Abstract
The lakes across China’s middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system have a long history of sustaining human pressures. These aquatic resources have been exploited for fisheries and irrigation over millennia at a magnitude of scales, with the result that many lakes have lost their ecological integrity. The consequences of these changes in the ecosystem health of lakes are not fully understood; therefore, a long-term investigation is urgently needed. Gastropods (aquatic snails) are powerful bio-indicators that link primary producers, herbivores, and detritivores associated with macrophytes and grazers of periphyton and higher-level consumers. They are sensitive to abrupt environmental change such as eutrophication, dehydration, flooding, and proliferation of toxicity in floodplain lake systems. The use of the remains of gastropod shells (subfossils) preserved in the sedimentary archives of the floodplain lakes of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system holds high significance, as their potential in environmental change has not been studied in detail in the past. Here, we aim to test the hypothesis that modern and sub-fossil gastropods in the sediments of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River floodplains systems have significant value as bioindicators, as they have the ability to reveal health-gradients of lake-ecosystem change in the region.
1. Introduction
“Ecologically healthy” lake systems must possess three basic characteristics to conserve in their ability to maintain structure, function, and resilience [1]. Broadly, how biological diversity and assemblages, and their potential interactions with the environment (vigor or processes), are changing over a period of time (resilience) determine ecosystem health is crucial to understand. Hence, the concept of a healthy ecosystem relies on the sustainability of the assemblage structure, function, and resilience of the biota present in a lake, as it usually occurs in natural conditions. In natural conditions, when lakes experience water level and thermal variations, biological assemblages are able to adapt to the change through their evolutionary ontogenetic behavior. Healthy and sustainable lake ecosystems play an integral role in generating important ecosystem services including clean water, fisheries, and aesthetic values. However, the number of lakes with high ecological integrity has substantially declined, as many lakes and wetlands are profoundly embedded within the complex socio-ecological system, where human domination of the environment has caused unprecedented perturbations [2]. As human activities have also driven the significant loss of biodiversity and the extinction of species, the application of the concept of healthy ecosystems in lake restoration should maintain the system as “natural” if possible or return the system to its “pre-disturbance” condition [3,4].
China’s middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system hold one of the oldest civilizations, where humans have interacted with lakes for millennia [5,6]. The vast areas of productive Yangtze River floodplain lakes have been used since the Neolithic Period (7700 cal a BP) for water resource development, including paddy culture, fisheries, irrigation, and navigation [7]. The exploitation for land reclamation, urbanization, and industrialization is at such a magnitude of scales that most lakes have lost their ecological integrity [8,9]. Some lakes have either disappeared, or their areas have been considerably reduced due to reclamation, resulting in unprecedented ecosystem and biodiversity loss in the area, risking the demise of ecological productivity and genetic exchanges of natural populations. For example, poor dispersal abilities of molluscs have already been reported [10,11].
The water quality required to maintain ecologically healthy lake ecosystems has been perturbed by the release of large quantities of commercial fertilizers (nutrients), toxic compounds from adjacent agriculture, and heavy metals from domestic and industrial sewage systems [8,12,13]. To some extent, the socio-economic developments in the basin have brought about a catastrophic failure in the maintenance of the lakes’ ecosystem health [8]. Eutrophication has become prevalent in many economically viable lakes in the region, including the Taihu and Chaohu, causing a significant loss of restoration investments [14,15].
Yet, the complex lake ecosystems in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system have shown disparity in their state of health. The degree of human disturbance in these lakes has been found to vary largely. Some lakes remain in relatively “good condition”, reflecting a more stable community structure, function, and resilience [6,8]. Some of the most productive lakes contain diverse fish communities (> 70 species), abundant invertebrate resources, and dense submerged macrophyte beds, forming one of the most important fishery bases of this economically viable region [16]. Further, increased conservation efforts, together with a strong partnership among governmental and non-governmental agencies and local communities, have improved the ecological resilience of some lakes [17,18].
Despite their high indicator values, subfossil gastropods of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system have rarely been explored for their potential to track ecological health [19,20]. Gastropods play a central role in linking primary producers, herbivores, and detritivores associated with macrophytes and grazers of periphyton and higher level consumers [21,22]. They graze on periphyton, enhance macrophyte growth, and transfer energy to higher trophic levels, such as molluscivorous fish [23,24]. Lake nutrient conditions and the variability in grazing behaviour of epiphytic gastropods also affect the species composition, biomass, and productivity of epiphytes and stimulate macrophyte growth [19]. While submerged macrophytes provide gastropod habitats for oviposition, cascading effects of fish predation at different nutrient levels determine the dynamics of gastropods and macrophyte communities [25]. Gastropods show both species-specific and community level responses to a range of environmental factors, such as macrophyte and epiphyte dynamics, eutrophication, dehydration, flooding, sedimentation, and the proliferation of toxic compounds [21,26,27,28].
Individual responses of gastropods to anthropogenic impacts have been reported to be of a higher sensitivity to ecosystem health than that of the community level responses [29]. For example, pulmonate Lymnaea peregra and prosobranch Valvata piscinalis snails strongly reflect the dynamics of submerged macrophytes, while other pulmonate species, Planorbis vortex, and prosobranch Bithynia tentaculata species, may in certain cases, reflect the presence of emergent macrophytes [30]. Similarly, Radix swinhoei strongly responds to microcystin toxicity in its tissues during cyanobacterial blooms [31,32]. Other major components of essential minerals for gastropod growth and development are phosphates, calcium, and bicarbonate ions [33]. While epiphytes are a major component of the diet of gastropods, the silicon (Si) from these algae can also influence their dynamics, as Si keeps aquatic ecosystems healthy through viable plant production [34]. In addition, several studies focus on the effects of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous (CNP) stoichiometry on snails [35], including physiological responses to stoichiometric constraints: nutrient limitation and compensatory feeding in a freshwater snail [36,37].
Given their significant response to environmental change in lakes, gastropods are used as bioindicators of ecosystem health [38]. For example, gastropods utilize epiphytic macrophytes as a source of food. Any loss of macrophytes due to disturbances can have direct impacts on the food habits of gastropods and subsequent reductions in abundance and assemblage diversity [19]. The population structure of epiphytic gastropods across many shallow lakes of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system has been significantly altered over the recent past due to increased human impacts [19]. Basin-wide habitat fragmentation has led to the loss of macrophytes and consequent changes in epiphytic gastropod communities. Apart from macrophyte density, other biotic (fish, parasitism) and abiotic (e.g., temperature, lake depth, and minerals) factors have also had an effect on gastropod distribution [21,39]. Hence, the remains of gastropods have become increasingly useful for the long-term study of the ecological health of these lakes. Gastropod assemblage composition and diversity archived in lake sediments can act as strong biological indicators for both ecological and hydrological changes [40]. The shells of gastropods reflect the lakes’ past hydrology and food web dynamics [41,42]. The chemical components of gastropod shells, as well as the structure and shape of the shells, can provide indications of past conditions in lakes, including water quality and predator-prey interactions. For example, the available calcium and other inorganic and organic compounds in water are revealed by shell biogeochemistry [43,44,45]. Gastropods use carbon and mineral ions during metabolism, and the signature of carbon and ions are also preserved in their shells. The use of sedimentary remains of gastropods in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River holds significance to understand the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem health. Even though the region is exposed to a wide range of anthropogenic impacts, recent environmental regulations have mitigated the impacts. As a result, some lakes display improved water quality and ecosystem health. However, the differences between lake responses to recent environmental changes have not yet been examined using gastropod subfossils. Here, we test the hypothesis that gastropod remains retrieved as individuals or as assemblages from the sediments of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River lake system have the ability to reveal gradients of lake-ecosystem health in the region. A study of this kind will potentially help environmental resource managers to better allocate resources and efforts for lake conservation and management in the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The research is part of the large Key National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) River Resilience project. It covers a large number of shallow lakes across the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. This study focused on 32 lakes with available records of gastropod remains in surface sediments across the geo-referenced sites extending between 28°32′27.43″ North and 113°23′28.83″ East (Figure 1). The middle and lower reaches of the 6300 km-long Yangtze River extend from Yichang and Hukou (Poyang Lake mouth) and Hukou and Yangtze estuary (Shanghai). The region is referred to as the “Water Realm” of China’s major agricultural district (http://www.cjw.gov.cn/zjzx/cjyl/). The area contains over 600 large and small lake groups surrounded by medium to large cities, forming a prosperous industrial belt [8,46]. These lakes comprise rich floral and faunal diversity, and crop cultivation generating significant agro-ecosystem services. The gross domestic product of metropolitan cities in the basin had reached about 20 trillion Yuan by 2014, benefitting more than 320 million people.
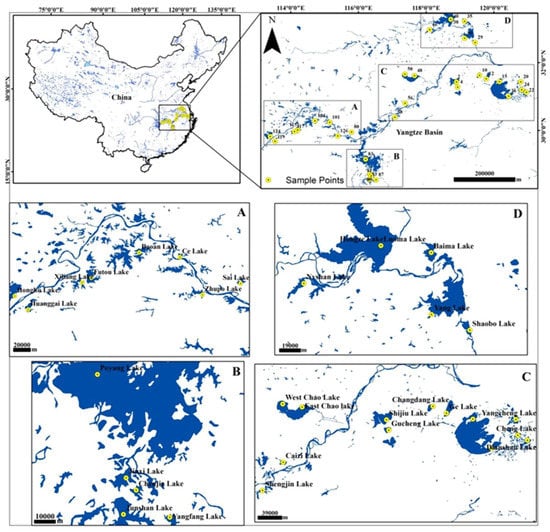
Figure 1.
Location of study sites in middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system (China) in anti-clockwise order. (A) Enlargement of the study sites showing the upper section of the reach; (B) Enlargement of the study sites showing the middle section of the river reach; (C) Enlargement of the study sites showing the lower section of the river reach; (D) Enlargement of the study sites showing the sites around the Honge Lake complex. The largest lake among the study sites, the Poyang Lake, is at the middle section, while the other large lake, Taihu Lake, is at the lower section of river.
Historically, most shallow lake systems in the study area have been in a healthy ecological state, 2–5 m deep, and connected with the main river channel, showing regular flood-pulse events [47,48,49]. Poyang Lake, for example, one of the largest Yangtze lake systems, has six nature reserves containing important native species of fish, birds, and molluscs [50]. The ecosystems of these lakes, where plant growth is determined largely by light intensity and depth, or, clearer and shallower aquatic habitats, have a greater carrying capacity for submersed vegetation [51]. However, human population growth coupled with rapid economic development has led to an increased discharge of domestic sewage and industrial effluents to Yangtze River lakes, causing serious damage to ecological health [5,15]. The study area is also climatically sensitive. Being located in the subtropical zone, it is highly regulated by the East Asian monsoon system, giving higher exposure to cold and dry winters and hot and wet summers. The temperature ranges between 15 °C and 20 °C during summer with rainfall > 1000 mm annually, where 40–60% of precipitation falls between June and August [52].
2.2. Sediment Collection
Thirty-two lakes were investigated for at least three consecutive seasons on a quarterly basis, between April 2016 and July 2017. For each lake, two surface sediment samples from each season were collected from the centre of the lake using a Kajak gravity corer [53]. Each season, the top 1 cm (200 g wet sediment weight) of one of the cores was extruded in the field. Because gastropod remains were rare in some cases, samples from two or more seasons were harmonized (mixed) to make a sufficient mud sample (as high as 600 g) for subfossil gastropod analysis. Sediment cores from Changdang Lake were taken from the center of the lake using a UWITEC gravity corer (Mondsee, Austria) with a 90-mm-diameter coring tube in July 2016. The core was subsampled in the field at a 1 cm resolution and samples were transferred to the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGLAS) laboratory for further analysis.
2.3. Physico-Chemical Analysis of Water
The measurements of physico-chemistry of water samples were carried out either in the field or in the laboratory. Water samples (one representative sample for each season) were collected from the shore using acid-washed polyethylene bottles and then stored at 4 °C until further laboratory analyses [14]. A total of 31 physical and chemical variables were measured and some key variables are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mean annual values of physical and chemical variables collected from the 32 study lakes across the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system, China. SD (Secchi disk depth); Cond (conductivity); NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit); DO (dissolved oxygen); TN (total nitrogen); TP (total phosphorous); Chl-a (chlorophyll-a), SS (suspended solid).
2.4. Gastropod Subfossil Analysis
For surface sediment analysis, about half of every surface sediment sample collected during the three sampling periods, September (2016), January (2017), and May (2017), were mixed together to obtain a sufficient number (about 10 or more per sample) of shells prior to the analysis. The resulting weight of the mud samples from the three seasons combined was about 600 g. Gastropod subfossil shells were primarily sieved through a 1 mm mesh to retain all size groups preserved. After the sample was cleaned (mud washed-out), gastropod shells were hand-picked under a dissecting microscope, dried, and identified under a dissection microscope (10×) using regional keys [54,55].
For sediment core analysis, at least four short sediment cores (each 45 cm long) were retrieved in parallel from the Changdang Lake for subfossil analysis of gastropods. The preservation of gastropod remains was limited to the upper 36 cm of accumulation, spanning the past 50 years. In order to increase the number of gastropod remains, each sediment core (of three of the cores collected) was subsampled at a 3 cm resolution (interval). Each 3 cm resolution sample with the same depth profile from each core was mixed prior to hand-picking and identifying the shells under a dissection microscope. The fourth core was subsampled at a 0.5 cm resolution and was used for pollen analysis, thus the results are not reported in this study. Only the full body gastropod shells (fragments were discarded) were identified based on regional keys [54,55].
2.5. Numerical Assessment of Lake Ecosystems Health
The spatial gradient of ecosystem health across the study sites was assessed by identifying the changes in physico-chemical parameters, as well as biological responses to the environmental variables. Selected physico-chemical variables from the 32 sites were assessed to identify the gradients of water quality change and possible effects on gastropod populations. Correlation and regression analyses including direct and indirect ordination techniques were used to understand lake environmental change across the study region. Biological responses to the environmental variables were assessed both at spatial and temporal scales. Responses at the spatial scale were assessed at population and community levels of gastropods. The community level response was assessed using direct ordination techniques, such as canonical correspondence analysis (CCA). The population level response of gastropod species was assessed using a generalized linear model (GLM). Unlike linear regression models, which are limited by the errors assumed to be identically and independently distributed with a normal Gaussian distribution, GLMs are better suited for positive non-normally distributed data. The GLM fits regression models for univariate response data that follow a very general class of statistical distributions called the exponential family, including normal, binomial, Poisson, geometric, negative binomial, exponential, and inverse normal distributions [56].
2.6. Development of Age-Depth Model
Sub-samples of dried sediment (0.5–3 g) were used to establish the core chronology as described by Choudhary et al. [57]. The excess 210Pb activity (210Pbex) exhibited a monotonic decrease with depth, from a maximum of 286.73 Bq/kg near the surface to 7.59 Bq/kg at 49 cm (Figure 2). The sediment core records of 210Pbex show an exponential distribution. The upward decreasing trend of 210Pbex in the upper 5 cm indicates mixing. We used the constant initial concentration (CIC) model to estimate the sedimentation rate and age-depth chronology (Figure 2). The average sedimentation rate was 0.45 cm/annum. The core covered 111 years (1905–2016). Except for a few samples, the records of 137Cs activity were extremely low for reliable detection and unsuitable to be used as a time marker. Instead, we used local historical events to validate our age-depth model. All trace metals increased abruptly at 20 cm and then plateaued around 15 cm (Figure 2). These were coincident with the beginning of industrialization in the 1970s in the Changang lake catchment. The 210Pb results were consistent with 20 cm and the 15 cm depths, corresponding to 1970 and 1980, respectively.
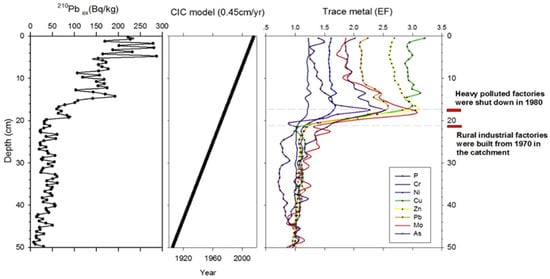
Figure 2.
The constant initial concentration (CIC) profile of the 210Pb activity, age-depth model, and trace metals and other elements in the sediment core of the Changdang Lake. All trace metals increased abruptly at 20 cm and then plateaued around 15 cm in the sediment core. These results coincide with the initial industrial period in 1970 across the catchment. Most factories were forced to shut down or were asked to reform in the 1980s due to high water pollution. The records indicate that the depths of 20 cm and 15 cm in the core correspond to 1970 and 1980, respectively, which is also consistent with the 210Pb results.
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Gradients
All study lakes were relatively shallow (< 3 m depth). The Secchi disk measurements showed high turbidity. Other eutrophication parameters such as total phosphorous (TP) and chlorophyll (Chl-a) showed poor water quality among the study sites. However, pH, conductivity, and salinity measurements suggested that all studied lakes are relatively fresh (Table 1). Relatively higher standard deviations of calcium and magnesium, two essential elements required for gastropod shell development, indicated differences in the concentration and dynamics of these minerals among the study sites (Table 1).
The principal components analysis (PCA) of the 31 environmental variables measured in the 32 lakes suggested that more than 30% of the total variation was explained by axis 1 (λ1 = 0.31), while axis 2 (λ2 = 0.14) accounted for about 15% of the total variation (Figure 3). Axis 1 was largely influenced by anthropogenic-derived factors such as TP, PO4–P, and TN (total nitrogen), as well as water temperature, turbidity, and water depth. Axis 2 was driven more by factors associated with phycocyanin, Chl-a, suspended solids, and Secchi disk depth (Figure 3). In axis 1, most nutrients (TP, TN, DOC (dissolved organic carbon), and DIC (dissolved inorganic carbon)), elements (Na, K, Ca, and Mg), and salinity were positively correlated.
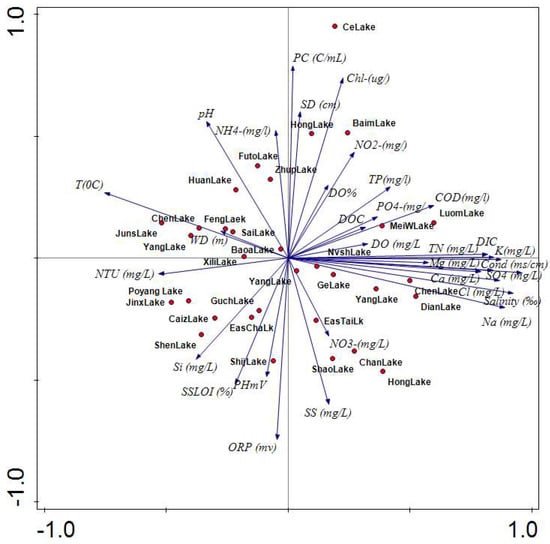
Figure 3.
Principal components analysis of 31 physical and chemical variables from 32 lakes. SD = Secchi depth; DO (dissolve oxygen); SS = suspended solid; LOI = loss on ignition; WD = water depth; DOC = dissolve organic carbon; DIC = dissolved inorganic carbon; ORP = organic reactive phosphate; COD = chemical oxygen demand.
The concentration of TP in water provides strong evidence of water quality and the ecological health of lakes [58]. Based on the standard used in [58], TP measurements showed that a large number (N = 25) of lakes among the study sites were eutrophic, and about six lakes were hypertrophic (Figure 4). Other variables which are influenced by TP, including Chl-a, coincided with elevated turbidity, with high concentrations of suspended sediment particulates in some lakes (Figure 5). Two lakes, Ce and Melliangan Bay, were found to have poor water quality, which means having higher eutrophication, as revealed by TP and Chl-a measurements (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
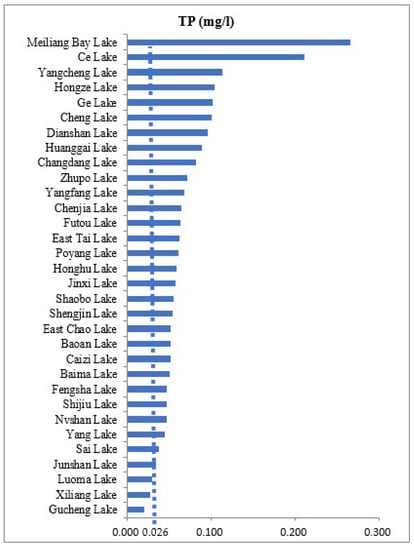
Figure 4.
Gradient of water quality with TP pollution in 32 study sites. Total phosphorous concentration > 0.026 µg/L is shown by the vertical line, i.e., eutrophic and hypertrophic lakes. Lakes are presented on the basis of the smallest to the largest measurements of TP.
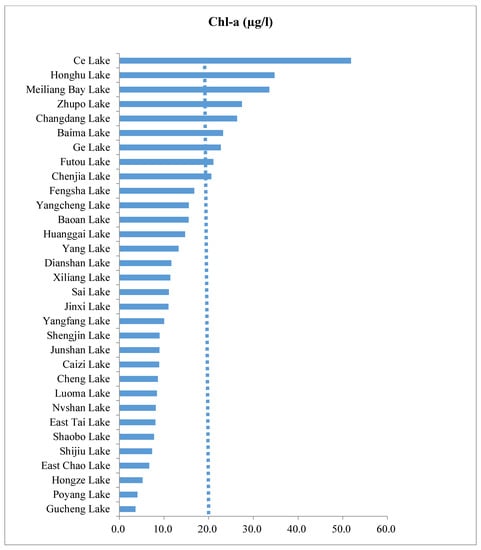
Figure 5.
Gradient of water quality with Chl-a concentration in 32 study sites. Lakes with >20 Chl-a µg/L are shown by a vertical line indicating medium to high turbidity. Lakes are presented on the basis of the smallest to the largest measurements of Chl-a.
3.2. Detrended Corespondence Analysis (DCA)
A total of 11 species of subfossil gastropods were collected from the 32 study lakes. The taxon Cipangopaludina miyagii was the most common species recorded, followed by Parafossarulus striatulus and Radix plicatula, Alocinma longicornis, and Radix swinhoei (Table 2). The compositional gradients of sub-fossil gastropods after detrending by segments, squared-root transformation, down-weighting of rare taxa, and non-linear rescaling of axes [59], revealed that a total of 37% of the total variation was explained by the first two DCA axes (Table 3, Figure 6). Gastropod species such as R. swinhoei were closely associated with DCA axis 1, while the species Stenothyra glabra and Hippeutis cantori were associated with DCA axis 2 (Figure 6).

Table 2.
Mean abundance ± SD of the gastropods collected from 32 lakes.

Table 3.
Summary of a Detrended correspondence cnalysis (DCA) of the 11 species of gastropods in 32 sites.
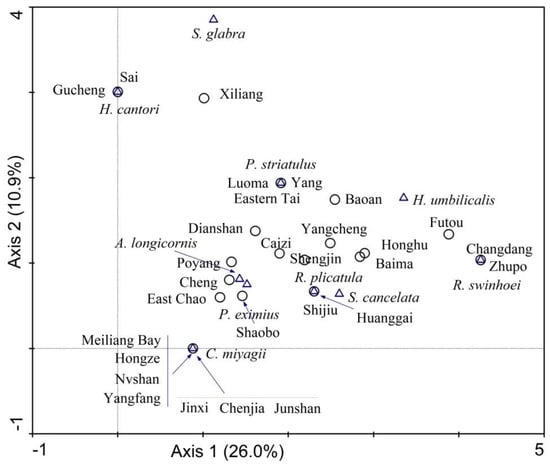
Figure 6.
Detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) of subfossil gastropods in 32 surface sediment samples. Open triangles represent gastropod species and open circles represent the study sites.
3.3. Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA)
The compositional gradient length of the first DCA axis was more than 4, thus non-linear ordination (CCA) was used to examine species-environment relationships. A preliminary CCA, when constrained with all environmental variables and 11 sub-fossil gastropods in ordination, identified two lakes (Meiliang Bay and Ce) as outliers. A forward selection method in unrestricted Monte Carlo tests of 999 random permutations in a reduced model in CCA showed that four environmental variables: Chl-a, TP, Ca, and K, were significant in the species data (p < 0.05) (Figure 7). The first two CCA axes explained 17.1% and 8.7% of the total variation in the species data, while the species-environment relationships of each axis explained 51.7% and 26.2% of the total data, respectively (Table 4). The biplots (Figure 7B) showed that the taxon Hippeutis umbilicalis was positively related to Ca concentrations and was abundant in Zhupo and Futou Lakes, while the taxon Semisulcospira cancelata was related to TP and the taxon Radix swinhoei was related to Chl-a.
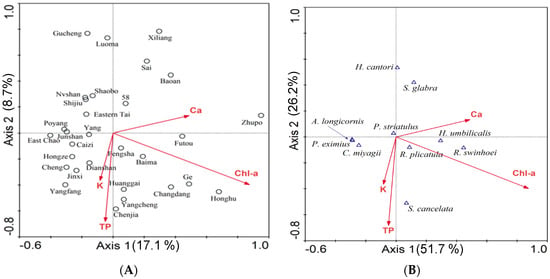
Figure 7.
(A) Biplots of canonical correspondence analsysis (CCA): Samples vs. environmental variables in 30 surface sediment samples. The cumulative percentage variance of species data (%) are shown in Axis 1 and Axis 2; (B) Biplots of CCA: species of subfossil gastropods vs. environmental variables in 30 surface sediment samples. Cumulative percentage variance of species-environment (%) are shown in Axis 1 and Axis 2.

Table 4.
Summary of canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) forward selection of 11 species of gastropods in 30 sites.
3.4. Generalized Linear Model (GLM)
Out of 11 species of subfossil gastropods identified from the surface sediment samples, only Cipangpaludina miyagii showed strong sensitivity to increasing concentrations of Chl-a. The C. miyagii populations declined substantially in lakes with Chl-a concentrations > 5 µg/L (Figure 8).
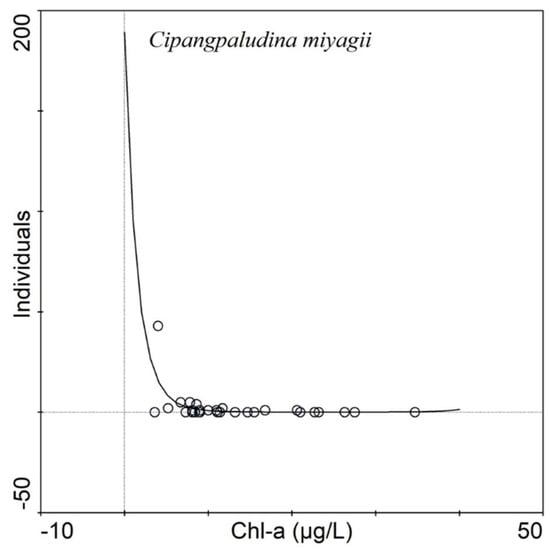
Figure 8.
Response of C. miyagii to Chl-a (µg/L) in 30 surface sediment samples under GLM (generalized linear model).
3.5. Subfossil Gastropod Stratigraphy
Altogether, six species of subfossil gastropods, Ballamya aeruginosa, Parafossarulus eximius, Parafossarulus striatulus, Alocinma longicornis, Radix swinhoei, and Semisulcospira cancelata, were recorded in a 36 cm long sediment core collected from Changdang Lake. The preservation was scarce as only a few complete individuals from each species were retrieved. The relative abundance of all five species was common in the 1950s. The subfossil abundance of Ballamya aeruginosa was dominant among species collected throughout the period (1935–2015 AD between a 36 and 27 cm depth (c. 1935–1955 AD). The preservation of the other five species was relatively poor. P. eximius remains were rarely encountered. The abundance of P. striatulus was low with sporadic abundance. The abundance of the other three species, A. longicornis, R. swinhoei, and S. cancelata, was also low, where the abundance of A. longicornis and S. cancelata declined, while the abundance of Radix swinhoei increased over time (Figure 9).
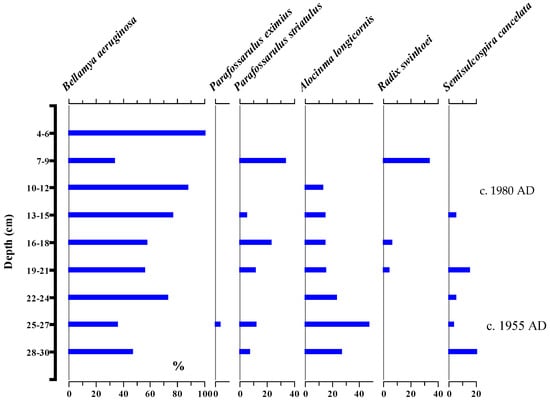
Figure 9.
Sediment stratigraphy of subfossil gastropods (relative abundance) in Changdang Lake in the lower Yangtze River.
4. Discussion
4.1. Gastropods and Aquatic Ecosystem Health in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Floodplain Lake System
How freshwater gastropod communities respond to changes in floodplain lakes’ ecosystem health in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system is the key question of our study. Gastropods show strong interactions with fish, macroinvertebrates, and littoral macrophytes in shallow lake ecosystems [60]. Macrophyte communities play a central role in regulating water quality and lake ecosystem health, while gastropods graze on periphyton and transfer carbon energy to higher trophic levels [61,62]. However, ecosystem health in the floodplain lakes of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system has declined due to the excessive use of fertilizers in agricultural catchments and aquaculture, and the release of nutrients into the lake systems [48]. In our study, a large number of lakes are classified as eutrophic and six lakes are considered hypertrophic, as shown by high TP concentrations (Figure 4). The loss of ecological health in these lakes is due to the cumulative effects of a range of stressors, which include nutrients, carbon, salts, and toxins. Freshwater gastropods are reportedly sensitive to high toxic compounds such as microsystin LR in eutrophic lakes [63]. For example, Radix swinhoei lives in aquatic plants and is commonly exposed to the microsystin LR toxin during cyanobacterial blooms in the lower Yangtze lakes, with altered metabolism and reproductive performance [28,63,64]. In our study, at least nine lakes also have a >20 µg/L Chl-a concentration, leading to significantly reduced transparency and hypoxia (Figure 5). Gastropod diversity was poor in lakes with high TP and Chl-a, due to the loss of aquatic macrophytes. Macrophytes have attached periphyton, which is an important element of the diet of gastropods [19].
4.2. Community Level Response to Lake Ecosystem Health
Although the number of species was low, the DCA discriminated the sites as per the gastropod affiliation. Species such as H. catori and S. glabra were associated with lakes characteristic to ”healthy“ conditions with a relatively good quality, consisting of a high macrophyte density. The CCA indicated strong relationships between gastropod species and four environmental variables. The species H. umbilicalis was related to Ca-rich lakes such as Zhupo and Futou lakes (Figure 7B). Studies suggest that hard water lakes provide a favourable environment for gastropod populations as these lakes contain a rich source of minerals and calcium needed for shell development [40,65]. Shells are formed during ecological processes, where water biogeochemistry plays a central role in physiological processes of snails [44,45].
The temporal response of gastropods to the ecosystem health of lacustrine systems is poorly known. The decline in the subfossil abundances of S. cancelata and A. longicornis in the sediment core from Changdang Lake suggests a rapid deterioration of Lake ecosystem health, possibly caused by high concentrations of TP in the water. Both S. cancelata and A. longicornis are sensitive to water pollution. Gastropods are also sensitive to changes in the hydrodynamics of lake systems. The modification of environmental flows is common in the region, which has considerable implications for lake levels and macrophyte dynamics in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze system [6,66,67,68]. Despite the aquatic macrophytes which play a significant role in gastropod composition, we were not able to analyse the macrophyte records for our subfossil gastropod records. Gastropods receive food from epiphytic macrophytes [19]. Prior to the 1970s, Changdang Lake would likely have had a more diverse assemblage of macrophytes (submersed, emergent, and floating-leaved) and morphology supporting the growth of gastropods; however, after the 1970s (around 20 cm depth in the core), the catchment of the lake was modified by humans, subsequently leading to the loss of submerged and emergent macrophytes (Figure 2). As the Changdang Lake is very shallow and exposed to frequent wind-induced turbidity, this leads to considerable implications for the dynamics of macrophytes and thereby for gastropod populations and diversity. The deterioration amplified by increased nutrient loading and climate change over the past 60 years in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system is widely reported by various authors [19].
4.3. Population Level Response of Lake-Ecosystem Health
Gastropods show an increased heterogeneity to environmental gradients in shallow lakes, which ultimately determines their populations [19]. Understanding of individual species’ requirements to the environment holds crucial information to decipher changes in Lake ecosystem health [33]. For example, Cai et al. [69] examined the ecological stoichiometry (i.e., maintenance of fixed elemental composition in body or elemental homoeostasis) of two of the most widely distributed gastropods in the lower Yangtze River. The carbon:nitrogen:phosphorus (CNP) stoichiometry of Corbicula fluminea and Bellamya aeruginosa exhibited substantial natural intraspecific variation in tissue stoichiometry. Unlike other gastropod species, the characteristic of having CNP stoichiomertry in these species is thought to help them adapt to nutrient enriched environment [69]. In our study, only one species of gastropod, Cipangopaludina miyagii, showed a significant decreasing monotonic response to Chl-a concentrations in the GLM (Figure 8), indicating that the species is more likely to occur at eutrophic to hypertrophic conditions. This evidence suggests that there has possibly been a rapid deterioration of ecosystem health in some Yangtze River floodplain lakes as a result of multiple stressors including nutrients, heavy metals, and several other toxic compounds in the river system. Further studies are crucial to better understand the relationships between gastropods and environmental variables.
5. Conclusions
The floodplain lake ecosystems of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system, China, have gone through rapid environmental change over the past 50–60 years. Spatial and temporal responses of subfossil gastropods (freshwater snails) in the region suggest that the ecosystem health of some of the Yangtze River lake systems is likely to have declined over time. Response of the taxon, Cipangopaludina miyagii in GLM, for example, indicates highly polluted water bodies and associated ecosystems of some study sites possibly caused by nutrient loading, and the release of heavy metals and toxic compounds into the water courses from the catchments. Considerable decline in the abundance of subfossil gastropod taxa Semisulcospira cancelata and Alocinma longicornis over the past 50 years possibly indicates a rapid increase in water pollution in the region due to increasing concentrations of TP loading in some Yangtze lakes, including Chenjia and Yangcheng. This study shows that gastropods have the potential to constitute important bioindicators. The use of subfossil gastropods in lake sediments shows that the approach can have promising application for better understanding long term ecological health and contributing to a science-based allocation of resources in the conservation and management of ecosystems across the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system and beyond.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.K.; Methodology, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z., X.H.; Software, G.K., Y.C.; Validation, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z.; Formal Analysis, G.K., Y.C.; Investigation, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z., X.H., R.W., X.D.; Resources, X.Y., K.Z., R.W.; Data Curation, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, G.K.; Writing-Review & Editing, G.K.; Visualization, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z., X.H., R.W., X.D.; Supervision, G.K., Y.C., X.Y., K.Z.; Project Administration, X.Y., K.Z., R.W.; Funding Acquisition, X.Y., K.Z.
Funding
G.K. would like to acknowledge the CAS-PIFI Professorial Fellowship Program (Grant #2016VEA050) at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGLAS) and the National Natural Science Foundation China (NSFC) Grants (#41530753 and #41272379).
Acknowledgments
We would also like to thank three anonymous reviewers, and the guest editor Émilie Saulnier-Talbot, whose comments improved the quality of the manuscript significantly. Temitope Oyedotun assisted for Figure 1 in GIS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; Mageau, M. What is a healthy ecosystem? Aquat. Ecol. 1999, 33, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Shan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G. Ecosystem health assessment of the Liao River basin upstream region based on ecosystem services. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem health and ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 45, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Q.; Gippel, C.J.; Wang, H.-Z.; Leigh, C.; Jiang, X.-H. Assessment of the ecological health of heavily utilized, large lowland rivers: Example of the lower Yellow River, China. Limnology 2016, 18, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gao, C.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Dynamics of the lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China, since late nineteenth century. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4005–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattel, G.R.; Dong, X.; Yang, X. A century-scale, human-induced ecohydrological evolution of wetlands of two large River basins in Australia (Murray) and China (Yangtze). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 2151–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chao, Z.; Gu, M.; Li, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xing, B.; et al. Evidence for a neolithic age fire-irrigation paddy cultivation system in the lower Yangtze River delta, China. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zeng, H.; Yu, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, L.; Qin, B. Water and sediment quality in lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3601–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.-N.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yang, J.-X. Effect of eutrophication on molluscan community composition in the lake Dianchi (China, Yunnan). Limnologica 2011, 41, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouetard, A.; Cote, J.; Besnard, A.L.; Collinet, M.; Coutellec, M.A. Environmental versus anthropogenic effects on population adaptive divergence in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; An, S.; Gu, B. Assessment of ecosystem health during the past 40 years for lake Taihu in the Yangtze River delta, China. Limnology 2010, 12, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Z. Simplification of macrozoobenthic assemblages related to anthropogenic eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms in two large shallow subtropical lakes in China. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Anderson, N.J.; Dong, X.; Shen, J.I. Surface sediment diatom assemblages and epilimnetic total phosphorus in large, shallow lakes of the Yangtze floodplain: Their relationships and implications for assessing long-term eutrophication. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zeng, D.; Liu, D.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of PAHS, OCPS, and PCBS in Taihu lake basin. Ecol. Indic. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ye, S.; Lek, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, J.; Li, Z. The need for improved fishery management in a shallow macrophytic lake in the Yangtze River basin: Evidence from the food web structure and ecosystem analysis. Ecol. Model. 2013, 267, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Couture, R.-M.; Larssen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, X.; Bu, X.; et al. Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Brookes, J.D.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Improving water quality in China: Environmental investment pays dividends. Water Res. 2017, 118, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-J.; Pan, B.-Z.; Liang, X.-M.; Wang, H.-Z. Gastropods on submersed macrophytes in Yangtze lakes: Community characteristics and empirical modelling. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2006, 91, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Gong, Z. Composition, diversity, and environmental correlates of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in the five largest freshwater lakes of China. Hydrobiologia 2016, 788, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Carpentier, A.; Paillisson, J.-M. Long-term dynamics and community structure of freshwater gastropods exposed to parasitism and other environmental stressors. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Gong, Z.; Qin, B. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structure in lake Taihu, China: Effects of trophic status, wind-induced disturbance and habitat complexity. J. Great Lakes Res. 2012, 38, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Jeppesen, E. The response of two submerged macrophytes and periphyton to elevated temperatures in the presence and absence of snails: A microcosm approach. Hydrobiologia 2014, 738, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, G.J.C.; Thomas, J.D.; Baker, J.H. An experimental investigation of interactions in snail-macrophyte-epiphyte systems. Oecologia 1992, 91, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollum, E.W.; Crowder, L.B.; McCollum, S.A. Complex interactions of fish, snails, and littoral zone periphyton. Ecology 1998, 79, 1980–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, I.; Irvine, K. Size-specific effects of increased sediment loads on gastropod communities in Lake Tanganyika, Africa. Hydrobiologia 2004, 522, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, K.R.; Collas, F.P.L.; van der Velde, G.; Verberk, W.C.E.P. Oxygen can limit heat tolerance in freshwater gastropods: Differences between gill and lung breathers. Hydrobiologia 2015, 763, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhou, Q. Intoxication and biochemical responses of freshwater snail Bellamya aeruginosa to ethylbenzene. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, P.B.; Mitchell, E.; France, K.; Rivers, A.; Hakizimna, P.; Cohen, A.S. Individual and assemblage level effects of anthropogenic sedimentation on snails in Lake Tanganyika. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.M.; Kelly, P. Habitat disturbance and the stability of freshwater gastropod populations. Oecologia 1985, 68, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, C.; Brient, L.; Rouzic, B.L. Variation in the response of juvenile and adult gastropods (Lymnaea stagnalis) to cyanobacterial toxin (microcystin-LR). Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lance, E.; Paty, C.; Bormans, M.; Brient, L.; Gerard, C. Interactions between cyanobacteria and gastropods ii. Impact of toxic Planktothrix agardhii on the life-history traits of Lymnaea stagnalis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsak, M. Mollusc community patterns and species response curves along a mineral richness gradient: A case study in fens. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Carstensen, J.; Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Ecosystem thresholds with hypoxia. Hydrobiologia 2009, 629, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, P.; Von Elert, E. Physiological responses to stoichiometric constraints: Nutrient limitation and compensatory feeding in a freshwater snail. Oikos 2006, 115, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Schampel, J.H.; Kyle, M.; Watts, J.; Carson, E.W.; Dowling, T.E.; Tang, C.; Roopnarine, P.D. Response of grazing snails to phosphorus enrichment of modern stromatolitic microbial communities. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, A.; Hillebrand, H. Role of nutrient supply in grazer–periphyton interactions: Reciprocal influences of periphyton and grazer nutrient stoichiometry. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2006, 25, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhou, Y.; Strid, A.; Zheng, Z.; Bignert, A.; Ma, T.; Athanassiadis, I.; Qiu, Y. Spatial distribution and bioaccumulation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBS) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDES) in snails (Bellamya aeruginosa) and sediments from Taihu lake area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 7740–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niggebrugge, K.; Durance, I.; Watson, A.M.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Ormerod, S.J. Applying landscape ecology to conservation biology: Spatially explicit analysis reveals dispersal limits on threatened wetland gastropods. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, C.G.; Hassan, G.S. The significance of molluscs as paleoecological indicators of freshwater systems in central-western Argentina. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 274, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Yu, N.; Jiang, X.; Han, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Giesy, J.P.; Yu, H. Influence of blooms of phytoplankton on concentrations of hydrophobic organic chemicals in sediments and snails in a hyper-eutrophic, freshwater lake. Water Res. 2017, 113, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolinarska, K.; Pełechaty, M.; Kossler, A. Within-sample variability of δ13C and δ18O values of freshwater gastropod shells and the optimum number of shells to measure per sediment layer in the Paddenluch palaeolacustrine sequence, Germany. J. Paleolimnol. 2015, 54, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, C.G.; Zárate, M.A.; Miquel, S.E. Late Pleistocene mollusc assemblages and inferred paleoenvironments from the Andean piedmont of Mendoza, Argentina. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2007, 251, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Campos, J.; Coghill, L.M.; de Leon, F.J.G.; Johnson, S.G. The effect of aquatic plant abundance on shell crushing resistance in a freshwater snail. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, D.; Fagel, N.; Araneda, A.; Jana-Pinninghoff, P.; Keppens, E.; Urrutia, R. Late Holocene climate variability on the eastern flank of the Patagonian Andes (Chile): A δ18O record from mollusks in Lago Cisnes (47°S). Holocene 2015, 25, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Jiao, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, W. An overview of reclaimed water reuse in china. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yu, D.; Ni, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, P.; Da, L.; et al. Biodiversity changes in the lakes of the central Yangtze. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Hu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Ju, W.; Jiang, J.; Yang, G. A half-century of changes in China’s lakes: Global warming or human influence? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Jiao, L.; Wu, F. Nitrogen fractions and release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River area, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 187, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.; Liu, E.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 2015, 125, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Davidson, T.A.; Jeppesen, E. Using palaeolimnological data and historical records to assess long-term dynamics of ecosystem services in typical Yangtze shallow lakes (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renberg, I. The HON-Kajak sediment corer. J. Paleolimnol. 1991, 6, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, E.Y. Economic Fauna of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1979. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Zhang, Z. The Freshwater Bivalves of China; Conch Books: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi-Nedushan, B.; St-Hilaire, A.; Bérubé, M.; Robichaud, É.; Thiémonge, N.; Bobée, B. A review of statistical methods for the evaluation of aquatic habitat suitability for instream flow assessment. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Routh, J.; Chakrapani, G.J. An environmental record of changes in sedimentary organic matter from Lake Sattal in Kumaun Himalayas, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, D.G.; Cumming, B.F. Sedimentary cladoceran remains and their relationship to nutrients and other limnological variables in 53 lakes from British Columbia, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2003, 60, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and Canodraw for Window’s User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.I.; Sayer, C.D. Does the fish–invertebrate–periphyton cascade precipitate plant loss in shallow lakes? Ecology 2003, 84, 2155–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liess, A.; Hillebrand, H. Invited review: Direct and indirect effects in herbivore-periphyton interactions. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2004, 159, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzahn, A.M.; Hantzsche, F.; Schoo, K.L.; Boersma, M.; Aberle, N. Differential effects of nutrient-limited primary production on primary, secondary or tertiary consumers. Oecologia 2010, 162, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; Ni, L. Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in a freshwater snail (Bellamya aeruginosa) from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, T. Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Tang, T.; Xie, Z.; Ye, L.; Li, D.; Cai, Q. Distribution of the macroinvertebrate communities in the Xiangxi River system and relationships with environmental factors. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2005, 20, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheifhacken, N.; Fiek, C.; Rothhaupt, K.O. Complex spatial and temporal patterns of littoral benthic communities interacting with water level fluctuations and wind exposure in the littoral zone of a large lake. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2007, 169, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.M.; Thomaz, S. Aquatic macrophytes diversity in lagoons of a tropical floodplain: The role of connectivity and water level. Austral Ecol. 2007, 32, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.S.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Metcalfe, R.A.; Somers, K.M. On the role of natural water level fluctuation in structuring littoral benthic macroinvertebrate community composition in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongjiu, C.; Xuea, Q.; Xub, J.; Zhanga, L.; Gonga, Z.; Achraya, K. Widespread natural intraspecific variation in tissue stoichiometryof two freshwater molluscs: Effect of nutrient enrichment. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).