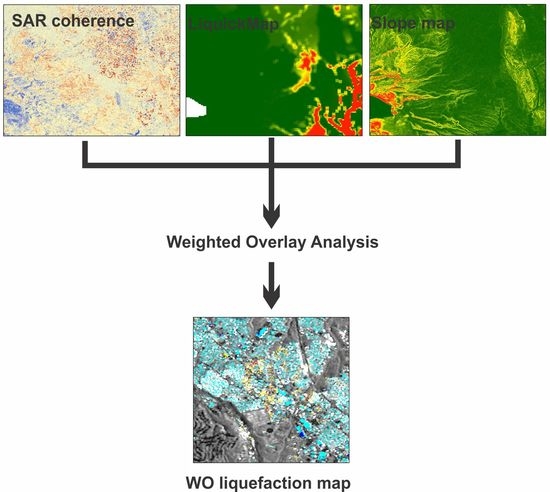
A Weighted Overlay Method for Liquefaction-Related Urban Damage Detection: A Case Study of the 6 September 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and LiquickMap
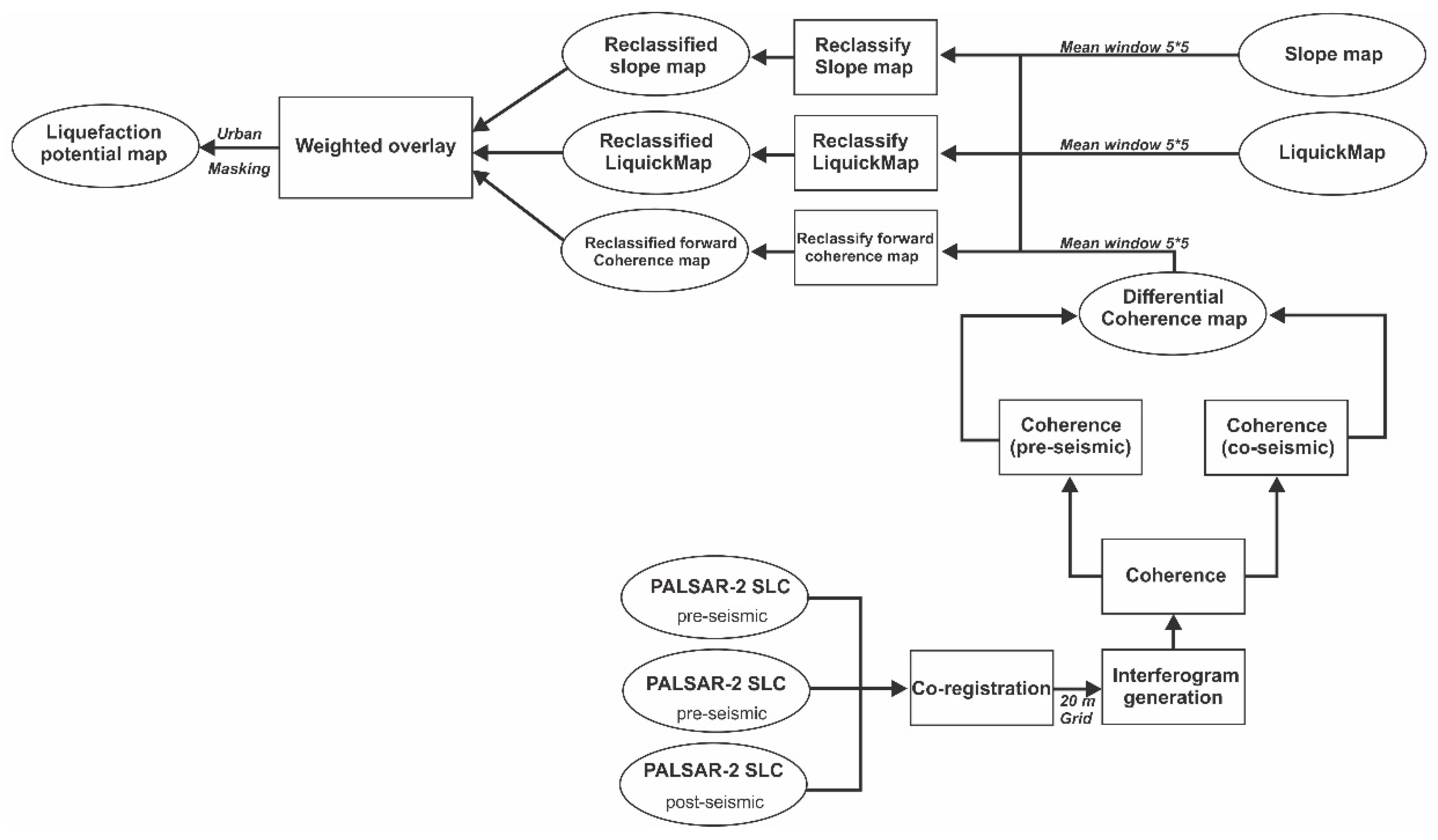
3. Materials and Methods
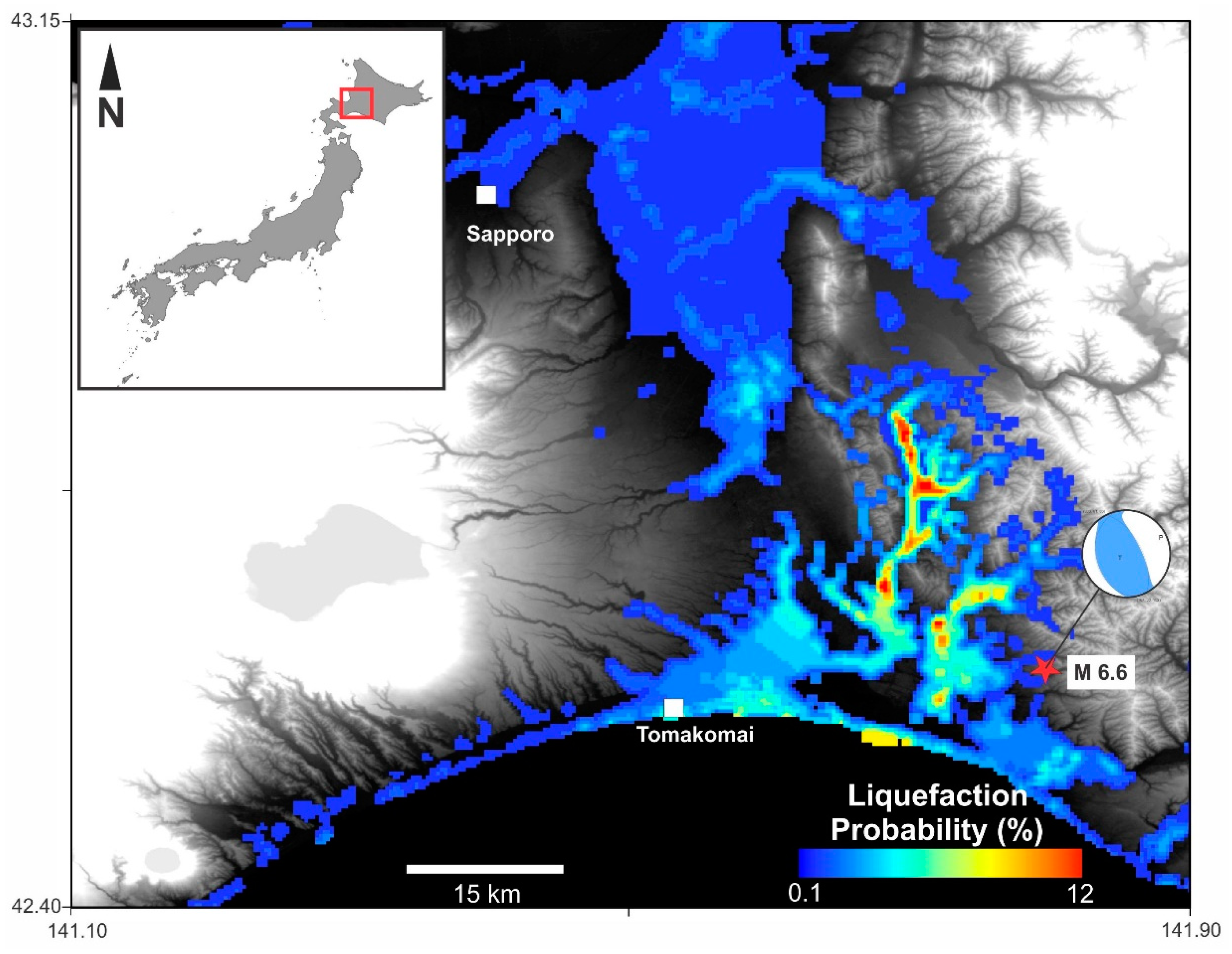
4. Results
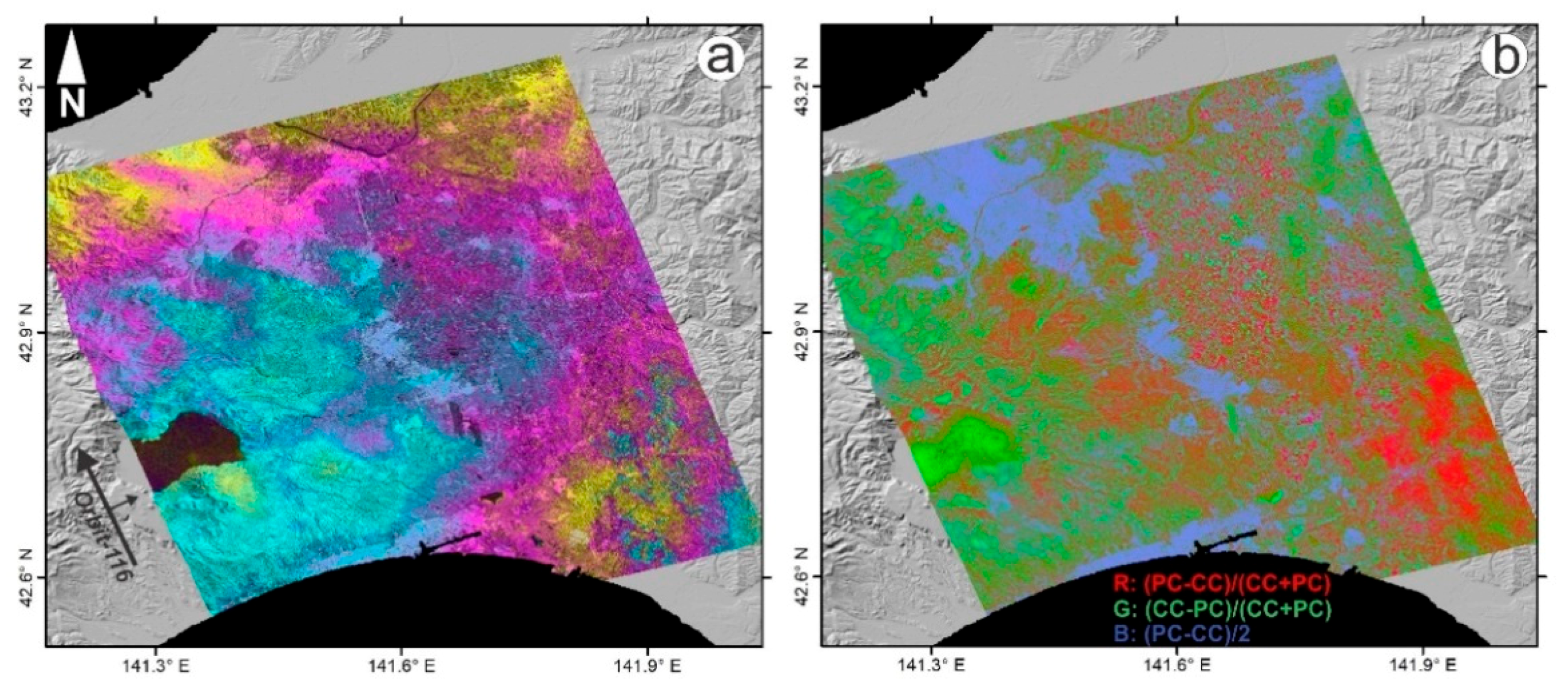
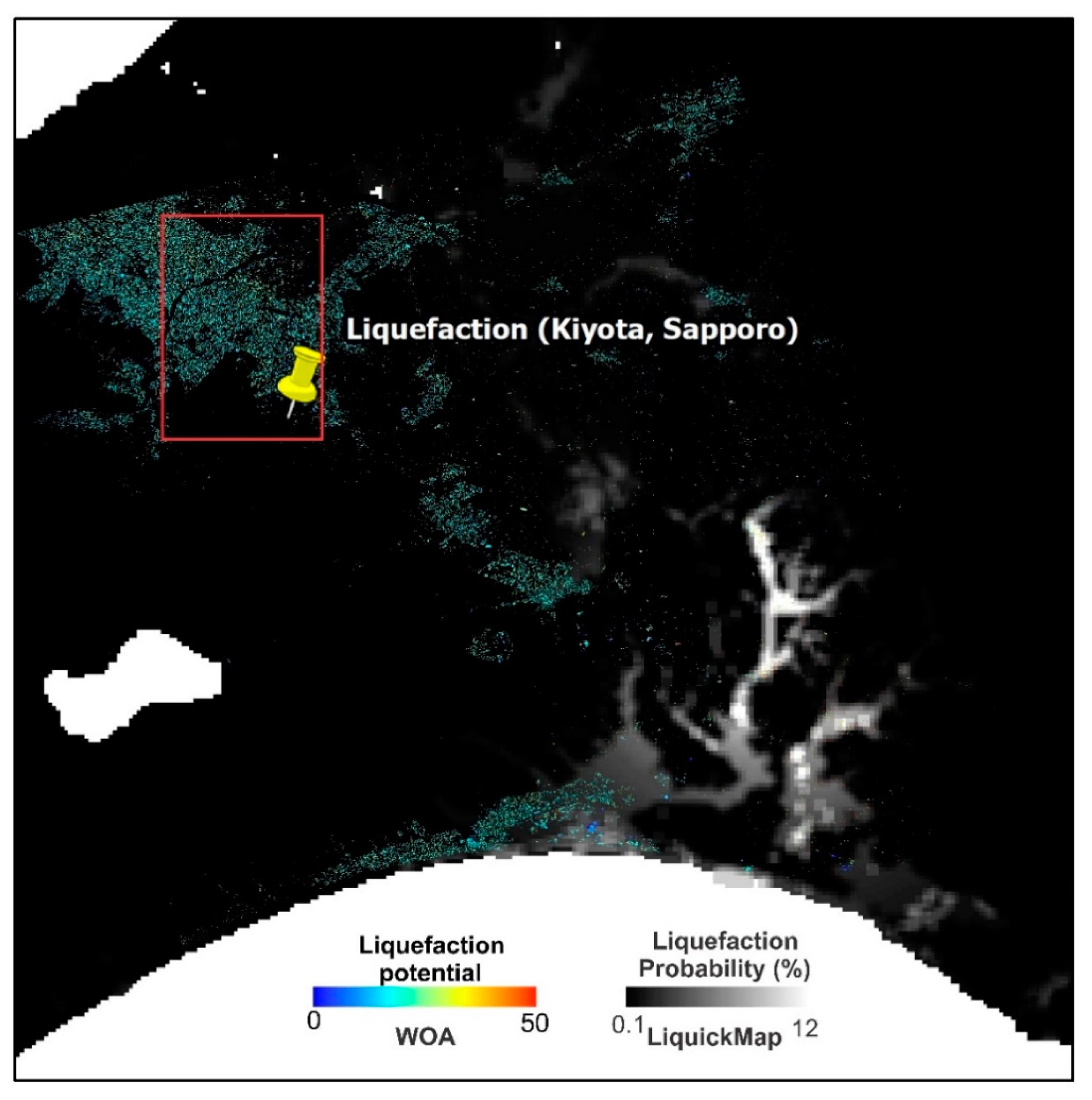
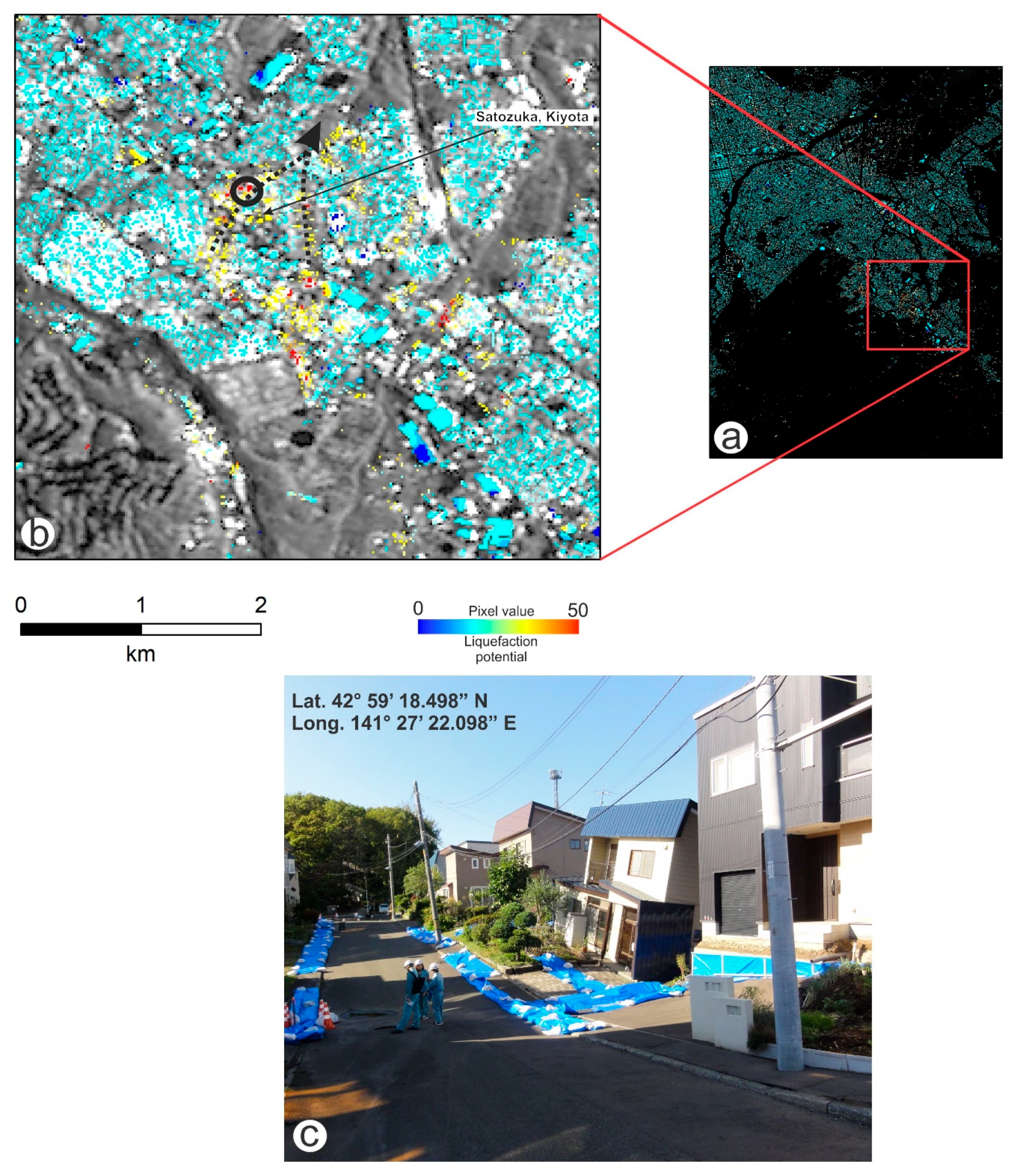
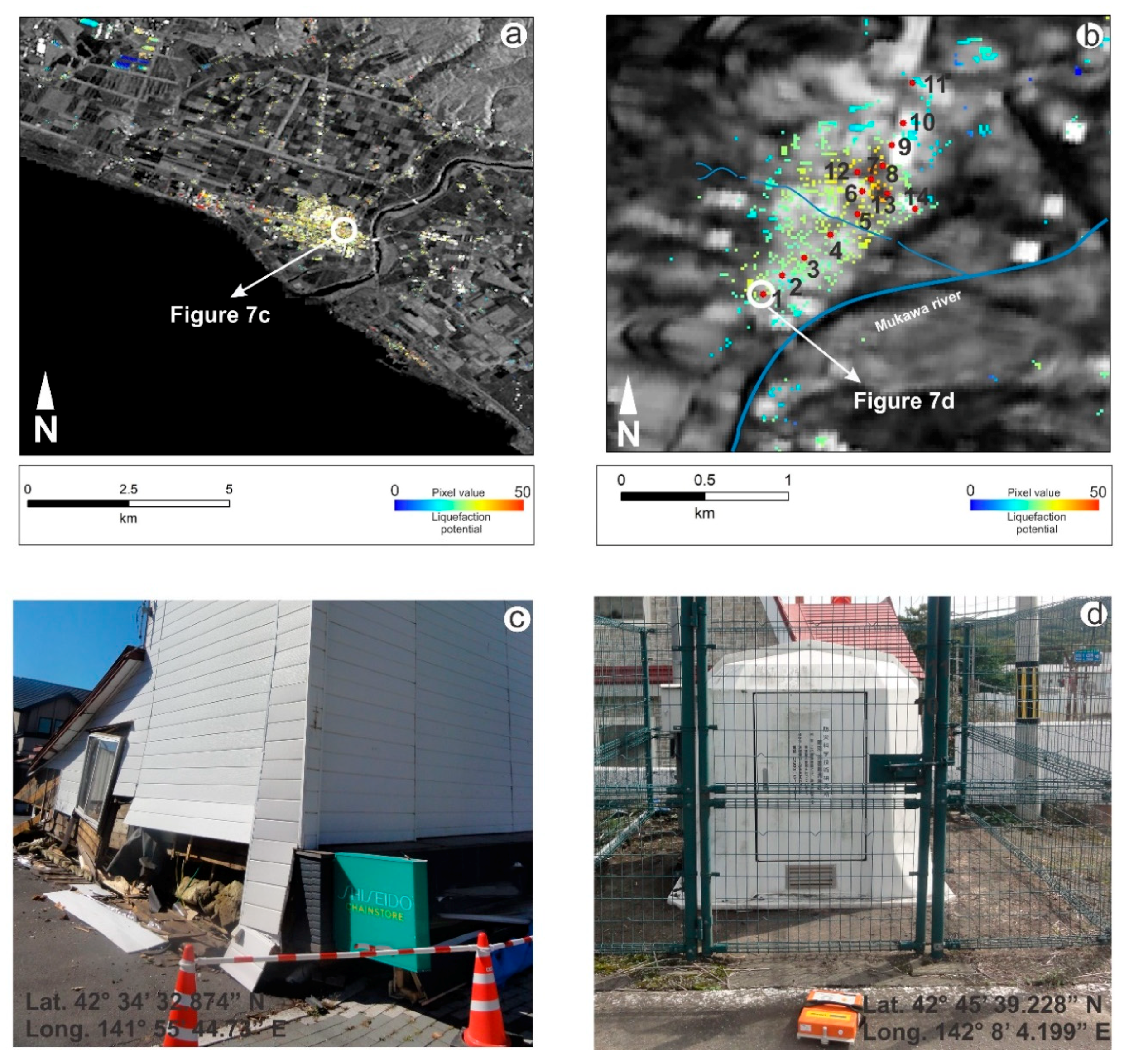
4.1. Weighted Overlay (WO) Results
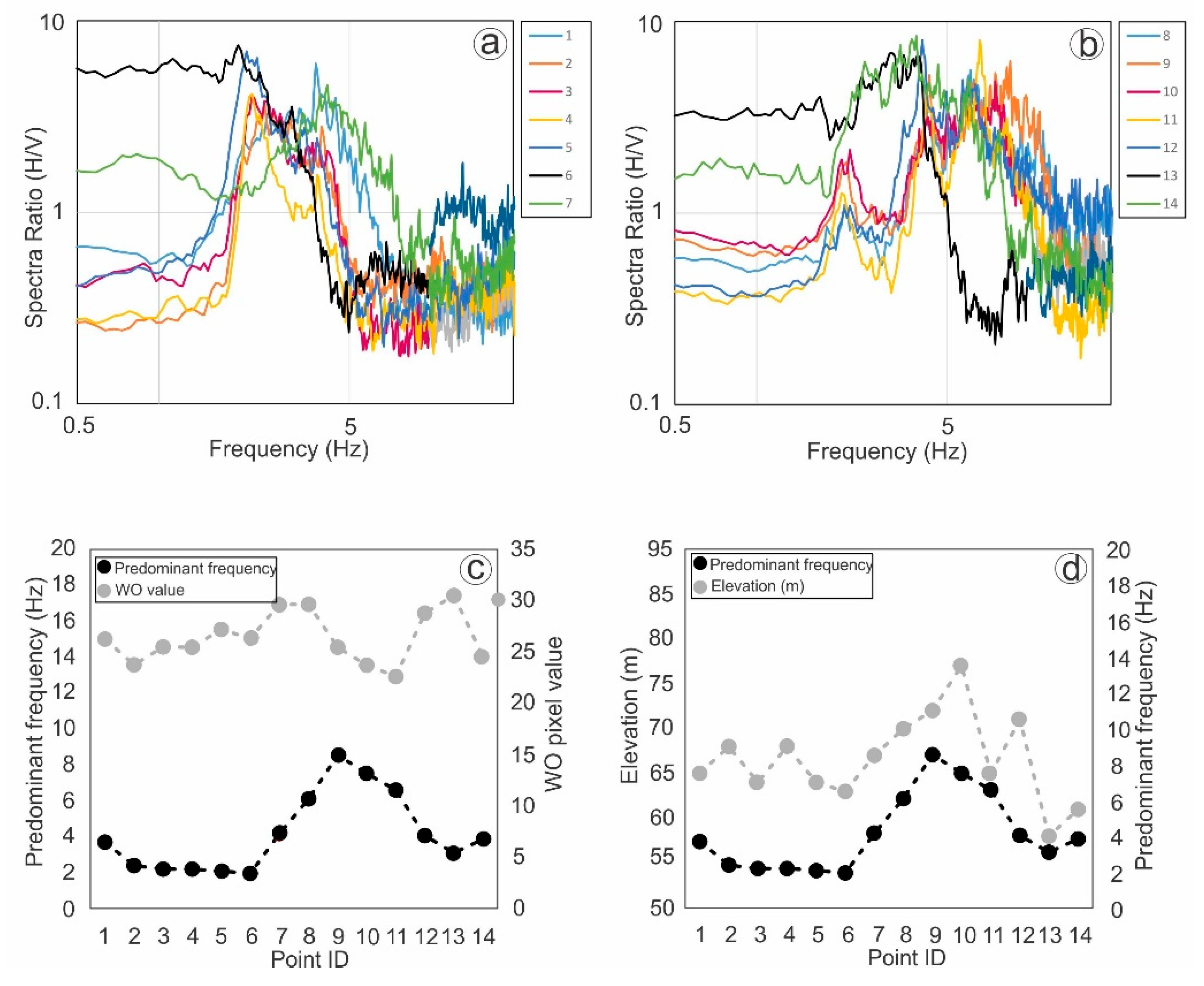
4.2. Microtremor Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Statistics Portal. Global Death Toll due to Earthquakes from 2000 to 2015. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/263108/global-death-toll-due-to-earthquakes-since-2000/ (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Milillo, P.; Giardina, G.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Multi-Temporal InSAR Structural Damage Assessment: The London Crossrail Case Study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Hudnut, K.; Owen, S.; Webb, F.; Simons, M.; Sacco, P.; Milillo, P. Rapid Damage Mapping for the 2015 M w 7.8 Gorkha Earthquake Using Synthetic Aperture Radar Data from COSMO–SkyMed and ALOS-2 Satellites. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2015, 86, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Porcu, M.C.; Lundgren, P.; Soccodato, F.; Salzer, J.; Fielding, E.; Biondi, F. The ongoing destabilization of the Mosul dam as observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 6279–6282. [Google Scholar]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Ogushi, F. Spatiotemporal deformation patterns of the Lake Urmia Causeway as characterized by multisensor InSAR analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Samsonov, S.; Matsuoka, M. Block-based damage assessment of the 2012 Ahar-Varzaghan, Iran, earthquake through SAR remote sensing data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalpin, J.P. Paleoseismology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 95, 629p, ISBN 288 9780123735768. [Google Scholar]
- Reicherter, K.; Michetti, A.M.; Silva, P.G. (Eds.) Palaeoseismology: Historical and Prehistorical Records of Earthquake Ground Effects for Seismic Hazard Assessment; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2009; Volume 316, p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, H.; Yamazaki, F. Landslides by the 2018 Hokkaido Iburi-Tobu Earthquake on September 6. Landslides 2018, 15, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, F.; Matsuoka, M. Remote Sensing: Assessing the Built Environment by Remote Sensing Technologies. In Proceedings of the 2nd InternationalWorkshop on Earthquakes and Megacities, Earthquakes and Megacities Initiative (EMI), Manila, Philippines, 1–3 December 1999; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa, C.; Takeuchi, S. Detection of urban damage using interferometric SAR decorrelation. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’99 (Cat. No.99CH36293), Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; IEEE: Hamburg, Germany, 1999; pp. 925–927. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa, C.; Takeuchi, S. Decorrelation of SAR data by urban damages caused by the 1995 Hyogoken–Nanbu earthquake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Yamazaki, F. Use of satellite SAR intensity imagery for detecting building areas damaged due to earthquakes. Earthq. Spectra 2004, 20, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Mohanty, K.K.; Nayak, S.R.; Chandran, R.V. Mapping the liquefaction induced soil moisture changes using remote sensing technique: An attempt to map the earthquake induced liquefaction around Bhuj, Gujarat, India. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2006, 24, 1581–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, T.; Baise, L.G.; Gens, R.; Prakash, A.; Gupta, R.P. Documenting earthquake-induced liquefaction using satellite remote sensing image transformations. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2013, 19, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Tsuji, T.; Matsuoka, T. Detection and mapping of soil liquefaction in the 2011 Tohoku earthquake using SAR interferometry. Earth Planets Space 2012, 64, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M 6.6–27km E of Tomakomai, Japan. United States Geological Survey. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us2000h8ty/executive (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- M 6.6–27km E of Tomakomai, Japan. Prompt Assessment of Global Earthquakes for Response. Available online: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/us2000h8ty/pager (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Wald, D.J.; Earle, P.S.; Allen, T.I.; Jaiswal, K.S.; Porter, K.A.; Hearne, M.J. Development of the U.S. Geological Survey’s PAGER system (Prompt Assessment of Global Earthquakes for Response). In Proceedings of the 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China, 12–17 October 2008. Paper No. 10-0008. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Senna, S.; Midorikawa, S. Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential for Large Areas Based on Geomorphologic Classification. Earthq. Spectra 2015, 31, 2375–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Yamamoto, N. Web-based quick estimation system of strong ground motion maps using engineering geomorphologic classification map and observed seismic records. In Proceedings of the 15th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–28 September 2012; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience (NIED). Available online: http://www.kyoshin.bosai.go.jp/kyoshin/instant/index_en.html (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- QuiQuake—Quick Estimation System for Earthquake Map Triggered by Observed Records. Available online: https://gbank.gsj.jp/QuiQuake/index.en.html (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, I.; Stewart, M.P.; Kampes, B.M.; Perski, Z.; Lilly, P. A modification to the Goldstein radar interferogram filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Matsuoka, M. Building damage characterization for the 2016 Amatrice earthquake using ascending–descending COSMO-SkyMed data and topographic position index. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2668–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Miyajima, M.; Adriano, B.; Fallahi, A.; Karashi, J. Sequential SAR coherence method for the monitoring of buildings in Sarpole-Zahab, Iran. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellel, M.; Chatelain, J.-L.; Guillier, B.; Machane, D.; Salem, R.B.; Oubaiche, E.H.; Haddoum, H. Heavier damages without site effects and site effects with lighter damages: Boumerdes city (Algeria) after the May 2003 earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2010, 81, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, J.-L.; Guillier, B.; Parvez, I.A. False site effects: The Anjar case, following the 2001 Bhuj (India) earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2008, 79, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. Q. Rep. Railw. Technol. Res. Inst. 1989, 30, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
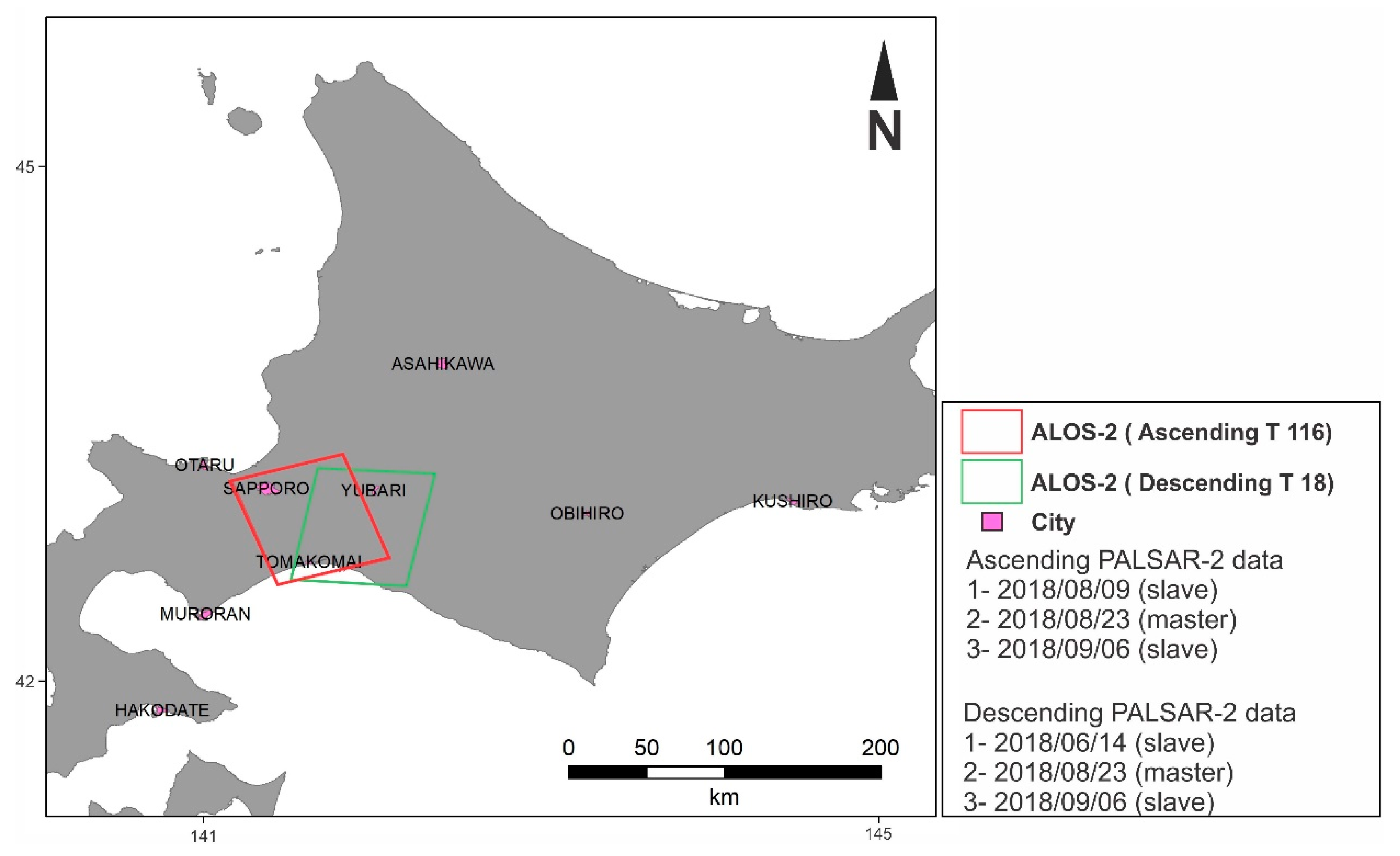
| Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | Polarization | Orbit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018/08/09 | 42.9 | 0.005 | HH | A 116 | 68 | 14 |
| 2018/08/23 * | 42.9 | - | HH | A 116 | - | - |
| 2018/09/09 | 42.9 | 0.006 | HH | A 116 | -40 | 14 |
| 2018/06/14 | 36.1 | 0.018 | HH | D 18 | 237 | 70 |
| 2018/08/23 * | 36.1 | - | HH | D 18 | - | - |
| 2018/09/06 | 36.1 | 0.010 | HH | D 18 | 69 | 14 |
| Point ID | Latitude | Longitude | Predominant Frequency (Hz) | WO Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42.7608 | 142.1345 | 3.7 | 26.25 |
| 2 | 42.7619 | 142.1355 | 2.4 | 23.75 |
| 3 | 42.7628 | 142.1367 | 2.19 | 25.5 |
| 4 | 42.7640 | 142.1381 | 2.19 | 25.45 |
| 5 | 42.7652 | 142.1396 | 2.09 | 27.2 |
| 6 | 42.7664 | 142.1398 | 1.95 | 26.3 |
| 7 | 42.7670 | 142.1403 | 4.15 | 29.6 |
| 8 | 42.7678 | 142.1409 | 6.1 | 29.65 |
| 9 | 42.7689 | 142.1387 | 8.54 | 24.65 |
| 10 | 42.7701 | 142.1421 | 7.51 | 23.7 |
| 11 | 42.7722 | 142.1425 | 6.59 | 22.6 |
| 12 | 42.7674 | 142.1396 | 4.05 | 28.8 |
| 13 | 42.7663 | 142.1412 | 3.1 | 30.5 |
| 14 | 42.7655 | 142.1427 | 3.85 | 24.55 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karimzadeh, S.; Matsuoka, M. A Weighted Overlay Method for Liquefaction-Related Urban Damage Detection: A Case Study of the 6 September 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Japan. Geosciences 2018, 8, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120487
Karimzadeh S, Matsuoka M. A Weighted Overlay Method for Liquefaction-Related Urban Damage Detection: A Case Study of the 6 September 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Japan. Geosciences. 2018; 8(12):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120487
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarimzadeh, Sadra, and Masashi Matsuoka. 2018. "A Weighted Overlay Method for Liquefaction-Related Urban Damage Detection: A Case Study of the 6 September 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Japan" Geosciences 8, no. 12: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120487
APA StyleKarimzadeh, S., & Matsuoka, M. (2018). A Weighted Overlay Method for Liquefaction-Related Urban Damage Detection: A Case Study of the 6 September 2018 Hokkaido Eastern Iburi Earthquake, Japan. Geosciences, 8(12), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8120487