Coccolithophore Assemblage Dynamics and Emiliania huxleyi Morphological Patterns During Three Sampling Campaigns Between 2017 and 2019 in the South Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Oceanographic Setting
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
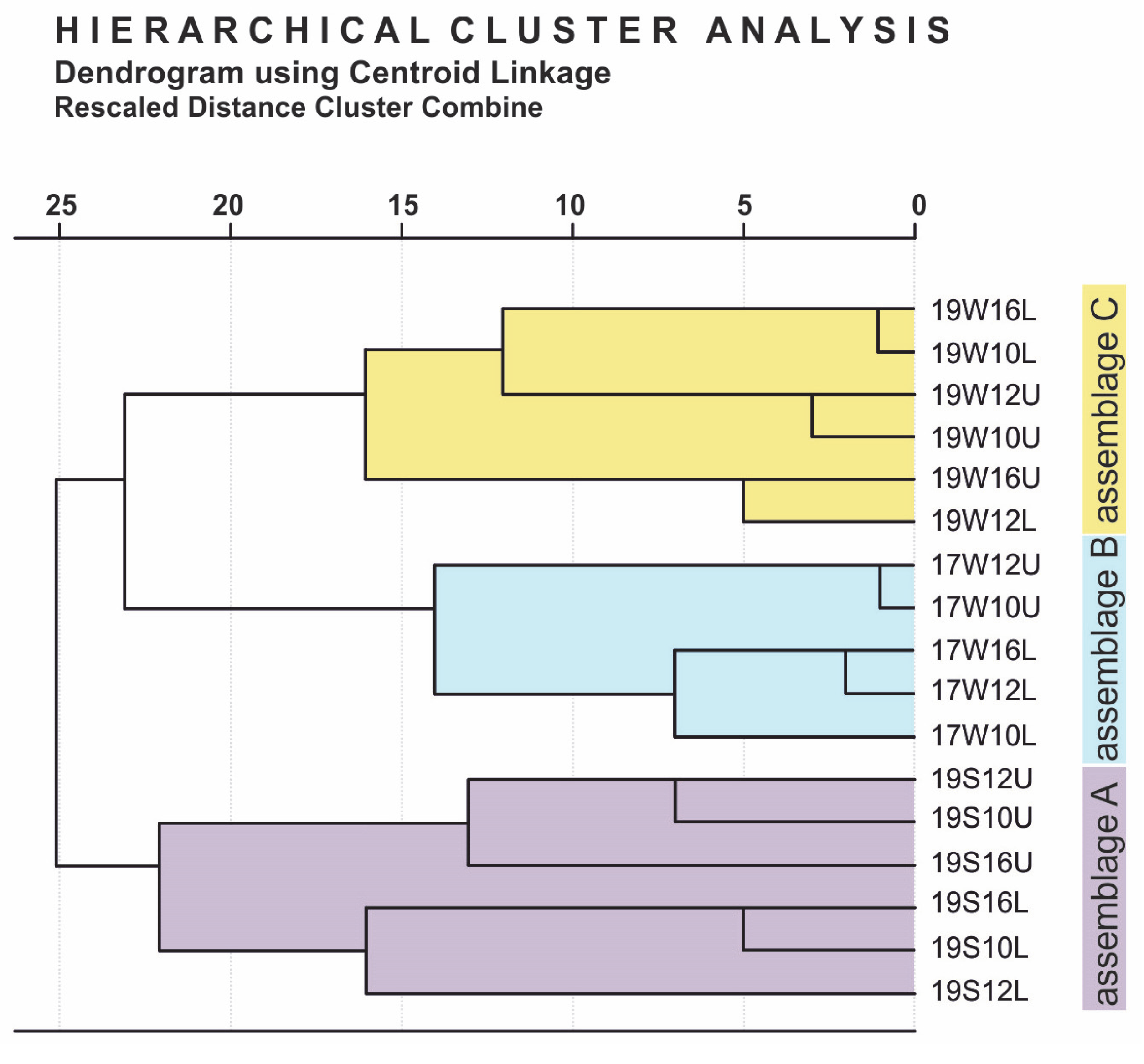
4.1. Total Abundance and Diversity Indices
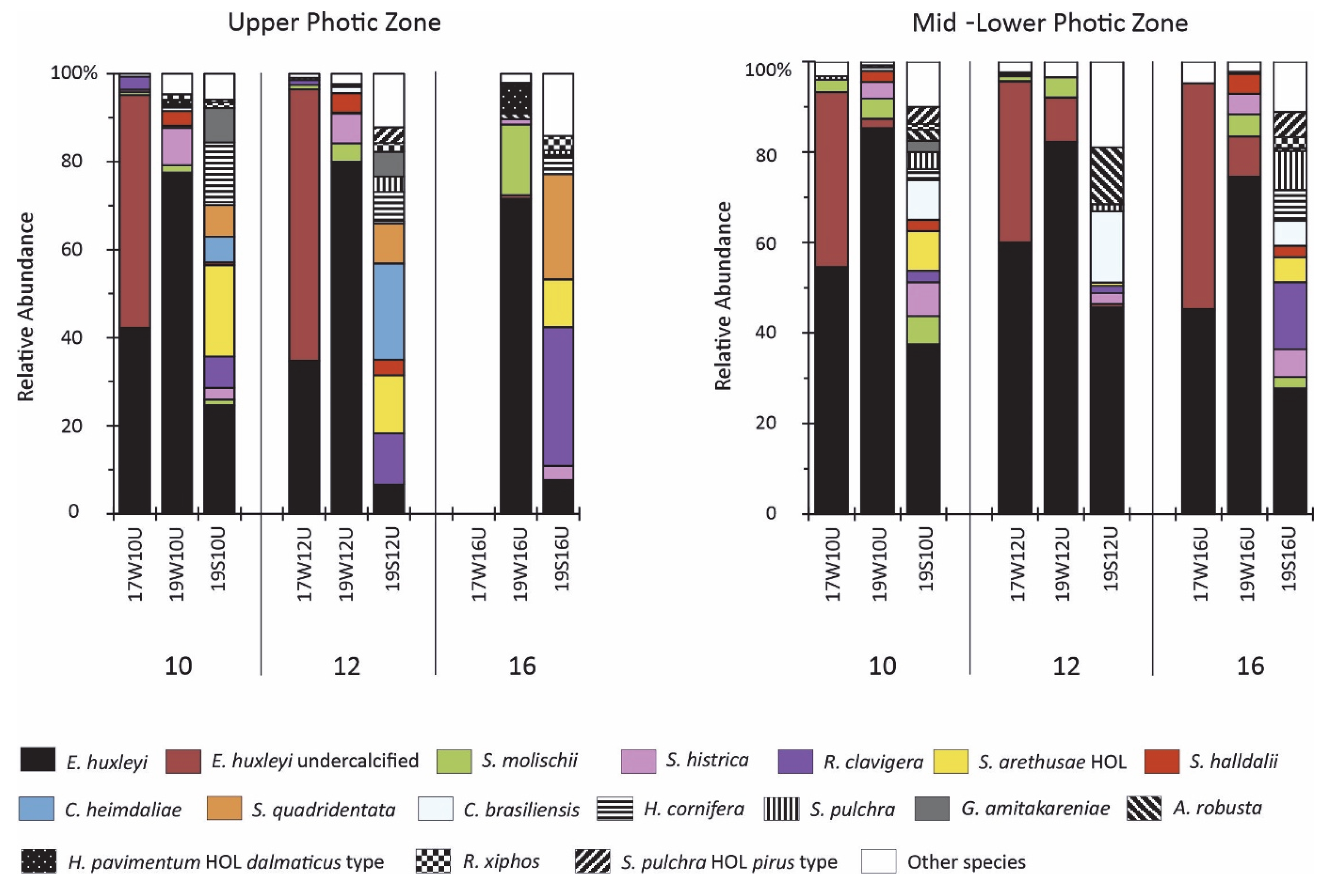
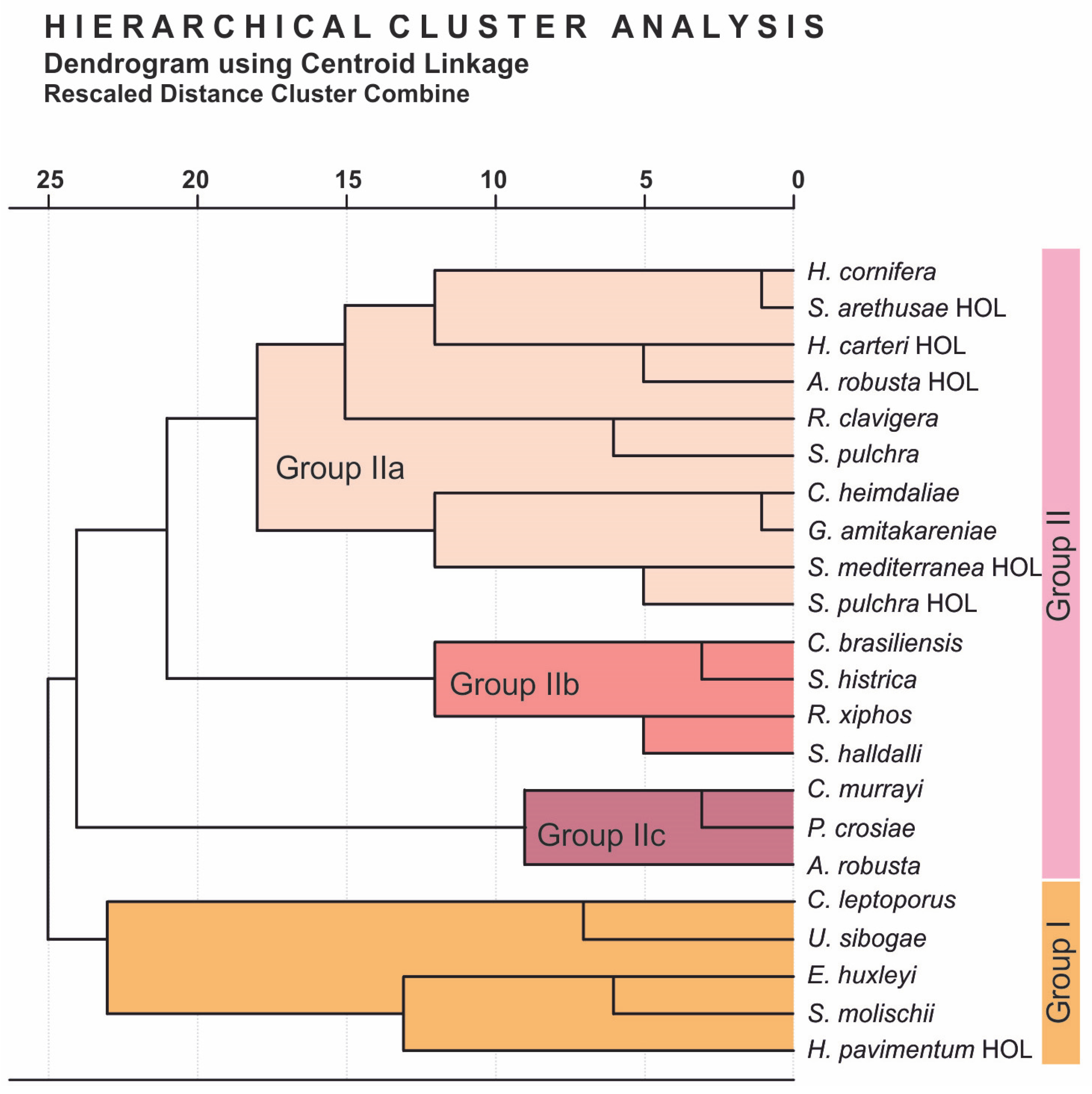
4.2. Coccolithophore Community Structure and E. huxleyi Coccolith Morphology
5. Discussion
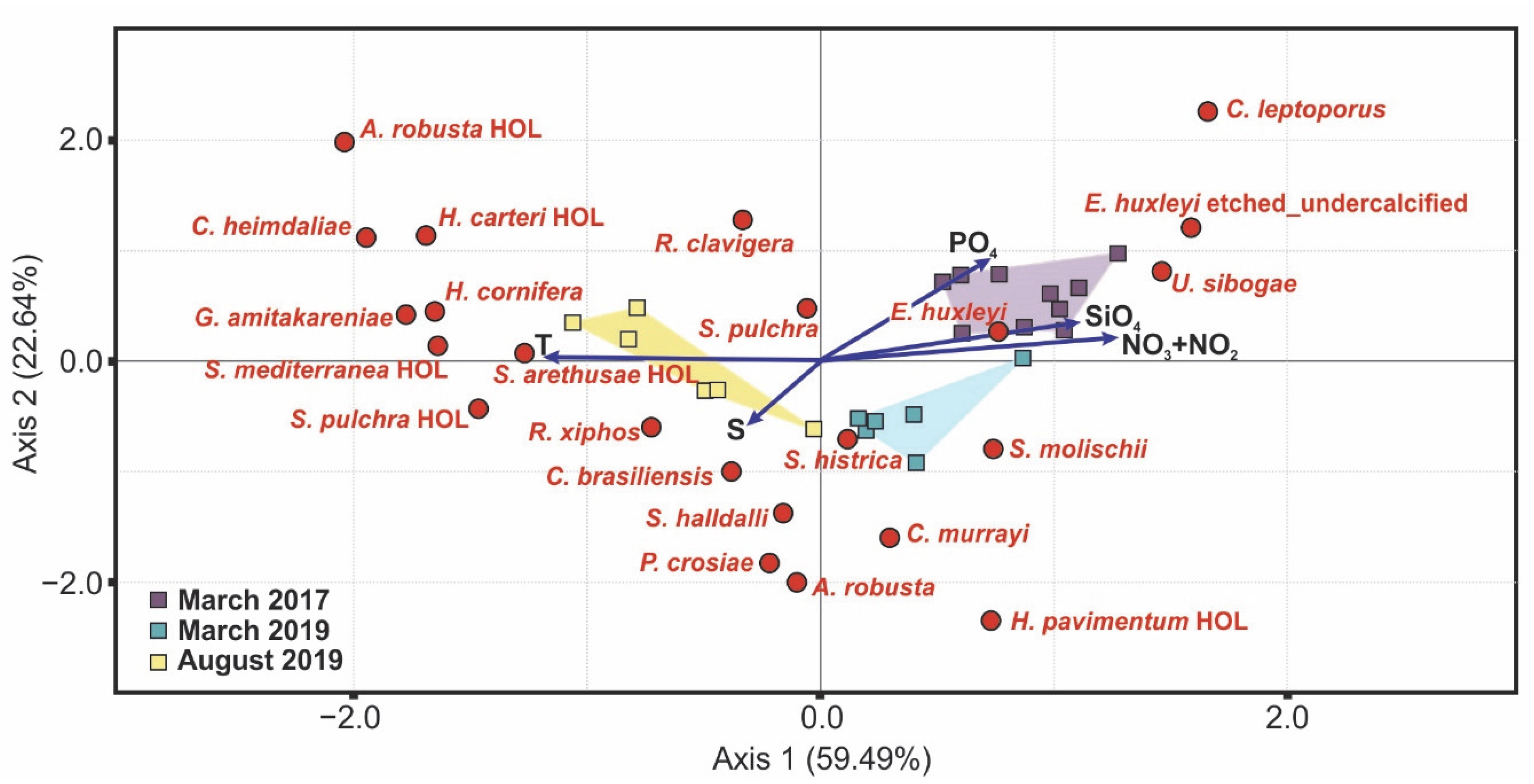
5.1. Assemblage Composition and Dominant Species
5.2. Imprint of the Extreme 2016–2017 Winter on South Aegean Sea Coccolithophore Abundance
5.3. Μorphological Patterns of E. huxleyi
6. Conclusions
- A distinct imprint of seasonality patterns on coccolithophore abundance, diversity, and assemblage was observed across the stations in the South Aegean Sea, mainly affected by temperature, NO3 + NO2, and SiO4. Both the March 2017 and 2019 sampled assemblages were dominated by E. huxleyi and other r-strategist taxa typical of lower temperatures and increased nutrient conditions. The March 2017 assemblage was mainly featured by high dominance of E. huxleyi, with etched/undercalcified specimens, while the March 2019 assemblages were more diverse and presented higher contributions of other taxa, e.g., Syracosphaeracea. The August 2019 coccolithophore community was characterized by high diversity, with abundant holococcolithophores and other K-strategist taxa.
- The South Aegean Sea coccolithophore assemblages appear to have been affected by the extreme winter of 2016–2017, as evidenced by noticeably lower overall coccosphere densities (March 2017: max.17.8 × 103 coccospheres L−1 in mid-lower photic zone; March 2019: max 27.7 × 103 coccospheres L−1 in upper photic zone), species richness, and diversity, and even the complete absence of coccospheres in some cases, accompanied by the significant presence of diatoms. The decreased coccosphere densities during March 2017 may be attributed to nitrogen enrichment in the photic zone following strong mixing of the water column, which caused a prolonged diatom bloom, resulting in a delay in the regular phytoplanktonic succession. The resulting nitrogen-limited setting, coupled with the enhanced CO2 concentration in surface waters promoted by the extremely cold conditions and wind stress on the ocean surface, probably caused the etching/undercalcification mostly, but not only, in E. huxleyi coccoliths. By contrast, the March 2019 assemblages reflected the dominance of heavily calcified E. huxleyi, demonstrating the return to the typical calcification pattern in the Aegean. The coccolithophore assemblage and morphology responses during March 2017 may provide evidence for the expected increased acidification and nitrogen-limiting conditions in the future.
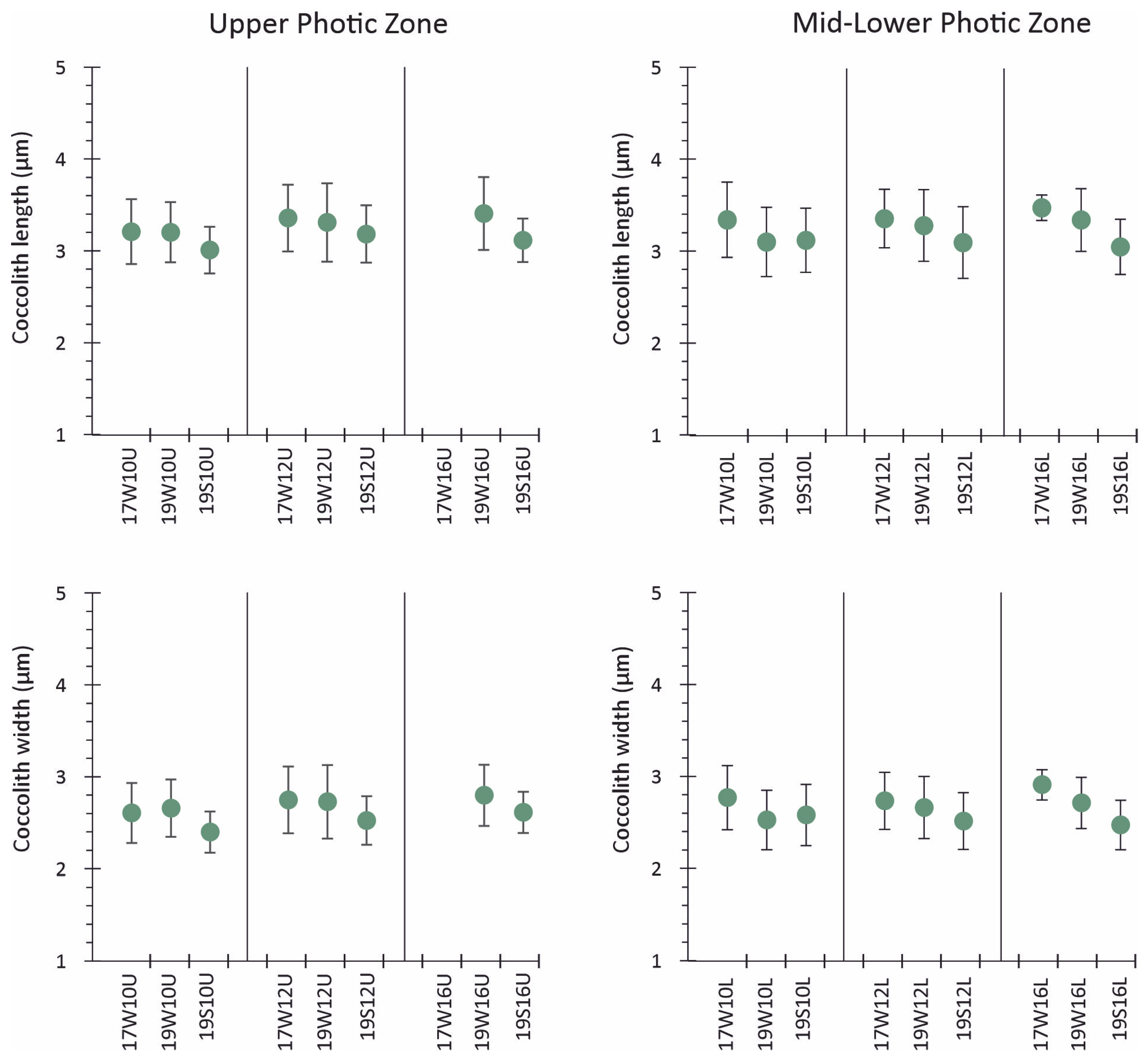
- Morphometric analysis of E. huxleyi coccolith length and width from March 2017 revealed overall slightly higher values as compared to those from March 2019. Lower size of E. huxleyi coccoliths was observed during August 2019, following the seasonal calcification variability of the Aegean Sea.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DWF | Dense Water Formation |
| SST | Sea Surface Temperature |
| SSS | Sea Surface Salinity |
| BSW | Black Sea Water |
| LW | Levantine Water |
| LIW | Levantine Intermediate Water |
| AMC | Asia Minor Current |
| CIW | Cretan Intermediate Water |
| CDW | Cretan Deep Water |
| MAW | Modified Atlantic Water |
| TMW | Transient Mediterranean Water |
| HCMR | Hellenic Centre for Marine Research |
| EMT | Eastern Mediterranean Transient |
| ENSO | El Niño-Southern Oscillation |
References
- Haidar, A.T.; Thierstein, H.R. Coccolithophore Dynamics off Bermuda (N. Atlantic). Deep-Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 1925–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, B.; Riebesell, U. Coccolithophores and the Biological Pump: Responses to Environmental Changes. In Coccolithophores: From Molecular Processes to Global Impact; Thierstein, H.R., Young, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2004; pp. 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbroek, P.; Brown, C.W.; van Bleijswijk, J.; Brownlee, C.; Brummer, G.J.; Conte, M.; Egge, J.; Fernández, E.; Jordan, R.; Knappertsbusch, M.; et al. A Model System Approach to Biological Climate Forcing. The Example of Emiliania huxleyi. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1993, 8, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dermitzakis, M.D. Seasonality and Ecology of Living Coccolithophores in Eastern Mediterranean Coastal Environments (Andros Island, Middle Aegean Sea). Micropaleontology 2008, 54, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiza, M.D.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Malinverno, E.; Psarra, S.; Karatsolis, B.-T.; Mara, P.; Lagaria, A.; Gogou, A. The Composition and Distribution of Living Coccolithophores in the Aegean Sea (NE Mediterranean). Micropaleontology 2015, 61, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Krasakopoulou, E. Diversification of Phytoplankton Community Structure and Related Parameters along a Large-Scale Longitudinal East-West Transect of the Mediterranean Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinverno, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Stavrakakis, S.; Ziveri, P.; Lykousis, V. Seasonal and Spatial Variability of Coccolithophore Export Production at the South-Western Margin of Crete (Eastern Mediterranean). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2009, 71, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Ziveri, P.; Tselepides, A. Coccolithophore Export Production and Response to Seasonal Surface Water Variability in the Oligotrophic Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean). Micropaleontology 2004, 50 (Suppl. 1), 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Malinverno, E.; Lianou, V.; Souvermezoglou, E. Seasonal Variation in Emiliania Huxleyi Coccolith Morphology and Calcification in the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Geobios 2010, 43, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatsolis, B.-T.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Malinverno, E.; Lagaria, A.; Mara, P.; Archontikis, O.; Psarra, S. Coccolithophore Assemblage Response to Black Sea Water Inflow into the North Aegean Sea (NE Mediterranean). Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 149, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkitzi, I.; Psarra, S.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Pavlidou, A.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Velaoras, D.; Papathanassiou, E.; Pagou, K. Phytoplankton dynamics and bloom formation in the oligotrophic Eastern Mediterranean: Field studies in the Aegean, Levantine and Ionian seas. Deep-Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2020, 171, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Rickaby, R.E.M. Size-Dependent Dynamics of the Internal Carbon Pool Drive Isotopic Vital Effects in Calcifying Phytoplankton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 373, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, J.; Herrle, J.O. Morphological Variation of Emiliania huxleyi and Sea Surface Salinity. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 255, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, G.; Benner, I. Effect of Elevated Nitrate Concentration on Calcification in Emiliania huxleyi. J. Nannoplankton Res. 2009, 30, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasche, E. A Review of the Coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae), with Particular Reference to Growth, Coccolith Formation, and Calcification-Photosynthesis Interactions. Phycologia 2001, 40, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, N.; Wilbur, K.M. Effects of Temperature on Growth, Calcification, and Coccolith Form in Coccolithus huxleyi (Coccolithineae). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1966, 11, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skampa, E.; Triantaphyllou, M.V.; Dimiza, M.D.; Gogou, A.; Malinverno, E.; Stavrakakis, S.; Panagiotopoulos, I.P.; Parinos, C.; Baumann, K.-H. Coupling Plankton—Sediment Trap—Surface Sediment Coccolithophore Regime in the North Aegean Sea (NE Mediterranean). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2019, 152, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Georgopoulos, D.; Drakopoulos, P.G. The Role of the North Aegean in Triggering the Recent Eastern Mediterranean Climatic Changes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 26103–26116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Krokos, G.; Velaoras, D.; Korres, G. An Internal Mechanism Driving the Alternation of the Eastern Mediterranean Dense/Deep Water Sources. In The Mediterranean Sea: Temporal Variability and Spatial Patterns; edited by Borzelli, G.L.E., Gaèiæ, M., Lionello, P., Malanotte-Rizzoli, P., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series; John Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Velaoras, D.; Krokos, G.; Nittis, K.; Theocharis, A. Dense Intermediate Water Outflow from the Cretan Sea: A Salinity Driven, Recurrent Phenomenon, Connected to Thermohaline Circulation Changes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 4797–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Papadopoulos, V.P.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Papageorgiou, D.K.; Pavlidou, A. The Response of the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean) to the Extreme 2016–2017 Winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9416–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Christaki, U.; Mazzocchi, M.G.; Montresor, M.; Ribera d’Alcalá, M.; Vaqué, D.; Zingone, A. Plankton in the open Mediterranean Sea: A review. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 1543–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijne, A. Holococcolithophorids from the Indian ocean, red sea, Mediterranean Sea and north atlantic ocean. Mar. Micropaleontol. 1991, 17, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebesell, U.; Zondervan, I.; Rost, B.; Tortell, P.D.; Zeebe, R.E.; Morel, F.M. Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO2. Nature 2000, 407, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; John, U.; Ziveri, P.; Reichart, G.-J.; Hoins, M.; Sluijs, A.; Rost, B. Ocean Acidification Reduces Growth and Calcification in a Marine Dinoflagellate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasakopoulou, E.; Souvermezoglou, E.; Giannoudi, L.; Goyet, C. Carbonate System Parameters and Anthropogenic CO2 in the North Aegean Sea during October 2013. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 149, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykousis, V.; Chronis, G.; Tselepides, A.; Price, N.B.; Theocharis, A.; Siokou-Frangou, I.; Van Wambeke, F.; Danovaro, R.; Stavrakakis, S.; Duineveld, G.; et al. Major Outputs of the Recent Multidisciplinary Biogeochemical Researches Undertaken in the Aegean Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 33–34, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Balopoulos, E.; Kioroglou, S.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Iona, A. A Synthesis of the Circulation and Hydrography of the South Aegean Sea and the Straits of the Cretan Arc (March 1994–January 1995). Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 469–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Theocharis, A.; Georgopoulos, D. Circulation and Hydrography of the Open Seas. In State of the Hellenic Marine Environment; Papathanassiou, E., Zenetos, A., Eds.; HCMR Publications: Athens, Greece, 2005; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Souvermezoglou, Ε.; Krasakopoulou, Ε.; Pavlidou, A. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Nutrients and Oxygen in the North Aegean Sea during the Last Thirty Years. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2014, 15, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Georgopoulos, D.; Chronis, G.; Zervakis, V.; Lykousis, V.; Poulos, S.; Iona, A. Hydrology and circulation in the southern Cretan Sea during the CINCS experiment (May 1994–September 1995). Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 46, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarra, S.; Tselepides, A.; Ignatiades, L. Primary Productivity in the Oligotrophic Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean): Seasonal and Interannual Variability. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 46, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souvermezoglou, E.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Pavlidou, A. Temporal variability in oxygen and nutrients concentrations in the southern Aegean Sea and the straits of the Cretan Arc. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 573–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselepides, A.A.; Zervakis, V.; Polychronaki, T.; Danovaro, R.; Chronis, G. Distribution of nutrients and particulate organic matter in relation to the prevailing hydrographic features of the Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean). Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 46, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakakis, S.; Chronis, G.; Tselepides, A.; Heussner, S.; Monaco, A.; Abassi, A. Downward Fluxes of Settling Particles in the Deep Cretan Sea (NE Mediterranean). Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 46, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L.; Psarra, S.; Zervakis, V.; Pagou, K.; Souvermezoglou, E.; Assimakopoulou, G.; Gotsis-Skretas, O. Phytoplankton size-based dynamics in the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 36, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.W.; Winter, A. Assemblages of Coccolithophorids and Other Living Microplankton off the Coast of Puerto Rico during January–May 1995. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2000, 39, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.R.; Geisen, M.; Cros, L.; Kleijne, A.; Probert, I.; Østergaard, J.B. A Guide to Extant Coccolithophore Taxonomy. J. Nannoplankton Res. 2003, S1, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.R.; Bown, P.R.; Lees, J.A.; Nannotax3 website. International Nannoplankton Association. Available online: www.mikrotax.org/Nannotax3 (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.R.; Poulton, A.J.; Tyrrell, T. Morphology of Emiliania Huxleyi Coccoliths on the Northwestern European Shelf—Is There an Influence of Carbonate Chemistry? Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4771–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.R.; Kucera, M.; Chung, H.-W. Automated Biometrics on Captured Light Microscope Images of Coccoliths of Emiliania huxleyi. In Microfossils and Oceanic Environments; University of Wales, Aberystwyth Press: Aberystwyth, UK, 1996; pp. 261–277. [Google Scholar]
- Acker, J.G.; Leptoukh, G. Online analysis enhances use of NASA earth science data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2007, 88, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.R. Variation in Emiliania huxleyi coccolith morphology in samples from the Norwegian EHUX experiment, 1992. Sarsia 1994, 79, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addante, M.; Grelaud, M.; Langer, G.; Maiorano, P.; Bonomo, S.; Álvarez, M.; Johnson, R.; Ziveri, P. Local Hydrodynamic in Coastal System Affects the Coccolithophore Community at a Short Spatial Scale. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2023, 185, 102309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerino, F.; Malinverno, E.; Fornasaro, D.; Kralj, M.; Cabrini, M. Coccolithophore Diversity and Dynamics at a Coastal Site in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros Miguel, L. Planktonic Coccolithophores of the NW Mediterranean. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo, S.; Placenti, F.; Quinci, E.M.; Cuttitta, A.; Genovese, S.; Mazzola, S.; Bonanno, A. Living Coccolithophores Community from Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Central Mediterranean—Summer 2009). Mar. Micropaleontol. 2017, 131, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappertsbusch, M. Geographic Distribution of Living and Holocene Coccolithophores in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Micropaleontol. 1993, 21, 219–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skejić, S.; Arapov, J.; Kovačević, V.; Bužančić, M.; Bensi, M.; Giani, M.; Bakrač, A.; Mihanović, H.; Gladan, Ž.N.; Urbini, L.; et al. Coccolithophore Diversity in Open Waters of the Middle Adriatic Sea in Pre- and Post-Winter Periods. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2018, 143, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godrijan, J.; Young, J.R.; Marić Pfannkuchen, D.; Precali, R.; Pfannkuchen, M. Coastal Zones as Important Habitats of Coccolithophores: A Study of Species Diversity, Succession, and Life-cycle Phases. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 1692–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijne, A. Morphology, Taxonomy and Distribution of Extant Coccolithophorids (Calcareous Nannoplankton); Drukkerij FEBO BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Andruleit, H.; Rogalla, U. Coccolithophores in Surface Sediments of the Arabian Sea in Relation to Environmental Gradients in Surface Waters. Mar. Geol. 2002, 186, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuter, S.; Koplovitz, G.; Torfstein, A.; Frada, M.J. Two-Year Seasonality (2017, 2018), Export and Long-Term Changes in Coccolithophore Communities in the Subtropical Ecosystem of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Deep-Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2023, 191, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Rost, B.; Hilbrecht, H.; Elbrächter, M. Vertical and horizontal distribution of coccolithophores in the Caribbean Sea. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2002, 22, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Pagou, K.; Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, M.; Ignatiades, L. Seasonal horizontal and vertical variability in primary production and standing stocks of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the Cretan Sea and the Straits of the Cretan Arc (March 1994–January 1995). Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 625–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, B.; Ziveri, P.; Grelaud, M.; Oviedo, A.; Kralj, M. Coccolithophore Haploid and Diploid Distribution Patterns in the Mediterranean Sea: Can a Haplo-Diploid Life Cycle Be Advantageous under Climate Change? J. Plankton Res. 2017, 39, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuter, S.; Silverman, J.; Krom, M.D.; Sisma-Ventura, G.; Yu, J.; Tsemel, A.; Ben-Ezra, T.; Sher, D.; Reich, T.; Koplovitz, G.; et al. Seasonal Patterns of Coccolithophores in the Ultra-Oligotrophic South-East Levantine Basin, Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2022, 175, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.W.; Abe, K.; Cruz, J.; Eriksen, R.; Guerreiro, C.; Hagino, K.; Heldal, M.; Hernández-Becerril, D.U.; Malinverno, E.; Nishida, S.; et al. Observations on the Morphological Diversity and Distribution of Two Siliceous Nannoplankton Genera, Hyalolithus and Petasaria. Micropaleontology 2015, 61, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Mohan, R.; Shetye, S.; Gazi, S.; Jafar, S.A. Prymnesium neolepis (Prymnesiaceae), a Siliceous Haptophyte from the Southern Indian Ocean. Micropaleontology 2014, 60, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Noël, M.-H.; Nakayama, T.; Naganuma, T.; Inouye, I. A Haptophyte Bearing Siliceous Scales: Ultrastructure and Phylogenetic Position of Hyalolithus neolepis Gen. et Sp. Nov. (Prymnesiophyceae, Haptophyta). Protist 2006, 157, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, E.; Incarbona, A.; Bonomo, S.; Pelosi, N. Coccolithophores in Water Samples and Fossil Assemblages in Sedimentary Archives of the Mediterranean Sea: A Review. In New Oceanography Research Developments; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 127–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomo, S.; Grelaud, M.; Incarbona, A.; Malinverno, E.; Placenti, F.; Bonanno, A.; Di Stefano, E.; Patti, B.; Sprovieri, M.; Genovese, S.; et al. Living Coccolithophores from the Gulf of Sirte (Southern Mediterranean Sea) during the Summer of 2008. Micropaleontology 2012, 58, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, A.; Ziveri, P.; Álvarez, M.; Tanhua, T. Is Coccolithophore Distribution in the Mediterranean Sea Related to Seawater Carbonate Chemistry? Ocean Sci. 2015, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D. Atmospheric Processes over the Broader Mediterranean Region: Effect of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation? Atmosphere 2024, 15, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Ocean Service. Available online: https://origin.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ONI_v5.php (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Yun, M.; Narale, D.D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Thangaraj, S. IOD-ENSO interaction with natural coccolithophore assemblages in the tropical eastern Indian Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 193, 102545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoucheas, P.; Koukousioura, O.; Psarra, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Dimiza, M.D.; Skampa, E.; Michailidis, I.; Nomikou, P.; Triantaphyllou, M.V. Phytoplankton Community Structure Changes during Autumn and Spring in Response to Environmental Variables in Methana, Saronikos Gulf, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33854–33865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulou, I.; Skampa, E.; Varkitzi, I.; Dimiza, M.D.; Parinos, C.; Kambouri, G.; Stavrakaki, I.; Gogou, A.; Triantaphyllou, M.V. The Contribution of Siliceous Plankton to Vertical Export Flux in the Eastern Mediterranean: A Comparative Study of the North Aegean, Cretan, and Ionian Seas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgis, A.P.; Georgopoulos, D.; Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Mikkelsen, O.A.; Pagou, K.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Pavlidou, A.; Anagnostou, C. Spatial and seasonal variability of particulate matter optical and size properties in the Eastern Mediterranean. Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 105, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, S.; Scalco, E.; Audic, S.; Vincent, F.; Veluchamy, A.; Poulain, J.; Wincker, P.; Ludicone, D.; de Vargas, C.; Bittner, L.; et al. Insights into global diatom distribution and diversity in the world’s ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1516–E1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkitzi, I.; Markogianni, V.; Pantazi, M.; Pagou, K.; Pavlidou, A.; Dimitriou, E. Effect of river inputs on environmental status and potentially harmful phytoplankton in a coastal area of eastern Mediterranean (Maliakos Gulf, Greece). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Temporal Succession and Spatial Heterogeneity in Phytoplankton. In Perspectives in Marine Biology; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1958; pp. 323–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaria, A.; Mandalakis, M.; Mara, P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Pitta, P.; Tsiola, A.; Kagiorgi, M.; Psarra, S. Phytoplankton Response to Saharan Dust Depositions in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: A Mesocosm Study. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 3, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broerse, A.T.C.; Brummer, G.-J.A.; Hinte, J.E.V. Coccolithophore Export Production in Response to Monsoonal Upwelling off Somalia (Northwestern Indian Ocean). Deep-Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 2179–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, L.; Taylor, A.R.; Lucken, U.; Ryan, K.P.; Brownlee, C. Calcification and Inorganic Carbon Acquisition in Coccolithophores. Funct. Plant Biol. 2002, 29, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, L.T.; Bauke, C.; Meier, K.J.S.; Riebesell, U.; Schulz, K.G. Influence of Changing Carbonate Chemistry on Morphology and Weight of Coccoliths Formed by Emiliania Huxleyi. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 3449–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, H.; Fujita, K.; Iguchi, A.; Inoue, M.; Iwasaki, S.; Kuroyanagi, A.; Maeda, A.; Manaka, T.; Moriya, K.; Takagi, H.; et al. Perspective on the Response of Marine Calcifiers to Global Warming and Ocean Acidification—Behavior of Corals and Foraminifera in a High CO2 World “Hot House”. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, G.; Nehrke, G.; Probert, I.; Ly, J.; Ziveri, P. Strain-Specific Responses of Emiliania huxleyi to Changing Seawater Carbonate Chemistry. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, V.; León, P.; Gordillo, F.J.L.; Jiménez, C.; Concepción, I.; Mackenzie, K.; Bresnan, E.; Segovia, M. High-CO2 Levels Rather than Acidification Restrict Emiliania huxleyi Growth and Performance. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amario, B.; Pérez, C.; Grelaud, M.; Pitta, P.; Krasakopoulou, E.; Ziveri, P. Coccolithophore Community Response to Ocean Acidification and Warming in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: Results from a Mesocosm Experiment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheward, R.M.; Poulton, A.J.; Young, J.R.; de Vries, J.; Monteiro, F.M.; Herrle, J.O. Cellular Morphological Trait Dataset for Extant Coccolithophores from the Atlantic Ocean. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Honjo, S. Distribution of Coccolithophores in Marginal Seas along the Western Pacific Ocean and in the Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 1975, 31, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båtvik, H.; Heimdal, B.R.; Fagerbakke, K.M.; Green, J.C. Effects of Unbalanced Nutrient Regime on Coccolith Morphology and Size in Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 1997, 32, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, G.; Jie, V.W.; Kottmeier, D.; Flori, S.; Sturm, D.; de Vries, J.; Harper, G.M.; Brownlee, C.; Wheeler, G. Distinct Physiological Responses of Coccolithus braarudii Life Cycle Phases to Light Intensity and Nutrient Availability. Eur. J. Phycol. 2022, 58, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimer, N.A.; Merrett, M.J. Calcification Rate in Emiliania Huxleyi Lohmann in Response to Light, Nitrate and Availability of Inorganic Carbon. New Phytol. 1993, 123, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, C.T.; Grubb, A.R.; Nissimov, J.I.; Natale, F.; Knapp, V.; Mui, A.; Fredricks, H.F.; Van Mooy, B.A.S.; Bidle, K.D. The mutual interplay between calcification and coccolithovirus infection. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1896–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.H.; Tarran, G.A.; Schroeder, D.; Cox, M.; Oke, J.; Malin, G. Isolation of viruses responsible for the demise of an Emiliania huxleyi bloom in the English Channel. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2002, 82, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeush, M.G.; Rajendran, S.; Valsala, V.; Pentakota, S.; Prasad, K.V.S.R.; Murtugudde, R. Variability, Trend and Controlling Factors of Ocean Acidification over Western Arabian Sea Upwelling Region. Mar. Chem. 2019, 209, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, P.J.; Aumont, O.; Bopp, L.; Mahaffey, C.; Tagliabue, A. Impact of Intensifying Nitrogen Limitation on Ocean Net Primary Production Is Fingerprinted by Nitrogen Isotopes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
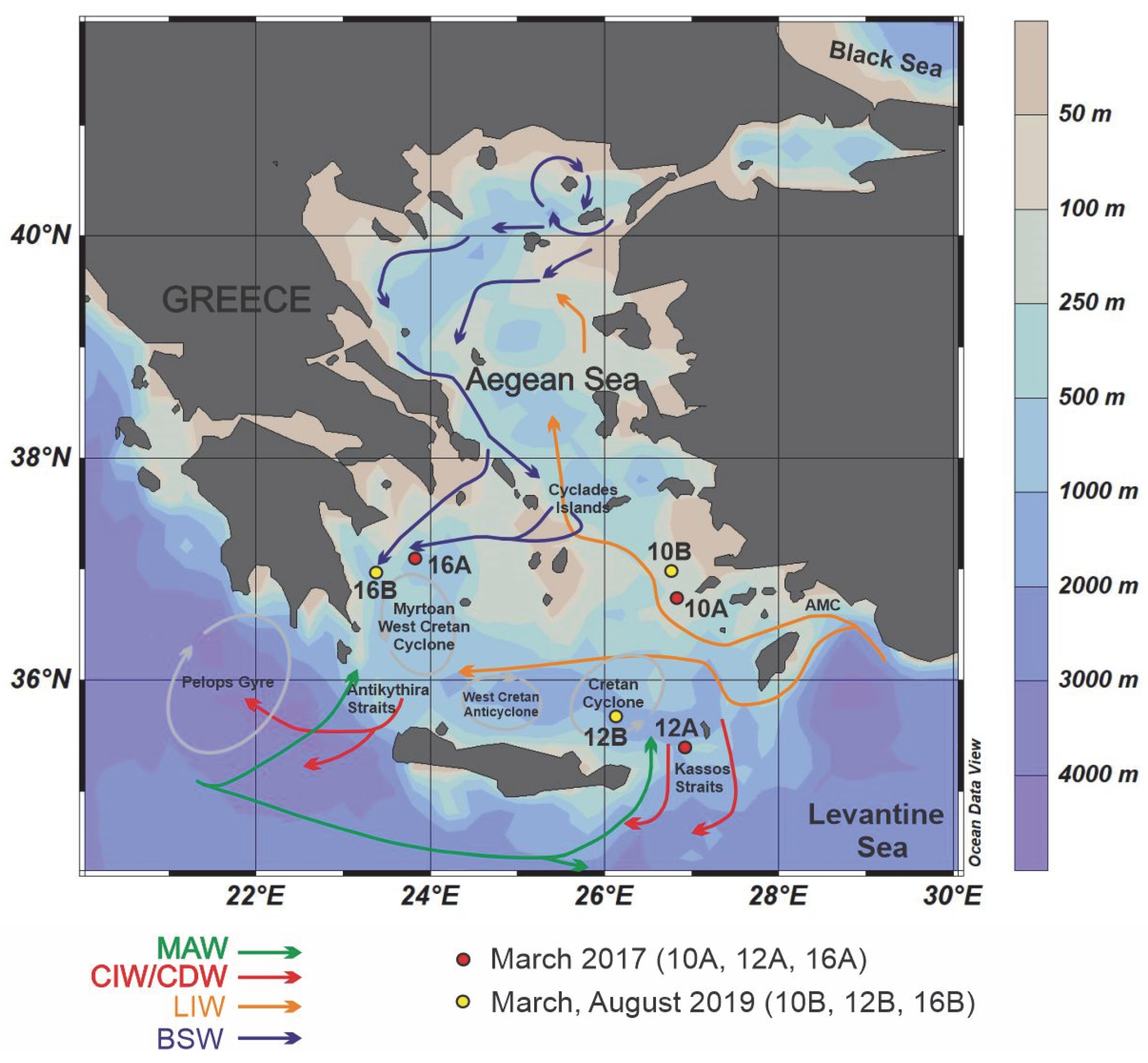
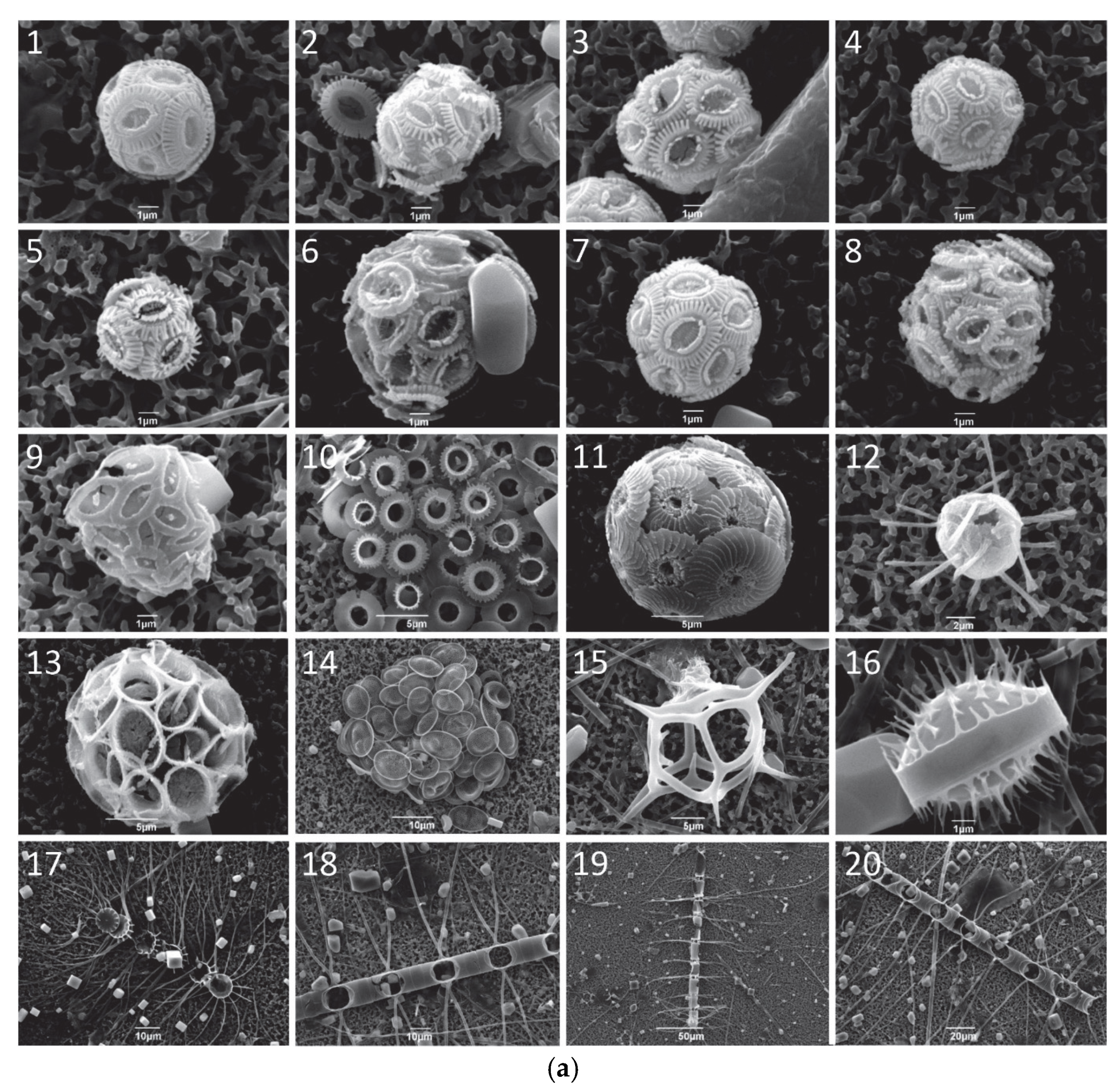

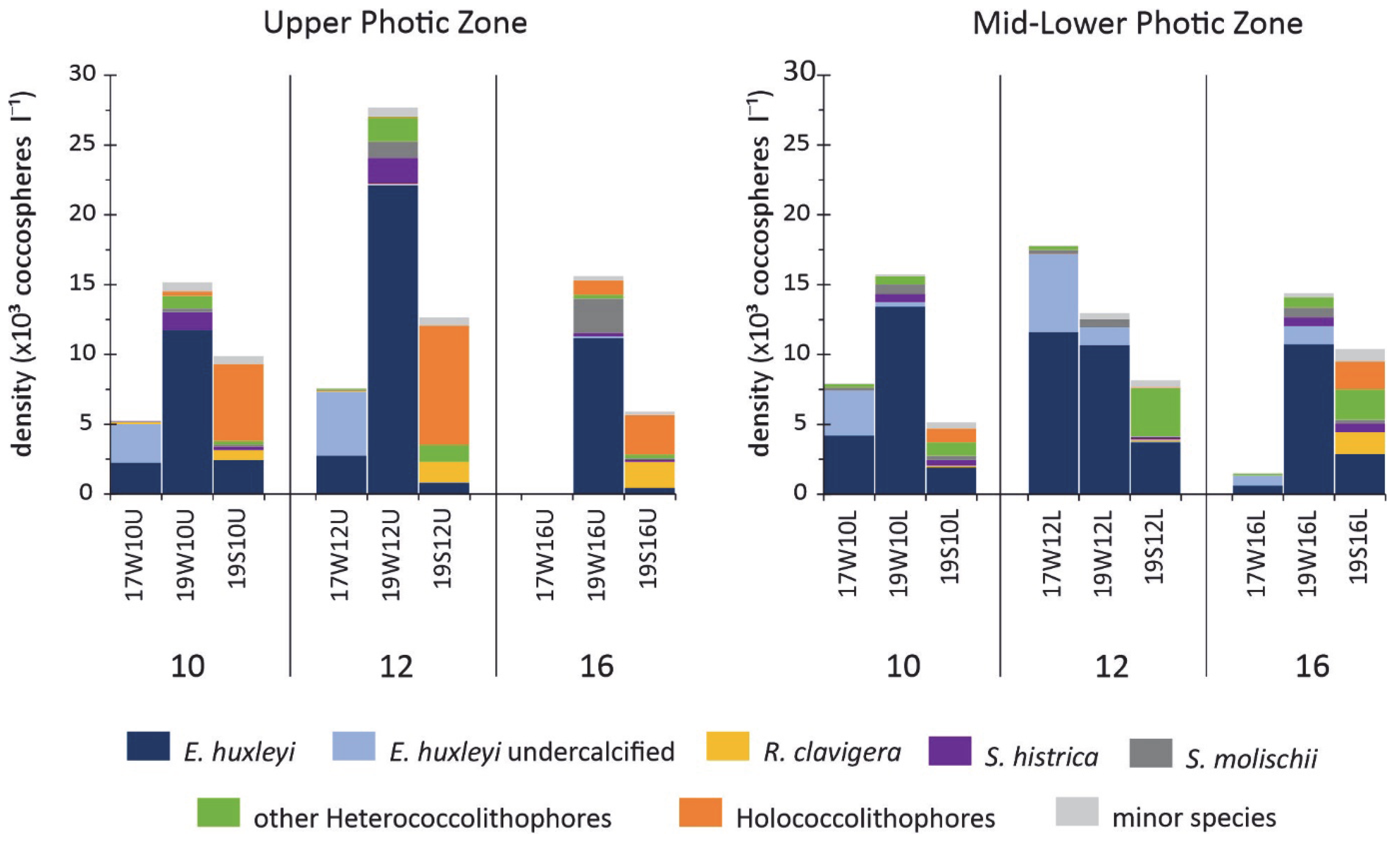
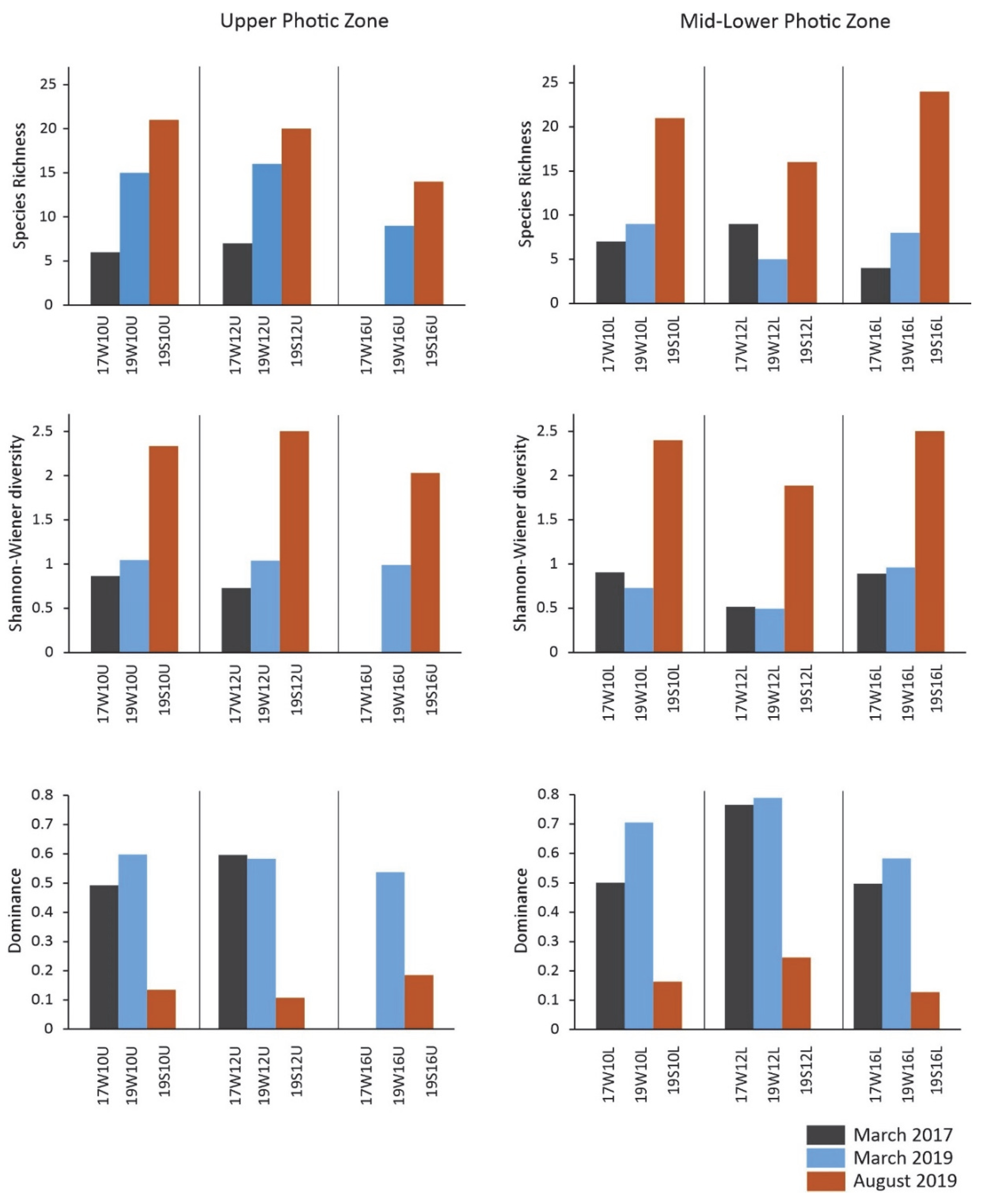
| Station Number | Sampling Code | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Sampling Period | Water Depth (m) | Temperature (°C) | Salinity (psu) | NO3− + NO2 (μmol/L) | SiO4 (μmol/L) | PO4 (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10A | 17W10U | 36°33′27.72″ | 26°42′17.28″ | March 2017 | 2, 10 | 16.32 | 39.16 | 0.53 | 1.67 | 0.02 |
| 17W10L | 50, 75 | 16.15 | 39.16 | 0.70 | 1.56 | 0.01 | ||||
| 12A | 17W12U | 35°15′17.64″ | 26°40′19.56″ | March 2017 | 2, 10 | 16.49 | 39.14 | 0.54 | 1.41 | 0.01 |
| 17W12L | 50, 75 | 16.15 | 39.15 | 0.58 | 1.29 | 0.02 | ||||
| 16A | 17W16U | 36°58′48″ | 23°57′36″ | March 2017 | 2, 10 | 15.67 | 39.10 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 0.04 |
| 17W16L | 50, 75 | 15.22 | 39.03 | 1.02 | 1.21 | 0.01 | ||||
| 10B | 19W10U | 37°0′32.4” | 26°37′15.6” | March 2019 | 20 | 17.33 | 39.37 | 0.557 | 1.049 | 0.01 |
| 19W10L | 75 | 17.33 | 39.37 | 0.593 | 0.942 | 0.01 | ||||
| 12B | 19W12U | 35°45′10.8″ | 26°13′40.8″ | March 2019 | 20 | 17.3 | 39.36 | 0.474 | 1.307 | 0.01 |
| 19W12L | 75 | 17.25 | 39.38 | 0.929 | 1.308 | 0.01 | ||||
| 16B | 19W16U | 36°48′18″ | 23°27′54″ | March 2019 | 20 | 15.59 | 39.17 | 0.277 | 1.522 | 0.01 |
| 19W16L | 75 | 15.36 | 39.14 | 1.120 | 1.601 | 0.01 | ||||
| 10B | 19S10U | 37°0′32.4″ | 26°37′15.6″ | August 2019 | 20 | 21.21 | 39.12 | 0.01 | 0.67 | 0.01 |
| 19S10L | 75 | 17.73 | 39.24 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 0.01 | ||||
| 12B | 19S12U | 35°45′10.8″ | 26°13′40.8″ | August 2019 | 20 | 22.13 | 39.32 | 0.01 | 0.798 | 0.01 |
| 19S12L | 75 | 17 | 39.27 | 0.62 | 0.96 | 0.01 | ||||
| 16B | 19S16U | 36°48′18″ | 23°27′54″ | August 2019 | 20 | 25.84 | 38.98 | 0.01 | 1.10 | 0.01 |
| 19S16L | 75 | 16.89 | 39.15 | 0.01 | 0.72 | 0.01 |
| T | S | NO3 + NO2 | PO4 | SiO4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. huxleyi | −0.223 | 0.376 | 0.339 | 0.108 | 0.379 |
| E. huxleyi etched/undercalcified | −0.669 | −0.380 | 0.557 | 0.676 | 0.675 |
| S. molischii | −0.036 | 0.333 | 0.060 | −0.331 | 0.113 |
| H. pavimentum HOL | 0.009 | 0.387 | −0.193 | −0.271 | 0.043 |
| C. leptoporus | −0.421 | −0.255 | 0.234 | 0.447 | 0.154 |
| U. sibogae | −0.310 | −0.120 | 0.264 | 0.255 | 0.245 |
| H. cornifera | 0.634 | −0.012 | −0.724 | −0.367 | −0.665 |
| S. arethusae HOL | 0.734 | 0.083 | −0.649 | −0.456 | −0.759 |
| H. carteri HOL | 0.452 | 0.086 | −0.535 | −0.271 | −0.387 |
| A. robusta HOL | 0.604 | 0.100 | −0.535 | −0.271 | −0.405 |
| R. clavigera | 0.589 | −0.119 | −0.704 | −0.041 | −0.446 |
| S. pulchra | 0.392 | −0.028 | −0.451 | −0.136 | −0.437 |
| C. heimdaliae | 0.454 | 0.223 | −0.426 | −0.216 | −0.422 |
| G. amitakareniae | 0.539 | 0.100 | −0.535 | −0.271 | −0.571 |
| S. mediterranea HOL | 0.430 | 0.223 | −0.426 | −0.216 | −0.445 |
| S. pulchra HOL | 0.477 | 0.038 | −0.632 | −0.320 | −0.661 |
| C. brasiliensis | 0.617 | 0.328 | −0.390 | −0.590 | −0.696 |
| S. histrica | 0.331 | 0.261 | −0.382 | −0.486 | −0.392 |
| R. xiphos | 0.656 | 0.414 | −0.735 | −0.546 | −0.662 |
| S. halldalii | 0.380 | 0.575 | −0.278 | −0.500 | −0.427 |
| C. murrayi | 0.157 | −0.118 | 0.156 | −0.149 | −0.207 |
| P. crosiae | 0.142 | −0.171 | −0.085 | −0.216 | −0.359 |
| A. robusta | 0.099 | −0.254 | −0.299 | −0.320 | −0.331 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penales, P.J.F.; Skampa, E.; Dimiza, M.D.; Parinos, C.; Velaoras, D.; Pavlidou, A.; Malinverno, E.; Gogou, A.; Triantaphyllou, M.V. Coccolithophore Assemblage Dynamics and Emiliania huxleyi Morphological Patterns During Three Sampling Campaigns Between 2017 and 2019 in the South Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean). Geosciences 2025, 15, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070268
Penales PJF, Skampa E, Dimiza MD, Parinos C, Velaoras D, Pavlidou A, Malinverno E, Gogou A, Triantaphyllou MV. Coccolithophore Assemblage Dynamics and Emiliania huxleyi Morphological Patterns During Three Sampling Campaigns Between 2017 and 2019 in the South Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean). Geosciences. 2025; 15(7):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070268
Chicago/Turabian StylePenales, Patrick James F., Elisavet Skampa, Margarita D. Dimiza, Constantine Parinos, Dimitris Velaoras, Alexandra Pavlidou, Elisa Malinverno, Alexandra Gogou, and Maria V. Triantaphyllou. 2025. "Coccolithophore Assemblage Dynamics and Emiliania huxleyi Morphological Patterns During Three Sampling Campaigns Between 2017 and 2019 in the South Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean)" Geosciences 15, no. 7: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070268
APA StylePenales, P. J. F., Skampa, E., Dimiza, M. D., Parinos, C., Velaoras, D., Pavlidou, A., Malinverno, E., Gogou, A., & Triantaphyllou, M. V. (2025). Coccolithophore Assemblage Dynamics and Emiliania huxleyi Morphological Patterns During Three Sampling Campaigns Between 2017 and 2019 in the South Aegean Sea (Greece, NE Mediterranean). Geosciences, 15(7), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15070268












