Abstract
Remotely sensed data, including rainfall estimates and digital elevation models (DEMs), are increasingly available at various temporal and spatial scales, offering new opportunities for rainfall regionalization in regions with limited ground-based observations. We evaluate the efficacy of NASA’s Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) rainfall estimates and SRTM-derived elevation data as alternative spatial covariates for regionalizing average and extreme rainfall patterns across Greece. Using the Bilinear Surface Smoothing (BSS) framework, we assess and compare the regionalization of average daily rainfall and average annual maximum rainfall across multiple timescales (0.5 h to 48 h) by leveraging both IMERG-derived estimates and the elevation data as covariates. Additionally, the BSS framework is herein extended to provide Bayesian credible intervals for the final estimates, using the posterior variance estimate and the equivalent degrees of freedom determined through the Generalized Cross Validation error minimization procedure. Elevation-based models outperformed IMERG, particularly for indices of extreme rainfall, capturing the differential effects of orography. The exploration of the orographic effect based on the BSS framework revealed that the average annual rainfall maxima at small timescales exhibit a negative relation to elevation, which becomes positive and more significant with increasing timescale. However, IMERG proved valuable for regionalizing average daily rainfall, demonstrating its utility as a complementary tool. The results also underscore the role of temporal scale in regionalization efficiency of extreme rainfall, with higher accuracy observed at longer timescales (24 h and 48 h) and greater uncertainty at finer scales.
1. Introduction
Regional rainfall estimates have a pivotal role for hydrological design, water resources management, and broader applications in geosciences, including the designing of infrastructure and modeling of natural hazards such as floods, droughts, and landslides [1,2,3,4,5]. Typically, the most reliable source of rainfall information is obtained from ground-level measurements, either from automated censors or gauges managed by observers. Yet, such data refer to point measurements, which albeit indispensable are spatially sparse due to managerial and economic costs, with a declining availability observed in recent years [6]. This study addresses this critical gap by evaluating how satellite-derived rainfall and elevation data can enhance spatial rainfall estimation, especially in regions where in situ measurements are scarce.
Advances in earth observation, such as satellite products, reanalysis datasets, and weather radars, have provided additional rainfall information [7,8,9,10]. These products offer global coverage, frequent temporal updates, and the potential for near-real-time applications, making them invaluable tools for rainfall regionalization and hydrological modeling [11,12,13]. Among them, the satellite-based rainfall has received increased attention due to its global coverage and short latency that also supports operational applications. Still, such sources cannot replace traditional ground-based rainfall information due to their short length (<50 years), biases over different regions, and increased uncertainties involved in the estimation of rainfall [6,14]. Therefore, it is crucial to estimate rainfall at ungauged locations utilizing the records from rainfall stations as the ground reference, a task that has attracted long-term efforts in geosciences and particularly hydrology [1].
There is a proliferation of methods to regionalize rainfall in space, ranging from traditional approaches in geostatistics, such as kriging-based approaches and the inverse-distance method, to smoothing based approaches as well as recent methods involving machine learning techniques such as neural networks [15,16,17,18,19,20]. In most cases, other than the spatial coordinates themselves, additional spatial covariates can increase the power of the regionalization. Covariates mainly include topographic features such as elevation, distance from the shore, slope, as well as atmospheric covariates and other sources of rainfall information [21,22,23]. Among them, elevation is the most common covariate due to its well-known effect on rainfall, the so-called orographic enhancement of precipitation, which is observed in mountainous regions globally [24].
While elevation has been widely explored as a covariate in the regionalization of daily rainfall extremes [1], its impact on sub-daily rainfall is still unclear. Iliopoulou et al. [25] in the regionalization of design rainfall relationships in Greece found elevation to control the scaling parameter of the intensity–timescale–return period relationships and postulated that a complex relationship occurs between elevation and multi-scale rainfall maxima that warrants further investigation. Similar results in terms of elevation were reported by Avanzi et al. [26] in Italy, who found a reverse orographic effect for small timescales. Mazzoglio et al. [22,27] examined various covariates for extreme rainfall in Italy and identified elevation as one of the most important ones, with increasing effect on the daily scale but a “reverse” effect on finer scales. Differential effects of elevation with respect to temporal scale were reported in other regional analyses [28].
Covariates from alternative data sources, including satellite-derived rainfall data, may be considered as promising for rainfall regionalization. Although satellite data have been actively studied as a replacement of conventional rain gauge data in rainfall frequency analyses, with results being mixed [25,29], the extent to which they can be useful as a covariate has been less explored in the literature, with only a few studies on the topic [30]. Koutsoyiannis et al. [31] employed IMERG data for the regionalization of average daily rainfall in Greece in the scope of climatic investigation and concluded that the IMERG data tend to underestimate the rainfall extremes. Yet, their potential in the regionalization of extreme rainfall variables has not been systematically evaluated till now.
We thus explored the effectiveness of two spatial covariates, namely elevation, derived from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) [32], and IMERG satellite rainfall estimates [7], in the regionalization of average daily and extreme rainfall patterns. We revisited the effect of elevation focusing on the average of sub-daily rainfall maxima and compared the strength of the effect across the different timescales. Further, we assessed the potential of IMERG rainfall data as an alternative covariate in rainfall regionalization by systematically comparing its performance to that of elevation. Despite known biases relative to gauge measurements, particularly during extreme events, IMERG offers consistent temporal coverage and dense spatial resolution, making it a potentially valuable covariate, particularly for capturing rainfall patterns in regions with limited gauge data. We examined the power of satellite-derived rainfall estimates for average daily rainfall and average maximum rainfall (also called “index-rainfall” in some of the literature [33]) across various timescales ranging from sub-hourly (0.5 h) to 48 h and to the regionalization of average daily rainfall and multi-scale average maximum rainfall, respectively. These were compared against the widely used elevation covariate to assess their effectiveness in capturing spatial rainfall variability of average and extreme rainfall patterns.
Both covariates were studied in the framework of the Bilinear Surface Smoothing method [18,19] designed for spatial regionalization that integrates additional explanatory variables while minimizing cross-validation errors. The BSS method has demonstrated robust performance, particularly in data-scarce regions [34], making it well-suited for addressing the challenges of spatial rainfall estimation [2,25]. The BSS framework is herein extended to incorporate Bayesian credible intervals, offering a new means of quantifying the uncertainty in regional rainfall estimates.
The methodology was applied over all of Greece, which serves as a challenging case study, encompassing highly diverse topography and rainfall patterns. The findings are herein discussed in view of practical applications of rainfall regionalization and novel insights into the spatial structure of average and extreme rainfall patterns across multiple temporal scales.
The remainder is structured as follows: The regionalization methodology, including the BSS framework, the credible intervals, and performance assessment, are presented in Section 2. Information on the study area and data sources is provided in Section 3. The results and discussion are presented in Section 4, and conclusions are provided in Section 5.
2. Methodology
2.1. Bilinear Surface Smoothing
A brief overview of the mathematical framework is presented since it is detailed in the aforementioned publications [18,19,34]. The general idea behind both methods is to compromise the trade-off between the objectives of minimizing the fitting error and the roughness of the fitted bilinear surface, therefore termed Bilinear Surface Smoothing (BSS). The larger the weight of the first objective, the rougher the surface will appear, while the opposite is true for a larger weight of the second objective.
The mathematical framework of BSS suggests that fitting is based on minimizing the Generalized Cross Validation error (GCV) [35] between the set of the given data points and the corresponding estimates.
The general estimation function, for a point z with spatial coordinates (x, y) on a plane, according to the BSS method, is
where d is the value of the fitted bilinear surface at that point.
The BSS method was extended by the introduction of an additional explanatory variable (Bilinear Surface Smoothing with an Explanatory variable; BSSE) available at a denser dataset compared to that of the main variable, as follows. We assume that at the locations of the given data points, we also know the value of an explanatory variable , and therefore, for each point z, there corresponds a value t. In this case, the general estimation function is
where d and e are the values of two fitted bilinear surfaces at that point. This is not a global linear relationship but a local linear one, as the quantities d and e change in space.
In the case of the BSS, there are four adjustable parameters for surface d: the numbers of intervals along the horizontal and vertical direction, respectively, i.e., mx, my, and the corresponding smoothing parameters τλx and τλy. The incorporation of the explanatory variable, for the BSSE case, adds two more adjustable parameters: the smoothing parameters τμx and τμy corresponding to surface . The values of all the smoothing parameters are restricted in the interval [0, 1) for both directions. When the smoothing parameters are close to 1, the resulting bilinear surfaces exhibit greater smoothness, whereas for small values of these parameters, interpolation among the known points is obtained.
A notable advantage of this method for regional analyses is its proven reliability, even when data are limited and sparse. This sets it apart from traditional geostatistical techniques, which typically require a denser network of data points to function effectively (e.g., semivariogram estimation for kriging) [34]. Additionally, the method is highly efficient, with fewer parameters and decisions needed during modeling. In contrast, the standard geostatistical approaches involve selection from numerous variants; selection of variogram between several models, e.g., linear, spherical, exponential, Gaussian, and power; and determining values for parameters such as range, sill, and nugget, adding both complexity and potential subjectivity, as no universally objective framework exists for these decisions.
2.2. Credible Intervals in the BSS Framework
Credible or Bayesian intervals treat their bounds as fixed and the estimated parameter as a random variable, whereas frequentist confidence intervals treat their bounds as random variables and the parameter as a fixed value. We delineate the assessment of credible intervals for the fitted bilinear surface using the BSS mathematical framework.
This approach leverages a Bayesian framework similar to the smoothing spline method [36] to account for uncertainty in the estimated variance. It incorporates the smoother matrix, residual sum of squares (RSS), and the posterior covariance matrix of the fitted surface. The residual errors are modeled as random variables with a certain variance, which reflects the unexplained variability in the data. By estimating the variance from the residual sum of squares and adjusting for the degrees of freedom, the Bayesian framework captures the uncertainty in this variance. This uncertainty is then propagated to the fitted values of the surface.
Using the variance, we built the posterior covariance matrix for the fitted surface. This matrix represents the variance of the fitted surface at each observation point, incorporating the estimated noise from residual errors. The credible intervals are derived from this posterior covariance, which directly reflects the variability of the surface values rather than the residuals themselves.
2.2.1. Formulation Based on the BSS Framework
In the BSS framework, a bilinear surface is fitted to a set of n observed data points corresponding to spatial coordinates (for i = 1, …, n) by minimizing the GCV. The observed data are the combination of two components: (a) the signal, i.e., the fitted surface that is the part of the data that the model tries to explain, i.e., , and (b) the noise, i.e., the random error that is the part of the data that is random or cannot be captured by the model, i.e., the residual errors. Thus, the model complies with the following relationship between the observed and fitted values:
where are the observed values at the data points, and is the estimation from the bilinear surface at point obtained through the smoothing process, i.e., the minimization of the GCV, while ri ∼ N(0, σ2) represents the normally distributed random residual errors with zero mean and variance σ2.
Equations (1) and (2) can be written in the following form to provide the fitted values at the observation points:
The smoother matrix A, which captures how the observed data are mapped to the fitted values, is for BSS
while for BSSE, it is
where
A := Π(ΠTΠ + λxΨxTΨx + λyΨyTΨy)–1ΠT
Matrix Π contains the weights of each element of the bilinear surfaces, while T is a diagonal matrix with its elements being the values of the explanatory variable at the given data points. Matrices Ψx and Ψy represent the smoothness of the bilinear surfaces and assure a unique solution of the fitting problem. The elements of these two matrices are the differences of slopes between consecutive segments of the bilinear surface according to the x and y directions. For the detailed definition of matrices Π, T, Ψx, and Ψy along with the estimation and transformation of the smoothing terms λx, λy and μx, μy, the reader may refer to [18].
By using the above-presented formulation, the procedure of acquiring the credible intervals follows.
2.2.2. Computation of the Residual Sum of Squares
The vector of residuals r, i.e., the difference between the observed values and the fitted values in the BSS framework, is defined as
The Residual Sum of Squares (RSS) measures the total squared difference between the observed values and the fitted surface, thus providing the total discrepancy between them:
2.2.3. Estimation of the Error Variance
The error variance σ2 represents the expected squared magnitude of the random errors ri, i.e., how much the observed values deviate from the true underlying surface due to randomness or uncertainty. This quantifies the uncertainty or variability in the data that is not explained by the model. This variance is key when constructing credible intervals, as it tells us how much we expect the actual observations to deviate from the fitted values due to random fluctuations or errors.
In the context of constructing credible intervals, the error variance plays a crucial role because it influences the width of the intervals since higher error variance means that the data are noisier, leading to wider credible intervals (greater uncertainty), and lower error variance indicates that the model fits the data well, leading to narrower credible intervals (less uncertainty).
The error variance is estimated by scaling the RSS by the effective residual degrees of freedom. Thus, in the BSS framework, the variance is estimated as
where ν represents the equivalent degrees of freedom for error, which indicates the degrees of freedom that remain after fitting the bilinear surface to the data. By analogy to regression, the equivalent degrees of freedom for the surface are ν = trace(A). This formulation for considers both the smoothing applied by A and the residual degrees of freedom that reflect how well the data are fit.
2.2.4. Posterior Covariance Matrix of the Fitted Surface and Credible Interval Assessment
To quantify the uncertainty in the fitted bilinear surface, we compute the posterior covariance matrix Σ of the fitted surface values. This matrix is given by
Σ = σ2 (I − A)
The diagonal elements of matrix Σ, i.e., Σii, represent the posterior variances of the fitted values at each observation point.
In typical cases, credible intervals can be computed using the normal distribution when the variance is known and accurately estimated. However, in practice, especially for finite sample sizes, the variance is estimated from the data and thus subject to uncertainty.
To account for this uncertainty in the estimated variance, we use the Student’s t-distribution for constructing the BSS’s credible intervals. The t-distribution adjusts for the fact that is estimated from the data rather than known, and the degrees of freedom are reduced by the smoothing process, which consumes some of the data’s information. This leads to more accurate credible intervals for the fitted surface compared to the normal distribution, especially when the equivalent degrees of freedom are less than 30. As those increase above this limit, the t-distribution converges to the normal distribution.
The credible intervals for the fitted bilinear surface at each observation point are given by
where is the fitted value at point , is the critical value from the Student’s t-distribution with ν = trace(I − A) degrees of freedom and confidence level 1 − α, and Σii is the ith diagonal element of the posterior covariance matrix Σ, representing the posterior variance of the fitted value at point .
This credible interval reflects uncertainty around each estimated point by means of the fitted surface, based on the observed data and prior information about the smoothness, as controlled by the smoothing parameters.
2.3. Regionalization Performance Assessment
The performance of regionalization was assessed using several criteria, including the mean bias error (MBE), mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), coefficient of determination (r2), the Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) [34], and the normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) [37]. The smoothness of each surface was quantified by the standard deviation, σ, of the estimates. However, relying on different statistical metrics to evaluate spatial interpolation methods may not accurately reflect the validity of the results beyond the locations included in the interpolation process. To address this issue, a leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) approach was also employed to evaluate the effectiveness of the interpolation methods between the two covariates (elevation and IMERG) based on the aforementioned criteria.
LOOCV is widely used for assessing spatial interpolation methods and has been applied extensively in water resources research, as documented by numerous studies [34,38,39]. This technique is also a standard feature in most Geographic Information System (GIS) software platforms.
Finally, a summary of the overall research workflow is presented in Figure 1. This diagram consolidates the methodological steps described above, providing a visual overview of the data sources, modeling procedures, uncertainty analysis, and validation framework employed in the study.
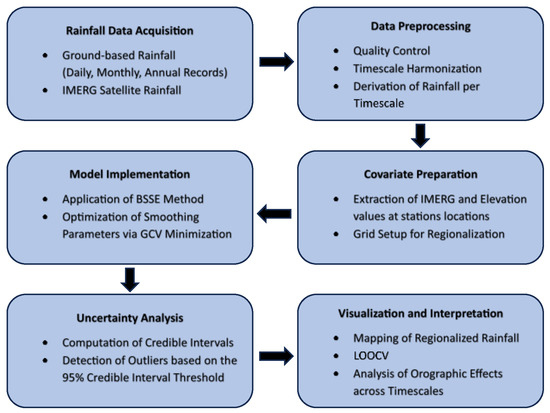
Figure 1.
Overview of the research workflow used for average and extreme rainfall regionalization.
3. Study Area and Data
3.1. Study Area
The study area is the entire Greek territory, spanning 131,957 km2 and including a multitude of islands and a diverse landscape (Figure 2). Although the climate is predominantly Mediterranean, there are considerable differences in rainfall distribution across the country. Particularly, Greece includes four climatic types (arid, temperate, cold, and polar) and 11 sub-types (BSh, BSk, Csa, Csb, Cfa, Cfb, Dsb, Dsc, Dfb, Dfc, and ET) based on Köppen–Geiger climate classification [40]. Daily rainfall averages range from 0.6 mm/day (approximately 219 mm/year) to 7.3 mm/day (around 2666 mm/year) [31]. Northwestern Greece receives the highest rainfall, while the driest areas include Athens, several Aegean islands, and parts of central Macedonia and Thessaly. The intricate interplay of topography and climate makes Greece a particularly challenging region for rainfall modeling [31], so the presented methodology and conclusions may be used as reference for other regions.
Figure 2.
Physical map of Greece (source: https://github.com/der-stefan/OpenTopoMap, CC BY-SA 3.0, accessed on 31 May 2025).
3.2. Ground-Based Data
Respecting the methodological framework summarized in Figure 1, the following sections describe the ground-based data sources employed to estimate average daily rainfall (Section 3.2.1) and average maximum rainfall across different scales (Section 3.2.2) to serve as ground reference for the regionalization experiments.
3.2.1. Daily and Monthly Records
We utilized ground-based observations from 128 stations, including records at both daily and monthly resolution, which were deemed sufficiently reliable for estimating average daily rainfall across Greece [31]. To address boundary-related issues in some experiments, the study area was extended to include neighboring regions, specifically sections of Turkey, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Albania.
The dataset comprises the following components:
- Stations with daily records: 61 rainfall series with over 60 years of data, 56 of which are sourced from the Hydroscope database (http://www.hydroscope.gr/, accessed on 10 February 2023) and 5 from the Greek Meteorological Service;
- Stations with monthly records within Greece: 31 rainfall series from the Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN), each spanning more than 30 years;
- Stations with monthly records from neighboring countries: 36 stations from the GHCN, located in Turkey, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Albania, also with data spanning over 30 years.
While the 56 Hydroscope records are directly accessible through its platform, the remaining records can be obtained via the KNMI Climate Explorer tool (http://climexp.knmi.nl/, accessed on 10 February 2023). All data underwent quality control in a prior study on Greek climatic trends [31]. The daily series, which represent the longest continuous records available in Greece, have also been utilized to derive rainfall intensity–duration–frequency relationships [25].
3.2.2. Annual Maxima Records
To derive the average annual maxima estimates across different temporal scales, we employed available records of annual maxima in Greece from a recent regionalization of design rainfall curves [25]. Following rigorous quality control, a dataset of 783 stations was employed (Table 1), which includes

Table 1.
Type and number of ground-based stations with data at each timescale.
- 503 daily rain gauges, with 130 situated at sites also equipped with a rain recorder;
- 280 rain recorders, providing sub-daily resolution data.
These stations are distributed across 651 unique geographic locations. The longest dataset is from a daily rain gauge in Athens, which spans the period from 1863 to 2022.
3.3. Satellite Data
We utilized satellite data from NASA’s Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Mission (IMERG, https://gpm.nasa.gov/data/imerg, https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni/ accessed on 8 November 2024) [7]. Specifically, precipitation estimates from the IMERG Final Precipitation L3 Half-Hourly 0.1° × 0.1° V06 product (GPM_3IMERGHH), which underwent post-processing gauge calibration, were retrieved for the entire geographical extent of Greece and its neighboring regions.
The dataset offers a spatial resolution of 0.1°, corresponding to 8991 grid points for the study area, 1373 of which represent the mainland portion of Greece. This high spatial resolution ensures excellent coverage, enabling the creation of detailed precipitation maps. The dataset spans from 1 June 2000 to 30 September 2021, covering a total of 21 hydrological years.
The temporal resolution of the IMERG data allows for their use in estimating both average daily rainfall across Greece and average annual maximum rainfall values over varying timescales.
3.4. Elevation Data
The elevation of each station to be incorporated as an additional explanatory variable was derived from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) dataset and available as 3 arc second, i.e., approximately 90 m resolution at the equator [32]. The SRTM data, with their high spatial resolution and global coverage, provide reliable elevation information that enhances the analysis by accounting for the impact of topography on rainfall patterns.
4. Results and Discussion
In view of BSSE implementation, the global minimum of GCV for every temporal scale was reached by implementing the methodology for different numbers of segments mx and my (1 ≤ mx ≤ 200, 1 ≤ my ≤ 200) and minimizing GCV for each combination by altering each one of the adjustable parameters, as detailed in [18]. Additionally, we assessed larger values of mx and my up to 1000 segments in either direction by setting each smoothing parameter to its minimum value (0.001) in order to reduce the computational effort. The results of the above procedure are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
BSSE optimal parameter values.
4.1. Regionalization of Average Daily Rainfall
The BSSE framework was first applied to the regionalization of average daily rainfall as estimated from the ground stations described in Section 3.2.1. Next, the BSSE model was applied by employing the elevation and the IMERG-derived average daily rainfall as alternative covariates.
The respective maps are shown in Figure 3, while the full dataset performance metrics and the LOOCV metrics are presented in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively. Both applications resulted in very good performance with high NSE values, considering the all-data statistics (0.9 and 0.74, respectively) and the LOOCV (0.74 and 0.67) evaluation as well. The elevation-based regionalization is, however, superior in both evaluations. The resulting surfaces (Figure 3) reveal similar climatic patterns, with higher rainfall rates in Western Greece and lower in the central part, yet the overall variability appears smoother in the IMERG-based map. In particular, the IMERG-based regionalization does not capture the range of variability apparent in the elevation-based regionalization, resulting in greater smoothing, as also depicted in terms of the standard deviation, σ, of the estimates (Table 3).
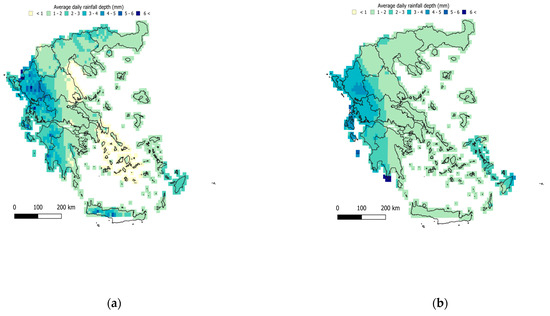
Figure 3.
Regionalized map of average daily rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.

Table 3.
Performance assessment statistics for the regionalization based on the elevation and IMERG covariates for average daily rainfall.

Table 4.
Performance assessment LOOCV statistics for the regionalization based on the elevation and IMERG covariates for average daily rainfall.
4.2. Regionalization of Average Maximum Rainfall for Different Scales
The regionalization experiments were repeated for the case of average annual maximum rainfall at different scales, i.e., 0.5 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h. For this evaluation, the respective IMERG-derived estimates (i.e., the average annual maximum rainfall depth at each temporal scale) were used in the IMERG-based regionalization. The maps are presented in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 for the 0.5 h, 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h cases. The performance assessment metrics are given in Table 5 and Table 6 considering all data and the LOOCV, respectively. The NSE values for both evaluations (elevation and IMERG) in terms of the timescale of rainfall maxima are shown in Figure 11.
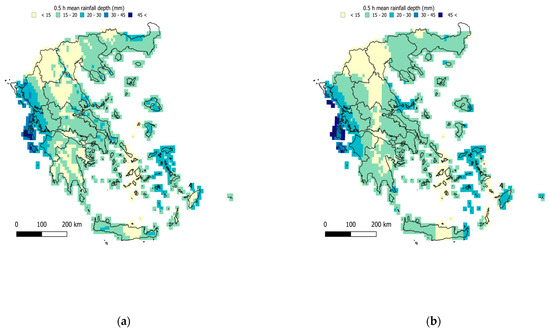
Figure 4.
Regionalized map of average 0.5 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
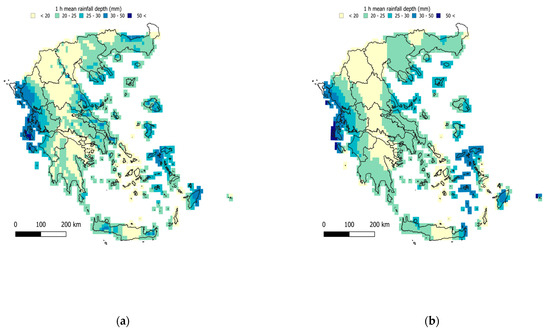
Figure 5.
Regionalized map of average 1 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
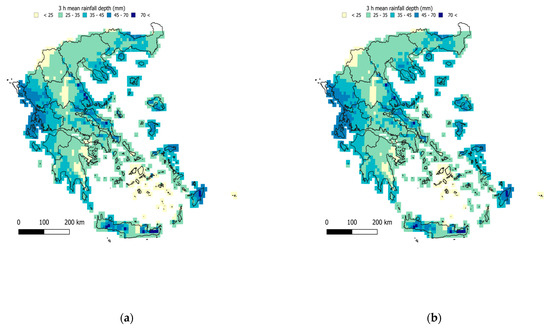
Figure 6.
Regionalized map of average 3 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
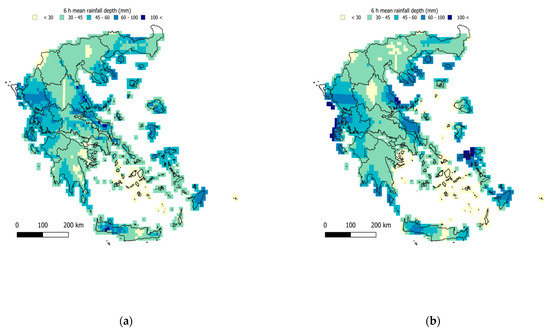
Figure 7.
Regionalized map of average 6 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
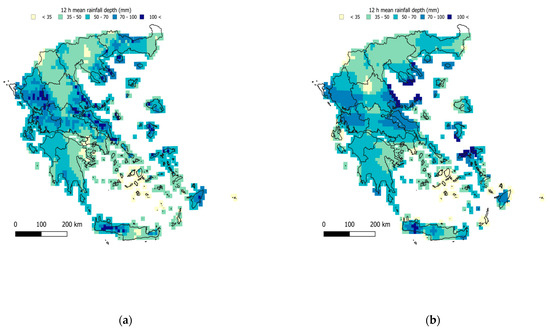
Figure 8.
Regionalized map of average 12 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
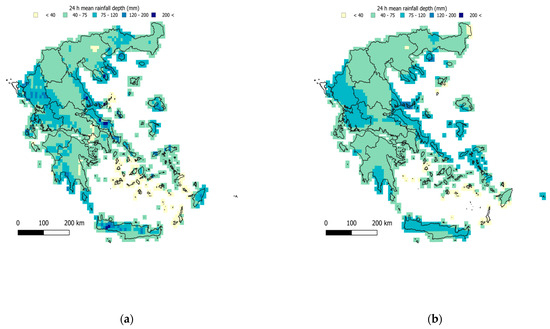
Figure 9.
Regionalized map of average 24 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.
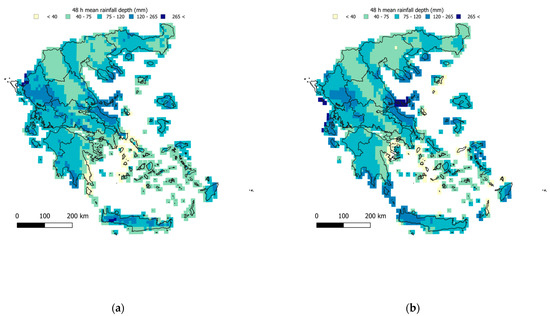
Figure 10.
Regionalized map of average 48 h maximum rainfall (mm) (a) using the elevation as a covariate and (b) using the IMERG satellite data as a covariate.

Table 5.
Performance assessment statistics for the regionalization based on the elevation and IMERG covariates for each timescale.

Table 6.
Performance assessment LOOCV statistics for the regionalization based on the elevation and IMERG covariates for each timescale.
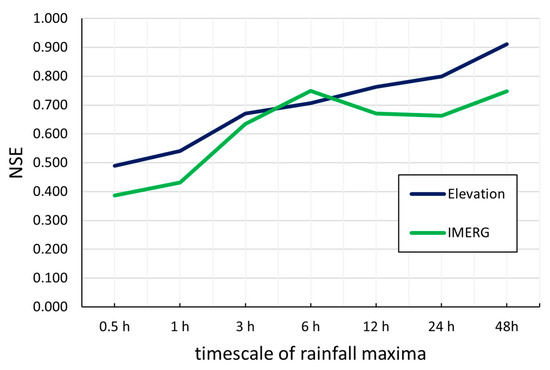
Figure 11.
NSE comparison of the elevation-based and the IMERG-based regionalization schemes.
It is evident that with increasing timescale of aggregation of the rainfall amounts, the regionalization uncertainty decreases, as evidenced by the increasing r2 values (Table 5) and the increasing efficiency (also Figure 11). A slight divergence is observed in the case of the IMERG covariate, with the peak performance being observed in 6 h and not increasing further for the 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h timescales.
Performance varied from acceptable to high for both covariates (NSE values in the range 0.4–0.9) in the case where the full dataset was employed (Table 5). Although results are comparable, the elevation-based regionalization systematically outperformed the IMERG one, which also yielded smoother surfaces (in terms of the standard deviation, σ, of the estimates), with the only exception on the 6 h scale (although small, with NSE: 0.71 and σ: 10.35 mm for the elevation against NSE: 0.75 and σ: 10.60 mm for the IMERG covariate).
The uncertainty of extreme rainfall is, however, showcased in the results of the LOOCV (Table 6), which are markedly inferior compared to those of the case of average daily rainfall (Table 4). In this evaluation, the regionalization performance remained robust only for the case of 24 h and 48 h, when employing elevation as a covariate. The poor values of the LOOCV in the remaining cases are indicative both of the inherent uncertainty involved in indices of extremes but also of the need for a denser network of stations for the sub-daily records.
4.3. Assessment of Credible Intervals
To delve further into the estimation uncertainty, the credible intervals were assessed, and stations falling outside the 95% probability band were identified. Figure 12 illustrates this for (a) the average 24 h maximum rainfall and (b) the average 24 h rainfall. The identified stations were examined, revealing no unrealistic behavior, and their occurrence remained within the expected 5% threshold, specifically at 4.9% for the maxima and 4.7% for the average rainfall. Most of these “outliers” align with established patterns of either very high or low average maximum rainfall values. A few stations were flagged due to limited data length and higher associated uncertainty. Nevertheless, the identified stations highlight areas where the gauge network is sparse, emphasizing the need for prioritized station installation. Such efforts should focus on regions with complex rainfall patterns, where additional data are crucial for robust characterization.
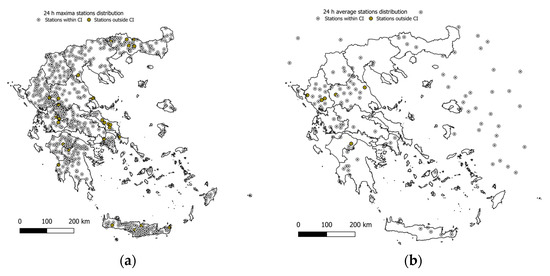
Figure 12.
Distribution of stations along the 95% credible intervals for (a) the average 24 h maximum rainfall and (b) the average 24 h rainfall.
4.4. Effect of Elevation on Multi-Scale Rainfall Patterns
The BSS framework allows for the investigation of the orographic influence on the rainfall maxima across different timescales. This is accomplished by exploring the corresponding regionalization scheme in terms of the values of surface e (Equation (2)), namely the weights assigned to the explanatory variable, i.e., the elevation. The median values of the elevation surface weights are shown in Figure 13, with positive values indicative of a tendency of positive association to the rainfall amount, while the opposite is true for negative values. The positive values towards the larger scales demonstrate the increasing effect of orography on precipitation, the well-known “orographic enhancement”. It is interesting, however, that this effect becomes significant above the 6 h scale, peaking at the 48 h scale with median weight of 6.5 times higher than the 3 h scale. At smaller scales, the average annual rainfall maxima exhibit very low values of the elevation weights, with the median value for the 0.5 h scale being negative, suggesting that the orographic effect acts inversely to the precipitation processes. This suggests that orography exerts complicated controls on the rainfall amount in Greece across different scales, acting as an increasing factor at large temporal scales while demonstrating mixed or even negative influence on small scales.
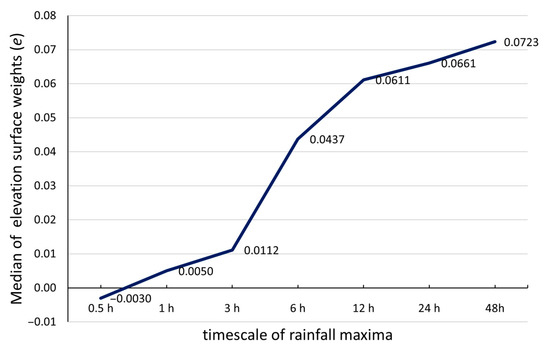
Figure 13.
Regionalization weights for the elevation surface for each timescale of rainfall maxima.
It is worth noting that the corresponding median value of surface e in case of average daily rainfall was 0.0008, exhibiting a non-systematic spatial influence of the orography in this case.
5. Conclusions
We investigated the regionalization of average and extreme rainfall patterns in Greece using the BSSE framework, incorporating both elevation (DEM) and satellite-derived IMERG rainfall estimates as alternative covariates. The results reveal the comparative performance of these covariates, shedding light on the role of temporal scale, the robustness of orographic effects, and the distinct dynamics of average and extreme rainfall.
While both DEM and IMERG showed promising performance in regionalizing rainfall patterns, elevation-based models outperformed IMERG. The higher spatial variability of the SRTM-derived DEM in the Greek territory allowed it to capture fine-scale orographic features, which were particularly important for modeling rainfall variability across different regions. In contrast, IMERG provided spatially smoother rainfall estimates, particularly for the average annual maximum rainfall across 0.5 h to 48 h scales. This finding suggests that IMERG rainfall estimates may not be accurate enough to support extreme-oriented analyses, such as regionalization of design rainfall curves particularly in areas with complex terrain as Greece, as noted in the literature [25]. This is consistent with reported findings that IMERG underestimates orographic rainfall over NW-W Greece and greatly overestimates rainfall over islands and coastal areas [41]. The need for caution when using IMERG, especially in regions with significant topographic variation, has been emphasized globally [42]. In contrast, elevation-based models showed higher efficiency, providing a more accurate representation of rainfall patterns. Despite this limitation, IMERG still proved useful, particularly for the regionalization of average daily rainfall, with its performance being comparable to the elevation-based one, especially for the 6 h scale maxima, a finding which demonstrates its value as a complementary tool for regional rainfall climatic analyses.
Regionalization efficiency was also greatly impacted by the temporal scale of maxima, peaking at higher scales (24 h and 48 h) and being poorer at smaller scales, particularly under the LOOCV assessment. This is reflective of both the higher uncertainty present in fine-scale rainfall but also of the poorer density of the station network in Greece at these scales. The 24 h scale proved as one of the most effective for regionalizing average maximum rainfall, which also validates the choice of the records from the daily rain gauges network as the basis for the regionalization of the distribution parameters in the design of rainfall curves in previous studies [2,25]. The orographic enhancement effect was robust at higher timescales (>6 h), with a clear increase in rainfall observed at higher elevations, consistent with previous findings [2,25]. At the smaller temporal scales (e.g., 0.5 to 6 h), the orographic effect exhibited more complexity, with some regions showing negative weights for elevation, suggesting a reverse orographic effect, which was more significant at the 0.5 h scale. This may suggest the presence of different regimes in the interaction between precipitation systems and orography, each influenced by different dominant processes such as convective and stratiform processes [28]. Therefore, the relationship between average maximum rainfall depth and elevation is not consistent across different temporal scales in Greece. In this light, the above-presented analysis can be useful not only in rainfall regionalization techniques but also in various other tasks, such as weather forecasting systems through satellite data.
Furthermore, the use of credible intervals proved instrumental in assessing the uncertainty in the regionalization process. The credible intervals highlighted areas where the station network may be insufficient or where unusual rainfall patterns might exist. This information is invaluable for improving network design, as it can guide the placement of new stations or the adjustment of existing ones to better capture spatial variability, especially in regions prone to extreme rainfall events. By focusing on areas outside the 95% credible interval, the network can be optimized to provide more accurate rainfall estimates both for flood risk management and climatic studies.
Overall, this work underscores the importance of selecting appropriate covariates and temporal scales when regionalizing rainfall patterns in complex terrains like Greece. While elevation-based models demonstrated superior performance, particularly for patterns of multi-scale extreme rainfall, satellite-derived IMERG estimates provided valuable complementary insights in the case of climatic analysis of the average daily rainfall patterns. Moreover, the use of credible intervals emphasized the value of uncertainty analysis in identifying gaps in station coverage and guiding network optimization. Further research, alongside a denser station network or additional data sources, is needed to enhance the representation of spatial dynamics in fine-scale extreme rainfall patterns to improve the accuracy of regional rainfall models in various climatic regimes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M. and T.I.; methodology N.M., T.I., and D.K.; supervision, N.M. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.M. and T.I.; data curation, T.I. and P.D.; software, N.M. and P.D.; visualization, N.M. and T.I.; validation, T.I. and P.D.; writing—reviewing and editing N.M. and D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
IMERG satellite precipitation data were obtained from the NASA GPM database (https://gpm.nasa.gov/data/imerg, accessed on 8 November 2024), and SRTM elevation data were acquired from the CIAT-CSI SRTM website (https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/, accessed on 20 January 2023). Daily and monthly rainfall data were obtained from the Hydroscope database (http://www.hydroscope.gr/, accessed on 10 February 2023) and from the KNMI Climate Explorer tool (http://climexp.knmi.nl/, accessed on 10 February 2023). Records of annual maxima used in this study are not publicly available, but their sources are described in detail in [25].
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Academic Editor and the three anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful and thorough comments, which have considerably helped us to improve our manuscript during revision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Claps, P.; Ganora, D.; Mazzoglio, P. Rainfall regionalization techniques. In Rainfall; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 327–350. [Google Scholar]
- Iliopoulou, T.; Malamos, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Regional ombrian curves: Design rainfall estimation for a spatially diverse rainfall regime. Hydrology 2022, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, T.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, Y.D.; Xiao, M. Regional frequency analysis of droughts in China: A multivariate perspective. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1767–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Song, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zuo, S. Regional-scale modeling of rainfall-induced landslides under random rainfall patterns. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 155, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G. Regionalization of rainfall thresholds: An aid to landslide hazard evaluation. Environ. Geol. 1998, 35, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Stocker, E.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Tan, J. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 Half Hourly 0.1 Degree x 0.1 Degree V06. Greenbelt 2019, MD: Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/data/imerg (accessed on 8 November 2024).
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltikoff, E.; Friedrich, K.; Soderholm, J.; Lengfeld, K.; Nelson, B.; Becker, A.; Hollmann, R.; Urban, B.; Heistermann, M.; Tassone, C. An overview of using weather radar for climatological studies: Successes, challenges, and potential. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 1739–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, T.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Have Rainfall Patterns Changed? A Global Analysis of Long-Term Rainfall Records and Re-Analysis Data; 47 pages, SR 306; The Heritage Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Alfieri, L.; Avanzi, F.; Delogu, F.; Gabellani, S.; Bruno, G.; Campo, L.; Libertino, A.; Massari, C.; Tarpanelli, A.; Rains, D.; et al. High resolution satellite products improve hydrological modeling in northern Italy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomopoulou, V.; Iliopoulou, T.; Kossieris, P.; Bariamis, G.; Tsoukalas, I.; Efstratiadis, A.; Makropoulos, C. A com-prehensive approach to building a continuous hydrologic model with Soil Moisture Accounting using Earth Observation data. Hydrol. Res. 2024, 55, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Leyland, J.; Dadson, S.J.; Cohen, S.; Slater, L.; Wortmann, M.; Ashworth, P.J.; Bennett, G.L.; Boothroyd, R.; Cloke, H.; et al. Global scale evaluation of precipitation datasets for hydrological modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 2023, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Belemtougri, A.; Fowé, T.; Mounirou, L.A.; Nkiaka, E.; Dembélé, M.; Komlavi, A.; Coly, S.M.; Koïta, M.; Karambiri, H. Rainfall Estimation in the West African Sahel: Comparison and Cross-Validation of Top-down vs. Bottom-up Precipitation Products in Burkina Faso. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2391956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Pellicone, G.; Modica, G.; Guagliardi, I. Comparative analysis of different spatial interpolation methods applied to monthly rainfall as support for landscape management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, B. Distance in spatial interpolation of daily rain gauge data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Zheng, S.; Liu, S.; Loáiciga, H.A.; Li, W. Regional precipitation model based on geographically and temporally weighted regression kriging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamos, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Bilinear surface smoothing for spatial interpolation with optional incorporation of an explanatory variable. Part 1: Theory. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamos, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Bilinear surface smoothing for spatial interpolation with optional incorporation of an explanatory variable. Part 2: Application to synthesized and rainfall data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliero, L.; Bouraoui, F.; Diels, J.; Willems, P.; McIntyre, N. Investigating regionalization techniques for large-scale hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, J.; Jurado, O.E.; Peter, M.; Scheibel, M.; Rust, H.W. Estimating IDF curves consistently over durations with spatial covariates. Water 2020, 12, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoglio, P.; Butera, I.; Claps, P. A local regression approach to analyze the orographic effect on the spatial variability of sub-daily rainfall annual maxima. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, Z.E.; Khaliq, M.N.; Wheater, H.S. Regionalization of precipitation characteristics in the Canadian Prairie Provinces using large-scale atmospheric covariates and geophysical attributes. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, T.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Malamos, N.; Koukouvinos, A.; Dimitriadis, P.; Mamassis, N.; Tepetidis, N.; Markantonis, D. A stochastic framework for rainfall intensity–time scale–return period relationships. Part ΙΙ: Point modelling and regionalization over Greece. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2024, 69, 1092–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzi, F.; De Michele, C.; Gabriele, S.; Ghezzi, A.; Rosso, R. Orographic signature on extreme precipitation of short durations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoglio, P.; Butera, I.; Alvioli, M.; Claps, P. The role of morphology in the spatial distribution of short-duration rainfall extremes in Italy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formetta, G.; Marra, F.; Dallan, E.; Zaramella, M.; Borga, M. Differential orographic impact on sub-hourly, hourly, and daily extreme precipitation. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 159, 104085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Bárdossy, A.; Morin, E. Precipitation frequency analysis from remotely sensed datasets: A focused review. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Matyas, C.J. Regionalization of precipitation associated with tropical cyclones using spatial metrics and satellite precipitation. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 542–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Iliopoulou, T.; Koukouvinos, A.; Malamos, N.; Mamassis, N.; Dimitriadis, P.; Tepetidis, N.; Markantonis, D. In search of climate crisis in Greece using hydrological data: 404 not found. Water 2023, 15, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-Filled SRTM for the Globe Version 4, Available from the CGIAR-CSI SRTM 90m Database. 2008. Available online: http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Dalrymple, T. Flood-Frequency Analyses (No. 1543); US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Malamos, N.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Field survey and modelling of irrigation water quality indices in a Mediterranean island catchment: A comparison between spatial interpolation methods. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1447–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, G.; Wendelberger, J. Some new mathematical methods for variational objective analysis using splines and cross validation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1980, 108, 1122–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, G. Bayesian “confidence intervals” for the cross-validated smoothing spline. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1983, 45, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadou, S.; Nikolakopoulos, K.G. Development of the Statistical Errors Raster Toolbox with Six Automated Models for Raster Analysis in GIS Environments. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. A Review of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Environmental Scientists; Geoscience Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Burrough, P.A.; McDonnell, R.A.; Lloyd, C.D. Principles of Geographical Information Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, H.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Lutsko, N.J.; Dufour, A.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, X.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Miralles, D.G. High-Resolution (1 Km) Köppen-Geiger Maps for 1901–2099 Based on Constrained CMIP6 Projections. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazamias, A.P.; Sapountzis, M.; Lagouvardos, K. Evaluation of GPM-IMERG rainfall estimates at multiple temporal and spatial scales over Greece. Atmos. Res. 2022, 269, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.K.; Markonis, Y.; Godoy, M.R.V.; Villalba-Pradas, A.; Andreadis, K.M.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Rahim, A.; Tapiador, F.J.; Hanel, M. Review of GPM IMERG performance: A global perspective. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).