Gravity Rate of Change Due to Slow Tectonics: Insights from Numerical Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Two-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling
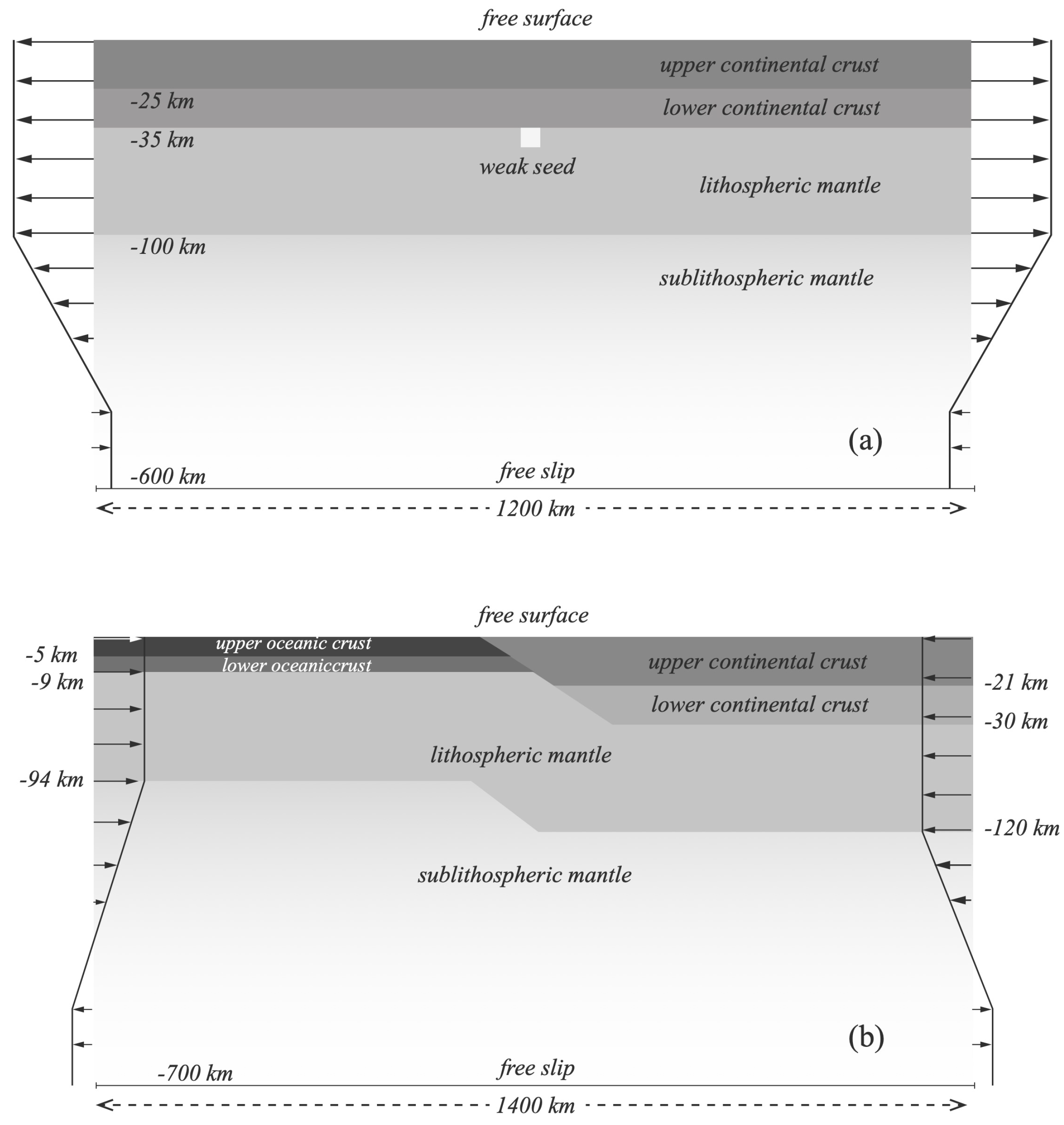
2.1.1. Model Setup—Rifting
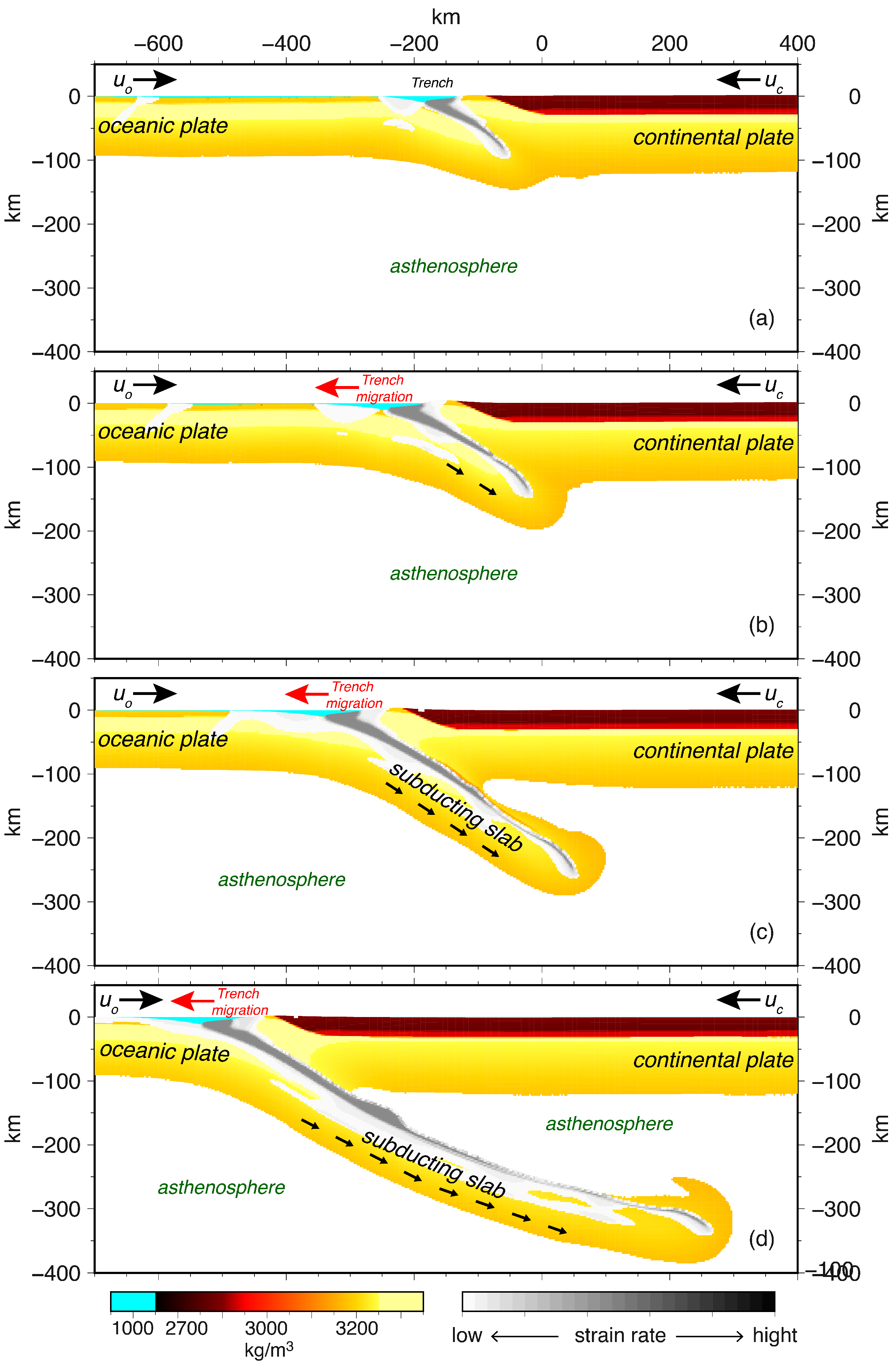
2.1.2. Model Setup—Subduction
| Diffusion Creep df | Dislocation Creep ds | Plasticity | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Exponential Factor | Activation Energy | Activation Volume | Grain Size Exponent | Grain Size | Pre-Exponential Factor | Activation Energy | Activation Volume | Stress Exponent | Friction Angle | Cohesion | |||
| Adf | Qdf | Vdf | m | d | Ads | Qds | Vds | nds | ϕ | c | |||
| Layer | Flow Law | (10−17 Pa/s) | (103 J/mol) | (10−6 m3/mol) | - | (10−3 mm) | (10−17 Pa/s) | (103 J/mol) | (10−6 m3/mol) | - | (°) | (MPa) | |
| Sediments | Wet Quartzite 1,2 | - | - | - | - | - | 8.57 × 10−11 | 223 | 0.0 | 4.0 | |||
| Upper Continental Crust | Wet Quartzite 1,2 | - | - | - | - | - | 8.57 × 10−11 | 223 | 0.0 | 4.0 | |||
| Lower Continental Crust | rm | Columbia Diabase 3 | 6.08 × 10−2 | 300 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 1.19 × 10−9 | 485 | 0.0 | 4.7 | ||
| sm | Wet Anorthite 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.713 | 345 | 0.0 | 3.0 | |||
| Upper Oceanic Crust | rm | Microgabbro 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.99 × 106 | 497 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 5–25 | 4–20 |
| sm | Antigorite 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.39 × 10−20 | 89 | 3.2 | 3.8 | |||
| Lower Oceanic Crust | rm | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| sm | Microgabbro 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.99 × 106 | 497 | 0.0 | 3.4 | |||
| Lithospheric Mantle | rm | Dry Dunite 6 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.12 × 10−4 | 535 | 0.0 | 3.6 | ||
| sm | Dry Olivine 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 65.2 | 530 | 18 | 3.5 | |||
| Asthenospheric Mantle | rm | Dry Dunite 6 | 2.5 | 375 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 1.12 × 10−4 | 535 | 0.0 | 3.6 | ||
| sm | Dry Olivine 1 | 237 | 375 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 65.2 | 530 | 18 | 3.5 | |||
| Serpentine | Antigorite 5 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.39 × 10−20 | 89 | 3.2 | 3.8 | |||
| Melt | rm | Dry Dunite 6 | 2.5 | 375 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 1.12 × 10−4 | 535 | 0.0 | 3.6 | ||
| sm | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
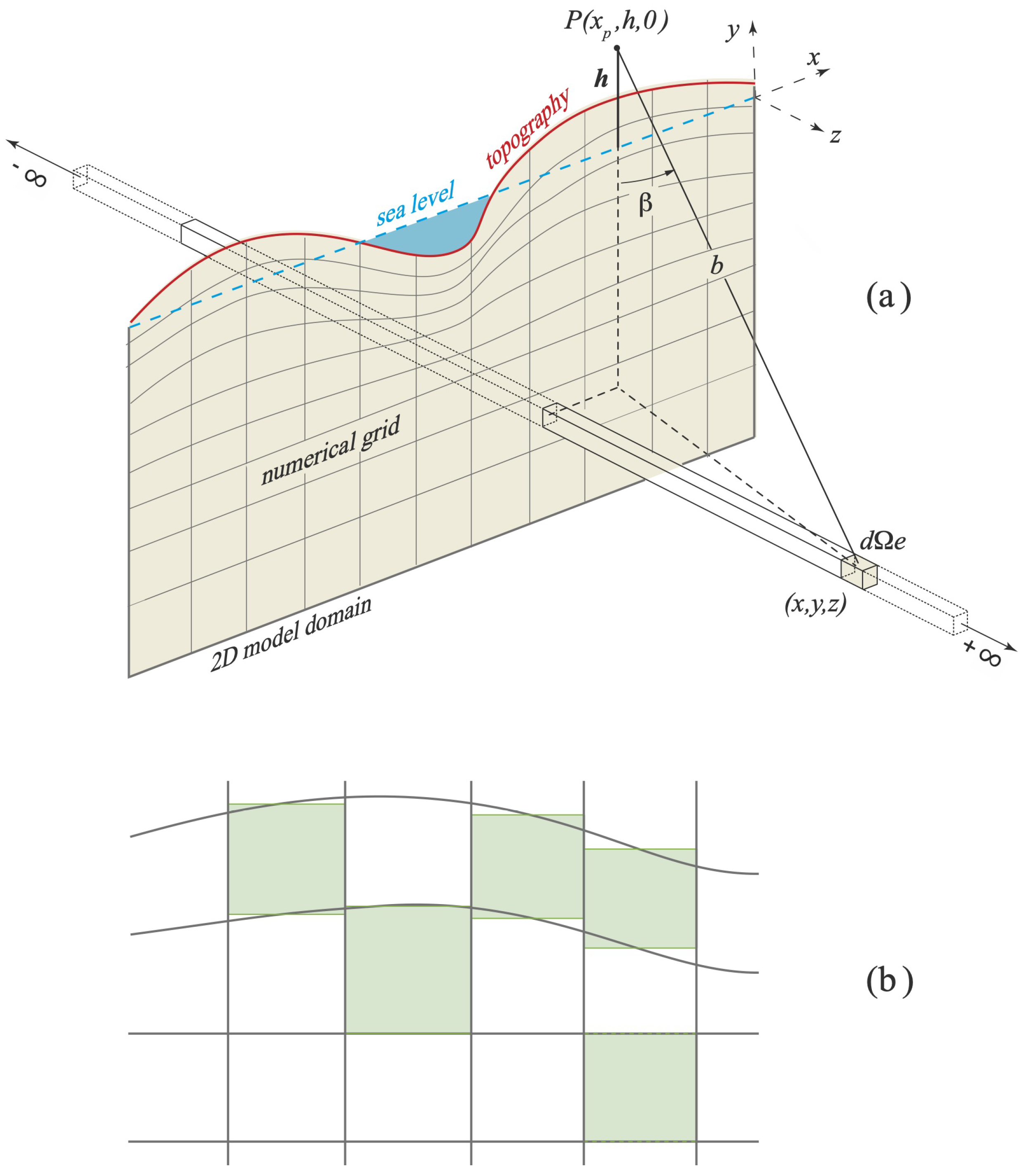
2.2. Gravity Model
3. Model Results
- The pattern and magnitude of the modeled gravity rate of change and the contributions from deep-seated masses and dynamic topography.
- The correlation between the gravity rate of change and the density rate of change.
- How the gravity rate of change varies with the velocity prescribed at the edges.
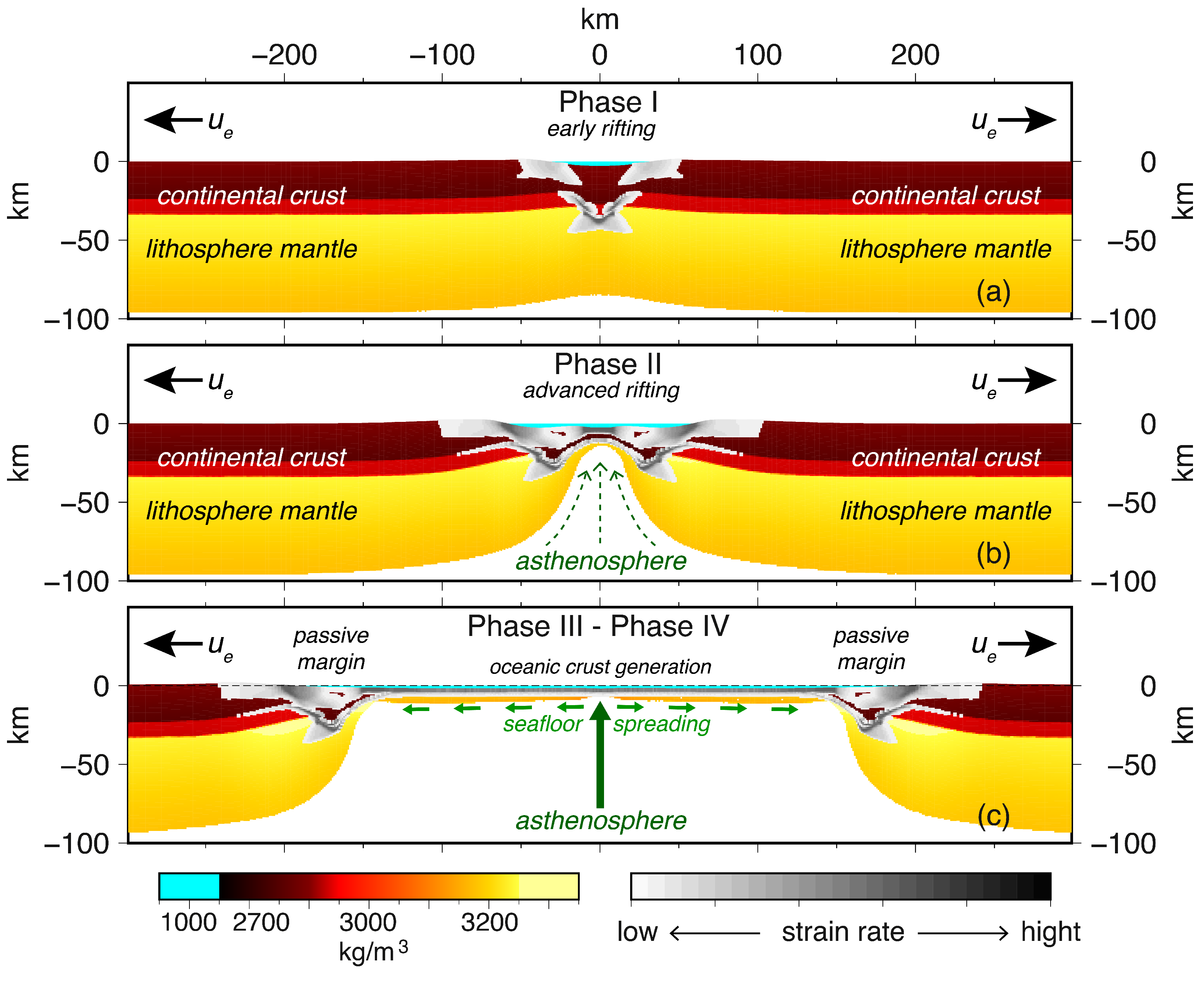
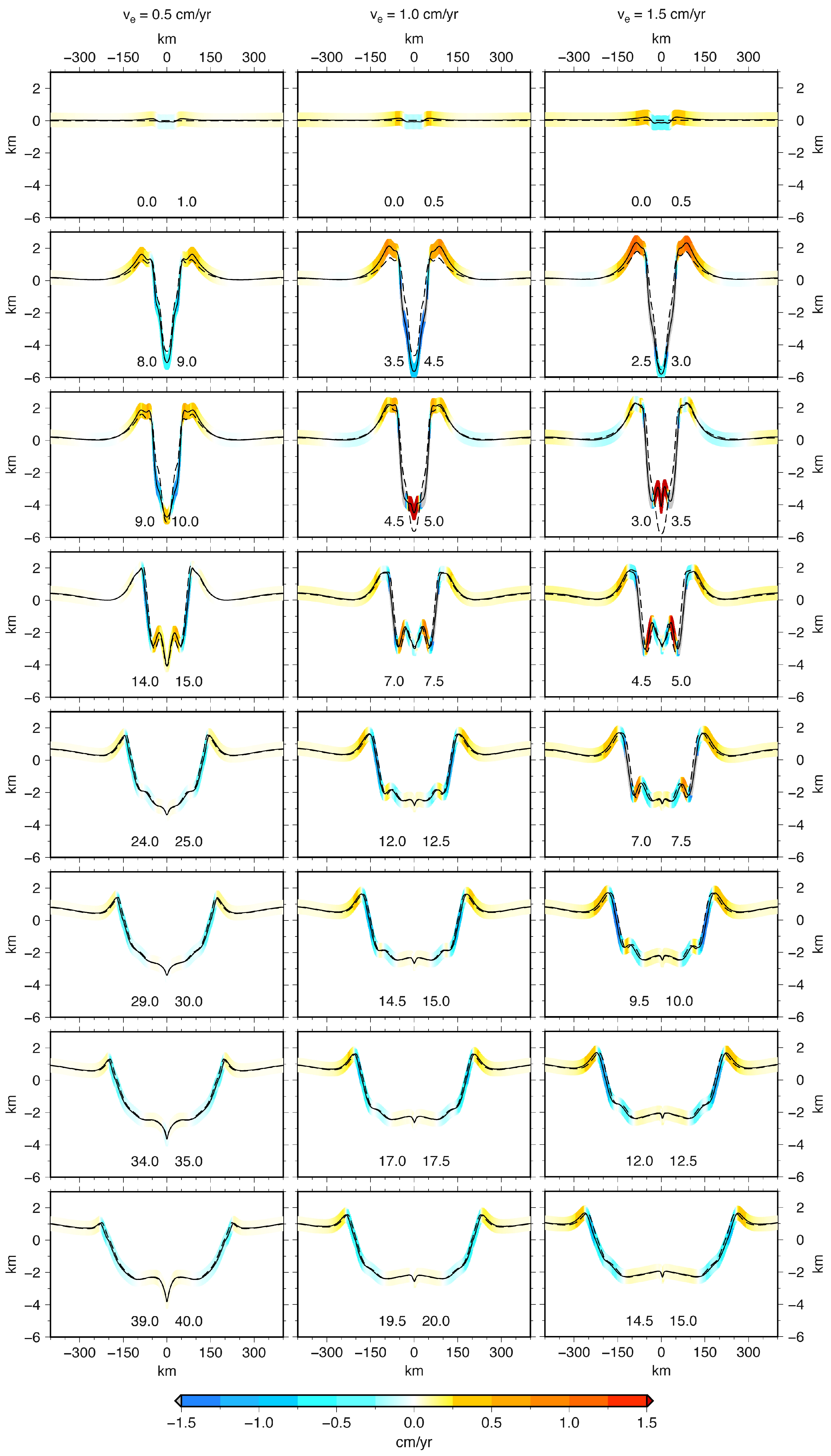
3.1. Rifting
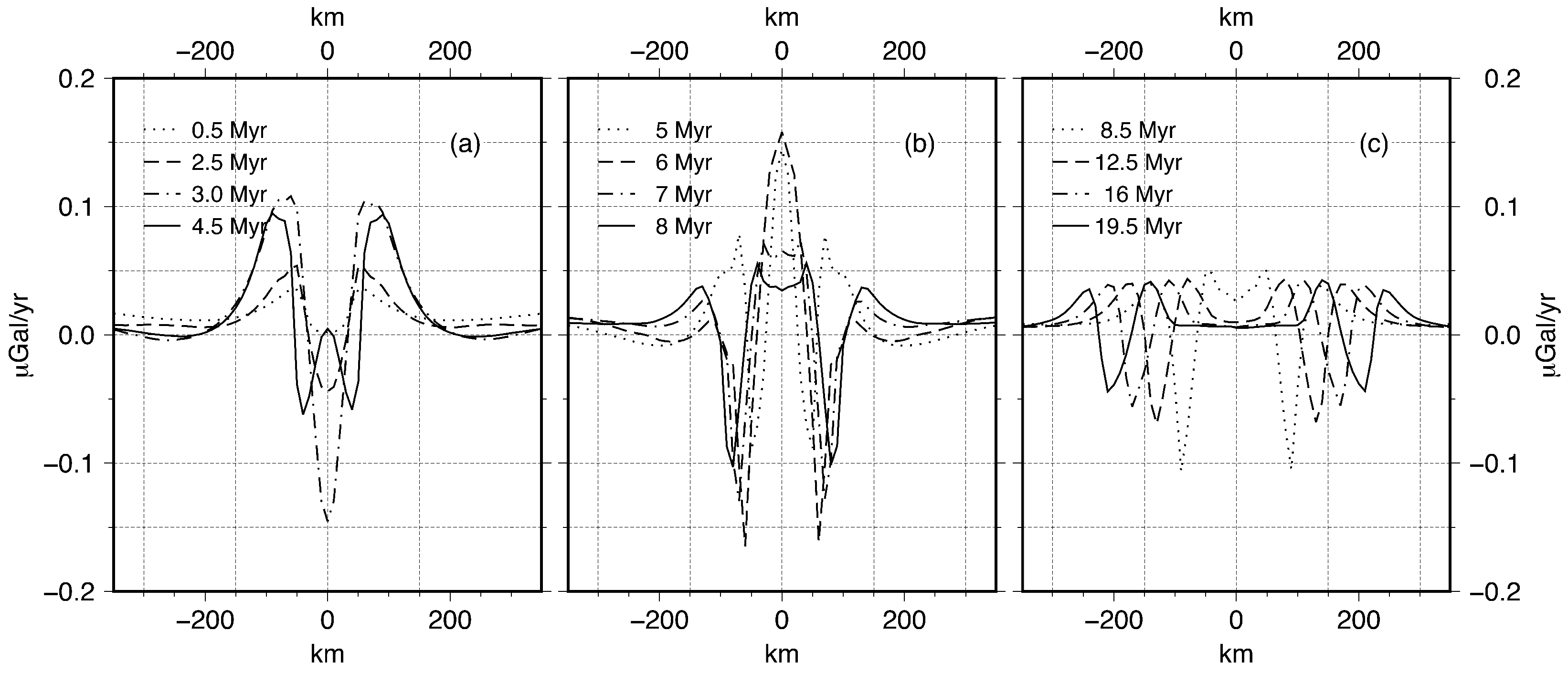
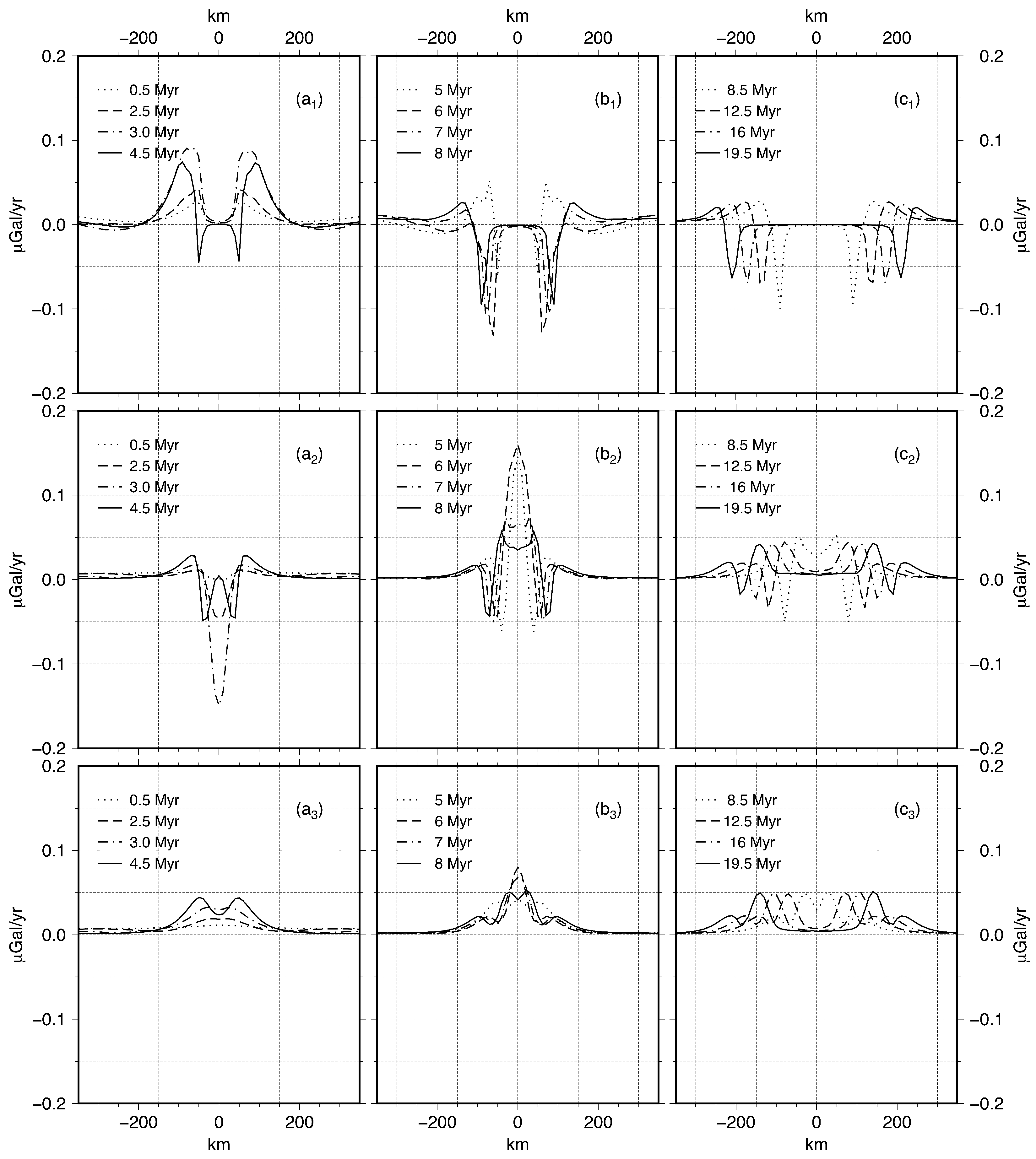
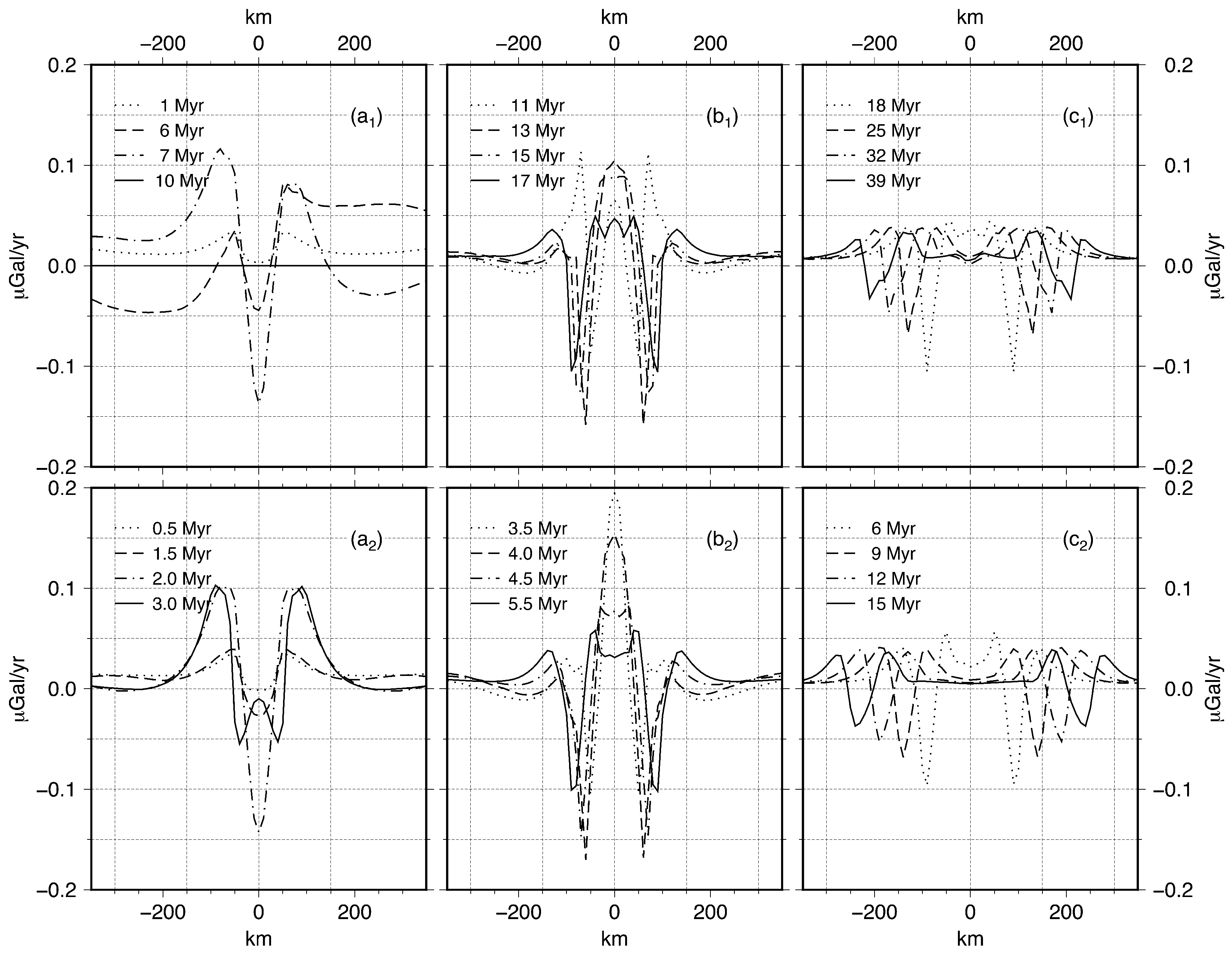
3.1.1. Modeled Gravity Rate of Change
3.1.2. Gravity Rate of Change vs. Density Rate of Change
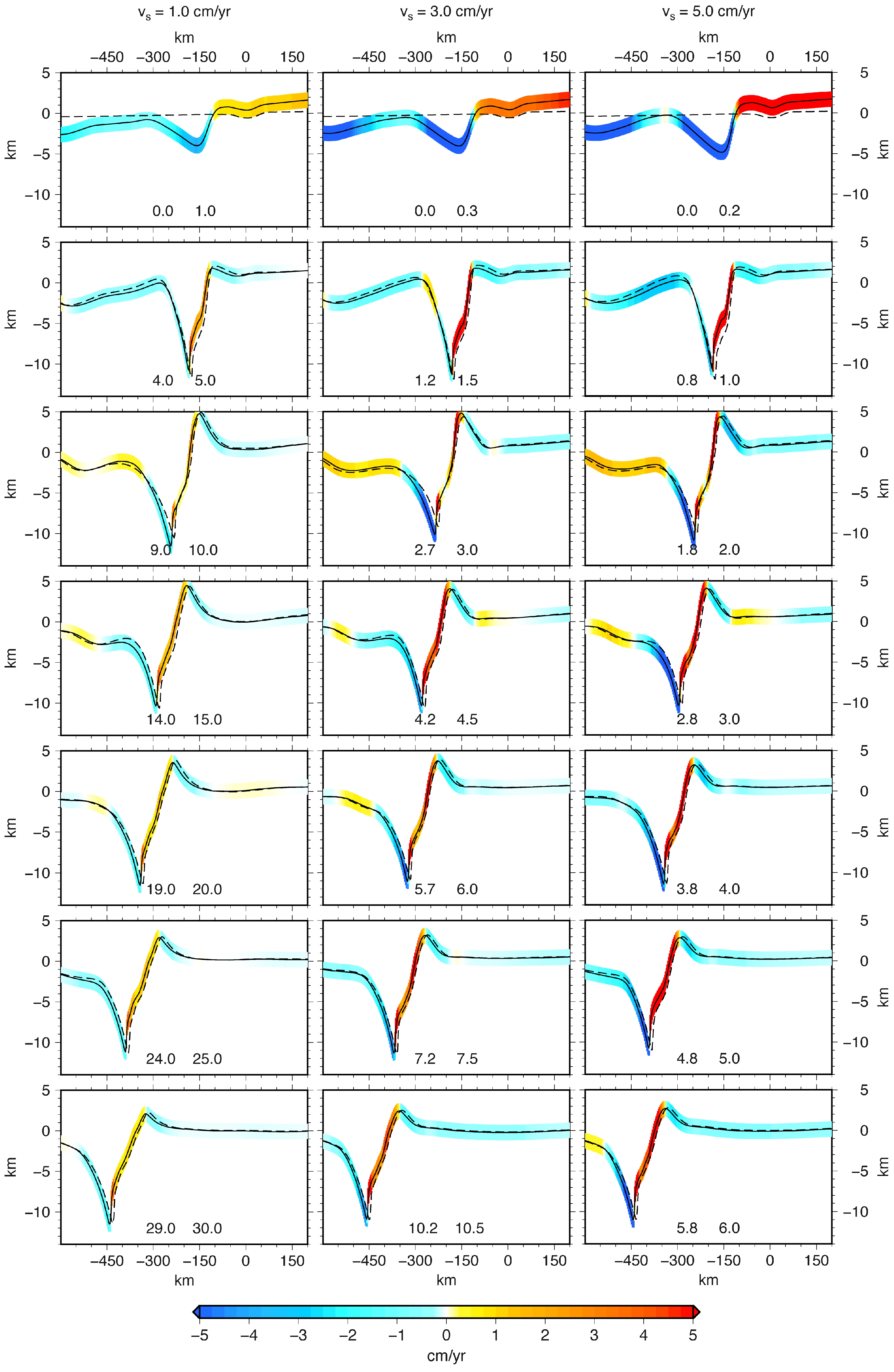
3.1.3. Gravity Rate of Change vs. Extensional Velocity Prescribed at the Edges
3.1.4. Topography
3.2. Subduction
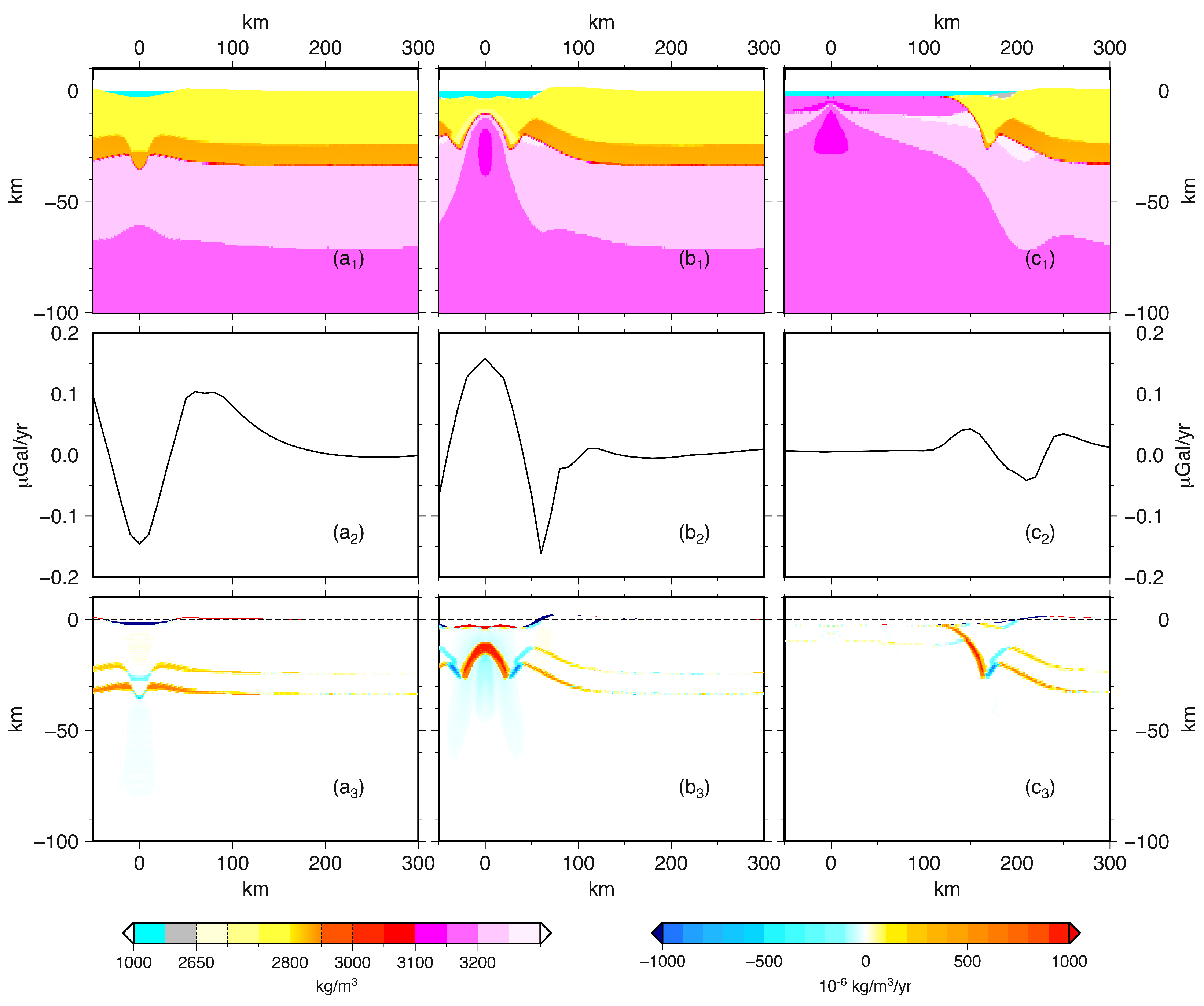
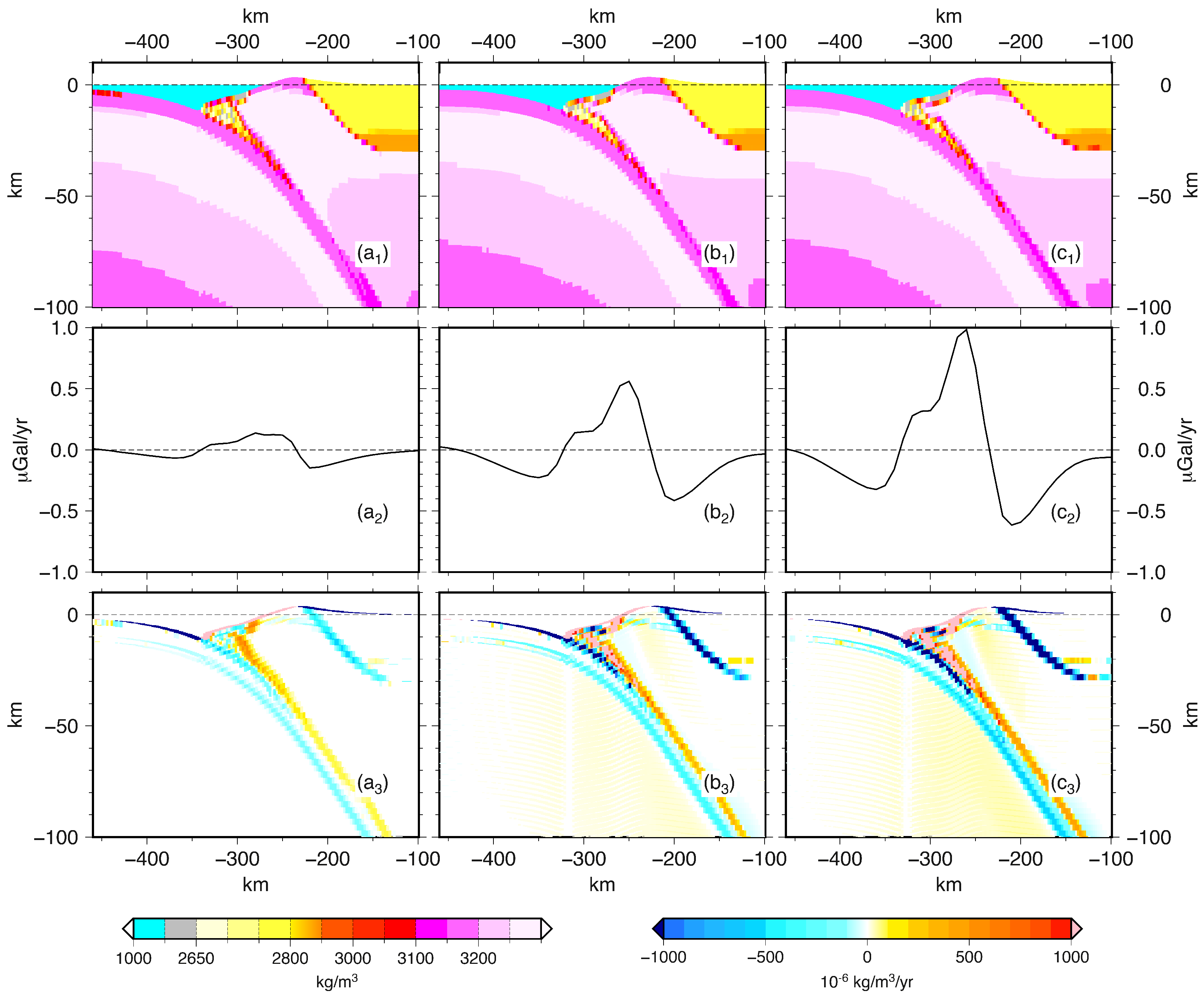
3.2.1. Modeled Gravity Rate of Change
3.2.2. Gravity Rate of Change vs. Density Rate of Change
3.2.3. Topography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIA | Glacial Isostatic Adjustment |
| GOCE | Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer |
| GRACE | Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment |
| GRACE-FO | GRACE Follow-On |
| MAGIC | Mass Change and Geophysics International Constellation |
| PGR | Post-Glacial Rebound |
References
- Matsuo, K.; Heki, K. Coseismic gravity changes of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake from satellite gravimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L00G12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Seismologic applications of GRACE time-variable gravity measurements. Earthq. Sci. 2014, 27, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cambiotti, G.; Sun, W.; Sabadini, R. Co-seismic slip distribution of the 2011 Tohoku (MW 9.0) earthquake inverted from GPS and space-borne gravimetric data. Earth Planet. Phys. 2018, 2, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiotti, G. Joint estimate of the coseismic 2011 Tohoku earthquake fault slip and post-seismic viscoelastic relaxation by GRACE data inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 220, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiotti, G.; Douch, C.; Cesare, S.; Haagmans, R.; Sneeuw, N.; Anselmi, A.; AM, M.; Sabadini, R. On Earthquake Detectability by the Next-Generation Gravity Mission. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 1049–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.C.; Sauber, J.; Broerse, T.; Pollitz, F.; Okal, E.; Jeon, T.; Seo, K.-W.; Stanaway, R. GRACE and GRACE Follow-on gravity observations of intermediate-depth earthquakes contrasted with those of shallow events. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2024, 129, e2023JB028362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, P.A.; Milne, G.; Scherneck, H.G.; Ågren, J. The relation between gravity rate of change and vertical displacement in previously glaciated areas. J. Geodyn. 2015, 83, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olsson, P.A.; Breili, K.; Ophaug, V.; Steffen, H.; Bilker-Koivula, M.; Nielsen, E.; Oja, T.; Timmen, L. Postglacial gravity change in Fennoscandia—three decades of repeated absolute gravity observations. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 217, 1141–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałdyn, F.; Sośnica, K.; Zajdel, R.; Meyer, U.; Jäggi, A. Long-term ice mass changes in Greenland and Antarctica derived from satellite laser ranging. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.B.; Creveling, J.R.; Mitrovica, J.X. The sensitivity of tectonic uplift corrections to the penultimate deglacial ice volume and configuration. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2025, 353, 109210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Sasgen, I.; Bevis, M.; Van Dam, T.; Bamber, J.L.; WahR, J.; Willis, M.; Kjær, K.H.; Wouters, B.; Helm, V.; et al. Geodetic measurements reveal similarities between post–Last Glacial Maximum and present-day mass loss from the Greenland ice sheet. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancinelli, P.; Ranalli, G.; Pauselli, C. Non-Linear Effects of Gravity Change on Mantle Dynamics. Geosciences 2024, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Denis, C.; Varga, T. Tidal friction and its consequences in palaeogeodesy, in the gravity field variations and in tectonics. J. Geodyn. 1998, 25, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P. Temporal variation of geodynamical properties due to tidal friction. J. Geodyn. 2006, 41, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard, Y.; Fleitout, L.; Froidevaux, C. Geoid heights and lithospheric stresses for a dynamic Earth. Ann. Geophys. 1984, 2, 267–286. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, M.A.; Hager, B.H. Geoid anomalies in a dynamic Earth. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 5987–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Gurnis, M. Viscous flow model of a subduction zone with a faulted lithosphere: Long and short wavelength topography, gravity and geoid. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.M.; Spelta, E.; Rizzetto, C. Gravity signature of crustal subduction inferred from numerical modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 166, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, D.; Watts, A. Gravity anomalies, crustal structure, and seismicity at subduction zones: 1. Seafloor roughness and subducting relief. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2015, 16, 1508–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhong, S. The long-wavelength geoid from three-dimensional spherical models of thermal and thermochemical mantle convection. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 4572–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhong, S. Constraints on mantle viscosity from intermediate-wavelength geoid anomalies in mantle convection models with plate motion history. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.M.; Barzaghi, R.; Bollino, A.; Regorda, A.; Sabadini, R. The gravitational signature of the dynamics of oceanization in the Gulf of Aden. Tectonophysics 2023, 869, 230110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.M.; Restelli, F.; Bollino, A.; Regorda, A.; Sabadini, R. The static and time-dependent signature of ocean–continent and ocean–ocean subduction: The case studies of Sumatra and Mariana subductions. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 788–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushurst, G.; Mahatsente, R. Lithospheric Structure of the Central Andes Forearc from Gravity Data Modeling: Implication for Plate Coupling. Lithosphere 2020, 2020, 8843640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gurnis, M. Dynamic topography, gravity and the role of lateral viscosity variations from inversion of global mantle flow. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 207, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer Mission—GOCE. Report of European Space Agency for Mission Selection; The 4th Candidate Earth Explorer Core Missions, SP-1233; Technical Report; ESA: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, R.; Gruber, T. Gravity and steady-state ocean circulation explorer GOCE. In System Earth via Geodetic-Geophysical Space Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.C.; Thompson, P.F.; Watkins, M.M. GRACE measurements of mass variability in the Earth system. Science 2004, 305, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The gravity recovery and climate experiment: Mission overview and early results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L09607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regorda, A.; Thieulot, C.; van Zelst, I.; Erdos, Z.; Maia, J.; Buiter, S. Rifting Venus: Insights from numerical modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2023, 128, e2022JE007588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regorda, A.; Roda, M. Thermo-Mechanical Effects of Microcontinent Collision on Ocean-Continent Subduction System. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2024, 129, e2024JB029908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donea, J.; Huerta, A.; Ponthot, J.P.; Rodríguez-Ferran, A. Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian Methods. In Encyclopedia of Computational Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Chapter 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Fischer, T.P.; Muirhead, J.D.; Ebinger, C.J.; Kattenhorn, S.A.; Sharp, Z.D.; Kianji, G.; Takahata, N.; Sano, Y. Incipient rifting accompanied by the release of subcontinental lithospheric mantle volatiles in the Magadi and Natron basin, East Africa. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 346, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellart, W.P.; Stegman, D.R.; Freeman, J. Global trench migration velocities and slab migration induced upper mantle volume fluxes: Constraints to find an Earth reference frame based on minimizing viscous dissipation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 88, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naliboff, J.; Buiter, S.J.H. Rift reactivation and migration during multiphase extension. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 421, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, G.C.; Tullis, J. A flow law for dislocation creep of quartz aggregates determined with the molten salt cell. Tectonophysics 1995, 247, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackwell, S.J.; Zimmerman, M.E.; Kohlstedt, D.L. High-temperature deformation of dry diabase with application to tectonics on Venus. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, K.R.; Carter, N.L. Rheology of some continental lower crustal rocks. Tectonophysics 1990, 182, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.D.; Schiffer, C. Wilson cycle passive margins: Control of orogenic inheritance on continental breakup. Gondwana Res. 2016, 39, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, P.N.; Paterson, M.S. The experimental deformation of dunite. Tectonophysics 1981, 78, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, D.L.; Schubert, G. Geodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bollino, A.; Regorda, A.; Sabadini, R.; Marotta, A. From rifting to oceanization in the Gulf of Aden: Insights from 2D numerical models. Tectonophysics 2022, 838, 229483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.H.; Koczynski, T.A.; Hutchins, D.G. Evidence for incipient rifting in southern Africa. Geophys. J. Int. 1976, 44, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Kolawole, F.; Williams, J. Evolution of rift faulting in incipient, magma-poor divergent plate boundaries: New insights from the Okavango-Makgadikgadi Rift Zone, Botswana. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2024, 646, 118957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, D. Seismicity supports the theory of incipient rifting in the western Ionian sea, central Mediterranean. Ann. Geophys. 2020, 63, SE225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F.; Scharroo, R.; Luis, J.F.; Wobbe, F. Generic Mapping Tools: Improved version released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Initial Thickness | Density | Heat Capacity | Conductivity | Thermal Expansion | Radiogenic Heat Production | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | ρ | Cp | K | α | H | ||
| Layer | (km) | (kg/m3) | (K m2/s2) | (W/m/K) | (10−5/K) | (10−6 μW/m2) | |
| Sediments | - | 2650 | 800 | 2.5 | 3.28 | 1.3 | |
| Upper Continental Crust | rm | 25 | 2800 | 800 | 2.5 | 3.28 | 1.3 |
| sm | 21 | ||||||
| Lower Continental Crust | rm | 10 | 2950 | 800 | 2.5 | 3.28 | 1.3 |
| sm | 7 | ||||||
| Upper Oceanic Crust | rm | - | 3200 | 800 | 2.6 | 3.28 | 1.3 |
| sm | 5 | 1.8 | 0.2 | ||||
| Lower Oceanic Crust | rm | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| sm | 4 | 3200 | 800 | 2.6 | 3.28 | 0.2 | |
| Lithospheric Mantle | rm | 65–90 | 3300 * | 1250 | 2.25 | 3.0 | 0.0 |
| sm | 81–90 | ||||||
| Asthenospheric Mantle | rm | 580–606 | 3300 * | 1250 | 2.25 | 3.0 | 0.0 |
| sm | 500–610 | ||||||
| Serpentine | - | 3000 | 1250 | 2.25 | 3.0 | 0.0 | |
| Melt | - | 2900 | 1250 | 2.25 | 3.0 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marotta, A.M.; Fedeli, V.; Regorda, A.; Sabadini, R. Gravity Rate of Change Due to Slow Tectonics: Insights from Numerical Modeling. Geosciences 2025, 15, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090359
Marotta AM, Fedeli V, Regorda A, Sabadini R. Gravity Rate of Change Due to Slow Tectonics: Insights from Numerical Modeling. Geosciences. 2025; 15(9):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090359
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarotta, Anna Maria, Valeria Fedeli, Alessandro Regorda, and Roberto Sabadini. 2025. "Gravity Rate of Change Due to Slow Tectonics: Insights from Numerical Modeling" Geosciences 15, no. 9: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090359
APA StyleMarotta, A. M., Fedeli, V., Regorda, A., & Sabadini, R. (2025). Gravity Rate of Change Due to Slow Tectonics: Insights from Numerical Modeling. Geosciences, 15(9), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15090359






