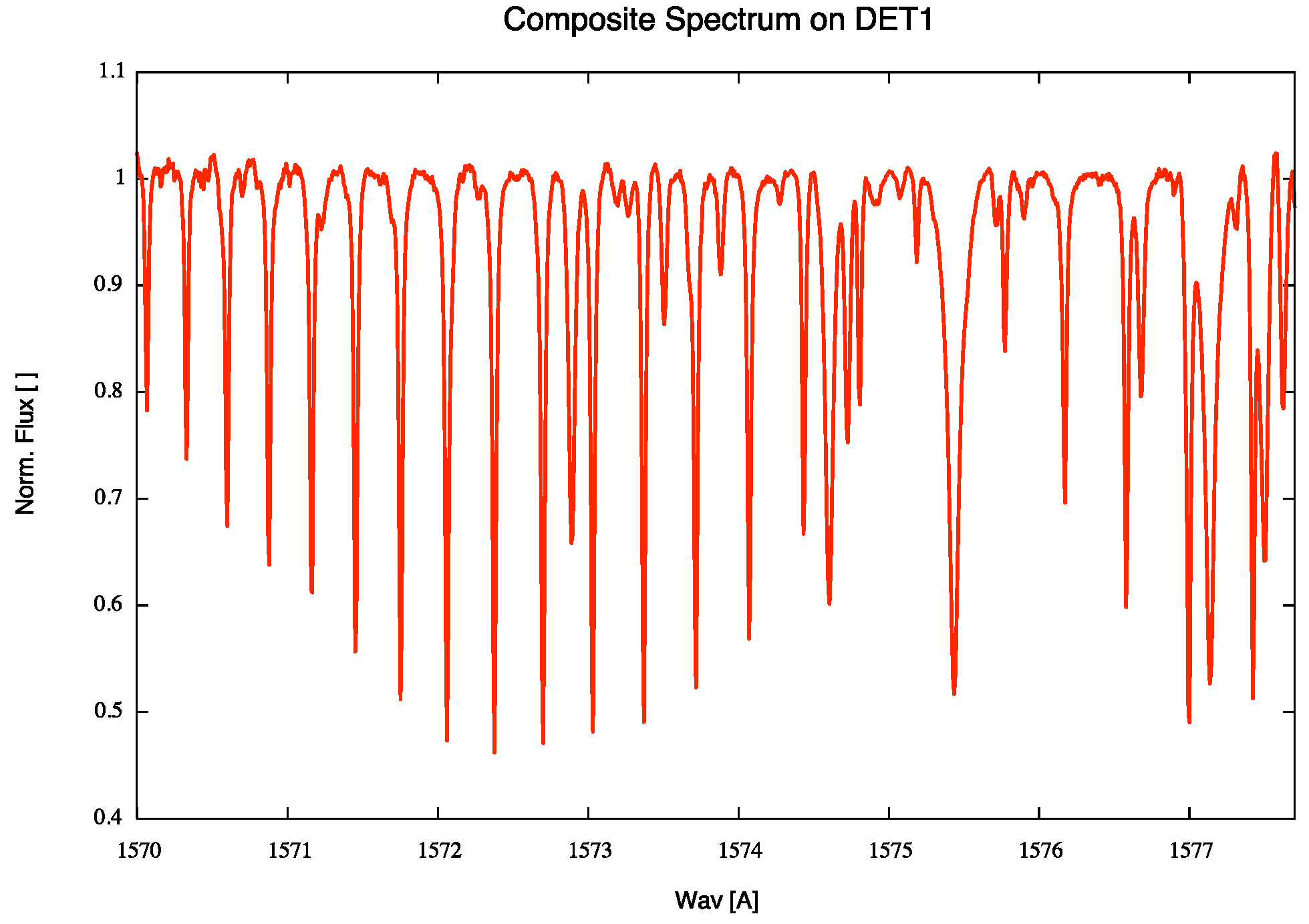
- Artigau, É.; Astudillo-Defru, N.; Delfosse, X.; Bouchy, F.; Bonfils, X.; Lovis, C.; Pepe, F.; Moutou, C.; Donati, J.F.; Doyon, R.; et al. Telluric-line subtraction in high-accuracy velocimetry: A PCA-based approach. In Observatory Operations: Strategies, Processes, and Systems V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9149, p. 914905. [Google Scholar]
- Sameshima, H.; Matsunaga, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Kawakita, H.; Hamano, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kondo, S.; Fukue, K.; Taniguchi, D.; Mizumoto, M.; et al. Correction of Near-infrared High-resolution Spectra for Telluric Absorption at 0.90–1.35 μm. Astron. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2018, 130, 074502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.P.; Tokunaga, A.T.; Toomey, D.W.; Carr, J.B. CSHELL: A high spectral resolution 1–5 μm cryogenic echelle spectrograph for the IRTF. In Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation; Fowler, A.M., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1993; Volume 1946, pp. 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, I.S.; Becklin, E.E.; Bendiksen, O.; Brims, G.; Canfield, J.; Figer, D.F.; Graham, J.R.; Hare, J.; Lacayanga, F.; Larkin, J.E.; et al. Design and development of NIRSPEC: A near-infrared echelle spectrograph for the Keck II telescope. In Infrared Astronomical Instrumentation; Fowler, A.M., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3354, pp. 566–578. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle, K.H.; Blum, R.D.; Joyce, R.R.; Sharp, N.; Ridgway, S.T.; Bouchet, P.; van der Bliek, N.S.; Najita, J.; Winge, C. The Phoenix Spectrograph at Gemini South. In Discoveries and Research Prospects from 6- to 10-Meter-Class Telescopes II; Guhathakurta, P., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 4834, pp. 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kaeufl, H.U.; Ballester, P.; Biereichel, P.; Delabre, B.; Donaldson, R.; Dorn, R.; Fedrigo, E.; Finger, G.; Fischer, G.; Franza, F.; et al. CRIRES: A high-resolution infrared spectrograph for ESO’s VLT. In Ground-Based Instrumentation for Astronomy; Moorwood, A.F.M., Iye, M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5492, pp. 1218–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Follert, R.; Dorn, R.J.; Oliva, E.; Lizon, J.L.; Hatzes, A.; Piskunov, N.; Reiners, A.; Seemann, U.; Stempels, E.; Heiter, U.; et al. CRIRES+: A cross-dispersed high-resolution infrared spectrograph for the ESO VLT. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 914719. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, E.L.; Guenther, E.; Zapatero Osorio, M.R.; Bouy, H.; Wainscoat, R. A Multiwavelength Radial Velocity Search for Planets around the Brown Dwarf LP 944-20. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 644, L75–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, L.; Huerta, M.; Johns-Krull, C.M.; Mahmud, N.; Jaffe, D.T.; Hartigan, P. A Young-Planet Search in Visible and Infrared Light: DN Tauri, V836 Tauri, and V827 Tauri. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 687, L103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, C.J.; Mahmud, N.I.; Prato, L.; Johns-Krull, C.M.; Jaffe, D.T.; Hartigan, P.M.; Beichman, C.A. A Search for Giant Planet Companions to T Tauri Stars. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N.I.; Crockett, C.J.; Johns-Krull, C.M.; Prato, L.; Hartigan, P.M.; Jaffe, D.T.; Beichman, C.A. Starspot-induced Optical and Infrared Radial Velocity Variability in T Tauri Star Hubble I 4. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gully-Santiago, M.A.; Herczeg, G.J.; Czekala, I.; Somers, G.; Grankin, K.; Covey, K.R.; Donati, J.F.; Alencar, S.H.P.; Hussain, G.A.J.; Shappee, B.J.; et al. Placing the Spotted T Tauri Star LkCa 4 on an HR Diagram. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setiawan, J.; Henning, T.; Launhardt, R.; Müller, A.; Weise, P.; Kürster, M. A young massive planet in a star-disk system. Nature 2008, 451, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huélamo, N.; Figueira, P.; Bonfils, X.; Santos, N.C.; Pepe, F.; Gillon, M.; Azevedo, R.; Barman, T.; Fernández, M.; di Folco, E.; et al. TW Hydrae: Evidence of stellar spots instead of a Hot Jupiter. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 489, L9–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.S.; Reffert, S.; Trifonov, T.; Quirrenbach, A.; Fischer, D.A. Precise radial velocities of giant stars. V. A brown dwarf and a planet orbiting the K giant stars τ Geminorum and 91 Aquarii. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 555, A87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Álvarez, E.; Affer, L.; Micela, G.; Maldonado, J.; Carleo, I.; Damasso, M.; D’Orazi, V.; Lanza, A.F.; Biazzo, K.; Poretti, E.; et al. The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG. XV. A substellar companion around a K giant star identified with quasi-simultaneous HARPS-N and GIANO measurements. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.T.; Robertson, P. The Third Workshop on Extremely Precise Radial Velocities: The New Instruments. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2017, 1, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quirrenbach, A.; Amado, P.J.; Caballero, J.A.; Mundt, R.; Reiners, A.; Ribas, I.; Seifert, W.; Abril, M.; Aceituno, J.; Alonso-Floriano, F.J.; et al. CARMENES instrument overview. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 91471F. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, E.L.; Guenther, E.; Barrado y Navascués, D.; Esparza, P.; Manescau, A.; Laux, U. NAHUAL: A near-infrared high-resolution spectrograph for the GTC optimized for studies of ultracool dwarfs. Astron. Nachr. 2005, 326, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, P.J.; Quirrenbach, A.; Caballero, J.A.; Mandel, H.; Ribas, I.; Reiners, A.; Sanchez-Carrasco, M.A.; Seifert, W.; Mundt, R.; Carmenes Consortium. CARMENES: A radial-velocity survey for terrestrial planets in the habitable zones of M dwarfs. A historical overview. arXiv, 2012; arXiv:1210.5465. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, P.J.; The Carmenes Consortium. CARMENES: Commissioning and first scientific results at the telescope. A precursor for HiRES@E-ELT. In Proceedings of the XII Scientific Meeting of the Spanish Astronomical Society, Bilbao, Spain, 18–22 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, W.; Sánchez Carrasco, M.A.; Xu, W.; Cárdenas, M.C.; Sánchez-Blanco, E.; Becerril, S.; Feiz, C.; Ramón, A.; Dreizler, S.; Rohde, P.; et al. CARMENES. II: Optical and opto-mechanical design. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy IV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8446, p. 844633. [Google Scholar]
- Becerril, S.; Mirabet, E.; Lizon, J.L.; Abril, M.; Cárdenas, C.; Ferro, I.; Morales, R.; Pérez, D.; Ramón, A.; Sánchez-Carrasco, M.A.; et al. CARMENES-NIR channel spectrograph cooling system AIV: Thermo-mechanical performance of the instrument. In Advances in Optical and Mechanical Technologies for Telescopes and Instrumentation II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9912, p. 991262. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero, J.A.; Guàrdia, J.; López del Fresno, M.; Zechmeister, M.; de Juan, E.; Alonso-Floriano, F.J.; Amado, P.J.; Colomé, J.; Cortés-Contreras, M.; García-Piquer, Á.; et al. CARMENES: Data flow. In Observatory Operations: Strategies, Processes, and Systems VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9910, p. 99100E. [Google Scholar]
- Zechmeister, M.; Reiners, A.; Amado, P.J.; Azzaro, M.; Bauer, F.F.; Béjar, V.J.S.; Caballero, J.A.; Guenther, E.W.; Hagen, H.J.; Jeffers, S.V.; et al. Spectrum radial velocity analyser (SERVAL). High-precision radial velocities and two alternative spectral indicators. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, A.; Zechmeister, M.; Caballero, J.A.; Ribas, I.; Morales, J.C.; Jeffers, S.V.; Schöfer, P.; Tal-Or, L.; Quirrenbach, A.; Amado, P.J.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. High-resolution optical and near-infrared spectroscopy of 324 survey stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 612, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Floriano, F.J.; Morales, J.C.; Caballero, J.A.; Montes, D.; Klutsch, A.; Mundt, R.; Cortés-Contreras, M.; Ribas, I.; Reiners, A.; Amado, P.J.; et al. CARMENES input catalogue of M dwarfs. I. Low-resolution spectroscopy with CAFOS. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 577, A128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Contreras, M.; Béjar, V.J.S.; Caballero, J.A.; Gauza, B.; Montes, D.; Alonso-Floriano, F.J.; Jeffers, S.V.; Morales, J.C.; Reiners, A.; Ribas, I.; et al. CARMENES input catalogue of M dwarfs. II. High-resolution imaging with FastCam. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, S.V.; Schoefer, P.; Lamert, A.; Reiners, A.; Montes, D.; Caballero, J.A.; Cortes-Contreras, M.; Marvin, C.J.; Passegger, V.M.; Zechmeister, M.; et al. CARMENES input catalogue of M dwarfs: III. Rotation and activity from high-resolution spectroscopic observations. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1802.02102. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, R.; Lovis, C.; Pepe, F.; Cameron, A.C.; Latham, D.W.; Molinari, E.; Udry, S.; Bezawada, N.; Buchschacher, N.; Figueira, P.; et al. HARPS-N @ TNG, two year harvesting data: Performances and results. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 91478C. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, E.; Origlia, L.; Baffa, C.; Biliotti, C.; Bruno, P.; D’Amato, F.; Del Vecchio, C.; Falcini, G.; Gennari, S.; Ghinassi, F.; et al. The GIANO-TNG spectrometer. In Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6269, p. 626919. [Google Scholar]
- Iuzzolino, M.; Sanna, N.; Tozzi, A.; Oliva, E. Laboratory measurements of modal noise on optical fiber. Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 2015, 86, 490. [Google Scholar]
- Origlia, L.; Oliva, E.; Baffa, C.; Falcini, G.; Giani, E.; Massi, F.; Montegriffo, P.; Sanna, N.; Scuderi, S.; Sozzi, M.; et al. High resolution near IR spectroscopy with GIANO-TNG. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 91471E. [Google Scholar]
- Claudi, R.; Benatti, S.; Carleo, I.; Ghedina, A.; Guerra, J.; Ghinassi, F.; Harutyunyan, A.; Micela, G.; Molinari, E.; Oliva, E.; et al. GIARPS: Commissioning and first scientific results. Astron. Telescopes Instrum. 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Claudi, R.; Benatti, S.; Carleo, I.; Ghedina, A.; Guerra, J.; Micela, G.; Molinari, E.; Oliva, E.; Rainer, M.; Tozzi, A.; et al. GIARPS@TNG: GIANO-B and HARPS-N together for a wider wavelength range spectroscopy. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, U.; Tozzi, A.; Ghedina, A.; Anwand-Heerwart, H.; Claudi, R.; Benatti, S.; Carleo, I.; Guerra, J.; Ghinassi, F.; Harutyunyan, A.; et al. The TNG/GIARPS gas-absorption cell for near-infrared precision radial velocities. Astron. Telescopes Instrum. 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Rainer, M.; Harutyunyan, A.; Carleo, I.; Oliva, E.; Benatti, S.; Bignamini, A.; Claudi, R.; Gonzalez–Alvarez, E.; Sanna, N.; Ghedina, A.; et al. Introducing GOFIO: A DRS for the GIANO-B near-infrared spectrograph. Astron. Telescopes Instrum. 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Benatti, S.; Claudi, R.; Desidera, S.; Gratton, R.G.; Lanza, A.F.; Micela, G.; Pagano, I.; Piotto, G.; Sozzetti, A.; Boccato, C.; et al. The GAPS Project: First Results. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.04166. [Google Scholar]
- Carleo, I.; Sanna, N.; Gratton, R.; Benatti, S.; Bonavita, M.; Oliva, E.; Origlia, L.; Desidera, S.; Claudi, R.; Sissa, E. High precision radial velocities with GIANO spectra. Exp. Astron. 2016, 41, 351–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
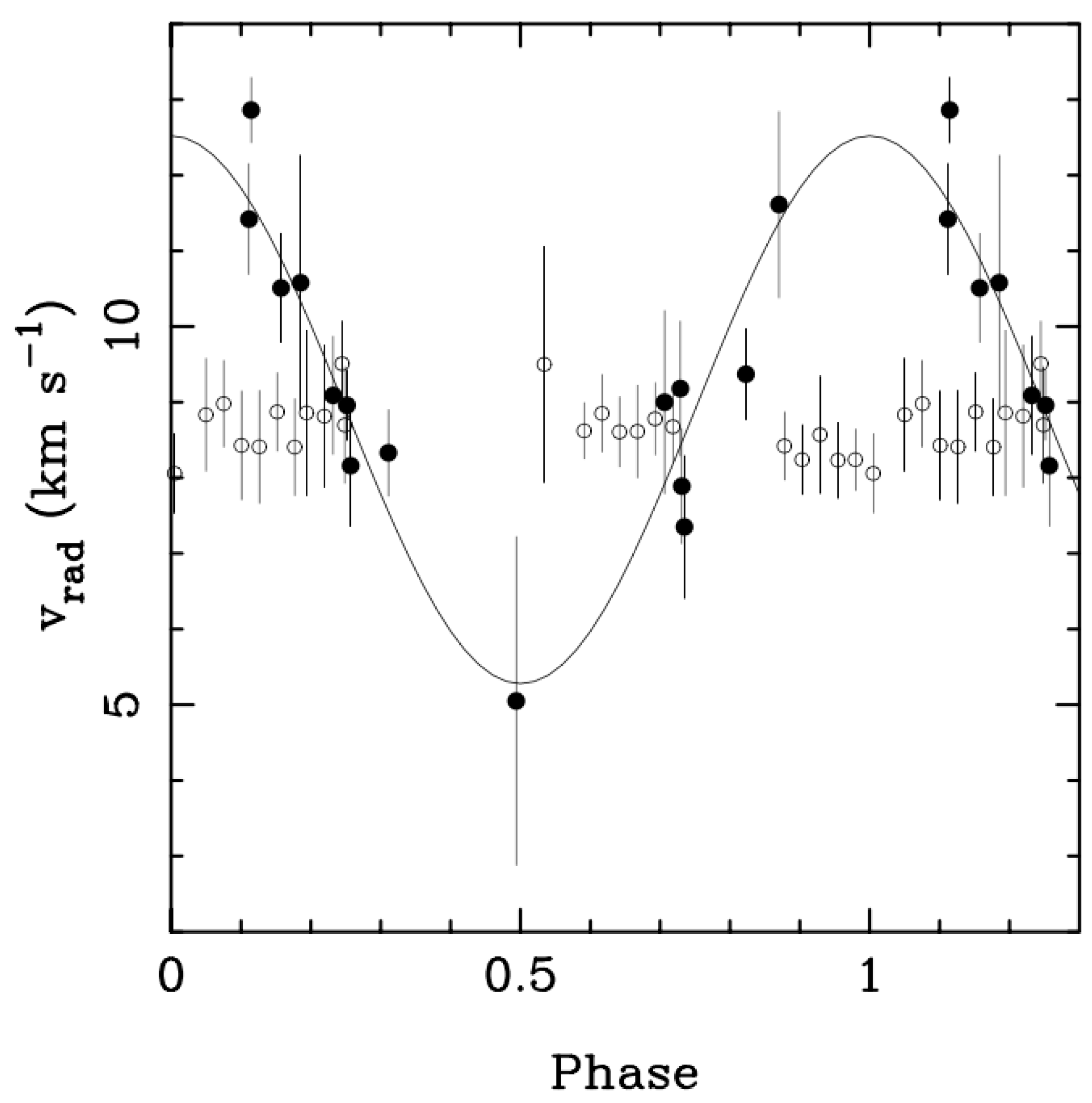
- Carleo, I.; Benatti, S.; Lanza, A.F.; Gratton, R.; Claudi, R.; Desidera, S.; Mace, G.N.; Messina, S.; Sanna, N.; Sissa, E.; et al. Multi-band high resolution spectroscopy rules out the hot Jupiter BD+20 1790b. First data from the GIARPS Commissioning. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 613, A50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildi, F.; Blind, N.; Reshetov, V.; Hernandez, O.; Genolet, L.; Conod, U.; Sordet, M.; Segovilla, A.; Rasilla, J.L.; Brousseau, D.; et al. NIRPS: An adaptive-optics assisted radial velocity spectrograph to chase exoplanets around M-stars. In Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets VIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10400, p. 1040018. [Google Scholar]
- Schipani, P.; Claudi, R.; Campana, S.; Baruffolo, A.; Basa, S.; Basso, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Cascone, E.; Cosentino, R.; D’Alessio, F.; et al. The new SOXS instrument for the ESO NTT. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9908, p. 990841. [Google Scholar]
- Conod, U.; Blind, N.; Wildi, F.; Pepe, F. Adaptive optics for high resolution spectroscopy: A direct application with the future NIRPS spectrograph. In Adaptive Optics Systems V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9909, p. 990941. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, G.R.; Winn, J.N.; Vanderspek, R.; Latham, D.W.; Bakos, G.Á.; Bean, J.L.; Berta-Thompson, Z.K.; Brown, T.M.; Buchhave, L.; Butler, N.R.; et al. Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). In Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2014: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9143, p. 914320. [Google Scholar]
- Dressing, C.D.; Charbonneau, D.; Dumusque, X.; Gettel, S.; Pepe, F.; Collier Cameron, A.; Latham, D.W.; Molinari, E.; Udry, S.; Affer, L.; et al. The Mass of Kepler-93b and The Composition of Terrestrial Planets. Astrophys. J. 2015, 800, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudi, R.; Pace, E.; Ciaravella, A.; Micela, G.; Piccioni, G.; Billi, D.; Cestelli Guidi, M.; Cocola, L.; Erculiani, M.S.; Fedel, M.; et al. Atmosphere in a Test Tube. Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 2016, 87, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, R.A.; McCarthy, P.J.; Raybould, K.; Bigelow, B.C.; Bouchez, A.H.; Filgueira, J.M.; Jacoby, G.; Johns, M.; Sawyer, D.; Shectman, S.; et al. Overview and status of the Giant Magellan Telescope project. In Ground-Based and Airborne Telescopes V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9145, p. 91451C. [Google Scholar]
- Szentgyorgyi, A.; Barnes, S.; Bean, J.; Bigelow, B.; Bouchez, A.; Chun, M.Y.; Crane, J.D.; Epps, H.; Evans, I.; Evans, J.; et al. A preliminary design for the GMT-Consortium Large Earth Finder (G-CLEF). In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 914726. [Google Scholar]
- Mace, G.; Kim, H.; Jaffe, D.T.; Park, C.; Lee, J.J.; Kaplan, K.; Yu, Y.S.; Yuk, I.S.; Chun, M.Y.; Pak, S.; et al. 300 nights of science with IGRINS at McDonald Observatory. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 99080, p. 99080C. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Yuk, I.S.; Lee, H.; Wang, W.; Park, C.; Park, K.J.; Chun, M.Y.; Pak, S.; Strubhar, J.; Deen, C.; et al. GMTNIRS (Giant Magellan Telescope near-infrared spectrograph): Design concept. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy III; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7735, p. 77352K. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, D.T.; Barnes, S.; Brooks, C.; Gully-Santiago, M.; Pak, S.; Park, C.; Yuk, I. GMTNIRS (Giant Magellan Telescope Near-Infrared Spectrograph): Optimizing the design for maximum science productivity and minimum risk. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9147, p. 914722. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, D.T.; Barnes, S.; Brooks, C.; Lee, H.; Mace, G.; Pak, S.; Park, B.G.; Park, C. GMTNIRS: Progress toward the Giant Magellan Telescope near-infrared spectrograph. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9908, p. 990821. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, A.; Di Marcantonio, P.; D’Odorico, V.; Cristiani, S.; Maiolino, R.; Oliva, E.; Origlia, L.; Riva, M.; Valenziano, L.; Zerbi, F.M.; et al. EELT-HiRES the high-resolution spectrograph for the E-ELT. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9908, p. 990823. [Google Scholar]
- Rauer, H.; Catala, C.; Aerts, C.; Appourchaux, T.; Benz, W.; Brandeker, A.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J.; Deleuil, M.; Gizon, L.; Goupil, M.J.; et al. The PLATO 2.0 mission. Exp. Astron. 2014, 38, 249–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquini, L.; Cristiani, S.; García López, R.; Haehnelt, M.; Mayor, M.; Liske, J.; Manescau, A.; Avila, G.; Dekker, H.; Iwert, O.; et al. Codex. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy III; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7735, p. 7352F. [Google Scholar]
- Origlia, L.; Oliva, E.; Maiolino, R.; Gustafsson, B.; Piskunov, N.; Kochucov, O.; Vanzi, L.; Minniti, D.; Zoccali, M.; Hatzes, A.; et al. SIMPLE: A high-resolution near-infrared spectrometer for the E-ELT. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy III; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7735, p. 77352B. [Google Scholar]
- Maiolino, R.; Haehnelt, M.; Murphy, M.T.; Queloz, D.; Origlia, L.; Alcala, J.; Alibert, Y.; Amado, P.J.; Allende Prieto, C.; Ammler-von Eiff, M.; et al. A Community Science Case for E-ELT HiRES. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:astro-ph.IM/1310.3163. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, S.; Winn, J.N.; Johnson, J.A.; Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W.; Butler, R.P.; Arriagada, P.; Crane, J.D.; Shectman, S.A.; Thompson, I.B.; et al. Obliquities of Hot Jupiter Host Stars: Evidence for Tidal Interactions and Primordial Misalignments. Astrophys. J. 2012, 757, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmeister, B.; Czesla, S.; Schmitt, J.H.M.M.; Jeffers, S.V.; Caballero, J.A.; Zechmeister, M.; Reiners, A.; Ribas, I.; Amado, P.J.; Quirrenbach, A.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs: Wing asymmetries of Hα, Na I D, and He I lines. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1801.10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passegger, V.M.; Reiners, A.; Jeffers, S.V.; Wende-von Berg, S.; Schoefer, P.; Caballero, J.A.; Schweitzer, A.; Amado, P.J.; Bejar, V.J.S.; Cortes-Contreras, M.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs-Photospheric parameters of target stars from high-resolution spectroscopy. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1802.02946. [Google Scholar]
- Tal-Or, L.; Zechmeister, M.; Reiners, A.; Jeffers, S.V.; Schöfer, P.; Quirrenbach, A.; Amado, P.J.; Ribas, I.; Caballero, J.A.; Aceituno, J.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs: Radial-velocity variations of active stars in visual-channel spectra. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.SR/1803.02338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiners, A.; Ribas, I.; Zechmeister, M.; Caballero, J.A.; Trifonov, T.; Dreizler, S.; Morales, J.C.; Tal-Or, L.; Lafarga, M.; Quirrenbach, A.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. HD147379 b: A nearby Neptune in the temperate zone of an early-M dwarf. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifonov, T.; Kürster, M.; Zechmeister, M.; Tal-Or, L.; Caballero, J.A.; Quirrenbach, A.; Amado, P.J.; Ribas, I.; Reiners, A.; Reffert, S.; et al. The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. First visual-channel radial-velocity measurements and orbital parameter updates of seven M-dwarf planetary systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 609, A117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W.; Fischer, D.A.; Isaacson, H.; Muirhead, P.S.; Henry, G.W.; Boyajian, T.S.; von Braun, K.; Becker, J.C.; Wright, J.T.; et al. The NASA-UC-UH ETA-Earth Program. IV. A Low-mass Planet Orbiting an M Dwarf 3.6 PC from Earth. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister, M.; Kürster, M. The generalised Lomb-Scargle periodogram. A new formalism for the floating-mean and Keplerian periodograms. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 496, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinamonti, M.; Damasso, M.; Marzari, F.; Sozzetti, A.; Desidera, S.; Maldonado, J.; Scandariato, G.; Affer, L.; Lanza, A.F.; Bignamini, A.; et al. The HADES RV Programme with HARPS-N@TNG VIII. Gl15A: A multiple wide planetary system sculpted by binary interaction. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:astro-ph.EP/1804.03476. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Tuomi, M.; Jones, H.R.A.; Barnes, J.; Anglada-Escudé, G.; Vogt, S.S.; Butler, R.P. Color Difference Makes a Difference: Four Planet Candidates around τ Ceti. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montet, B.T.; Morton, T.D.; Foreman-Mackey, D.; Johnson, J.A.; Hogg, D.W.; Bowler, B.P.; Latham, D.W.; Bieryla, A.; Mann, A.W. Stellar and Planetary Properties of K2 Campaign 1 Candidates and Validation of 17 Planets, Including a Planet Receiving Earth-like Insolation. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benneke, B.; Werner, M.; Petigura, E.; Knutson, H.; Dressing, C.; Crossfield, I.J.M.; Schlieder, J.E.; Livingston, J.; Beichman, C.; Christiansen, J.; et al. Spitzer Observations Confirm and Rescue the Habitable-zone Super-Earth K2-18b for Future Characterization. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, P.; Henning, T.; Kürster, M.; Trifonov, T.; Zechmeister, M.; Tal-Or, L.; Anglada-Escudé, G.; Hatzes, A.P.; Lafarga, M.; Dreizler, S.; et al. The CARMENES Search for Exoplanets around M Dwarfs: A Low-mass Planet in the Temperate Zone of the Nearby K2-18. Astron. J. 2018, 155, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cloutier, R.; Astudillo-Defru, N.; Doyon, R.; Bonfils, X.; Almenara, J.M.; Benneke, B.; Bouchy, F.; Delfosse, X.; Ehrenreich, D.; Forveille, T.; et al. Characterization of the K2-18 multi-planetary system with HARPS. A habitable zone super-Earth and discovery of a second, warm super-Earth on a non-coplanar orbit. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán-Obispo, M.; Gálvez-Ortiz, M.C.; Anglada-Escudé, G.; Kane, S.R.; Barnes, J.R.; de Castro, E.; Cornide, M. Evidence of a massive planet candidate orbiting the young active K5V star BD+20 1790. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 512, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán-Obispo, M.; Tuomi, M.; Gálvez-Ortiz, M.C.; Golovin, A.; Barnes, J.R.; Jones, H.R.A.; Kane, S.R.; Pinfield, D.; Jenkins, J.S.; Petit, P.; et al. Analysis of combined radial velocities and activity of BD+20 1790: Evidence supporting the existence of a planetary companion. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 576, A66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, P.; Marmier, M.; Bonfils, X.; di Folco, E.; Udry, S.; Santos, N.C.; Lovis, C.; Mégevand, D.; Melo, C.H.F.; Pepe, F.; et al. Evidence against the young hot-Jupiter around BD +20 1790. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 513, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seager, S. Exoplanet Habitability. Science 2013, 340, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.R.; Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W.; Edelstein, J.; Wishnow, E.H.; Poppett, C.L. KPF: Keck Planet Finder. In Ground-Based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9908, p. 990870. [Google Scholar]


© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benatti, S. Multi-Wavelength High-Resolution Spectroscopy for Exoplanet Detection: Motivation, Instrumentation and First Results. Geosciences 2018, 8, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080289
Benatti S. Multi-Wavelength High-Resolution Spectroscopy for Exoplanet Detection: Motivation, Instrumentation and First Results. Geosciences. 2018; 8(8):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080289
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenatti, Serena. 2018. "Multi-Wavelength High-Resolution Spectroscopy for Exoplanet Detection: Motivation, Instrumentation and First Results" Geosciences 8, no. 8: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080289
APA StyleBenatti, S. (2018). Multi-Wavelength High-Resolution Spectroscopy for Exoplanet Detection: Motivation, Instrumentation and First Results. Geosciences, 8(8), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8080289





