Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data Sources
4. Methodology
5. Results
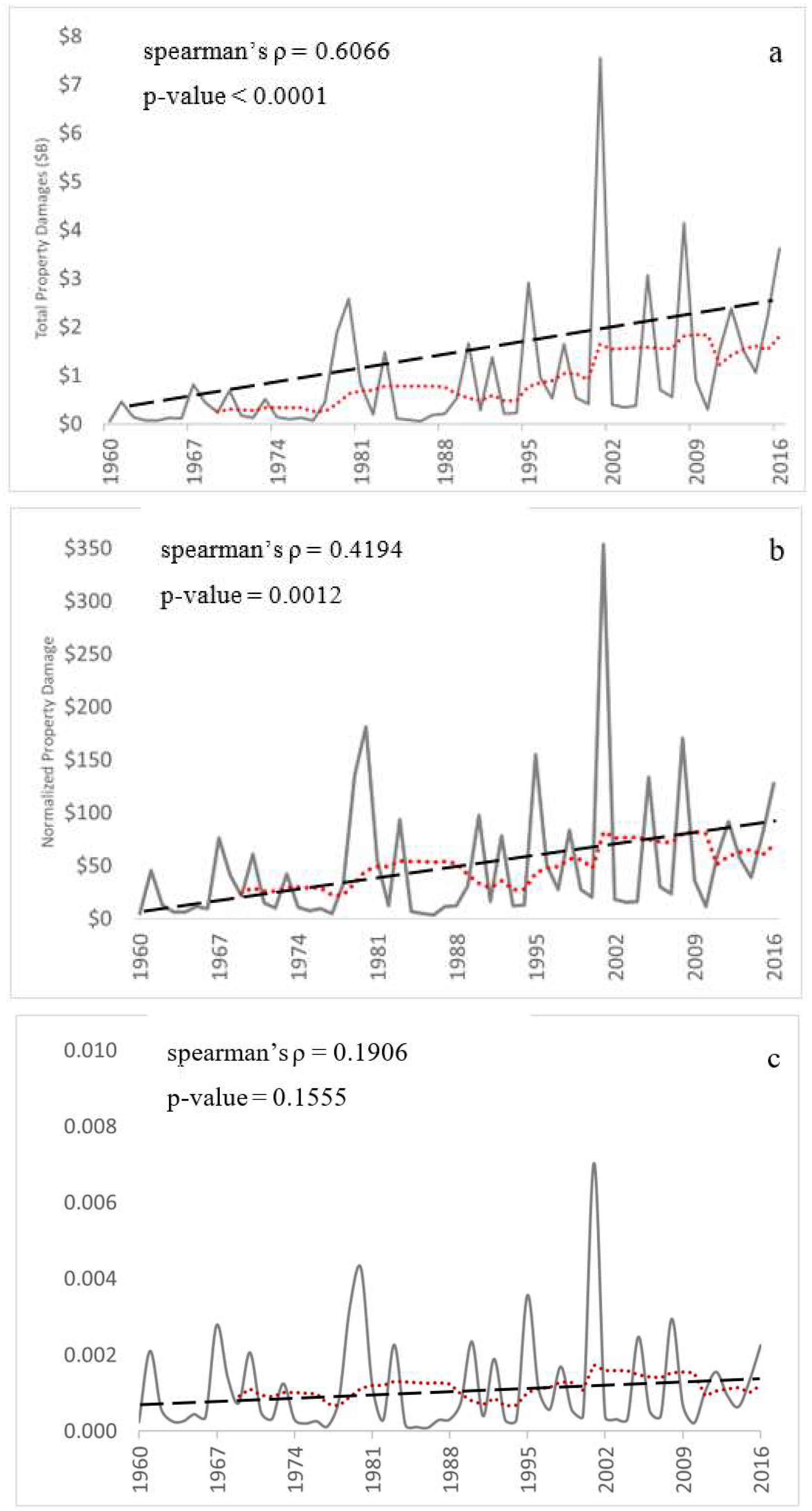
5.1. Annual Distribution of Damage
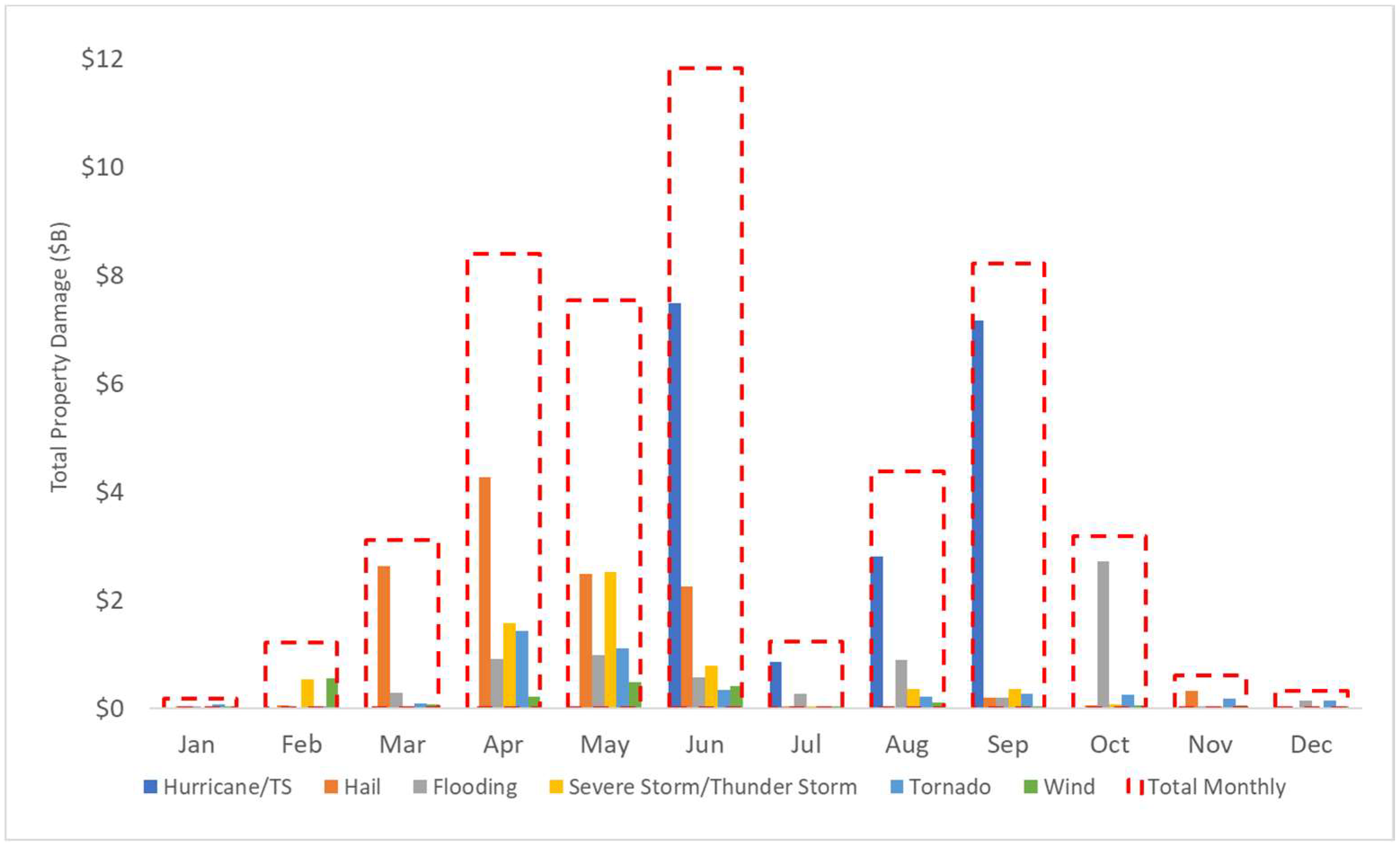
5.2. Monthly Distribution of Damage
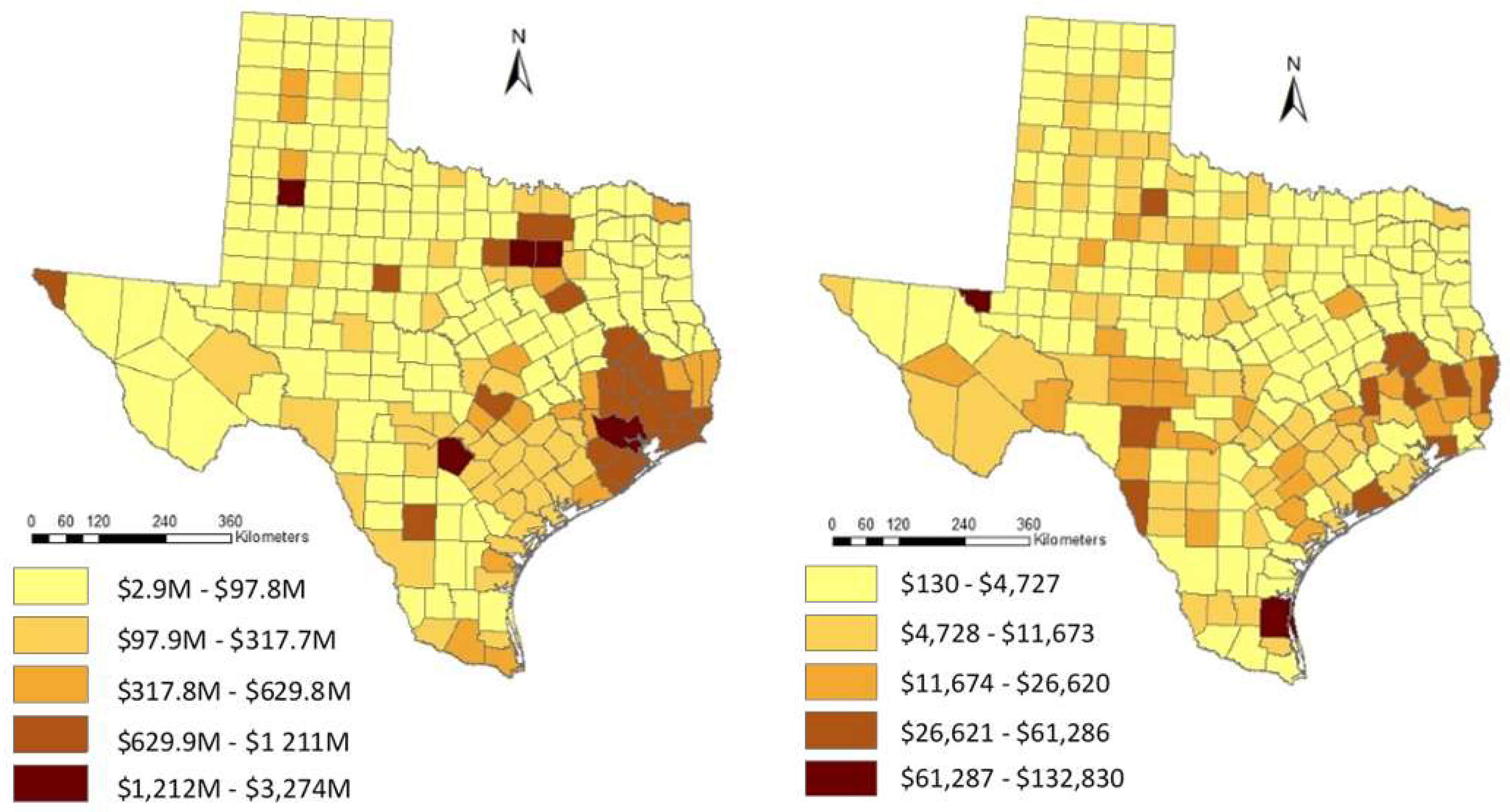
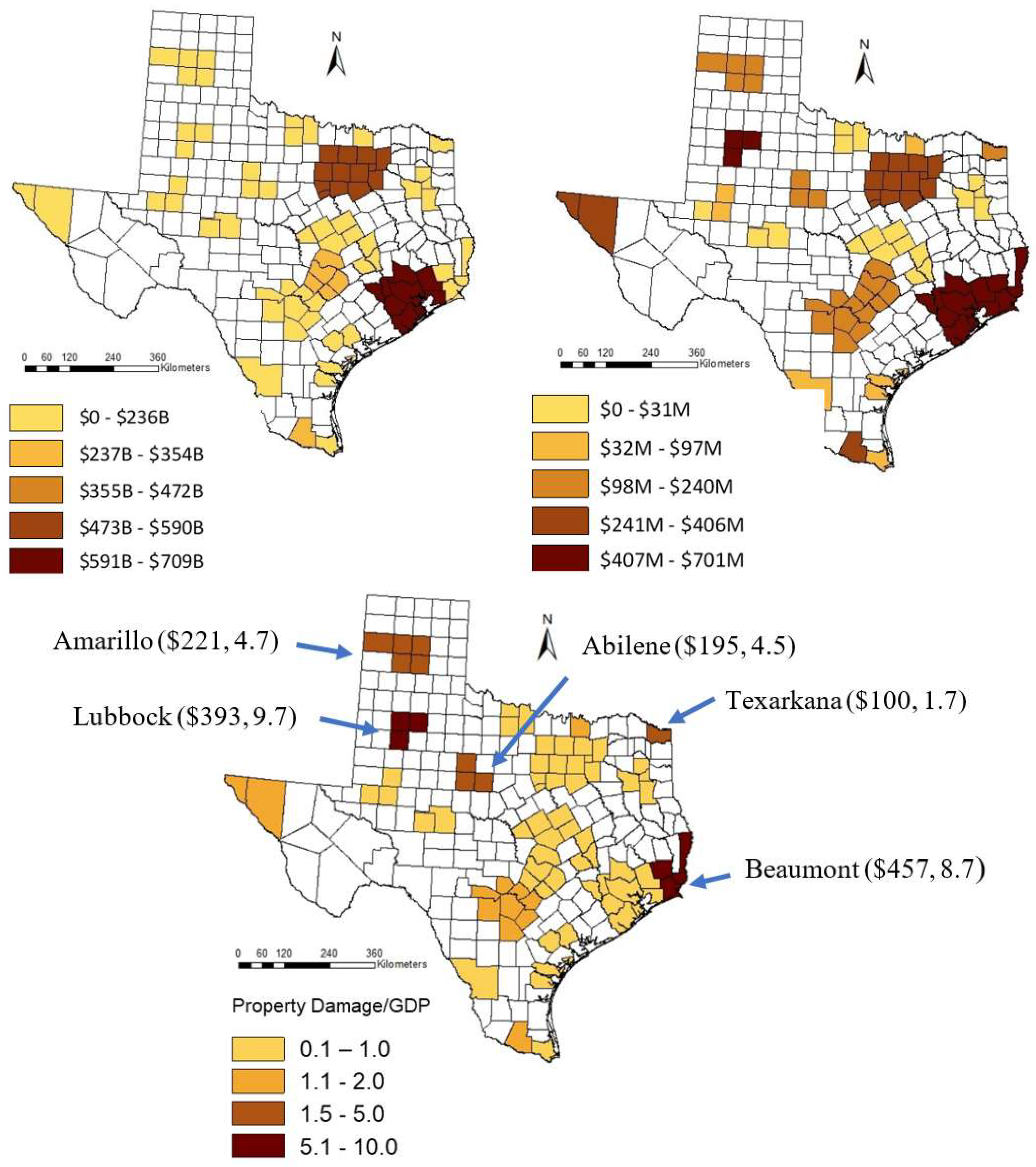
5.3. Regional Normalized Trends and Spatial Distribution of Damage
5.4. Detailed Event Damage
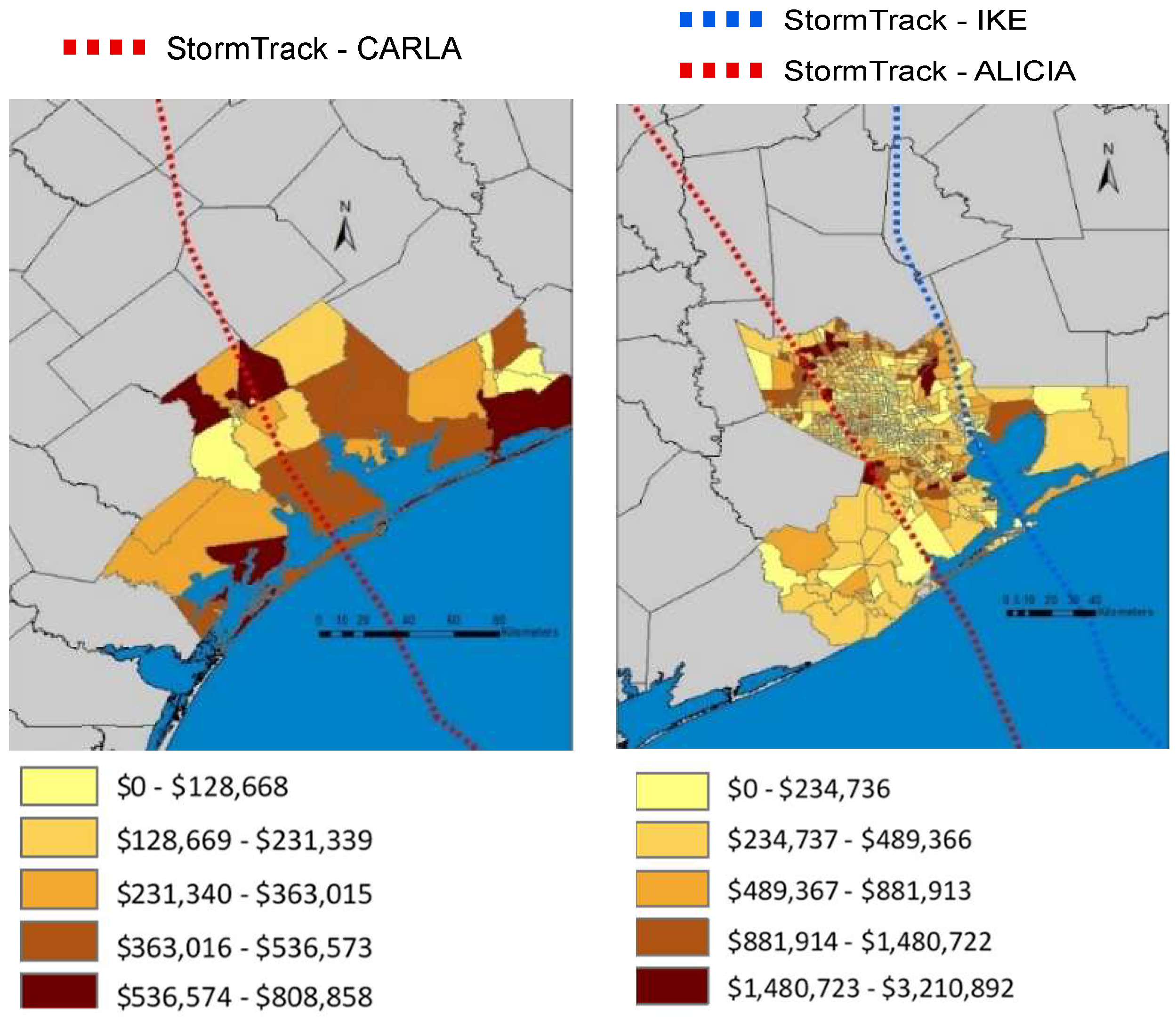
5.4.1. Hurricane Carla (2014 U.S. dollars)
5.4.2. Hurricane Alicia (2014 U.S. dollars)
5.4.3. Hurricane Ike (2014 U.S. dollars)
5.4.4. Variability and Limitations in Damage Estimates
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munich, R. NatCatSERVICE, Natural Catastrophe Know-how for Risk Management and Research. Natural Catastrophe Online Tool. Available online: http://natcatservice.munichre.com/ (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). National Centers for Environmental Information. Storm Events Database 2017. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/billions/overview (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Irfan, U.; Resnick, B. Megadisasters Devastated America in 2017. And They’re Only Going to Get Worse. Storms, Fires, Floods, and Heat Caused at Least $306 Billion in Destruction Last Year. 2018. Available online: https://www.vox.com/energy-and-environment/2017/12/28/16795490/natural-disasters-2017-hurricanes-wildfires-heat-climate-change-cost-deaths (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Gall, M.; Borden, K.A.; Emrich, C.T.; Cutter, S.L. The Unsustainable Trend of Natural Hazard Losses in the United States. Sustainability 2011, 3, 2157–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.; Eichner, J.F.; Faust, E.; Steuer, M. Rising Variability in Thunderstorm-Related U.S. Losses as a Reflection of Changes in Large-Scale Thunderstorm Forcing. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A.; Landsea, C.W. Normalized Hurricane Damage in the United States: 1925–95. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 13, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A.; Gratz, J.; Landsea, C.W.; Collins, D.; Saunders, M.A.; Musulin, R. Normalized Hurricane Damage in the United States: 1900–2005. Nat. Hazards Rev. ASCE 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzbach, P.J.; Bowen, S.G.; Pielke, R.A.; Bell, M. Continental U.S Hurricane Landfall Frequency and Associated Damage, Observations and Future Risks. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Sharif, H.; Crawford, A. Fatalities Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas. Geosciences 2018, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, H.; Jackson, T.; Hossain, M.; Zane, D. Analysis of Flood Fatalities in Texas. Nat. Disasters Rev. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, J.; Hunt, H. Tierra Grande. Housing Markets. Publication 2028. 2013. Available online: https://assets.recenter.tamu.edu/documents/articles/2028.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Potter, L. The Changing Population of Texas and West Texas. In Proceedings of the Cross Roads Healthcare Transformation in West Texas Conference, Lubbock, TX, USA, 5 June 2013; Office of State Demographer: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- CEMHS. Spatial Hazard Events and Losses Database for the United States, Version 16.1; Center for Emergency Management and Homeland Security, Arizona State University: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, P.; Schauer, B. Hazus-Its development and its future. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2006, 7, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, J.; Lin, J.; Skerlj, P.; Twisdale, L.; Huang, K. Hazus-MH hurricane model methodology I: Hurricane hazard, terrain, and wind load modeling.” and “Hazus-MH hurricane model methodology II: Damage and loss estimation. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2006, 7, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Emmanuelle, V.; Ross, C. Multi-Hazard Mapping of the U.S. J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P.; Richardson, H.W.; Davis, B. Transport-related impacts of the Northridge earthquake. J. Transp. Stat. 1998, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Burrus, R.; Dumas, C.F.; Farrell, C.H.; Hall, W.W., Jr. Impact of low-intensity hurricanes on regional economic activity. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2002, 3, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q. Case Study: Economic Losses from a Hypothetical Hurricane Event in the Houston-Galveston Area. ASCE Nat. Hazards Rev. 2011, 12, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrometeorological Hazards. Disaster Risk Reduction. Natural Sciences. United Nations Education, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). Available online: http://www.unesco.org/new/en/natural-sciences/special-themes/disaster-risk-reduction/natural-hazards/hydro-meteorological-hazards/ (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Gautheir, T. Detecting Trends Using Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient. Environ. Forensics 2001, 2, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.T. Statistical Correlation. 2009. Available online: https://explorable.com/statistical-correlation (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Statistics Solutions, Complete Dissertation. Available online: https://www.statisticssolutions.com/kendalls-tau-and-spearmans-rank-correlation-coefficient/ (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Guci, L.; Mead, C.; Panek, S. A Research Agenda for Measuring GDP at the County Level, Bureau of Economic Analysis. 2016. Available online: https://www.bea.gov/system/files/papers/WP2016-4.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Mustapha, K.; Mcheick, H.; Mellouli, S. Modeling and Simulation Agent-Based of Natural Disaster Complex Systems. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Emerging Ubiquitous Systems and Pervasive Networks (EUSPN-2013), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 21–24 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- FV3: Finite-Volume Cubed Sphere Dynamical Core, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL), Princeton University Forrestal Campus. Available online: https://www.gfdl.noaa.gov/fv3/ (accessed on 18 September 2018).
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). U.S. Hazard Multi-hazard Estimation Tool, Hurricane Model; HAZUS-MH 4.0; Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA): Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Weather Service (NWS). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Carla 50th Anniversary, Storm Summary. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/crp/hurricanecarla (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Savage, R.P. National Research Council (NRC), Committee on Natural Disasters, Commission on Engineering and Technical Systems. In Hurricane Alicia: Galveston and Houston, TX, USA, 17–18 August 1983; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Colley, J.; DeBlasio, S.M. Hurricane Ike Impact Report-December 2008; Office of Homeland Security, Division of Emergency Management: Austin, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- International Panel on Climate Change (IPPC). Summary for Policymakers of IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C Approved by Government. 2018. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/news_and_events/pr_181008_P48_spm.shtml (accessed on 8 October 2018).
| Disaster Type | TX ($2016) | US ($2016) |
|---|---|---|
| Hurricane/Trop Strm | 18,325,926,908 | 258,877,397,419 |
| Hail | 12,301,331,729 | 37,295,600,013 |
| Flooding | 7,035,494,246 | 152,447,938,320 |
| Severe /TStrm | 6,298,129,432 | 35,434,257,137 |
| Tornado | 4,103,255,471 | 58,871,799,205 |
| Wind | 2,095,538,316 | 33,335,423,825 |
| Drought | 1,454,769,396 | 5,121,265,940 |
| Coastal | 940,709,789 | 2,955,956,179 |
| Winter Weather | 795,182,868 | 26,391,427,257 |
| Wildfire | 692,696,316 | 22,497,632,949 |
| Lightning | 159,383,681 | 3,101,409,332 |
| Fog | 6,885,490 | 58,142,521 |
| Heat | 1,794,114 | 504,346,195 |
| Landslide | 179,521 | 18,864,695,667 |
| Avalanche | 1,064 | 30,299,599 |
| Grand Total | 54,211,278,340 | 655,787,591,561 |
| 16-year Average | 16-year Annual Trend | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSA—Actual/GDP | Adj PD/Capita | Act PD/GDP | Spearman | p | Kendall | p |
| Dallas-Fort Worth-Arlington | $48.12 | 0.706 | 0.8176 | 0.0001 | 0.6500 | 0.0004 |
| Lubbock | $393.40 | 9.672 | 0.4853 | 0.0567 | 0.3667 | 0.0476 |
| Texarkana | $100.05 | 1.732 | 0.2796 | 0.2942 | 0.1757 | 0.3439 |
| McAllen-Edinburg-Mission | $27.87 | 1.262 | 0.2264 | 0.4364 | 0.1868 | 0.3520 |
| Tyler | $1.90 | 0.030 | 0.1319 | 0.6676 | 0.1026 | 0.6255 |
| El Paso | $57.66 | 1.741 | 0.0682 | 0.8020 | 0.0342 | 0.8558 |
| Austin-Round Rock | $43.82 | 0.727 | 0.0643 | 0.8199 | 0.0476 | 0.8046 |
| Corpus Christi | $25.53 | 0.583 | 0.0440 | 0.8866 | 0.0769 | 0.7143 |
| Killeen-Temple | $4.51 | 0.106 | 0.0382 | 0.8882 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Sherman-Denison | $39.40 | 1.212 | 0.0382 | 0.8882 | −0.0167 | 0.9283 |
| Longview | $10.99 | 0.229 | 0.0059 | 0.9827 | 0.0084 | 0.9640 |
| Laredo | $16.25 | 0.527 | −0.0604 | 0.8445 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| San Angelo | $36.72 | 0.882 | −0.1273 | 0.7092 | −0.0909 | 0.6971 |
| Waco | $5.13 | 0.122 | −0.1471 | 0.5868 | −0.1167 | 0.5285 |
| Brownsville-Harlingen | $16.00 | 0.712 | −0.1729 | 0.5377 | −0.1409 | 0.4788 |
| San Antonio-New Braunfels | $44.83 | 0.956 | −0.2341 | 0.4010 | −0.2297 | 0.2344 |
| Amarillo | $221.04 | 4.698 | −0.2357 | 0.3977 | −0.1619 | 0.4002 |
| Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land | $69.44 | 1.034 | −0.2634 | 0.3242 | −0.1925 | 0.2999 |
| Odessa | $5.41 | 0.117 | −0.2813 | 0.2912 | −0.2017 | 0.2789 |
| Victoria | $2.32 | 0.055 | −0.3091 | 0.3848 | −0.3333 | 0.1797 |
| Beaumont-Port Arthur | $457.18 | 8.690 | −0.3176 | 0.2306 | −0.2667 | 0.1497 |
| College Station-Bryan, | $6.04 | 0.168 | −0.3370 | 0.2018 | −0.2427 | 0.1912 |
| Abilene | $194.88 | 4.499 | −0.3626 | 0.2026 | −0.2527 | 0.2080 |
| Wichita Falls | $14.09 | 0.261 | −0.4059 | 0.1188 | −0.2833 | 0.1258 |
| Midland | $91.18 | 0.693 | −0.4794 | 0.0706 | −0.3942 | 0.0420 |
| Disaster Event Name | Hurricane Carla | Hurricane Alicia | Hurricane Ike |
|---|---|---|---|
| Month/Days | September 8–14 | August 15–21 | September 11–12 |
| Saffir-Simpson Classification | Cat-5 | Cat-3 | Cat-2 |
| Year | 1961 | 1983 | 2008 |
| Landfall | Port O’Connor, Tx | Galveston, Tx | |
| Primary Cause of Damage | Wind/Storm Surge | Wind/Tornadoes | Flooding |
| Texas Almanac (total damage) | $2.4 billion | $7.2 billion | $15.6 billion |
| NWS/NOAA (total damage) | NA | $7.3 billion | $33.4 billion |
| SHELDUS (property damage) | $204.4 million | $1.23 billion | $3.8 billion |
| SHELDUS (crop damage) | $204.4 million | $1.23 billion | NA |
| HAZUS model counties | Aransas, Calhoun, Jackson, Matagorda, Refugio, Victoria | Brazoria, Chambers, Galveston, Harris | |
| Counties population (2010) | 189,492 | 4,732,030 | |
| Hazus model (2010 building exposure) | $20.9 billion (80% wood residential) | $529 billion (80% wood residential) | |
| Hazus model (property damage) | $689 million | $10.3 billion | $6.63 billion |
| Hazus model (business interruption) | $119 million | $1.23 billion | $697 million |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, S.H.; Sharif, H.O. Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016. Geosciences 2018, 8, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8100384
Paul SH, Sharif HO. Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016. Geosciences. 2018; 8(10):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8100384
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Srikanto H., and Hatim O. Sharif. 2018. "Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016" Geosciences 8, no. 10: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8100384
APA StylePaul, S. H., & Sharif, H. O. (2018). Analysis of Damage Caused by Hydrometeorological Disasters in Texas, 1960–2016. Geosciences, 8(10), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8100384






