Morphological Parameters of Gullies Formed on Sandy Soils and Effects of Check Dams in Central Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
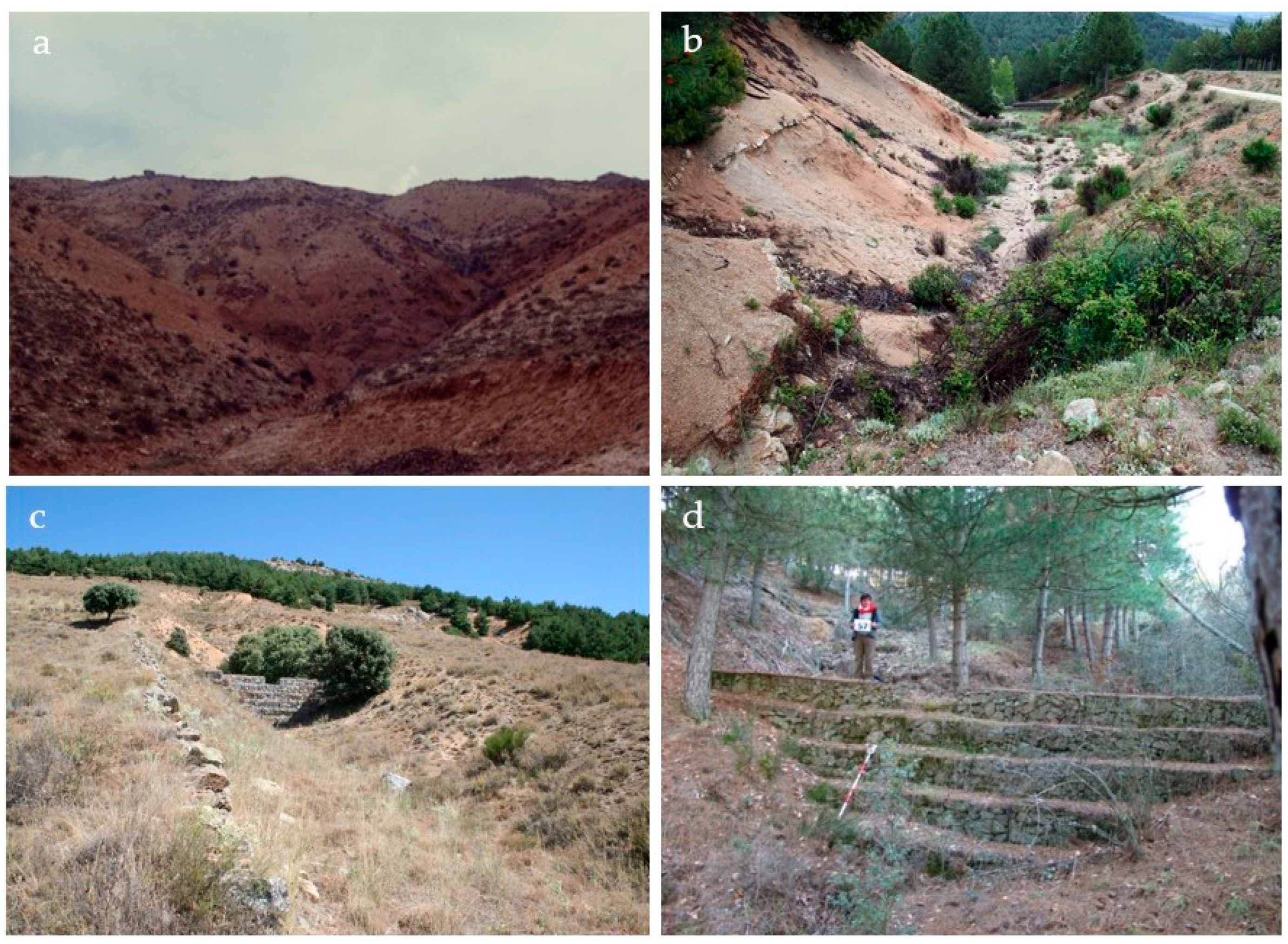
2.1. Study Area
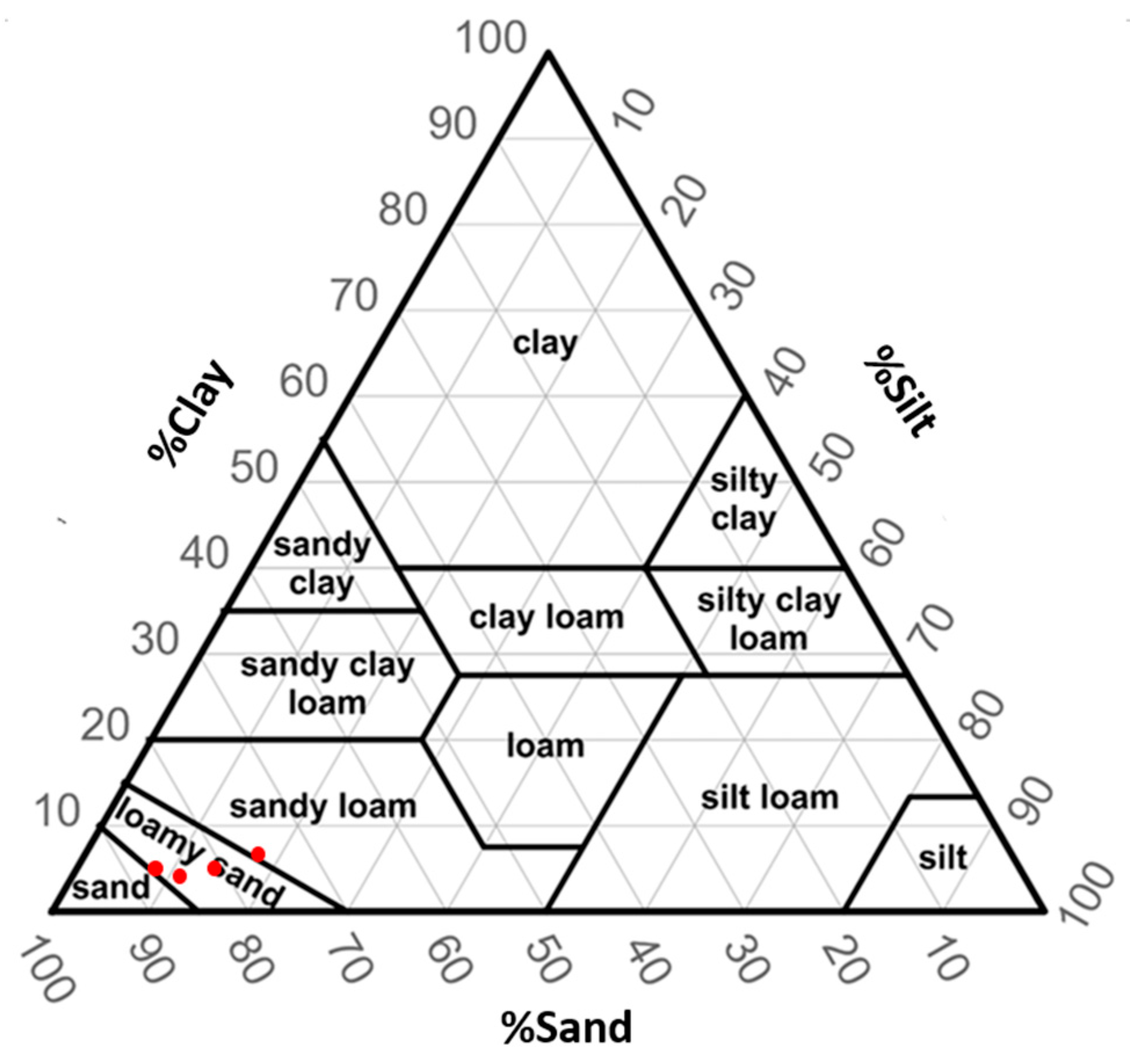
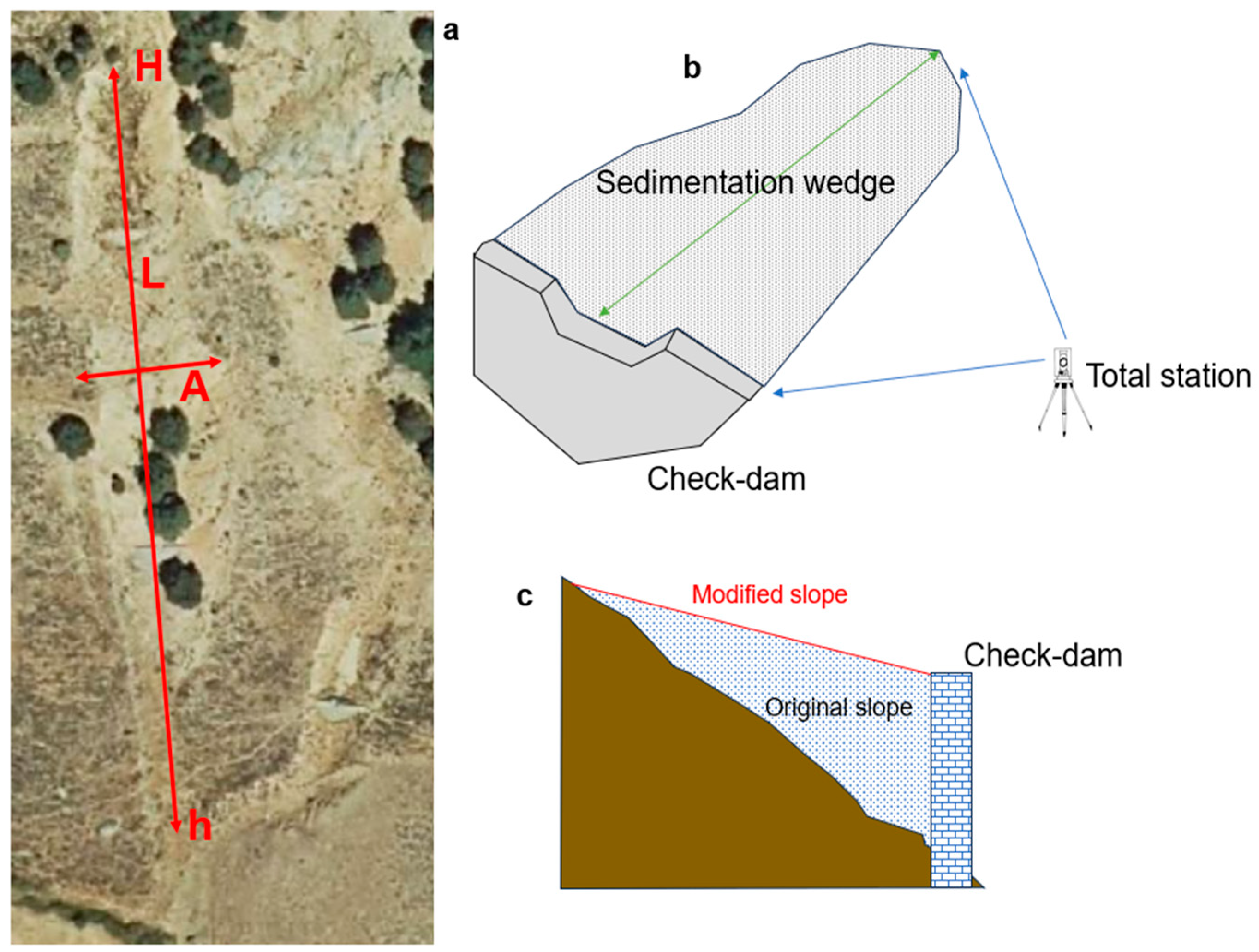
2.2. Data Collection
- -
- Catchment Area: Determined using the basin measurement tool (SAGA 9.7.0).
- -
- Gully Length (L): Measured using the length measurement tool (SAGA 9.7.0).
- -
- Maximum Altitude (H) and Minimum Altitude (h) of the Gully: The highest and lowest points of each gully were identified on the orthophoto, and their elevations were obtained by overlaying the 1:5000 topographic map from the National Geographic Institute.
- -
- Mean Gully Width (W): Calculated as the mean between the maximum width and the minimum width, both measured in the field using a total station. This method was chosen for its simplicity and the precision offered by direct field measurement.
- -
- Mean Gully Depth (D): Also calculated as the mean between the maximum depth and the minimum depth, measured using a total station.
2.3. Data Analysis
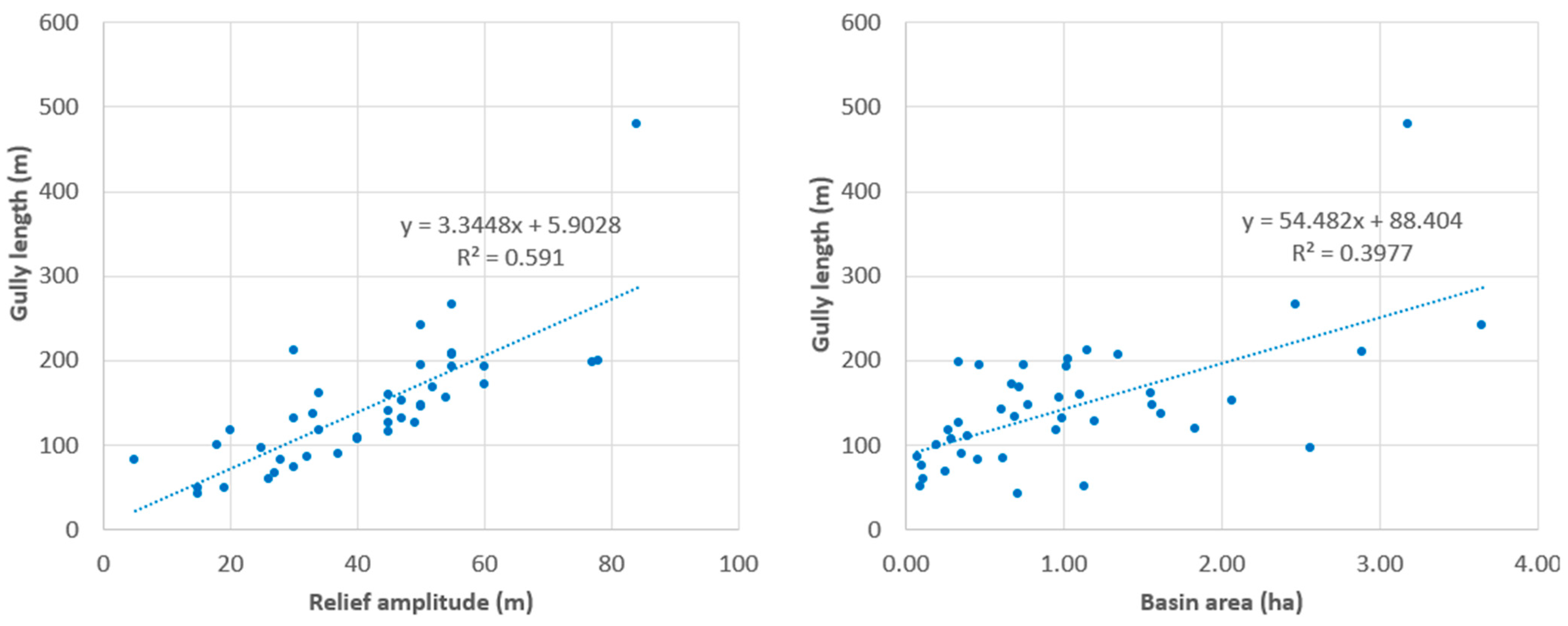
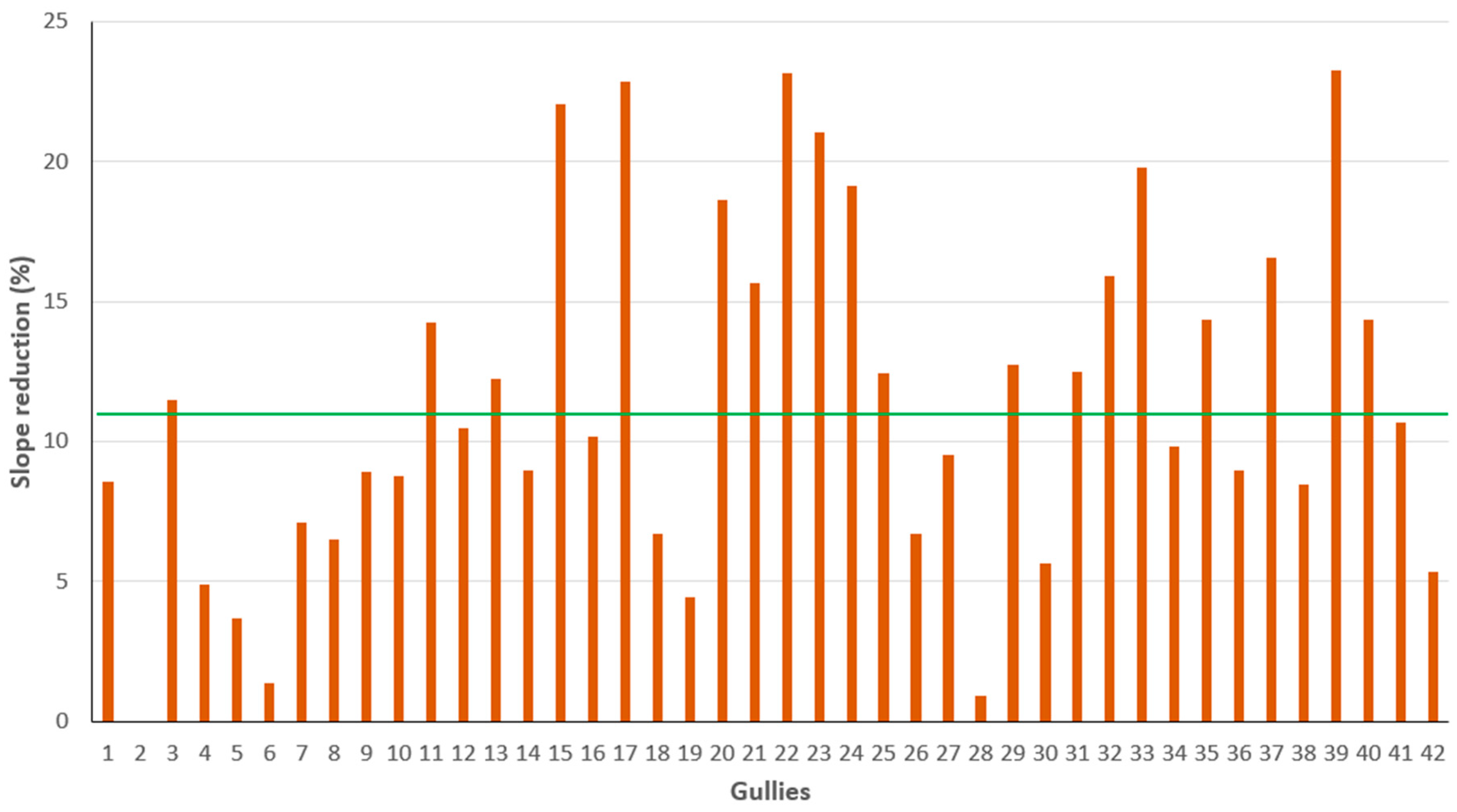
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gully | A (ha) | H (m) | h (m) | RA (m) | L (m) | W (m) | D (m) | W/D | J (%) | DD (km·km−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.62 | 1380 | 1375 | 5 | 83 | 2.80 | 2.05 | 1.37 | 6.02 | 13.42 |
| 2 | 2.56 | 1395 | 1370 | 25 | 96 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 0.67 | 26.04 | 3.75 |
| 3 | 1.00 | 1372 | 1342 | 30 | 131 | 5.22 | 1.9 | 2.74 | 22.90 | 13.15 |
| 4 | 2.89 | 1401 | 1346 | 55 | 209 | 2.00 | 1.9 | 1.05 | 26.32 | 7.23 |
| 5 | 1.62 | 1378 | 1345 | 33 | 136 | 2.27 | 1.9 | 1.19 | 24.26 | 8.40 |
| 6 | 1.83 | 1370 | 1350 | 20 | 118 | 1.51 | 1.2 | 1.26 | 16.95 | 6.45 |
| 7 | 3.18 | 1346 | 1262 | 84 | 479 | 2.94 | 2.8 | 1.05 | 17.54 | 15.06 |
| 8 | 0.96 | 1296 | 1262 | 34 | 117 | 1.28 | 1.1 | 1.17 | 29.06 | 12.21 |
| 9 | 0.20 | 1350 | 1332 | 18 | 100 | 6.20 | 2.6 | 2.38 | 18.00 | 50.08 |
| 10 | 0.72 | 1352 | 1300 | 52 | 168 | 3.59 | 1.9 | 1.89 | 30.95 | 23.43 |
| 11 | 0.29 | 1358 | 1318 | 40 | 107 | 2.59 | 1.6 | 1.62 | 37.38 | 36.47 |
| 12 | 0.07 | 1350 | 1318 | 32 | 86 | 5.15 | 1.65 | 3.12 | 37.21 | 118.62 |
| 13 | 0.47 | 1351 | 1291 | 60 | 193 | 3.40 | 1.00 | 3.40 | 31.09 | 41.43 |
| 14 | 2.47 | 1325 | 1270 | 55 | 266 | 3.29 | 1.6 | 2.06 | 20.68 | 10.77 |
| 15 | 0.25 | 1329 | 1302 | 27 | 67 | 3.85 | 3.1 | 1.24 | 40.30 | 26.60 |
| 16 | 0.75 | 1335 | 1285 | 50 | 194 | 8.67 | 1.4 | 6.19 | 25.77 | 25.89 |
| 17 | 0.11 | 1276 | 1250 | 26 | 59 | 6.95 | 3.30 | 2.11 | 44.07 | 51.44 |
| 18 | 0.34 | 1320 | 1275 | 45 | 126 | 4.16 | 2.6 | 1.60 | 35.71 | 37.60 |
| 19 | 0.98 | 1345 | 1291 | 54 | 156 | 4.33 | 1.05 | 4.12 | 34.62 | 15.99 |
| 20 | 0.34 | 1388 | 1311 | 77 | 198 | 3.75 | 2.4 | 1.56 | 38.89 | 58.32 |
| 21 | 1.03 | 1389 | 1311 | 78 | 200 | 2.14 | 2.30 | 0.93 | 39.00 | 19.42 |
| 22 | 0.78 | 1350 | 1300 | 50 | 146 | 4.58 | 3.2 | 1.43 | 34.25 | 18.82 |
| 23 | 1.56 | 1335 | 1285 | 50 | 147 | 4.96 | 2.70 | 1.84 | 34.01 | 9.42 |
| 24 | 0.35 | 1327 | 1290 | 37 | 89 | 2.60 | 3.16 | 0.82 | 41.57 | 25.31 |
| 25 | 0.69 | 1307 | 1260 | 47 | 132 | 7.53 | 2.60 | 2.89 | 35.61 | 19.09 |
| 26 | 0.68 | 1310 | 1250 | 60 | 171 | 4.16 | 2.6 | 1.60 | 35.09 | 25.31 |
| 27 | 1.15 | 1260 | 1230 | 30 | 212 | 14.40 | 3.05 | 4.72 | 14.15 | 18.43 |
| 28 | 0.10 | 1335 | 1305 | 15 | 50 | 3.33 | 1.80 | 1.85 | 60.00 | 51.12 |
| 29 | 0.71 | 1312 | 1297 | 15 | 42 | 1.97 | 1.80 | 1.09 | 35.71 | 5.89 |
| 30 | 0.27 | 1340 | 1295 | 45 | 116 | 6.66 | 2.25 | 2.96 | 38.79 | 42.30 |
| 31 | 0.11 | 1325 | 1295 | 30 | 74 | 7.68 | 2.40 | 3.20 | 40.54 | 68.46 |
| 32 | 0.39 | 1310 | 1270 | 40 | 109 | 5.65 | 2.50 | 2.26 | 36.70 | 27.78 |
| 33 | 0.61 | 1320 | 1275 | 45 | 141 | 6.00 | 4.09 | 1.47 | 31.91 | 23.28 |
| 34 | 1.20 | 1319 | 1270 | 49 | 127 | 4.60 | 2.10 | 2.19 | 38.58 | 10.58 |
| 35 | 1.02 | 1340 | 1285 | 55 | 192 | 4.62 | 2.40 | 1.92 | 28.65 | 18.82 |
| 36 | 3.65 | 1335 | 1285 | 50 | 241 | 3.35 | 3.50 | 0.96 | 20.75 | 6.60 |
| 37 | 2.07 | 1337 | 1290 | 47 | 152 | 4.16 | 2.70 | 1.54 | 30.92 | 7.34 |
| 38 | 1.13 | 1330 | 1311 | 19 | 50 | 4.03 | 2.55 | 1.58 | 38.00 | 4.42 |
| 39 | 1.10 | 1338 | 1293 | 45 | 159 | 2.29 | 2.70 | 0.85 | 28.30 | 14.45 |
| 40 | 0.46 | 1338 | 1310 | 28 | 82 | 4.80 | 2.65 | 1.81 | 34.15 | 17.81 |
| 41 | 1.35 | 1340 | 1285 | 55 | 206 | 4.97 | 2.85 | 1.74 | 26.70 | 15.26 |
| 42 | 1.55 | 1319 | 1285 | 34 | 161 | 2.33 | 2.55 | 0.91 | 21.12 | 10.39 |
| Gully | NCD | OS (%) | MSR (%) | LSR (m) | AF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 6.59 | 8.57 | 5.00 | 6.02 |
| 2 | 1 | 26.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 2 | 25.87 | 11.48 | 18.40 | 14.05 |
| 4 | 2 | 27.66 | 4.88 | 12.55 | 6.00 |
| 5 | 2 | 25.20 | 3.70 | 15.70 | 11.54 |
| 6 | 3 | 17.18 | 1.37 | 37.30 | 31.61 |
| 7 | 12 | 18.88 | 7.12 | 128.40 | 26.81 |
| 8 | 3 | 31.09 | 6.52 | 26.40 | 22.56 |
| 9 | 2 | 19.77 | 8.93 | 59.08 | 57.92 |
| 10 | 8 | 33.92 | 8.74 | 43.10 | 25.65 |
| 11 | 2 | 43.60 | 14.26 | 5.18 | 4.84 |
| 12 | 1 | 41.57 | 10.49 | 5.70 | 6.63 |
| 13 | 1 | 35.42 | 12.24 | 5.80 | 3.01 |
| 14 | 4 | 22.72 | 8.98 | 30.90 | 11.62 |
| 15 | 3 | 51.69 | 22.04 | 12.90 | 19.25 |
| 16 | 2 | 28.69 | 10.17 | 12.90 | 6.65 |
| 17 | 1 | 57.13 | 22.86 | 5.80 | 9.83 |
| 18 | 4 | 38.29 | 6.72 | 33.10 | 26.27 |
| 19 | 1 | 36.22 | 4.43 | 4.50 | 2.88 |
| 20 | 3 | 47.80 | 18.65 | 14.50 | 7.32 |
| 21 | 6 | 46.23 | 15.64 | 17.00 | 8.37 |
| 22 | 4 | 44.58 | 23.18 | 21.75 | 14.90 |
| 23 | 3 | 43.09 | 21.06 | 17.70 | 12.04 |
| 24 | 2 | 51.40 | 19.13 | 5.60 | 6.29 |
| 25 | 4 | 40.66 | 12.43 | 40.14 | 30.41 |
| 26 | 4 | 37.61 | 6.72 | 33.10 | 19.36 |
| 27 | 1 | 15.64 | 9.50 | 29.40 | 13.87 |
| 28 | 1 | 60.54 | 0.89 | 6.00 | 12.00 |
| 29 | 1 | 40.92 | 12.72 | 2.92 | 6.95 |
| 30 | 1 | 41.11 | 5.63 | 7.20 | 6.21 |
| 31 | 2 | 46.32 | 12.47 | 14.50 | 19.59 |
| 32 | 3 | 43.65 | 15.93 | 39.90 | 36.61 |
| 33 | 1 | 39.77 | 19.76 | 11.90 | 8.44 |
| 34 | 3 | 42.79 | 9.83 | 30.80 | 24.25 |
| 35 | 2 | 33.44 | 14.34 | 19.05 | 9.92 |
| 36 | 2 | 22.78 | 8.94 | 30.54 | 12.67 |
| 37 | 3 | 37.06 | 16.56 | 37.20 | 24.47 |
| 38 | 1 | 41.51 | 8.45 | 10.70 | 21.40 |
| 39 | 2 | 36.89 | 23.27 | 16.70 | 10.50 |
| 40 | 1 | 39.86 | 14.33 | 8.00 | 9.76 |
| 41 | 1 | 29.89 | 10.69 | 9.80 | 4.76 |
| 42 | 1 | 22.31 | 5.34 | 11.40 | 7.08 |
References
- Rubio, J.L. Desertification. Ambienta 2005, 47, 26–31. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- MITERD. Inventario Nacional de Erosión de Suelos 2002–2022. Resumen; Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico: Madrid, Spain, 2022.
- Gómez, A.; Schnabel, S.; Lavado, F. Processes, factors, and consequences of gully erosion; studies conducted in the Iberian Peninsula. Bol. Asoc. Geógr. Esp. 2011, 55, 59–80. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Casalí, J.; López, J.J.; Giráldez, J.V. Ephemeral gully erosion in Southern Navarre (Spain): Description and quantification. Ing. Agua 1999, 6, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, J.H.; Sinisterra, J.A.; Calle, Z. Restauracion Ecológica de Suelos Degradados por Erosión en Cárcavas en el Enclave Xerofítico de Dagua, Valle del Cauca, Colombia; Fundación CIVAP: Cali, Colombia, 2007; Available online: http://www.cipav.org.co/noticias/noticias-n01.html (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Hudson, N. Soil Conservation; Batsford: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, M.L.; Rendell, H.M. Process-form relationships in southern italian badlands: Erosion rates and implications for landform evolution. Earth Suf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Manual de sistemas de labranza para América Latina. Boletín Suelos FAO 1992, 66, 1–193. [Google Scholar]
- León, J.D. Strategies for gully erosion control and management. Cuad. Ambient. 2005, 2, 88–101. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Clotet, N.; Gallart, F.; Sala, M. Badlands: Characteristics, theoretical interest, dynamics, and erosion rates. Notes Geogr. Física 1987, 15–16, 28–37. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, M.L.; Rendell, H.M. Climate-driven decrease in erosion in extant Mediterranean badlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Darby, S. The Nature and Significance of Incised River Channels. In Incised Rivers; Darby, S.E., Simon, A., Eds.; Jhon Wiley ans Sons Press: Chichester, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Schultz, R.C.; Tufekcioglu, M. Gully and stream bank erosion in three pastures with different management in southeast Iowa. J. Iowa Acad. Sci. 2009, 116, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J.; Mackenzie, D.H. Topographic effects on the distribution of surface soil water and the location of ephemeral gullies. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Govers, G. Gully Erosión in the Loam Belt of Belgium: Typology and Control Measures. In Soil Erosión on Agricultural Land; Boardman, J., Foster, I.D.L., Dearing, J.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Londres, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, G.R. Understanding Ephemeral Gully Erosión. In Soil Conservation. Assesing the National Resources Inventory; Committee on Conservation Needs and Opportunities, Board on Agriculture, National Research Council, National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 90–125. [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J. Gully Typology and Gully Control Measures in the European Loess Belt. In Farm Land Erosión in Températe Plains Environment and Hills; Wicherek, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Schumm, S.A. Causes and Control of Channel Incision. In Incised Rivers; Darby, S.E., Simon, A., Eds.; Jhon Wiley ans Sons Press: Chichester, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, J. Manejo y Conservación de Suelos; EUNED: San José, Costa Rica, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- FEDERACAFÉ. Manual de Conservación de Suelos de Ladera; Centro Nacional de Investigaciones del Café, Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia: Chinchiná, Colombia, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Stocking, M.; Murnaham, N. Manual para la Evaluación de Campo de la Degradación de la Tierra; Mundi-Prensa Ed.: Madrid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccacci, S.; Galiano, M.; Roma, M.A.; Salvatore, M.C. Morphological analysis and erosion rate evaluation in badlands of Radicofani area (Southern Tuscany-Italy). Catena 2008, 74, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, A.; Sharon, D.; Lavee, H. Trends in runoff and erosion processes over an arid limestone hillside, northern Negev, Israel. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1980, 25, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- López-Bermúdez, F.; Torcal, L. Tunnel erosion (piping) processes in sedimentary basins of Murcia (Spain). Preliminary study using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. Papeles Geogr. Física 1986, 11, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Benito, G.; Gutiérrez, M.; Sancho, C. Erosion rates in badland areas of the central Ebro basin (NE Spain). Catena 1992, 19, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.; Serrano, C.; Ugalde, M.; Oria de Rueda, J.A.; Jonte, M.A. Utilización de Geotextiles en la Corrección de Cárcavas del Cristo del Otero (Palencia); I Congreso Forestal Hispano-Luso: Pamplona, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cantón, Y.; Domingo, F.; Solé-Benet, A.; Puigdefábregas, J. Hydrological and erosion response of a badlands system in semiarid SE Spain. J. Hydrol. 2001, 252, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Duque, J.F. Erosión Hídrica en Cárcavas y Barrancos de la Provincia de Segovia, España; Geología & Yacimientos Minerales: Madrid, Spain, 2007; Available online: www.aulados.net (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C.; García-Hernández, D. Effects of land-use changes in vegetation cover and sidewall erosion in a gully head of the Penedés region (Northeast Spain). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, F. Climat et Érosion; Presses Universitaires de France: Paris, France, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses. A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA Agricultural Handbook, No. 537; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- ICONA. Agresividad de la Lluvia en España. Valores del Factor R de la Ecuación Universal de Pérdidas de Suelo; Instituto para la Conservación de la Naturaleza, Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Thornthwaite, C.W. An approach towards a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev. 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. World Atlas of Desertification, 2nd ed.; United Nations Environment Programme: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, R. Versuch einer exakten Klassifikation der Boden in klimatischer Hinsicht. Interne Mitt. Boden-Kunde 1915, 5, 312–346. [Google Scholar]
- IGME. Mapa Geológico de España. Escala 1:50.000. Santa María del Berrocal; Instituto Geológico y Minero de España: Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washinton, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guanglu, L.; Klik, A.; Faqi, W. Gully Erosion Features and its Causes of Formation on the (Yuan) Land in the Loess Plateau, China. In Gully Erosion Under Global Change; Li, Y., Poesen, J., Valentin, C., Eds.; Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tebebu, T.Y.; Abiy, A.Z.; Zegeye, A.D.; Dahle, H.E.; Easton, Z.M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Collick, A.S.; Kidnau, S.; Moges, S.; Dadgari, F.; et al. Surface and subsurface flow effect on permanent gully formation and upland erosion near Lake Tana in the northern highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbonna, U. Understanding gully erosion vulnerability in Old Imo State using geographic information system and geostatistics. Am. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shit, P.K.; Bhunia, G.S.; Maiti, R. Assessment of factors affecting ephemeral gully development in badland topography: A case study at Garbheta Badland (Pashchim Medinipur, West Bengal, India). Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, H.K.; Adugna, B.; Gebretsadik, M.; Ayalew, B. Gully morphology and rehabilitation measures in different agroecological environments of Northwestern Ethiopia. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2015, 2015, 789479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustomji, P. Analysis of gully dimensions and sediment texture from southeast Australia for catchment sediment budgeting. Catena 2006, 67, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoane, M.; Radoane, N. Chapter 16. Gully erosion. In Landform Dynamics and Evolution in Romania; Radoane, M., Vespremeanu-Stroe, A., Eds.; Springer Geography: Geneve, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, J.; De Araújo, J.C.; Mongil, J. Assessment of 80 years of ancient-badlands restoration in Saldaña, Spain. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Mongil-Manso, J.; Navarro-Hevia, J.; Díaz-Gutiérrez, V.; Cruz, V.; Ramos-Díez, I. Badlands forest restoration in Central Spain after 50 years under a Mediterranean-continental climate. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineli, C.F.; De Almeida-Prado, L. Analysis of the influence of gully erosion in the flow pattern of catchment streams, Southeastern Brazil. Catena 2007, 69, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, H. Soil degradation and overland flow as causes of gully erosion on mountain pastures and in forests. Catena 2005, 50, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongil-Manso, J.; Díaz-Gutiérrez, V.; Navarro-Hevia, J.; Espina, M.; San Segundo, L. The role of check dams in retaining organic carbon and nutrients. A study case in the Sierra de Ávila mountain range (Central Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 657, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts factors and control. Catena 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Challenges in gully erosion research. Landf. Anal. 2011, 17, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Radoane, M.; Ichim, I.; Radoane, N. Gully distribution and development in Moldavia, Romania. Catena 1995, 24, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, F.; Chiocchini, U. Effects of land use changes on badland erosion in clayey drainage basins, Radicofani, Central Italy. Geomorphology 2012, 169–170, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moreno, C.; Fidalgo-Hijano, C.; Martín-Duque, J.F.; González-Martín, J.A.; Zapico-Alonso, I.; Laronne, J.B. The Ribagorda sand gully (east-central Spain): Sediment yield and human-induced origin. Geomorphology 2014, 224, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucía, A.; Martín-Duque, J.F.; Laronne, J.B.; Sanz-Santos, M.A. Geomorphic dynamics of gullies developed in sandy slopes of Central Spain. Landf. Anal. 2011, 17, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lucía, A.; Laronne, J.B.; Martín-Duque, J.F. Geodynamic processes on sandy slope gullies in central Spain field observations, methods and measurements in a singular system. Geodin. Acta 2012, 24, 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Zou, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, Z. Morphology parameters of ephemeral gully in characteristics hillslopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heede, B.H. Morphology of gullies in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1970, 15, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Poesen, J.; Scholiers, N.; Jacob, M.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Factors controlling the morphology and volume (V)–length (L) relations of permanent gullies in the northern Ethiopian Highlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2013, 38, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Qin, F.C.; Fang, H.D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Shu, C.Q.; Deng, Q.C.; Liu, G.C.; Yang, Q.Q. Morphology and controlling factors of the longitudinal profile of gullies in the Yuanmou dry-hot valley. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 674–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, R.N.; Brooks, A.P.; Pietsch, T.J.; Spencer, J.R. What type of gully is that? The need for a classification of gullies. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2022, 47, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenneman, N.M. Physiographic provinces and sections in western Oklahoma and adjacent parts of Texas. Bull. U.S. Geol. Surv. 1922, 730, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- MAAMA. National Soil Erosion Inventory 2002–2012. 2011, Ávila, Castilla y León; Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2012. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, C.G.; Hill, B.R.; Lehre, A.K. Chapter 6. Gully Development. In Groundwater Geomorphology; The Role of Subsurface Water in Earth Surface Processes and Landforms; Higgins, C.G., Coates, D.R., Eds.; The Geological Society of America Special Paper 252; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ireland, H.; Sharpe, C.F.S.; Eargle, D.H. Principles of Gully Erosion in the Piedmont of South Carolina; Tech. rep.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1939.
- Sumner, M.E.; Stewart, B.A. (Eds.) Soil Crusting: Chemical and Physical Processes; Lewis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. Sodic Soils, Processes, Characteristics, and Classification. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Lal, R., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, H. Piping hazard on dispersive and collapsible soils in Europe. In Soil Erosion in Europe; Poesen, J., Boardman, J., Eds.; John Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco, D. The Chuy flour mill, in Bonilla de la Sierra (Ávila): Analysis historical-descriptive and its temporal evolution (XII–XXI centuries). Cuad. Abulenses 2019, 48, 11–64. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, H. Badlands in marl lithologies: A field guide to soil dispersion, subsurface erosion and piping-origin gullies. Catena 2013, 106, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatek-Jakiel, A.; Poesen, J. Subsurface erosion by soil piping: Significance and research needs. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 1107–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienks, S.M.; Botha, G.A.; Hughes, J.C. Some physical and chemical properties of sediments exposed in a gully (donga) in northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and their relationship to the erodibility of the colluvial layers. Catena 2000, 39, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.P.; Shellberg, J.G.; Knight, J.; Spencer, J. Alluvial gully erosion across the Mitchell fluvial megafan, Queensland Australia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1951–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanin-Grubin, M.; Bryan, R. Lithological properties and weathering response on badland hillslopes. Catena 2004, 70, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Gutiérrez, V.; Mongil-Manso, J.; Navarro-Hevia, J.; Ramos-Diez, I. Check dams and sediment control: Final results of a case study in the upper Corneja River (Central Spain). J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J. La Mesta; Alianza Universidad: Madrid, Spain, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Estévez, J.J. Sheep livestock in the History of Spain. Anales de la Real Academia de Ciencias Veterinarias de Andalucía Oriental; Real Academia de Ciencias Veterinarias de Andalucía Oriental: Granada, Spain, 1990; pp. 21–46. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Zheng, F.; Qin, C.; He, X. Gully morphological characteristics in the loess hilly-gully region based on 3D laser scanning technique. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yibeltal, M.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Adgo, E.; Meshesha, D.T.; Masunaga, T.; Tsubo, M.; Billi, P.; Ebabu, K.; Fenta, A.A.; et al. Morphological characteristics and topographic thresholds of gullies in different agro-ecological environments. Geomorphology 2019, 341, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Veyret-Picot, M.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J.; Govers, G. The effectiveness of loose rock check dams for gully control in Tigray, northern Etiopia. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Piton, G.; Yu, Y.; Castillo, C.; Zema, D.A. Check dams worldwide: Objetives, functions, effectiveness and undesired effects. Catena 2021, 204, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, P.; Gessler, J. Ultimate bed slope in Calabrian streams upstream of check dams: Field study. J. Hydraul. Eng.-ASCE 1999, 125, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani, R. Evaluating the Effect of Check Dams on Flood Peaks to Optimize the Flood Control Measures (Kan Case Study in Iran). Master’s Thesis, International Institute for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation Enschede, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sobrino, M.A.; Caba, J. Análisis Comparativo a Nivel Técnico y Económico de Distintas Tipologias de Solución para la Corrección Hidrológica en las Cabeceras de las Cuencas de Alta Montaña en la Comarca del Berguedá. (Barcelona); VI Congreso Iberoamericano de Control de la Erosión y los Sedimentos: Granada, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| A (ha) | H (m) | h (m) | RA (m) | L (m) | W (m) | D (m) | W/D | J (%) | DD (km·km−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 1.04 | 1338.88 | 1296.95 | 41.57 | 144.95 | 4.33 | 2.32 | 1.96 | 31.15 | 24.68 |
| SD | 0.88 | 29.66 | 31.57 | 17.39 | 75.64 | 2.39 | 0.69 | 1.12 | 9.65 | 21.75 |
| Median | 0.76 | 1337.50 | 1292.00 | 45.00 | 134.00 | 4.09 | 2.40 | 1.61 | 32.96 | 18.63 |
| Max | 3.65 | 1401.00 | 1375.00 | 84.00 | 479.00 | 14.4 | 4.09 | 6.19 | 60.00 | 118.62 |
| Min | 0.07 | 1260.00 | 1230.00 | 5.00 | 42.00 | 1.28 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 6.02 | 3.75 |
| CV | 84.36 | 2.22 | 2.43 | 41.82 | 52.18 | 55.18 | 29.74 | 57.33 | 30.97 | 88.13 |
| NCD | OS (%) | MSR (%) | LSR (m) | AF (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 2.55 | 35.56 | 11.40 | 21.39 | 14.77 |
| SD | 2.11 | 11.66 | 6.23 | 21.66 | 11.19 |
| Median | 2.00 | 37.33 | 10.33 | 15.10 | 134.00 |
| Max | 12.00 | 60.54 | 23.27 | 128.40 | 57.92 |
| Min | 1.00 | 6.59 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CV | 82.79 | 32.80 | 54.66 | 101.26 | 75.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mongil-Manso, J.; Navarro-Hevia, J.; Velázquez, J.; Díaz-Gutiérrez, V.; Toledo-Rocha, A.-C. Morphological Parameters of Gullies Formed on Sandy Soils and Effects of Check Dams in Central Spain. Geosciences 2025, 15, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15060208
Mongil-Manso J, Navarro-Hevia J, Velázquez J, Díaz-Gutiérrez V, Toledo-Rocha A-C. Morphological Parameters of Gullies Formed on Sandy Soils and Effects of Check Dams in Central Spain. Geosciences. 2025; 15(6):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15060208
Chicago/Turabian StyleMongil-Manso, Jorge, Joaquín Navarro-Hevia, Javier Velázquez, Virginia Díaz-Gutiérrez, and Ana-Carolina Toledo-Rocha. 2025. "Morphological Parameters of Gullies Formed on Sandy Soils and Effects of Check Dams in Central Spain" Geosciences 15, no. 6: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15060208
APA StyleMongil-Manso, J., Navarro-Hevia, J., Velázquez, J., Díaz-Gutiérrez, V., & Toledo-Rocha, A.-C. (2025). Morphological Parameters of Gullies Formed on Sandy Soils and Effects of Check Dams in Central Spain. Geosciences, 15(6), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15060208









