Analysis of Ionospheric Response and GNSS Positioning on Geodetic and Low-Cost Receivers in Mexico During the May 2024 Geomagnetic Storm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. GNSS Data
2.2. TEC Calculation
2.3. Kinematic PPP-GNSS Processing Strategies
| Item | Strategy |
|---|---|
| GNSS | GPS |
| Positioning mode | PPP Kinematic |
| Observation types | Code + Carrier-phase |
| Frequencies | GPS L1 and L2 |
| Sampling interval | 30 s |
| Elevation mask angle | 12° |
| Satellite orbit and clock | CODE precise ephemeris and precise clock files |
| Troposphere delays | Saastamoinen model [51] and Global Mapping Function (GMF) |
| Ionosphere delays | First-order delays eliminated in the ionosphere-free combination |
| Tidal displacements | Solid/Ocean/Pole corrected |
| Satellite antenna phase center correction | Igs20_2309.atx |
| Observation weighting | Elevation-dependent weight |
| Relativistic effect | Corrected |
| Ambiguity Resolution Method | Rounding |
| Output coordinate system | ECEF (Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed) |
- Window 1 (W1): 07:00–17:00 UT on 5 May 2024. This window was selected considering a quiet day in the ionosphere before the geomagnetic storm.
- Window 2 (W2): 07:00–17:00 UT on 10 May 2024. This window was selected 10 h before the onset of the geomagnetic storm.
- Window 3 (W3): 17:00–03:00 UT on 10–11 May 2024. This window corresponds to the geomagnetic storm phenomenon.
- Window 4 (W4): 03:00–13:00 UT on 11 May 2024. This window corresponds to 10 h after the end of the geomagnetic storm.
- Window 5 (W5): 03:00–13:00 UT on 15 May 2024. This window was selected considering a quiet day for the ionosphere after the geomagnetic storm.
3. Results
3.1. Ionospheric Response over Mexico
3.2. Low-Cost vs. Geodetic Receiver Performance in the Dominican Republic
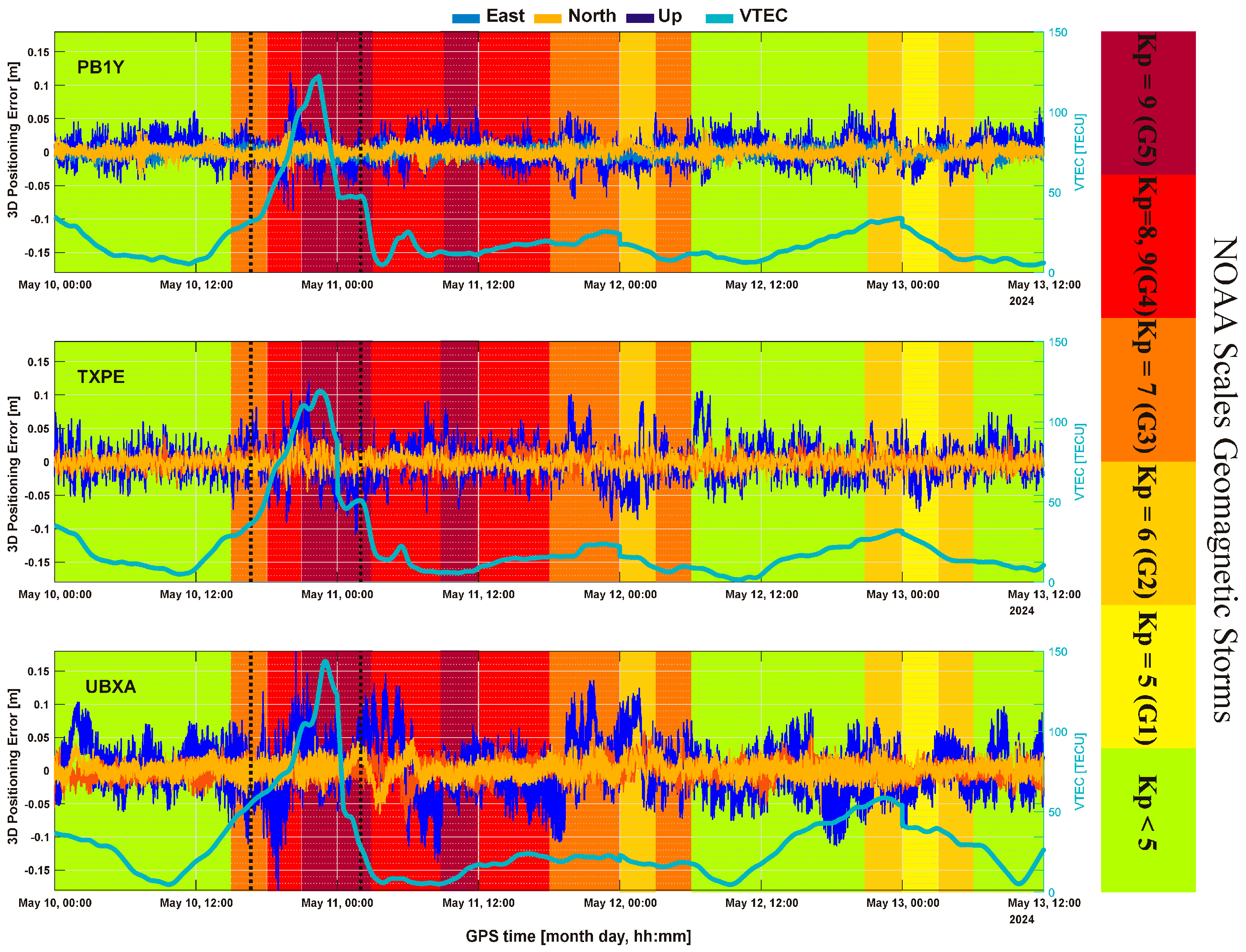
3.3. Kinematic PPP-GNSS Performance During Geomagnetic Storm
3.4. Mitigation of the Solar Storm on GNSS Positioning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.; Morton, Y.T.J. Impacts of the May 2024 Extreme geomagnetic Storm on Global High—Accuracy GPS Positioning Solutions. Space Weather 2025, 23, e2025SW004547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, M.A.; Maltseva, O.A.; Caraballo, R.; Gonzalez-Esparza, J.A.; Corona-Romero, P. Latitudinal dependence of the ionospheric slab thickness for estimation of ionospheric response to geomagnetic storms. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Verkhoglyadova, O.P.; Mannucci, A.J.; Saito, A.; Araki, T.; Yumoto, K.; Tsuda, T.; Abdu, M.A.; Sobral, J.H.A.; Gonzalez, W.D.; et al. Prompt penetration electric fields (PPEFs) and their ionospheric effects during the great magnetic storm of 30–31 October 2003. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, A05311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, L.; Wu, L. Statistical study of loss of GPS signals caused by severe and great geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Veenadhari, B.; Dimri, A.P.; Bulusu, J.; Bagiya, M.; Gurubaran, S.; Parihar, N.; Remya, B.; Seemala, G.; Singh, R.; et al. Super-intense geomagnetic storm on 10–11 May 2024: Possible mechanisms and impacts. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW004126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordiyenko, G.; Arikan, F.; Litvinov, Y.; Zhiganbaev, M. Ionospheric response to the extreme geomagnetic storm of 10–11 May 2024 based on total electron content observations in the Central Asian and East Asian regions. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, H.; Ebihara, Y.; Mishev, A.; Koldobskiy, S.; Kusano, K.; Isobe, H.; Bechet, S.; Yashiro, S.; Iwai, K.; Shinbori, A.; et al. The solar and geomagnetic storms in May 2024: A flash data report. Astrophys. J. 2025, 979, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, E.; Chen, Y.; Luo, B. Dynamic expansion and merging of the equatorial ionization anomaly during the 10–11 May 2024 super geomagnetic storm. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, P.N. What is a geomagnetic index? In Derivation, Meaning, and Use of Geomagnetic Indices; Mayaud, P.N., Ed.; AGU: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Esparza, J.A.; Sanchez-Garcia, E.; Sergeeva, M.; Corona-Romero, P.; Gonzalez-Mendez, L.X.; Valdes-Galicia, J.F.; Aguilar-Rodriguez, E.; Rodriguez-Martinez, M.; Ramirez-Pacheco, C.; Castellanos, C.I.; et al. The Mother’s Day geomagnetic storm on 10 May 2024: Aurora observations and low latitude space weather effects in Mexico. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW004111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spogli, L.; Alberti, T.; Bagiacchi, P.; Cafarella, L.; Cesaroni, C.; Cianchini, G.; Coco, I.; Di Mauro, D.; Ghidoni, R.; Giannattasio, F.; et al. The effects of the May 2024 Mother’s Day superstorm over the Mediterranean sector: From data to public communication. Ann. Geophys. 2024, 67, PA218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, R.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Lakhina, G.S.; Lu, Q.; Du, A. Interplanetary causes and impacts of the 2024 May superstorm on the Geosphere: An overview. Astrophys. J. 2024, 974, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Sen, A.; Hajra, R.; Lakhina, G.S.; Horne, R.B.; Hada, T. Review of the August 1972 and March 1989 (Allen) space weather events: Can we learn anything new from them? J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA032622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Scipión, D.E.; Kuyeng, K.; Condor, P.; De La Jara, C.; Velasquez, J.P.; Flores, R.; Ivan, E.; Souza, J.R.; Migliozzi, M. Ionospheric disturbances observed over the Peruvian sector during the Mother’s Day storm (G5-level) on 10–12 May 2024. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Fu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, K.; Cui, Y. The poleward shift of the equatorial ionization anomaly during the main phase of the superstorm on 10 May 2024. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Trivedi, R.; Jain, S.; Choudhary, R.K. Effects of the super intense geomagnetic storm on 10–11 May 2024 on total electron content at Bhopal. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, C.S.; Dai, L.; Wrasse, C.M.; Barros, D.; Takahashi, H.; Figueiredo, C.A.O.B.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Liu, Z. Ionospheric response to the extreme 2024 Mother’s Day geomagnetic storm over the Latin American sector. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW004054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraballo, R.; González-Esparza, J.A.; Pacheco, C.R.; Corona-Romero, P.; Arzate-Flores, J.A.; Castellanos-Velazco, C.I. The impact of geomagnetically induced currents (GIC) on the Mexican power grid: Numerical modeling and observations from the 10 May 2024 geomagnetic storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Berdermann, J.; Forte, B.; Hapgood, M.; Bisi, M.M.; Romano, V. Space weather impact on radio communication and navigation. Adv. Space Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.S.; Schäfer, S. Observed effects of a geomagnetic storm on an RTK positioning network at high latitudes. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2012, 2, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeot, N.; Bruyninx, C.; Defraigne, P.; Pireaux, S.; Legrand, J.; Pottiaux, E.; Baire, Q. Impact of the Halloween 2003 ionospheric storm on kinematic GPS positioning in Europe. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.S.; Andalsvik, Y.L. Overview of the 2015 St. Patrick’s day storm and its consequences for RTK and PPP positioning in Norway. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2016, 6, A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Xiong, C.; Chen, B.; Jin, X. Assessing the performance of GPS precise point positioning under different geomagnetic storm conditions during solar cycle 24. Sensors 2018, 18, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Luo, B. Assessing the kinematic GPS positioning performance under the effect of strong ionospheric disturbance over China and adjacent areas during the magnetic storm. Radio Sci. 2022, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, C.; Meng, Y.; Chen, Y. Ionosphere disturbances on GNSS signal and positioning performance: Analysis of the solar flare and geomagnetic storm events in September 2017 and October 2021. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 4608–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Bezerra, L.; de Oliveira, P.S., Jr.; Krueger, C.P. Performance Analysis of multi-GNSS PPP under the Effects of Extreme Geomagnetic Event: A Case Study of Mother’s Day Solar Storm (10–15 May 2024). Adv. Space Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Lu, R. Comparative analysis of higher-order ionospheric delay on PPP long-term coordinate time series and residual modeling using horizontal gradients and RINEX data. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW004178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hu, Z.; Wang, F.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, T. Ionospheric response characteristics and PPP accuracy analysis at different latitudes during strong geomagnetic storms. Acta Geophys. 2024, 72, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilchuk, E.; Yasyukevich, Y.; Vesnin, A.; Klyusilov, A.; Zhang, B. Impact of the May 2024 Extreme Geomagnetic Storm on the Ionosphere and GNSS Positioning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Spogli, L.; Azeez, A.; Alfonsi, L.; Cesaroni, C.; Romano, V.; Akande, A. The impact of Mother’s Day Storms in May 2024 on Precise Point Positioning at mid-latitudes. Ann. Geophys. 2025, 68, A214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nischan, T. GFZRNX-RINEX GNSS Data Conversion and Manipulation Toolbox, Version 1.05; German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ): Potsdam, Germany, 2016.
- Janos, D.; Kuras, P.; Ortyl, Ł. Evaluation of low-cost RTK GNSS receiver in motion under demanding conditions. Measurement 2022, 201, 111647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Erol, C.B.; Arikan, O. Regularized estimation of vertical total electron content from Global Positioning System data. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Erol, C.B.; Arikan, O. Regularized estimation of vertical total electron content from GPS data for a desired time period. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, RS6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayir, H.; Arikan, F.; Arikan, O.; Erol, C.B. Total electron content estimation with Reg-Est. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, A11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagoveshchensky, D.V.; Maltseva, O.A.; Sergeeva, M.A. Impact of magnetic storms on the global TEC distribution. Ann. Geophys. 2018, 36, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemala, G.K. Estimation of ionospheric total electron content (TEC) from GNSS observations. In Earth Observation, Atmospheric Remote Sensing; Singh, A.K., Tiwari, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anderle, R.J. Point positioning concept using precise ephemeris. Satell. Doppler Position 1976, 1, 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héroux, P.; Kouba, J. GPS precise point positioning using IGS orbit products. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A Solid Earth Geod. 2001, 26, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Subirana, J.; Juan Zornoza, J.M.; Hernández-Pajares, M. GNSS Data Processing; Volume I: Fundamentals and algorithms; ESA Communications: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J.; Lahaye, F.; Tétreault, P. Precise point positioning. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 723–751. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Mao, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, K. PRIDE PPP-AR: An open-source software for GPS PPP ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Ontiveros, J.R.; Padilla-Velazco, J.; Gaxiola-Camacho, J.R.; Vázquez-Becerra, G.E. Evaluation and Analysis of the Accuracy of Open-Source Software and Online Services for PPP Processing in Static Mode. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiao, G.; Chang, G.; Xu, T.; Yang, L. Assessment of GPS/Galileo/BDS precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using products from different analysis centers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krietemeyer, A.; van der Marel, H.; van de Giesen, N.; Ten Veldhuis, M.C. A field calibration solution to achieve high-grade-level performance for low-cost dual-frequency GNSS receiver and antennas. Sensors 2022, 22, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krietemeyer, A.; van der Marel, H.; van de Giesen, N.; ten Veldhuis, M.C. High quality zenith tropospheric delay estimation using a low-cost dual-frequency receiver and relative antenna calibration. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.M.; Jakowski, N. Estimate of higher order ionospheric errors in GNSS positioning. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, B. Evaluation of Empirical Tropospheric Models Using Satellite-Tracking Tropospheric Wet Delays with Water Vapor Radiometer at Tongji, China. Sensors 2016, 16, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odolinski, R.; Teunissen, P.J. An assessment of smartphone and low-cost multi-GNSS single-frequency RTK positioning for low, medium and high ionospheric disturbance periods. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, V.; Stopar, B.; Ambrožič, T.; Sterle, O. Performance evaluation of low-cost multi-frequency gnss receivers and antennas for displacement detection. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, V.; Stopar, B.; Sterle, O.; Pavlovčič-Prešeren, P. Observations and positioning quality of low-cost GNSS receivers: A review. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Psimoulis, P.; Horsfall, A.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, X. Assessment of the accuracy of low-cost multi-GNSS receivers in monitoring dynamic response of structures. Appl. Geomat. 2023, 15, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Observational study of ionospheric irregularities and GPS scintillations associated with the 2012 tropical cyclone Tembin passing Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 4705–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Low-latitude ionospheric density irregularities and associated scintillations investigated by combining COSMIC RO and ground-based Global Positioning System observations over a solar active period. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 3998–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashcheyev, A.; Nava, B.; Radicella, S.M. Estimation of higher-order ionospheric errors in GNSS positioning using a realistic 3-D electron density model. Radio Sci. 2012, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yang, S.; Guo, J. Assessing IGS GPS/Galileo/BDS-2/BDS-3 phase bias products with PRIDE PPP-AR. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, C.; Seemala, G.K.; Katual, I.; Dimri, A. Ionospheric response to PPEF events in the Indian region during high and low intense geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 4329–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller-Rowell, T.J.; Codrescu, M.V.; Moffett, R.J.; Quegan, S. Response of the thermosphere and ionosphere to geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1994, 99, 3893–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prölss, G.W. Density perturbations in the upper atmosphere caused by the dissipation of solar wind energy. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 101–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.V.; Parkinson, M.L. A global scale picture of ionospheric peak electron density changes during geomagnetic storms. Space Weather 2017, 15, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linty, N.; Minetto, A.; Dovis, F.; Spogli, L. Effects of phase scintillation on the GNSS positioning error during the September 2017 storm at Svalbard. Space Weather 2018, 16, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Bian, C.; Ban, W.; Hancock, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K. Analysis of global ionospheric scintillation and GPS positioning interference triggered by full-halo CME-driven geomagnetic storm: A case study. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 2492–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Luo, X.; Xie, Z.; Peng, X. Performance analysis of four PPP service software under different intensity geomagnetic storms. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, W.; Nishimura, Y.; Liao, W.; Semeter, J.L.; Mrak, S.; Morton, Y.J.; Groves, K.M. Spatio-temporal evolution of mid-latitude GPS scintillation and position errors during the May 2024 solar storm. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2025, 130, e2025JA033839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
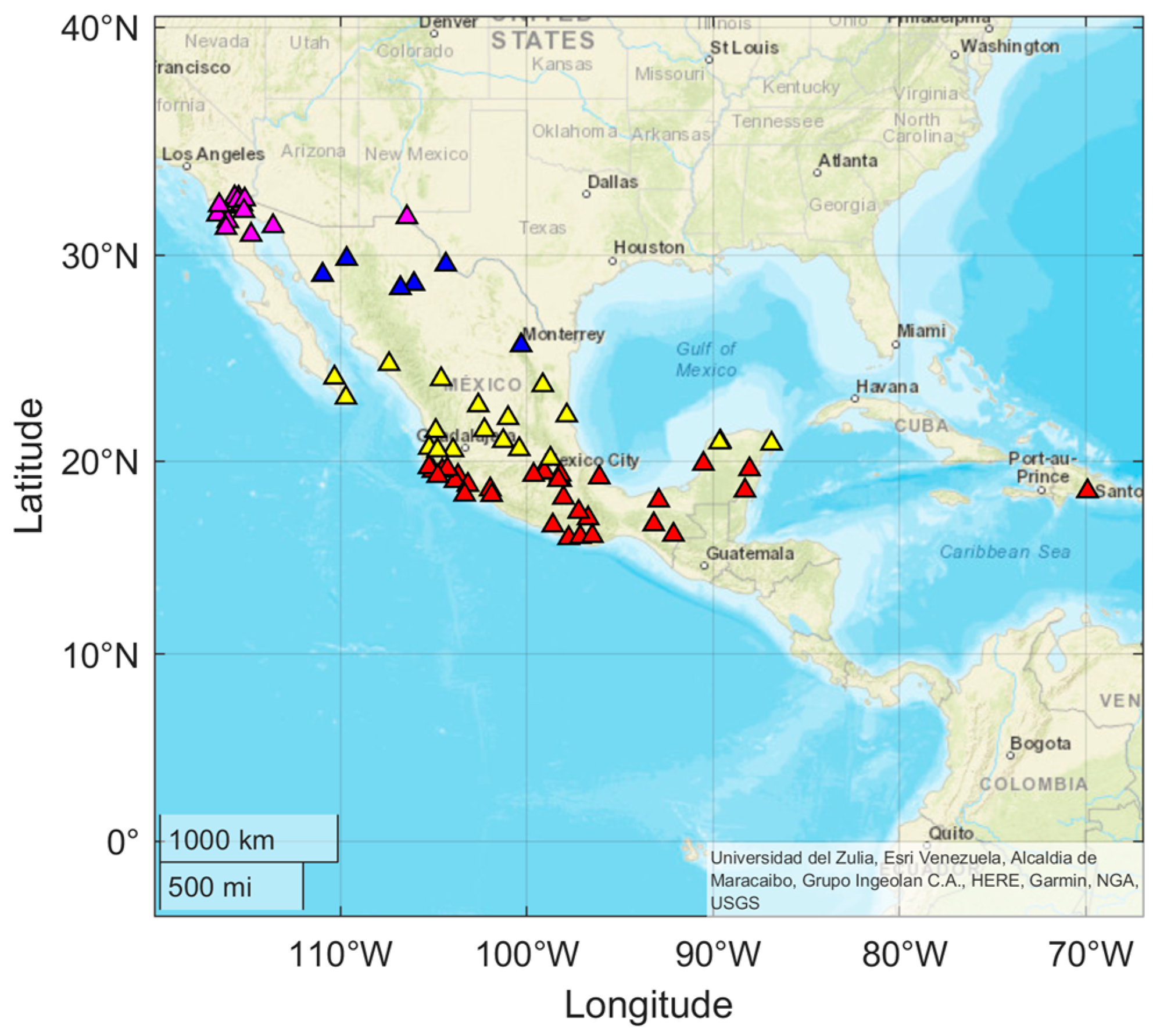
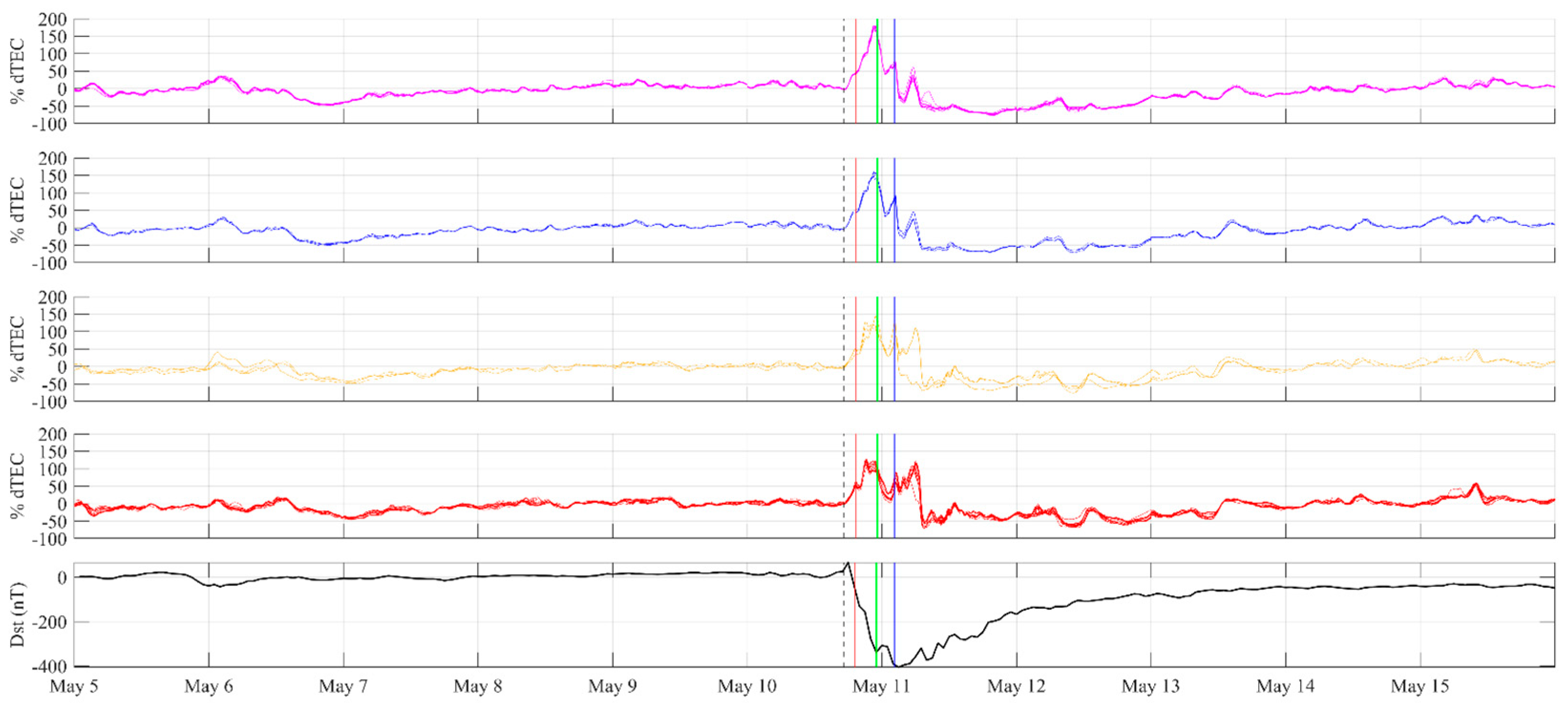

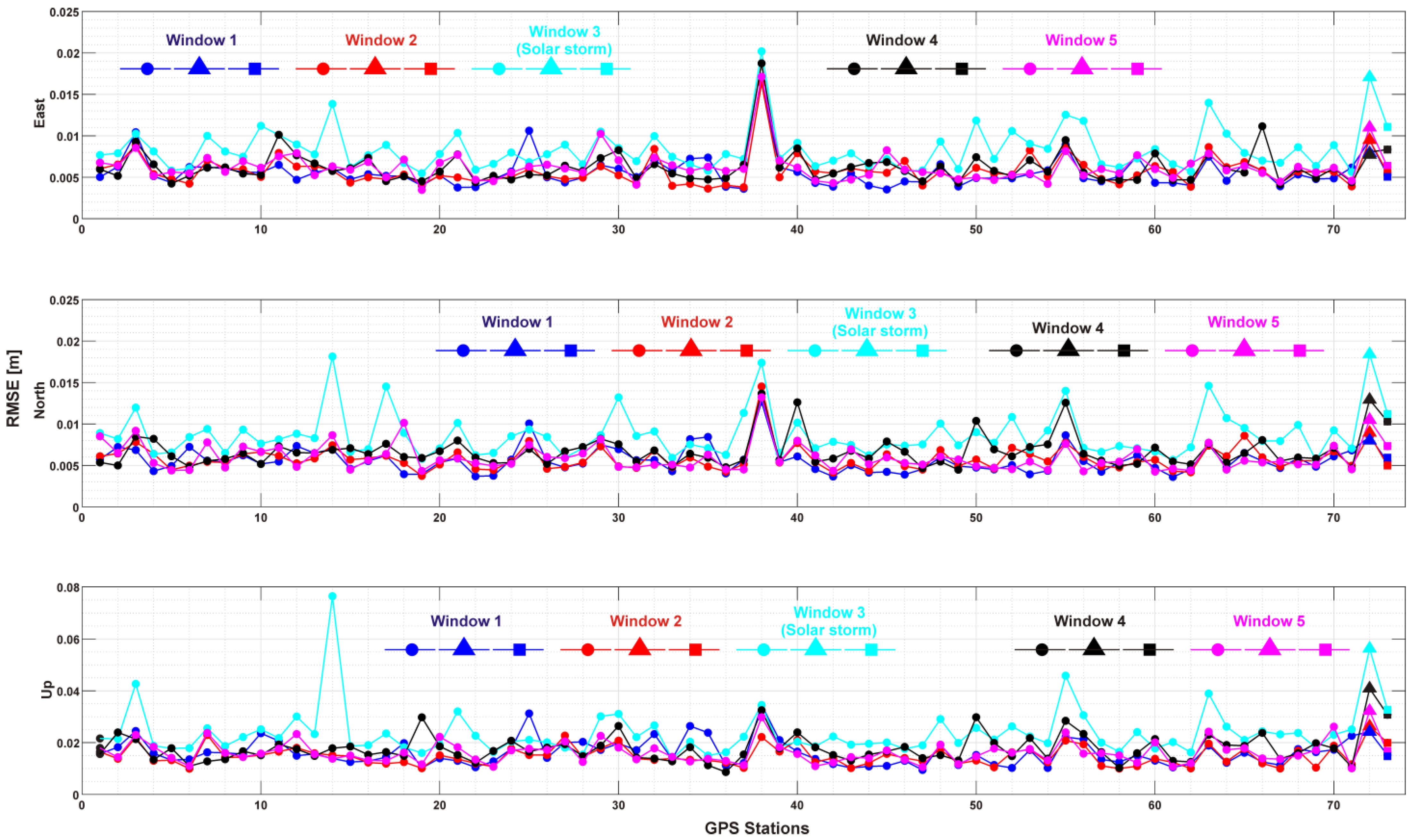
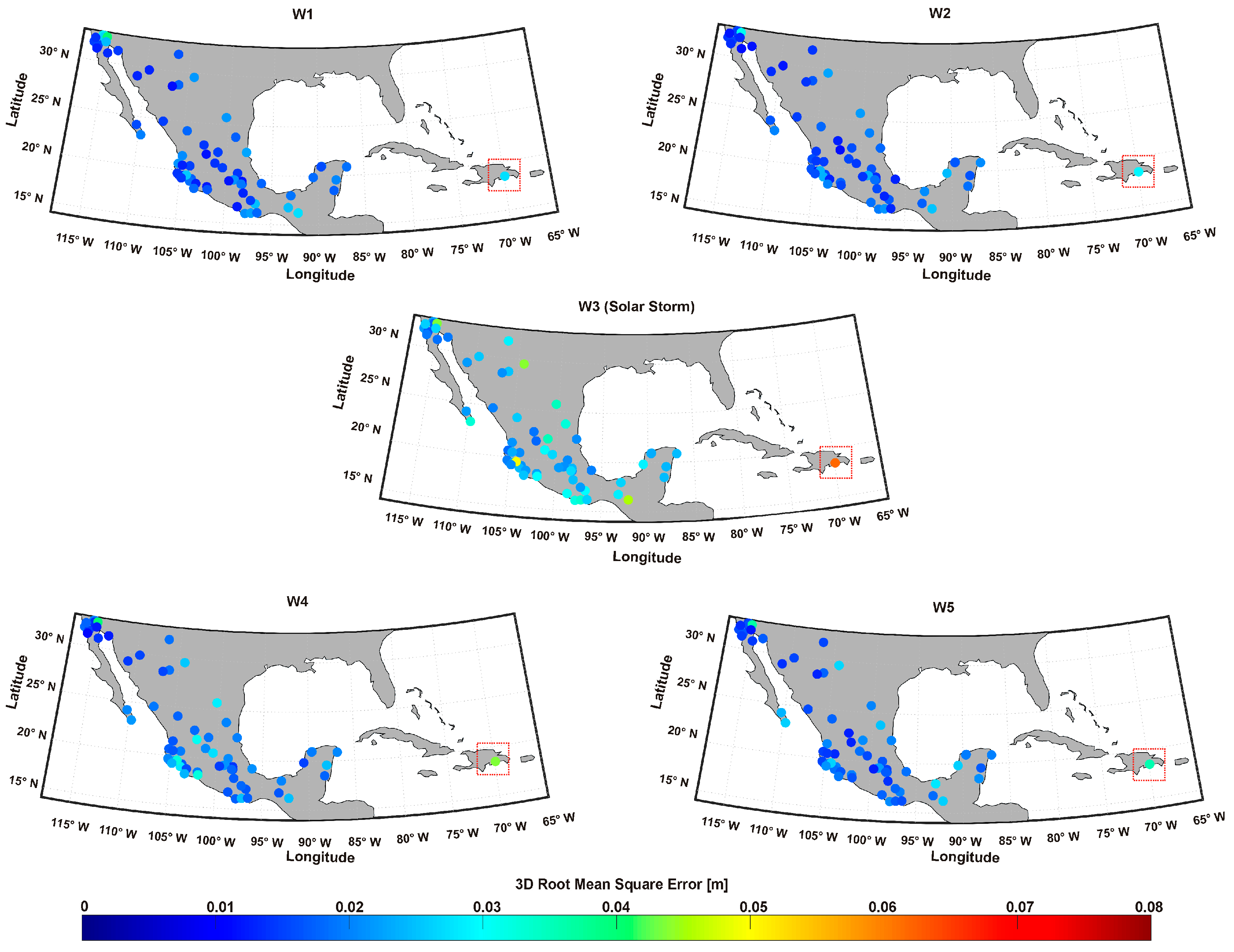


| # | Station | Lat ° (N) | Lon ° (W) | Onset Time (UT) | Max %dTEC | Time Max %dTEC | Min %dTEC | Time Min %dTEC | PPD (Hours) | NPD (Hours) | Overall (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | daex | 32.225 | −115.419 | 10 May, 18:29 | 178.46 | 10 May, 22:32 | −74.13 | 11 May, 19:40 | 11.21 | 55.45 | 64.60 |
| 2 | nayx | 32.324 | −115.296 | 10 May, 18:27 | 180.65 | 10 May, 22:35 | −76.49 | 11 May, 19:40 | 8.22 | 43.92 | 53.01 |
| 3 | pb1y | 32.648 | −115.692 | 10 May, 18:28 | 175.06 | 10 May, 22:52 | −75.04 | 11 May, 19:22 | 8.20 | 56.54 | 65.38 |
| 4 | phjx | 32.490 | −115.550 | 10 May, 18:25 | 169.16 | 10 May, 22:40 | −71.14 | 11 May, 19:21 | 8.26 | 55.82 | 64.98 |
| 5 | plcx | 31.255 | −116.158 | 10 May, 18:32 | 172.13 | 10 May, 22:38 | −73.60 | 11 May, 19:31 | 11.52 | 40.61 | 52.89 |
| 6 | ptex | 32.288 | −116.521 | 10 May, 18:29 | 173.07 | 10 May, 22:52 | −77.75 | 11 May, 19:35 | 11.34 | 40.36 | 52.61 |
| 7 | quex | 32.549 | −115.153 | 10 May, 18:29 | 177.29 | 10 May, 22:31 | −74.58 | 11 May, 19:27 | 8.17 | 56.93 | 65.57 |
| 8 | tnpp | 31.336 | −113.632 | 10 May, 18:27 | 167.49 | 10 May, 22:54 | −70.01 | 11 May, 19:17 | 11.32 | 43.53 | 52.79 |
| 9 | yumx | 32.028 | −115.199 | 10 May, 18:27 | 178.29 | 10 May, 22:35 | −75.21 | 11 May, 19:21 | 11.20 | 55.41 | 64.60 |
| 10 | tncu | 28.451 | −106.794 | 10 May, 18:24 | 149.43 | 10 May, 22:31 | −70.56 | 11 May, 19:17 | 8.28 | 41.43 | 53.58 |
| 11 | tnhm | 29.081 | −110.970 | 10 May, 18:30 | 161.33 | 10 May, 22:35 | −68.62 | 11 May, 19:11 | 11.47 | 41.26 | 53.50 |
| 12 | usmx | 29.823 | −109.680 | 10 May, 18:28 | 159.55 | 10 May, 22:33 | −70.52 | 12 May, 09:41 | 8.22 | 55.52 | 64.85 |
| 13 | tnam | 20.536 | −103.967 | 10 May, 18:35 | 128.35 | 10 May, 21:10 | −59.21 | 12 May, 11:01 | 12.26 | 52.02 | 64.57 |
| 14 | tnms | 20.535 | −104.797 | 10 May, 18:34 | 110.90 | 10 May, 21:06 | −64.45 | 12 May, 09:55 | 12.29 | 51.80 | 64.38 |
| 15 | unpm | 20.869 | −86.868 | 10 May, 19:01 | 144.42 | 10 May, 22:52 | −75.79 | 12 May, 10:04 | 7.80 | 53.90 | 63.46 |
| 16 | cn25 | 16.232 | −92.135 | 10 May, 18:50 | 104.50 | 10 May, 22:59 | −70.11 | 11 May, 07:31 | 10.93 | 52.49 | 64.56 |
| 17 | teco | 18.985 | −103.861 | 10 May, 18:40 | 128.36 | 10 May, 21:08 | −68.88 | 12 May, 10:56 | 12.28 | 52.26 | 64.80 |
| 18 | tnat | 18.130 | −98.041 | 10 May, 18:35 | 111.70 | 10 May, 21:05 | −69.49 | 11 May, 07:32 | 12.19 | 52.60 | 65.06 |
| 19 | tncc | 18.791 | −103.173 | 10 May, 18:44 | 125.42 | 10 May, 21:06 | −65.24 | 12 May, 07:59 | 12.19 | 50.71 | 63.16 |
| 20 | tncm | 19.498 | −105.045 | 10 May, 18:44 | 122.29 | 10 May, 21:16 | −66.28 | 12 May, 10:32 | 12.20 | 44.63 | 57.15 |
| 21 | tnct | 19.681 | −105.259 | 10 May, 18:44 | 125.74 | 10 May, 21:12 | −67.65 | 12 May, 10:35 | 12.19 | 44.67 | 57.18 |
| 22 | tncy | 16.059 | −97.759 | 10 May, 18:38 | 119.74 | 10 May, 21:14 | −59.17 | 12 May, 09:40 | 12.30 | 52.19 | 64.77 |
| 23 | tnif | 18.272 | −101.896 | 10 May, 18:43 | 125.78 | 10 May, 21:07 | −66.76 | 12 May, 08:46 | 12.20 | 52.26 | 64.72 |
| 24 | tnlc | 19.506 | −104.549 | 10 May, 18:40 | 128.71 | 10 May, 21:10 | −63.28 | 12 May, 10:29 | 12.27 | 44.70 | 57.27 |
| 25 | tnmq | 16.710 | −98.612 | 10 May, 18:37 | 125.23 | 10 May, 21:14 | −60.27 | 12 May, 19:32 | 12.30 | 52.24 | 64.82 |
| 26 | tnmt | 19.586 | −104.274 | 10 May, 18:44 | 123.27 | 10 May, 21:13 | −68.21 | 12 May, 10:24 | 12.18 | 52.11 | 64.55 |
| 27 | tnnp | 16.120 | −97.142 | 10 May, 18:38 | 119.30 | 10 May, 21:15 | −58.77 | 12 May, 09:44 | 12.25 | 52.38 | 64.90 |
| 28 | tnnx | 17.408 | −97.224 | 10 May, 18:35 | 114.26 | 10 May, 21:13 | −66.34 | 11 May, 07:41 | 12.20 | 52.60 | 65.08 |
| 29 | tntm | 19.239 | −104.790 | 10 May, 18:39 | 116.84 | 10 May, 21:13 | −63.42 | 12 May, 10:32 | 12.28 | 44.64 | 57.24 |
| 30 | uton | 19.033 | −98.316 | 10 May, 18:32 | 110.94 | 10 May, 21:04 | −65.52 | 11 May, 07:35 | 12.16 | 52.64 | 65.10 |
| 31 | ubxa | 18.468 | −69.910 | 10 May, 18:58 | 236.30 | 10 May, 23:16 | −79.58 | 11 May, 03:52 | 14.76 | 26.55 | 67.85 |
| 32 | rdsd | 18.461 | −69.911 | 10 May, 18:36 | 194.32 | 10 May, 23:48 | −71.60 | 11 May, 03:52 | 14.91 | 38.41 | 77.90 |
| Windows | Average of RMSEs [m] | 3D RMSE [m] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | ||
| W1 | 0.0056 | 0.0056 | 0.0161 | 0.0179 |
| W2 | 0.0057 | 0.0058 | 0.0148 | 0.0169 |
| W3 | 0.0083 | 0.0087 | 0.0238 | 0.0267 |
| W4 | 0.0062 | 0.0067 | 0.0178 | 0.0201 |
| W5 | 0.0061 | 0.0058 | 0.0161 | 0.0182 |
| Station | Strategy | RMSE in m | 2D RMSE in m | 3D RMSE in m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | N | U | ||||
| ICAM | 1-order GPS | 0.0093 | 0.0086 | 0.0270 | 0.0120 | 0.0290 |
| 2-order GPS | 0.0096 | 0.0081 | 0.0270 | 0.0120 | 0.0290 | |
| 1-order GREC | 0.0065 | 0.0063 | 0.0188 | 0.007 | 0.0200 | |
| 2-order GREC | 0.0066 | 0.0059 | 0.0187 | 0.0080 | 0.020 | |
| ICHI | 1-order GPS | 0.0074 | 0.0093 | 0.0221 | 0.0110 | 0.0250 |
| 2-order GPS | 0.0073 | 0.0091 | 0.0221 | 0.0110 | 0.0240 | |
| 1-order GREC | 0.0069 | 0.0058 | 0.0197 | 0.0080 | 0.0216 | |
| 2-order GREC | 0.0070 | 0.0057 | 0.0195 | 0.0090 | 0.0214 | |
| UBXA | 1-order GPS | 0.0170 | 0.0184 | 0.0563 | 0.0250 | 0.0612 |
| 2-order GPS | 0.0190 | 0.0185 | 0.0577 | 0.0260 | 0.0630 | |
| 1-order GREC | 0.0090 | 0.0090 | 0.0255 | 0.0127 | 0.0285 | |
| 2-order GREC | 0.0090 | 0.0090 | 0.0257 | 0.0127 | 0.0286 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vazquez-Ontiveros, J.R.; Melgarejo-Morales, A.; Martinez-Felix, C.A.; Martinez-Batlle, J.R. Analysis of Ionospheric Response and GNSS Positioning on Geodetic and Low-Cost Receivers in Mexico During the May 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Geosciences 2025, 15, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15110408
Vazquez-Ontiveros JR, Melgarejo-Morales A, Martinez-Felix CA, Martinez-Batlle JR. Analysis of Ionospheric Response and GNSS Positioning on Geodetic and Low-Cost Receivers in Mexico During the May 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Geosciences. 2025; 15(11):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15110408
Chicago/Turabian StyleVazquez-Ontiveros, J. Rene, Angela Melgarejo-Morales, Carlos A. Martinez-Felix, and J. Ramon Martinez-Batlle. 2025. "Analysis of Ionospheric Response and GNSS Positioning on Geodetic and Low-Cost Receivers in Mexico During the May 2024 Geomagnetic Storm" Geosciences 15, no. 11: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15110408
APA StyleVazquez-Ontiveros, J. R., Melgarejo-Morales, A., Martinez-Felix, C. A., & Martinez-Batlle, J. R. (2025). Analysis of Ionospheric Response and GNSS Positioning on Geodetic and Low-Cost Receivers in Mexico During the May 2024 Geomagnetic Storm. Geosciences, 15(11), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences15110408








