Optimizing Geophysical Inversion: Versatile Regularization and Prior Integration Strategies for Electrical and Seismic Tomographic Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Inversion Algorithm
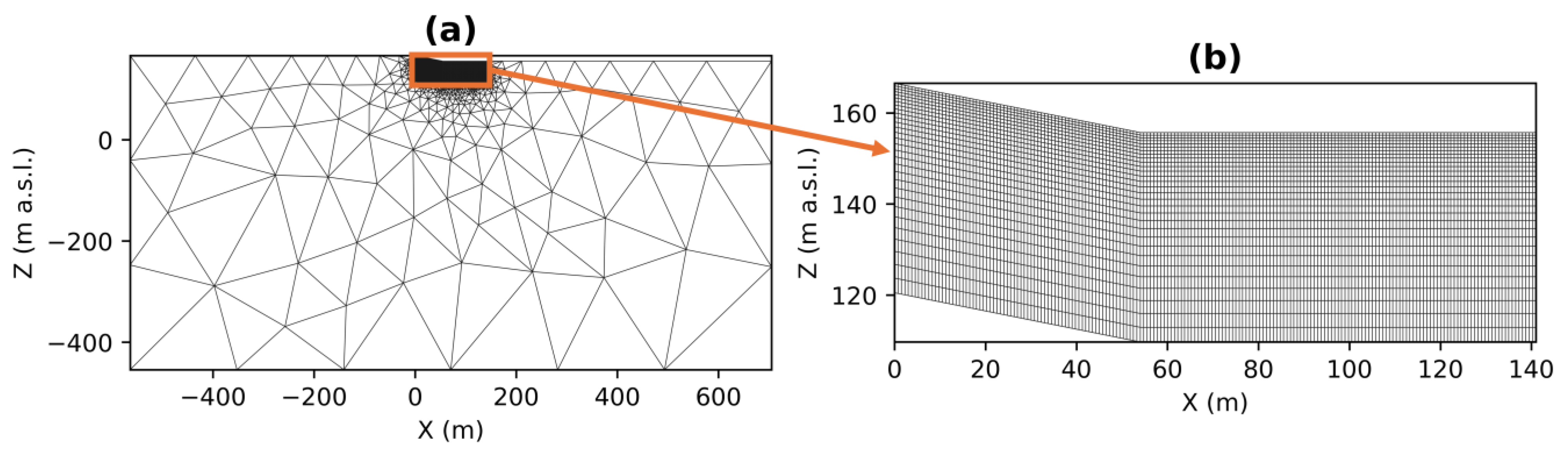
2.1. Meshing
2.2. Forward Modeling
2.3. Inversion
2.3.1. Blocky Inversion
2.3.2. Selection of the Regularization Parameter
2.3.3. Prior Information
3. Examples
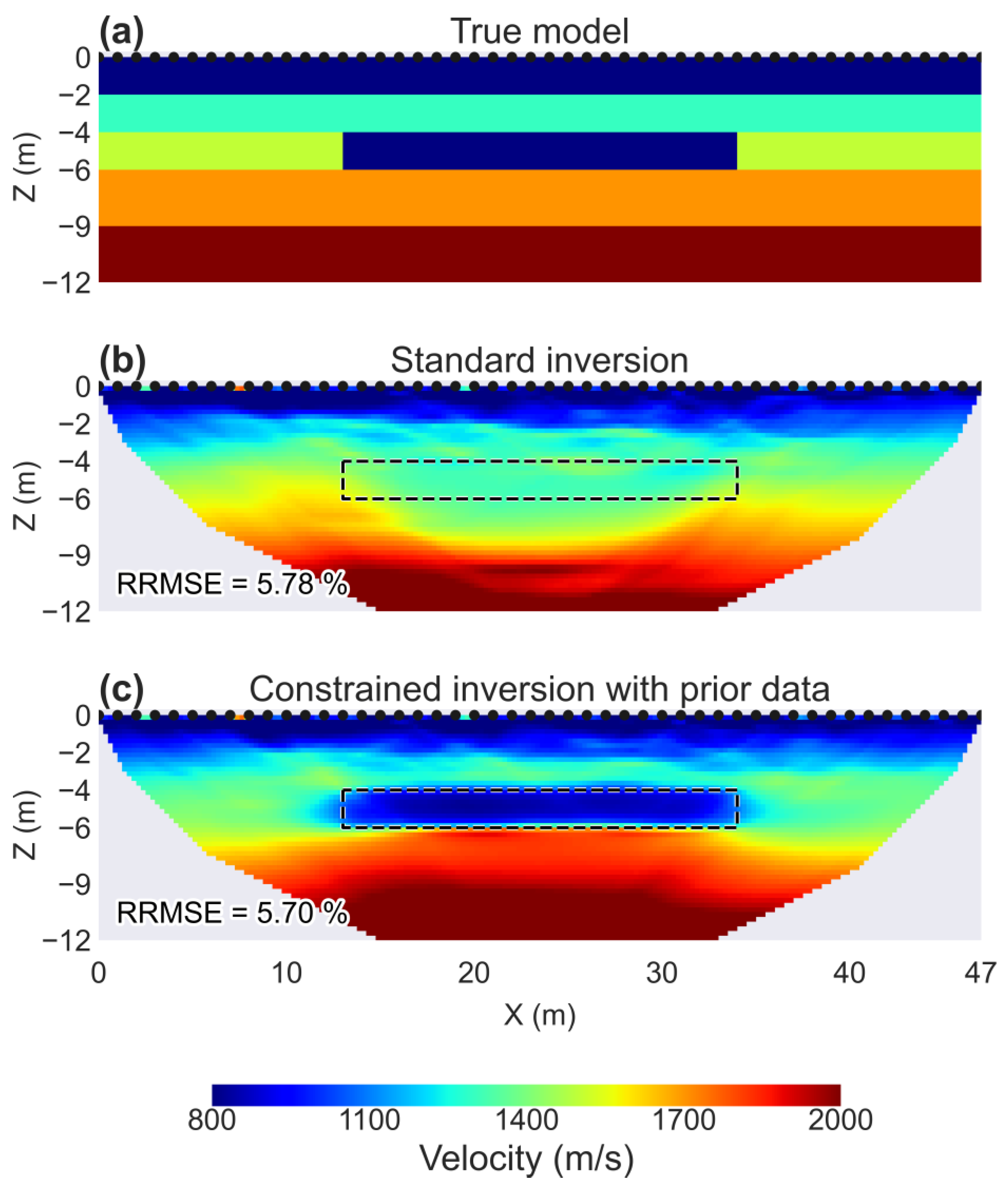
3.1. SYN: SRT Data in the Case of Velocity Inversion
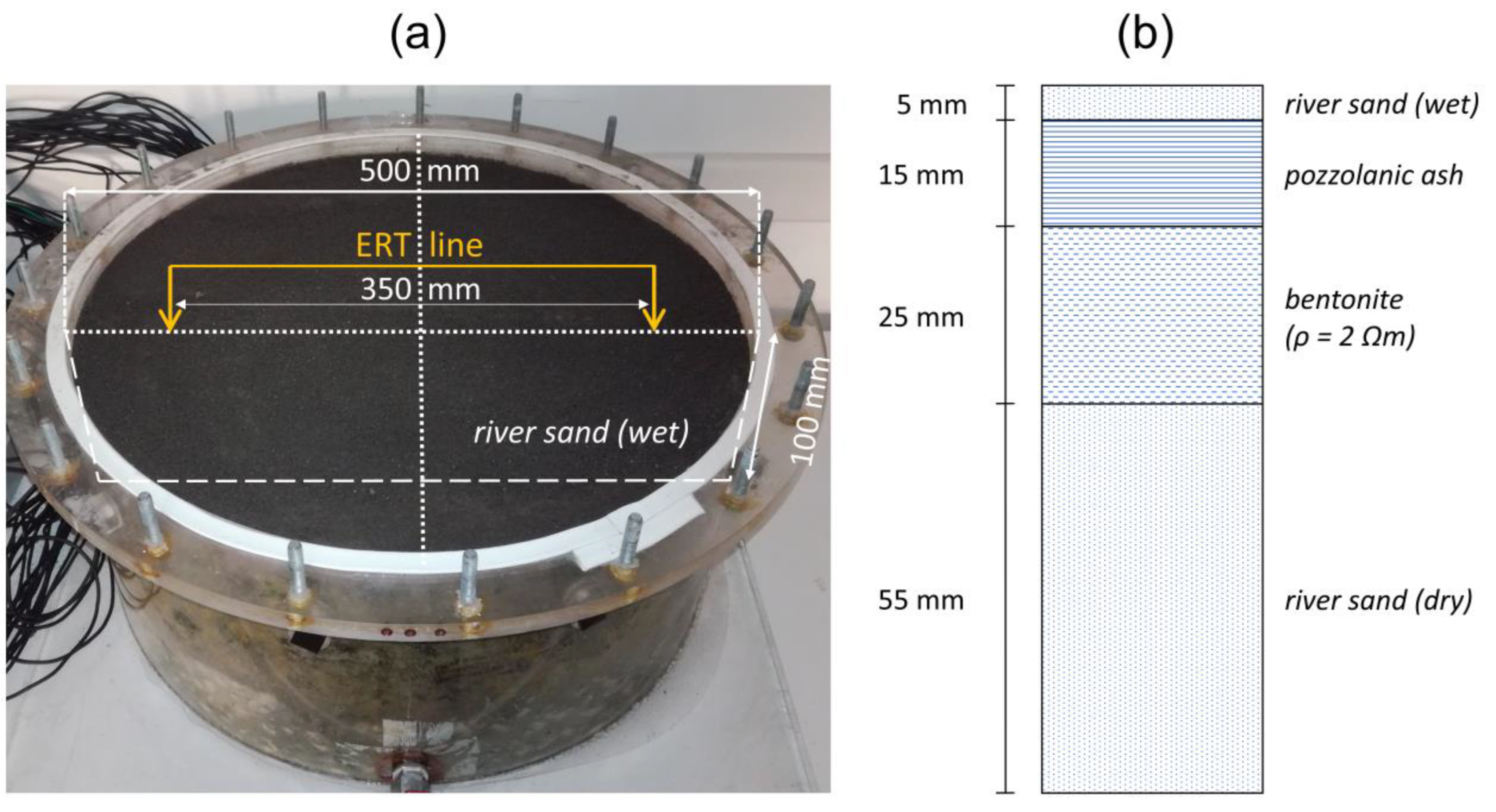
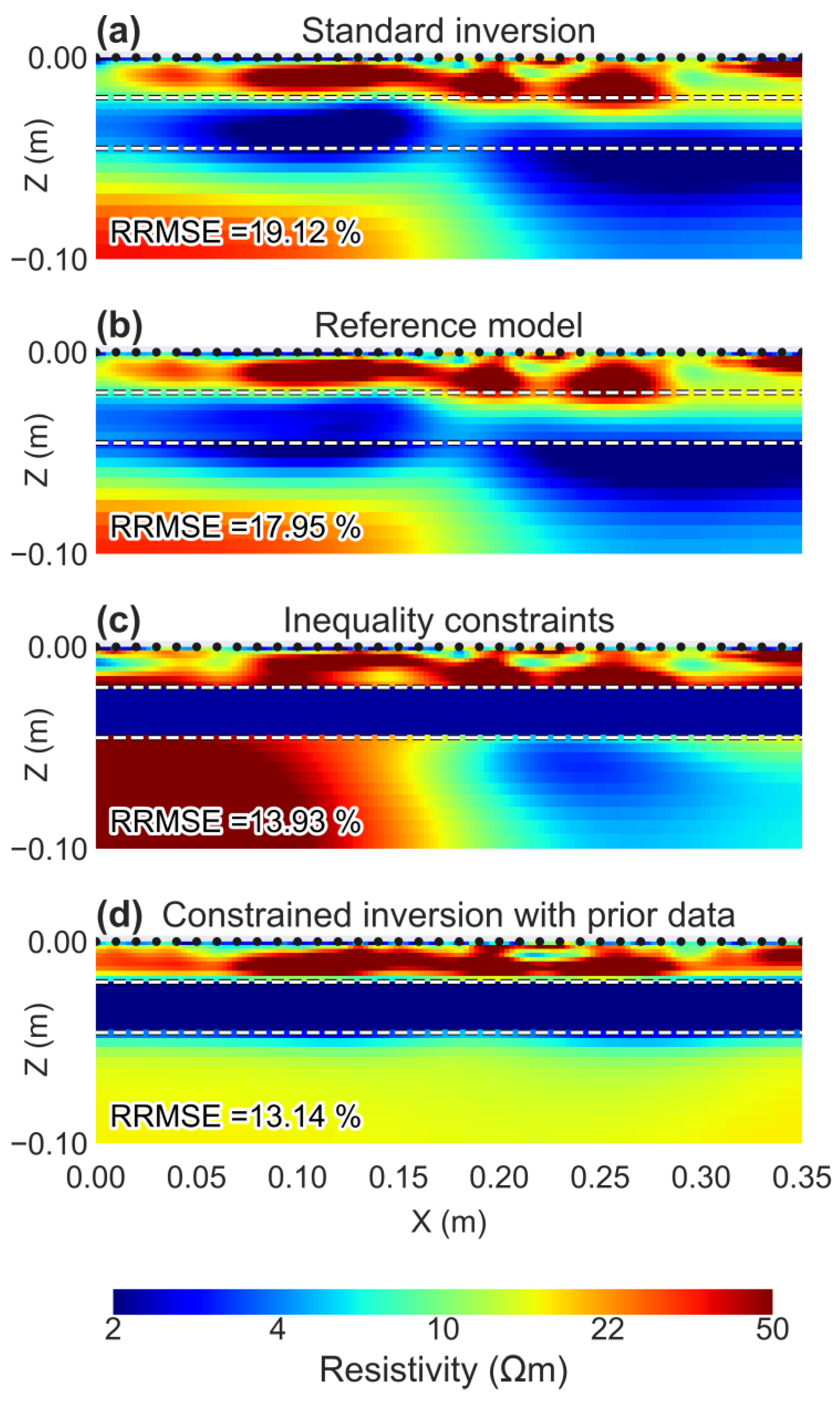
3.2. LAB: ERT Data for a Laboratory Model
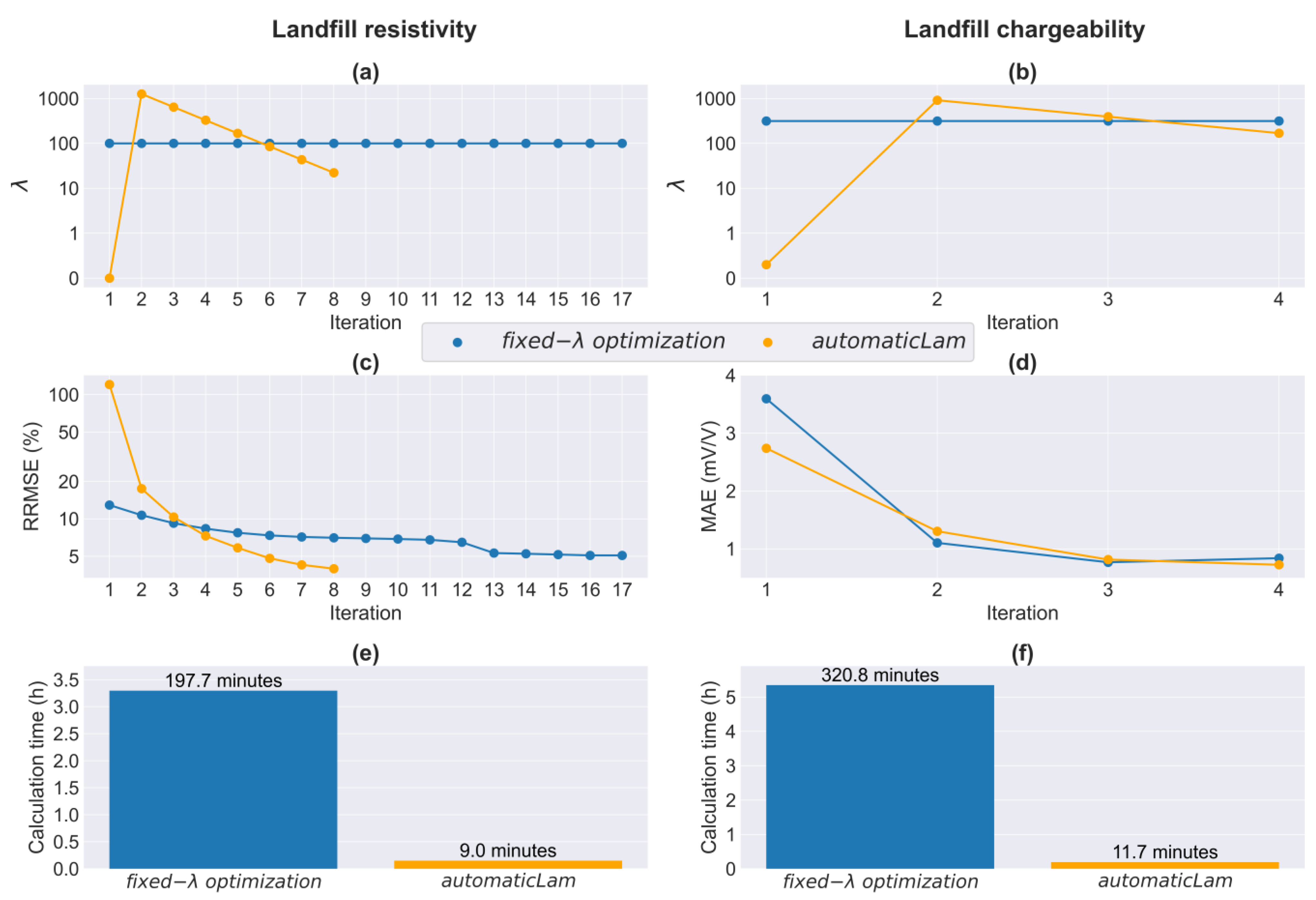
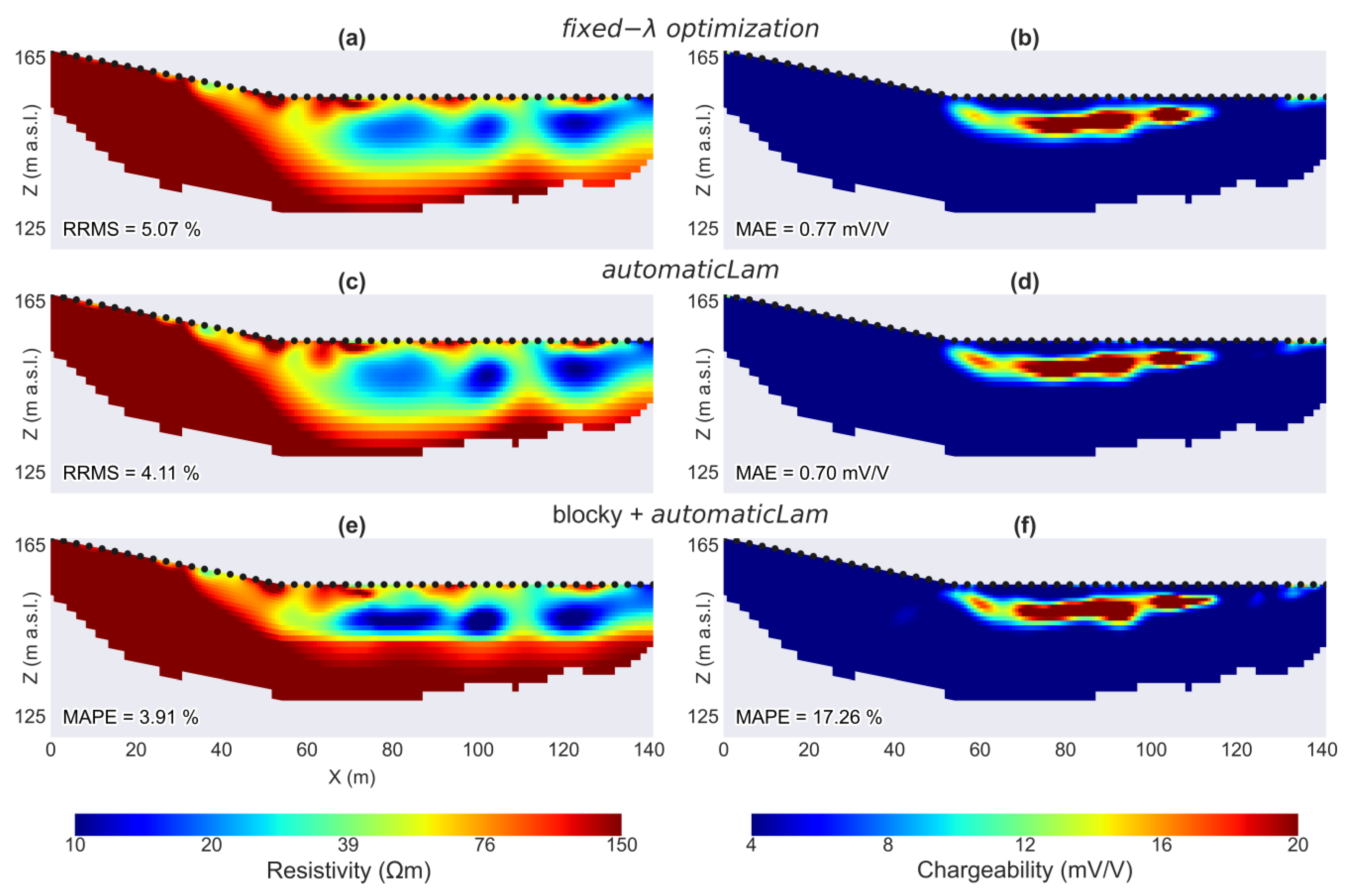
3.3. RW: ERT/TDIP for Landfill Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perrone, A.; Lapenna, V.; Piscitelli, S. Electrical resistivity tomography technique for landslide investigation: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 135, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupios, P.; Ntarlagiannis, D. Characterization and Monitoring of Solid Waste Disposal Sites Using Geophysical Methods: Current Applications and Novel Trends; Sengupta, D., Agrahari, S., Eds.; Modelling Trends in Solid and Hazardous Waste Management; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, L. Near Surface Electrical Characterization of Hydraulic Conductivity: From Petrophysical Properties to Aquifer Geometries—A Review. Surv. Geophys. 2007, 28, 169–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, G.; Cardarelli, E. Tomographic inversion of time-domain resistivity and chargeability data for the investigation of landfills using a priori information. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Fiandaca, G.; Schamper, C.; Behroozmand, A.A.; Binley, A.; Nielsen, E.; Effersø, F.; Christensen, N.B.; Sørensen, K.I.; et al. An overview of a highly versatile forward and stable inverse algorithm for airborne, ground-based and borehole electromagnetic and electric data. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchy, G.; Saneiyan, S.; Boyd, J.; McLachlan, P.; Binley, A. ResIPy, an intuitive open source software for complex geoelectrical inversion/modelling. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 137, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoulis, M.; Revil, A.; Tsourlos, P.; Werkema, D.D.; Minsley, B.J. IP4DI: A software for time-lapse 2D/3D DC-resistivity and induced polarization tomography. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 54, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, V.J.C.B.; Maciel, S.T.R.; Rocha, M.P. Refrapy: A Python program for seismic refraction data analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 159, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyen, H.; Léger, E. PyRefra—Refraction seismic data treatment and inversion. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 185, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockett, R.; Kang, S.; Heagy, L.J.; Pidlisecky, A.; Oldenburg, D.W. SimPEG: An open source framework for simulation and gradient based parameter estimation in geophysical applications. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 85, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Günther, T.; Wagner, F.M. pyGIMLi: An open-source library for modelling and inversion in geophysics. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 109, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s inversion; a practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. GEOPHYSICS 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.N.; Arsenin, V.Y. Solution of Ill-Posed Problems; Winston and Sons: Washington, DC, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson, C.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. A comparison of automatic techniques for estimating the regularization parameter in non-linear inverse problems. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 156, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.R. Non-convergence of the L-curve regularization parameter selection method. Inverse Probl. 1996, 12, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S. Geophysical Inverse Theory and Regularization Problems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. Two-dimensional joint inversion of magnetotelluric and dipole-dipole resistivity data. GEOPHYSICS 1989, 54, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Günther, T.; Spitzer, K. Three-dimensional modeling and inversion of dc resistivity data incorporating topography—I. Modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 166, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penta de Peppo, G.; Cercato, M.; De Donno, G. Cross-gradient joint inversion and clustering of ERT and SRT data on structured meshes incorporating topography. Geophys. J. Int. 2024, 239, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, T.J. Shortest path calculation of seismic rays. GEOPHYSICS 1991, 56, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Li, Y.G. Inversion of induced polarization data. GEOPHYSICS 1994, 59, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D Electrical Imaging Surveys; Geotomo Software: Houston, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Seigel, H.O. Mathematical formulation and type curves for induced polarization. GEOPHYSICS 1959, 24, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillivray, P.R.; Oldenburg, D.W. Methods for calculating frechet derivatives and sensitivities for the non-linear inverse problem: A comparative study. Geophys. Prospect. 1990, 38, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemna, A. Tomographic Inversion of Complex Resistivity. Ph.D. Thesis, Ruhr-Universität, Bochum Institut für Geophysik, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Aki, K.; Richards, P.G. Quantitative Seismology, 2nd ed.; University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Matsuoka, T.; Ashida, Y. Seismic traveltime tomography using Fresnel volume approach. SEG Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 1999, 18, 1402–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, C.C.; Saunders, M.A. LSQR: An algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least squares. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1982, 8, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, T. Inversion Methods and Resolution Analysis for the 2D/3D Reconstruction of Resistivity Structures from DC Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.R. Measuring forecast accuracy: Some practical suggestions. Prod. Inventory Manag. J. 1997, 38, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson, C.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. Non-linear inversion using general measures of data misfit and model structure. Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 134, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Acworth, I.; Dahlin, T. A comparison of smooth and blocky inversion methods in 2D electrical imaging surveys. Explor. Geophys. 2003, 34, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.W.; Welsch, R.E. Robust regression using iteratively reweighted least-squares. Commun. Stat. —Theory Methods 1977, 6, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, R.; Schwetlick, H. Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares: Algorithms, Convergence Analysis, and Numerical Comparisons. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 1988, 9, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedrahmati, R.; Moradzadeh, A.; Moradpouri, F. An effective estimate for selecting the regularization parameter in the 3D inversion of magnetotelluric data. Acta Geophys. 2022, 70, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Wan, L.; Gribenko, A.; Čuma, M.; Key, K.; Constable, S. Large-scale 3D inversion of marine magnetotelluric data: Case study from the Gemini prospect, Gulf of Mexico. GEOPHYSICS 2011, 76, F77–F87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, M.; Moradzadeh, A.; Kalate, A.N.; Aghajani, H. Fast 3D Focusing Inversion of Gravity Data Using Reweighted Regularized Lanczos Bidiagonalization Method. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, Y.; Lee, K.H. Inequality constraint in least-squared inversion of geophysical data. Earth Planets Space 1999, 51, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, M.; Nabi-Bidhendi, M.; Ghanati, R.; Shomali, Z.-H. Hidden layer imaging using joint inversion of P-wave travel-time and electrical resistivity data. Near Surf. Geophys. 2021, 19, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.A.; Benjumea, B.; Harris, J.B.; Miller, R.D.; Pullan, S.E.; Burns, R.A.; Good, R.L. Surface and downhole shear wave seismic methods for thick soil site investigations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donno, G. 2D tomographic inversion of complex resistivity data on cylindrical models. Geophys. Prospect. 2013, 61, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Günther, T. The simulation of finite ERT electrodes using the complete electrode model. GEOPHYSICS 2011, 76, F227–F238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Kalscheuer, T. Uncertainty and resolution analysis of 2D and 3D inversion models computed from geophysical electromagnetic data. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 47–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W. Funnel functions in linear and nonlinear appraisal. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 7387–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penta de Peppo, G.; Cercato, M.; De Donno, G. Optimizing Geophysical Inversion: Versatile Regularization and Prior Integration Strategies for Electrical and Seismic Tomographic Data. Geosciences 2025, 15, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070274
Penta de Peppo G, Cercato M, De Donno G. Optimizing Geophysical Inversion: Versatile Regularization and Prior Integration Strategies for Electrical and Seismic Tomographic Data. Geosciences. 2025; 15(7):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070274
Chicago/Turabian StylePenta de Peppo, Guido, Michele Cercato, and Giorgio De Donno. 2025. "Optimizing Geophysical Inversion: Versatile Regularization and Prior Integration Strategies for Electrical and Seismic Tomographic Data" Geosciences 15, no. 7: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070274
APA StylePenta de Peppo, G., Cercato, M., & De Donno, G. (2025). Optimizing Geophysical Inversion: Versatile Regularization and Prior Integration Strategies for Electrical and Seismic Tomographic Data. Geosciences, 15(7), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070274







