SPI Trend Analysis of New Zealand Applying the ITA Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Standardized Precipitation Index
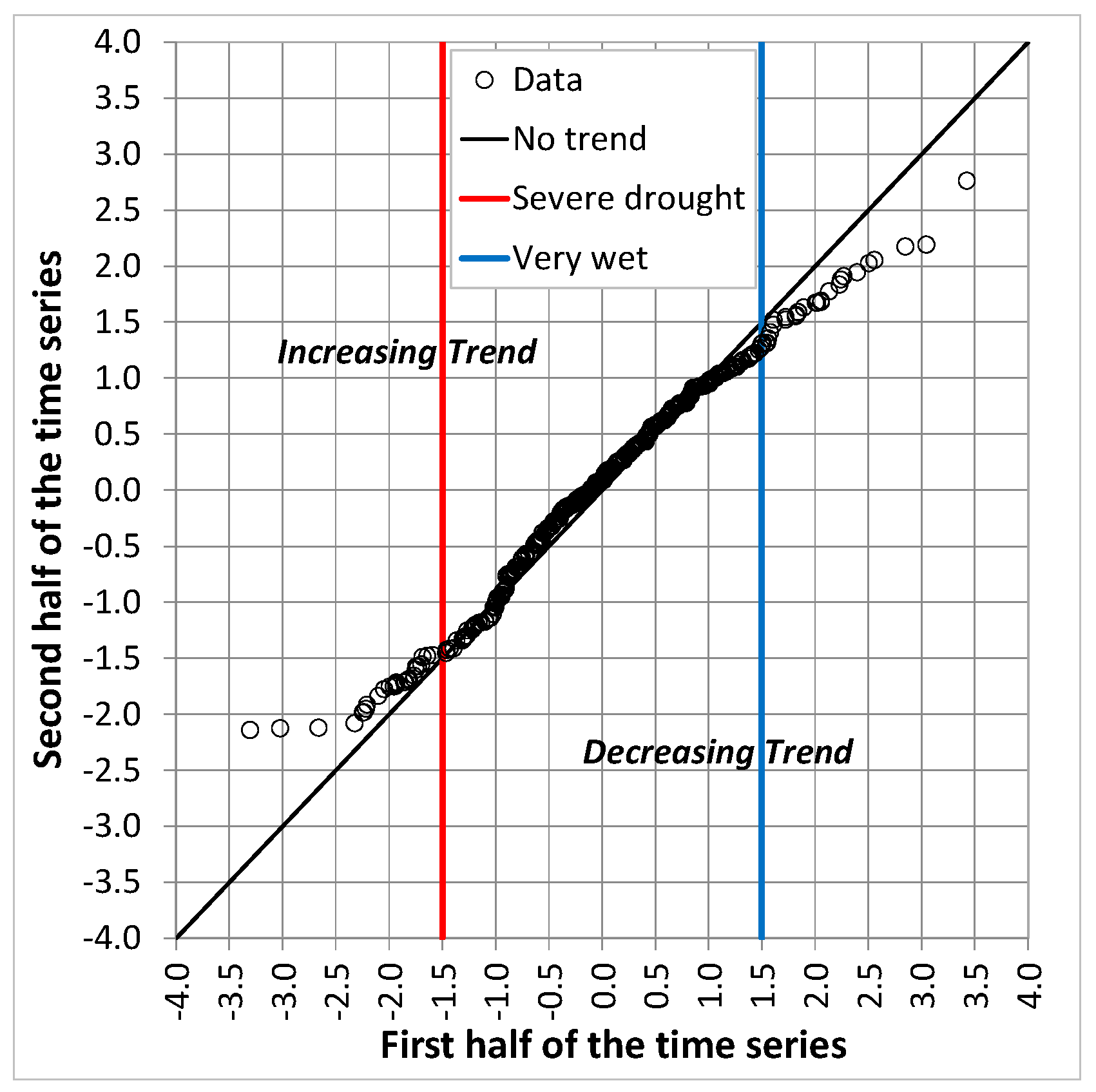
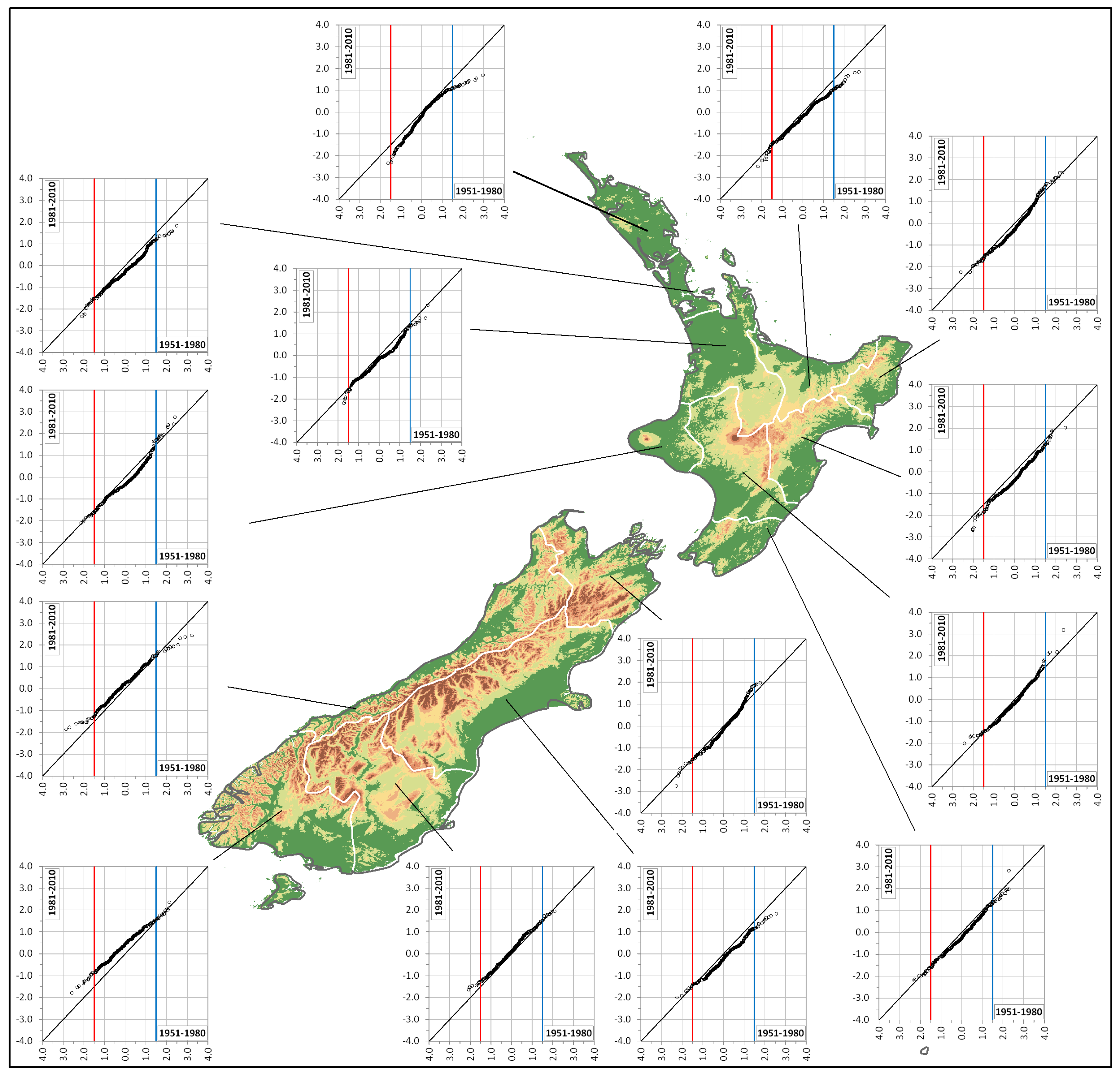
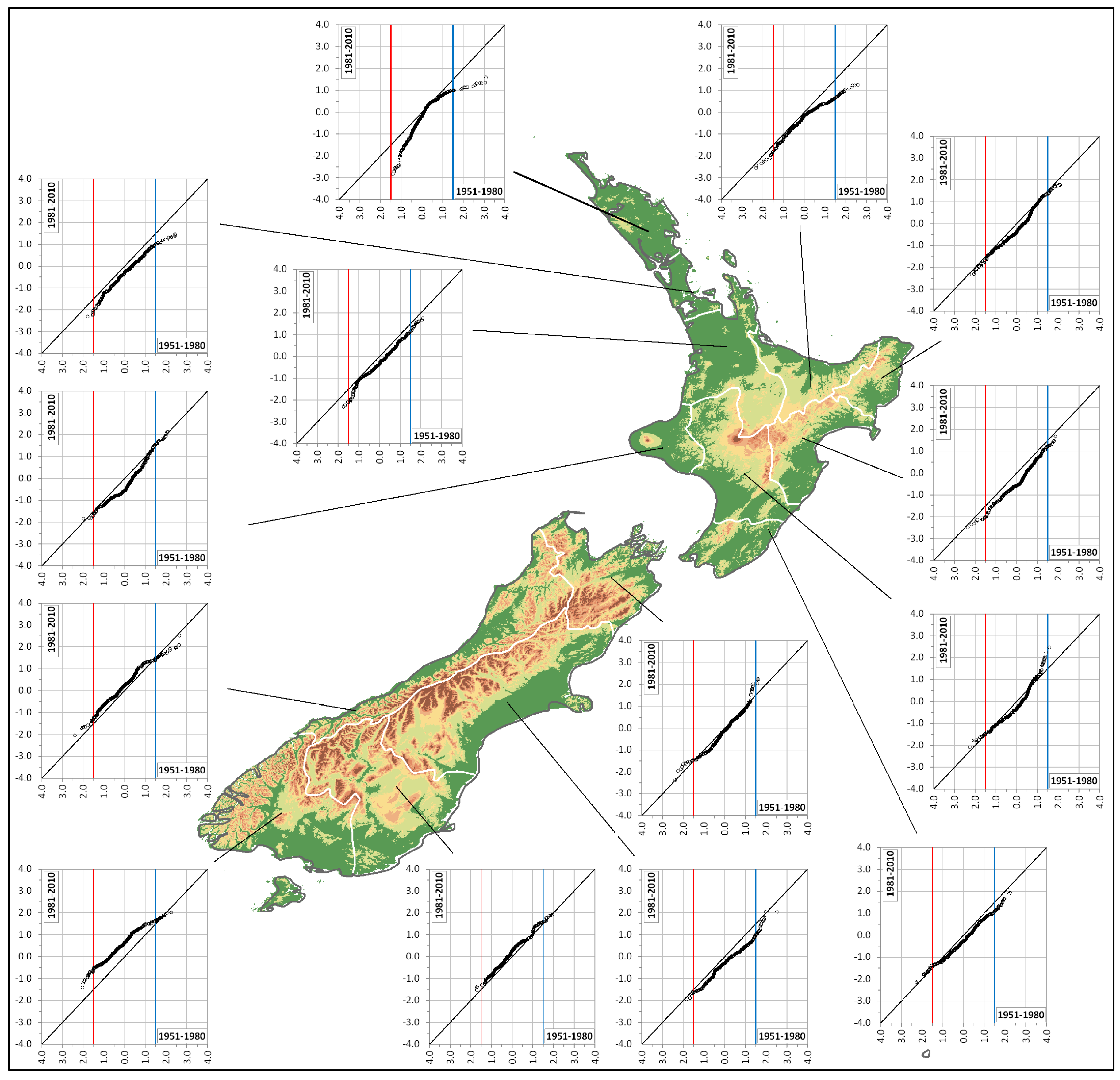
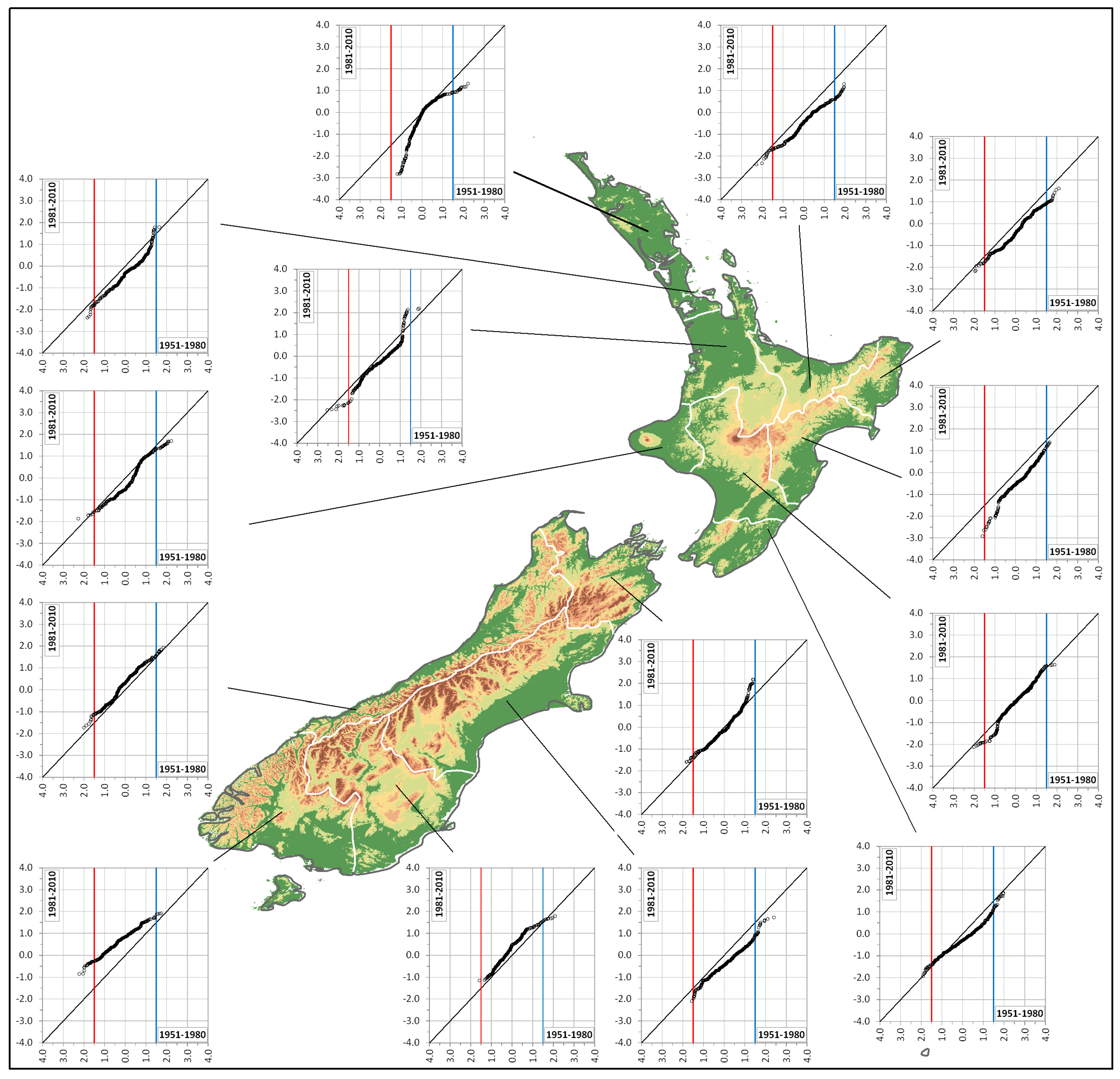
2.2. Innovative Trend Analysis (ITA)
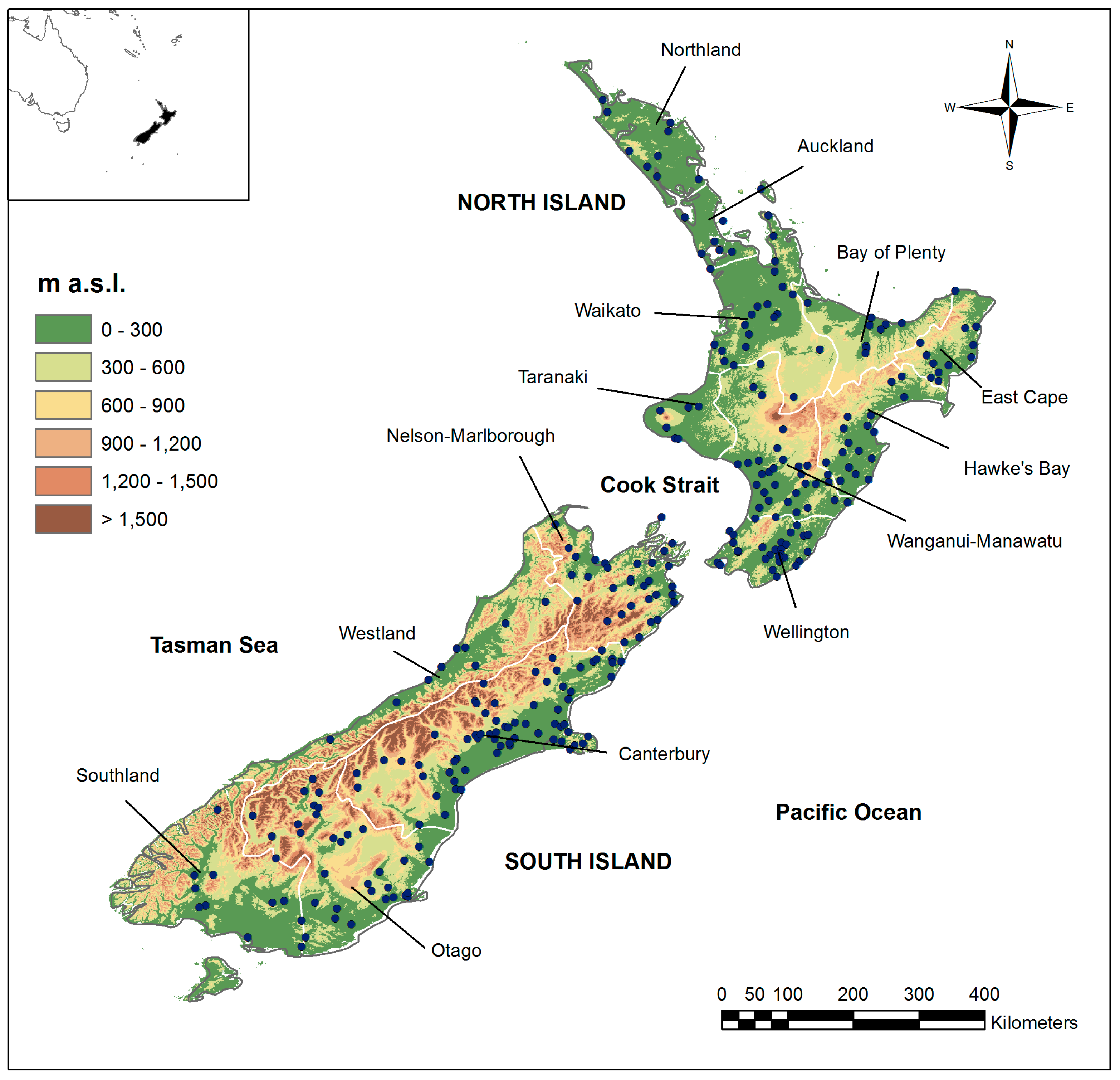
3. Study Area
- The water masses surrounding the country, which results in cool summers and moderately cold winters, and the cold air masses from Antarctica, which cause snow and frost in some areas of the country;
- The mountains crossing both the islands, which constitute a barrier against air flows coming in from south-south west, cause significant differences in the rainfall amounts, also within short distances;
- The proximity of the Australia’s eastern land/sea boundary, which is characterized by a low-pressure region of cyclonic circulation toward the Tasman Sea.
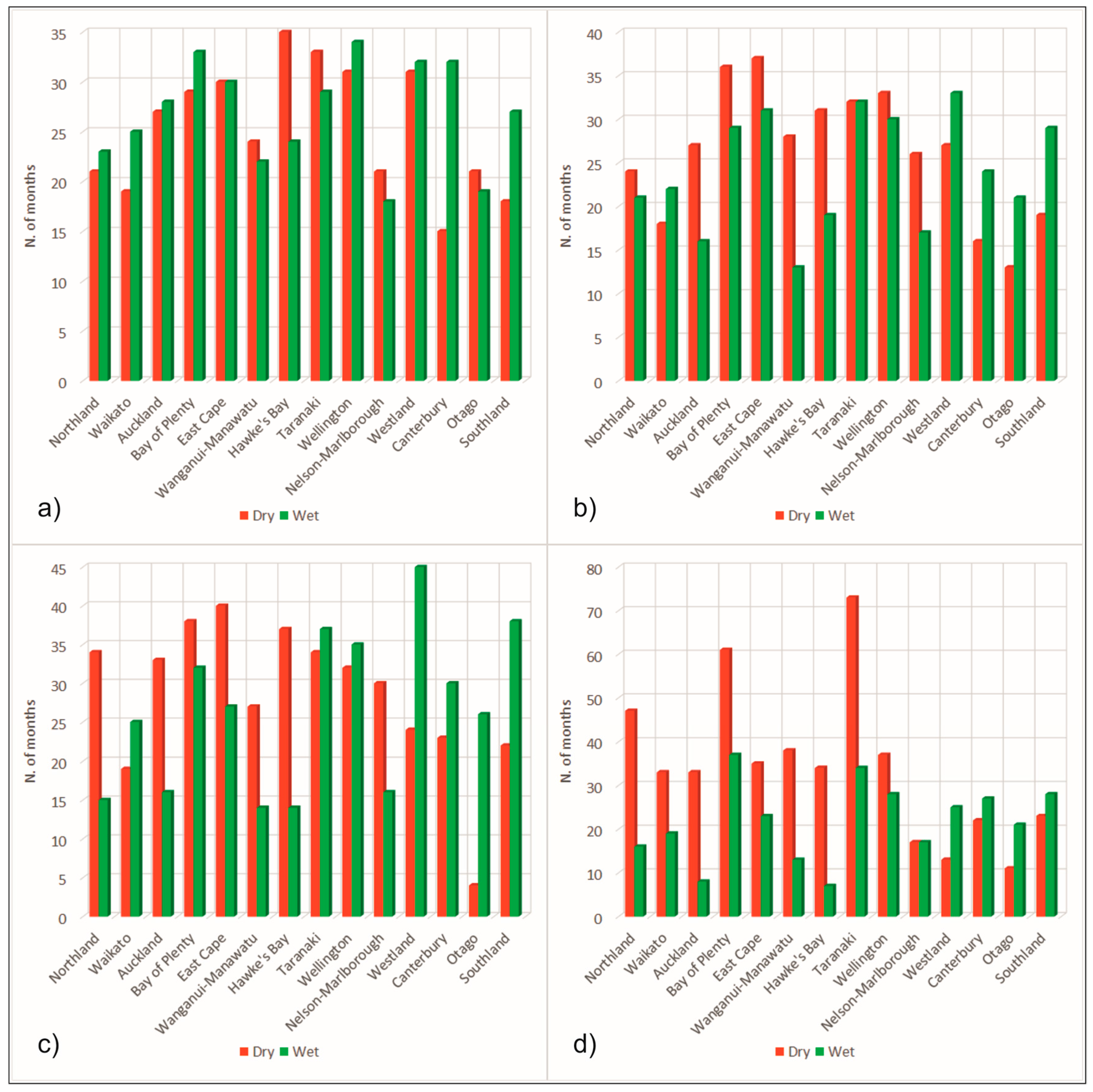
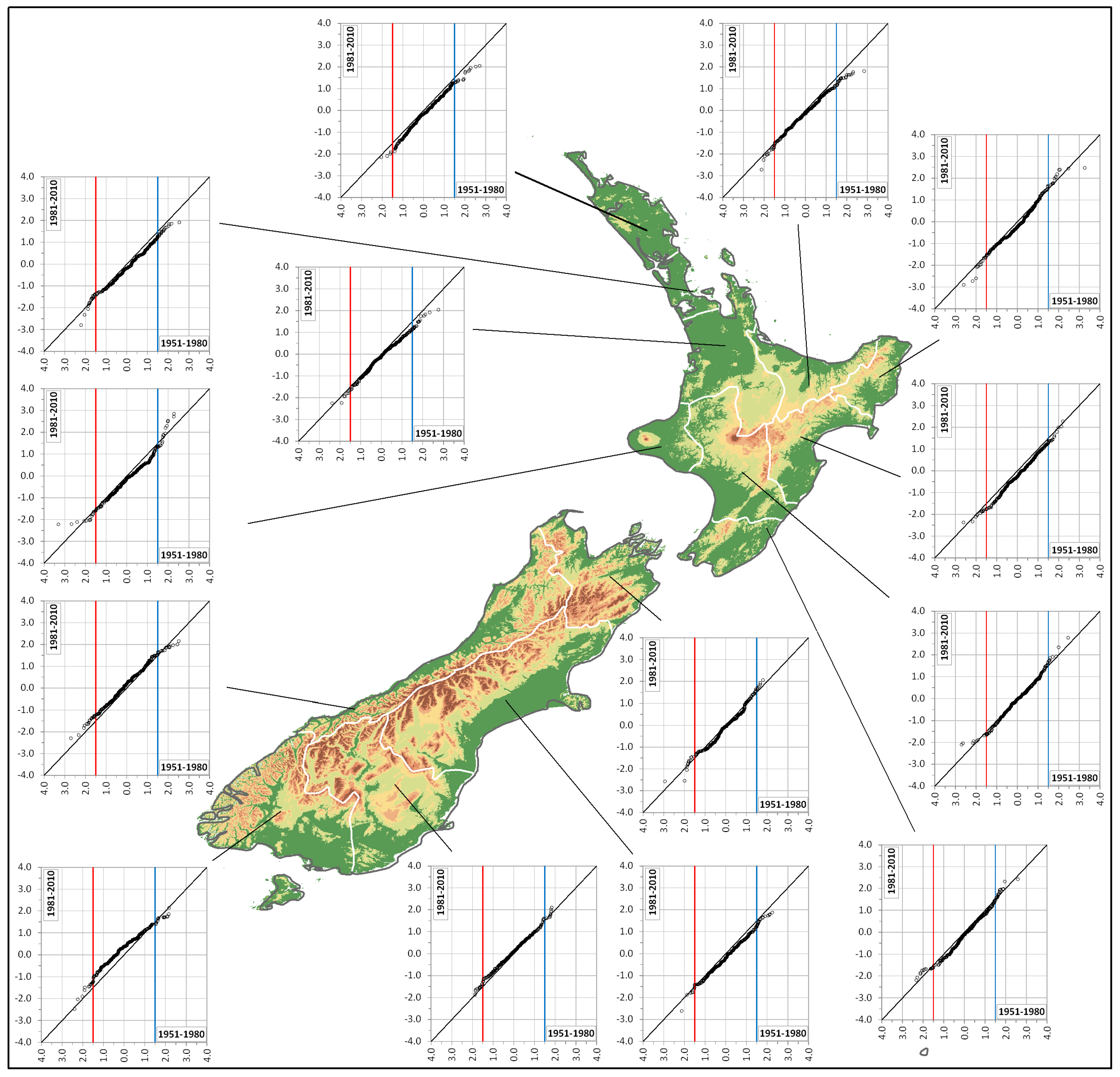
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estrela, T.; Vargas, E. Drought management plans in the European Union. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 26, 1537–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Vorogushyn, S.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Apel, H.; Aronica, G.T.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Bouwer, L.M.; Bubeck, P.; Caloiero, T.; et al. Adaptation to flood risk: Results of international paired flood event studies. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Hayes, M.J.; Svodoba, M.D. Drought monitoring and assessment in the US. In Drought and Drought Mitigation in Europe; Voght, J.V., Somma, F., Eds.; Kluwers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yevjevich, V.; Da Cunha, L.; Vlachos, E. Coping with Droughts; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, A.H.; Brücher, T.; Krüger, A.; Leckebush, G.C.; Pinto, J.G.; Ulbrich, U. The 2003 European summer heatwaves and drought-synoptic diagnosis and impacts. Weather 2004, 59, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Huhes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidman, M.D.; Rees, H.G.; Young, A.R. Spatio-temporal development of streamflow droughts in north-west Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 5, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, J.; Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Keef, C.; Parry, S.; Prudhomme, C. Examining the large-scale spatial coherence of European drought using regional indicators of precipitation and streamflow deficit. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Summary for Policymakers; Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buttafuoco, G.; Caloiero, T.; Ricca, N.; Guagliardi, I. Assessment of drought and its uncertainty in a southern Italy area (Calabria region). Measurement 2018, 113, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E.; Sirangelo, B. Analysis of Dry Spells in Southern Italy (Calabria). Water 2015, 7, 3009–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Gou, X.; Chen, F.; Davi, N.; Liu, C. Spatiotemporal drought variability for central and eastern Asia over the past seven centuries derived from tree-ring based reconstructions. Quat. Int. 2013, 283, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hu, Q.; Oglesby, R.J. Influence of Atlantic sea surface temperatures on persistent drought in North America. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, C.X.; Lang, L.L. Temporal and spatial variations in the Palmer Drought Severity Index over the past four centuries in arid, semiarid, and semihumid East Asia. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4143–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, J.L.; Vargas, W.M.; Poblete, A.G.; de la Zerda, L.R.; Acuña, L.R. Regional droughts in southern South America. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 102, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirangelo, B.; Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E. A stochastic model for the analysis of the temporal change of dry spells. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirangelo, B.; Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E. Stochastic analysis of long dry spells in Calabria (Southern Italy). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional drought assessment based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Abghari, H.; Hosseinzadeh Talaee, P. Temporal trends and spatial characteristics of drought and rainfall in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3351–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayissa, Y.A.; Moges, S.A.; Xuan, Y.; Van Andel, S.J.; Maskey, S.; Solomatine, D.P.; Griensven, A.; Van Tadesse, T. Spatio-temporal assessment of meteorological drought under the influence of varying record length: The case of Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1927–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Gabriel, H.F.; Rana, T. Standard precipitation index to track drought and assess impact of rainfall on watertables in irrigation areas. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, K.E.; Brunsell, N.A.; Jones, A.R.; Feddema, J.J. Assessing spatiotemporal variability of drought in the US central plains. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatsa, D.; Mukwada, G.; Siziba, E.; Chinyanganya, T. Analysis of multidimensional aspects of agricultural droughts in Zimbabwe using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 102, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.R.; Yadav, K. Monitoring spatio-temporal pattern of drought stress using integrated drought index over Bundelkhand region, India. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziei, T.; Saghafian, B.; Paulo, A.A.; Pereira, L.S.; Bordi, I. Spatial patterns and temporal variability of drought in Western Iran. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttafuoco, G.; Caloiero, T. Drought events at different timescales in southern Italy (Calabria). J. Maps 2014, 10, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Feng, Q. Spatial and temporal pattern of precipitation and drought in Gansu Province Northwest China. Nat. Hazards 2009, 49, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Spatiotemporal variability of drought on a short–medium time scale in the Calabria Region (Southern Italy). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 3, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, M.J.; Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D. The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Differences in spatial patterns of drought on different time sales: An analysis of the Iberian Peninsula. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttafuoco, G.; Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R. Analyses of Drought Events in Calabria (Southern Italy) Using Standardized Precipitation Index. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E.; Sirangelo, B. An Analysis of the Occurrence Probabilities of Wet and Dry Periods through a Stochastic Monthly Rainfall Model. Water 2016, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. Accepting the standardized precipitation index: A calculating algorithm. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, A.; Di Mauro, G.; Bonaccorso, B.; Rossi, G. Drought forecasting using the Standardised Precipitation Index. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, I.; Fraedrich, K.; Sutera, A. Observed drought and wetness trends in Europe: An update. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golian, S.; Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. Trends in meteorological and agricultural droughts in Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Su, B.; Krysanova, V.; Vetter, T.; Gao, C.; Jiang, T. Spatial variation and trends in PDSI and SPI indices and their relation to streamflow in 10 large regions of China. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. An innovative trend analysis methodology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haktanir, T.; Citakoglu, H. Trend, independence, stationarity, and homogeneity tests on maximum rainfall series of standard durations recorded in Turkey. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Ay, M. Comparison of Mann–Kendall and innovative trend method for water quality parameters of the Kizilirmak River, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Trend identification simulation and application. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, M.; Kisi, O. Investigation of trend analysis of monthly total precipitation by an innovative method. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Austria, P.F.; Bandala, E.R.; Patiño-Gómez, C. Temperature and heat wave trends in northwest Mexico. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 91, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O. An innovative method for trend analysis of monthly pan evaporations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Willems, P. Investigation of streamflow variation using an innovative trend analysis approach in northwest Iran. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Nederland, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.G.; Cook, E.R.; Turney, C.S.M.; Allen, K.; Fenwick, P.; Cook, B.; O’Donnell, A.J.; Lough, J.M.; Grierson, P.F.G.; Baker, P. Drought variability in the eastern Australia and New Zealand summer drought atlas (ANZDA, CE 1500–2012) modulated by the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAF. Regional and National Impacts of the 2007–2008 Drought; Butcher Partners Ltd.: Tai Tapu, New Zealand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kamber, G.; McDonald, C.; Price, G. Drying Out: Investigating the Economic Effects of Drought in New Zealand; Reserve Bank of New Zealand: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mullan, B.; Porteous, A.; Wratt, D.; Hollis, M. Changes in Drought Risk with Climate Change; National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research: Wellington, New Zealand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.; Mullan, B.; Porteous, A. Scenarios of Regional Drought under Climate Change; National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, D.; McKee, T. Characteristics of 20th Century Drought in the United States at Multiple Scale; Atmospheric Science Paper 634; Department of Atmospheric Science Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorso, B.; Bordi, I.; Cancelliere, A.; Rossi, G.; Sutera, A. Spatial variability of drought: An analysis of SPI in Sicily. Water Resour. Manag. 2003, 17, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, P.; Maris, F.; Kotsovinos, N.; Hrissanthou, V. Computation of drought index SPI with Alternative Distribution Functions. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2453–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, H.C.S. A note on the gamma distribution. Mon. Weather Rev. 1958, 86, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Dover Publications, INC.: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.E. Encyclopedia of World Climatology; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- NIWA. Overview of New Zealand Climate. Available online: http://www.niwa.co.nz/education-and-training/schools/resources/climate/overview (accessed on 26 February 2018).
- Salinger, M.J.; Mullan, A.B. New Zealand climate: Temperature and precipitation variations and their links with atmospheric circulation 1930–1994. Int. J. Climatol. 1999, 19, 1049–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.M.; Salinger, M.J.; Leleu, I. Trends in extreme daily rainfall across the South Pacific and relationship to the South Pacific Convergence Zone. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 847–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dravitzki, S.; McGregor, J. Extreme precipitation of the Waikato region, New Zealand. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T. Analysis of daily rainfall concentration in New Zealand. Nat. Hazards 2014, 72, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T. Analysis of rainfall trend in New Zealand. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2015, 73, 6297–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T. Drought analysis in New Zealand using the standardized precipitation index. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2017, 76, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T. Trend of monthly temperature and daily extreme temperature during 1951–2012 in New Zealand. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Agricultural drought in a future climate: Results from 15 global climate models participating in the IPCC 4th assessment. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 25, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SPI Value | Class | Probability (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SPI ≥ 2.00 | Extremely wet | 2.3 |
| 1.5 ≤ SPI < 2.00 | Severely wet | 4.4 |
| SPI < 1.50 | Moderately wet | 9.2 |
| SPI < 1.00 | Mildly wet | 34.1 |
| −1.00 ≤ SPI < 0.00 | Mild drought | 34.1 |
| −1.50 ≤ SPI < −1.00 | Moderate drought | 9.2 |
| −2.00 ≤ SPI < −1.50 | Severe drought | 4.4 |
| SPI < −2.00 | Extreme drought | 2.3 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caloiero, T. SPI Trend Analysis of New Zealand Applying the ITA Technique. Geosciences 2018, 8, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030101
Caloiero T. SPI Trend Analysis of New Zealand Applying the ITA Technique. Geosciences. 2018; 8(3):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030101
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaloiero, Tommaso. 2018. "SPI Trend Analysis of New Zealand Applying the ITA Technique" Geosciences 8, no. 3: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030101
APA StyleCaloiero, T. (2018). SPI Trend Analysis of New Zealand Applying the ITA Technique. Geosciences, 8(3), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030101





