Abstract
El Dabaa city is located along the northwestern coast ridge zone of Egypt, where the groundwater is the major water source for drinking, domestic, and agricultural purposes. The groundwater salinity increased over the last decades, therefore, geochemical techniques and environmental isotopes have been utilized to identify the main groundwater recharge and salinization sources. The study area comprises two main groundwater aquifers: the porous oolitic Pleistocene and the fractured limestone Miocene aquifers. The groundwater salinity of the Pleistocene aquifer ranges from 751 to 27,870 mg/L, with an average value of 6006 mg/L. The salinity of the Miocene aquifer ranges from 3645 to 41,357 mg/L, with an average value of 11,897 mg/L. Fresh and brackish groundwater have been recorded in the shallow hand-dug wells, while saline groundwater has been found in deeper wells close to the shoreline. Groundwater samples have been categorized into two distinct groups according to the salinity ranges, hydrochemical ion ratios, and stable isotopic content. Group I is composed of groundwater with salinity less than 10,000 mg/L, and depleted stable isotopic content (−5.64 < δ18O < −2.45; −23.5 < δ2H < −0.02), while Group II contains groundwater with salinity values above 10,000 mg/L and relatively enriched stable isotopic content (−1.86 < δ18O < −0.48; −10.3 < δ2H < −2.0). The weight mass balance mixing model shows that Group I falls close to the rain and/or water extract samples, indicating meteoric water origin that has evolved due to leaching and dissolution processes. Group II is mostly located between the rainwater and the seawater samples, revealing mixing with water of marine origin due to groundwater overexploitation. The estimated seawater mixing index (SMI) of groundwater samples of Group II is greater than one, which confirms mixing with seawater. The water-rock reaction NETPATH (geochemical groundwater reaction and mixing code) model scenarios representing Group I suggests that gypsum, dolomite, and halite are dissolved, while calcite is formed with a slight influence from evaporation processes. Six mixing models representing Group II are used to investigate seawater mixing scenarios. The models suggest that illite and dolomite are dissolved, while calcite and gypsum are precipitated with a seawater mixing ratios ranging from 28% to 98%. In conclusion, due to the scarcity of annual groundwater recharge in the El Dabaa area, groundwater withdrawal should be well managed to avoid groundwater salinization and further seawater intrusion.
1. Introduction
EI Dabaa city is considered to be one of the most promising districts for land reclamation in Egypt. El Dabaa is located in the southern part of the Mediterranean coastal (semi-)arid region. Groundwater supplies are generally insufficient to meet the probable increases in water demands. Therefore, in the last decades, serious strategies for water development have been established to fully exploit surface and groundwater resources [1].
In the Mediterranean basin, water resources are essentially found in the alluvial Pleistocene aquifers that are connected with stream deltas, and in karst aquifers that are generally scattered over the elevated coastline ridge zones [2,3]. The main source of freshwater supply is groundwater extraction from the Pleistocene oolitic and the Miocene fractured limestone aquifers. These aquifers receive considerable recharge during the winter, where depressions located in between the elongated coastal ridges act as favorable sites for groundwater replenishment [4]. However, saltwater intrusion deteriorates the groundwater quality located along the northwestern coastal zone of Egypt [5,6]. Additionally, the groundwater quality is greatly evolved due to interaction with geological formations and anthropogenic activities [7,8,9]. Understanding the mechanisms of the groundwater evolution in the coastal (semi-)arid groundwater aquifers is necessary for assessing how groundwater extraction in large-scale basins may affect the natural interface between saline–fresh aquifers systems [10].
The groundwater geochemistry in coastal aquifers reflects the prior geological conditions and the current anthropogenic processes influencing groundwater quality [11,12,13]. However, the importance of these aquifers in the local and the regional scale, the main hydrogeologic patterns, hydrochemical features, and the groundwater origins, remain poorly understood [14]. Combining geochemistry and isotopic tools can lead to relevant information regarding the origin of karst water mineralization [15,16]. In this complex system, the origin of salinization and the hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater quality have been identified using dissolved major ions, conservative tracer (Br and Cl), and stable environmental isotopes (δ18O and δ2H). In addition, the geochemical processes has been simulated using NETPATH modeling, a geochemical groundwater reaction and mixing code [17], to determine the main source(s) of groundwater mineralization in different aquifers. The framework of the present study aims to provide baseline information about: (1) the hydrochemical features of groundwater, (2) the main processes deteriorating the groundwater quality and (3) the sources of groundwater recharge and their mixing pathways.
2. Background
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located between latitudes 30.55°, 30.35° N, and longitudes 27.65°, 28.65° E (Figure 1). It lies within the southern Mediterranean coastal (semi-)arid zone and has been subjected to an intensive evaluation by governmental authorities for the establishment of new communities, tourist villages, and land reclamation projects. The changes being considered are driven by an attempt to address the continuous growth of the population, which will also increase water demand in the area.
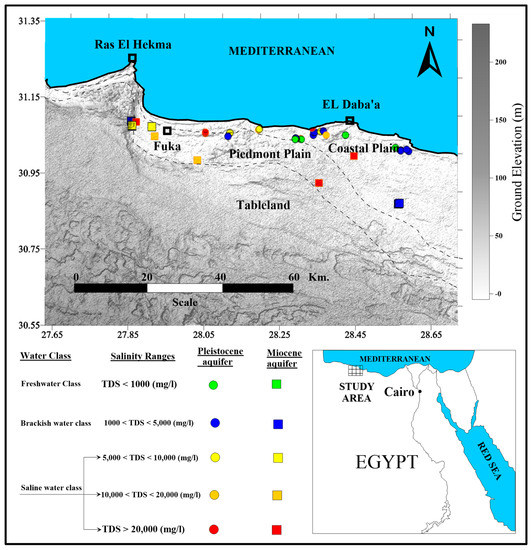
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area.
2.2. Geology, Geomorphology and Hydrogeology
The study area consists of sedimentary succession ranging in age from the Tertiary to the Quaternary (Figure 2). It comprises three main geomorphic units: the coastal plain, the Piedmont plains, and the tableland [18]. The coastal plain is located near the Mediterranean shoreline and is covered by sand dunes, composed mainly of oolitic carbonate sands forming an unconfined porous aquifer [19]. The Piedmont plain rises to about 100 m above the mean sea level, regionally slopes northward and built up by fissured limestone [20]. The tableland is located in the south and formed of a fractured carbonate plateau, which represents the main watershed area [19].
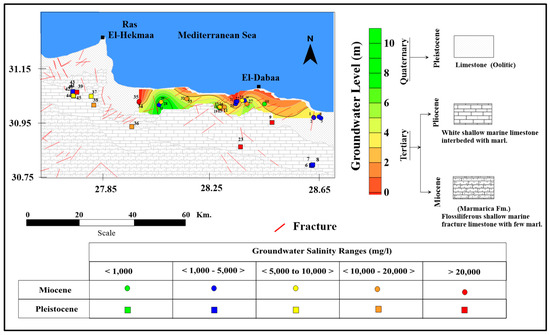
Figure 2.
Geological map along the northwestern coastal zone.
Two aquifers are recognized in the investigated area: the porous Pleistocene aquifer (oolitic) and the fractured Miocene (Marmarica) aquifer (Figure 2). The Pleistocene oolitic aquifer has a wide distribution extending 10 km from the shoreline and to the south. The groundwater exists in a porous oolitic limestone as a free water table aquifer [21]. The foreshore oolitic limestone ridges are characterized by less cementing materials, when compared to the inland ridges, and are more porous in nature [22]. The flanks of the ridges are covered by loose foreshore sand accumulations, which permit a direct infiltration and percolation of rainfall [6].
The groundwater in the oolitic Pleistocene aquifer flows north toward the sea (Figure 2). The primary recharge originates from the tableland plateau, forming the watershed on the southern side of the aquifer [23]. In a (semi-)arid region, groundwater in porous coastal aquifers occurs as a thin layer of fresh water floating over a deep saline one, as result of a natural balance between the surplus of recharge from precipitation and the discharge through seepage to the sea [24,25] (Paver and Pretorius, 1954; Eissa, 2018). The hydraulic gradient is gentle in the northern (0.0002) and southern (0.0003) part of the study area [22]. The fractured limestone aquifer has developed as a secondary aquifer. It extends along the northwestern Mediterranean coastal area to the west of Alexandria and is explored at El Dabaa, Fuka, Matruh and El Sallum localities [26]. This aquifer is largely fractured and composed of sequences of limestone, dolomite, and shale related to the middle Miocene age, where groundwater occurs in successive horizons separated by impervious clays, with occasional bands of sandstone [27]. The average hydraulic conductivity of the two investigated aquifers are greatly varying [28]. It reaches 1.2 m/day in the Pleistocene aquifer, while the Miocene aquiferreaches 0.35 m/day [29].
3. Methods
Forty-one groundwater samples, tapping both the Pleistocene oolitic and the Miocene groundwater aquifers, were collected in March 2015 (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Fifteen groundwater samples were collected from the Miocene aquifer and 26 samples from the Pleistocene aquifer (ESM 1). Additionally, seawater and rainwater samples were collected during the field trip. The depth to water (DTW), total depth (TD) and the ground elevation (GE) were also measured (ESM 1). Each water sample was filtered through 0.45 cellulous acetate filter paper and then filled into two polyethylene bottles to determine major chemical constituents (500 mL) and to conduct isotopic analyses (50 mL). The pH, temperature (T, °C), electrical conductivity (EC, micro mohs/cm), and the total dissolved solids (TDS, mg/L) were determined in the field site. The pH and temperature were measured using a 3510, Jenway, UK meter, while EC was determined using an Orion 150A+, Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA.
The collected water samples were analyzed to determine the concentrations of major cations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+) and major anions (CO32−, HCO3−, SO42− and Cl−) according to the methods adopted by [30,31,32,33] at the Centre Laboratories of the Desert Research Centre in Cairo, Egypt. Bromide (Br−) was determined using an ion selectivity meter, Orion EA 940, Thermo Electron Corporation, USA (ESM 1).
In order to determine the impact of the aquifer matrix on the groundwater chemistry, rock-water extract has been performed for three core samples obtained from groundwater well No. 17 located down gradient of El Dabaa area. The three samples were crushed and ground to a fine powder. A 1:1 volume ratio of water and rock was shaken for three weeks to obtain equilibrium. The samples were centrifuged and filtered through 0.45 mm filter paper to obtain the water extract for each sample and were analyzed to determine the major ions content (ESM 1).
The cations, anions, and TDS data were used to give quantitative information on groundwater mixing via a mass balance mixing model that has been described by [34,35]. Rainwater and seawater samples were utilized to examine the recharge and salinization source(s) for the study area and were considered as representative end members. The weighted mass balance equation was utilized with different implicit mixing ratios of the two end members ranging from 0 to 100% to determine the main source(s) of groundwater salinization as follows:
F(T) = F1(Sea) + F2(Rain) = 1
C(T)model = [F1(Sea) ∗ X(Sea)] + [F2(Rain)∗ X(Rain)]
(X refers to cations and anions), F(T) and C(T) are the sums of total mixing fractions, and F1, F2, are the anticipated mixing fractions from the two end members.
Statistical methods for chemical data were used in the coastal area to understand how geochemical processes influence groundwater quality [36,37,38]. Seawater Mixing Index (SMI) was used to estimate the relative degree of seawater mixing (%) with groundwater, based on the concentrations of four major ions (Na+, Cl−, Mg2+ and SO42 −) as follows:
Park et al. 2005 [39] estimated the constant factors a, b, c, and d according to the relative proportion of Na+, Mg2+, Cl− and SO42− in seawater, respectively. Ti represents the calculated threshold values of the selected ions, and can be estimated from the distribution of the cumulative probability curves for each ion in a specific site. Ci is the measured ion concentration in mg/L.
Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes for the water samples were measured at the IT2 (Isotope Tracers and Technologies) laboratory in Waterloo, Canada using the CRDS (Model L1102-i) Piccaro, CA, USA by the method described by [40,41]. Both hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions are reported in per mil (‰), the conventional notation used for any deviation from isotopic standard reference material, where, δ = [(R sample/R standard) − 1] × 1000. R sample and R standard are the measured isotopic ratios (18O/16O) and (2H/1H) of the sample and standard material. The reference material is Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW) and all results are evaluated, corrected and reported against VSMOW [42]. The typical standard deviation for oxygen is ±0.1‰ and ±0.6‰ for hydrogen.
The major chemical analyses of groundwater were used as input data for the geochemical modeling. NETPATH-WIN, a geochemical groundwater model using windows as operating system, was used to calculate the saturation index (SI) of minerals in the groundwater [17]. The SI of relevant minerals was determined by the following equation [43]: SI = log (IAP/KT), where IAP is the ion activity product, and KT is the equilibrium constant of mineral dissolution at a certain temperature.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Groundwater Chemistry
The term salinity refers to the total dissolved concentrations of major and minor constituents in water. The concentration of dissolved solutes can vary widely as a function of the mineral content of the aquifer matrix through which the groundwater flows. According to results of the chemical analyses (ESM 1), the Pleistocene aquifer groundwater salinity ranges from 751 mg/L to 27,870 mg/L, with an average value of 6006 mg/L. In the Miocene aquifer, groundwater salinity ranges from 3645 mg/L to 41,357 mg/L, with an average value of 11,897 mg/L. Using the TDS values, groundwater is classified into fresh, brackish, and saline [44]. In the study area, the majority of groundwater samples are categorized as saline (44%) and brackish (41%) water classes, while a minority is considered freshwater class (15%). In general, most of the freshwater samples are recorded within the Pleistocene aquifer (23%). Freshwater from annual recharge dominates the Pleistocene oolitic aquifer, where rainfall percolates downward toward the shallow groundwater through the foreshore oolitic sand. In addition, the oolitic aquifer is dissected by several elongated ridges running parallel to the shoreline, which act as barriers for surface water flow and consequently enhance the entrapment of recharge water. On the other hand, the groundwater samples with higher TDS values indicate the occurrence of leaching and dissolution processes of marine origin deposits, as well as mixing with seawater [45].
Dissolved major ions in water make up the majority of total groundwater salinity (Figure 3). Calcium, magnesium, sodium, and sulfate concentrations, as well as the corresponding saturation indices of calcite, dolomite, halite, and gypsum (ESM 1) show positive correlations with the TDS of the two investigated aquifers (Figure 3a–h). The groundwater samples tapping the investigated aquifers are plotted between the recharge water (rainwater) and the seawater samples, which indicate leaching and dissolution processes due to water-rock interaction with aquifer matrix and marine deposits, and/or mixing with seawater [46,47,48]. The groundwater samples could be classified into two distinct groups (Figure 3). Group I includes groundwater samples that have relatively lower concentrations of Ca, Mg, Na, SO4, with salinity less than 10,000 mg/L, while Group II has higher concentrations of these ions and high saline samples. The Group I is plotted close to the rainwater and/or water extract samples, indicating the groundwater has evolved due to leaching and dissolution processes of the aquifer matrix.
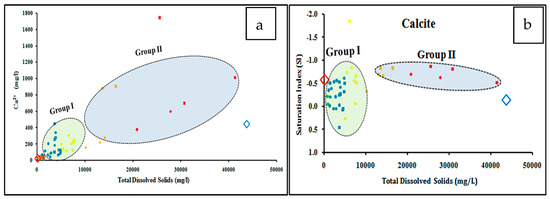
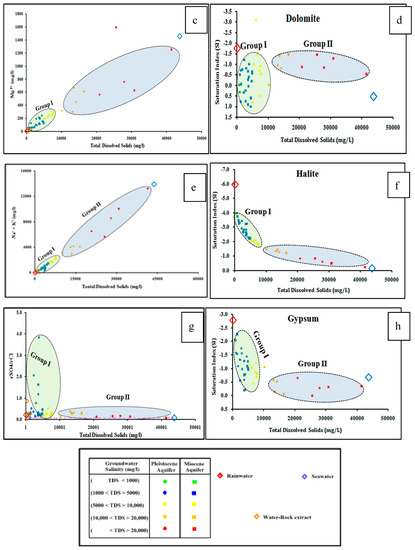
Figure 3.
Relationships between the dissolved major ions and the equivalent mineral saturation indices ((a) Ca, (b) Calcite, (c) Mg, (d) Dolomite, (e) Na, (f) Halite, (g) SO4, and (h) Gypsum) versus the total dissolved solids of the studied groundwater samples.
Group I is more highly saturated with calcite and dolomite and less saturated with halite and gypsum minerals relative to Group II. Group II is mostly plotted in between the recharge water and the seawater, indicating mixing with seawater due to groundwater overexploitation.
Gibbs (1970) [49] describes five mechanisms (precipitation dominance, rock dominance, evaporation, precipitation, and mixing) that control global groundwater chemistry (Figure 4a,b). The groundwater samples are plotted in the upper right corner of our Gibbs diagram, indicating that groundwater Group I is mostly affected by evaporation processes, while groundwater Group II is plotted close to the seawater sample, which indicates mixing with seawater.
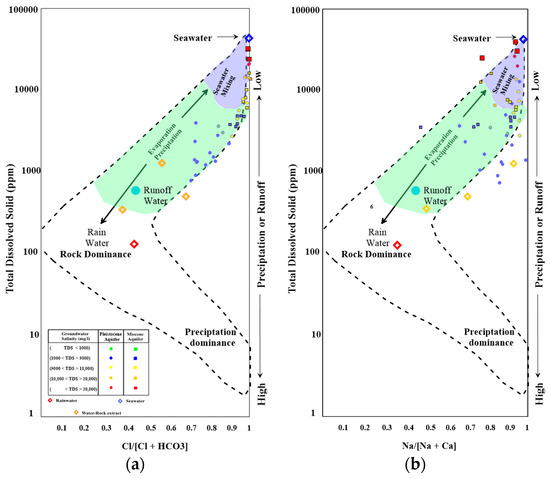
Figure 4.
Gibbs diagram for the groundwater wells tapping the Pleistocene and Miocene aquifers; (a) Total dissolved solids (TDS) versus Cl/[Cl+HCO3]; (b) TDS versus Na/[Na+Ca].
4.2. Ion Chemical Ratios
Ion chemical ratios are helpful for detecting the hydrochemical processes affecting water quality, such as leaching, mixing, ion exchange; and assessing the impact of seawater intrusion on groundwater chemistry [50,51,52,53]. Table 1 represents the range and mean values of different ion ratios in groundwater of different aquifers. The values of rNa+/rCl− are always higher than unity in fresh and meteoric water, and less than unity in sea water or saline water [32,54]. A rNa+/rCl− value is higher than unity indicates that sodium has increased relative to chloride. In Figure 5a, most of Group I has rNa+/rCl− values more than unity, due to water-rock interaction processes. While Group II has rNa+/rCl−values less than unity, due to mixing with the seawater as a result of overexploitation [55]. About 62% of the Pleistocene groundwater samples have rNa+/rCl−less than unity and 38% of the samples have rNa+/rCl− exceeding unity. In the Miocene groundwater, about 93% of the water samples have rNa+/rCl−values less than unity, and 7% nearly equal to unity.

Table 1.
Ranges and mean values of hydrochemical ratios of the different aquifers in the study area.
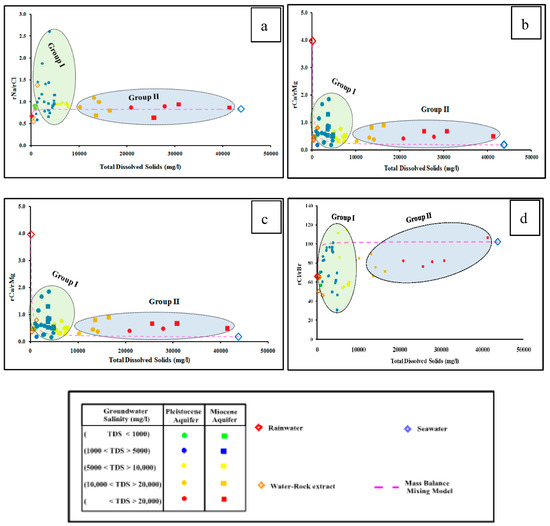
Figure 5.
Ion ratios ((a) rNa+/rCl−, (b) rCa2+/rMg2+, (c) rSO42−/rCl−and (d) Br−/Cl−) of the studied groundwater samples versus the total dissolved solids.
The rCa2+/rMg2+ratio gives an indication of the nature of the carbonate aquifer [56]. When this ratio has a value close to unity, it is concluded that the groundwater is flowing entirely through dolomite terrain. However, when this ratio equals or exceeds four, the groundwater is likely to have flowed in pure limestone [57]. In Figure 5b fresh groundwater samples have low rCa2+/rMg2+ values, due to the dissolution of sequences of limestone, dolomite, and shale that have been reported in the subsurface lithology. Group II has rCa2+/rMg2+ values similar to the ratio in the modern seawater. In addition, the rSO42−/rCl− ratio can be used as an indicator of an excess of sulfate in the groundwater, due to mixing with seawater, where Group II falls close to the seawater sample while Group I falls close to the water-rock extract samples (Figure 5c).
Finally, Br−/Cl− ratios are utilized to detect the salinity of marine and non-marine origins [58]. The Cl and Br ions are not adsorbed into any mineral or organic surfaces and are not affected by redox reactions, therefore, they are considered conservative ions (Fetter, 1993). The Br−/Cl− ratio versus the total dissolved solids plot shown in Figure 5d indicates that Group I has relatively low values, where the majority of groundwater samples have fallen into the left side, close to the water-rock extract indicating the main source of groundwater salinization is the leaching and dissolution of the aquifer matrix. High saline groundwater samples are characterized by high Br−/Cl− value, indicating mixing with seawater.
4.3. Seawater Mixing
The SMI parameter was used for the quantitative estimation of seawater mixing ratios with groundwater, using the concentrations of the four dissolved major ions (Na+, Mg+2, Cl−, SO4−2).
The SMI is used to detect the occurrences of hydrogeochemical and mixing processes in shallow and deep aquifers [23]. The probability distribution curves shown in Figure 6 have great implications in understanding the geochemical data and the segregation processes affecting the groundwater chemistry [59,60,61].
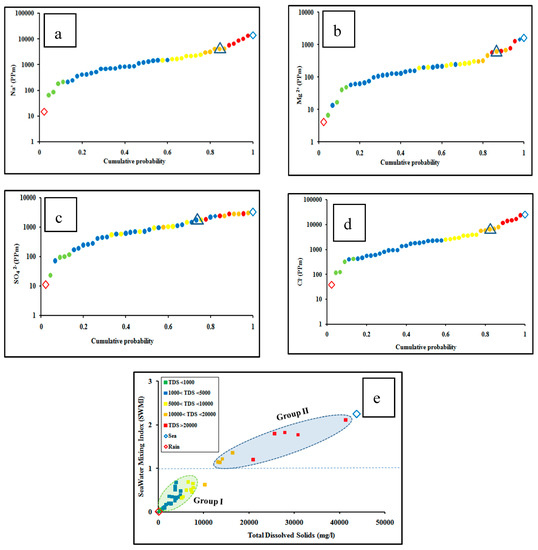
Figure 6.
Cumulative probability curves for the distribution of (a) Na+, (b) Mg2+, (c) Cl−, (d) SO42−in groundwater samples), (e) Cross-plot of seawater mixing index vs. total dissolved solids of the studied groundwater samples. Black triangles refer to the inflection points.
In Figure 6a–d, the inflection points indicate the equivalent regional threshold values (Ti) for Na+, Mg2+, Cl− and SO42− ions [36,37]. The values of inflection points are determined from the distribution probability curves extended between the rain and seawater end members. The usual cumulative probability curves have inflection points between the concave up and concave down portion of the curve at cumulative probability ~0.8. The estimated focal threshold (Ti) values for different ions are 4100 mg/L for Na+, 455 mg/L for Mg2+, 5509 mg/L for Cl− and 1734 mg/L for SO42−.
From the SMI results, it was found that groundwater is classified into two groups (Figure 6). Group I (0.06 < SMI < 0.79) is less than unity and has a groundwater salinity range from 750 to 10,000 mg/L, which indicates subsurface meteoric groundwater recharge from the watershed. Group II (1.29 < SMI < 2.25) has salinity ranging from 13,000 to 41,000, which confirms mixing with seawater [36,39].
4.4. Environmental Isotopes
Oxygen (δ18O) and hydrogen (δ2H) are ideal tracers that can be used to determine recharge source(s). They do not enter into geochemical reactions, and normally be used to understand physical processes such as groundwater mixing and evaporation [62,63].
The results of δ18O and δ2H analyses in ESM 1 shows that the isotopic composition of groundwater ranges from −5.64 to +2.87‰ for δ18O and from −26.2 to +25.8‰ for δ2H.The weighted mean isotopic value for precipitation between October and April was estimated by −5.0‰ for δ18O and −15.14‰ for δ2H [23].Seawater, which is considered one of the main sources of groundwater salinity in the study area, is represented by a sample collected from the Mediterranean and is characterized by relatively enriched isotopic values (δ18O 1.12‰, δ2H 8.5‰) (Figure 7).
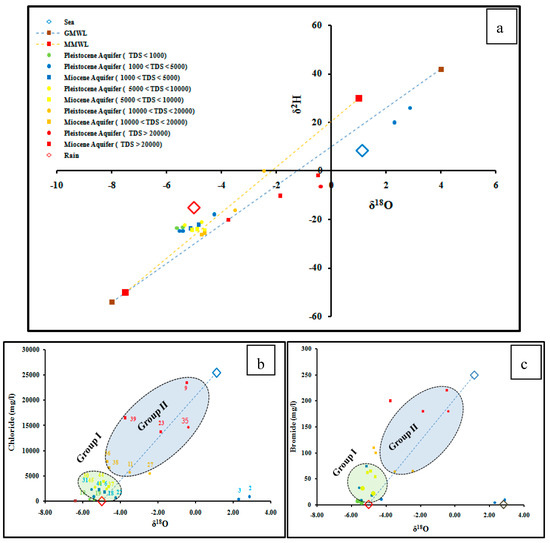
Figure 7.
(a) The relationship between δ18O and δ2H; (b) The relationship between δ18O and Cl; (c) The relationship between δ18O and Br.
The δ18O versus δ2Hrelationship (Figure 7a) shows that the samples are divided into two groups. Group I represents samples that are depleted with both δ18O and δ2H. Group I plots close to the Mediterranean meteoric water line (MMWL) [64,65] and represents most of the fresh and brackish groundwater samples, indicating meteoric water origin. Group II, have high salinity, relatively enriched with δ18O and δ2H, and located close to the seawater sample, indicating seawater intrusion. In Figure 7b,c, the relationship between δ18O versus chloride and bromide show that sample numbers 6, 10, 13, 18, 19, 22, 30, 31, 37, 41, 44, and 45 receive a great amount of meteoric recharge water, while other groundwater samples show mixing with seawater.
4.5. Water–Rock Interaction and Mixing Model
Water chemistry and isotopic data has been used in a NETPATH model to evaluate potential groundwater flow paths and the source of groundwater mineralization [63,66]. To provide a valid groundwater flow path, the observed water chemistry at the end of a flow path has to have undergone reasonable geochemical reactions and/or been changed by mixing with chemically different waters along the flow path [17].
The NETPATH model estimates the net geochemical reactions and the observed variations in groundwater chemistry between an initial and final groundwater well along the groundwater subsurface flow path. The NETPATH approach is limited by the input data that describe the subsurface groundwater aquifer [67]. In this study, the water-rock interaction and mixing model scenarios are constrained by the groundwater chemical analyses of major ions and the most dominant minerals phases forming the Miocene and Pleistocene aquifers (Table 2). Calcite and dolomite are involved in the model because they of the presence of carbonate rocks. Halite, gypsum, and clay minerals are particularly embedded in the successive shale and marine deposit layers forming the aquifer matrix [68]. The model results show water-rock interaction and seawater mixing scenarios.

Table 2.
Constraints, phases, and parameters used in NETPATH models.
Three reaction models created using NETPATH investigated the sources of salinization in the groundwater aquifer representing Group I (Table 2). The upgradient groundwater sites 5, 20, and 44 (Initial Water) in the Pleistocene and Miocene aquifers flows down gradient to sites 2, 22, and 38 (Final Water), respectively (Table 3). Water-rock reaction models for groundwater flow from the upgradient to the downgradient suggest that gypsum, dolomite, and halite dissolve, while calcite is formed due to evaporation, ranging from 1.36 to 2.1. The changes in mineral phases estimated by the NETPATH model are consistent with the calculated saturation indices (SI) charges indicated in ESM 2. Six mixing models representing groundwater Group II were also used to investigate mixing with seawater (Table 4, Figure 8). The seawater sample has been identified as initial water 1, which mixed with the upgradient groundwater sites 10, 19, and 36, and flows down gradient to sites 27, 35, and 11 (final water) in the Pleistocene aquifers and sites 9, 23, and 39 (final water) in the Miocene aquifer. The models suggest that illite and dolomite dissolve while calcite and gypsum are formed, with the mixing proportion with seawater (Initial 1) ranging from 28% to 98%.

Table 3.
NETPATH water-rock interaction model results (mmol/L) representing groundwater Group I.

Table 4.
NETPATH seawater mixing model results (mmol/L) representing groundwater Group II.
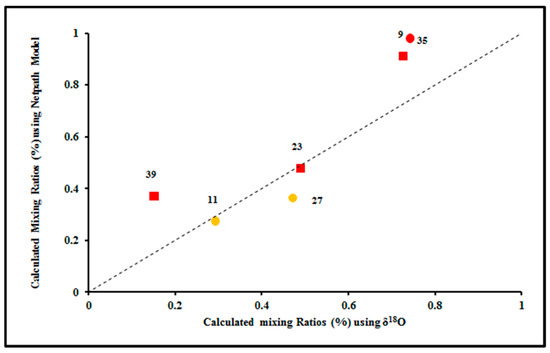
Figure 8.
Relation between calculated seawater mixing percent using δ18O and NETPATH model.
The NETPATH model was calibrated using the mixing proportions estimated by the stable isotopes, using the equations have been shown in Section 3 (Figure 8). The NETPATH model results were also consistent with the isotopic and geochemical results, where the geochemical processes affecting groundwater quality in the Pleistocene and the Miocene aquifers are water-rock interaction, mixing with seawater, and evaporation processes.
5. Conclusions
The hydrogeochemical results demonstrate wide ranges of groundwater salinity and major ions in the oolitic Pleistocene and fractured Miocene aquifers. In the Pleistocene aquifer, the total dissolved solids vary between 751 mg/L and 27,870 mg/L, with an average value of 6006 mg/L. The Miocene aquifer groundwater salinity ranges from 3645 mg/L to 41,357 mg/L, with an average value of 11,897 mg/L. Lower groundwater salinity was recorded toward the south, close to the tableland plateau, as well as in the shallow-drilled wells. On the other hand, groundwater of high salinity is located near the Mediterranean, and in the inland deep-drilled wells.
The calculated SMI geochemical ion ratio water samples can be divided into two groups. The first group (Group I) is located close to the recharge water (rainwater) and the water extract of the rock samples, which indicates the leaching and dissolution process of the aquifer matrix; while the second group (Group II) is plotted closer to the sea, indicating seawater mixing. Based on the water chemistry and stable isotopes, groundwater recharge is limited and the main source for groundwater recharge is annual precipitation. The relatively low groundwater salinity of Group I is more depleted in δ2H and δ18O, while the higher groundwater salinity of Group II is mostly enriched in these isotopes. Higher groundwater salinity is enriched in δ2H and δ18O, due to mixing with seawater. The main factors deteriorating the groundwater quality in the Pleistocene and Miocene aquifers are the water-rock interactions with the carbonate rocks of marine origin, and mixing with seawater. Fresh groundwater resources in the El Dabaa area are limited to a thin layer of fresh water which is very sensitive to pumping stresses. Therefore, pumping groundwater has to be managed to avoid deterioration of groundwater quality due to upwelling of seawater.
Author Contributions
In this work, M.A.E. supervise the project and conceived the original idea. Chemist: A.S. carried out the experiment and wrote the manuscript with support from M.A.E. and H.S., M.M.H.K. and M.E.M. were involved in planning and supervised the work. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The Authors gratefully acknowledge the Science & Technology Development Fund (STDF) in Egypt for supportive funding through project # 6723. Authors would like to thank the editors of the Geosciences journal as well as the reviewers who have generously given up valuable time to review the manuscript. Particular great appreciation to Laura Craig for editing the language of the manuscript as a native English speaker.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mohallel, S.A. Hydrochemistry and Treatment of Groundwater in the Area between Marsa Matruh and El Salloum, Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aureli, A.; Ganoulis, J.; Margat, J. Groundwater Resources in the Mediterranean Region: Importance, Uses and Sharing; UNESCO International Hydrological Programme (IHP): Paris, France, 2008; pp. 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Nicod, J. Sur quelques sources littoraleset sous-marines autour de laMéditerranée. Et. Géogr. Phys. 2009, XXXVI, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, F.A. The Geology of Water Supplies in Ras El Hekma Area, Western Mediterranean Coastal Zone, Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, M.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Parker, B.; De Dreuzy, J. Managing saltwater intrusion in a poorly-constrained arid aquifer, utilizing isotopes and geochemistry, Northwestern coast. Egypt (abstract). Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. Programs 2015, 47, 324. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shiekh, A.E.; Eissa, M.A.; Mahmoud, H.H. Study the phenomenon of sea water intrusion and its impact on the groundwater of the Quaternary aquifer in Delta Wadi Heneash, Northwestern Coast, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 32nd Anual Meeting Program, Cairo, Egypt, 21 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, W.C. Groundwater Resources Evaluation; McGraw Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Magesh, N.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Evaluation of spatial variations in groundwater quality by WQI and GIS technique: A case study of Virudunagar District, Tamil Nadu. India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 6, 1883–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, S.V.; Magesh, N.S.; Jitheshlal, K.V.; Chandrasekar, N.; Gangadhar, K. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, G.; Dogramaci, S.; Grierson, P.F. Geochemical and hydrological processes controlling groundwater salinity of a large inland wetland of northwest Australia. Chem. Geol. 2013, 357, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M. Renewable and non-renewable groundwater in semi-arid and arid regions. Dev. Water Sci. 2003, 50, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Vengosh, A.; Kloppmann, W.; Marie, A.; Livshitz, Y.; Gutierrez, A.; Bana, M.; Guerrot, C.; Pankratov, I.; Ranan, H. Sources of salinity and boron in Gaza Strip: Natural contaminant flow in southern Mediterranean Coastal aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W01013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennetts, D.A.; Webb, J.A.; Stone, D.J.M.; Hill, D.M. Understanding the salinization process for groundwater in an area of south-eastern Australia, using hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. J. Hydrol. 2006, 323, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Parker, B.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Hosni, M.H.; El Shiekh, A. Electrical resistivity tomography, geochemistry and isotope tracers for saltwater intrusion characterization along the Northwestern coast. Egypt. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. Programs 2015, 47, 486. [Google Scholar]
- Aquilina, L.; Ladouche, B.; Doerfliger, N.; Seidel, J.L.; Bakalowicz, M.; Dupuy, C.; LeStrat, P. Origin, evolution and residence time of saline thermal fluids (Balaruc springs, southern France): Implications for fluid transfer across thecontinental shelf. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Q. Strontium isotope characterization and major iongeochemistry of karst water flow, Shentou, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, L.N.; Prestemon, E.C.; Parkhurst, D.L. NETPATH: An interactive code for interpreting NET geochemical reactions from chemical and isotopic data along a flow. In Proceedings of the International 7th Symposium on Water-Rock Interaction, Park City, UT, USA, 9–23 July 1992; pp. 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, M.; Geldern, R.V.; Bubenzer, O. Hydrogeological investigation of shallow aquifers in an arid data-scarce coastal region (El Daba’a, northwestern Egypt). J. Hydrogeol. 2016, 24, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, F.A. The Geology of Soil and Water Resources in the Area between Ras El-Hekma and RasAlam El-Rum, Western Mediterranean Coastal Zone, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, M.H. Assessment of Surface Water Runoff in Marsa Matruh Area, Northwestern Coastal Zone, A.R.E. Ph.D. Thesis, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rizk, Z.S. Geological and Hydrogeological Studies on the North Western Coast of Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Menoufia University, Al Minufya, Egypt, 1982; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Atwa, S.M. Hydrogeology and Hydrogeochemistry of the Northwestern Coast of Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Alexandria University, Alexandria, Egypt, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, M.; Mahmoud, H.H.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; El-Shiekh, A.; Parker, B. Geophysical and geochemical studies to delineate seawater intrusion in Bagoush area, Northwestern coast, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 121, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paver, G.L.; Pretorius, D.A. Report on reconnaissance hydrogeological investigation in the western desert coastal zone. Publ. Inst. Desert Egypt 1954, 5, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, M. Application of Multi-Isotopes and Geochemical Modeling for Delineating Recharge and Salinization Sources in Dahab Basin Aquifers (South Sinai, Egypt). Hydrology 2018, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslan, S.M. Geomorphological and Hydrogeological Studies on Some Localities along the Northwestern Coast of Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Menoufia University, Al Minufya, Egypt, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, G.A. Hydrochemistry of the Groundwater in the Area between El Dabaa and Mersa Matruh, North Western Coast, Egypt. Master’s Thesis, Menoufia University, Al Minufya, Egypt, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Morad, N.A.; Masoud, M.H.; Abdel Moghith, S.M. Hydrologic Factors Controlling groundwater salinity in North Western coastal zone, Egypt. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, E. Hydrogeological, Geomorphological and Geoenvironmental Implications for Future Sustainable Development of the Northwestern Coastal Zone of Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater, F.H.; Thatcher, L.L. Methods for Collection and Analysis of Water Samples; Paper No. 1454; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1960; p. 301.
- Fishman, M.J.; Friedman, L.C. Methods for Determination of Inorganic Substances in Water and Fluvial Sediments; Open-File Report, 85–495; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1985; Chapter A1; Volume 5.
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water, 3rd ed.; Paper 1473; U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 2254.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 11, 939p. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, G. Principles of ISOTOPE Geology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, I. Groundwater Geochemistry and Isotopes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, N.C.; Singh, V.P. Hydrochemical analysis of salinization for a tannery belt in Southern India. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.J.S. Evolution of groundwater chemistry in and around Vaniyambadi Industrial Area: Differentiating the natural and anthropogenic sources of contamination. Chem. Erde-Geochem. 2014, 74, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isawi, H.; El-Sayed, M.H.; Eissa, M.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Shawky, H.; Abdel Mottaleb, M.S. Integrated geochemistry, isotopes, and geostatistical techniques to investigate groundwater sources and salinization origin in the Sharm EL-Shiekh Area, South Sinia, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Yun, S.T.; Chae, G.T.; Yoo, I.S.; Shin, K.S.; Heo, C.H.; Lee, S.K. Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, the western coastal area of South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Wildman, J.D.; Chen, J. Improvements in the gaseous hydrogen-water equilibrium technique for hydrogen isotope ratio analysis. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B. Reporting of stable hydrogen carbon and oxygen isotopic abundances. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrels, R.; Mackenzie, F. Origin of the chemical compositions of some springs and lakes. In Equilibrium Concepts in Natural Water Systems; Ground, R.F., Ed.; American Chemical Society Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Chebotarev, I.I. Metamorphism of natural waters in the crust of weathering—I. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1955, 8, 22–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Thomas, J.M.; Pohll, G.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Hershey, R.L.; Dawoud, M. Groundwater recharge and salinization in the arid coastal plain aquifer of the WadiWatir delta, Sinai, Egypt. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 71, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Rosenthal, E. Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J. Hydrol. 1994, 156, 389–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, P.; Dupre’, B.; Martin, F.; Viers, J. The role of trace minerals in chemical weathering in a high elevation granitic watershed (Estibe’re, France): Chemical and mineralogical evidence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2223–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengoush, A. Salinization, and saline environments. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.T., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Burlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhija, B.S.; Varma, V.N.; Nagabhushanam, P.; Reddy, D.V. Differentiation of paleomarine and modern seawater intrudedsalinities in coastal groundwaters (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprintsand radiocarbon dating. J. Hydrol. 1996, 174, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Spivack, A.J.; Artzi, Y.; Ayalon, A. Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1877–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Moujabber, M.; BouSamra, B.; Darwish, T.; Atallah, T. Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzana, L.; Benassi, R.; Ben Mammou, A.; SfarFelfoul, M. Geophysical and hydrochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi-arid zones.The case of the Korba coastal aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2009, 58, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaska, M.; La Salle, C.; Lancelot, J.; Aster, M.A.; Verdoux, P.; Noret, A.; Simler, R. Origin of groundwater salinity (current seawater vs. saline deep water) in a coastal karst aquifer based on Sr and Cl isotopes. Case study of the La Clape massif (southern France). Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, F.J.; Custodio, E. Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer toidentify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, R.L.; Langmuir, D. The chemical history of some spring waters in carbonate rocks. Groundwater 1970, 8, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesler, H.; Becher, A.E. Hydrogeologic Significance of Calcium/Magnesium Ratios in Groundwater from Carbonate Rocks in the Lancaster Quadrangle, Southern Pennsylvania; The Geological Professional Paper; USGS: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; pp. 232–235.
- Andreasen, D.C.; Fleck, W.B. Use of bromide: Chlorideratiosto differentiate potential sources of chloride in a shallow, unconfined aquifer affected by the brackish-water intrusion. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.M. Element distribution laws in geochemistry. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 1961, 23, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J. Selection of threshold values in geochemical data using probability graphs. J. Geochem. Explor. 1974, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J. Application of Probability Graphs in Mineral Exploration; Special Volume No. 4; Association of Exploration Geochemists: Rexdale, ON, Canada, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R.; Mazor, E.; Tzur, Y. The stable isotope composition of mineral waters in the Jordan Rift Valley Israel. J. Hydrol. 1969, 76, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA; WISER. Water Isotope System for Data Analysis, Visualization, and Electronic Retrieval. WISER Version 0.7.2008. Available online: https://websso.iaea.org (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Eissa, M.A.; Thomas, J.M.; Hershey, R.L.; Dawoud, M.I.; Pohll, G.; Dahab, K.A.; Gomaa, M.A.; Shabana, A.R. Geochemical and isotopic evolution of groundwater in the WadiWatir watershed, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 1855–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, R.L.; Heilweil, V.M.; Gardner, P.; Lyles, B.; Earman, S.; Thomas, J.; Lundmark, K.W. Ground-Water Chemistry Interpretations Supporting the Basin and Range Regional Carbonate-Rock Aquifer System (BARCAS) Study, Eastern Nevada and Western Utah; DHS Publication No. 41230; Desert Research Institute: Reno, NV, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, A.M.; Sawires, R.F. Hydrogeological studies on the Nubian sandstone aquifer in El-Bahariya oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).