Abstract
Taking into account recent studies on the tsunamigenic potential of strike-slip faults, it is concluded that there is a need to reassess their near-source tsunami hazard and risk. One of the areas which needs reassessment is Western Greece, especially the Ionian Islands and the western coastal Peloponnese, where major seismogenic strike-slip structures occur. In this context, an extensive review of the available literature is conducted, including not only earthquake and tsunami catalogues but also tsunamis’ imprints on the stratigraphic record. It is concluded that the Ionian Islands and the western Peloponnese have a rich history of tsunamis since 6000 BC, revealing that they are subjected to high tsunami hazard. In addition to the teletsunami effects of distant earthquakes, there are also local tsunamis with smaller physical quantities and slighter coastal impact that are attributed mainly to local offshore faults and earthquake-triggered landslides. The fact that no destructive local tsunamis have been detected so far does not exclude the possibility of future triggering. In order to identify areas susceptible to future tsunami impact, we extract tsunami quantities and coastal impact data from available sources and we apply the Integrated Tsunami Intensity Scale 2012 (ITIS-2012) for all the events with available and adequate information. The highly susceptible areas comprise straits, funnel-shaped bays and extensive coastal areas exposed to major strike-slip seismogenic sources in the Ionian Sea and the western Hellenic Trench. Based on the aforementioned information, the inclusion of the Ionian Sea in the tsunamigenic zones of Greece is strongly recommended.
1. Introduction
Tsunamis may result from various triggering events, such as earthquakes causing rapid displacement of the seafloor, coastal and submarine landslides, submarine volcanic eruptions and partial or total collapse of volcano flanks, as well as the impact of extraterrestrial objects in the ocean [1]; however, they can also be triggered by the synergy of phenomena such as earthquakes and landslides [2,3,4] or atmospheric pressure waves and volcano mass movements [5]. Their occurrence in zones of large earthquakes and strong volcanic eruptions gives these phenomena high potential to have a notable impact on coastal environments, especially on the population (e.g., [6,7,8]) and coastal structures and infrastructure (e.g., [9]), making them a significant threat to coastal communities around the world and highlighting the need for the immediate adoption of effective measures for the protection of the built environment [10] and public health [7,8].
In areas of high seismicity where strike-slip tectonics prevail, the probability of tsunami generation due to earthquakes was considered by many to be low. This view of low probability was attributed to the fact that the deformation caused by such a coseismic slip and seafloor rupture, which mainly involves lateral movement of the fault, does not have high tsunami potential.
Contrary to previous beliefs, there are many historical and recent examples of earthquakes worldwide with focal mechanisms that show the prevalence of horizontal slip, but which have caused tsunamis with significant impact on the population, and on the natural and built environment of coastal areas.
Typical examples worldwide are the 7 June 1692 Mw = 7.5 Port Royal earthquake and the 14 January 1907 Mw = 6.5 Kingston earthquake in Jamaica; the 18 April 1906 Mw = 7.9 San Francisco earthquake in Northern California; the 15 November 1994 Mw = 7.1 Mindoro earthquake in Philippines; the 17 August 1999 Mw = 7.6 earthquake in Izmit (Turkey); the 20 January 2010 Mw = 7.0 Haiti earthquake; and the 11 April 2012 Mw = 8.6 and the 2 March 2016 Mw = 7.8 earthquakes in the Wharton Basin, offshore southwestern Sumatra (Indonesia) [2,3,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. The most recent example of a strike-slip seismic event which triggered a destructive tsunami is the 28 September 2018 Mw = 7.5 earthquake on the Indonesian Sulawesi island, which had a severe impact on the coastal area of Palu Bay [18,19,20]. These earthquakes proved that the older concept of the low tsunamigenic potential of strike-slip faults and related earthquakes is wrong for the reasons developed below.
The tsunamigenic potential of large strike-slip earthquakes is strongly related to the tectonics of strike-slip systems, the characteristics of the causative strike-slip faults and their associated structures. Strike-slip fault systems are composed of various sites of localized transpressional and transtensional deformation, namely restraining and releasing bends, respectively [21]. Restraining bends are mainly characterized by topographic uplift, crustal shortening and exhumation of the crystalline basement, which result in elongated, individual massifs with anomalously high topographic elevations, while releasing bends are defined by subsidence, crustal extension, significant basin sedimentation, high fluid flow and possible volcanism, which produce pull-apart basins and fault-bounded troughs [21]. All these structures produce areas with steep slopes and weakly consolidated deposits, which are favorable conditions for the triggering of submarine landslides along either a pop-up structure or a pull-apart basin. Moreover, the uplift at a pop-up structure and the subsidence at a pull-apart basin at different scales, ranging from outcrop to regional, are effective and efficient processes for tsunami triggering after a strike-slip earthquake [16].
The generation of a strike-slip earthquake can trigger extensive environmental effects including onshore, coastal and offshore slope failures and coastal liquefaction. These accompanying effects can trigger the occurrence of an individual tsunami, which, along with the contribution of the seabed morphology and the parameters of the seismic rupture process, can contribute and lead to a major disaster. Sassa and Takagawa [22] suggested that the occurrence of extensive liquefaction in coastal areas of the Palu Bay induced a gravity flow of liquefied soil mass that triggered a tsunami. More specifically, the coastal land of Palu Bay totally collapsed due to large-scale liquefaction phenomena. The liquefied sediments flowed to deeper parts of the bay, resulting in the displacement of a large sea-water volume in at least nine coastal sites, and consequently, multiple tsunamis [22]. It is also implied that less than 20% of the tsunami height was attributed to tectonic processes (uplift or subsidence of the sea floor strongly related to the offshore extension of the Palu-Koro strike-slip fault), while the rest was attributed to liquefied gravity flows [22].
Williamson et al. [4] concluded that the coseismic source contributed primarily to the generation of the devastating 2018 tsunami near Palu City, while the rest of Palu Bay suffered the destructive impact of a tsunami that gained its potential for destruction through subaerial and submarine landsliding.
This is the second time that this tsunami generation mechanism has been observed after a strike-slip earthquake. The first was after the 20 January 2010 Mw = 7.0 Haiti earthquake, which was a predominantly strike-slip event that caused vertical deformation and several local tsunamis reported west, north and south of the epicenter [3]. Due to the fact that there is no evidence for significant coseismic deformation close to the tsunami-affected areas, Hornbach et al. [3] concluded that modest uplift, together with sliding and probable shoreline liquefaction, caused a slide-generated tsunami after the 2010 Haiti earthquake.
Based on a computational framework that integrates models for earthquake rupture dynamics with models of tsunami generation and propagation, Elbanna et al. [23] suggested that ground motions induced by strike-slip earthquakes are generally characterized by high potential for triggering a large tsunami (>1 m). More specifically, ruptures spreading along strike-slip faults into narrow, funnel-shaped and shallow bays are among the main causes of tsunami triggering and propagation. The findings of Elbanna et al. [23] show that tsunami triggering by strike-slip earthquakes does not require complicated submarine terrain, complex seismic sources or the generation of submarine landslides and coastal liquefaction phenomena along the coast.
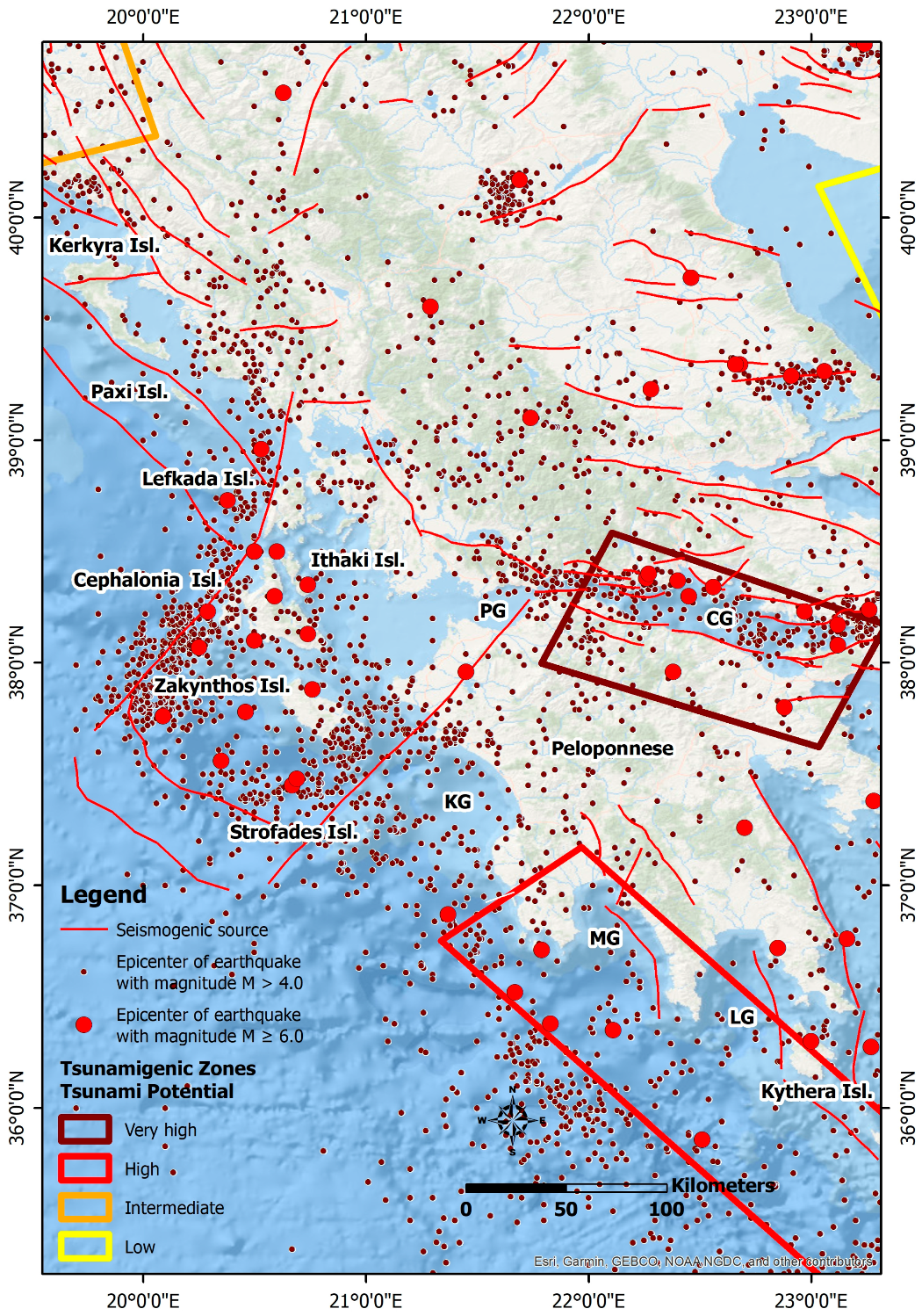
Considering the above, near-source tsunami hazard and risk need to be re-evaluated in areas where strike-slip seismogenic sources prevail. One such area is the western part of Greece including the Ionian Islands and the Ionian coast of Peloponnese (Figure 1). This is a region of high seismicity, including the occurrence of strong and destructive earthquakes, both recently and during the historical period [24]. These earthquakes, some of which are among the most powerful and destructive not only in Greece but also in the Eastern Mediterranean, are characterized by the clear prevalence of horizontal slip with a small contribution of either the normal or the reverse component of the movement [24]. Typical recent examples comprise the August 1953 and the early 2014 earthquakes in Cephalonia, the 2003 and 2015 Lefkada earthquakes, the 2008 Andravida earthquake in the northwestern Peloponnese and the 2018 Zakynthos earthquake, among others. As a result, these earthquakes have had a multitude of effects: (i) on the local population, including human losses, injuries and internal migration; (ii) on the natural environment, including mainly rockfalls and slides on steep slopes and fault scarps and liquefaction in coastal areas; and (iii) on the built environment, including severe structural and non-structural damage to buildings and infrastructure [25,26,27,28,29,30,31].
However, the Ionian Islands have been classified as an area with low tsunamigenic potential due to the fact that strike-slip faults are considered to be capable of causing only moderate seafloor deformation, but also due to the fact that no tsunamis from earthquakes have been recorded in the region so far [32]. It is important to mention that in the map of tsunamigenic zones of the Mediterranean compiled by Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [33] (Figure 1), there is no tsunamigenic zone in the Ionian Sea.
Taking into account all of the above, and especially the new data on tsunami occurrence from recent strike-slip earthquakes, we re-examine the available literature on all known earthquakes and their secondary environmental effects in the Ionian Sea and western and southern Peloponnese since historical times with emphasis on tsunamis, including analyses and interpretations of historical archives, contemporary sources and related scientific research publications. This review aims to compile a complete list of the historical and recent tsunamigenic earthquakes that have generated and affected the study area, to present tsunamis’ physical characteristics and to precisely and accurately describe the impact of the triggered tsunamis on the coastal zone of the study area based on the available literature. This approach is an important tool for understanding the tsunamigenic potential of the study area on the basis of existing data and past events. Furthermore, it aims to highlight the coastal areas susceptible to tsunami impact as derived from the already existing published literature.
In the context of this research, the Integrated Tsunami Intensity Scale 2012 (ITIS-2012) proposed by Lekkas et al. [34] is applied in the study area based on the available qualitative and quantitative information for the physical properties and the impact of the triggered tsunamis on the coastal zone. This application aims first to assign intensities to the recorded tsunami-affected localities, and then, to highlight the coastal areas prone to tsunami occurrence and highly susceptible to their impact. This is the first time such an approach has been applied to all known tsunamis triggered by earthquakes in a region from historical times to the present for which there is available and sufficient information for such an application.
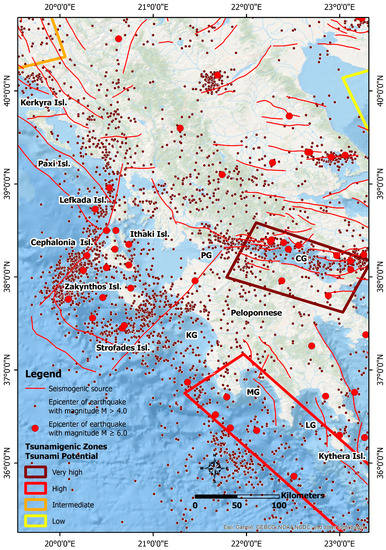
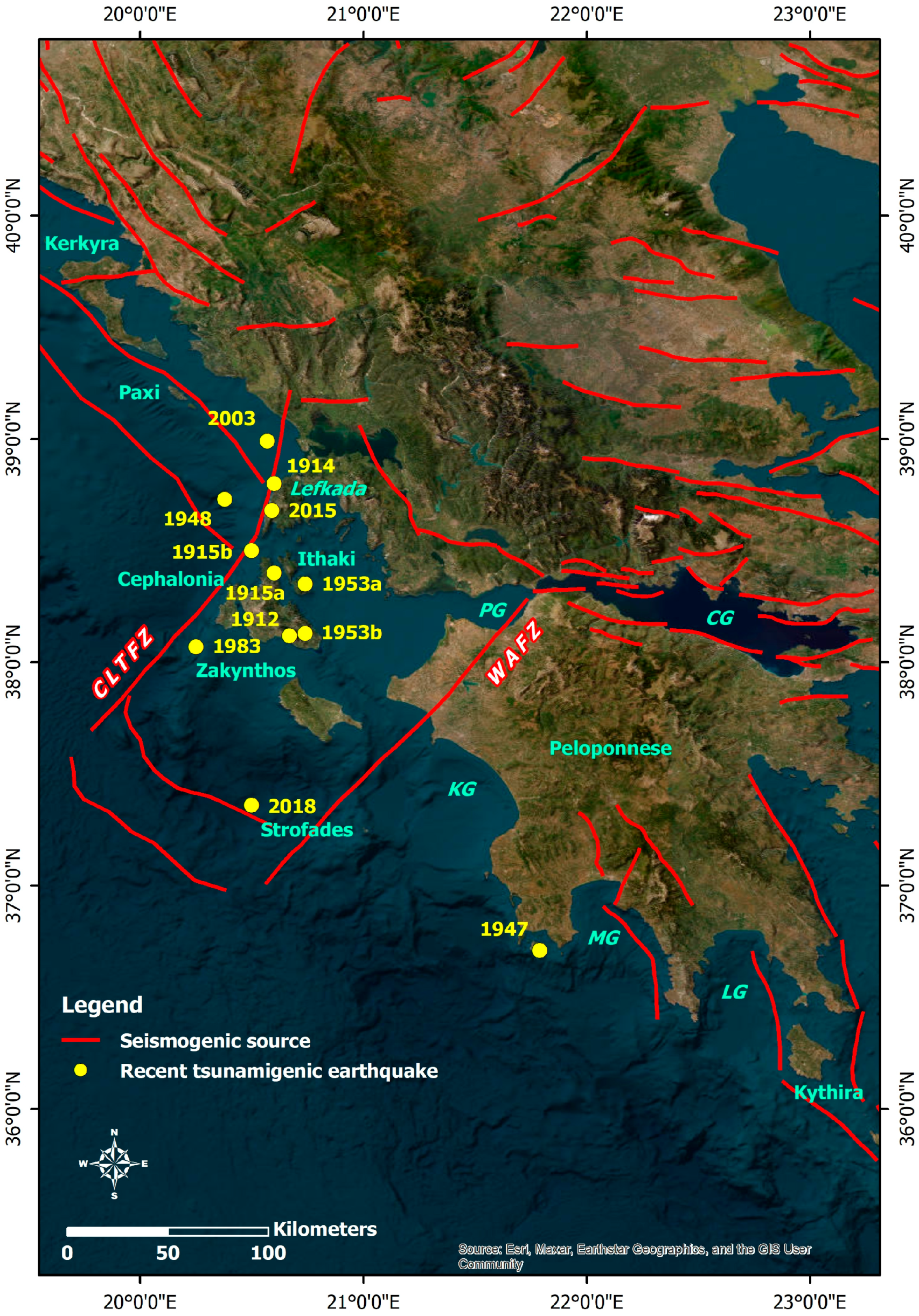
Figure 1.
Western Greece comprising the Ionian Islands and offshore western and southern Peloponnese along with the seismogenic sources, the tsunamigenic zones and the epicenters of earthquakes with M > 4.0 and M ≥ 6.0 based on the earthquake catalogue of Makropoulos et al. [35]. The Ionian Island is not included in the list of tsunamigenic zones of the Eastern Mediterranean region to date, while the zone of the west Hellenic Trench (the area in red frame in the lower right part) is considered a zone of high tsunamigenic potential by Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [33]. The seismogenic sources are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36].
Figure 1.
Western Greece comprising the Ionian Islands and offshore western and southern Peloponnese along with the seismogenic sources, the tsunamigenic zones and the epicenters of earthquakes with M > 4.0 and M ≥ 6.0 based on the earthquake catalogue of Makropoulos et al. [35]. The Ionian Island is not included in the list of tsunamigenic zones of the Eastern Mediterranean region to date, while the zone of the west Hellenic Trench (the area in red frame in the lower right part) is considered a zone of high tsunamigenic potential by Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [33]. The seismogenic sources are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36].
2. Methodology
The methodology includes a review of the available literature, which comprises information on the historically reported and instrumentally recorded earthquake-triggered tsunamis in the western part of Greece including the Ionian Islands and the western and southern offshore Peloponnese. The provided information was obtained from the following sources (Figure 2):
- Historical and recent tsunami databases comprising information about tsunamis worldwide, such as the National Centers for Environmental Information/World Data System (NCEI/WDS) Global Historical Tsunami Database (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration—National Centers for Environmental Information) [37] and the Euro-Mediterranean Tsunami Catalogue compiled by Maramai et al. [38]. The Global Historical Tsunami Database provides information about over 2400 tsunamis from 2000 BC to the present in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans, and the Mediterranean and Caribbean Seas [37]. It consists of two related files. The first file, the Tsunami Source Event comprises information on the source, location, occurrence date and time of the triggered tsunami, its magnitude and intensity, the maximum water height, the total number of fatalities and injuries as well as a description of the destruction and damage induced by the event and an estimation of the total damage due to the triggered tsunami. The second file includes information about run-ups and, more specifically, about locations where tsunami effects occurred including the arrival date and time, travel time, maximum water heights, horizontal inundation distances, and socioeconomic data comprising fatalities, injuries, and damage for specific run-up locations. The Euro-Mediterranean Tsunami Catalogue (EMTC) comprises information about 290 tsunami events that have occurred in the European and Mediterranean seas from 6150 BC to the present [38]. It constitutes the outcomes of systematic and detailed reviews of about 900 documentary sources, such as historical documents, books, scientific reports, newspapers and 26 examined datasets, many of which have also been evaluated and used in the frame of this research, including the studies of Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39], Papadopoulos [40], Soloviev et al. [41], Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [32], etc. Thus, the EMTC contains detailed descriptions, pictures, photos, tide-gauge records and a complete list of literature sources. The Euro-Mediterranean Tsunami Catalogue (EMTC) comprises information about 290 tsunami events that have occurred in the European and Mediterranean seas from 6150 BC to the present [38]. It constitutes the outcomes of systematic and detailed reviews of about 900 documentary sources, such as historical documents, books, scientific reports, newspapers and 26 examined datasets, many of which have also been evaluated and used in the frame of this research, including the studies of Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39], Papadopoulos [40], Soloviev et al. [41], Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [32], etc. Thus, the EMTC contains detailed descriptions, pictures, photos, tide-gauge records and a complete list of literature sources.
- Historical and recent tsunami databases comprising information about tsunami events for the Area of Greece and Adjacent Seas such as the one compiled by Papadopoulos [42]. This catalogue comprises 160 entries. The earthquake- and tsunami-related information was derived from original historical documents, previous tsunami catalogues, scientific reports, studies or books and, in a few cases, from field observations made by the author and collaborating people at selected coastal sites. It offers several pieces of information including the occurrence time; the region; the type and the location of the triggering event, along with the location and occurrence reliability, a short description of the event, the intensity, the surface-wave magnitude and the focal depth of the tsunamigenic earthquake; the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of the tsunamigenic volcanic eruption; the reported maximum tsunami run-up; as well as the magnitude, the intensity and the reliability of the triggered tsunami.
- Books containing catalogues of and information about earthquakes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Greece and their triggered effects, including tsunamis, among others, e.g., [43,44].
- Books containing catalogues of and information about tsunamis in the Eastern Mediterranean and Greece and their impact on coastal areas, e.g., [32,41].
- Scientific articles comprising information about earthquakes and their triggered effects, including tsunamis, among others, e.g., [28,45,46,47,48,49,50,51].
- Scientific articles comprising catalogues and information about tsunamigenic zones and tsunamis in Greece from antiquity to the present and their impact on coastal areas, e.g., [39,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63].
- Official field survey and reconnaissance reports on the impact of earthquakes and subsequent tsunamis on the coastal environment of the affected areas, e.g., [64].
- Contemporary sources, such as newspapers of local and national circulation.
All these sources have been reviewed with emphasis on earthquake-triggered tsunamis and other sea disturbances reported in the study area. Based on the available sources and descriptions of these effects, related qualitative and quantitative information was extracted.
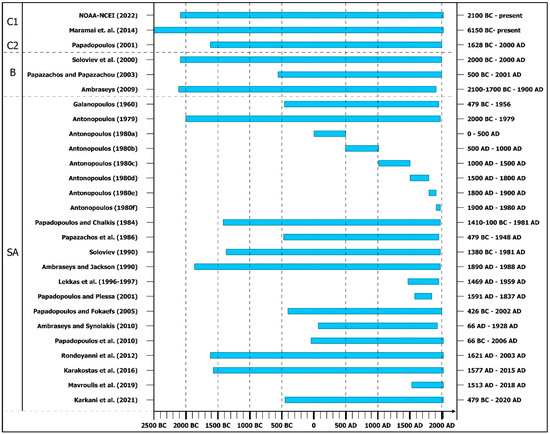
Figure 2.
The main tsunami-related sources [33,37,38,39,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65] for the study area used in this research. These references also include information from contemporary sources on individual seismic events and subsequent tsunamis in the study area, which are also cited in the following sections. (C1: historical and recent tsunami databases and catalogues comprising information about tsunamis worldwide, C2: historical and recent tsunami databases and catalogues comprising information about tsunamis in Greece and adjacent Seas, B: scientific books, SA: scientific research articles).
Figure 2.
The main tsunami-related sources [33,37,38,39,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65] for the study area used in this research. These references also include information from contemporary sources on individual seismic events and subsequent tsunamis in the study area, which are also cited in the following sections. (C1: historical and recent tsunami databases and catalogues comprising information about tsunamis worldwide, C2: historical and recent tsunami databases and catalogues comprising information about tsunamis in Greece and adjacent Seas, B: scientific books, SA: scientific research articles).
In addition to the sources used to obtain information related to tsunami quantities and their impact on coastal segments of the study area from the historical period to the present, the results of an extensive multiparametric and interdisciplinary research approach conducted in coastal parts of the study area were also evaluated and used. These studies aimed to identify the tsunamigenic imprint on Holocene coastal geoarchives based mainly on geomorphological, sedimentological, micromorphological, micropaleontological, geochemical and geophysical studies. By using these sources and their results, it is possible to expand the tsunami history in the study area, including major periods of the Holocene, even starting from the late Pleistocene to the early Holocene. Details about these studies and their results are presented in the following sections.
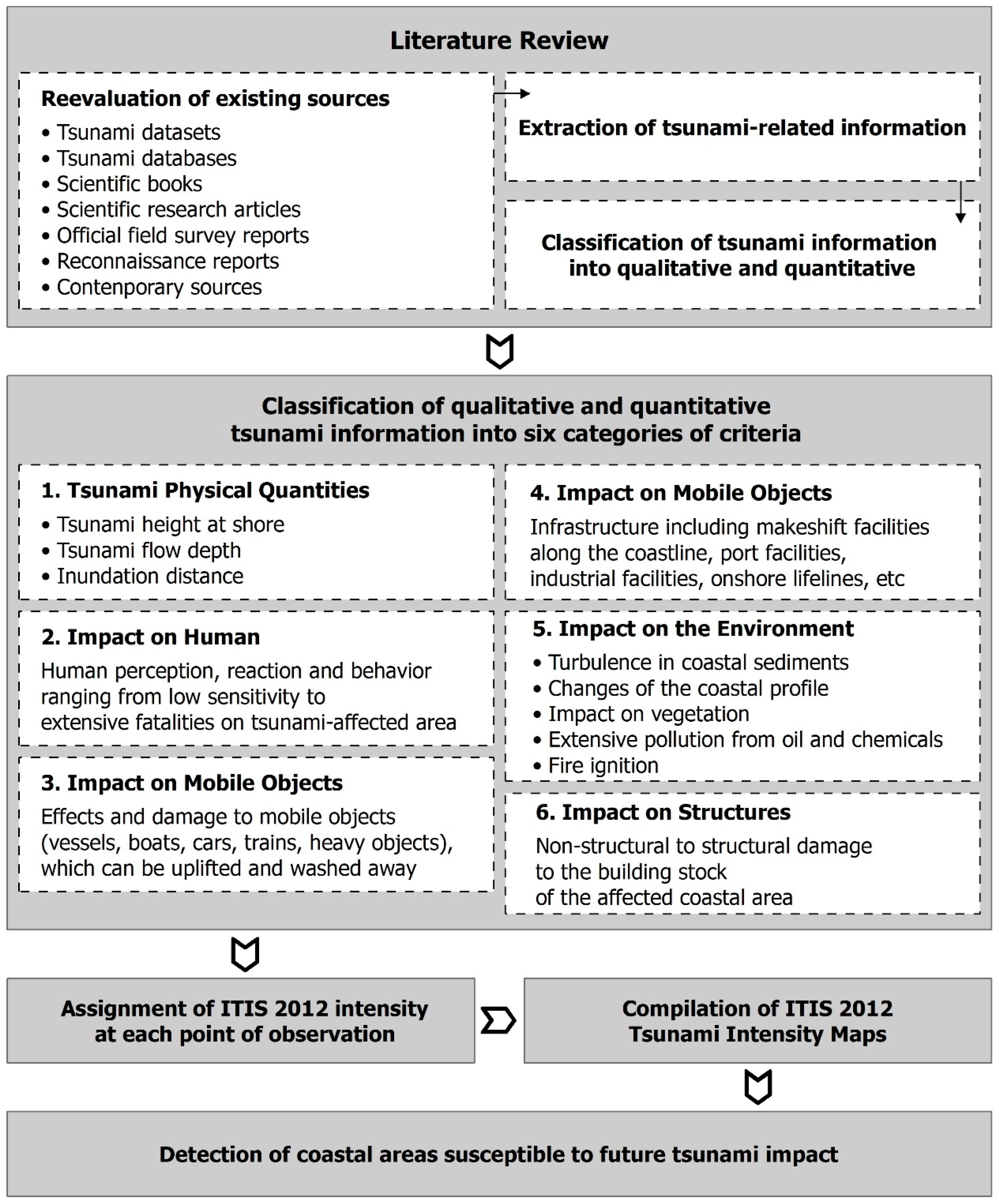
Furthermore, this study discusses the first application of the ITIS-2012 scale to all known triggered tsunamis in the study area from the historical period, with the related impact on the coastal zone reported by various researchers and travelers of the time, to the recent period, with installed monitoring systems and instrumental recordings of the tsunamis’ physical quantities (Figure 3).
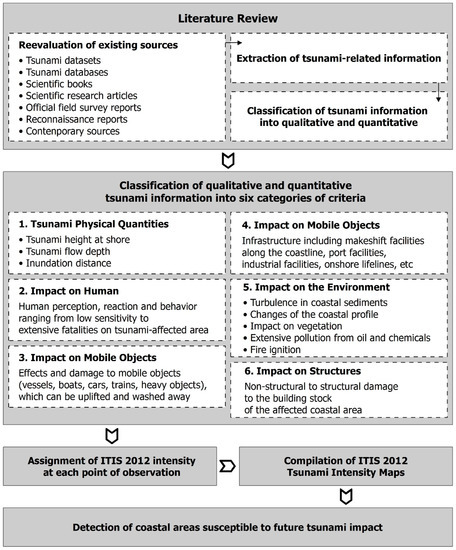
Figure 3.
Flowchart for the detection of areas susceptible to future tsunami impact based on the results of the application of ITIS-2012 for historical and recent earthquake-triggered tsunamis.
ITIS-2012 is a 12-grade scale ranging from I (not felt) to XII (completely devastating) that benefited mainly from the collection of large datasets following the two great tsunami events in 2004 and 2011 (Boxing Day 2004 Indonesian tsunami and 11 March 2011 Japan tsunami) and from other significant contemporary and historical events which were also taken into account [34]. It is based on the assessment of a large number of objective criteria, grouped into six categories ((i)physical quantities such as tsunami wave height, flow depth and inundation extent, (ii) impact on humans, (iii) impact on mobile objects such as boats and cars, (iv) impact on infrastructure, (v) environmental effects and (vi) impact on structures) [34] (Figure 3). This scale works well for modern events where large amounts of data are available [34,66], while Reicherter [67] argued that such scales are of limited use in paleotsunami studies due to the small datasets, the absence of instrumental records and the difficulties in obtaining the minimum necessary parameters for intensity evaluation and related assignments. Until the present, the ITIS-2012 scale has been applied for highlighting and quantifying the impact of recent earthquake-triggered tsunamis on the coastal zones of earthquake-affected areas in Japan [68], New Zealand [66], Greece [69] and Indonesia [70].
3. Geological Setting
The Ionian Islands in western Greece are defined by high seismicity characterized by frequent strong and destructive seismic events resulting in intense ground deformation [24], extensive environmental effects of earthquakes [25,26,27,28,29,31] and building damage [71,72,73]. This intense seismicity is mainly attributed to the NNE–SSW-trending, right-lateral Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) which is located at offshore western Cephalonia and Lefkada [24,74,75,76,77]. The CLTFZ constitutes a major boundary in the kinematic field of the region as it separates the Ionian margin into two parts with different kinematic and seismological properties: the northern part comprises the northern Ionian Islands (the Diapontia, Corfu, Paxi and Antipaxi Islands), which are moving slowly northward and northwestward at rates lower than 5 mm/year with respect to Eurasia, and the southern part comprises the Lefkada, Cephalonia, Ithaki and Zakynthos Islands, which are moving rapidly southwestward at rates ranging from 6 to 30 mm/year [78,79,80].
The high seismicity also recorded on the southern part of the Ionian Islands (Zakynthos and Strofades) has been attributed mainly to the proximity to the CLTFZ and the northwesternmost tip of the Hellenic Trench, which constitutes an active plate boundary between the subducting eastern Mediterranean lithosphere and the overriding Aegean one. This boundary terminates against the southern part of the CLTFZ.
The CLTFZ is not the only major active right-lateral strike-slip fault zone in the Ionian Sea. A few kilometers south of Zakynthos, another structure occurs. It constitutes the southward extension of the seismic NE–SW-striking, right-lateral strike-slip Western Achaia fault zone (WAFZ), which extends from the northwestern part of the Peloponnese to offshore southern Zakynthos [81]. The epicenter of the 8 June 2008 Mw = 6.4 Andravida earthquake and its aftershock sequence were distributed along the onshore part of the WAFZ, at the northwestern part of the Peloponnese [82,83]. Furthermore, the onshore part of the WAFZ has no direct surficial morphotectonic or geological evidence in the onshore Western Peloponnese [84]. On the contrary, its offshore extension is linked with an offshore pull-apart basin located northeast of the Strofades Islands [85,86].
South of Zakynthos, the Ionian Sea contains a downthrown block of the External Hellenides near the northern extremity of the Hellenic Trench. Flat thrusts, strike-slip faults and normal faults have been discovered [85], with thrusting dominating over strike-slip or normal faulting [87,88]. This region is notable for its 46 km long, NW-SE-trending thrust system [89], which was responsible for the 1997 Mw = 6.6 [35] and the 26 October 2018 Mw = 6.7 [90] Zakynthos earthquakes.
The area’s complicated tectonic setting has resulted in considerable seismic activity in the middle and southern parts of the Ionian Sea, as well as the western half of the Peloponnese. Increased seismicity has been reported over the past decade, particularly between 2014 and 2018, with strong earthquakes with M > 6.0 shocking the central Ionian Islands. Early in 2014, two earthquakes (Mw = 6.1 and Mw = 5.9) struck Cephalonia Island, while in November 2015 and October 2018, two earthquakes with Mw = 6.4 and Mw = 6.7 struck the southern part of Lefkada and offshore southern Zakynthos, respectively [24], with extensive environmental effects [25,26,27,28].
As regards the western and southern Peloponnese, onshore and offshore studies revealed that it is composed of megahorsts and megagrabens bounded by N-S- and E-W-trending active fault zones and seismogenic faults [84,85,91,92,93,94,95,96]. Offshore studies conducted in the Kyparissia [96], Messenian [97] and Laconian [98] Gulfs demonstrated that active faults observed onshore in the study area continue in several cases offshore.
4. Review of the Earthquakes and Earthquake-Triggered Tsunamis in Western Greece
Based on the above literature, we conducted an extensive review of earthquakes in the study area that have had significant environmental effects, particularly tsunamis with considerable impact on the coastal natural and built environments. The recorded impact includes a tsunamigenic imprint on the stratigraphic record, geo-scientific evidence on coastal areas of prehistoric earthquakes during the early and mid-Holocene, and a mainly destructive impact on the population, objects, buildings and infrastructure of the coastal zone during historical (pre-1900) events and recent (post-1900) events. Related information is presented in the following subsections and it is summarized in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
4.1. Holocene Tsunamigenic Evidence in the Stratigraphic Record of Coastal Areas and Related Tsunami Events
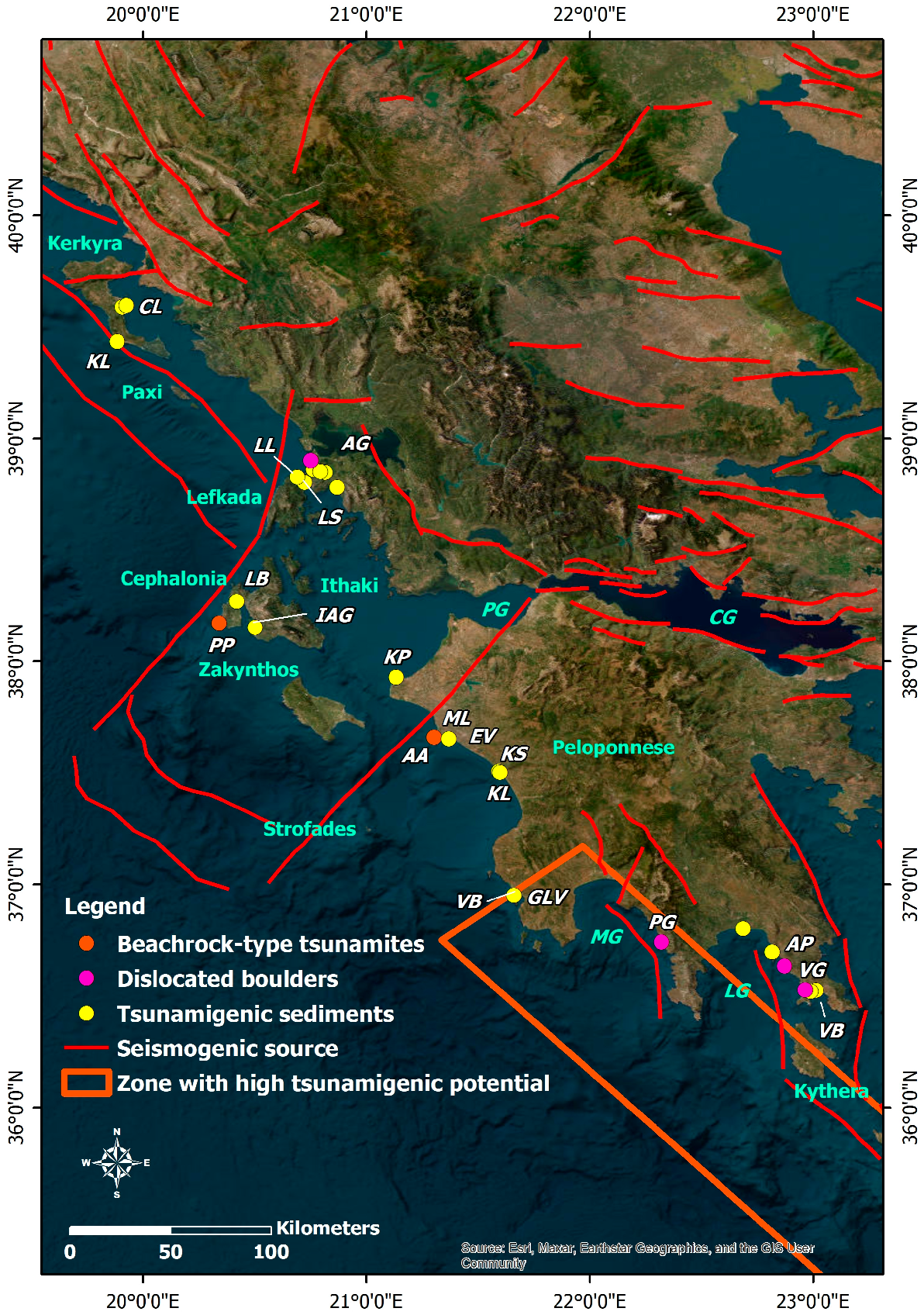
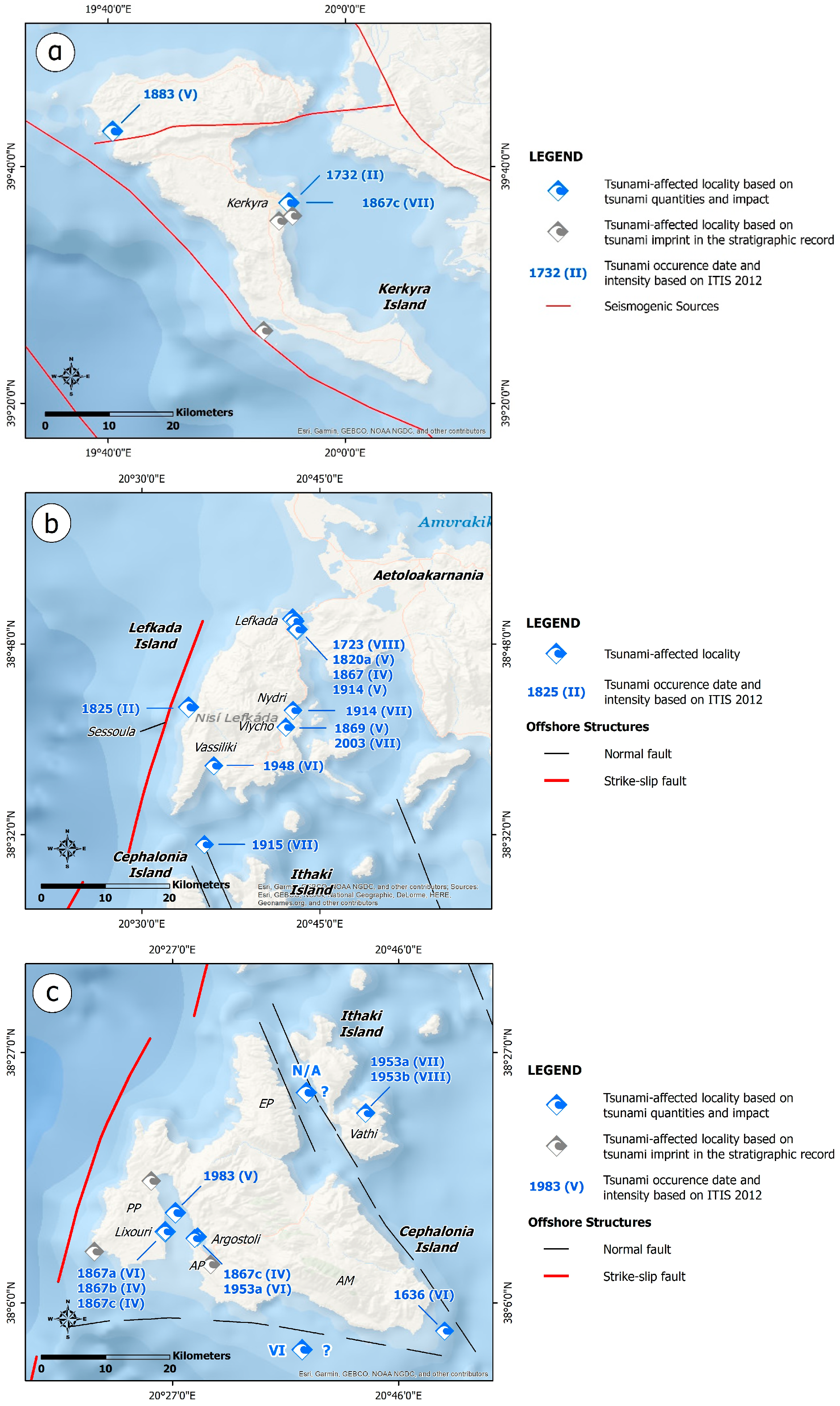
Interdisciplinary and multiparametric studies for detecting tsunamis’ impact on the stratigraphic record of the study area revealed a rich history of tsunamigenic prehistoric and historical earthquakes and related tsunami events in many coastal segments (Figure 4 and Figure 5). In particular, starting from N to S, tsunami deposits and related events were detected and identified on Corfu Island [99], Lefkada Island [100,101], the adjacent Ambracian Gulf [102], Cephalonia Island [103,104,105], the coastal zones of the northwestern Peloponnese [106], the Kyparissia Gulf [103,107,108,109,110], the Messenia Gulf [111] and the Laconia Gulf [111,112] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
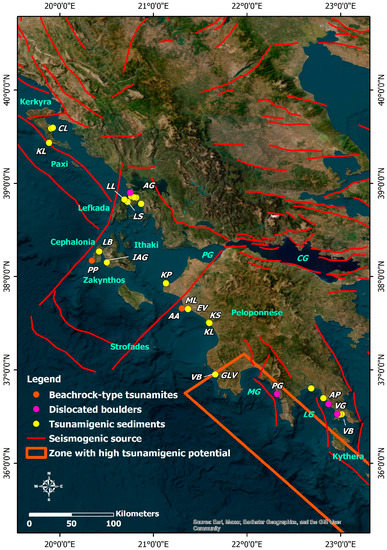
Figure 4.
Distribution of tsunami signature on the stratigraphic record of coastal areas affected mainly by distant tsunamigenic prehistoric and historical earthquakes in the western part of Greece. Based on related studies [99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112], the tsunami signature has been classified into: beachrock-type tsunamigenic calcarenites (orange circles), dislocated boulders (purple circles) and tsunamigenic sediments in the stratigraphic record (yellow circles). The seismogenic sources are also presented. They are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36]. CL: Chalikiopoulou Lagoon; KL: Korissia Lagoon; LL: Lefkada Lagoon; LS: Lefkada Sound; AG: Ambracian Gulf; LB: Livadi Bay; PP: Paliki Peninsula; IAG: Inner Argostoli Gulf; KP: Kyllini peninsula; AA: Ayios Andreas; ML: (former) Mouria Lagoon; EV: Epitalio Valley; KS: Kato Samiko; KL: Kaiafas Lagoon; VB: Voidokilia Bay; GLV: Gialova; PG: Porto Gatea; AP: Archangelos Peninsula; VG: Viglafia; VB: Vatika Bay.
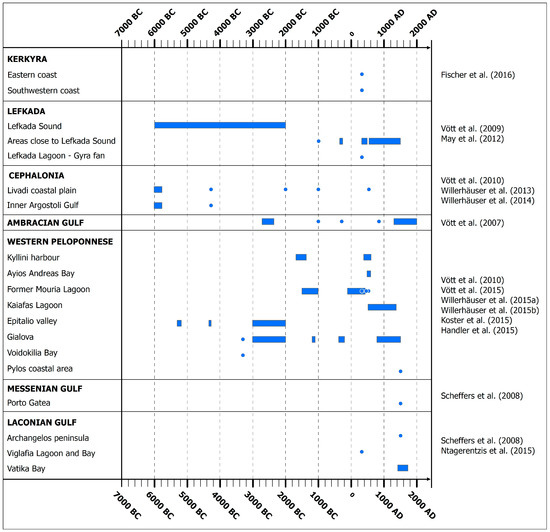
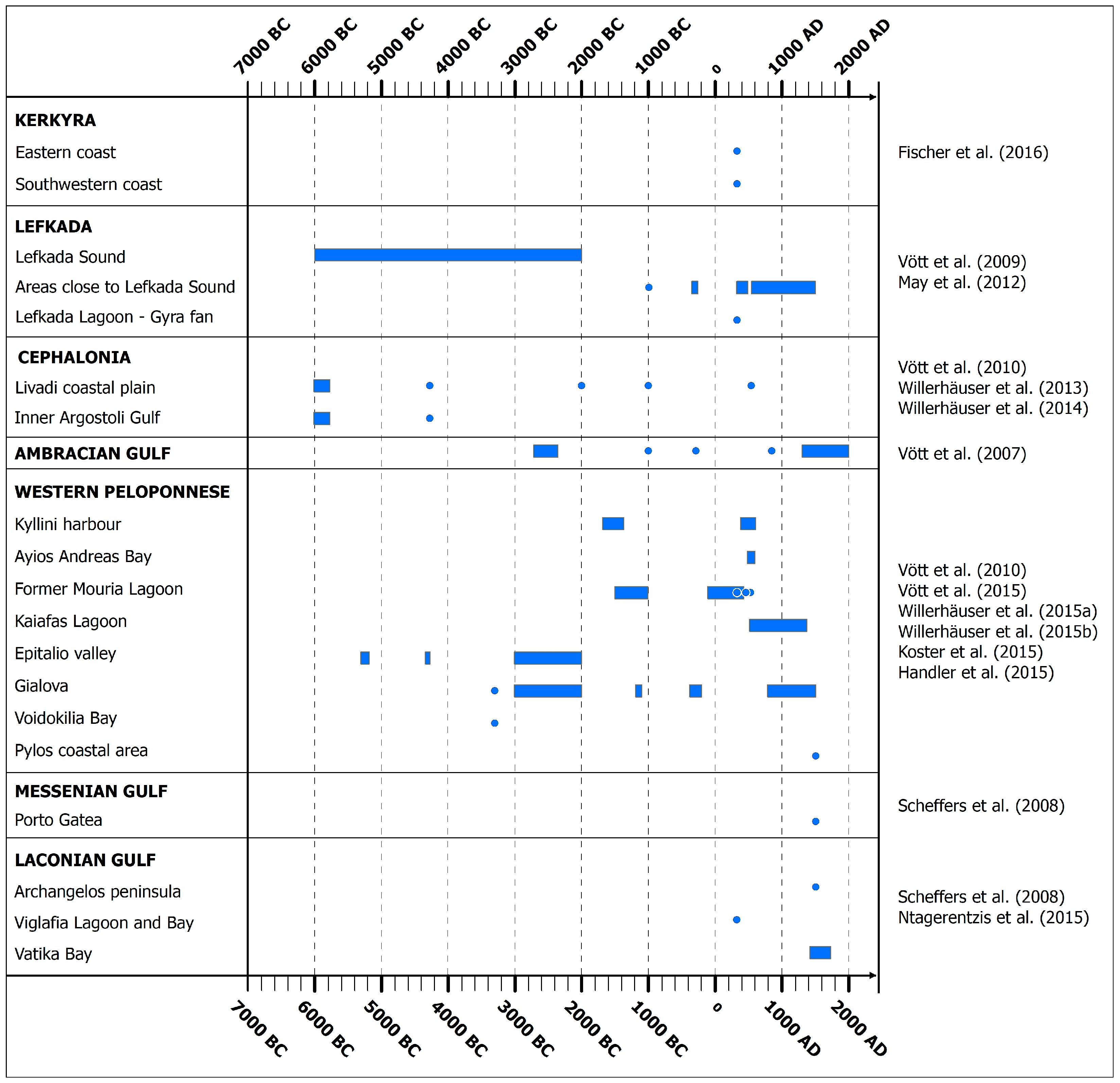
Figure 5.
Coastal areas on the Ionian Islands and western and southern Peloponnese affected by tsunamigenic prehistoric, historical and recent earthquakes. Points and bars correspond to time periods and years with tsunami occurrence, which were identified from geo-scientific evidence in the stratigraphic record of the affected areas in the frame of the listed interdisciplinary and multiparametric studies that focused on the tsunamigenic imprint on Holocene coastal geoarchives [99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112].
These above-cited research studies comprise the results of:
- High-resolution topographic surveys and 3D visualization using differential GPS and LiDAR measurements;
- Dating techniques including 14C-AMS dating of organic material or biogenetically produced carbonate, optically stimulated luminescence dating and archaeological age determination, and comparisons to earthquake catalogues and inventories of local tsunami;
- Vibracoring for detecting the influence of high-energy events in the stratigraphic record with emphasis on tsunamis, and analysis in the field using geomorphological and sedimentological methods, as well as microfaunal, microfloral and macrofaunal studies;
- Geochemical analysis of parameters such as electrical conductivity, pH-value, carbonate content, orthophosphate, loss of ignition, concentrations of heavy minerals, and alkaline and earth alkaline metal ions for detecting facies changes;
- Geophysical measurements including earth resistivity measurements;
- Underwater studies for detecting tsunami signatures on the seabed;
- Field mapping of sediment layers and their study in trenches;
- Use and evaluation of remote sensing data such as high-resolution satellite products for searching for and detecting spatial structures of tsunamigenic origin.
In Kerkyra, the eastern as well as the southwestern coasts of the island were repeatedly affected by extreme wave effects during the Holocene [99]. In particular, the eastern coast of Kerkyra is now preferentially affected by high-energy wave impacts from a southern direction like those related to teletsunamis from the Hellenic Trench, while the southwestern coast of Kerkyra is endangered by impacts from both western and southern directions like those related to teletsunamis triggered in the Hellenic Trench or the Etna (Italy) regions, or induced by submarine landslides at the steep continental shelf located at offshore western Kerkyra [99]. Furthermore, based on simulation results, Fischer et al. [99], suggested that the coasts of Kerkyra were also affected by the tsunami triggered by the 365 AD Crete (southern Greece) earthquake (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Several early tsunami impacts place the Lefkada Sound between the sixth and third millennium BC, while adjacent areas were affected by younger events determined around 1000 cal BC and 395–247 cal BC, as well as in Roman and Medieval times [100] (Figure 4 and Figure 5). These tsunami occurrences reveal a high tsunami risk for the Lefkada Sound, with at least one strong event every 500 to 1000 years [100].
In the northern part of Lefkada lagoon, the sequence of the prevailing Gyra fan is characterized by numerous properties of extreme wave deposits [101]. More specifically, the Gyra fan was formed by a tsunami with at least four inundation impulses, which are considered a teletsunami effect induced by the 365 AD earthquake generated off western Crete [101] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Several tsunami landfalls were reconstructed in the Ambracian Gulf and especially at the offshore Aktio headland [102]. A major tsunami struck the entire headland around 2780–2350 cal BC, while further tsunamis probably affected parts of the Ambracian Gulf around 1000 cal BC and 300 cal BC [102] (Figure 4 and Figure 5). These events are known to have also affected the adjacent Lefkada coastal zone. The minimum height of the tsunami surge is estimated at 6m [102]. Further tsunamis were also triggered in 840 cal AD and during the last 700 years (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Based on the aforementioned information, an extraordinarily high tsunami risk is documented for the study area [102].
Regarding the coastal zone of Cephalonia, beachrock-type calcarenitic tsunamites were detected on the southwestern part of the Paliki peninsula, in Langadakia bay and the Gerogombos and Schinou capes [103] (Figure 4). This formation reflects a strong tsunami landfall on the western coast of Cephalonia Island during the late Pleistocene or even the Holocene. Furthermore, the evolution of the Livadi coastal plain was significantly affected by tsunamis during the Holocene [104]. This is attributed to the detection of five tsunami generations on the stratigraphic record of the plain: (i) in the early sixth millennium BC, (ii) before around 4250 cal BC, (iii) probably at the beginning of the second millennium BC, (iv) at the beginning of the first millennium BC and (v) after 780 AD [104] (Figure 5). As regards the Inner Argostoli Gulf, possible megatsunamis of supra-regional nature were generated at the beginning of the sixth millennium BC and before around 4250 cal BC [104].
Several researchers have published studies on tsunami deposits in the stratigraphic record of coastal segments and tsunami occurrence times and their related intervals for the western Peloponnese [103,107,108,109,110]. It is revealed that tsunami events have played a significant role in the landscape evolution of the coastal zone extending from the Kyllini area in the north to the Pylia peninsula in the south (Figure 4).
The northernmost site of coastal Peloponnese with identified tsunami deposits is the Kyllni ancient harbor site (Figure 4). These deposits were detected after field work and sedimentological, geomorphological, geochemical and microfossil analyses of Holocene samples conducted by Handler et al. [106]. Based on their results, two tsunami generations are reported: (i) between the early seventh and late fourth centuries BC, prior to the harbor foundation and (ii) between the fourth and sixth centuries AD or later.
A rapidly cemented beachrock-type tsunami deposit was detected in the Ayios Andreas Bay located close to the Katakolo area [103]. The ancient harbor site Pheia in the Olympia area was destroyed by this tsunami, which impacted the coast in the sixth century AD [103] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Four tsunami generations were identified in the stratigraphic record in the former Mouria Lagoon near Ayios Ioannis and adjacent areas, namely around Kato Samiko and the former Agoulenitsa Lagoon [108] (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The first affected the Mouria Lagoon and probably the Kato Samiko coastal plain in the fifth millennium BC, the second in the mid-to-late second millennium BC, the third between the first century BC and the early fourth century AD, while the forth is strongly related to the well-known 365, 521 or 551 AD tsunamis with impacts in wide areas of the Eastern Mediterranean region [108].
A minimum of four tsunamis have been detected within the last 300 years at the Kyparissia Gulf based on sedimentological evidence for paleotsunami deposits in the coastal segments of the former Agoulinitsa Lake, the Kaiafas Lagoon and the extended Kakovatos beach [110]. A tsunami landfall was identified between 540 AD and, at minimum, 1274 AD in the Kaiafas Lagoon [110] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
The Epitalio valley suffered from repeat inundation by tsunamis, which were considered part of supra-regional events generated in about 5300–5200 cal BC, 4350–4250 cal BC and during the third millennium BC [107] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Six different tsunami generations were identified in Gialova since the mid-Holocene: (i) before around 3300 cal BC, (ii) between the end of the forth millennium BC and the end of the third millennium BC, (iii) around 1200–1000 cal BC, (iv) shortly after the 4th to 2nd centuries BC, (v) between the 8th and the 14th/15th centuries AD and (vi) after the mid-14th century to the beginning of the 15th century AD [109] (Figure 4 and Figure 5). These tsunami generations revealed a recurrence interval of around 1.2 ka [109]. Based on these findings, it is supported that the evolution of the Gialova Lagoon was mainly controlled by high-energy events and tsunamis triggered by earthquakes generated close to the Hellenic Trench subduction zone [109]. Furthermore, the development of Voidokilia Bay has been also strongly related to tsunamis and their impact after around 3300 cal BC [109] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
The southern coasts of the Peloponnese have been studied for palaeotsunamigenic impact by Scheffers et al. [111] and Ntagerentzis et al. [112]. A strong tsunami that occurred in the Laconia Gulf (Figure 4) around 1300 cal AD was documented based on dislocated boulders, partly imbricated and showing different generations of rock pools [111]. This tsunami signature is attributed to a strong earthquake that was evidently generated at the Hellenic Trench and, more specifically, to the catastrophic earthquake in 1303 AD [111] (Figure 5 and Figure 6) that affected large parts of the Eastern Mediterranean, extending from the islands of Rhodes and Crete and northern Egypt to the southern Peloponnese and which is known to have been locally associated with seismic sea waves [41,45,61,113].
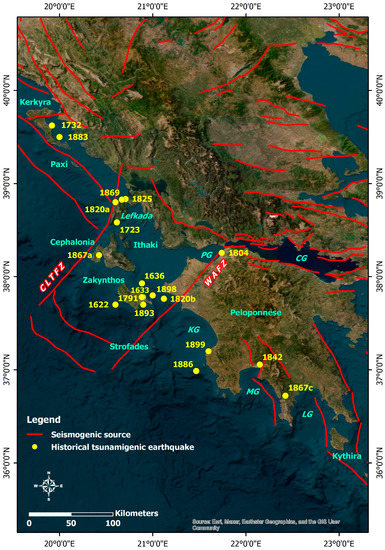
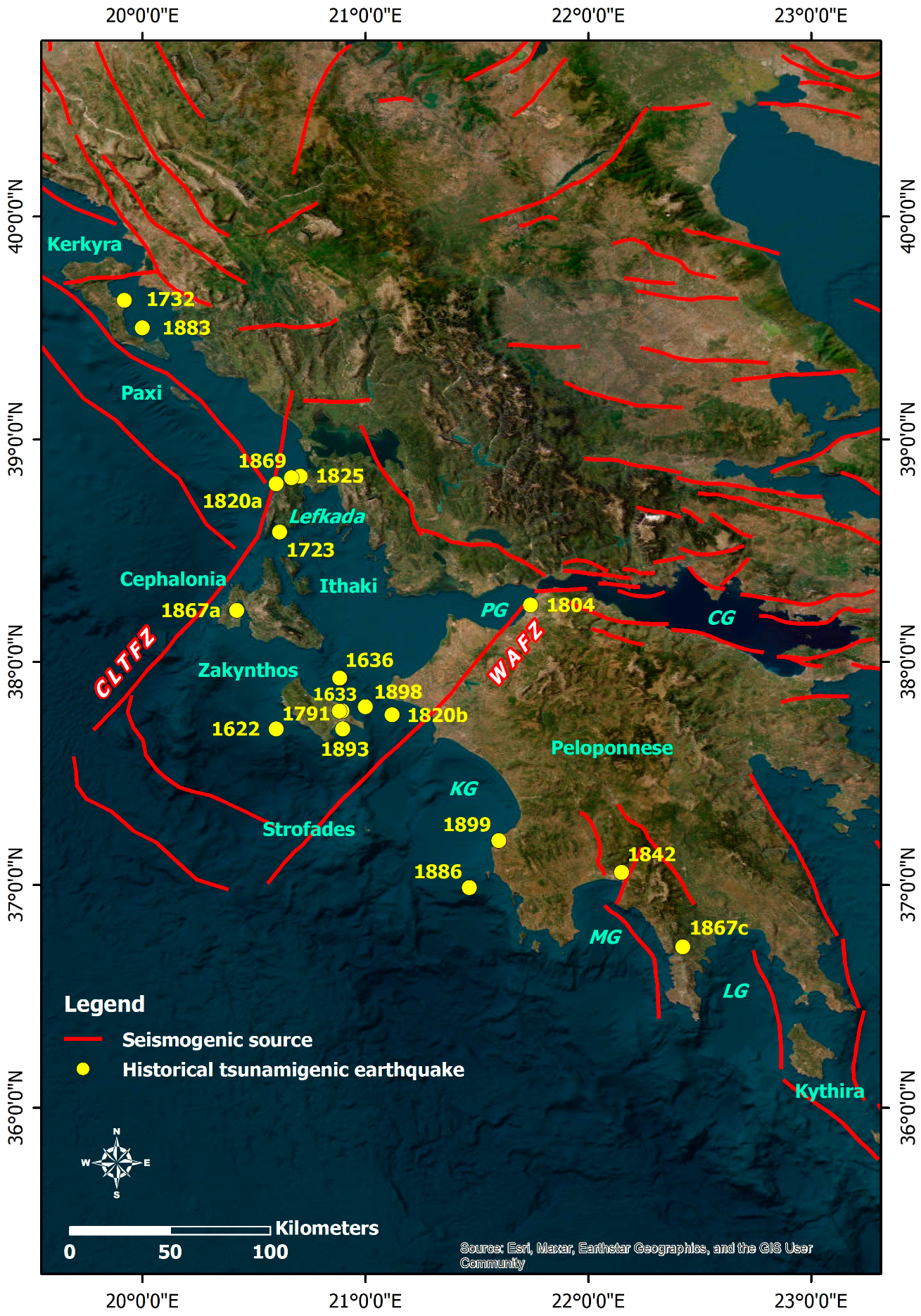
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of epicenters of the historical tsunamigenic earthquakes and occurrence dates in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese along with the seismogenic sources in the study area. The central part of the study area is dominated by strike-slip structures which comprise the Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) and the Western Achaia Fault Zone (WAFZ), both responsible for the generation of large and destructive strike-slip earthquakes. PG: Patras Gulf; CG: Corinth Gulf; KG: Kyparissiakos Gulf; MG: Messenian Gulf; LG: Laconian Gulf. The faults are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36], while the parameters of the earthquakes are presented in Table 1.
Tsunami evidence was also observed in the Pylos coastal area along the Ionian coast of Messenia, in Porto Gatea along the eastern coast of the Messenia Gulf and on the Archangelos peninsula along the eastern coast of the Laconia Gulf [111] (Figure 4). The geomorphological and sedimentological evidence comprised trim lines, dislocated vermetid rims, large boulders or marine sediments and shells washed onshore [111].
The absolute ages of large tsunami events along the coasts of the Peloponnese, during which boulders were moved onshore, are scattered in historical times. The results from dating shells and vermetid rims attached to dislocated boulders give conventional radiocarbon ages of 1110 ± 40 years BP, 950 ± 40 years BP and 1070 ± 50 years BP [111], indicating that the coasts of the southern Peloponnese were also affected by the 1303 AD catastrophic earthquake (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Different sediment layers related to high-energy event deposits were identified in the southeastern part of the Laconian Gulf [112]. Evidence at the Viglafia Lagoon and Bay were correlated with the well-known 356 AD Crete tsunami that affected a large part of the Eastern Mediterranean and to another younger event that affected Vatika Bay during or after the Renaissance period [112] (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
From the above, it is concluded that the geo-scientific evidence for tsunami impact in the stratigraphic record of the study area is strongly and mainly related to tsunami effects caused by prehistoric and historic earthquakes, mainly generated in several periods from 6000 cal BC to the Renaissance period. The earthquakes, whose tsunamis have left their imprint on the studied coastal areas, are very strong and mainly distant historical earthquakes with epicenters in the western part of the Hellenic Trench (e.g., the 365 AD and the 1303 AD Crete earthquakes), which has been classified as a zone of high tsunamigenic potential [33]. These seismic events resulted in teletsunami effects in the studied coastal sites of the Ionian Sea and the western and southern Peloponnese. However, local tsunamis are also detected and they are related to local earthquakes and subsequent submarine landslides.
4.2. Historical (Pre-1900) Earthquakes and Triggered Tsunami Events
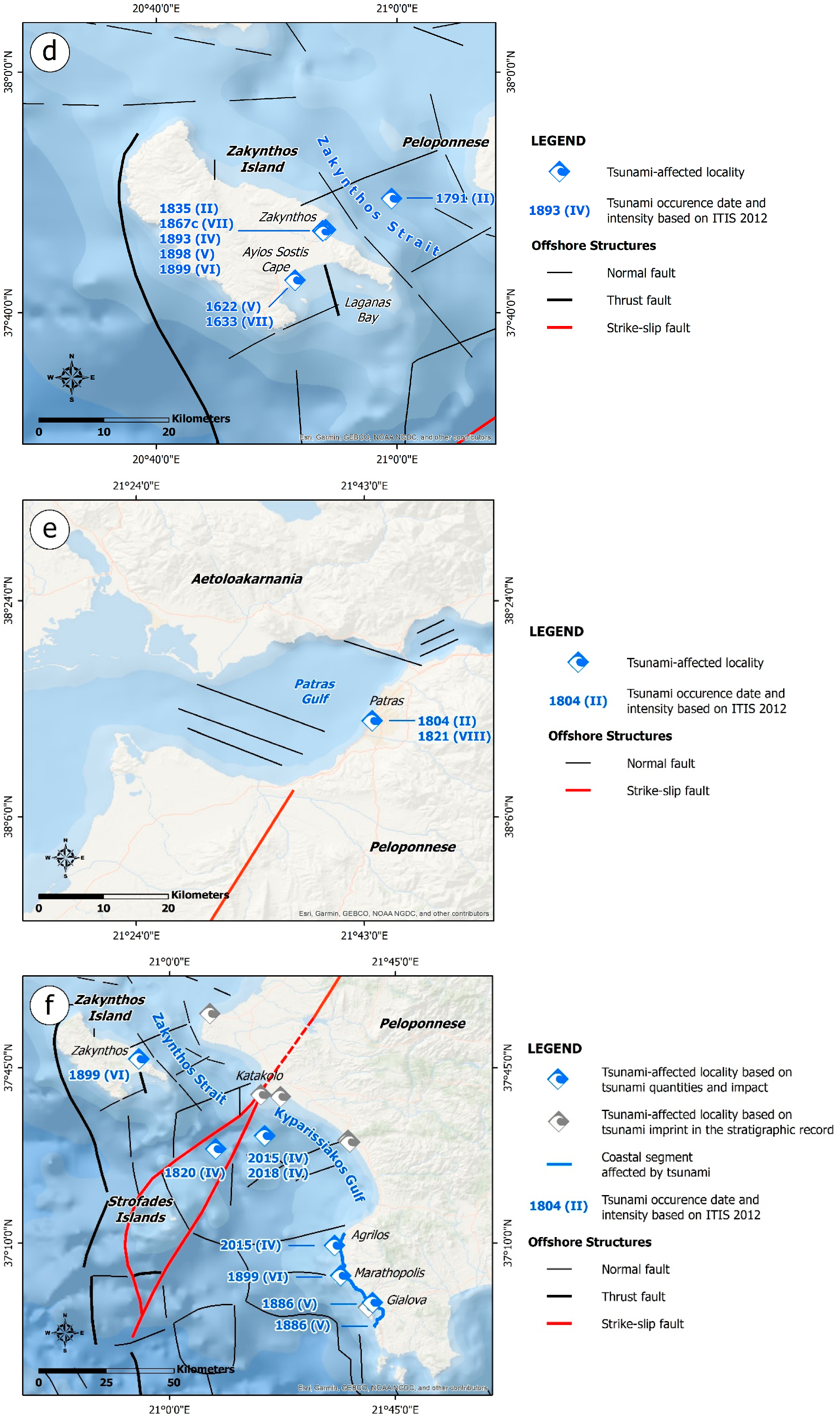
This section comprises information on the occurrence of the 22 historical tsunamigenic earthquakes and triggered tsunamis in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese from 1622 to 1899 (Table 1; Figure 6). Their impact on the local population and the building stock, as well as the triggered environmental effects, are briefly presented. Emphasis has been placed on the presentation of the available information on the tsunamis’ physical quantities and their impacts on the affected coastal zones.

Table 1.
Properties of the historical earthquakes (before 1900) that triggered sea disturbances, including tsunamis, in the Ionian Sea and offshore western and southern Peloponnese.
The properties of the studied historical tsunamigenic earthquakes are presented in Table 1. The information was obtained mainly from various earthquake catalogues including the SHARE European Earthquake Catalogue (SHEEC) 1000–1899 [114] and its updated version in the European Pre-Instrumental Earthquake Catalogue (EPICA) 1000–1899 [115]. When information about an earthquake was not available in these catalogues, it was searched in other sources, which are also cited in Table 1.
4.2.1. The 5 May 1622 Earthquake
The 5 May 1622 earthquake struck Zakynthos and destroyed the largest part of the island, resulting in human losses and injuries attributed to structural collapse [43,46,116,117,118,119,120]. It was followed by a large aftershock. Both events had a long duration. The earthquake triggered ground cracks in several sites [28,121].
Antonopoulos [57] conducted a study on the seismic sea waves in the Eastern Mediterranean from 1500 to 1800 A.D. In the frame of this study, he presented information about the 1622 earthquake and the subsequent tsunami derived from Sieberg [122], who used Barbiani and Barbiani [116] as an initial source. Based on the information provided by Barbiani and Barbiani [116], Sieberg [122] mentioned that the earthquake was followed by a seismic sea wave with an impact on the southern part of the island (Figure S1). More specifically, the Ayios Sostis cape located at the southeastern part of the Central Zakynthos fault block was washed away by the sea. This event and its impact on the coast has also been supported by Ambraseys [113], Galanopoulos [52,123,124], Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39], Soloviev [61], Lekkas et al. [46], Soloviev et al. [41] and Mavroulis et al. [28]. However, Antonopoulos [57] did not find any relevant tsunami information in the earthquake-related publications. As regards the reliability with which this tsunami occurrence is established, Soloviev et al. [41] characterized the tsunami-related information as questionable-to-wrong. As a result, this event is not included in several recent tsunami studies, e.g., [63].
4.2.2. The 5 November 1633
The 5 November 1633 earthquake struck Zakynthos, resulting in the collapse of many residential buildings and many fatalities [28,43,46,125]. As regards the earthquake’s environmental effects, ground cracks, hydrological anomalies, slope failures and a small seismic sea wave were triggered [28,46,125]. In particular, ground cracks appeared in several locations, with flames coming out of them, indicating the release of sulfur gases, which ignited and burned along these cracks [28]. Slope failures were probably triggered along the slopes of the mountains of Zakynthos (Skopos Mt or Vrachionas Mt) and in the Ayios Sostis cape area [28,46].
As regards the tsunami, Bonito [125] presented that the sea level rose, and the waves surged the coast with a great force and resulted in damage. Galanopoulos [52], based on Montandon [126] and Sieberg [122], supported that the tsunami’s occurrence was strongly associated with slumps and extensive faulting. Based on Bonito [125] and Coronelli [127], Antonopoulos [57] supported that the tsunami was attributed to rockfalls generated in the Ayios Sostis cape, resulting in the formation of an islet (Figure S2). This tsunami generation is also presented in the studies of Ambraseys [113], Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39], Papazachos et al. [60], Soloviev [61], Lekkas et al. [46] and Soloviev et al. [41].
4.2.3. The 30 September 1636 Earthquake
There were 520 fatalities and around 1500 injuries as a result of this earthquake [43,44,128,129]. The southern part of the island suffered more damage, with many communities completely devastated. The earthquake triggered environmental effects, mainly on the southern part of the island. The southern slopes of Aenos Mt experienced slope movements, including rockfalls and slides with considerable impacts on vegetation and livestock [43,121].
As regards sea effects, there was a major sea disturbance close to Cephalonia (Figure S3), resulting in a ship almost sinking [43]. These wave anomalies are also reported by Tselentis et al. [130] and Mavroulis [121].
4.2.4. The 22 February 1723 Earthquake
On 22 February 1723, a very strong earthquake occurred and caused the collapse of many buildings on Lefkada Island. The main earthquake was preceded by a strong earthquake on 20 February [43,44]. The same earthquake also caused damage in the northern and western parts of Cephalonia, mainly on the Paliki peninsula, where the majority of buildings in Lixouri town collapsed, as well as on the Erissos peninsula and in Argostoli town.
During the earthquake, a tsunami was also triggered [41,57,116,124] (Figure S4). The sea rushed onto the dry land, and then, returned, resulting in human losses [39,41,60,61,124]. Apart from the fact that the eastern coast of Lefkada was affected [50], there is no additional information on the exact geographical location of the affected area or on the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of these waves. However, taking into account the paleogeography and the previous tsunami-affected areas, it is suggested that the coastal areas of the Lefkada Sound were affected by the 21 February 1723 tsunami (Figure S4).
4.2.5. The November 1732 Earthquake
This strong earthquake was generated in the northern part of the Ionian Sea. It was destructive in Kerkyra, and felt up to the central part of the Ionian Sea, especially on the Lefkada, Ithaki, Cephalonia and Zakynthos Islands [43,116,131]. The shock was accompanied by a swell of the sea, destructive rain and a tsunami [113] (Figure S5). This tsunamigenic earthquake has been also mentioned by Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39], Soloviev [61] and Soloviev et al. [41].
4.2.6. The 2 November 1791 Earthquake
This earthquake affected the eastern hilly areas of Zakynthos Island, while its western part remained intact [116,124]. The aftershock sequence lasted more than 6 weeks, with the largest aftershock occurring 8 days after the mainshock, which resulted in 20 fatalities and 300 injured people. Due to the earthquake, ground cracks, sulfureous gas emissions in the Zakynthos city area, boiling of asphalt in the Keri swamp area and liquefaction phenomena were also observed [28,43,46,116,117,118,131,132]. The most violent agitation of the sea occurred in the Zakynthos Straits (Figure S6). Ambraseys [113] referred to the possible generation of a tsunami between Zakynthos and the Peloponnese. This is also included in other tsunami catalogues, e.g., [39,41,61].
4.2.7. The 8 June 1804 Earthquake
The 1804 earthquake was mainly felt in the Peloponnese and caused great damage to its northwestern part. Patras was destroyed, with many buildings razed to the ground, resulting in human losses. A tsunami was triggered by the earthquake and was noted in the northwestern part of the Peloponnese, especially in the coastal area of Patras [52,58,60,113] (Figure S7).
4.2.8. The 21 February and 17 March 1820 Earthquakes
From 31 January to 28 March 1820, hundreds of earthquakes occurred in Lefkada, the strongest of which were generated on 21 February and 17 March [43]. The first earthquake caused the collapse of some residential buildings in Lefkada, while the second destroyed a large part of the town, where all the stone masonry structures comprising houses and churches collapsed [116,133,134,135,136,137]. As for the secondary environmental effects of the second earthquake, noticeable subsidence was caused in the central square of Lefkada town and a tsunami also affected its coastal part [41,130,138] (Figure S8). The sea level in Lefkada town rose before the earthquake’s occurrence, resulting in inundation of the coastal zone, while a submarine landslide was triggered during the earthquake [41,130,138,139]. There are no further qualitative or quantitative characteristics for this effect.
4.2.9. The 29 December 1820 Earthquake
This earthquake affected Zakynthos. Recent structures behaved better than older ones, while coastal structures suffered the most. Based on Lekkas et al. [46], 500 buildings collapsed, more than 1000 remained standing but severely damaged, and four human losses and 39 injuries occurred.
Regarding environmental impact, ground cracking, sulfureous gas emissions, roughness in the sea surface and subsidence occurred due to the main earthquake [26,43,46,121,131].
A weak tsunami was reported offshore (Figure S9). The captain of a vessel coming from Istanbul reported that when the vessel was sailing at a distance of 20 miles from Strofades Islands (50 miles from the center of Zakynthos island) a very strong noise was noticed, and then, the vessel experienced a tremor which canceled all attempts to maintain its course [41,43]. Further details on the impact of this tsunami on the coasts of the earthquake-affected area are not available.
4.2.10. The 6 (9) January 1821 Earthquake
This seismic event hit Zakynthos. It was followed by a very strong aftershock located at the Zakythos Straits between Zakynthos Island and the adjacent Elis region in the western Peloponnese. The aftershock was responsible for the generation of a tsunami with considerable impact on the coastal part of Patras, located in the northwestern Peloponnese [52,126,128] (Figure S10). The sea level suddenly rose and the waves surged the Patras coast, resulting in inundation of the ancient temple of Dimitra, which was later devoted to Ayios Andreas, while harbor buildings and houses along the coastal front suffered serious damage [39,52,57,60,61,113,124,139,140,141].
Regarding the occurrence of this event, Barbiani and Barbiani [116] and Montandon [126] reviewed existing related documents and they did not mention any sea disturbance in association with the 6 January 1821 earthquake. Regarding the nature of the event, Papadopoulos and Plessa [47] commenting on Pouqueville’s [140] description, suggested that the reported wave was a storm surge rather than a real tsunami event.
4.2.11. The 19 January 1825 Earthquake
This event destroyed most of the settlements and the capital town of Lefkada Island [43]. In western Lefkada, many settlements were severely damaged and two of them were completely destroyed, while one was affected by extensive rockfalls [131,142]. The earthquake caused a total of 58 fatalities and 80 injuries. It was also felt in Kerkyra, Zakynthos and Messolonghi; however, it caused no damage there [143,144]. Preveza on the neighboring coast of mainland Greece suffered great destruction, resulting in many human losses.
Regarding the earthquake’s environmental effects, uplift, tsunami, ground cracks, slope failures and hydrocarbon-related phenomena were reported [44,121,136,137,142,145]. In particular, the tsunami has been reported between the eastern coast of Lefkada and the uninhabited island of Sessoula [41,58,113] (Figure S11), located west of Lefkada, opposite the Komilio settlement.
4.2.12. The 12 July 1835 Earthquake
On 12 July 1835 a weak tsunami was triggered by an earthquake and affected the island of Zakynthos (Figure S12). This information is included in tsunami-related studies by Ambraseys [113] and Antonopoulos [58] based on information found in Barbiani and Barbiani [116] and Colla [146], as well as in Soloviev [61] and Soloviev et al. [41].
4.2.13. The 18 April 1842 Earthquake
On 18 April 1842, an earthquake was generated on the southwestern coast of the Peloponnese [44]. It caused very heavy structural damage including the total or near-total collapse of buildings in many settlements located within the Pamisos River valley, in the western part of Messenia, and in Laconia [44]. As regards the tsunami’s generation and its impact, the coast close to Koroni (Figure S13), in the eastern part of the Falanthi basin, was inundated and ships swept onto the land by the earthquake-induced tsunami [44].
4.2.14. The 4 February 1867 Earthquake
An earthquake that occurred on 3 February 1867 and was felt on the Zakynthos, Ithaki, Paxi, Lefkada and Kerkyra islands was a precursor to the main event on 4 February [44]. It involved two shocks that occurred 45 min apart. The western part of Cephalonia, especially the Paliki peninsula, was most affected by the earthquake, with Lixouri and its surroundings, as well as the settlements in Thinia valley, being almost completely destroyed. Considerable damage was also reported in Argostoli. As a result, human losses amounted to 223, with half of them reported on the Paliki peninsula. The earthquake’s environmental effects also comprised liquefaction phenomena, subsidence and ground cracks [44,121,136,147,148,149,150].
Regarding the sea effects, a retreat was reported before and after the earthquake. This effect is commonly observed on the Ionian Islands when a strong earthquake occurs. A subtle tsunami was also generated [41,43]. Ambraseys [44] supported that there is no evidence that the earthquake was associated with a seismic sea wave (Figure S14).
4.2.15. The 10 April 1867 Earthquake
This earthquake in Cephalonia triggered a tsunami reported in Lixouri (Figure S15), on the eastern coastal part of the Paliki peninsula [41,44].
4.2.16. The 20 September 1867 Earthquake
The 20 September 1867 earthquake caused damage to western Mane (Peloponnese), where the collapse of buildings resulted in casualties. Lighter damage was also induced in the Meligalas horst separating the Kalamata and Ano Messenia basins. It was also felt in Malta, Sicily and Brindisi.
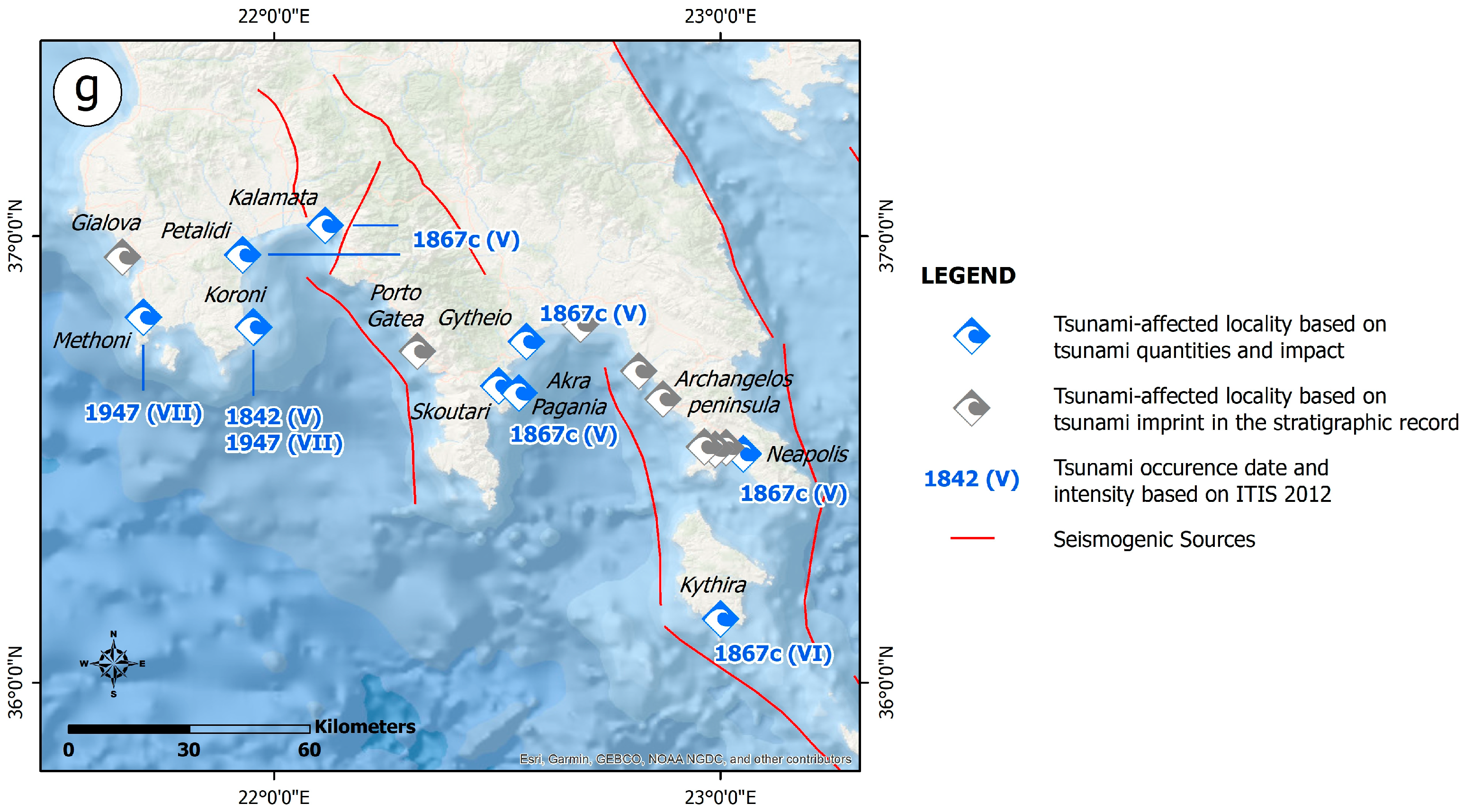
The 1867 earthquake triggered a tsunami which affected the southern and western parts of the Peloponnese, the Ionian Islands and the Cyclades complex in the Aegean Sea, while they also reached the eastern Italian coasts and the region of Shkoder in Albania [41,43,52,58,151,152,153] (Figure S16). The location of the earthquake and the tsunami’s occurrence belonged to the tsunamigenic zone of the west Hellenic Arc, which is characterized by high tsunami potential [33].
The triggered tsunamis had a considerable impact on the funnel-shaped gulfs and bays of the southern and western coasts of the Peloponnese that opened towards the epicentral area [41,43]. Thus, they severely affected the coastal areas of the Messenian and Laconian Gulfs (Figure S16).
The western shore of the Laconian Gulf was heavily affected (Figure S16). In Gytheion, changes to sea level were observed. The sea initially receded from the shore and the seabed dried up. Afterwards, the sea rose to 6 m above its usual level and it appeared to be boiling. A lot of fish were thrown out onto the coast. Gytheion was destroyed by the waves. The tsunami also affected the coastal area of Skoutari, south of Gytheion. The Akra Pagania Cape, located east of Skoutari, was heavily affected by the waves. In Neapoli, in the southeastern coastal part of the Laconian Gulf, the seabed also dried up, causing boats to touch the seabed more than once.
In the Kalamata area, located in the northern coastal part of the Messenian Gulf (Figure S16), changes to sea levels were similarly observed, with the sea receding slowly from the coast by approximately 15 m. Lower values of sea level fall were observed in the Petalidi area (Figure S16), in the northwestern part of the Messenian Gulf. The sea water level rose up to 2 m and caused inundation of the coastal area.
The tsunami also affected the Ionian Islands comprising Kerkyra in the north, and Lefkada, Cephalonia and Zakynthos in the central part of Ionian Sea, as well as Kythera and Crete, resulting in a similar impact on the affected coastal areas [41,52,58] (Figure S16).
In Zakynthos (Figure S16), the sea was rough for 10 h, the seabed was dried up in its shallow parts close to the shore, part of a small river flowing into the sea close to Zakynthos also dried up, and a lot of fish and eels coming not only from the sea but also from the river were exposed; then, the sea rose to 1 m above its usual level [41].
In Cephalonia, and more specifically offshore Argostoli (Figure S16), the sea was rough for 4.5 h [41].
In Lefkada, sea level change was also observed, comprising falling and rising (Figure S16). The arrival of the waves swept boats from the harbor to the quay, resulting in crush damage [41].
In Kerkyra, the arriving tsunami resulted in the inundation of an approximately 20 m wide coastal zone (Figure S16), while in all cases, a lot of fish were thrown out onto the shores or remained exposed on the seabed for a long time until the sea level rose [41].
On Kythera Island, the sea rose to 2–3 m above its usual level in Kythera town, resulting in inundation of the coastal area and flooding of the port facilities, while boats were also swept from the harbor to the quay [41] (Figure S16).
In the Chania coastal area, located in the northwestern part of Crete, short-term and periodic (10–15 min) sea level variations of 1 m occurred, while turbulent flows were generated and were perceived in Chania port (Figure S16). The oscillations of the sea level lasted for 14 h, with a gradually increasing period and decreasing height [41].
The earthquake also triggered effects in the Cyclades complex in the Aegean Sea [41,44,52,58]. Abnormal fluctuations of the sea level were reported from Siros [41,43,52,58], Santorini [44], Serifos [41] and Sifnos [44] (Figure S16).
The earthquake-triggered waves also reached the Italian shore and affected the Brindisi, Messina, Sicily and Catania coastal areas [41,43,52,58]. In Brindisi, the sea receded from the shore comparatively far, while in Sicily, Messina and Catania, low sea water was observed and reported. Oscillations of the sea level within the focal zone of the waves presented a long duration ranging from 5.5 to 10 h before the sea calmed down again.
4.2.17. The 28 December 1869 Earthquake
On 28 December 1869, an earthquake struck Lefkada, causing considerable damage in its northern part and resulting in 15 fatalities [43]. Lefkada town was turned into a pile of rubble with only 20–25 houses and a church left intact by the earthquake. Significant damage was also observed in villages on the northern part of the island. The stone masonry buildings were razed to the ground, while the wooden houses suffered less damage [154]. Damage was also reported in the adjacent mainland Greece [43], where many of the structures at the Nikopolis archaeological site collapsed.
Both before and after the earthquake, the sea was observed to initially rise and rush towards land, and then, retreat, a phenomenon known to locals as “basies” [41]. This phenomenon affected the eastern coast of the island [50] (Figure S17).
Three large tsunamis were also observed in the sea of Vlorë (Valona, Albania) [41,44,60,138,155,156].
4.2.18. The 27 June 1883 Earthquake
The 1883 earthquake struck Kerkyra, located in the northern part of the Ionian Sea, resulting in an impact on the coastal zone [39,41,52,58,61]. Sudden sea withdrawal was reported close to the Ayios Georgios area [52,113] (Figure S18). Three rowing boats were thrown onto the coast due to the movement of the sea [41,52,113].
4.2.19. The 27 August 1886 Earthquake
The 27 August 1886 Filiatra earthquake occurred on the Ionian coast of Messenia. It is characterized by a large macroseismic extent, from Cairo to Bern in the N-S direction and from Palermo to Callipolis in the E-W direction [44,157,158]. Many aftershocks occurred on a daily basis until 6 September, while the aftershock sequence lasted until September 1887, with large and destructive aftershocks generated on 28 August and September 1886 and in January, March and August of 1887.
A tsunami was generated and affected a 35 km long N-S coastal segment extending from Agrilos, located north of Filiatra, to Pylos bay (Figure S19). The waves washed several row boats onto the land of Gialova, located north of Pylos [41,44,52]. The sea close to Agrilos advanced, resulting in coastal inundation, with its width ranging from 10 to 15 m for a short time period [41,44,52]. It was reported that the tsunami was observed up to Izmir [41,52].
4.2.20. The 17 April 1893 Earthquake
This earthquake constitutes the mainshock of a seismic sequence that began in December 1892 and ended in May 1893. The mainshock was strongly felt in the southern part of the Ionian Sea (Strofades Islands), but also in cities on the neighboring Ionian coast of the Peloponnese (Patras, Katakolo, Pyrgos and Kyllini) and Aetoloakarnania (Messolonghi); it was less noticeable in the northern part of the Ionian Sea (Kerkyra) [43,44]. It was preceded by a destructive earthquake on 31 January, which could be considered a foreshock. The main earthquake caused 23 fatalities and more injured, with the southern and southwestern part of Zakynthos being the most affected and with many of the settlements completely destroyed [43,44]. The total account of this earthquake sequence included 2000 destroyed houses and 1700 with severe damage.
The environmental effects caused by the earthquake included landslides [43,44] and sea retreat in Zakynthos [37,42] (Figure S20). Additional qualitative and quantitative information on this disturbance is not available.
4.2.21. The 3 December 1898 Earthquake
The 3 December 1898 earthquake is another strong event that affected Zakynthos and triggered a tsunami [41,52,58]. Soloviev et al. [41] mentioned that the water receded from the shore (Figure S21). The sea rose 0.4 m and returned to its usual place between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m. [48].
4.2.22. The 22 January 1899 Earthquake
A very strong earthquake occurred in Kyparissia on 22 January 1899, causing no fatalities, many injuries and severe damage in many villages of Messenia [43,45,153]. A foreshock preceded the mainshock a few minutes earlier, while a strong aftershock followed 7 min later [153].
The subsequent earthquake-induced tsunami was about 1m high and resulted in inundation of the Marathopolis coastal area, while in Zakynthos, it was about 20–40 cm [43,44,45,157] (Figure S22). Fishermen at sea in the earthquake-affected area heard a noise like heavy rainfall and subsequent large waves almost sank their boats, while women collecting shells on the shore, where the water had receded, then found themselves waist-deep in water [41].
Galanopoulos [157] assumed that the tsunami was possibly triggered by co-seismic submarine slumps, a view also supported by Papadopoulos et al. [153]. However, no damage occurred in the submarine cables between Zakynthos and the mainland at Tripiti and Katakolo [44].
4.3. Recent Tsunamigenic Earthquakes and Tsunami Events
This section comprises information on the occurrence of the recent tsunamigenic earthquakes and the triggered tsunamis in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese after 1900, and more specifically, from 1914 to 2018 (Figure 7). Their impact on the local population and the building stock, as well as the triggered environmental effects, are briefly presented. Emphasis is given to the presentation of available information on the tsunamis’ physical quantities and their impacts on the affected coastal zones.
The properties of the studied recent tsunamigenic earthquakes are presented in Table 2. The information was obtained from various earthquake catalogues including the SHARE European Earthquake Catalogue (SHEEC) 1900–2006 [159], the updated and extended earthquake catalogue 1900–2012 for Greece and adjacent areas compiled by Makropoulos et al. [35], and the Catalogue of Significant earthquakes of the Seismological Laboratory of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens [160].

Table 2.
Properties of the recent earthquakes (after 1900) that triggered sea disturbances including tsunamis in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese.
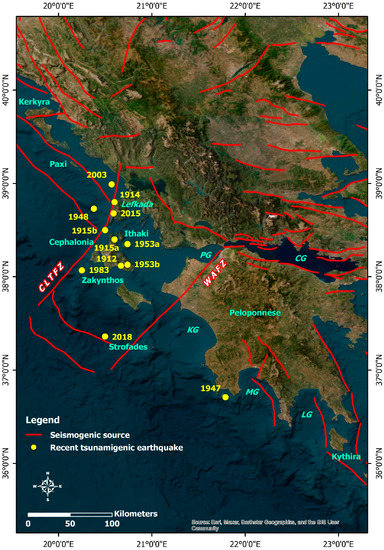
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of epicenters and occurrence dates of the recent tsunamigenic earthquakes in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese [35,37,160] along with their seismogenic sources. The central part of the study area is dominated by fault zones which accommodate right-lateral strike-slip deformation. The strike-slip Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) and the Western Achaia Fault Zone (WAFZ) are both responsible for the generation of large and destructive strike-slip earthquakes. PG: Patras Gulf; CG: Corinth Gulf; KG: Kyparissia Gulf; MG: Messenian Gulf; LG: Laconian Gulf. The faults are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36], while the parameters of the presented earthquakes are presented in Table 2.
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of epicenters and occurrence dates of the recent tsunamigenic earthquakes in the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese [35,37,160] along with their seismogenic sources. The central part of the study area is dominated by fault zones which accommodate right-lateral strike-slip deformation. The strike-slip Cephalonia–Lefkada Transform Fault Zone (CLTFZ) and the Western Achaia Fault Zone (WAFZ) are both responsible for the generation of large and destructive strike-slip earthquakes. PG: Patras Gulf; CG: Corinth Gulf; KG: Kyparissia Gulf; MG: Messenian Gulf; LG: Laconian Gulf. The faults are derived from the Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS) compiled by Caputo and Pavlides [36], while the parameters of the presented earthquakes are presented in Table 2.
4.3.1. The 24 January 1912 Earthquake
This earthquake occurred in the central part of the Ionian Sea and affected the southwestern part of Cephalonia and the northern part of Zakynthos, resulting in the destruction and desolation of many settlements [43]. Regarding the sea effects, available information is limited to one ship being attacked by a big wave [37,42] (Figure S23).
4.3.2. The 27 November 1914 Earthquake
This earthquake caused significant damage in the western part of Lefkada [43], where many villages were almost destroyed. In total, 16 fatalities were reported.
Regarding the effects triggered by the 27 November 1914 earthquake on the natural environment of Lefkada, ground cracks, slides, rockfalls, subsidence, liquefaction and lateral spreading phenomena, as well as hydrological anomalies, were observed in the northern, central-western and central-eastern parts of Lefkada [65,113,121,123,137,138,161,162].
According to Critikos [161], during the last days of November, an unusual sea level rise of 35 cm was observed in Lefkada, and particularly in Lefkada port [43] (Figure S24). The water rushed in at a distance of 6–7 m and inundated a large part of the coastal road in Lefkada [43,161] and the piers in the Nydri area. In contrast, during the earthquake, the waters were lowered. Ambraseys and Synolakis [62] did not consider this effect a tsunami, but attributed it to a typical phenomenon occurring in the Ionian Islands during the winter season. Furthermore, Lefkada residents have given this effect of sea level rise the name “basies” and consider it an earthquake precursor. A similar phenomenon was observed before and after the earthquake of 28 December 1869.
A major underwater landslide was triggered offshore of Nydri village. It caused failure of the dock and the generation of a 2–3 m high sea wave [39,50,59,113,138,139,163]. Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [33] reported that the maximum wave height at the coast was 3 m.
4.3.3. The 27 January 1915 Earthquake
This earthquake struck mainly the northwestern part of Ithaki, with many houses collapsing and others being severely damaged, while it was only felt in western Greece and the northwestern Peloponnese [43]. In terms of the earthquake’s environmental effects, ground cracking and subsidence were noted in many locations in the earthquake-affected area [43] and sea waves were also reported in Ithaki [42] (Figure S25).
4.3.4. The 7 August 1915 Earthquake
The 7 August 1915 earthquake mainly affected Ithaki and had a significant impact on its built and natural environment [43,139]. It was particularly felt in the northern part of the Ionian Islands, in the coastal areas of Epirus up to Ioannina, as well as in Magnesia (Volos town), Fthiotida (Lamia town), Arcadia (Tripolis town) and Messenia (Kyparissia town). The main shock was followed by a number of aftershocks, the largest of which occurred on 11 August with a magnitude of Mw = 6.4, not only aggravating the damage caused by the mainshock but also causing further damage.
Regarding the effects on the built environment, Ithaki and Cephalonia were the most affected, with significant damage reported in the northern part of Ithaki and in Sami town in Cephalonia [43]. Minor damage was reported in Lefkada, particularly in the eponymous capital town, located in the northeastern part of the island, and in Vassiliki village in its southwestern part, as well as on the Paxi islands and in the Preveza area.
As regards the triggered environmental effects, the 7 August 1915 earthquake caused ground cracks and subsidence at several sites [43] strongly related to liquefaction phenomena [121]. Furthermore, it triggered two waves with heights of 1.5 m in the area between Cephalonia and Lefkada [41,52,59] (Figure S26). These waves are also mentioned by Papadopoulos and Chalkis [39] and Soloviev [61]. The reported waves are considered earthquake precursory phenomena by Papazachos and Papazachou [43].
4.3.5. The 6 October 1947 Earthquake
On 6 October 1947, the southwestern Peloponnese was hit by a strong earthquake that caused three casualties and 40 injuries as well as severe damage in 54 villages of Pylia province [164]. Based on Ambraseys and Jackson [45], the earthquake was generated by a NE-SW-striking normal fault. The earthquake lasted 80 s in the Kamalata area and 65 s in Patras and it was felt in the Nile River in Egypt, southeastern Italy and eastern Sicily, but not in Northern Greece and the most of the Aegean Islands. Its largest aftershock was generated on 7 October (Μ = 5.0).
Tsunami waves were observed in the Methoni coastal area [41,43,52,59,164], with the inundation distance varying from 15 m [52,164] to 60 m [45] (Figure S27). This tsunami was attributed to submarine landslides generated along steep slopes of the seabed at a distance of 6 km SSW of the coast [43,164]. In the Koroni area, the sea permanently inundated the land [45].
4.3.6. The 22 April 1948 Earthquake
The 22 April 1948 earthquake struck the island of Lefkada. According to Galanopoulos [123], the most significant damage was caused on the southwestern part of the island, where 244 buildings were completely destroyed, 998 suffered severe structural damage and two fatalities were reported [43]. Vassiliki and Ayios Petros villages in the southern part of Lefkada and Kalamitsi and Egklouvi villages in the central-western part were severely affected, resulting in the total collapse of 189 houses, with two human casualties and 145 injured people. Minor damage was observed in Lefkada town. The most affected areas with severe damage outside Lefkada were located on the northern parts of the Cephalonia and Ithaki islands.
The southern part of Lefkada, especially the area of Vassiliki, was hit by a tsunami [39,41,52,59,60,61] (Figure S28). Its height on the coast reached 1 m [41,52,59].
4.3.7. The August 1953 Seismic Sequence
Three of the most catastrophic earthquakes to ever hit the Ionian Islands—and with substantial primary and secondary consequences on both the built environment and the natural environment—were part of the 1953 earthquake sequence [165].
Slope failures, coseismic uplift, hydrological anomalies, ground cracking, tsunami, liquefaction, dust clouds, hydrocarbon-related phenomena, jumping rocks and vegetation effects were most frequently observed in Cephalonia, with Ithaki and Zakynthos coming in second and third, respectively, in order of frequency [165]. The majority of secondary effects were created in particular zones with features that rendered them prone to earthquake-related hazards [165], while primary effects were mostly concentrated in eastern Cephalonia, which suffered up to 70 cm of uplift [166].
Mavroulis and Lekkas [165] created the most thorough reconstruction of the primary and secondary effects of the August 1953 earthquakes on the central Ionian Islands. According to contemporary or later-studied sources, the earthquakes that occurred on 11 and 12 August 1953 caused tsunamis that had a significant impact on the coastal areas of the central Ionian Sea.
Many coastal areas of the islands of Cephalonia, Ithaki and Zakynthos were damaged by the tsunami triggered by the earthquake generated on 11 August 1953 (Figure S29). The most typical case was documented along the coast of Vathi in Ithaki. A 1 km long part of the coastal zone was submerged by waves with heights of 1m that extended no further than 200 m from the shore. The Customs Office of Vathi was flooded by the inundation. The sea receded, then came back to cover the same ground. Similar effects were also triggered during the aftershock sequence and mainly after its largest shocks.
The Argostoli Bay was disturbed by sea effects that occurred on 12 August 1953 [165] (Figure S30). Eyewitnesses reported seeing whirlpools and a boiling sea in different areas of Argostoli Bay, as well as repeated cycles of coastline flooding and sea withdrawal that affected different areas of the bay. The Argostoli square was covered by the waves that flooded the coastal region. In order to avoid being harmed by the earthquake-induced waves, many vessels along the coastline promptly raised their anchors.
Petratos [167] provided information derived from prisoners in Argostoli prison about a tsunami that flooded the coast of Argostoli Bay.
Despite the aforementioned data, Soloviev et al. [41] repeated Grandazzi’s [64] statements that no tsunami was triggered by the earthquakes, despite the publicity in the contemporary sources, including daily press. Seaquakes were induced and felt intensely by people on the decks of ships in Argostoli Bay (Cephalonia) and Vathi Bay (Ithaki) [41,64]. The crew of a battleship in Argostoli Gulf, in particular, was severely disturbed, as if the ship had been hit by a naval mine, causing the moorings to break, radar equipment to be destroyed and damage to various elements of the vessel [64]. Furthermore, people on a boat in an anchorage near Vathi village in Ithaki were jolted with such power that they thought the boat was sinking. A sea disturbance was also observed in southwestern Ithaki; however, there was neither sea-level fluctuation nor coastal flooding. A passenger ship sailing to Patras was heavily shaken by this earthquake. In contrast, Kolosenko [168] and Ambraseys [169] backed the notion that a portion of Ithaki Island dropped into the sea, and the resulting sea surge overwhelmed the Vathi port.
Vathi in Ithaki Island was most devastated by the tsunami triggered by the earthquake on 12 August 1953 [165] (Figure S30). The squares of Vathi were reached by the waves as they moved further inland. The town’s streets were left with water stains of tiny seaweed fragments, indicating that the coastline area had been extensively flooded. There were several persons found along its path who were carried away, but there were no casualties.
Aetoloakarnania, located eastwards, was also affected by the 12 August 1953 earthquake and the subsequent tsunami [165]. More precisely, during the earthquake, the sea covered the Louros islet, which is located southwest of the Aetoliko area (Figure S30).
4.3.8. The 17 January 1983 Earthquake
The 17 January 1983 earthquake was generated offshore between Cephalonia and Zakynthos [43]. It was strongly felt on these two islands as well as in central-western Greece, but especially in the southwestern part of Cephalonia, as the seismogenic zone was located 40 km away from the respective coasts and the focal depths were limited to the first 27 km of the crust. The main earthquake caused minor damage in Cephalonia. The largest aftershock occurred on the same day as the main earthquake (M = 6.4) and caused more damage in Cephalonia, as its epicenter was located on the island.
The earthquake triggered liquefaction and slope failures in several sites in Cephalonia [121,170]. Papadopoulos and Fokaefs [33] reported tsunami triggering by the 17 January 1983 earthquake (Figure S31). This wave had a height of 50 cm upon arrival at the coast.
4.3.9. The 14 August 2003 Earthquake
The 14 August 2003 earthquake occurred off the coast of NW Lefkada. The earthquake was felt on the Ionian Islands, in western and central Greece and in the area from the Peloponnese to Albania. Apart from some serious injuries, given that it was a peak period for tourism, no human casualties were reported. Despite the strong ground motion within the town of Lefkada, only one building with a reinforced concrete load-bearing structure and infill walls collapsed [171]. The largest aftershock (Ms = 5.2) occurred on 14 August 2003 a few hours after the main earthquake. Only a small tsunami with a height of no more than 0.5 m hit the Vlychos Bay, located south of Nydri on the eastern part of the island, causing minor damage to boats and structures on the shoreline [172] (Figure S32). The mainshock also triggered ground cracks, liquefaction phenomena, shoreline changes and slope failures [172,173].
4.3.10. The 17 November 2015 Earthquake
The 17 November 2015 earthquake hit Lefkada. It was felt mainly in the western part of Lefkada and secondarily on the rest of the Ionian Islands, in western mainland Greece and the Peloponnese. It caused two casualties and eight injuries. Western Lefkada suffered the most serious impacts on its natural environment, construction and infrastructure [27].
Many environmental effects were caused by the large earthquake of November 2015 in the western part of Lefkada [27]. It triggered ground cracks, slope failures—including mainly rockfalls and slides—liquefaction phenomena and a tsunami [27,174].
Four tide gauges located in Katakolo and Kyparissia in Greece, and Le Castella and Crotone in Italy, measured a minor tsunami with a sampling rate of 1 min [174]. The highest amplitudes were measured at Katakolo (11 cm) and Kyparissia (10 cm) at distances of ~70 km NE and ~100 km SE from the epicenter, respectively (Figure S33). Lower amplitudes were measured at Le Castella (6 cm) and Crotone (8 cm), both located ~360 km NW of the earthquake epicenter [174].
4.3.11. The 26 October 2018 Earthquake
The most recent powerful earthquake, which was felt in Zakynthos, the Ionian Islands, the Peloponnese and central Greece on 26 October 2018, luckily, did not cause any fatalities or injuries. While the traditional masonry buildings in the southern part of Zakynthos sustained non-structural damage, the recent buildings with reinforced concrete frames and infill brick walls behaved very well during the earthquake and withstood the strong ground motion [73]. This is despite the fact that it was a strong earthquake with high values of acceleration, velocity and displacement [175].
The earthquake produced a weak tsunami that was clearly documented at four stations: two in Greece (Katakolo and Kyparissia) (Figure S34) and two in Calabria, Italy (Crotone and Le Castella) [51]. Station NOA-08 measured a maximum wave height (peak-to-trough) of 0.2 m. The signal was weaker in Katakolo, which was closer to the epicenter. The arriving waves at station NOA-08 may have been amplified locally, enhancing the signal.
A comparable wave height (0.16 m) was reported at the Crotone station (CR08), indicating limited dispersion over the Ionian Sea basin. It is worth noting that both stations on the Calabrian coast with a noticeable signal above noise are relatively close to each other. Other stations throughout the Greek coasts have been investigated, but they are either too far from the source location to record a signal or are fundamentally too noisy, resulting in no discernible signal above noise. The formation of a tsunami is supported by eyewitness testimonies; however, the amplitudes suggested by anecdotal reports (>1 m) are unreliable or the consequence of localized amplification.
Simulations by Ganas et al. [51] presented waves refracted to the south/southeast of Zakynthos, nearing Katakolo and Kyparissia. The ringing seen in the western Peloponnese stations might be caused by the varied wave arrivals. Separate wave trains of energy might have delivered force to the ports, causing waves to slosh back and forth. However, because of their installation within the harbor, the regional characteristics (continental shelf) and the bathymetric features offshore that direct wave energy to specific places, the Italian stations may be favored by tsunamis generated on the western end of the Hellenic Arc.
Local conditions may have favored the two Calabrian stations over Catania, which detected no signal. Crotone appears to be well-positioned for tsunamis induced by earthquakes or other geophysical events in the Ionian Sea. Although not reported by Greek coastal stations located in the Ionian Sea, a tsunami wave triggered by the 17 November 2015 Lefkada earthquake was recorded near Crotone [176]. Future incidents of equal magnitude or bigger may give helpful records from Italy or Greece (depending on location) for further analysis and a better understanding of tsunamigenesis and harbor conditions.
4.4. Results from the Review of Tsunamigenic Earthquakes in Western Greece
The literature review of the earthquake and tsunami history of the Ionian Islands and the western and southern Peloponnese revealed that the study area has been affected by tens of tsunami events from 6000 BC to 2018. More specifically, over 10 prehistoric events have been detected from interdisciplinary studies on the tsunami imprint on the stratigraphic record, while 22 historical (pre-1900) and 12 (post-1900) recent earthquakes have been generated with a variety of effects on coastal areas.
Regarding the inventory of prehistoric tsunami events, most of the tsunami-affected sites are located along the extended Ionian coast of the Peloponnese and the straits and funnel-shaped gulfs of the Lefkada and Cephalonia Islands, as well as of the southern Peloponnese.
Most of the historical earthquake-triggered effects have affected the Ionian Islands, with the Peloponnese coastline in second place. In particular, the most affected island is Zakynthos, which has been affected seven times by the effects considered, followed by Cephalonia and Lefkada in the central part of the Ionian Sea, which have been affected four times; Kerkyra in the northern part of the Ionian Sea, which has been affected two times; and the Strofades Islands in the southern part of the Ionian Sea, which has been affected only once during the historical period. The Peloponnese has been affected six times including two events along the coast of the Patras Gulf, one event on the southern coast of the Peloponnese, and in particular, along the coast of the Messenian and Laconian Gulf, while all other events have affected the Ionian coast of the Peloponnese.
Information relating to historical events has also been recorded in remote areas bordering the Ionian Sea, such as in the neighboring countries of Italy and Albania to the west and north of the Ionian Sea, respectively, but also in other coastal areas of the Aegean Sea such as the Cyclades and the northern coast of Crete.
Regarding events after 1900, the coastal areas of the Ionian Sea have been affected by nine events, while the Peloponnese has been affected by only three events. For the Ionian Islands in particular, Cephalonia has been affected by five events, with Lefkada having been affected four times and Ithaki only once.
The information on the above historical and recent tsunamis available from the sources examined is divided into qualitative and quantitative data. It can also be divided into two categories: (i) physical quantities, which deal with the anatomy and main characteristics of the tsunami at its arrival on the shoreline and its propagation on land, such as tsunami height on shoreline, inundation, extent of inundated areas, tsunami run-up and maximum tsunami water level, and (ii) tsunami impact, which deals with the impact of the tsunami on the population of the coastal zone, on objects that can be washed away regardless of size and on buildings and infrastructure in the coastal zone, and with changes in coastal morphology. These are the criteria used by the ITIS-2012 scale to assign tsunami intensities to affected areas. More specifically, the tsunami related information is classified into the following categories [34]:
- Tsunami quantities, including tsunami height, flow depth, run-up, coastal inundation, maximum inundation distance, etc.
- Tsunami’s impact on:
- Population, comprising human perception, reactions and behavior in general during the tsunami’s evolution, ranging from low sensitivity to extensive fatalities in the tsunami-affected area.
- Mobile objects, including effects and damage to vessels, boats, cars, trains and heavy objects, which can be uplifted and washed away by the tsunami.
- Infrastructure, comprising damage to makeshift facilities along the coastline; port facilities such as quays, jetties, marine breakwaters and erosion-protection works; industrial facilities; onshore lifelines, etc.
- The geoenvironment, including turbulence in coastal sediments, changes in the coastal profile attributed to erosion and deposition processes, impacts on vegetation such as the uprooting of bushes and trees, extensive pollution from oil and chemicals and fire ignition, etc.
- Structures, comprising non-structural-to-structural damage in the building stock of the affected coastal zone.
This classification was also applied in this research. More details are available in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2 compiled for the historical and the recent events, respectively. Thus, tsunami intensity was assigned to each location in the coastal zone for which tsunami quantity and tsunami impact information is available.
As part of this research, an attempt was made to identify information on tsunami quantities and impacts from prehistoric tsunamis in the affected area, but the available data were limited to the tsunami occurrence period. Thus, it was not possible to include the prehistoric events and their related information to the application of the ITIS-2012.
From the spatial distribution of these localities to which intensities were assigned (Figure 8), we find that the majority of historical and recent tsunamis are characterized by a limited number of localities (Table 3). For the historical period in particular, the number of localities that could be extracted from the available data was only one from each event. The exceptions to this rule were the tsunamis triggered by the earthquakes on 20 September 1867, 28 December 1869 and 22 January 1899, which occurred towards the end of the historical period and which are characterized by larger numbers of earthquake-triggered tsunami-affected localities. This difference is attributed to the more extensive and more severe effects of the above three tsunamis on the coastal zone of the study area compared to the previous events.

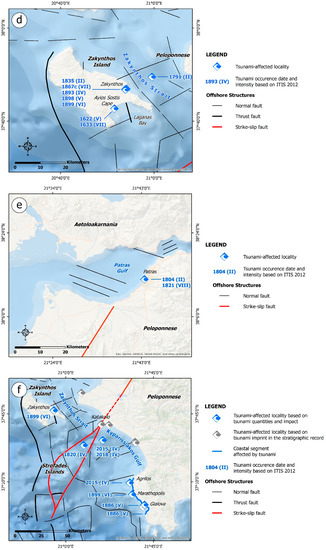
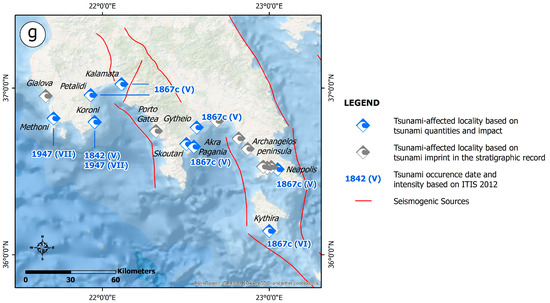
Figure 8.
The localities in the Ionian Islands and western and southern Peloponnese affected by earthquake-triggered tsunamis along with the assigned ITIS-2012 tsunami intensities. (a) Kerkyra, (b) Lefkada, (c) Cephalonia and Ithaki, (d) Zakynthos and (e,f,g) the Peloponnese with its northwestern (e), western (f) and southern (g) coastal segments, respectively. More details for tsunami-affected areas are available in the Supplementary Materials (Tables S1 and S2 and Supplementary Figures S1–S34). Faults in (a,g) from Caputo and Pavlides [36], and those in (b–e) from Makris et al. [81].

Table 3.
Tsunamigenic earthquakes in the Ionian Sea and offshore western and southern Peloponnese, along with the areas with noticeable effects, localities with assigned ITIS-2012 tsunami intensities and ITIS 2012 maximum intensities for each event. More details on the physical quantities and the impacts of the earthquake-triggered tsunamis on the coastal part of the study areas are available in Supplementary Tables S1 and S2.
From the assigned intensities, the maximum intensity for each event in the coastal zone was derived.
The highest tsunami intensity attributed to tsunami-affected areas of the Ionian Sea and the offshore western and southern Peloponnese was VIII. It was assigned to localities affected by tsunamis triggered by:
- The 21 February 1723 earthquake in southwestern Lefkada.
- The 6 January 1821 earthquake in the Zakynthos Straits.
- The 20 September 1867 earthquake on the southern part of the Peloponnese.
- The 12 August 1953 earthquake in southeastern Cephalonia.
The high intensities are associated with severe and widespread tsunami impact in the coastal zone, including human fatalities (e.g., caused by the 1723 Lefkada tsunami), severe damage to coastal buildings and infrastructure (e.g., the 1821 tsunami in Zakynthos and the 1867 tsunami (20 September) in Western Greece), as well as high values of physical quantities (e.g., large inundation distances in coastal areas affected by the 1953 Cephalonia earthquake-triggered tsunami).
A tsunami intensity of VII determined by the ITIS-2012 was assigned to coastal areas affected by tsunamis generated by the earthquakes:
- On 5 November 1633 in offshore southwestern Zakynthos, resulting in damage to the coastal zone.
- On 27 November 1914 along the western coastal part of Lefkada Island.
- On 7 August 1915 between Lefkada and Cephalonia with high wave heights upon arrival at the coast.
- On 6 October 1947, generated offshore of the southwestern Peloponnese with impacts on the Methoni and Koroni areas, located west and east of the Pylia peninsula, respectively.
- On 11 August 1953, generated offshore of northwestern Lefkada with impacts on Vathi in Ithaca and Argostoli in Cephalonia.
- On 14 August 2003, generated offshore of northwestern Lefkada with an impact on Nydri.
An intensity of VI was attributed to coastal areas affected by earthquakes that occurred:
- On 22 January 1899 in the central-western coastal Peloponnese with impacts on the same area and neighboring Zakynthos.
- On 22 April 1948, generated offshore of western Lefkada with an impact on the southwestern part of the island.
The lowest intensities ranging from II to V were assigned to coastal areas with slight impacts from minor tsunamis. Intensities ranging from II to VII were assigned to several segments of the Ionian Sea, far from the coast.
The areas with tsunami impacts recorded in the study area and that could be classified as highly susceptible to future tsunami impacts were:
- In Kerkyra, on the eastern and the southwestern coasts including the coastal part of Kerkyra town and the Chalkiopoulou and Korissia Lagoons.
- In Lefkada, in the coastal areas of sea straits and funnel-shaped gulfs, such as the Lefkada Sound and Lagoon, the Vlycho and Vassiliki Bays in the northeastern, central-eastern and southwestern parts of the island, respectively, and the offshore area between Lefkada Island in the east and Sessoula Islet in the west.
- In Cephalonia in the coastal areas of funnel-shaped gulfs such as the Livadi coastal plain and the Lixouri coastal area in the Argostoli Gulf and Argostoli town on the western side of the inner Argostoli Bay.
- In Ithaki, in the coastal area of Vathi town in the southern Vathi Gulf.
- In Zakynthos, in the coastal area of Zakynthos town and Laganas Bay, located in the eastern and southern part of the island, respectively, as well as the Zakynthos Straits between Zakynthos and the western Peloponnese.
- In the Peloponnese, from the northwestern to the southern part:
- The coastal area of the Gulf of Patras and especially the coastal part of Patras city.
- The coastal area of the Kyparissia Gulf with its extensive sandy beaches and the areas of Kyllini, Katakolo, Epitalio, Kato Samiko and Kaiafas, which are affected by prehistoric, historical and recent tsunami events.
- The western and eastern part of the Pylia peninsula in the southwestern Peloponnese extending from Agrilos to Methoni and from Petalidi to Koroni, respectively.
- The coastal areas of the Messenian Gulf, particularly the Kalamata area in the northern coastal part of the gulf.
- The western coastal areas of the Laconian Gulf (the Gytheio and Skoutari areas) and the coastal areas of Vatika Bay (Viglafia Lagoon and Bay, Vatika Bay and Neapolis).
In addition, wave anomalies have also been recorded in the open sea, far from the coast, such as between Lefkada and Sessoula, Lefkada and Cephalonia, Cephalonia and Zakynthos, Zakynthos and the Peloponnese, and Zakynthos and Strofades, with ITIS-2012 intensities ranging from II to VII.
5. Discussion
The application of ITIS-2012 is a useful and effective tool for highlighting areas susceptible to tsunami impact. The identification and mapping of these areas is the first important step in the assessment of tsunami risk and a very important element in the development of critical actions for tsunami impact mitigation, such as the definition of the coastal inundation zone, the determination of the optimal evacuation routes from the coastal zone in case of an upcoming tsunami, and the issue of early warning for tsunamis.
The cataloguing and the classification of tsunami-related information into different intensity levels are of great significance from a palaeotsunami point of view and, therefore, for tsunami hazards, moving beyond a focus on determining the tsunami hazard for a zone or assessing and mapping the damage caused by the earthquake-triggered tsunami.
The result of this approach comprises intensity maps for each of the historical and recent tsunami events for which relevant information on quantities and impacts on coastal areas is available. The maps also contribute to effectively identify areas prone to tsunami generation and highly susceptible to tsunami impact.
Furthermore, assigning intensities not only to locations where tsunamis’ physical quantities are known, but also to locations in the coastal zone where tsunami impact information is available, ensures more locations with tsunami intensities; this will enable the compilation of tsunami intensity maps, which is the first important step in the assessment of tsunami susceptibility and vulnerability and the development of risk maps for the coastal zone. The more data and attributed tsunami intensities are available, the more complete and clear the picture of tsunami impacts in the coastal zone, thus enabling both scientists and operational staff involved in the prevention and management of related disasters to discern specific patterns in the distribution of tsunami intensities and specific parts of the coastal zone that are particularly susceptible to tsunami impacts.
From the literature review and the classification of the available information into the above categories, important results on the availability of these data in historical and recent tsunamis were also extracted.
Regarding tsunamis’ physical quantities, quantitative information on height and flow depth was almost non-existent for prehistoric data and very limited for the historical tsunamis of the study area. In particular, of the 22 historical tsunamis included in this review, quantitative information was only available with relative accuracy for 3 of them. These tsunamis belong to the second half of the 19th century (earthquakes and subsequent tsunamis in 1867, 1898 and 1899), i.e., from the last events of the historical period. They had extensive effects on the coastal zone, and in particular, on mobile objects (boats touching the exposed seabed and sweeping away from the harbor to the quay, suffering crush damage and almost sinking due to large waves) and on coastal infrastructure (the flooding of port facilities, and the destruction of structures and networks on the coastal front).
With regard to information on the impacts on the coastal zone from prehistoric and historical tsunamis, it is found that no quantitative information is available, e.g., the number of vessels affected by the tsunami, human casualties caused by the tsunami, and buildings in the coastal zone that suffered structural or non-structural damage during tsunami propagation in the coastal zone. Furthermore, data on the type of construction of buildings in the coastal zone are missing, so that no direct conclusions can be drawn about the vulnerability of tsunami-affected structures.
These shortcomings and gaps in historical tsunami information are not limited to Greece, but have been observed in other inventories worldwide. Barberopoulou and Scheele [66], in the frame of a study on how to best utilize information from a historical tsunami database for implementing useful products illustrating the total impact of tsunamis, found that there are two categories of data on tsunamis, which are characterized by insufficient descriptions. The first category deals with the source of the tsunami, and the second with the physical characteristics of the tsunami. The limited and approximate nature of historical tsunami data is attributed to the synergy of factors such as the sparse distribution of coastal residential areas, low population density in the coastal zone, the focus of researchers’ interest in tsunamis’ impacts on coastal residential areas leaving large segments in the coastal zone without recorded observations, the absence of recording systems and instrumental records, and the prevalence of eyewitness accounts in surviving descriptions, whose accuracy and reliability are difficult to examine. It is therefore evident that a degree of uncertainty exists in many of the descriptions of tsunamis’ sources, their physical quantities and localities affected by historical tsunamis.
This situation seems to change at the beginning of the 20th century. Along with the beginning of instrumental seismology and the instrumental recording of earthquakes in Greece, the methods of recording the physical quantities and impacts of tsunamis in the coastal zone was also changing. For tsunamis that have occurred since 1900, there is not only extensive qualitative and quantitative information about their impact on the local population, moving objects, buildings and infrastructure and the natural environment of the coastal zone, but also more explicit and precise information about tsunamis’ physical quantities. The tsunamis’ physical quantities are not only limited to the height of the waves upon their arrival at the coastline, but are extended and include data on the run-up, run-in, length and width of the inundation zone in different areas, as well as wave amplitudes recorded by stations, especially for the most recent events in the catalogue, such as the 2015 and 2018 tsunamis on the Lefkada and Zakynthos islands, respectively.
The prehistoric tsunami events and their related information were not included in the ITIS-2012 application as there is no information on physical quantities and tsunami impacts in the coastal area. However, such events can be seriously taken into account for the assessment of tsunami hazard and risk in the region, as they reveal areas that have been repeatedly affected by tsunamis, but for which there is no recorded information.
6. Conclusions
Data on tsunami generation in the western part of Greece and their impacts on the coastal zone from prehistoric times to the present have been updated and re-evaluated in the frame of this study. New data from prehistoric, historical and recent events in the study area have been added to the pre-existing tsunami datasets.
The tsunami record in the Ionian Sea and the western and southern Peloponnese is extensive, with an extent of almost 8000 years, from 6000 BC to 2018. It includes over 40 earthquake-triggered sea anomalies including tsunamis, with at least 10 prehistoric, 22 historical (pre-1900) and 12 recent (post-1900) events with a considerable imprint on the coastal zone. The distinction of tsunamis into historical and recent events seems to adopt the distinction of earthquakes into historical and recent ones due to the introduction of instrumental seismic recordings in 1900 in Greece, but it is attributed mainly to the difference in the availability and completeness of tsunami data before and after 1900. The prehistoric and historical tsunamis affected both the Ionian Islands and the western and southern coastal Peloponnese. However, they are characterized by a lack of physical quantities, such as tsunami height and flow depth, run-up and run-in values, and other quantitative information that can completely determine the tsunami source and the full extent of the impact on the coastal zone. It is observed that the historical tsunami observations in the study area are spaced several kilometers apart due to the spatial distribution of the affected residential areas and the low population density on the coast.
This is not the case with tsunamis that have occurred since 1900. For these tsunamis, there are more details not only about the physical quantities, but also about the effects on the coastal zone, particularly on structures and infrastructure and on the natural environment.
In both historical and recent tsunamis, the application of the ITIS-2012 scale has made it possible to use all available quantitative and qualitative information and to assign intensities to each locality for which such information is available. Through this application, areas particularly susceptible to tsunami impacts are highlighted.
The assignment of intensity using the ITIS-2012 scale was beneficial for the following reasons:
- Qualitative observations are included in the analysis, increasing the number of points used to more accurately represent the impact of the tsunami on the coastal zone.
- Tsunami intensity maps provide a direct representation of tsunami impact even in cases where the quantitative characteristics (wave height upon arrival at the shore, depth of flow, run-up, run-in, etc.) are not recorded. They show a clearer pattern of tsunami impacts than that derived only from physical quantities.
- For past events, the assignment of intensities at affected locations based on the impact on the coastal zone is a more reliable approach as it is not based on physical parameters, which are scarcely available for historical events, while the description of the impact on the coastal zone is mainly based on eyewitness accounts.
This is particularly important for Greece, where instrumental recordings are available only for the most recent of all listed events, and in particular, for the tsunami caused by the Lefkada earthquake on 17 November 2015 and the Zakynthos earthquake on 26 October 2018.
According to the available data on the physical quantities of tsunamis, their impacts on the coastal zone and their assigned intensities, the areas that have been affected by tsunamis in the past and are susceptible to the impacts of a future tsunami event are:
- The coasts of straits such as the Lefkada Sound between Lefkada in the west and Aetoloakarnania in the east, the Zakynthos Strait between Zakynthos in the west and the western Peloponnese in the east, and the area between Lefkada in the east and Sessoula Island in the west;
- The funnel-shaped bays, such as the Vlychos and Vassiliki bays in the central-eastern and southwestern parts of Lefkada, respectively, the Argostoli Bay in Cephalonia, the Messenian Gulf in southwestern Peloponnese and the Laconian Gulf in the southeastern part of the Peloponnese;
- The extensive coastal areas, particularly in western Peloponnese, such as the coast of the Kyparissia Gulf and the Ionian coast of Messenia in the central-western and southwestern part of the Peloponnese, respectively.
In these zones, the synergy of various factors, such as the morphology of the seabed and the occurrence of seabed coseismic deformation or secondary submarine effects, mainly landslides, increases the potential for disaster in the coastal zone.
The tsunamigenic potential in the Ionian Sea does not appear to be low, as was previously reported. Contrary to previous research, which claimed this to be the case, it is found that there are a large number of prehistoric, historical and recent tsunami events, which reveal that the Ionian Sea islands and the Ionian and the southern coasts of the Peloponnese are subjected to high tsunami hazard. In addition to the effects caused by catastrophic tsunamis triggered by earthquakes along or close to the western part of the Hellenic Trench, there are also other local tsunamis with notable effects, triggered by earthquakes within the Ionian Sea. Local tsunamis have smaller physical quantities and slighter effects on the coastal zone compared to the teletsunami effects of distant earthquakes. However, the fact that there has been no such catastrophic event so far in the Ionian Sea does not mean that it cannot happen in the future. On the contrary, as has been shown for other regions dominated by seismogenic and tsunamigenic strike-slip structures around the world, this is very likely. Therefore, the identification of all areas affected by tsunamis in the past and the emergence of the most susceptible to future tsunami impact comprise a significant step for the reassessment of tsunami hazard and risk in the study area. Furthermore, based on the existing information, the inclusion of the Ionian Sea in the tsunamigenic zones of Greece is proposed, even if it does not have the tsunamigenic potential of neighboring zones, such as the western part of the Hellenic Trench and the Corinth Gulf located to the southwest and east, respectively.
Considering that (a) local tsunamis in the southern and southwestern Peloponnese have been attributed mainly to the occurrence of earthquake-triggered landslides [99,153] and (b) there are new data on the potential of strike-slip earthquakes to trigger destructive tsunamis—either directly by propagating rupture and seafloor displacement or indirectly through the occurrence of submarine landslides and coastal liquefaction—efforts should be intensified for detailed submarine mapping of the Ionian seabed and for the direct mapping of potential tsunamigenic sources, whether they are submarine faults or scarps which may fail due to seismic motion.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/geosciences13020028/s1, Figure S1: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 5 May 1622 tsunami; Figure S2: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 5 November 1633 tsunami; Figure S3: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 30 September 1636 tsunami; Figure S4: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 22 February 1723 tsunami; Figure S5: ITIS 2012 intensities for the November 1732 tsunami; Figure S6: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 2 November 1791 tsunami; Figure S7: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 8 June 1804 tsunami; Figure S8: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 17 March 1820 tsunami; Figure S9: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 29 December 1820 tsunami; Figure S10: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 6 (9) January 1821 tsunami; Figure S11: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 19 January 1825 tsunami; Figure S12: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 12 July 1835 tsunami; Figure S13: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 18 April 1842 tsunami; Figure S14: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 4 February 1867 tsunami; Figure S15: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 10 April 1867 tsunami; Figure S16: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 20 September 1867 tsunami; Figure S17: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 28 December 1869 tsunami; Figure S18: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 27 June 1883 tsunami; Figure S19: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 27 August 1886 tsunami; Figure S20: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 17 April 1893 tsunami; Figure S21: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 3 December 1898 tsunami; Figure S22: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 22 January 1899 tsunami; Figure S23: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 24 January 1912 tsunami; Figure S24: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 27 November 1914 tsunami; Figure S25: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 27 January 1915 tsunami; Figure S26: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 7 August 1915 tsunami; Figure S27: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 6 October 1947 tsunami; Figure S28: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 22 April 1948 tsunami; Figure S29: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 11 August 1953 tsunami; Figure S30: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 12 August 1953 tsunami; Figure S31: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 17 January 1983 tsunami; Figure S32: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 14 August 2003 tsunami; Figure S33: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 17 November 2005 tsunami; Figure S34: ITIS 2012 intensities for the 26 October 2018 tsunami; Table S1: Historical earthquakes and related tsunamis on the Ionian Islands and in the western and southern coastal Peloponnese along with their physical quantities, their impact along the coastal segments of the study area and the ITIS-2012 tsunami intensities; Table S2: Recent earthquakes and related tsunamis after 1900 on the Ionian Islands and in the western and southern coastal Peloponnese along with their physical quantities, their impact along the coastal segments of the study area and the ITIS-2012 tsunami intensities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.; methodology, S.M.; software, S.M.; validation, S.M.; formal analysis, S.M.; investigation, S.M. and M.G.; resources, E.L.; data curation, S.M. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.M., M.G. and E.L.; visualization, S.M.; supervision, S.M.; project administration, S.M. and E.L.; funding acquisition, E.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Telemachus—Innovative Operational Seismic Risk Management System of the Ionian Islands” project, included in the Priority Axis “Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development” of the Regional Operational Programme “Ionian Islands 2014–2020” (grant number MIS 5007986), which is funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and National Resources under the National Strategic Reference Framework NSRF 2014–2020.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Two anonymous reviewers are acknowledged for their constructive comments, which helped improve the initially submitted manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Keller, E.A.; DeVecchio, E. Natural Hazards—Earth’s Processes as Hazards, Disasters and Catastrophes, 5th ed.; Routledge: Milton Park, UK; Taylor & Francis Group: Milton Park, UK, 2019; 642p. [Google Scholar]
- Tinti, S.; Armigliato, A.; Manucci, A.; Pagnoni, G.; Zaniboni, F.; Yalçiner, A.C.; Altinok, Y. The generating mechanisms of the August 17, 1999 İzmit bay (Turkey) tsunami: Regional (tectonic) and local (mass instabilities) causes. Mar. Geol. 2006, 225, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbach, M.J.; Braudy, N.; Briggs, R.W.; Cormier, M.-H.; Davis, M.B.; Diebold, J.B.; Dieudonne, N.; Douilly, R.; Frohlich, C.; Gulick, S.P.S.; et al. High tsunami frequency as a result of combined strike-slip faulting and coastal landslides. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, A.L.; Melgar, D.; Xu, X.; Milliner, C. The 2018 Palu tsunami: Coeval landslide and coseismic sources. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2020, 91, 3148–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Gusman, A.; Ishibe, T.; Sabeti, R.; Šepić, J. Estimating the eruption-induced water displacement source of the 15 January 2022 Tonga volcanic tsunami from tsunami spectra and numerical modelling. Ocean Eng. 2022, 261, 112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogou, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Evelpidou, N.; Lekkas, E. Earthquakes and Tsunamis: Natural Hazards over the Aegean Archipelago. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Mavrouli, M.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. Impact of earthquake-induced tsunamis on public health. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2017, 19, EGU2017-3890. [Google Scholar]
- Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. Respiratory Infections Following Earthquake-Induced Tsunamis: Transmission Risk Factors and Lessons Learned for Disaster Risk Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.; Sato, S.; Tajima, Y. The 11 March 2011 East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami: Tsunami Effects on Coastal Infrastructure and Buildings. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2013, 170, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetjen, J.; Sundar, V.; Venkatachalam, S.; Reicherter, K.; Engel, M.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Sannasiraj, S.A. A comprehensive review on structural tsunami countermeasures. Nat. Hazards 2022, 113, 1419–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W. The Jamaican earthquake. Pop. Sci. Mon. 1970, 70, 385–403. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, M. Notes on the Jamaica earthquake. J. Geol. 1907, 15, 696–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taber, S. Jamaica earthquakes and the Bartlett trough. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1920, 10, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanioka, Y.; Satake, K. Tsunami generation by horizontal displacement of ocean bottom. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçiner, A.C.; Alpar, B.; Altinok, Y.; Özbay, I.; Imamura, F. Tsunamis in the Sea of Marmara. Historical documents for the past, models for the future. Mar. Geol. 2002, 190, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, M.; Borrero, J.; Synolakis, C. Tsunami Hazards from Strike-Slip Earthquakes. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; Moscone Center West: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Harada, T.; Satake, K.; Ishibe, T.; Takagawa, T. Tsunamis from strike-slip earthquakes in the Wharton Basin, northeast Indian Ocean: March 2016 Mw 7.8 event and its relationship with the April 2012 Mw 8.6 event. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 211, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Carydis, P.; Mavroulis, S. The September 2018 Mw 7.5 Palu (Sulawesi Island, Indonesia) earthquake and tsunami disaster—Scientific Report (Version 1.0). Newsl. Environ. Disaster Cris. Manag. Strateg. 2018, 9, 1–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Gogou, M.; Carydis, P.; Lekkas, E. Environmental effects of the September 2018 Mw 7.5 Palu (Sulawesi Island, Indonesia) earthquake and building damage induced by the earthquake and the subsequent tsunami and liquefaction phenomena. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2019, 21, EGU2019-15065. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarzadeh, M.; Muhari, A.; Wijanarto, A.B. Insights on the source of the 28 September 2018 Sulawesi tsunami, Indonesia based on spectral analyses and numerical simulations. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, W.D.; Mann, P. Tectonics of Strike-Slip Restraining and Releasing Bends. In Tectonics of Strike-Slip Restraining and Releasing Bends; Cunningham, W.D., Mann, P., Eds.; Geological Society, London, Special Publications: London, UK, 2007; Volume 290, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, S.; Takagawa, T. Liquefied gravity flow-induced tsunami: First evidence and comparison from the 2018 Indonesia Sulawesi earthquake and tsunami disasters. Landslides 2019, 16, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, A.; Abdelmeguid, M.; Ma, X.; Amlani, F.; Bhat, H.S.; Synolakis, C.; Rosakis, A.J. Anatomy of strike-slip fault tsunami genesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025632118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, V.; Kapetanidis, V.; Kaviris, G.; Spingos, I.; Mavroulis, S.; Diakakis, M.; Alexopoulos, J.D.; Kazantzidou-Firtinidou, D.; Kassaras, I.; Dilalos, S.; et al. Seismological and Ground Deformation Study of the Ionian Islands (W. Greece) during 2014–2018, a Period of Intense Seismic Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.L.; Mavroulis, S.D. Earthquake environmental effects and ESI 2007 seismic intensities of the early 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6.0). Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 1517–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.L.; Mavroulis, S.D. Fault zones ruptured during the early 2014 Cephalonia Island (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6.0) based on the associated co-seismic surface ruptures. J. Seism. 2015, 20, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Carydis, P.; Alexoudi, V. The 17 November 2015 Mw 6.4 Lefkas (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) Earthquake: Impact on Environment and Buildings. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 2109–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Stanota, E.-S.; Lekkas, E. Evaluation of environmental seismic intensities of all known historical and recent earthquakes felt in Zakynthos Island, Greece using the Environmental Seismic Intensity (ESI 2007) scale. Quat. Int. 2019, 532, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Carydis, P.; Alexoudi, V.; Grambas, A.; Lekkas, E. The January-February 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, western Greece) earthquakes: Tectonic and seismological aspects. In Proceedings of the 16th World Conference of Earthquake Engineering, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 January 2017. Paper No 413. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S.; Vassilakis, E.; Diakakis, M.; Konsolaki, A.; Kaviris, G.; Kotsi, E.; Kapetanidis, V.; Sakkas, V.; Alexopoulos, J.D.; Lekkas, E.; et al. The Use of Innovative Techniques for Management of High-Risk Coastal Areas, Mitigation of Earthquake-Triggered Landslide Risk and Responsible Coastal Development. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Diakakis, M.; Kranis, H.; Vassilakis, E.; Kapetanidis, V.; Spingos, I.; Kaviris, G.; Skourtsos, E.; Voulgaris, N.; Lekkas, E. Inventory of Historical and Recent Earthquake-Triggered Landslides and Assessment of Related Susceptibility by GIS-Based Analytic Hierarchy Process: The Case of Cephalonia (Ionian Islands, Western Greece). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A. Tsunamis in the European-Mediterranean Region: From Historical Record to Risk Mitigation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780124202245. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Fokaefs, A. Strong Tsunamis in the Mediterranean Sea: A Re-Evaluation. ISET J. Earthq. Technol. 2005, 42, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, E.L.; Andreadakis, E.; Kostaki, I.; Kapourani, E. A Proposal for a New Integrated Tsunami Intensity Scale (ITIS-2012). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2013, 103, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makropoulos, K.; Kaviris, G.; Kouskouna, V. An updated and extended earthquake catalogue for Greece and adjacent areas since 1900. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, R.; Pavlides, S. The Greek Database of Seismogenic Sources (GreDaSS), Version 2.0.0: A Compilation of Potential Seismogenic Sources (Mw > 5.5) in the Aegean Region. Available online: http://gredass.unife.it/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- National Geophysical Data Center. World Data Service: NCEI/WDS Global Historical Tsunami Database. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Available online: https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/hazel/view/hazards/tsunami/event-search (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Maramai, A.; Brizuela, B.; Graziani, L. The Euro-Mediterranean Tsunami Catalogue. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 57, S0435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Chalkis, B.J. Tsunamis observed in Greece and the surrounding area from Antiquity up to the present times. Mar. Geol. 1984, 56, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A. Tsunamis in the East Mediterranean: 1. A Catalogue for the Area of Greece and Adjacent Seas. Institute of Geodynamics, National Observatory of Athens, Greece. Online Listing of Events through 2000. Available online: http://www.gein.noa.gr/services/catalogue.htm (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Soloviev, S.L.; Solovieva, O.N.; Go, C.N.; Kim, K.S.; Shchetnikov, N.A. Tsunamis in the Mediterranean Sea 2000 B.C.-2000 A.D.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; 256p. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A. Tsunamis in the East Mediterranean: A catalogue for the area of Greece and adjacent seas. In Proceedings of the Joint IOC/IUGG International Workshop “Tsunami Risk Assessment beyond 2000: Theory, Practice and Plans”, Moscow, Russia, 14–16 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Papazachos, B.; Papazachou, K. The Earthquakes of Greece; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2003; 286p. [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N. Earthquakes in the Mediterranean and Middle East, a Multidisciplinary Study of Seismicity up to 1900; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; p. 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambraseys, N.N.; Jackson, J.A. Seismicity and associated strain of central Greece between 1890 and 1988. Geophys. J. Int. 1990, 101, 663–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Kolyva, M.; Antonopoulos, G.; Kopanas, I. The earthquakes of Zakynthos. An interpretation of the descriptions of earthquakes and correlation with the existing geological structure. Ann. Géol. Pays Hellén. 1996, 37, 1033–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Plessa, A. Historical earthquakes and tsunamis of the South Ionian Sea occurring from 1591 to 1837. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2001, 34, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Daskalaki, E.; Fokaefs, A.; Giraleas, N. Tsunami Hazard in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: Strong Earthquakes and Tsunamis in the West Hellenic Arc and Trench System. J. Earthq. Tsunami 2010, 4, 145–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoyanni, T.; Sakellariou, M.; Baskoutas, J.; Christodoulou, N. Evaluation of active faulting and earthquake secondary effects in Lefkada Island, Ionian Sea, Greece: An overview. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakostas, V.; Papadimitriou, E.; Patias, P.; Georgiadis, C. Coastal deformation in Lefkada Island associated with strong earthquake occurrence. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2019, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ganas, A.; Briole, P.; Bozionelos, G.; Barberopoulou, A.; Elias, P.; Tsironi, V.; Valkaniotis, S.; Moshou, A.; Mintourakis, I. The 25 October 2018 Mw = 6.7 Zakynthos earthquake (Ionian Sea, Greece): A low-angle fault model based on GNSS data, relocated seismicity, small tsunami and implications for the seismic hazard in the west Hellenic Arc. J. Geodyn. 2020, 137, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanopoulos, A. Tsunamis observed on the coasts of Greece from antiquity to present time. Ann. Geofis. 1960, 13, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Catalogue of tsunamis in the Eastern Mediterranean from antiquity to present time. Ann. Geophys. 1979, 32, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea-waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from the Birth of Christ to 500 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from 500 to 1000 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from 1000 to 1500 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from 1500 to 1800 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from 1800 to 1900 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, J. Data from investigation on seismic Sea waves events in the Eastern Mediterranean from 1900 to 1980 A.D. Ann. Geophys. 1980, 33, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazachos, B.C.; Koutitas, C.; Hatzidirnitriou, P.M.; Karacostas, B.G.; Papaioannou, C.A. Tsunami hazard in Greece and the surrounding area. Ann. Geophys. 1986, 4, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Soloviev, S.L. Tsunamigenic zones in the Mediterranean Sea. Nat. Hazards 1990, 3, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambraseys, N.; Synolakis, C. Tsunami Catalogs for the Eastern Mediterranean, Revisited. J. Earthq. Eng. 2010, 14, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Tzouxanioti, M.; Petropoulos, A.; Gogou, M.; Mloukie, E. Tsunamis in the Greek Region: An Overview of Geological and Geomorphological Evidence. Geosciences 2022, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandazzi, M. Le tremblement de terre des Iles Ioniennes (aout 1953). Ann. Georgr. 1954, 63, 431–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Alexoudi, V. Field observations of the 2015 (November 17, mw 6.4) Lefkas (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquake impact on natural environment and building stock of Lefkas Island. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2016, 50, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barberopoulou, A.; Scheele, F. Does the future of tsunami intensity scales lie in past events? Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicherter, K. Tsunamis as Paleoseismic Indicators. In Encyclopedia of Earthquake Engineering; Beer, M., Kougioumtzoglou, I., Patelli, E., Au, I.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsetsiadou, K.-N.; Andreadakis, E.; Lekkas, E. Ishinomaki Tsunami Intensity Mapping (ITIS2012) for the 9Mw Tohoku Event, March 11 2011, Japan. Res. Geoph. 2016, 5, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gogou, M.; Katsetsiadou, N.-E.; Lekkas, E.; Andreadakis, E. The 21 July 2017, Kos-Bodrum tsunami intensity mapping: Applying the integrated Tsunami Intensity Scale (ITIS2012). In Proceedings of the 15th Geological Society of Greece International Conference, Athens, Greece, 22–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S.; Gogou, M.; Carydis, P.; Lekkas, E. The impact of the 2018 Central-Western Sulawesi (Indonesia) tsunami on the Palu Bay and application of the Integrated Tsunami Intensity Scale (ITIS 2012). In Proceedings of the ATAG 23, 20th Anniversary of the 1999 Marmara Earthquakes, Istanbul, Turkey, 15–18 October 2019; pp. 164–165, Abstract Book. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Geology and Underground Research (IGUR). The Devastating Earthquakes of the Ionian Islands in August 1953: Proposals for the Reconstruction of Cities, Towns and Villages of the Earthquake-Affected Islands; Institute of Geology and Underground Research Monograph: Athens, Greece, 1954; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S.; Alexoudi, V.; Grambas, A.; Lekkas, E.; Carydis, P. The January-February 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, western Greece) earthquake sequence: Damage pattern on buildings. In Proceedings of the 16th World Conference of Earthquake Engineering, 96 Special Session—Evolution of EMS-98 Building Types, Vulnerability Classes and Damage Grade Description towards an International Macroseismic Scale, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 January 2017. Paper No 414. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, E.; Mavroulis, S. The Mw 6.8 October 26, 2018 Zakynthos (Ionian Sea, Greece) Earthquake. Newsl. Environ. Disaster Cris. Manag. Strateg. 2018, 10, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, R. Triassic evaporites and Plio-Quaternary diapirism in western Greece. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1988, 145, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvari, E.; Kiratzi, A.; Papazachos, B. The Cephalonia Transform Fault and its extension to western Lefkada Island (Greece). Tectonophysics 1999, 308, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachpazi, M.; Hirn, A.; Clément, C.; Haslinger, F.; Laigle, M.; Kissling, E.; Charvis, P.; Hello, Y.; Lépine, J.-C.; Sapin, M.; et al. Western Hellenic subduction and Cephalonia Transform: Local earthquakes and plate transport and strain. Tectonophysics 2000, 319, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokinou, E.; Kamberis, E.; Vafidis, A.; Monopolis, D.; Ananiadis, G.; Zelilidis, A. Deep seismic reflection data from offshore western Greece: A new crustal model for the Ionian Sea. J. Pet. Geol. 2005, 28, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzidei, M.; Baldi, P.; Casula, G.; Crespi, M.; Riguzzi, F. Repeated GPS surveys across the Ionian Sea: Evidence of crustal deformations. Geophys. J. Int. 1996, 127, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hollenstein, C.H.; Geiger, A.; Kahle, H.-G.; Veis, G. CGPS time-series and trajectories of crustal motion along the West Hellenic. Arc. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 164, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenstein, C.; Müller, M.; Geiger, A.; Kahle, H.-G. Crustal motion and deformation in Greece from a decade of GPS measurements, 1993–2003. Tectonophysics 2008, 449, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, J.; Papoulia, J. The backstop between the Mediterranean Ridge and western Peloponnese, Greece: Its crust and tectonization. An active seismic experiment with ocean bottom seismographs. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganas, A.; Serpelloni, E.; Drakatos, G.; Kolligri, M.; Adamis, I.; Tsimi, C.; Batsi, E. The MW 6.4 Achaia-Elia (Western Greece) Earthquake of 8 June 2008: Seismological, field, GPS observations and stress modeling. J. Earthq. Eng. 2009, 13, 1101–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakostas, V.; Mirek, K.; Mesimeri, M.; Papadimitriou, E.; Mirek, J. The aftershock sequence of the 2008 Achaia, Greece, Earthquake: Joint analysis of seismicity relocation and persistent scatterers interferometry. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 151–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.D.; Fountoulis, I.G.; Skourtsos, E.N.; Lekkas, E.L.; Papanikolaou, I.D. Seismic intensity assignments for the 2008 Andravida (NW Peloponnese, Greece) strike-slip event (June 8, Mw = 6.4) based on the application of the Environmental Seismic Intensity scale (ESI 2007) and the European Macroseismic scale (EMS-98). Ann. Geoph. 2013, 56, S0681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardell, N.; Camera, L.; Mascle, J.; Nicolich, R.; Marchi, M.; Barison, E. The structural framework of the Peloponnese continental margin from Zakynthos to Pylos from seismic reflection and morpho-bathymetric data. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, L.; Mascle, J.; Wardell, N.; Accettella, D.; The SEAHELLARC Team. The Peloponnese continental margin from Zakynthos Island to Pylos: Morphology and recent sedimentary processes. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulia, J.; Makris, J.; Tsambas, A. Microseismicity and crustal deformation of the Kyparissiakos Gulf, south-western Hellenic Arc, using an “amphibious” seismic array and a 3D velocity model obtained from active seismic observations. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 281–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kokinou, E.; Papadimitriou, E.; Karakostas, V.; Kamberis, E.; Vallianatos, F. The Kefalonia Transform Zone (offshore Western Greece) with special emphasis to its prolongation towards the Ionian Abyssal Plain. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2006, 27, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulia, J.; Nicolich, R.; Makris, J.; Slejko, D.; Mascle, J.; Papadopoulos, G.; Anagnostou, C.H.; Camera, L.; Daskalaki, E.; Fasoulaka, C.H.; et al. A new seismogenic model for the Kyparissiakos Gulf and western Peloponnese (SW Hellenic Arc). Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 405–432. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, P.; Kapetanidis, V.; Karakonstantis, A.; Spingos, I.; Pavlou, K.; Kaviris, G.; Kassaras, I.; Sakkas, V.; Voulgaris, N. The 25 October 2018 Zakynthos (Greece) earthquake: Seismic activity at the transition between a transform fault and a subduction zone. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 225, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, E.; Fountoulis, I.; Papanikolaou, D. Intensity Distribution and Neotectonic Macrostructure Pyrgos earthquake data (26 March 1993, Greece). Nat. Hazards 2000, 21, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulis, I.; Vassilakis, E.; Mavroulis, S.; Alexopoulos, J.; Dilalos, S.; Erkeki, A. Synergy of tectonic geomorphology, applied geophysics and remote sensing techniques reveals new data for active extensional tectonism in NW Peloponnese (Greece). Geomorphology 2015, 237, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulis, I. Neotectonic Deformation of the Central-Western Peloponnese. Ph.D. Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fountoulis, I.; Mariolakos, I.; Ladas, I. Quaternary basin sedimentation and geodynamics in SW Peloponnese (Greece) and late stage uplift of Taygetos Mt. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulis, I.G.; Mavroulis, S.D. Application of the Environmental Seismic Intensity scale (ESI 2007) and the European Macroseismic Scale (EMS-98) to the Kalamata (SW Peloponnese, Greece) earthquake (Ms = 6.2, September 13, 1986) and correlation with neotectonic structures and active faults. Ann. Geoph. 2013, 56, S0675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D.; Fountoulis, I.; Metaxas, C. Active faults, deformation rates and Quaternary paleogeography at Kyparissiakos Gulf (SW Greece) deduced from onshore and offshore data. Quat. Int. 2007, 171–172, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D.; Chronis, G.; Pavlakis, P.; Lykousis, V. Submarine Neotectonic Map of upper Messiniakos Gulf, Earthquake Planning and Protection Organization, National Center for Marine Research; National and Kapodistrian University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 1988; 31p. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, D.; Metaxas, C.; Chronis, G. Neotectonic structure of the Lakonikos gulf. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2001, 34, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fischer, P.; Finkler, C.; Robke, B.R.; Baika, K.; Hadler, H.; Willershauser, T.; Rigakou, D.; Metallinou, G.; Vott, A. Impact of Holocene tsunamis detected in lagoonal environments on Corfu (Ionian Islands, Greece): Geomorphological, sedimentary and microfaunal evidence. Quat. Int. 2016, 401, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vött, A.; Brückner, H.; Brockmüller, S.; Handl, M.; May, S.M.; Gaki-Papanastassiou, V.; Herd, R.; Lang, F.; Maroukian, H.; Nelle, O.; et al. Traces of Holocene tsunamis across the Sound of Lefkada, NW Greece. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 66, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, S.M.; Vött, A.; Bruckner, H.; Smedile, A. The Gyra washover fan in the Lefkada Lagoon, NW Greece-possible evidence of the 365 AD Crete earthquake and tsunami. Earth Planet Space 2012, 64, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vött, A.; Brückner, H.; May, M.; Lang, F.; Brockmüller, S. Late Holocene tsunami imprint at the entrance of the Ambrakian gulf (NW Greece). Mediterranee 2007, 108, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vött, A.; Bareth, G.; Brückner, H.; Curdt, C.; Fountoulis, I.; Grapmayer, R.; Hadler, H.; Hoffmeister, D.; Klasen, N.; Lang, F.; et al. Beachrock-type calcarenitic tsunamites along the shores of the eastern Ionian Sea (western Greece)—Case studies from Akarnania, the Ionian Islands and the western Peloponnese. Z. Geomorphol. 2010, 54, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willershäuser, T.; Vött, A.; Brückner, H.; Bareth, G.; Nelle, O.; Nadeau, M.-J.; Hadler, H.; Ntageretzis, K. Holocene tsunami landfalls along the shores of the inner Gulf of Argostoli (Cefalonia Island, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2013, 57, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willershäuser, T. Holocene Tsunami Events in the Eastern Ionian Sea—Geoscientific Evidence from Cefalonia and the Western Peloponnese (Greece). Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität, Mainz, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hadler, H.; Baika, K.; Pakkanen, J.; Evangelistis, D.; Emde, K.; Fischer, P.; Ntageretzis, K.; Röbke, B.; Willershäuser, T.; Vött, A. Palaeotsunami impact on the ancient harbour site Kyllini (western Peloponnese, Greece) based on a geomorphological multi-proxy approach. Z. Geomorphol. 2005, 59, 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vött, A.; Fischer, P.; Röbke, B.R.; Werner, V.; Emde, K.; Finkler, C.; Hadler, H.; Handl, M.; Ntageretzis, K.; Willershäuser, T. Holocene fan alluviation and terrace formation by repeated tsunami passage at Epitalio near Olympia (Alpheios River valley, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 81–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willershäuser, T.; Vött, A.; Hadler, H.; Fischer, P.; Röbke, B.; Ntageretzis, K.; Emde, K.; Brückner, H. Geo-scientific evidence of tsunami impact in the Gulf of Kyparissia (western Peloponnese, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 43–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willershäuser, T.; Vött, A.; Hadler, H.; Ntageretzis, K.; Emde, K.; Brückner, H. Holocene palaeotsunami imprints in the stratigraphical record and the coastal geomorphology of the Gialova Lagoon near Pylos (southwestern Peloponnese, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 215–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, B.; Vött, A.; Mathes-Schmidt, M.; Reicherter, K. Geoscientific investigations in search of tsunami deposits in the environs of the Agoulinitsa peatland, Kaiafas Lagoon and Kakovatos (Gulf of Kyparissia, western Peloponnese, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 125–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, A.; Kelletat, D.; Vött, A.; May, S.M.; Scheffers, S. Late Holocene tsunami traces on the western and southern coastlines of the Peloponnesus (Greece). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 269, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntageretzis, K.; Vött, A.; Emde, K.; Fischer, P.; Hadler, H.; Röbke, B.R.; Willershäuser, T. Palaeotsunami record in near-coast sedimentary archives in southeastern Lakonia (Peloponnese, Greece). Z. Geomorphol. 2015, 59, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambraseys, N.N. Data for the investigation of seismic sea-waves in the Eastern Mediterranean. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 1962, 52, 895–913. [Google Scholar]
- Stucchi, M.; Rovida, A.; Gomez Capera, A.A.; Alexandre, P.; Camelbeeck, T.; Demircioglu, M.B.; Gasperini, P.; Kouskouna, V.; Musson, R.M.W.; Radulian, M.; et al. The SHARE European Earthquake Catalogue (SHEEC) 1000–1899. J. Seismol. 2013, 17, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovida, A.; Antonucci, A. EPICA—European PreInstrumental Earthquake CAtalogue, Version 1.1; Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV): Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiani, D.G.; Barbiani, B.A. Mémoire sur les Tremblements de Terre Dans l’ ȋle de Zante; Mémoire de l’Académie Imperiale des Sciences: Dijon, France, 1864; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Katramis, N. Philological Analects of Zakinthos; Avgi Publications: Zakynthos, Greece, 1880. [Google Scholar]
- Zois, G. Earthquakes in Zakynthos. Moussai 1893, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitselis, E. Cefalonian Miscellaneous—A Contribution to the History and Laography of the Island of Cefalonia; Minas Mirtidis Publications: Athens, Greece, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Mouyaris, N. The Seismic History of the Aegean. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mavroulis, S. Environmental Effects and Evaluation of Environmental Intensities of Historic and Recent Earthquakes in Western Greece (Western Peloponnese and Central Ionian Islands) and Correlation with Active Tectonics and Seismological Parameters. Ph.D. Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sieberg, A. Erdbebengeographie. Handbuch der Geoph. 1932, 4, 708–744. [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, A.G. Erdbebengeographie von Griechenland. Ann. Géol. Pays Hellén. 1955, 6, 83–121. [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, A.G. Greece—A Catalogue of Shocks with Io ≥ VII for the Years Prior to 1800; National Observatory of Athens: Athens, Greece, 1961; 19p. [Google Scholar]
- Bonito, M. Terra Tremante, o Vero Continuatione de Terremoti dalla Creatione del Mondo Sino al Tempo Presente (Ristampa Anastatica, Sala Bolognese 1980). Napoli, 1691. Available online: http://www.cftilab.it/file_repository/pdf_R/000095-000003_R.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Montandon, F. Les Tremblements de Terre Destructeurs in Europe; UNESCO: Genève, Switzerland, 1953; 195p.
- Coronelli, V. Cronologia Universale Sacro-Profana del Padre Vincenzo Coronelli; Catolica, Ed: Venice, Italy, 1762; 516p. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.F. Essay on the Earthquake of Cefalonia on January 23, 1867; Ethniko Typogr.: Athens, Greece, 1867; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Papazachos, V.; Papazachou, K. The Earthquakes of Greece; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1989; 360p. [Google Scholar]
- Tselentis, G.-A.; Stavrakakis, G.; Sokos, E.; Gkika, F.; Serpetsidaki, A. Tsunami hazard assessment in the Ionian Sea due to potential tsunamogenic sources—Results from numerical simulations. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotis, P. Historical review of earthquakes in Greece with special reference to Zakynthos. Kipseli 1886, 256–259, 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, R. Report on the facts of earthquake phenomena. British Assoc. Advanc. Sci. 1858, 4, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Perrey, A. Memoire sur les Tremblements de Terre Ressentis dans la Peninsule Turco-Hellenique et en Syrie; Publ. Academie Royale de Belgique: Belgium, Brussel, 1848. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, R. Report on the facts of earthquake phenomena. Br. Assoc. Advanc. Sci. 1854, 3, 326. [Google Scholar]
- Kavassakalis, G.; Polymenakos, L. Seismicity of the Ionian Islands; Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Department of Geophysics: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1988; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanassiou, G.; Pavlides, S.; Ganas, A. The 2003 Lefkada earthquake: Field observations and preliminary microzonation map based on liquefaction potential index for the town of Lefkada. Eng. Geol. 2005, 82, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoyanni, T. Les seismes et l’environnement geólogique de l’ȋle de Lefkade, Grèce: Passe et Futur. In Engineering Geology and the Environment, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Geology and the Environment, Athens, Greece, 23–27 June 1997; Marinos, P., Koukis, G., Tsiambaos, G., Stournaras, G., Eds.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 1469–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, A. Die Seismizitat der Insel Leukas. I. Allgemeine historische Ubersicht. Gerl. Beitr. Geophys. 1952, 62, 256–263. [Google Scholar]
- Karnik, V. Tsunamis. In Seismicity of the European Area. Part II; D. Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1971; pp. 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Pouqueville, F.C.H.L. Histoire de la Regeneration de la Grece: Comprenant le Precis des Evenements Depuis 1740 Jusquén 1824; Firmin Didot Pere et Fils: Paris, France, 1824; 498p. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, M.; Faita, G. Primo Catalogo dei Maremoti delle Coste Italiane; Atti Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei, Memorie Classe Scienze Fisiche, Matematiche e Naturali: Rome, Italy, 1984; Volume 8, pp. 213–356. [Google Scholar]
- Machairas, K. Leukada and Leukadians during the English Protection (1810–1864); Library of Historical Studies: Kerkyra, Greece, 1940; 191p. [Google Scholar]
- Davy, J. Notes and Observations on the Ionian Islands and Malta; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1842. [Google Scholar]
- Zoras, G. The Ionian earthquakes of 1820 and 1825 in a description of documents from the Vatican’s secret archives. Parnassοs 1973, 15, 396–406. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatelos, N. The 13 Disasters of Lefkada from 1612 to 1869; Philological Newspaper of Philomaths: Athens, Greece, 1870; 726p. [Google Scholar]
- Colla, A. Terremoti Sentiti in Diverse Parti del Globo. Nell’anno 1835; Biblioteca Italiana: Milan, Italy, 1836; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Vergotis, P. The 23 January 1867 Earthquake; Typography of Kefallinia: Argostoli, Greece, 1867; 15p. [Google Scholar]
- Partsch, J. Cephalonia and Ithaki: Geographic Monograph; UNESCO: Athens, Greece, 1892; pp. 69–77.
- Papathanassiou, G.; Valkaniotis, S.; Ganas, A.; Papanikolaou, M. Evaluation of the macroseismic intensities triggered by the 3 February 2014 Cephalonia, Greece earthquake based on ESI-07 scale. In Proceedings of the 6th International INQUA Meeting on Paleoseismology, Active Tectonics and Archaeoseismology, Pescina, Italy, 19–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanassiou, G.; Valkaniotis, S.; Ganas, A. Evaluation of the macroseismic intensities triggered by the January/February 2014 Cephalonia, (Greece) earthquakes based on ESI-07 scale and their comparison to 1867 historical event. Quat. Int. 2017, 451, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J. Studien über Erdbeben; Alwin Georgi: Leipzig, Germany, 1879; 360p. [Google Scholar]
- Shebalin, N.V.; Karnik, V.; Hadzievski, D. Catalogue of Earthquakes of the Balkan Region; UNDP-UNESCO Survey of the Seismicity of the Balkan Region: Skopje, North Macedonia, 1974; 600p. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, G.A.; Daskalaki, E.; Fokaefs, A.; Novikova, T. Tsunamigenic potential of local and distant tsunami sources threatening SW Peloponnese. Boll. Geofis. Teor. Appl. 2014, 55, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porphyrios, D.T.G. Traditional Earthquake-Resistant Construction on a Greek Island. J. Soc. Archit. Hist. 1971, 30, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailovic, D.J. Catalogue des Tremblements de Terre Epiro-Albanais; Archive Séismologique de l’ Institut Séismologique de Beograd: Zagreb, Croatia, 1951; 73p. [Google Scholar]
- Morelli, C. Carta Sismica dell’ Albania; Reale Accademia d’Italia, Commissione Italiana di Studio per i problemi del soccorso alle popolazioni; INGV: Accumoli, Italy; Volume X, p. 23.
- Galanopoulos, A.G. Das Erdbeben von Messenien vom 22. Januar 1899. Proc. Acad. Athènes 1941, 16, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, A.G. The seismicity in Messinia province. Ann. Géol. Pays Hellén. 1947, 1, 38–59. [Google Scholar]
- Grünthal, G.; Wahlström, R.; Stromeyer, D. The SHARE European Earthquake Catalogue (SHEEC) for the time period 1900–2006 and its comparison to the European-Mediterranean Earthquake Catalogue (EMEC). J. Seismol. 2013, 17, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL-NKUA. Earthquake Catalogue Search: Significant Earthquakes 2003–2022. 2022. Available online: http://www.geophysics.geol.uoa.gr/stations/gmapv3_db/index.php (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Critikos, N. L’ ȋle de Leucade et des sismes du 23 et du 27 Novembre 1914. Ann. Obs. Nat. Athenes 1916, 7, 62–81. [Google Scholar]
- Papazachos, B.C.; Dimitriu, P.P. Tsunamis in and near Greece and their relation to the earthquake focal mechanisms. Nat. Hazards 1991, 4, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.S. Earthquakes and tsunami in the European area. In Proceedings of the 13th General Assembly of the European Seismological Commission, Brasov, Romania, 28 August–5 September 1972; pp. 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Galanopoulos, A.G. The Koroni, Messinia, earthquake of October 6, 1947. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1949, 39, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E. Revisiting the Most Destructive Earthquake Sequence in the Recent History of Greece: Environmental Effects Induced by the 9, 11 and 12 August 1953 Ionian Sea Earthquakes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiros, S.; Pirazzoli, P.A.; Laborel, J.; Laborel-Deguen, F. The 1953 earthquake in Cephalonia (Western Hellenic Arc): Coastal uplift and halotectonic faulting. Geophys. J. Int. 1994, 117, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petratos, P. The earthquakes of 1953—Argostoli Prison: The forgotten offer of political prisoners. Kefalonitiki Prood. 2013, 8, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kolosenko, M.N. An earthquake at the Ionic Islands. Priroda 1955, 1, 128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ambraseys, N. The seismicity of the eastern Mediterranean. Stud. Geoph. Geoph. Geodet. 1965, 9, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriou, A.; Mouyiaris, N. Macroseismic Reconnaissance in the Area of Cephalonia-Zakynthos (Earthquakes 17 & 19-1-83); Monograph; Institute of Geological and Mineral Research: Athens, Greece, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Benetatos, C.; Kiratzi, A.; Roumelioti, Z.; Stavrakakis, G.; Drakatos, G.; Latoussakis, I. The 14 August 2003 Lefkada Island (Greece) earthquake: Focal mechanisms of the mainshock and of the aftershock sequence. J. Seismol. 2005, 9, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaris, B.; Papaioannou, C.; Theodulidis, N.; Savvaidis, A.; Anastasiadis, A.; Klimis, N.; Makra, K.; Demosthenous, M.; Karakostas, C.; Lekidis, V.; et al. Preliminary Observations on the August 14, 2003 Lefkada Island (Western Greece) Earthquake, Nov. 2003, EERI Special Earthquake Report; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, E.; Danamos, G.; Lozios, S.; Skourtsos, E.; Verykiou, E. Geographical distribution of landslides in the Lefkada earthquake (14 August 2003) and factors favoring their occurrence. Bull. Hellen. Geogr. Soc. 2004, 1–4, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cirella, A.; Romano, F.; Avallone, A.; Piatanesi, A.; Briole, P.; Ganas, A.; Theodoulidis, N.; Chousianitis, K.; Volpe, M.; Bozionellos, G.; et al. The 2018 Mw 6.8 Zakynthos (Ionian Sea, Greece) earthquake: Seismic source and local tsunami characterization. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakostas, C.; Konstantinidou, K.; Lekidis, V.; Makra, K.; Margaris, B.; Morfidis, K.; Papaioannou, C.; Rovithis, E.; Salonikios, T.; Theodulidis, N. Southern Ionian Sea Earthquake M 6.8 on 25/10/2018—Strong Ground Motion and Effects on Soil and Built Environment. Available online: http://www.itsak.gr/uploads/news/earthquake_reports/EQ_ZAKYNTHOS_20181025_M6.8_v2_en.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Melgar, D.; Ganas, A.; Geng, J.; Liang, C.; Fielding, E.J.; Kassaras, I. Source characteristics of the 2015 Mw6.5 Lefkada, Greece, strike-slip earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 2260–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).