Stratigraphy, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Abadan Plain Basin: A Geological Review of a Prolific Middle Eastern Hydrocarbon Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
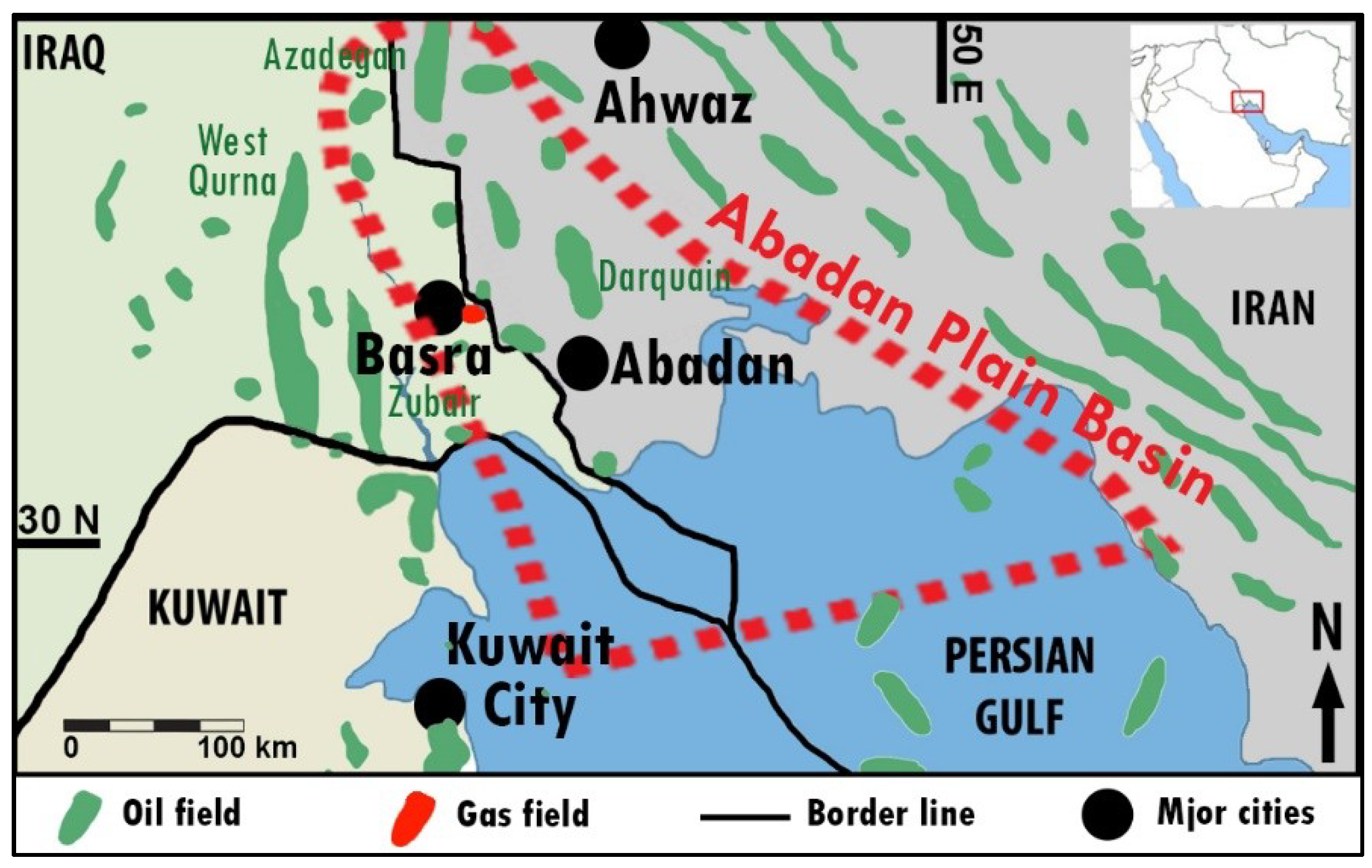
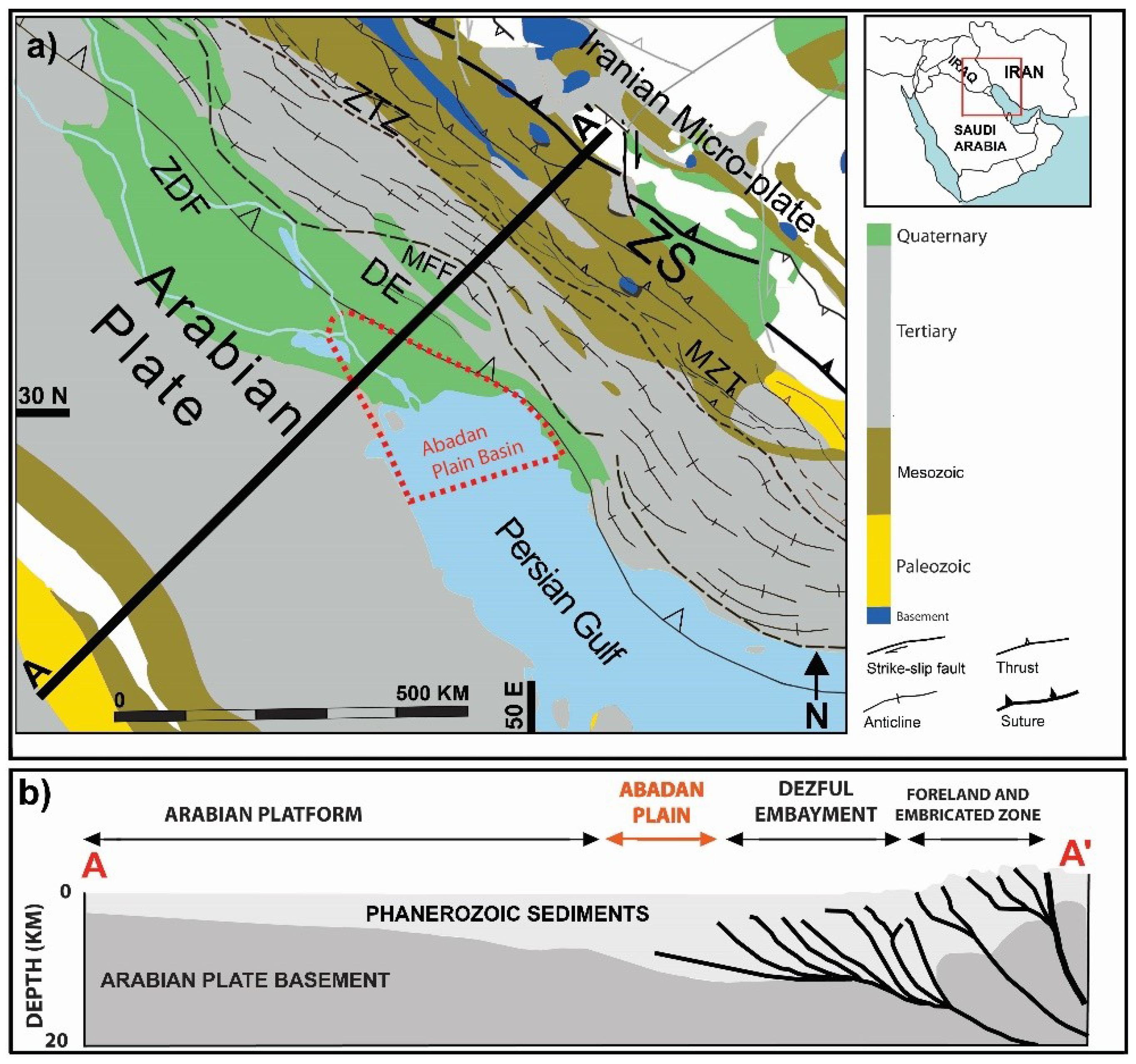
2. Geological Setting of the Abadan Plain Basin
- Almost continuous deposition of limestone, argillaceous limestone, marly limestone, and evaporites from Permian up to Pliocene in a marine environment;
- existing source rock, reservoir and cap rock in adequate placement;
- lack of intense tectonic activities during the period of Permian up to Pliocene (post collision tectonic settings), and;
- lack of metamorphic or magmatic activity since the Permian.
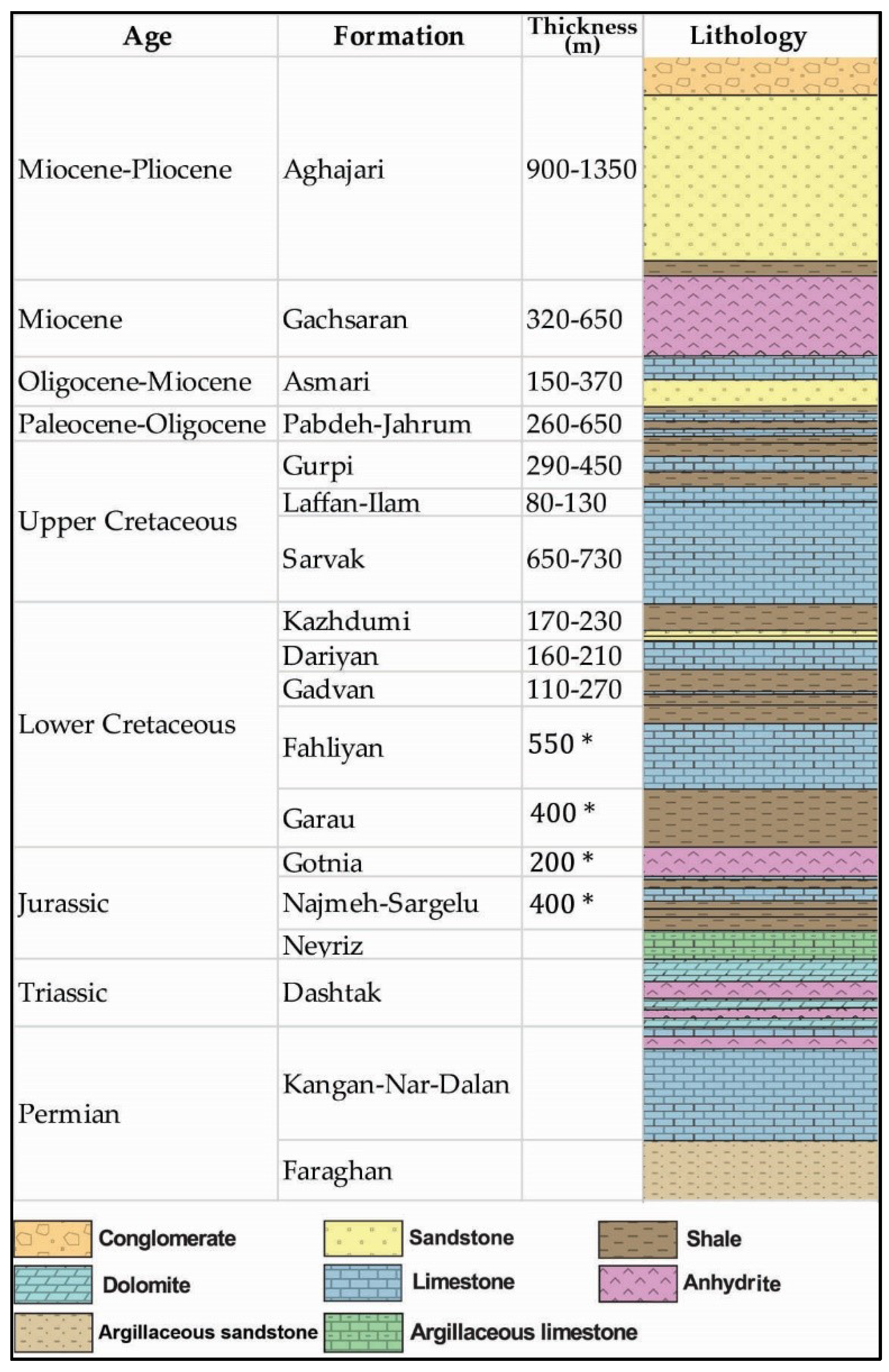
3. Abadan Plain Basin Stratigraphy
- (1)
- Epicontinental platform (Cambrian to Permian).
- (2)
- Continental rifting (Permian to Triassic).
- (3)
- Passive continental margin (Jurassic to late Cretaceous).
- (4)
- Marine and continental foreland (includes deposits from late Cretaceous to present).
- (1)
- Permian: A sea-level rise that caused the deposition of the Faraghan sandstone formation in Lower Permian, and then sequences of reef carbonates in the Middle and Upper Permian in a supratidal environment.
- (2)
- Triassic: A shallow marine and high-energy environment that formed the Khaneh Kat dolomitic formation. This formation is mainly cap rock with occasional gas shows in the porous members.
- (3)
- Lower and Middle Jurassic: A closed sea environment covering the north of the Dezful Embayment and central Iraq, in which a series of evaporites, argillaceous limestone and a few shales were deposited.
- (4)
- Upper Jurassic: A closed sea environment with evaporitic deposits such as the Gotnia Formation.
- (5)
- Lower Cretaceous: Following the sea level rise in late Jurassic, a trough existed in the Lower Cretaceous in which the Garau shale has been deposited in Northern parts of the Dezful Embayment. Concurrently, Fahliyan and Darian formations were deposited in a shallow marine environment. Ghorbani [26] believes that the Fahliyan, Gadvan and Dariyan formations were all deposited in the trough conditions. The origin of sediments of the Gadvan Formation were from the erosion of the Arabian Shield outcrops in the Arabian Peninsula and Fars region [31].
- (6)
- Middle Cretaceous: During the Albian-Cenomanian, the Fars platform was uplifted, but with concurrent sea level rise in adjacent areas. Erosional features are frequent prior to, and during, the Turonian. The Sarvak Formation was deposited before the erosion in the Cenomanian.
- (7)
- Upper Cretaceous: Following the Turonian erosion, the Laffan shale (and concurrent Surgah shale) was deposited during the sea level rise. The Ilam neritic carbonate then overlaid the Laffan shale. Gurpi accumulations dominated the entire basin from the middle Santonian.
- (8)
- Paleocene-Eocene: Cretaceous sea level rise made the depositional environment monotonic, while the Gurpi and Pabdeh formations, comprised of shale and carbonates, were deposited in a shallow marine to supratidal environment.
- (9)
- Oligocene-Miocene: Prior to this time, sea level started falling and the region was exposed to the erosion. There was a narrow trough in the region, in which Oligocene deposits accumulated. After a primary rise, there has been a sea level fall that continues until the present-day.
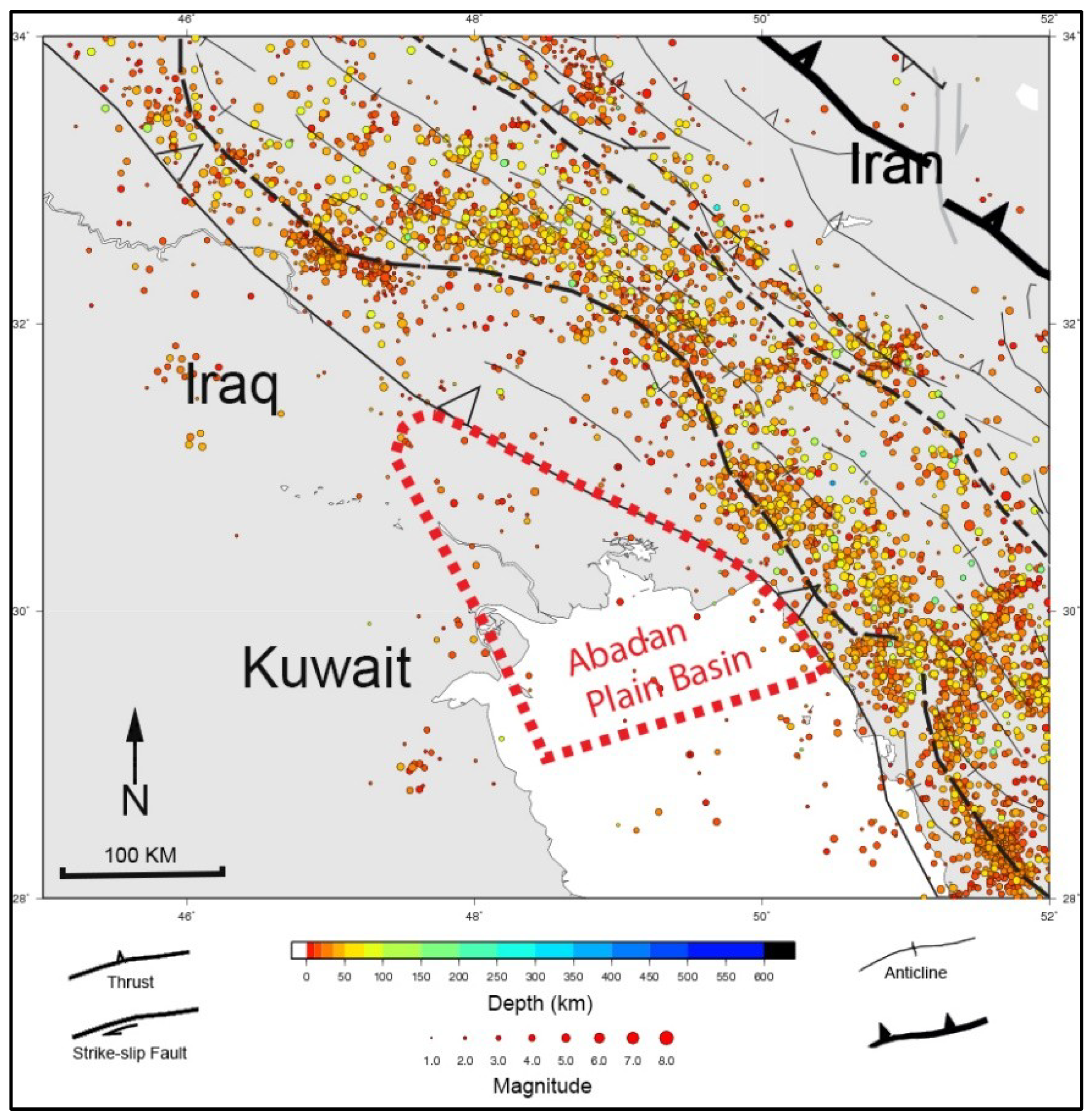
4. Regional Tectonic History
- (1)
- Mid to late Cretaceous time (115–85 Ma) corresponds to a distinctive period of perturbation of subduction processes and inter-plate mechanical coupling marked by blueschist exhumation and upper plate fragmentation;
- (2)
- Paleocene–Eocene time (60–40 Ma) witnesses slab break-off, major shifts in arc magmatism and distributed extension within the upper plate;
- (3)
- From the Oligocene time onwards (30 ± 5 Ma to present), collision develops with a progressive SW migration of deformation and topographic build-up, and is accompanied by a second, late Miocene slab break-off (~10 Ma to present).
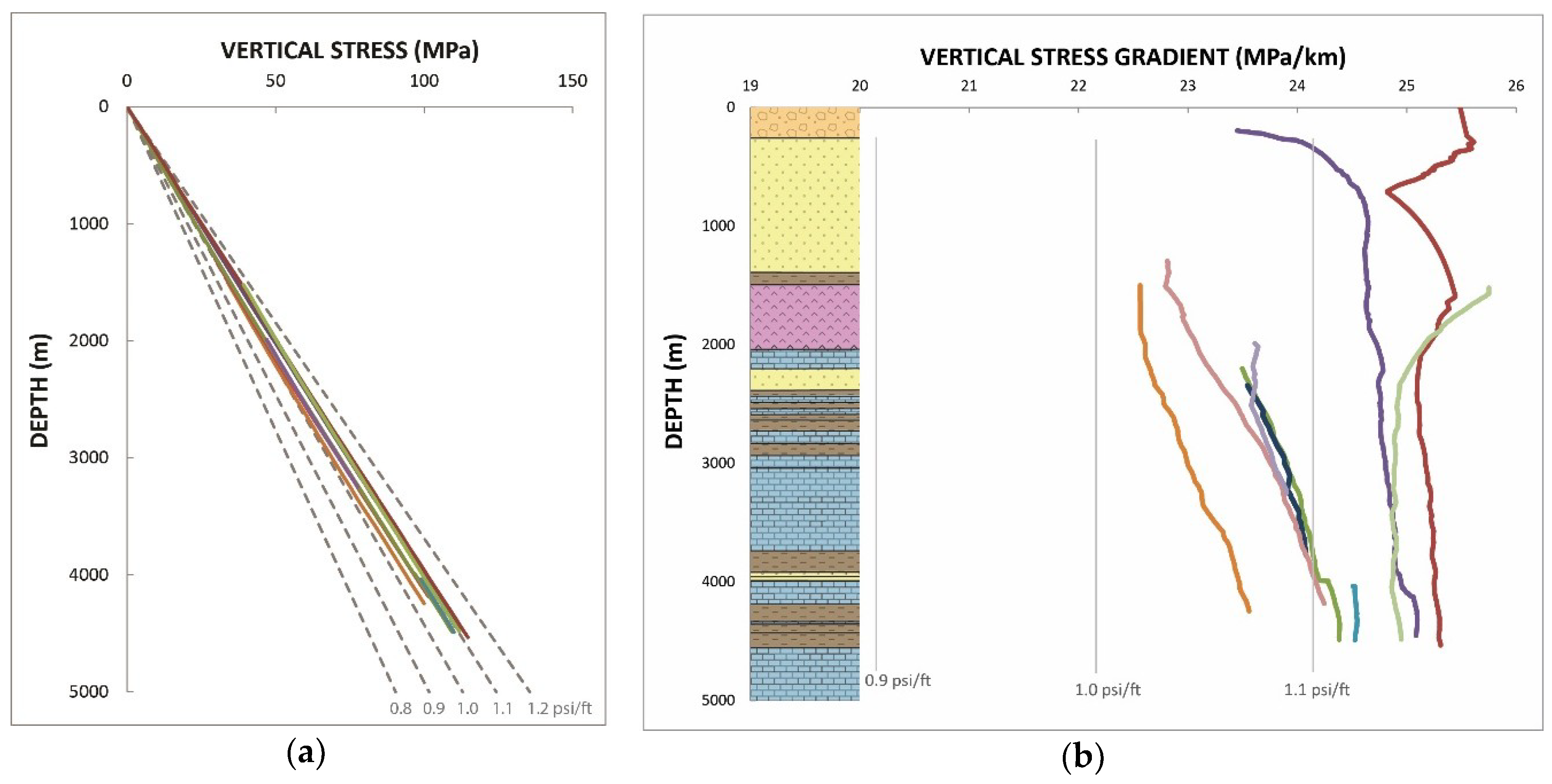
5. Overburden in the Abadan Plain Basin
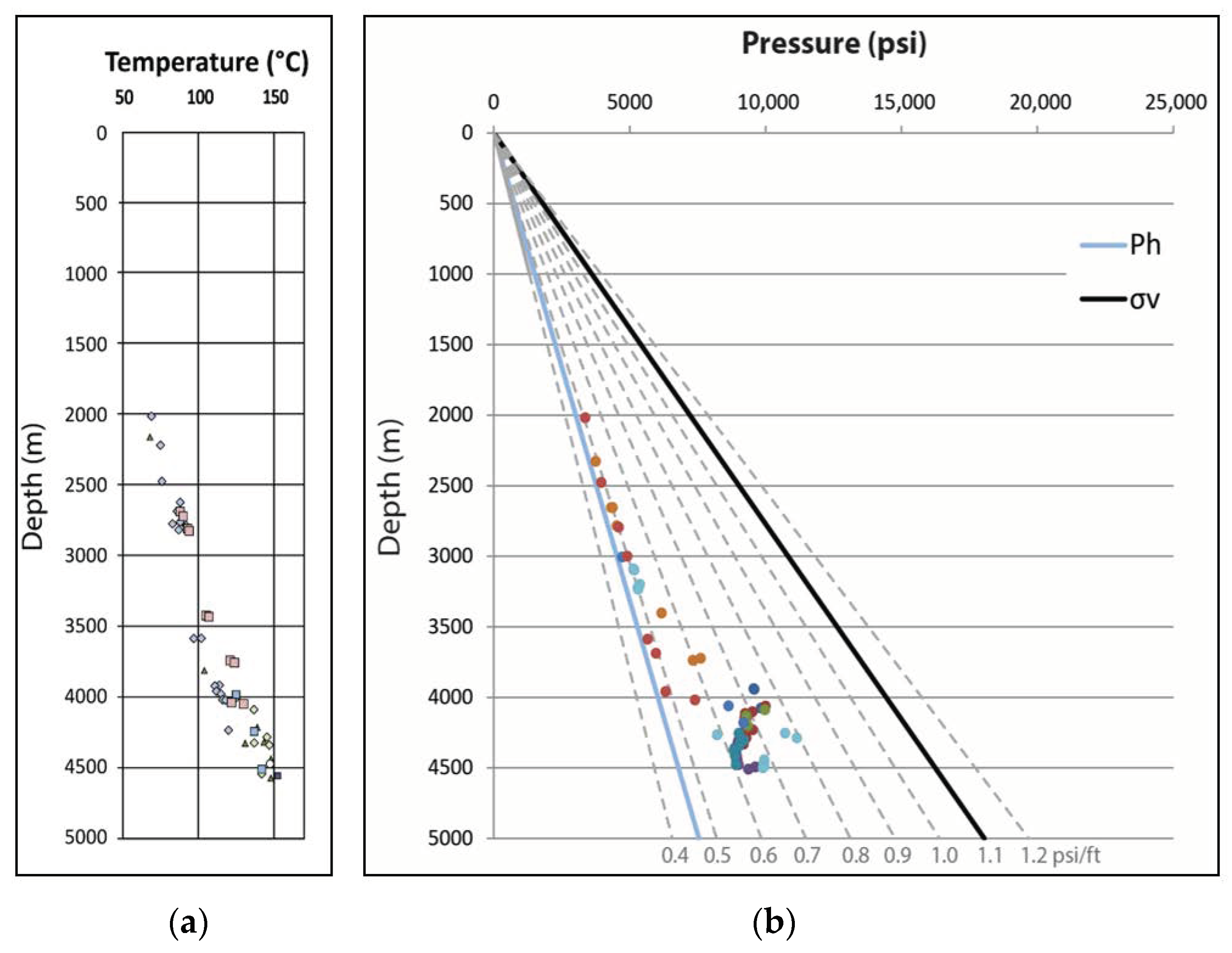
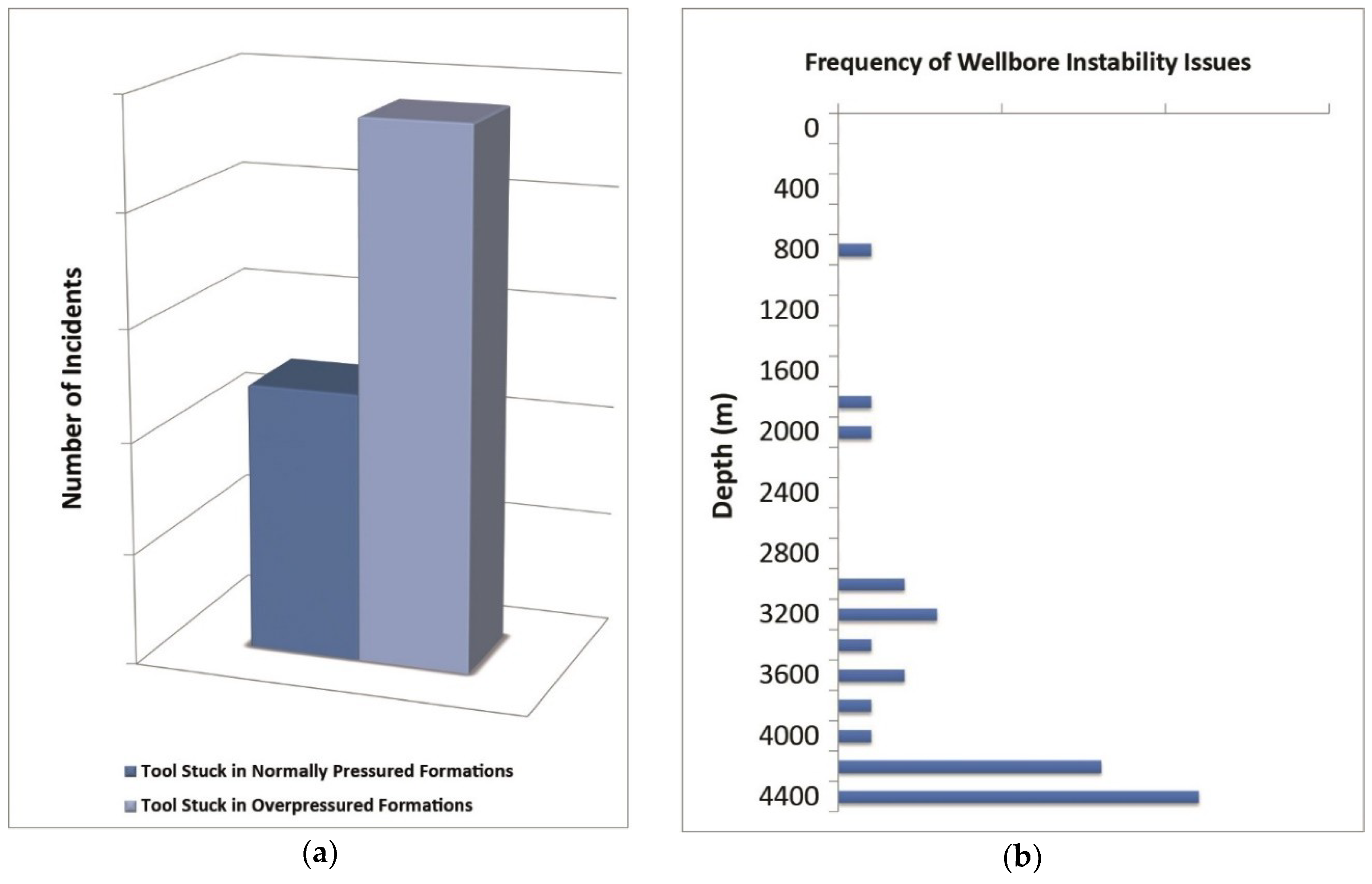
6. Pore Pressure in the Abadan Plain Basin
7. Summary of Hydrocarbon Geochemistry
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McQuillan, H. Proceeding of the Second Conference on Petroleum Geochemistry and exploration in the Afro-Asian Region The role of basement tectonics in the control of sedimentary facies, structural patterns and salt plug emplacements in the Zagros fold belt of southwest Iran. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1991, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenave, M.; Hegre, J. Current distribution of oil and gas fields in the Zagros Fold Belt of Iran and contiguous offshore as the result of the petroleum systems. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2010, 330, 291–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharhan, A.S.; Nairn, A.E.M. Chapter 12–The hydrocarbon habitat of the Zagros basin. In Sedimentary Basins and Petroleum Geology of the Middle East; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 651–736. [Google Scholar]
- Sepehr, M.; Cosgrove, J.W. Structural framework of the Zagros Fold–Thrust Belt, Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafighdoust, Y.; Eckstein, Y.; Harami, R.M.; Gharaie, M.H.M.; Griffith, E.M.; Mahboubi, A. Isotopic analysis, hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of Tang-Bijar oilfield springs, Zagros region, Iran. Geothermics 2015, 55, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Yassaghi, A.; Bahroudi, A.; Vergés, J.; Sherkati, S. Impact of the Late Triassic Dashtak intermediate detachment horizon on anticline geometry in the Central Frontal Fars, SE Zagros fold belt, Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 54, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, H.; Sherkati, S.; Sepehr, M. Structural style variation and its impact on hydrocarbon traps in central Fars, southern Zagros folded belt, Iran. J. Struct. Geol. 2012, 37, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfidari, E.; Zamanzadeh, S.M.; Dashti, A.; Opera, A.; Tavakkol, M.H. Comprehensive source rock evaluation of the Kazhdumi Formation, in the Iranian Zagros Foldbelt and adjacent offshore. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 71, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahie Fard, I.; Braathen, A.; Mokhtari, M.; Alavi, S.A. Interaction of the Zagros Fold–Thrust Belt and the Arabian-type, deep-seated folds in the Abadan Plain and the Dezful Embayment, SW Iran. Pet. Geosci. 2006, 12, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murris, R.J. Middle-East—Stratigraphic Evolution and Oil Habitat. AAPG Bull. 1980, 64, 597–618. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, M. Regional Stratigraphy of the Zagros Fold-Thrust Belt of Iran and Its Proforeland Evolution. Am. J. Sci. 2004, 304, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ala, M.A.; Kinghorn, R.R.F.; Rahman, M. Organic Geochemistry and Source Rock Characteristics of The Zagros Petroleum Province, Southwest Iran. J. Pet. Geol. 1980, 3, 61–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoneley, R. The Middle East Basin: A summary overview. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1990, 50, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, Z.R.; Hughes Clarke, M.W.; Stoneley, R. Petroleum in the Zagros Basin: A Late Tertiary Foreland Basin Overprinted onto the Outer Edge of a Vast Hydrocarbon-Rich Paleozoic-Mesozoic Passive-Margin Shelf. In AAPG Memoir 55 Foreland Basins and Fold Belts; U.S. Department of Energy: Wastington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 309–339. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, E.R. One Hundred Years of Middle Eastern Oil; Brandeis University, Crown Center for Middle East Studies: Waltham, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Al Naqib, K.M. Geology of the Arabian Peninsula; southwestern Iraq. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 1967, 560, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Arvandan Oil and Gas Co. Darquain Oil Field. Available online: http://aogc.ir/company/oilfields/82-darquin (accessed on 11 November 2014).
- Zeinalzadeh, A.; Moussavi-Harami, R.; Mahboubi, A.; Sajjadian, V.A. Basin and petroleum system modeling of the Cretaceous and Jurassic source rocks of the gas and oil reservoirs in Darquain field, south west Iran. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M. Structures of the Zagros fold-thrust belt in Iran. Am. J. Sci. 2007, 307, 1064–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, E.; Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Casciello, E.; Parravano, V.; Urruela, A.; Vergés, J. Modeling the flexural evolution of the Amiran and Mesopotamian foreland basins of NW Zagros (Iran-Iraq). Tectonics 2015, 34, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, P.; Omrani, J.; Jolivet, L.; Whitechurch, H.; Vrielynck, B.; Spakman, W.; Monie, P.; Meyer, B.; Wortel, R. Zagros orogeny: A subduction-dominated process. Geol. Mag. 2011, 148, 692–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallemi, S.A.; Kermanshah, M. Significances of integrated study of Abadan Plain depositional basin. Explor. Prod. 2012, 94, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, B.; Saadati, H.; Rashidi, M.; Kobraei, M. Geochemical investigation of oils from Cretaceous to Eocene Sedimentary sequences of the Abadan Plain, Southwest Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARAMCO. Oil and the Middle East; Arabian American Oil Company: Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- British Petroleum. Statistical Review of World Energy 2014; British Petroleum: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, M. An Introduction to the Economic Geology of Iran; Geological survey and mineral explorations of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Falcon, N.L. Southern Iran: Zagros Mountains. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1974, 4, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiei, H. Geology of Iran; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1995. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Haghi Pour, A.; Aghanabati, A. Geological Map of Iran; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani, B.; Hassani-Giv, M.; Abdollahi fard, I. Formation Pore Pressure Variation of the Neocomian Sedimentary Succession (the Fahliyan Formation) in the Abadan Plain Basin, SW of Iran. Geofluids 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motiei, H. Petroleum Geology of Zagros; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1993. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, E.J.P.; Allen, M.B.; Inger, S.; Hassani, H. Structural styles in the Zagros Simple Folded Zone, Iran. J. Geol. Soc. 2003, 160, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessami, K.; Koyi, H.A.; Talbot, C.J.; Tabasi, H.; Shabanian, E. Progressive unconformities within an evolving foreland fold-thrust belt, Zagros Mountains. J. Geol. Soc. 2001, 158, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuarrie, N. Crustal scale geometry of the Zagros fold–thrust belt, Iran. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Sherkati, S.; Bohloli, B.; Tingay, M. Subsurface fracture analysis and determination of in-situ stress direction using FMI logs: An example from the Santonian carbonates (Ilam Formation) in the Abadan Plain, Iran. Tectonophysics 2010, 492, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husseini, M.I. Origin of the Arabian Plate structures: Amar collision and Najd rift. GEOARABIA-MANAMA- 2000, 5, 527–542. [Google Scholar]
- Selley, R.C.; Sonnenberg, S.A. Elements of Petroleum Geology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Takin, M. Iranian Geology and Continental Drift in the Middle East. Nature 1972, 235, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, M.; King, G.C.P. Towards a Paleogeography and Tectonic Evolution of Iran. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1981, 18, 210–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkarinejad, K.; Azizi, A. Slip partitioning and inclined dextral transpression along the Zagros Thrust System, Iran. J. Struct. Geol. 2008, 30, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatinejad, M.R.; Sarkarinejad, K. Application of the spectral decomposition technique for characterizing reservoir extensional system in the Abadan Plain, southwestern Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, M.; Guezou, J.C.; Leturmy, P.; Eshraghi, S.A.; de Lamotte, D.F. The origin of changes in structural style across the Bandar Abbas syntaxis, SE Zagros (Iran). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2004, 21, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafkenscheid, E.; Wortel, M.; Spakman, W. Subduction history of the Tethyan region derived from seismic tomography and tectonic reconstructions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M. Tectonics of the Zagros Orogenic Belt of Iran—New Data and Interpretations. Tectonophysics 1994, 229, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y. New Evidence and Model on the Evolution of the Southeast Anatolian Orogen. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1993, 105, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Jackson, J.; Walker, R. Late Cenozoic reorganization of the Arabia-Eurasia collision and the comparison of short-term and long-term deformation rates. Tectonics 2004, 23, TC2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homke, S.; Vergés, J.; Serra-Kiel, J.; Bernaola, G.; Sharp, I.; Garcés, M.; Montero-Verdú, I.; Karpuz, R.; Goodarzi, M.H. Late Cretaceous–Paleocene formation of the proto–Zagros foreland basin, Lurestan Province, SW Iran. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2009, 121, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthereau, F.; Lacombe, O.; Vergés, J. Building the Zagros collisional orogen: Timing, strain distribution and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence. Tectonophysics 2012, 532–535, 27–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMets, C.; Gordon, R.G.; Argus, D.F.; Stein, S. Current Plate Motions. Geophys. J. Int. 1990, 101, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMets, C.; Gordon, R.G.; Argus, D.F. Geologically current plate motions. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 181, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClusky, S.; Balassanian, S.; Barka, A.; Demir, C.; Ergintav, S.; Georgiev, I.; Gurkan, O.; Hamburger, M.; Hurst, K.; Kahle, H.; et al. Global Positioning System constraints on plate kinematics and dynamics in the eastern Mediterranean and Caucasus. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 5695–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilforoushan, F.; Masson, F.; Vernant, P.; Vigny, C.; Martinod, J.; Abbassi, M.; Nankali, H.; Hatzfeld, D.; Bayer, R.; Tavakoli, F.; et al. GPS network monitors the Arabia-Eurasia collision deformation in Iran. J. Geod. 2003, 77, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernant, P.; Nilforoushan, F.; Hatzfeld, D.; Abbassi, M.R.; Vigny, C.; Masson, F.; Nankali, H.; Martinod, J.; Ashtiani, A.; Bayer, R.; et al. Present-day crustal deformation and plate kinematics in the Middle East constrained by GPS measurements in Iran and northern Oman. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouthereau, F.; Lacombe, O.; Tensi, J.; Bellahsen, N.; Kargar, S.; Amrouch, K. Mechanical Constraints on the Development of the Zagros Folded Belt (Fars). In Thrust Belts and Foreland Basins; Lacombe, O., Roure, F., Lavé, J., Vergés, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe, O.; Amrouch, K.; Mouthereau, F.; Dissez, L. Calcite twinning constraints on late Neogene stress patterns and deformation mechanisms in the active Zagros collision belt. Geology 2007, 35, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubourg, C.; Smith, B.; Eshraghi, A.; Lacombe, O.; Authemayou, C.; Amrouch, K.; Bellier, O.; Mouthereau, F. New magnetic fabric data and their comparison with palaeostress markers in the Western Fars Arc (Zagros, Iran): tectonic implications. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2010, 330, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J.F.; Helman, M.L.; Knott, S.D.; Turco, E.; Hutton, D.H.W. Kinematics of the western Mediterranean. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 45, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattarzadeh, Y.; Cosgrove, J.W.; Vita-Finzi, C. The interplay of faulting and folding during the evolution of the Zagros deformation belt. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1999, 169, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.R.; Stewart, I.C.F. Magnetically Inferred Basement Structure in Central Saudi-Arabia. Tectonophysics 1995, 245, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Seismological Centre. Event Catalogue; Internatl. Seis. Cent.: Thatcham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tingay, M.R.P. Situ Stress and Overpressures of Brunei Darussalam; The University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tingay, M.R.P.; Hillis, R.R.; Morley, C.K.; Swarbrick, R.E.; Okpere, E.C. Variation in vertical stress in the Baram Basin, Brunei: Tectonic and geomechanical implications. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashbari, V.; Tingay, M.R. Pore Pressure Prediction in Carbonate Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pitman, J.K.; Steinshouer, D.; Lewan, M. Petroleum generation and migration in the Mesopotamian Basin and Zagros Fold Belt of Iraq: Results from a basin-modeling study. GeoArabia 2004, 9, 41–72. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, K.; Moldowan, J. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, T.; Boreham, C. Terrestrially sourced oils: Where do they exist and what are our limits of knowledge?—A geochemical perspective. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1994, 77, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldowan, J.M.; Seifert, W.K.; Gallegos, E.J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks. AAPG Bull. 1985, 69, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Connan, J.; Bouroullec, J.; Dessort, D.; Albrecht, P. The microbial input in carbonate-anhydrite facies of a sabkha palaeoenvironment from Guatemala: A molecular approach. Org. Geochem. 1986, 10, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter. Org. Geochem. 1986, 9, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, W.B.; Holba, A.G.; Dzou, L.I. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3581–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, M.; Gaglianone, P.; Brassell, S.; Maxwell, J. Geochemical and biological marker assessment of depositional environments using Brazilian offshore oils. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1988, 5, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requejo, A.; Hieshima, G.; Hsu, C.; McDonald, T.; Sassen, R. Short-chain (C 21 and C 22) diasteranes in petroleum and source rocks as indicators of maturity and depositional environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2653–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A. Sedimentological studies on the Seyahou and Sarchahan formations in Tang-e-Zakeen of Kuh-e-Faraghan at Bardar Abbas area, southern Iran. Nat. Iran. Oil Co. 2005, 7, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.J.; Stump, T.E. Depositional and tectonic setting of the Lower Silurian hydrocarbon source rock facies, central Saudi Arabia. AAPG Bull. 1999, 83, 314–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavidel-syooki, M.; Álvaro, J.J.; Popov, L.; Pour, M.G.; Ehsani, M.H.; Suyarkova, A. Stratigraphic evidence for the Hirnantian (latest Ordovician) glaciation in the Zagros Mountains, Iran. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2011, 307, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoleikhaei, Y.; Amini, A.; Zamanzadeh, S.M. Integrated provenance analysis of Zakeen (Devonian) and Faraghan (early Permian) sandstones in the Zagros belt, SW Iran. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 101, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Nadri, A.; Raeisi, E.; Eggenkamp, H.G.M.; Kazemi, G.A.; Montaseri, A. Hydrochemical and isotopic (δ18O, δ2H, 87Sr/86Sr, δ37Cl and δ81Br) evidence for the origin of saline formation water in a gas reservoir. Chem. Geol. 2014, 384, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.H.; Rabbani, A.R. Origin of natural gases in the Permo-Triassic reservoirs of the Coastal Fars and Iranian sector of the Persian Gulf. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghazi, A. New evidence for the Early Devonian age of the Jauf Formation in northern Saudi Arabia. Rev. Micropaléontol. 2007, 50, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atashbari, V.; Tingay, M.; Amrouch, K. Stratigraphy, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Abadan Plain Basin: A Geological Review of a Prolific Middle Eastern Hydrocarbon Province. Geosciences 2018, 8, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120496
Atashbari V, Tingay M, Amrouch K. Stratigraphy, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Abadan Plain Basin: A Geological Review of a Prolific Middle Eastern Hydrocarbon Province. Geosciences. 2018; 8(12):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120496
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtashbari, Vahid, Mark Tingay, and Khalid Amrouch. 2018. "Stratigraphy, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Abadan Plain Basin: A Geological Review of a Prolific Middle Eastern Hydrocarbon Province" Geosciences 8, no. 12: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120496
APA StyleAtashbari, V., Tingay, M., & Amrouch, K. (2018). Stratigraphy, Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Abadan Plain Basin: A Geological Review of a Prolific Middle Eastern Hydrocarbon Province. Geosciences, 8(12), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120496



