Isotopes in Archeology: Perspectives on Post-Mortem Alteration and Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
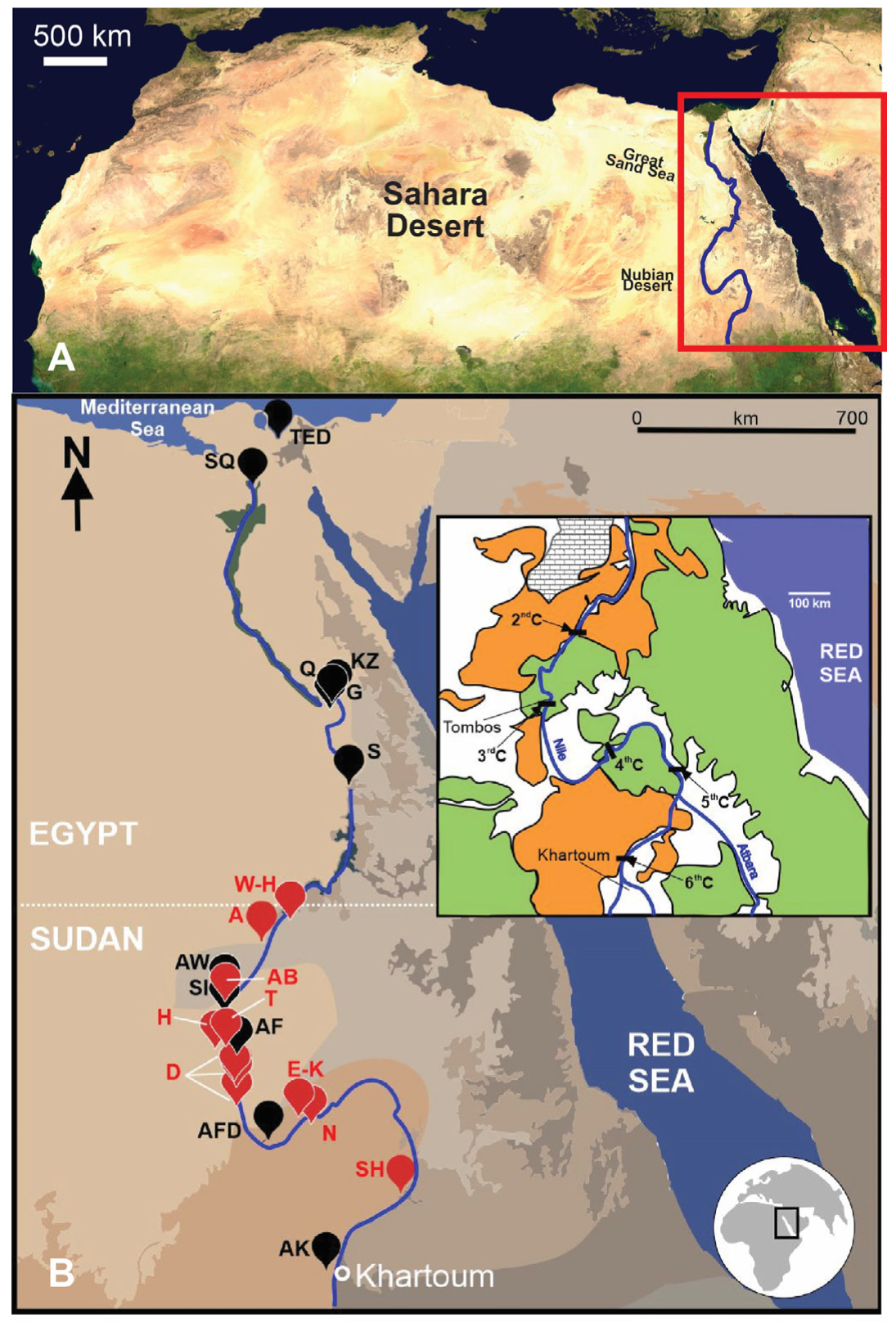
2. Samples and Methods
2.1. Tooth Enamel Preparation and Chemical Procedures
2.2. Multi-Collection Mass Spectrometry
3. Post-Mortem Alteration—Methods of Evaluation
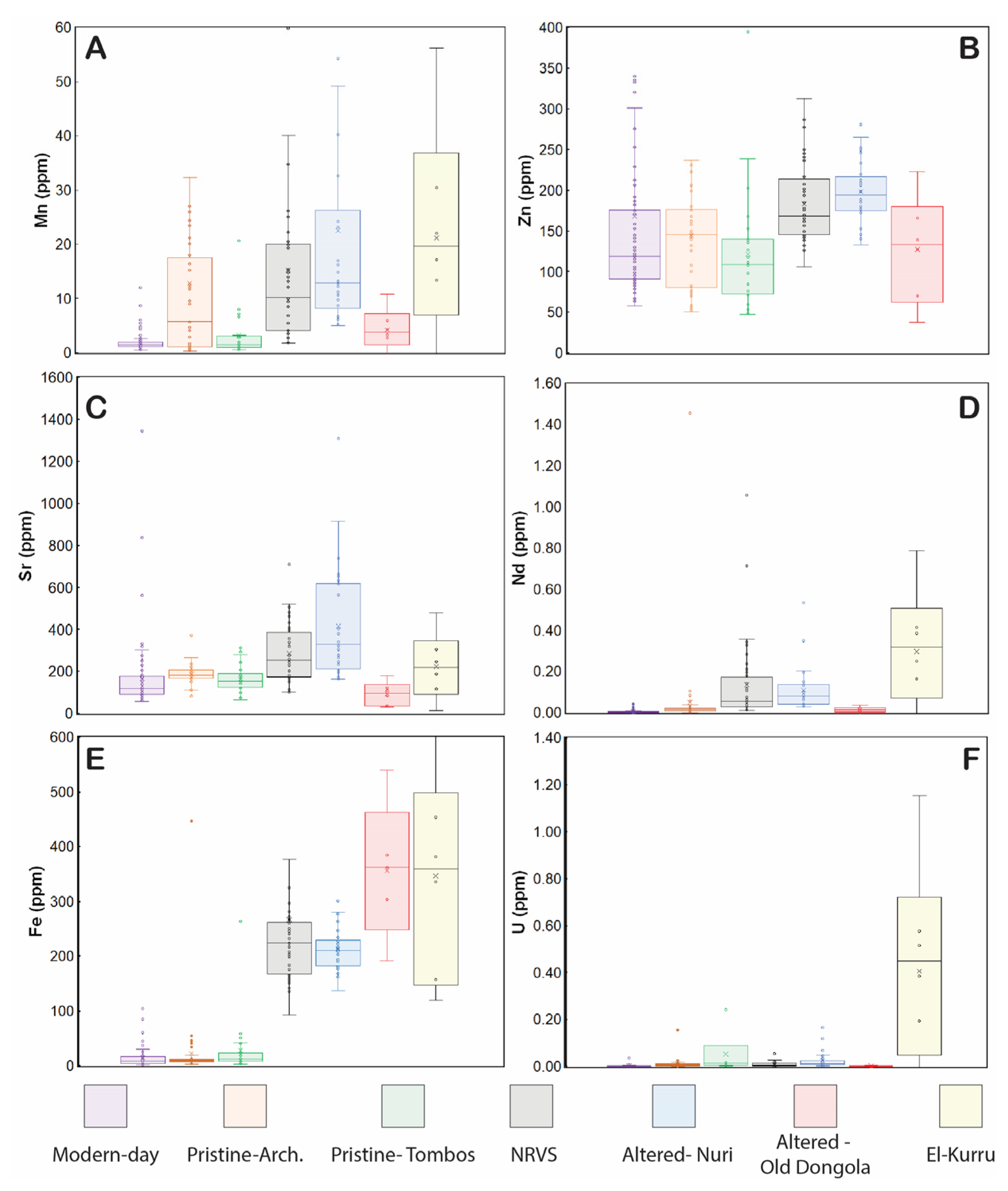
3.1. Box and Whisker (BW) Plot
3.2. Iron Contents as Diagenetic Indicator
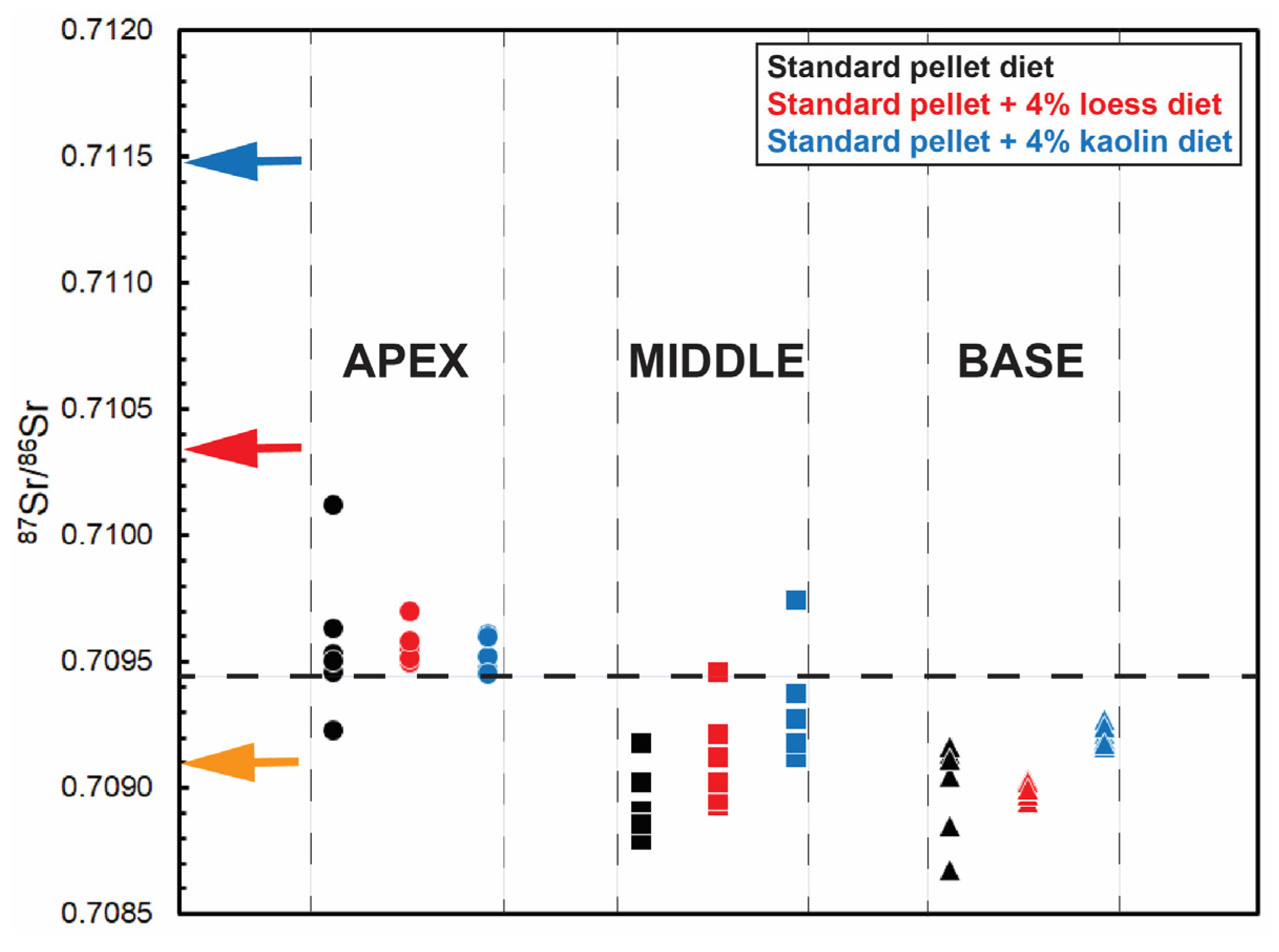
3.3. Maximum Threshold Concentration (MTC) Values
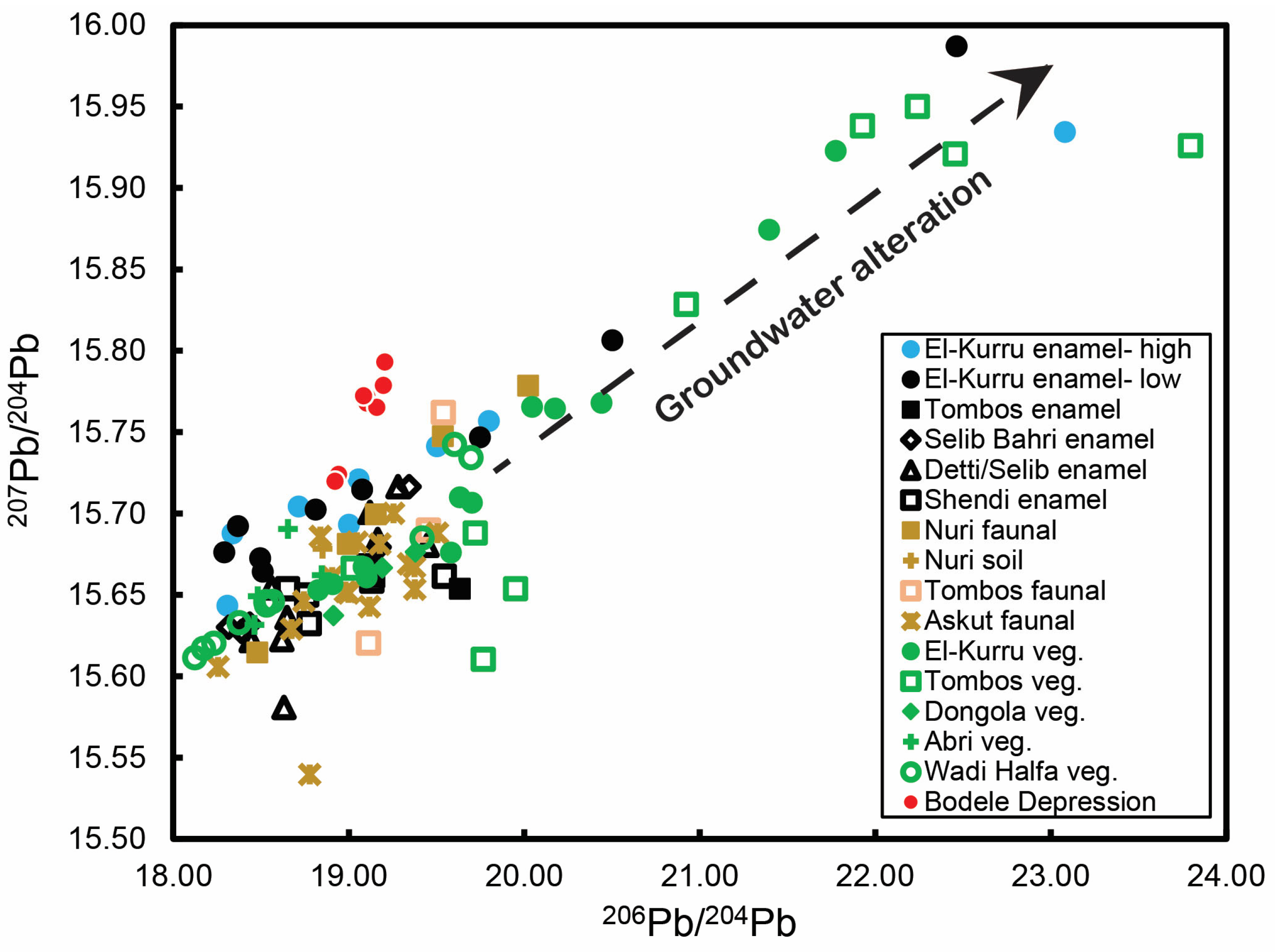
3.4. Pb Isotope Ratios
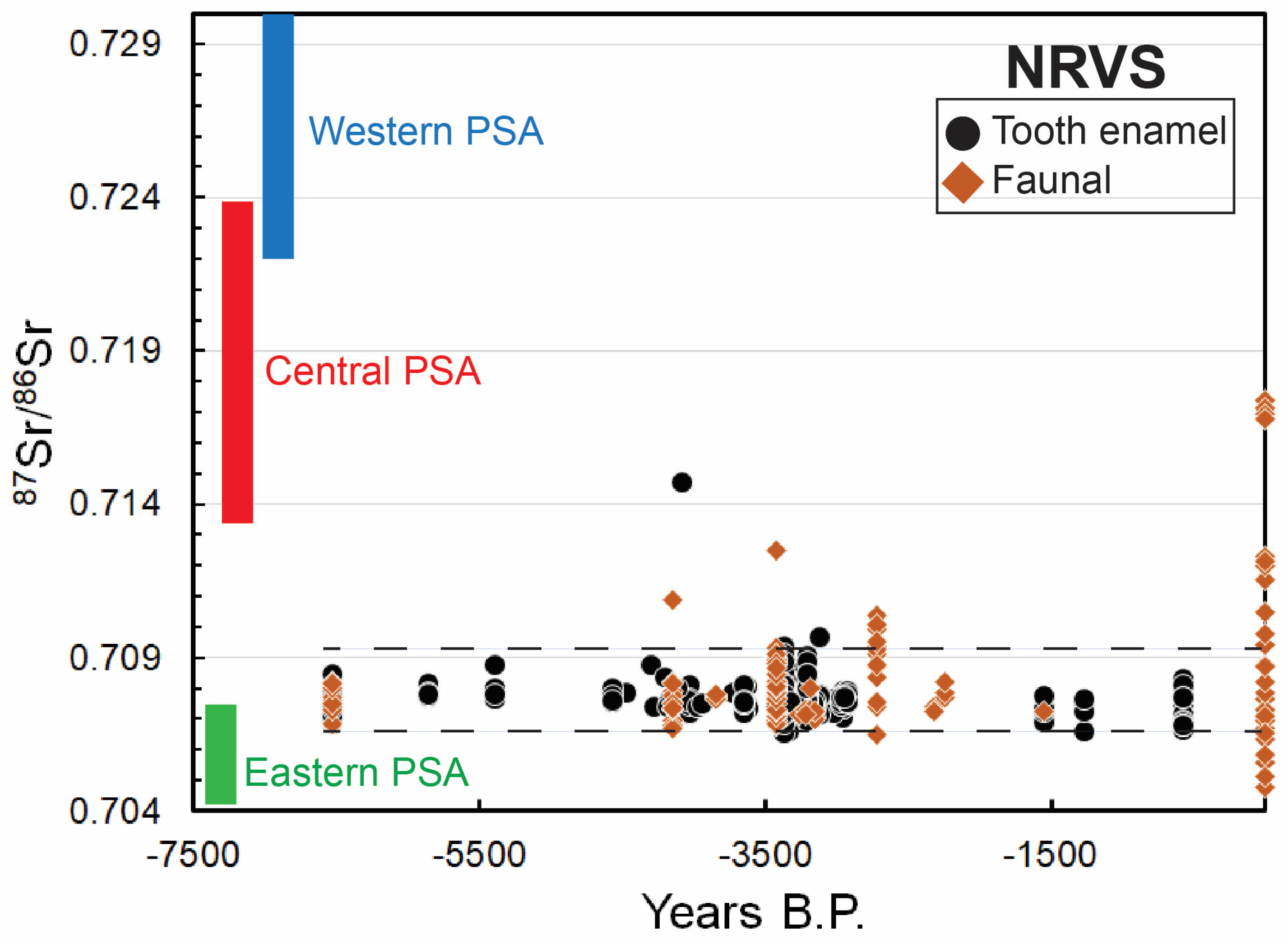
4. Possible Impact of Climate Change on the Budget of Bioavailable Sr?
4.1. Sources of Bioavailable Sr and Its Uptake by Humans
4.2. Trace Element Bioavailability and Climate Change
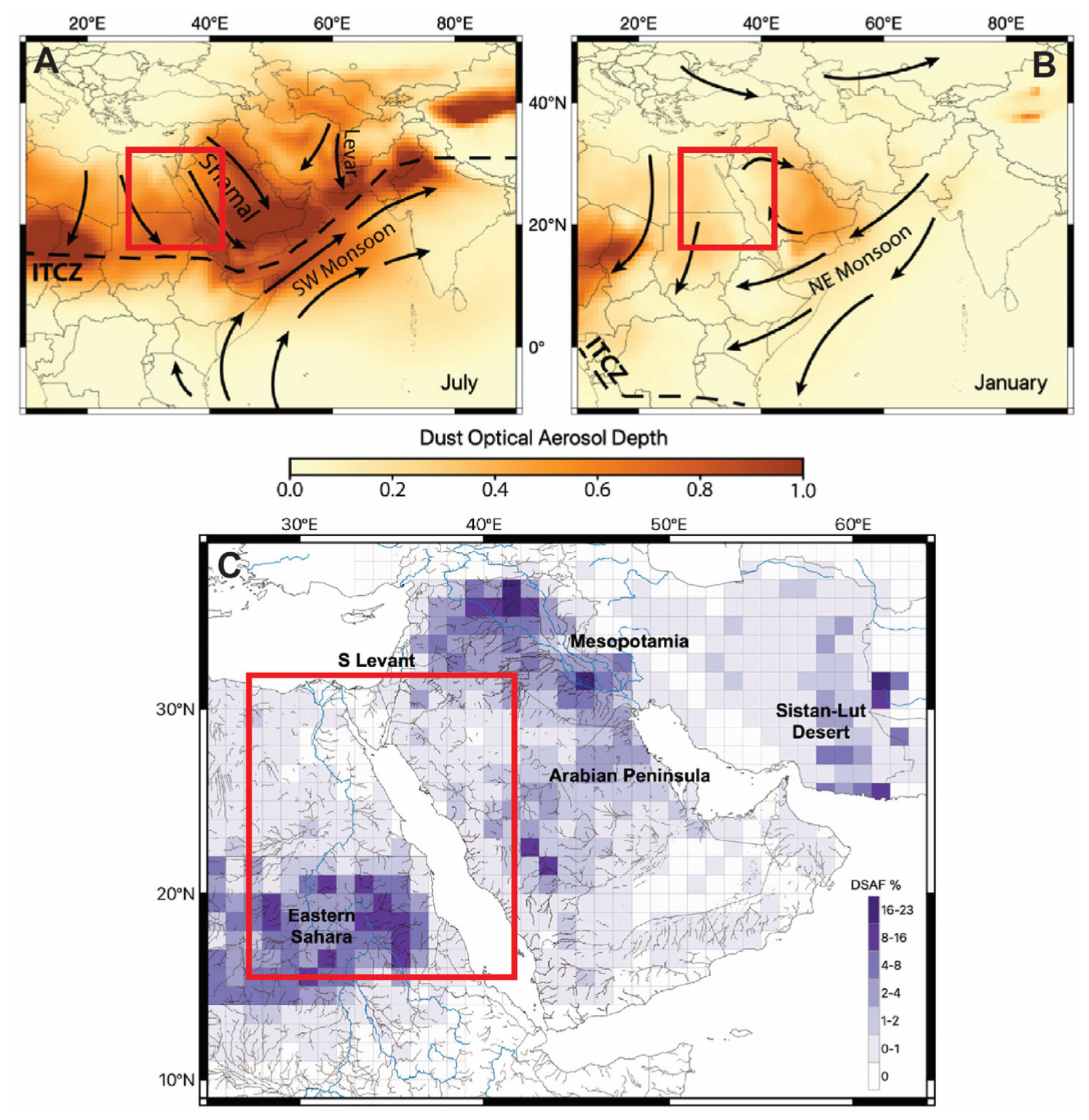
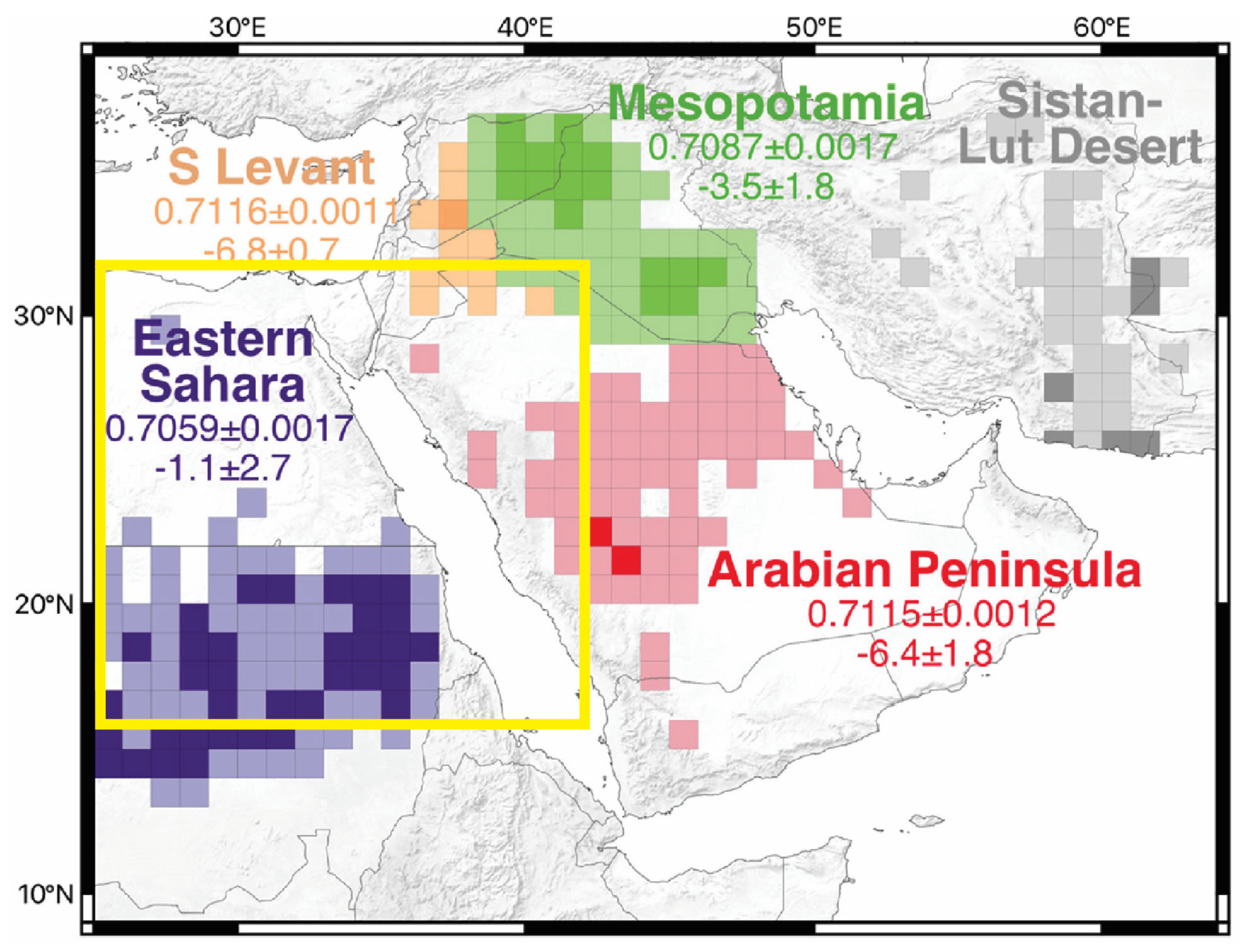
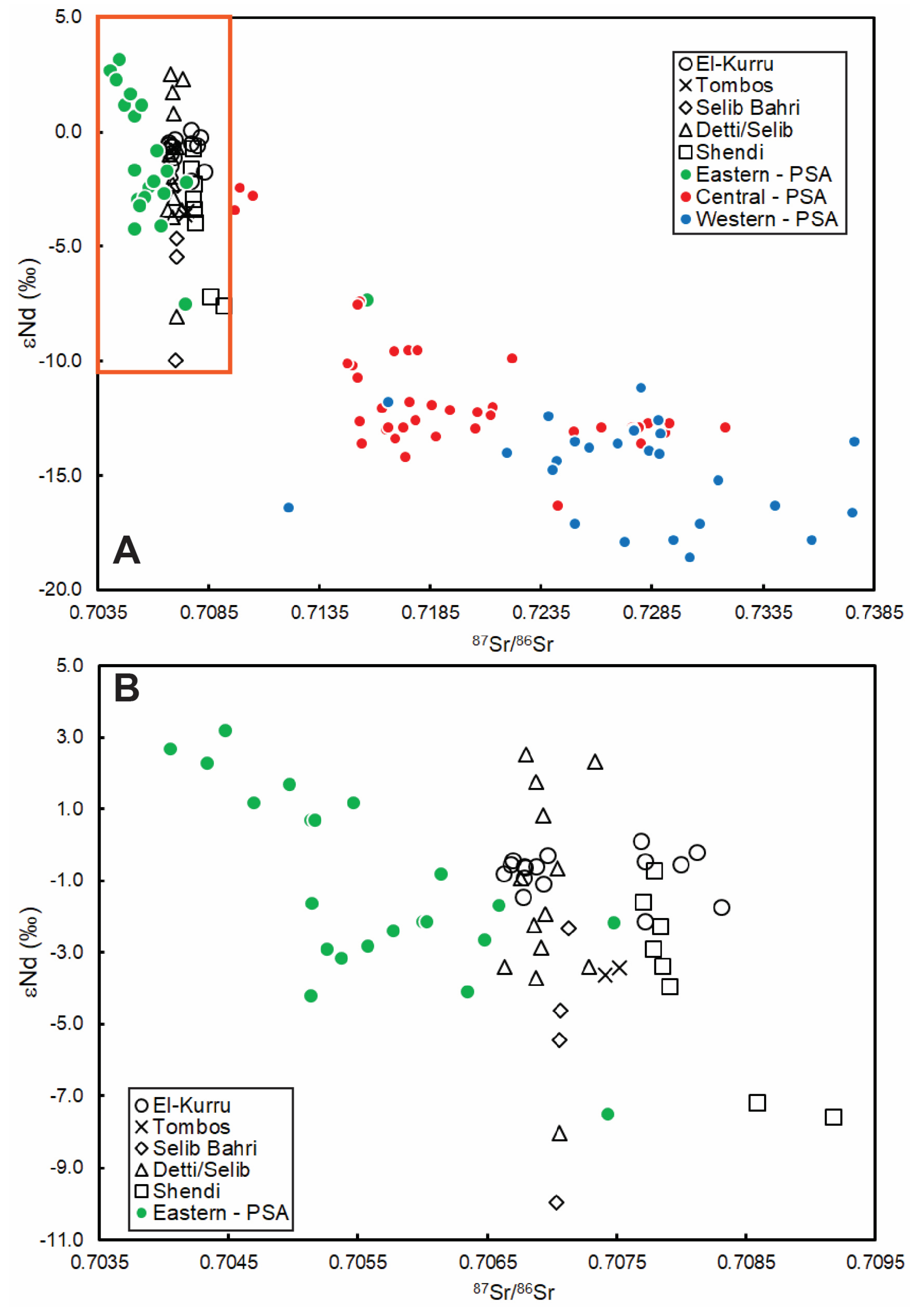
4.3. Geochemical and Isotopic Signatures of Preferential Dust Source Areas (PSAs)
4.4. Influence of Climate Change?
5. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodell, D.A.; Quinn, R.L.; Brenner, M.; Kamenov, G. Spatial Variation of Strontium Isotopes (87Sr/86Sr) in the Maya Region: A Tool for Tracking Ancient Human Migration. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.E. In Search of Yax Nunn Ayiin I: Revisiting the Tikal Project’s Burial 10. Anc. Mesoam. 2005, 16, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.E. Identifying Immigrants to Tikal, Guatemala: Defining Local Variability in Strontium Isotope Ratios of Human Tooth Enamel. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzo, J.A.; Johnson, C.M.; Price, T.D. Analytical Perspectives on Prehistoric Migration: A Case Study from East-Central Arizona. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1997, 24, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzo, J.A.; Price, T.D. Migration, Regional Reorganization, and Spatial Group Composition at Grasshopper Pueblo, Arizona. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 499–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Price, T.D.; Johnson, C.M.; Ezzo, J.A.; Ericson, J.; Burton, J.H. Residential Mobility in the Prehistoric Southwest United States: A Preliminary Study Using Strontium Isotope Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1994, 21, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Manzanilla, L.; Middleton, W.D. Immigration and the Ancient City of Teotihuacan in Mexico: A Study Using Strontium Isotope Ratios in Human Bone and Teeth. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2000, 27, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Tiesler, V.; Burton, J.H. Early African Diaspora in Colonial Campeche, Mexico: Strontium Isotopic Evidence. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2006, 130, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A.; Krause, R.; Price, T.D.; Kaufmann, B. Human Mobility at the Early Neolithic Settlement of Vaihingen, Germany: Evidence from Strontium Isotope Analysis. Archaeometry 2003, 45, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, R.A.; Price, T.D.; Stephan, E. Determining the ‘Local’ 87Sr/86Sr Range for Archaeological Skeletons: A Case Study from Neolithic Europe. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2004, 31, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupe, G.; Price, T.D.; Schröter, P.; Söllner, F.; Johnson, C.M.; Beard, B.L. Mobility of Bell Beaker People Revealed by Strontium Isotope Ratios of Tooth and Bone: A Study of Southern Bavarian Skeletal Remains. Appl. Geochem. 1997, 12, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Grupe, G.; Schröter, P. Migration in the Bell Beaker Period of Central Europe. Antiquity 1998, 72, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Bentley, R.A.; Lüning, J.; Gronenborn, D.; Wahl, J. Prehistoric Human Migration in the Linearbandkeramik of Central Europe. Antiquity 2001, 75, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Knipper, C.; Grupe, G.; Smrcka, V. Strontium Isotopes and Prehistoric Human Migration: The Bell Beaker Period in Central Europe. Eur. J. Archaeol. 2004, 7, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweissing, M.M.; Grupe, G. Stable Strontium Isotopes in Human Teeth and Bone: A Key to Migration Events of the Late Roman Period in Bavaria. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2003, 30, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, K.J.; Price, T.D.; Buikstra, J.E.; Blom, D.E. The Use of Strontium Isotope Analysis to Investigate Tiwanaku Migration and Mortuary Ritual in Bolivia and Peru. Archaeometry 2004, 46, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, K.J.; Tung, T.A.; Nystrom, K.C.; Price, T.D.; Fullagar, P.D. The Origin of the Juch’uypampa Cave Mummies: Strontium Isotope Analysis of Archaeological Human Remains from Bolivia. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2005, 32, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.; Sealy, J. Investigating Identity and Life Histories: Isotopic Analysis and Historical Documentation of Slave Skeletons Found on the Cape Town Foreshore, South Africa. Int. J. Hist. Archaeol. 1997, 1, 207–224. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20852885 (accessed on 7 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sillen, A.; Hall, G.; Armstrong, R. Strontium Calcium Ratios (Sr/Ca) and Strontium Isotopic Ratios (87Sr/86Sr) of Australopithecus Robustus and Homo Sp. from Swartkrans. J. Hum. Evol. 1995, 28, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Stoodley, N.; Chenery, C. A Strontium and Oxygen Isotope Assessment of a Possible Fourth Century Immigrant Population in a Hampshire Cemetery, Southern England. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2006, 33, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenery, C.; Müldner, G.; Evans, J.; Eckardt, H.; Lewis, M. Strontium and Stable Isotope Evidence for Diet and Mobility in Roman Gloucester, UK. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, K.J. Tiwanaku Influence in the South Central Andes: Strontium Isotope Analysis and Middle Horizon Migration. Lat. Am. Antiq. 2008, 19, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrushko, V.A.; Buzon, M.R.; Simonetti, A.; Creaser, R.A. Strontium Isotope Evidence for Prehistoric Migration at Chokepukio, Valley of Cuzco, Peru. Lat. Am. Antiq. 2009, 20, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovak, N.M.; Paytan, A.; Wiegand, B.A. Reconstructing Middle Horizon Mobility Patterns on the Coast of Peru through Strontium Isotope Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Kamenov, G.D.; Kingston, J.D.; Armelagos, G.J. Insights into Immigration and Social Class at Machu Picchu, Peru Based on Oxygen, Strontium, and Lead Isotopic Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzon, M.R.; Conlee, C.A.; Simonetti, A.; Bowen, G.J. The Consequences of Wari Contact in the Nasca Region during the Middle Horizon: Archaeological, Skeletal, and Isotopic Evidence. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2012, 39, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, A.J. Application of Lead Isotope Analysis to a Wide Range of Late Bronze Age Egyptian Materials. Archaeometry 2006, 48, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñañez, J.G.; Bellucci, J.J.; Rodríguez-Alegría, E.; Ash, R.; McDonough, W.; Speakman, R.J. Romita Pottery Revisited: A Reassessment of the Provenance of Ceramics from Colonial Mexico by LA-MC-ICP-MS. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurr, M.R.; Donohue, P.H.; Simonetti, A.; Dawson, E.L. Multi-Element and Lead Isotope Characterization of Early Nineteenth Century Pottery Sherds from Native American and Euro-American Sites. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 20, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.K.; Duke, M.J.M.; Simonetti, A.; Chen, G. Trace Element and Pb Isotope Provenance Analyses of Native Copper in Northwestern North America: Results of a Recent Pilot Study Using INAA, ICP-MS, and LA-MC-ICP-MS. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 1732–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.K.; Simonetti, A. Lead Isotope Analysis of Geological Native Copper: Implications for Archaeological Provenance Research in the North American Arctic and Subarctic. Minerals 2021, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.L. Tooth Analyses of Sources and Intensity of Lead Exposure in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.E.; Franklin, M.; Roh, H.; Austin, C.; Arora, M. Lead and Arsenic in Shed Deciduous Teeth of Children Living Near a Lead-Acid Battery Smelter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6000–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, G.D. High-Precision Pb Isotopic Measurements of Teeth and Environmental Samples from Sofia (Bulgaria): Insights for Regional Lead Sources and Possible Pathways to the Human Body. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Mielke, H.W.; Filippelli, G.M.; Johnson, D.L.; Gonzales, C.R. Seasonality and Children’s Blood Lead Levels: Developing a Predictive Model Using Climatic Variables and Blood Lead Data from Indianapolis, Indiana, Syracuse, New York, and New Orleans, Louisiana (USA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, H.W.; Gonzales, C.R.; Powell, E.T.; Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Berry, K.J.; Mielke, P.W.; Egendorf, S.P. The Concurrent Decline of Soil Lead and Children’s Blood Lead in New Orleans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22058–22064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, H.W.; Reagan, P.L. Soil Is an Important Pathway of Human Lead Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S1), 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purchase, N.G.; Fergusson, J.E. Lead in Teeth: The Influence of the Tooth Type and the Sample within a Tooth on Lead Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 52, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wychowanski, P.; Malkiewicz, K. Evaluation of Metal Ion Concentration in Hard Tissues of Teeth in Residents of Central Poland. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6419709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, G.D.; Krigbaum, J. Pb Isotopes and Human Mobility: Natural, Cultural, or Diagenetic Signal? In Isotopic Proveniencing and Mobility: The Current State of Research; Price, T.D., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 163–185. ISBN 978-3-031-25722-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gulson, B.L.; Mizon, K.J.; Law, A.J.; Korsch, M.J.; Davis, J.J.; Howarth, D. Source and Pathways of Lead in Humans from the Broken Hill Mining Community—An Alternative Use of Exploration Methods. Econ. Geol. 1994, 89, 889–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Gariépy, C.; Carignan, J. Pb and Sr Isotopic Compositions of Snowpack from Québec, Canada: Inferences on the Sources and Deposition Budgets of Atmospheric Heavy Metals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Gariépy, C.; Carignan, J. Tracing Sources of Atmospheric Pollution in Western Canada Using the Pb Isotopic Composition and Heavy Metal Abundances of Epiphytic Lichens. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2853–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Gariépy, C.; Banic, C.M.; Tanabe, R.; Wong, H.K. Pb Isotopic Investigation of Aircraft-Sampled Emissions from the Horne Smelter (Rouyn, Québec): Implications for Atmospheric Pollution in Northeastern North America. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3285–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, E.; Von Holstein, I.C.C.; Koornneef, J.M.; Smeets, R.J.; Font, L.; Baart, J.A.; Forouzanfar, T.; Davies, G.R. TIMS Analysis of Neodymium Isotopes in Human Tooth Enamel Using 1013 Ω Amplifiers. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, E.; Von Holstein, I.C.C.; Koornneef, J.M.; Smeets, R.J.; Baart, J.A.; Forouzanfar, T.; Davies, G.R. Evaluation of Neodymium Isotope Analysis of Human Dental Enamel as a Provenance Indicator Using 1013 Ω Amplifiers (TIMS). Sci. Justice 2019, 59, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipkey, C.E.; Capo, R.C.; Chadwick, O.A.; Stewart, B.W. The Importance of Sea Spray to the Cation Budget of a Coastal Hawaiian Soil: A Strontium Isotope Approach. Chem. Geol. 2000, 168, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J. Isoscapes: Spatial Pattern in Isotopic Biogeochemistry. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.T.; Regan, L.A.; Lundstrom, C.C.; Bower, N.W. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Spatiotemporal Pb Isoscapes for Provenancing of Human Remains. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 261, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschetti, C.; Henderson, J.; Evans, J. Mosaic Tesserae from Italy and the Production of Mediterranean Coloured Glass (4th Century BCE–4th Century CE). Part II: Isotopic Provenance. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2017, 11, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brems, D.; Pauwels, J.; Blomme, A.; Scott, R.B.; Degryse, P. Geochemical Heterogeneity of Sand Deposits and Its Implications for the Provenance Determination of Roman Glass. STAR Sci. Technol. Archaeol. Res. 2015, 1, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stephens, J.A.; Ducea, M.N.; Killick, D.J.; Ruiz, J. Use of Non-Traditional Heavy Stable Isotopes in Archaeological Research. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2021, 127, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, K.J.; Torres, C.M.; Pestle, W. Isotopic Analyses in the Andes: From the Macro- to Micro-Scale. In Isotopic Proveniencing and Mobility: The Current State of Research; Price, T.D., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 29–66. ISBN 978-3-031-25722-3. [Google Scholar]
- Simonetti, A.; Buzon, M.; Simonetti, S.; Guilbault, K.; Kordofani, M.A.; Miller, N. Assessing the Impact of Holocene Climate Change on Bioavailable Strontium Within the Nile River Valley: Geochemical and Radiogenic Isotope Perspectives. Bioarchaeol. Int. 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, M.; Garzanti, E.; Harlavan, Y.; Villa, I.M. Tracing Nile Sediment Sources by Sr and Nd Isotope Signatures (Uganda, Ethiopia, Sudan). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 3627–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Buzon, M.R.; Corcoran, L.; Breidenstein, A.M.; Emberling, G. Trace Element and Pb and Sr Isotope Investigation of Tooth Enamel from Archaeological Remains at El-Kurru, Sudan: Evaluating the Role of Groundwater-Related Diagenetic Alteration. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 132, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J. Lead and Strontium Isotope Compositions of Human Dental Tissues as an Indicator of Ancient Exposure and Population Dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D. An Introduction to Isotopic Proveniencing and Mobility. In Isotopic Proveniencing and Mobility: The Current State of Research; Price, T.D., Ed.; Interdisciplinary Contributions to Archaeology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-3-031-25721-6. [Google Scholar]
- Longerich, H.P.; Diegor, W. Introduction to Mass Spectrometry. In Laser-Ablation-ICPMS in the Earth Sciences; Short Course Series; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Tornto, ON, Canada, 2008; Volume 29, pp. 1–19. ISBN 0-921294-29-8. [Google Scholar]
- Retzmann, A.; Budka, J.; Sattmann, H.; Irrgeher, J.; Prohaska, T. The New Kingdom Population on Sai Island: Application of Sr Isotopes to Investigate Cultural Entanglement in Ancient Nubia. Int. J. Egypt. Archaeol. Relat. Discip. 2019, 29, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Pollard, A.M. Here Today, Gone Tomorrow? Integrated Experimentation and Geochemical Modeling in Studies of Archaeological Diagenetic Change. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.K.; Deniro, M.J.; Schoeninger, M.J.; De Paolo, D.J.; Hare, P.E. Effects of Diagenesis on Strontium, Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen Concentration and Isotopic Composition of Bone. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J.; Schoeninger, M.J.; Barker, W.W. Altered States: Effects of Diagenesis on Fossil Tooth Chemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Marsh, C.M.; Hedges, R.E.M. Patterns of Diagenesis in Bone I: The Effects of Site Environments. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2000, 27, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohaska, T.; Latkoczy, C.; Schultheis, G.; Teschler-Nicola, M.; Stingeder, G. Investigation of Sr Isotope Ratios in Prehistoric Human Bones and Teeth Using Laser Ablation ICP-MS and ICP-MS after Rb/Sr Separation. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, K.A.; Koch, P.L.; Furutani, T.T. Assessing the Preservation of Biogenic Strontium in Fossil Bones and Tooth Enamel. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2003, 13, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.-F.; Galer, S.J.G.; Knipper, C.; Beierlein, L.; Nunn, E.V.; Peters, D.; Tütken, T.; Alt, K.W.; Schöne, B.R. Bioavailable 87Sr/86Sr in Different Environmental Samples—Effects of Anthropogenic Contamination and Implications for Isoscapes in Past Migration Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudás, F.Ö.; LeBlanc, S.A.; Carter, S.W.; Bowring, S.A. Pb and Sr Concentrations and Isotopic Compositions in Prehistoric North American Teeth: A Methodological Study. Chem. Geol. 2016, 429, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Mensing, T.M. Isotopes: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Driessens, F.C.M.; Verbeeck, R.M.H. (Eds.) Biominerals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; ISBN 978-0-8493-5280-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sillen, A. Biogenic and Diagenetic Sr/Ca in Plio-Pleistocene Fossils of the Omo Shungura Formation. Paleobiology 1986, 12, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J.; Moses, R.J. Trace Element Diffusivities in Bone Rule out Simple Diffusive Uptake during Fossilization but Explain in Vivo Uptake and Release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueman, C.N.; Palmer, M.R.; Field, J.; Privat, K.; Ludgate, N.; Chavagnac, V.; Eberth, D.A.; Cifelli, R.; Rogers, R.R. Comparing Rates of Recrystallisation and the Potential for Preservation of Biomolecules from the Distribution of Trace Elements in Fossil Bones. Comptes Rendus Palevol 2008, 7, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, A.E.; Rogers, R.R.; Trueman, C.N. Visualizing Fossilization Using Laser Ablation–Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry Maps of Trace Elements in Late Cretaceous Bones. Geology 2009, 37, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.; Kinsley, L.; Willmes, M.; Defleur, A.; Kokkonen, H.; Mussi, M.; Grün, R. Laser Ablation Depth Profiling of U-Series and Sr Isotopes in Human Fossils. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2991–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmes, M.; Kinsley, L.; Moncel, M.-H.; Armstrong, R.A.; Aubert, M.; Eggins, S.; Grün, R. Improvement of Laser Ablation in Situ Micro-Analysis to Identify Diagenetic Alteration and Measure Strontium Isotope Ratios in Fossil Human Teeth. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 70, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, G.D.; Lofaro, E.M.; Goad, G.; Krigbaum, J. Trace Elements in Modern and Archaeological Human Teeth: Implications for Human Metal Exposure and Enamel Diagenetic Changes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2018, 99, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchi, A.; Zipkin, A.M.; Giblin, J.; Gordon, G.; Goepfert, T.; Asael, D.; Knudson, K.J. Trace Element Concentrations as Proxies for Diagenetic Alteration in the African Archaeofaunal Record: Implications for Isotope Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2024, 53, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, J.H. Effect of Post-Burial Contamination on the Concentrations of Major and Minor Elements in Human Bones and Teeth—The Implications for Palaeodietary Research. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1986, 13, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponheimer, M.; Lee-Thorp, J.A. Alteration of Enamel Carbonate Environments during Fossilization. J. Archaeol. Sci. 1999, 26, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, A.R. Strontium Isotopes from the Earth to the Archaeological Skeleton: A Review. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2006, 13, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J. Passports from the Past: Investigating Human Dispersals Using Strontium Isotope Analysis of Tooth Enamel. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2010, 37, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovak, N.M.; Paytan, A. Applications of Sr Isotopes in Archaeology. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Baskaran, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume I, pp. 743–768. ISBN 978-3-642-10637-8. [Google Scholar]
- Szostek, K.; Mądrzyk, K.; Cienkosz-Stepańczak, B. Strontium Isotopes as an Indicator of Human Migration—Easy Questions, Difficult Answers. Anthropol. Rev. 2015, 78, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, P.; Montgomery, J.; Barreiro, B.; Thomas, R.G. Differential Diagenesis of Strontium in Archaeological Human Dental Tissues. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, S.R.; Sponheimer, M.; Lee-Thorp, J.A.; le Roux, P.J.; de Ruiter, D.J.; Richards, M.P. Strontium Isotope Ratios in Fossil Teeth from South Africa: Assessing Laser Ablation MC-ICP-MS Analysis and the Extent of Diagenesis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Buzon, M.R.; Guilbault, K.A.; Simonetti, S.S. The Role of Post-Mortem Alteration in Tooth Enamel Revisited: A Combined Strontium Isotope and Geochemical Evaluation. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2024, 53, 104323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.; Buzon, M.R.; Creaser, R.A. In-situ Elemental ad Sr Isotope Investigation of Human Tooth Enamel by Laser Ablation-(MC)-ICP-MS: Successes and Pitfalls. Archaeometry 2008, 50, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofaro, E.M. Ad Majorem Dei Gloriam: An Isotopic Investigation of Indigenous Lifeways in a Jesuit Church from Early Colonial Huamanga (Ayacucho) Peru. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.-M.M.; Siegele, R. Iron Deposition in Modern and Archaeological Teeth. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2014, 335, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.D.; Bargeron, C.T.; Moorhead, D.J.; LaForest, J.H. IveGot1: Reporting and Tracking Invasive Species in Florida. Southeast. Nat. 2016, 15, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Chenery, S.R.N.; Smith, B.; Mason, C.; Tomkins, A.; Roberts, G.J.; Sserunjogi, L.; Tiberindwa, J.V. Environmental Influences on the Trace Element Content of Teeth—Implications for Disease and Nutritional Status. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004, 49, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anttila, A.; Anttila, A. Trace-Element Content in the Enamel Surface and in Whole Enamel of Deciduous Incisors by Proton-Induced X-Ray Emission of Children from Rural and Urban Finnish Areas. Arch. Oral Biol. 1987, 32, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshed, W.; Akanle, O.A.; Spyrou, N.M. The Distribution of Fluorine and Other Elements in Teeth Using Proton Induced Reaction Analysis Techniques. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1994, 179, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutress, T.W. The Inorganic Composition and Solubility of Dental Enamel from Several Specified Population Groups. Arch. Oral Biol. 1972, 17, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preoteasa, E.A.; Preoteasa, E.; Kuczumow, A.; Gurban, D.; Harangus, L.; Grambole, D.; Herrmann, F. Broad-Beam PIXE and µ-PIXE Analysis of Normal and in Vitro Demineralized Dental Enamel. X-Ray Spectrom. 2008, 37, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautray, T.R.; Das, S.; Rautray, A.C. In Situ Analysis of Human Teeth by External PIXE. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2010, 268, 2371–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, L.; Ogle, N.; Moussa, I.; Kalin, R.; Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M.; Bocherens, H. Implications of Diagenesis for the Isotopic Analysis of Upper Miocene Large Mammalian Herbivore Tooth Enamel from Chad. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 266, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczumow, A.; Cukrowska, E.; Stachniuk, A.; Gawęda, R.; Mroczka, R.; Paszkowicz, W.; Skrzypiec, K.; Falkenberg, R.; Backwell, L. Investigation of Chemical Changes in Bone Material from South African Fossil Hominid Deposits. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Winter, N.J.; Snoeck, C.; Schulting, R.; Fernández-Crespo, T.; Claeys, P. High-Resolution Trace Element Distributions and Models of Trace Element Diffusion in Enamel of Late Neolithic/Early Chalcolithic Human Molars from the Rioja Alavesa Region (North-Central Spain) Help to Separate Biogenic from Diagenetic Trends. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 532, 109260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, A.; Montgomery, J.; Trickett, M.; Beaumont, J.; Evans, J.; Chenery, S. Childhood Lead Exposure in the British Isles during the Industrial Revolution. In Modern Environments and Human Health; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 279–299. ISBN 978-1-118-50433-8. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, J.; Evans, J.A.; Cooper, R.E. Resolving Archaeological Populations with Sr-Isotope Mixing Models. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C.; Ericson, J.; Manea-Krichten, M.; Shirahata, H. Natural Skeletal Levels of Lead in Homo Sapiens Sapiens Uncontaminated by Technological Lead. Sci. Total Environ. 1991, 107, 205–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, P.; Montgomery, J.; Evans, J.; Trickett, M. Human Lead Exposure in England from Approximately 5500 Bp to the 16th Century Ad. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 318, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouchami, W.; Näthe, K.; Kumar, A.; Galer, S.J.G.; Jochum, K.P.; Williams, E.; Horbe, A.M.C.; Rosa, J.W.C.; Balsam, W.; Adams, D.; et al. Geochemical and Isotopic Characterization of the Bodélé Depression Dust Source and Implications for Transatlantic Dust Transport to the Amazon Basin. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 380, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Tacail, T.; Lugli, F.; Clauss, M.; Weber, K.; Leichliter, J.; Winkler, D.E.; Mertz-Kraus, R.; Tütken, T. Strontium Uptake and Intra-Population 87Sr/86Sr Variability of Bones and Teeth—Controlled Feeding Experiments With Rodents (Rattus Norvegicus, Cavia Porcellus). Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 569940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillen, A.; Hall, G.; Richardson, S.; Armstrong, R. 87Sr/86Sr Ratios in Modern and Fossil Food-Webs of the Sterkfontein Valley: Implications for Early Hominid Habitat Preference. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.D.; Burton, J.H.; Bentley, R.A. The Characterization of Biologically Available Strontium Isotope Ratios for the Study of Prehistoric Migration. Archaeometry 2002, 44, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, K.M.; Frei, R. The Geographic Distribution of Strontium Isotopes in Danish Surface Waters—A Base for Provenance Studies in Archaeology, Hydrology and Agriculture. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varo, P.; Saari, E.; Paaso, A.; Koivistoinen, P. Strontium in Finnish Foods. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1982, 52, 342–350. [Google Scholar]
- Piette, M.; Desmet, B.; Dams, R. Determination of Strontium in Human Whole Blood by ICP-AES. Sci. Total Environ. 1994, 141, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Gu, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L. Association of Urinary Strontium with Cardiovascular Disease Among the US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 3583–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Anti-Inflammatory and Prochondrogenic In Situ-Formed Injectable Hydrogel Crosslinked by Strontium-Doped Bioglass for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 59772–59786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, P.J.; Ammann, P.; Boivin, G.; Rey, C. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potential of Strontium in Bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2001, 69, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, H.L.; McNeal, B.L.; O’Connor, G.A. Soil Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979; ISBN 978-0-471-04082-8. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Su, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.-H. Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 during Chinese Spring Festival at Xinxiang, a Heavily Polluted City in North China: Fireworks and Health Risks. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Srivastava, R.R.; Ojasvi. Assessment of Legislation and Practices for the Sustainable Management of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment in India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Furuta, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Iwai, I. Growth Response of Cabbage Plants to Beryllium and Strontium under Water Culture Conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1977, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.C.; Quade, J.; Betancourt, J.L. Strontium Isotopes and Nutrient Sourcing in a Semi-Arid Woodland. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Bian, W.; Zhu, W.; Guo, Y. Microelement Strontium and Human Health: Comprehensive Analysis of the Role in Inflammation and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs). Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1367395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.S.; Squire, H.M. The Absorption and Distribution of Strontium in Plants: I. Preliminary Studies in Water Culture. J. Exp. Bot. 1958, 9, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Qin, X.; Li, F.-M.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Brandl, H.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Uptake and Distribution of Stable Strontium in 26 Cultivars of Three Crop Species: Oats, Wheat, and Barley for Their Potential Use in Phytoremediation. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2015, 17, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, W.; Krafft, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, F. Effects of Several Environmental Factors on Longevity and Health of the Human Population of Zhongxiang, Hubei, China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, K. Regional Distribution of Longevity Population and Elements in Drinking Water in Jiangjin District, Chongqing City, China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curzon, M.E.J.; Spector, P.C.; Iker, H.P. An Association between Strontium in Drinking Water Supplies and Low Caries Prevalence in Man. Arch. Oral Biol. 1978, 23, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, C.G. Relevance, Essentiality and Toxicity of Trace Elements in Human Health. Mol. Aspects Med. 2005, 26, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, D.; Ju, W.; Wu, G.; Li, Z.; Gao, X. Comparison of the Mineral Elements in Drinking Water between Mengshan Longevity District and Jinan City. Trace Elem. Electrolytes 2016, 33, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pors Nielsen, S. The Biological Role of Strontium. Bone 2004, 35, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B.W.; Capo, R.C.; Chadwick, O.A. Quantitative Strontium Isotope Models for Weathering, Pedogenesis and Biogeochemical Cycling. Geoderma 1998, 82, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, O.A.; Derry, L.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Huebert, B.J.; Hedin, L.O. Changing Sources of Nutrients during Four Million Years of Ecosystem Development. Nature 1999, 397, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, R.C.; Stewart, B.W.; Chadwick, O.A. Strontium Isotopes as Tracers of Ecosystem Processes: Theory and Methods. Geoderma 1998, 82, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.; Pike, A.W.G.; Coath, C.D.; Evershed, R.P. Strontium Concentration, Radiogenic (87Sr/86Sr) and Stable (δ88Sr) Strontium Isotope Systematics in a Controlled Feeding Study. STAR Sci. Tech. Archaeol. Res. 2017, 3, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, J.; Macklin, M.; Fielding, L.; Millar, I.; Spencer, N.; Welsby, D.; Williams, M. Shifting Sediment Sources in the World’s Longest River: A Strontium Isotope Record for the Holocene Nile. Quat. Sci. Revi. 2015, 130, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzon, M.R.; Simonetti, A.; Creaser, R.A. Migration in the Nile Valley during the New Kingdom Period: A Preliminary Strontium Isotope Study. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Rahman, E.M. Geochemical and geotectonic controls of the metallogenic evolution of selected ophiolite complexes from the Sudan. In Berliner Geowissenschaftliche Abhandlungen; Reihe A, Geologie und Paläontologie; Selbstverlag Fachbereich Geowissenschaften FU Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 145, p. 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Stern, R.J.; Copeland, P.; Elfaki, E.M.; Elhur, B.; Ibrahim, F.M. The Neoproterozoic Keraf Suture in NE Sudan: Sinistral Transpression along the Eastern Margin of West Gondwana. J. Geol. 1998, 106, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, D.; Liégeois, J.-P., Sr. Nd Isotopes and Geochemistry of the Bayuda Desert High-Grade Metamorphic Basement (Sudan): An Early Pan-African Oceanic Convergent Margin, Not the Edge of the East Saharan Ghost Craton? Precambrian Res. 2001, 109, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Meinhold, D.K. Mineral prospecting in the Bayuda Desert. In Investigation of Mineral Potential; Technical Report Sudanese-German Exploration Project; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe: Hannover, Germany, 1979; Part 1, Volume A. [Google Scholar]
- Küster, D.; Liégeois, J.-P.; Matukov, D.; Sergeev, S.; Lucassen, F. Zircon Geochronology and Sr, Nd, Pb Isotope Geochemistry of Granitoids from Bayuda Desert and Sabaloka (Sudan): Evidence for a Bayudian Event (920–900Ma) Preceding the Pan-African Orogenic Cycle (860–590Ma) at the Eastern Boundary of the Saharan Metacraton. Precambrian Res. 2008, 164, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evuk, D.; Franz, G.; Frei, D.; Lucassen, F. The Neoproterozoic Evolution of the Central-Eastern Bayuda Desert (Sudan). Precambrian Res. 2014, 240, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pik, R.; Deniel, C.; Coulon, C.; Yirgu, G.; Marty, B. Isotopic and Trace Element Signatures of Ethiopian Flood Basalts: Evidence for Plume–Lithosphere Interactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2263–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evuk, D.; Lucassen, F.; Franz, G. Lead Isotope Evolution across the Neoproterozoic Boundary between Craton and Juvenile Crust, Bayuda Desert, Sudan. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 135, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, E.G.; Jean Stanley, D.; Timothy Patterson, R. Strontium Isotopic-Paleontological Method as a High-Resolution Paleosalinity Tool for Lagoonal Environments. Geology 1998, 26, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkelova, T.; Crocker, A.J.; Jewell, A.M.; Breeze, P.S.; Drake, N.A.; Cooper, M.J.; Milton, J.A.; Hennen, M.; Shahgedanova, M.; Petraglia, M.; et al. Dust Sources in Westernmost Asia Have a Different Geochemical Fingerprint to Those in the Sahara. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 294, 107717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Daryanoosh, S.M.; Amrane, A.; Polosa, R.; Hopke, P.K.; Goudarzi, G.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Sicard, P.; Armin, H. Impact of Middle Eastern Dust Storms on Human Health. Atmos. Polluction Res. 2017, 8, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, W.W.; Wong, T.W.; Wong, A.H.; Hui, D.S. Effect of Dust Storm Events on Daily Emergency Admissions for Respiratory Diseases. Respirology 2012, 17, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental Characterization of Global Sources of Atmospheric Soil Dust Identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (Toms) Absorbing Aerosol Product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Torres, O.; Chin, M. Long-Term Simulation of Global Dust Distribution with the GOCART Model: Correlation with North Atlantic Oscillation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, R.; Todd, M.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust-Storm Source Areas Determined by the Total Ozone Monitoring Spectrometer and Surface Observations. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2003, 93, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Remer, L.A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Rudich, Y. The Effect of Smoke, Dust, and Pollution Aerosol on Shallow Cloud Development over the Atlantic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11207–11212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, A.J.; Naafs, B.D.A.; Westerhold, T.; James, R.H.; Cooper, M.J.; Röhl, U.; Pancost, R.D.; Xuan, C.; Osborne, C.P.; Beerling, D.J.; et al. Astronomically Controlled Aridity in the Sahara since at Least 11 Million Years Ago. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K.; Tegen, I.; Macke, A. Comparison of Satellite Based Observations of Saharan Dust Source Areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennen, M. Characterisation of Mineral Dust Emission in the Middle East Using Remote Sensing Techniques; University of Reading: Reading, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, S.C.; Murray, D.W.; Prell, W.L. Nonstationary Phase of the Plio-Pleistocene Asian Monsoon. Science 1996, 274, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutuzov, S.; Legrand, M.; Preunkert, S.; Ginot, P.; Mikhalenko, V.; Shukurov, K.; Poliukhov, A.; Toropov, P. The Elbrus (Caucasus, Russia) Ice Core Record—Part 2: History of Desert Dust Deposition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14133–14148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaks, A.; Woodhead, J.; Bar-Matthews, M.; Ayalon, A.; Cliff, R.A.; Zilberman, T.; Matthews, A.; Frumkin, A. Pliocene–Pleistocene Climate of the Northern Margin of Saharan–Arabian Desert Recorded in Speleothems from the Negev Desert, Israel. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 368, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.-M.; Dominguez, J.J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS Reanalysis of Atmospheric Composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeze, P.S.; Drake, N.A.; Groucutt, H.S.; Parton, A.; Jennings, R.P.; White, T.S.; Clark-Balzan, L.; Shipton, C.; Scerri, E.M.L.; Stimpson, C.M.; et al. Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques for Reconstructing Arabian Palaeohydrology and Identifying Archaeological Sites. Quat. Int. 2015, 382, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deMenocal, P.B. African Climate Change and Faunal Evolution during the Pliocene–Pleistocene. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 220, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchan, D.; Stein, M.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Erel, Y.; Goldstein, S.L. Dust Transport and Synoptic Conditions over the Sahara–Arabia Deserts during the MIS6/5 and 2/1 Transitions from Grain-Size, Chemical and Isotopic Properties of Red Sea Cores. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 382, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Schütz, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S. Bulk Composition of Northern African Dust and Its Source Sediments—A Compilation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonieczny, C.; Bory, A.; Bout-Roumazeilles, V.; Abouchami, W.; Galer, S.J.G.; Crosta, X.; Diallo, A.; Ndiaye, T.A. Three-Year Time Series of Mineral Dust Deposits on the West African Margin: Sedimentological and Geochemical Signatures and Implications for Interpretation of Marine Paleo-Dust Records. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 364, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, A.M.; Drake, N.; Crocker, A.J.; Bakker, N.L.; Kunkelova, T.; Bristow, C.S.; Cooper, M.J.; Milton, J.A.; Breeze, P.S.; Wilson, P.A. Three North African Dust Source Areas and Their Geochemical Fingerprint. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2021, 554, 116645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, N.L.; Drake, N.A.; Bristow, C.S. Evaluating the Relative Importance of Northern African Mineral Dust Sources Using Remote Sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10525–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, J.E.; Lewis, S.C.; Cook, B.I.; LeGrande, A.N.; Schmidt, G.A. Model, Proxy and Isotopic Perspectives on the East African Humid Period. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 307, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzon, M.R.; Simonetti, A. Strontium Isotope (87 Sr/86 Sr) Variability in the Nile Valley: Identifying Residential Mobility during Ancient Egyptian and Nubian Sociopolitical Changes in the New Kingdom and Napatan Periods. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2013, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, N.J.; Ikram, S.; Moritz, G.L.; Wheatley, P.V.; Christensen, J.N.; Chipman, J.W.; Koch, P.L. Mummified Baboons Reveal the Far Reach of Early Egyptian Mariners. eLife 2020, 9, e60860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregoricka, L.A.; Baker, B.J. Residential mobility, pastoralism, and community in ancient Kush. In Proceedings of the Meeting of the American Association of Physical Anthropologists, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–28 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Herrick, H. Applying Sr Geoprovenance to anthropogenic charcoal: In theory & practice. In Proceedings of the Frontiers in Archaeological Science, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 27–29 August 2018; Simon Fraser University: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kozieradzka-Ogunmakin, I. Chapter 7 Isotope Analysis and Radiocarbon Dating of Human Remains from El-Zuma; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maritan, L.; Gravagna, E.; Cavazzini, G.; Zerboni, A.; Mazzoli, C.; Grifa, C.; Mercurio, M.; Mohamed, A.A.; Usai, D.; Salvatori, S. Nile River Clayey Materials in Sudan: Chemical and Isotope Analysis as Reference Data for Ancient Pottery Provenance Studies. Quat. Int. 2023, 657, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osypinska, M.; Osypinski, P.; Belka, Z.; Chlodnicki, M.; Wiktorowicz, P.; Ryndziewicz, R.; Kubiak, M. Wild and Domestic Cattle in the Ancient Nile Valley: Marks of Ecological Change. J. Field Archaeol. 2021, 46, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, S.A.; Buzon, M.R.; Corcoran, L.; Simonetti, A. Intraregional 87Sr/86Sr Variation in Nubia: New Insights from the Third Cataract. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 24, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stantis, C.; Kharobi, A.; Maaranen, N.; Nowell, G.M.; Bietak, M.; Prell, S.; Schutkowski, H. Who Were the Hyksos? Challenging Traditional Narratives Using Strontium Isotope (87Sr/86Sr) Analysis of Human Remains from Ancient Egypt. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stantis, C.; Kharobi, A.; Maaranen, N.; Macpherson, C.; Bietak, M.; Prell, S.; Schutkowski, H. Multi-Isotopic Study of Diet and Mobility in the Northeastern Nile Delta. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzeau, A.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Amiot, R.; Fourel, F.; Martineau, F.; Cockitt, J.; Hall, K.; Flandrois, J.-P.; Lécuyer, C. Egyptian Mummies Record Increasing Aridity in the Nile Valley from 5500 to 1500yr before Present. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 375, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinoiseau, D.; Singh, S.P.; Galer, S.J.G.; Abouchami, W.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Kandler, K.; Bristow, C.; Andreae, M.O. Characterization of Saharan and Sahelian Dust Sources Based on Geochemical and Radiogenic Isotope Signatures. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 293, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Fountain, D.M. Nature and Composition of the Continental Crust: A Lower Crustal Perspective. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 267–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G. Principles of Isotope Geology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ericson, J.E. Strontium Isotope Characterization in the Study of Prehistoric Human Ecology. J. Hum. Evol. 1985, 14, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Silvestri, A.; Degryse, P.; Ganio, M.; Longinelli, A.; Molin, G. Roman and Late-Roman Glass from North-Eastern Italy: The Isotopic Perspective to Provenance Its Raw Materials. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 62, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.J.A.; Davies, G.R.; Ganssen, G.M.; Kroon, D. Stepwise Holocene Aridification in NE Africa Deduced from Dust-Borne Radiogenic Isotope Records. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 221, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tütken, T.; Vennemann, T.W.; Pfretzschner, H.-U. Nd and Sr Isotope Compositions in Modern and Fossil Bones—Proxies for Vertebrate Provenance and Taphonomy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 5951–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, R.H.; Wampler, J.M. Isotope Studies of Ancient Lead. Am. J. Archaeol. 1967, 71, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, D.F.; Outridge, P.M.; Davis, W.J. Stable Lead Isotope Characteristics of Lead Ore Deposits of Environmental Significance. Environ. Rev. 2000, 8, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnejad, H.; Simonetti, A.; Molasalehi, F. Pb Isotopic Compositions of Some Zn–Pb Deposits and Occurrences from Urumieh–Dokhtar and Sanandaj–Sirjan Zones in Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnejad, H.; Simonetti, A.; Molasalehi, F. Origin and Formational History of Some Pb-Zn Deposits from Alborz and Central Iran: Pb Isotope Constraints. Int. Geol. Rev. 2015, 57, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, J.R.; Potra, A. Biologically Available Pb: A Method for Ancient Human Sourcing Using Pb Isotopes from Prehistoric Animal Tooth Enamel. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2020, 115, 105079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutress, T.W.; Curzon, M.E.J. Trace Elements and Dental Disease. In Postgraduate Dental Handbook Series; J. Wright/PSG Inc.: Littleton, MA, USA, 1983; Volume 9, ISBN 978-0-7236-7035-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, E.A.; Kohn, M.J. The Effect of Tissue Structure and Soil Chemistry on Trace Element Uptake in Fossils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3213–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, D.G.; Bramblett, C.A. The Anatomy and Biology of the Human Skeleton; Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Arends, J.; Ten Cate, J.M. Tooth Enamel Remineralization. J. Cryst. Growth 1981, 53, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Derry, L.A.; Hendricks, D.M. Changing Sources of Base Cations during Ecosystem Development, Hawaiian Islands. Geology 1998, 26, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Kennedy, M.J.; Derry, L.A.; Chadwick, O.A. Weathering versus Atmospheric Sources of Strontium in Ecosystems on Young Volcanic Soils. Oecologia 1999, 121, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canadell, J.; Jackson, R.B.; Ehleringer, J.B.; Mooney, H.A.; Sala, O.E.; Schulze, E.-D. Maximum Rooting Depth of Vegetation Types at the Global Scale. Oecologia 1996, 108, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horstwood, M.S.A.; Evans, J.A.; Montgomery, J. Determination of Sr Isotopes in Calcium Phosphates Using Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry and Their Application to Archaeological Tooth Enamel. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5659–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, G.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A. Comments on Richards et al., Journal of Archaeological Science 35, 2008 “Strontium Isotope Evidence of Neanderthal Mobility at the Site of Lakonis, Greece Using Laser-Ablation PIMMS”. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simonetti, A.; Buzon, M.R. Isotopes in Archeology: Perspectives on Post-Mortem Alteration and Climate Change. Geosciences 2025, 15, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080307
Simonetti A, Buzon MR. Isotopes in Archeology: Perspectives on Post-Mortem Alteration and Climate Change. Geosciences. 2025; 15(8):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimonetti, Antonio, and Michele R. Buzon. 2025. "Isotopes in Archeology: Perspectives on Post-Mortem Alteration and Climate Change" Geosciences 15, no. 8: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080307
APA StyleSimonetti, A., & Buzon, M. R. (2025). Isotopes in Archeology: Perspectives on Post-Mortem Alteration and Climate Change. Geosciences, 15(8), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15080307







