3D Geophysical Modeling Based on Multi-Scale Edge Detection, Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion, and Magnetization Vector Inversion in Panjshir, Afghanistan to Detect Probabilistic Fe-Polymetallic Bearing Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
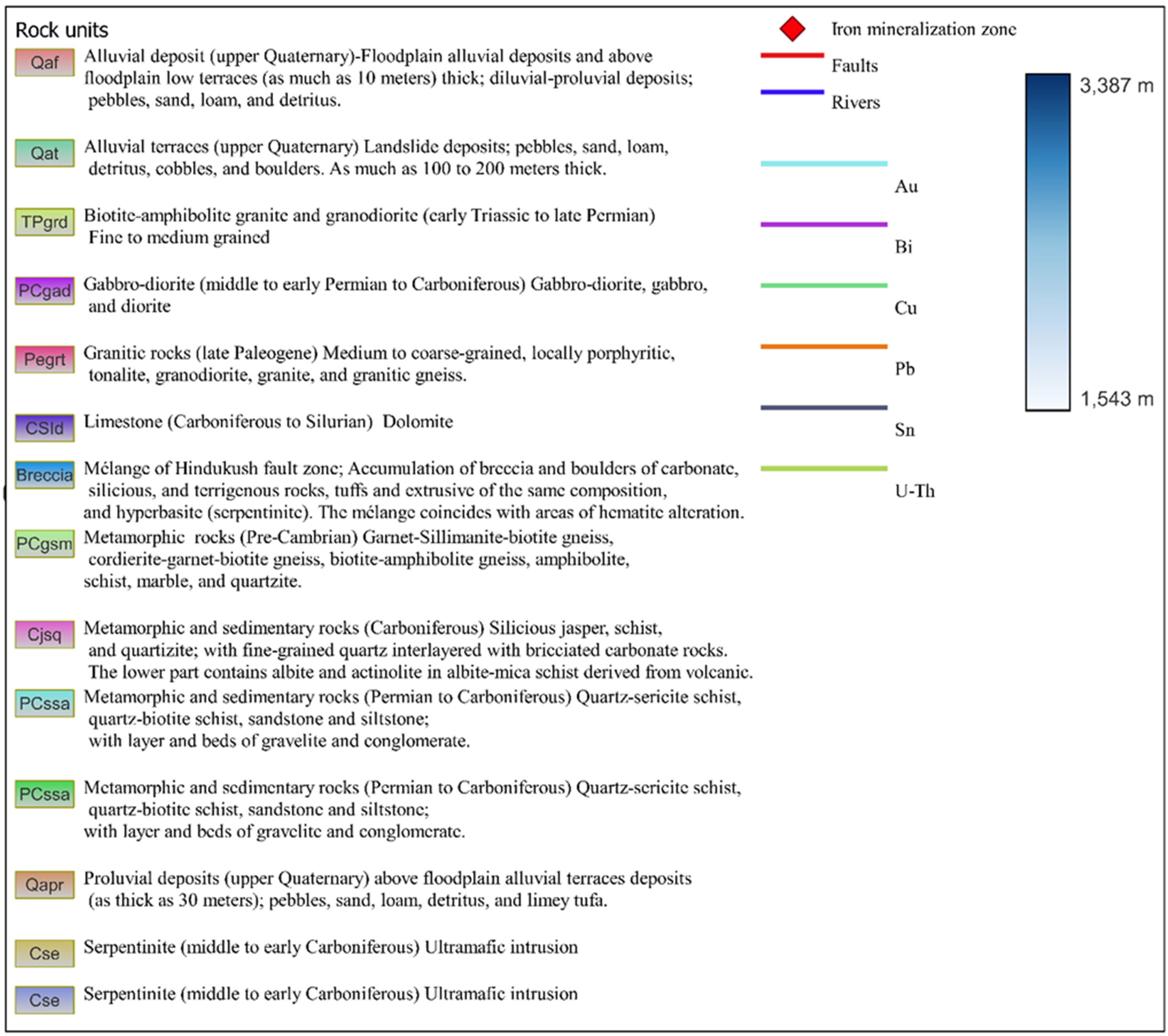
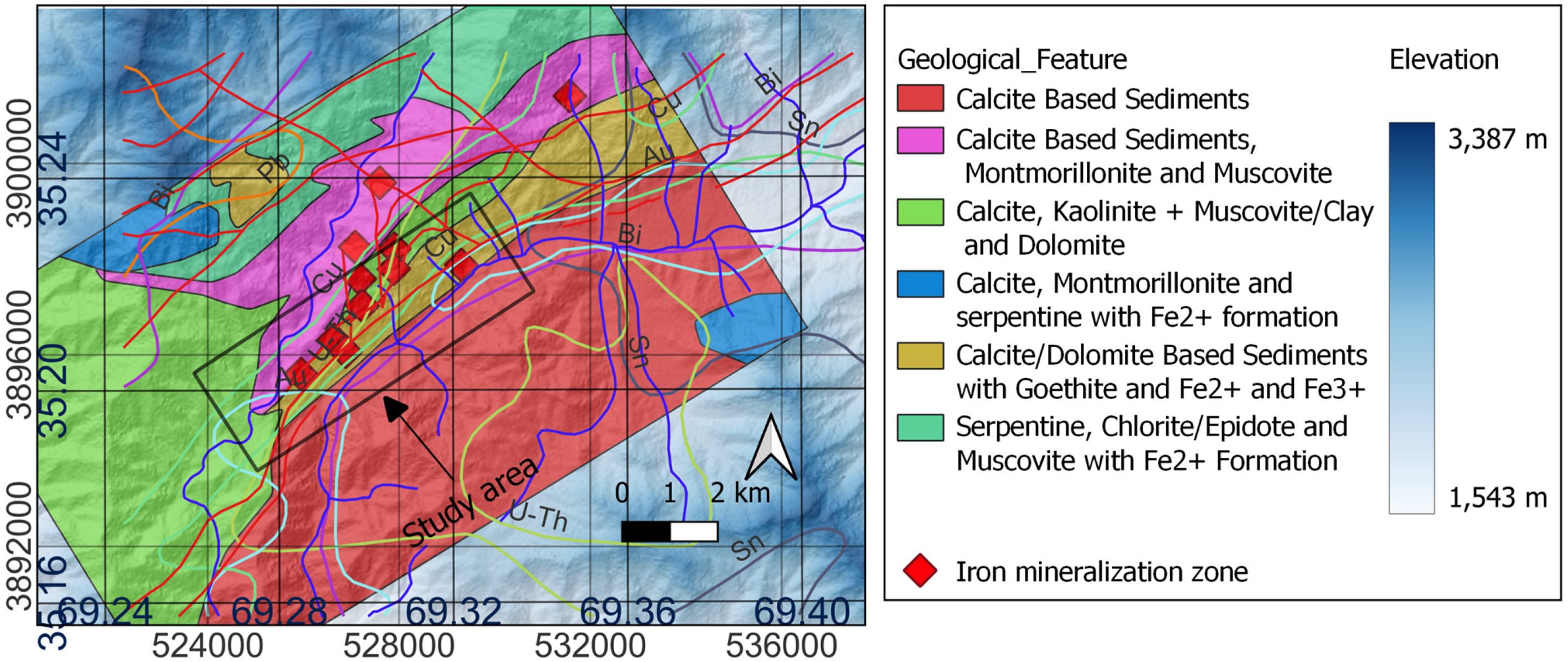
2. Geological Background
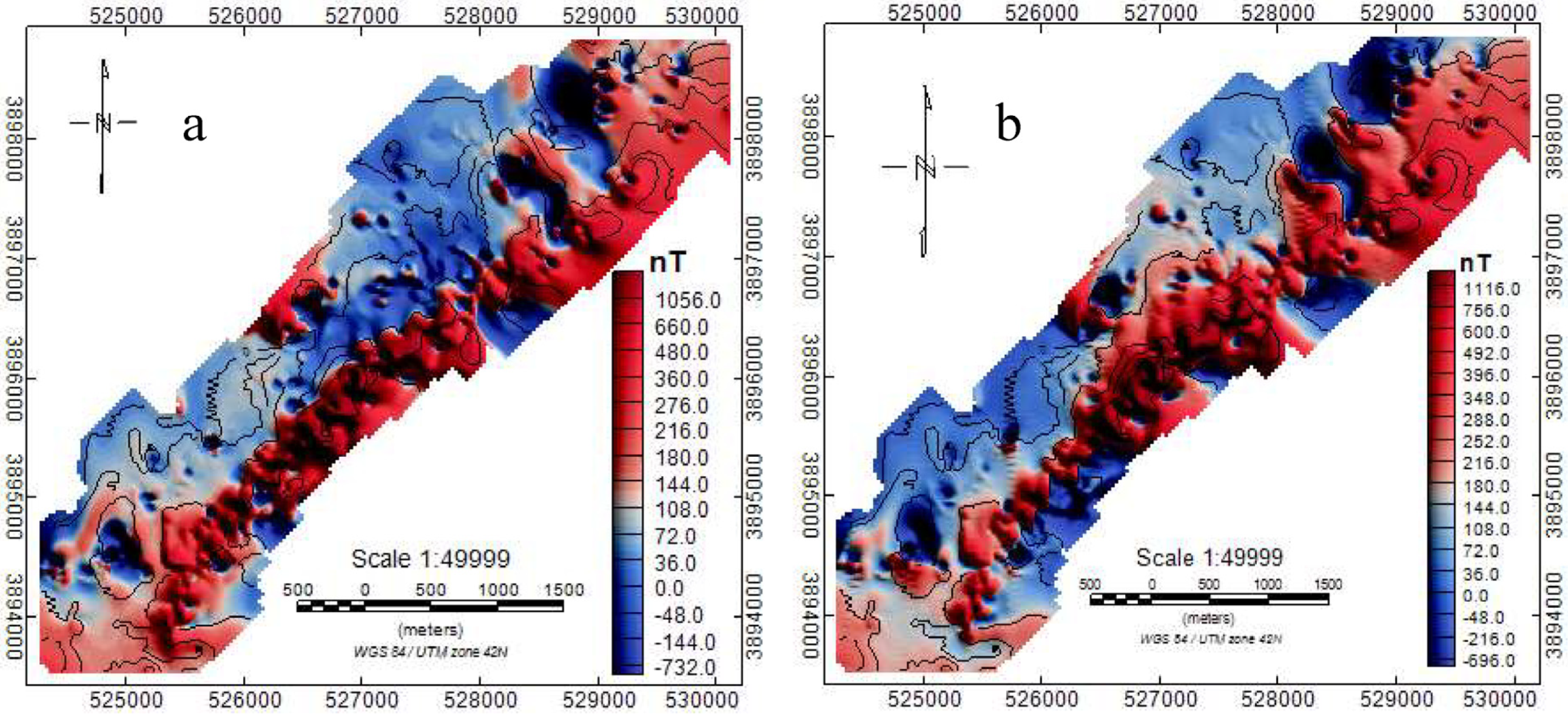
3. Magnetic Data
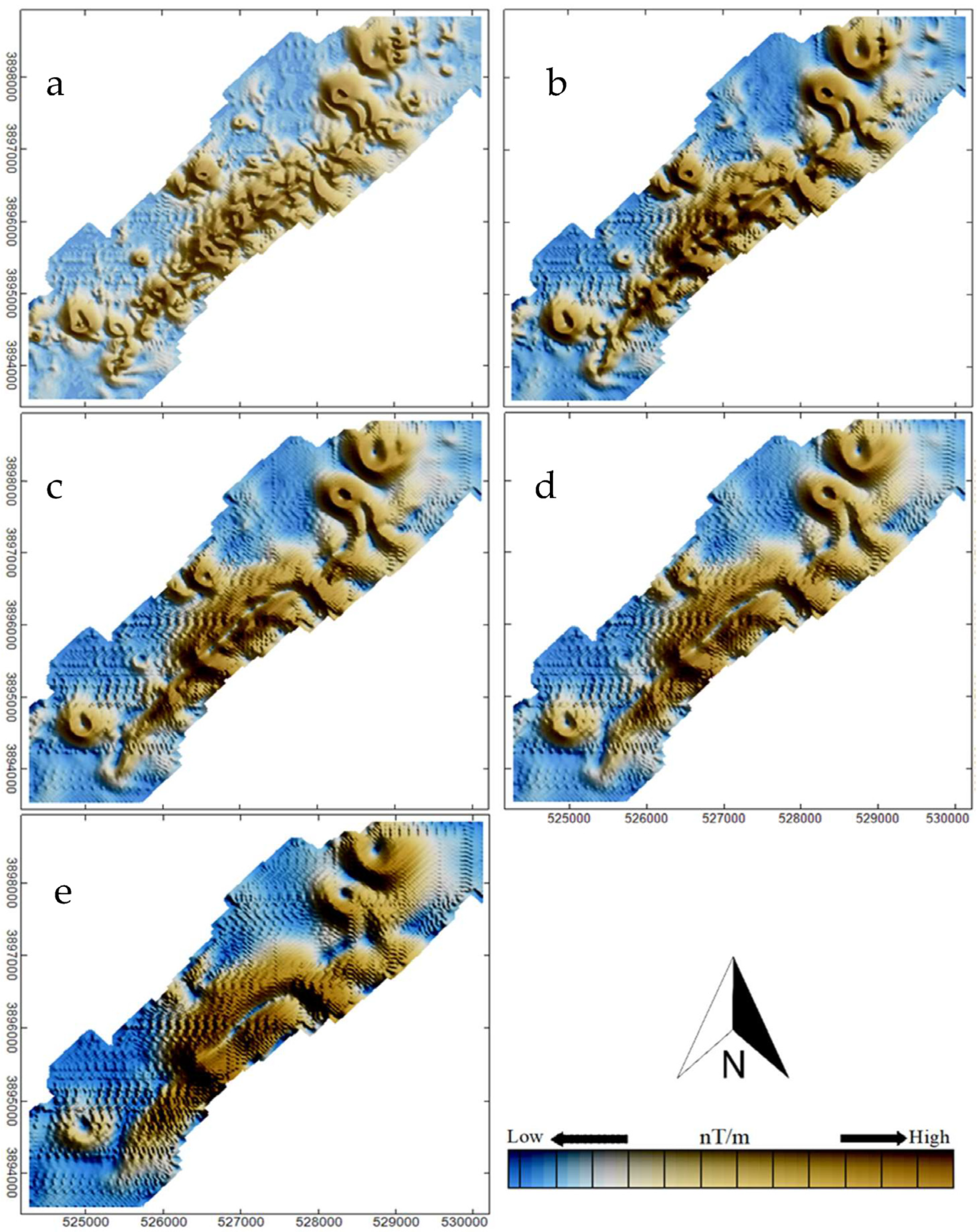
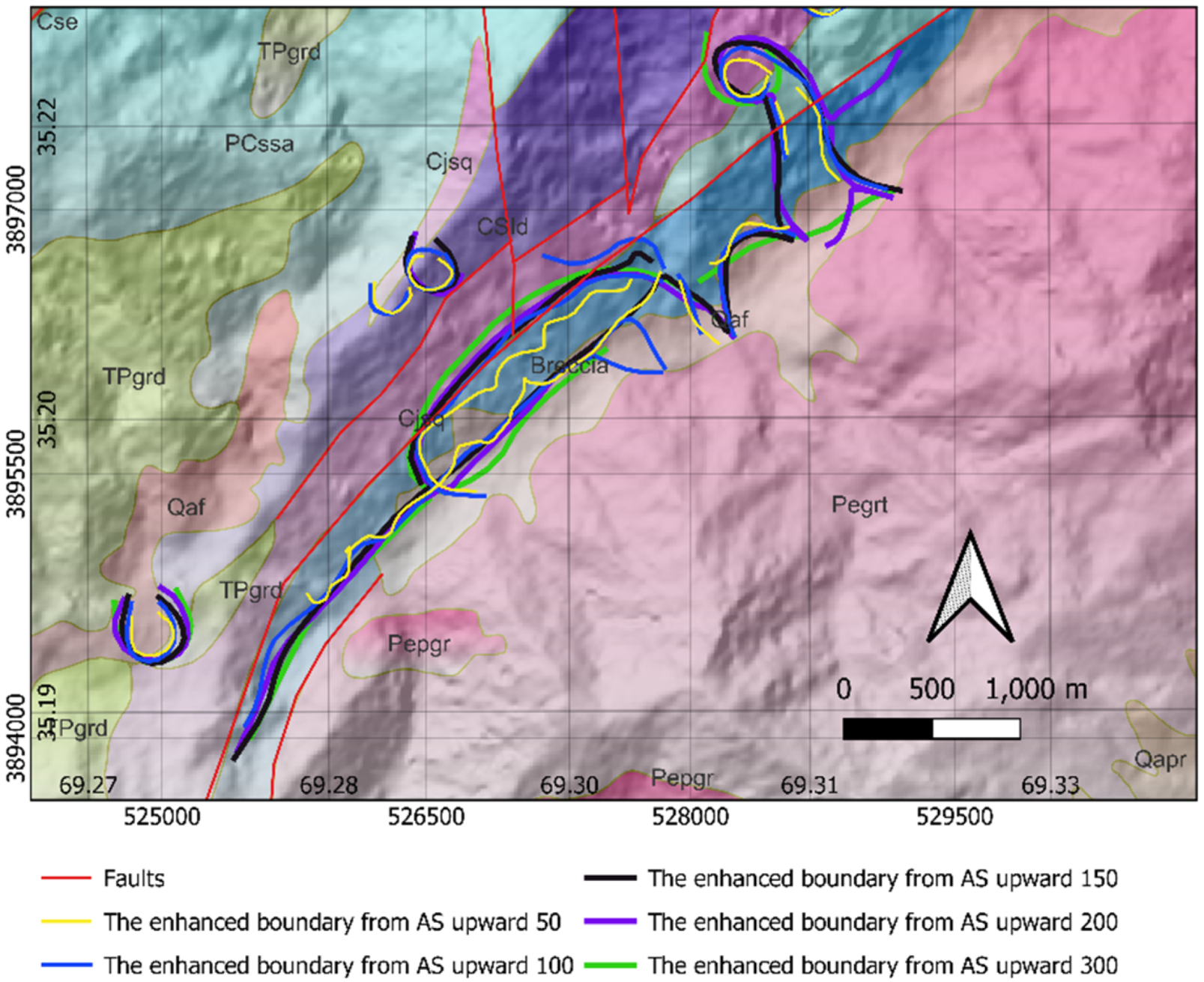
4. Multi-Scale Edge Detection
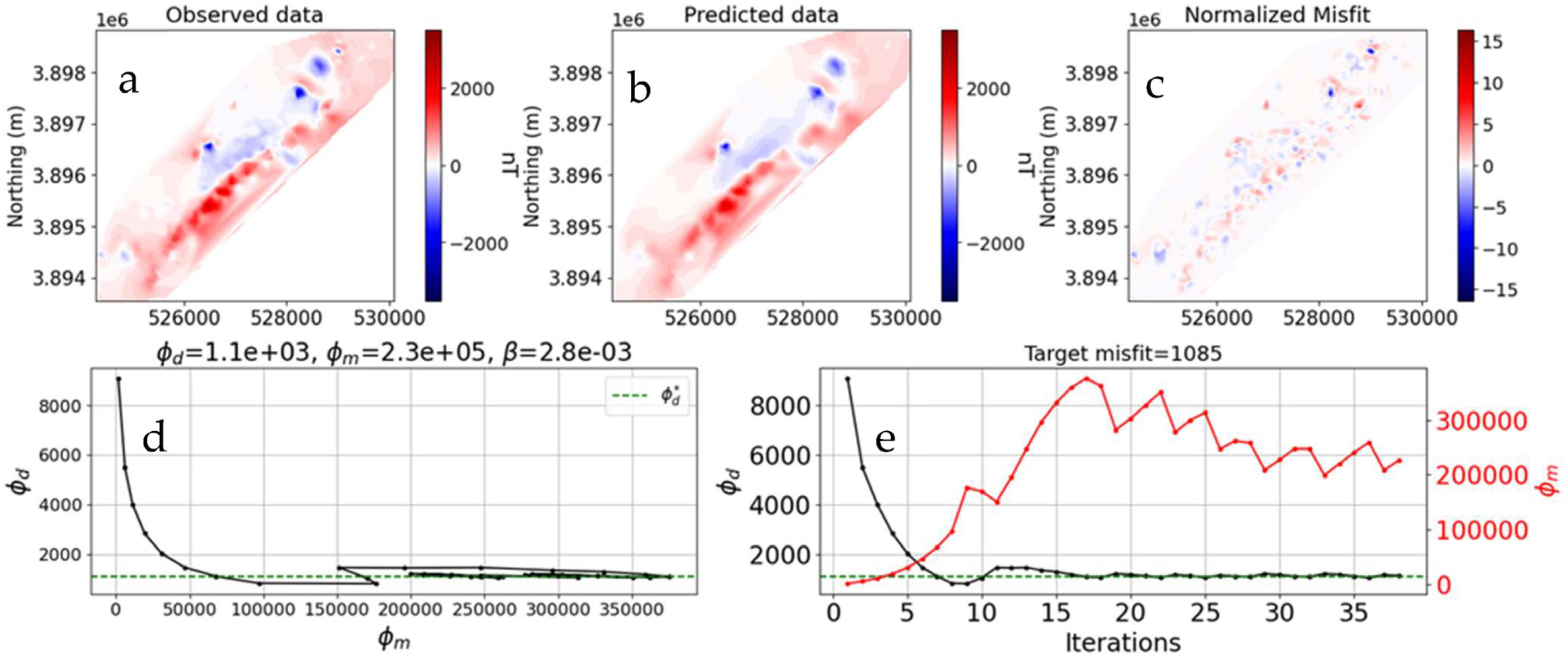
5. Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion
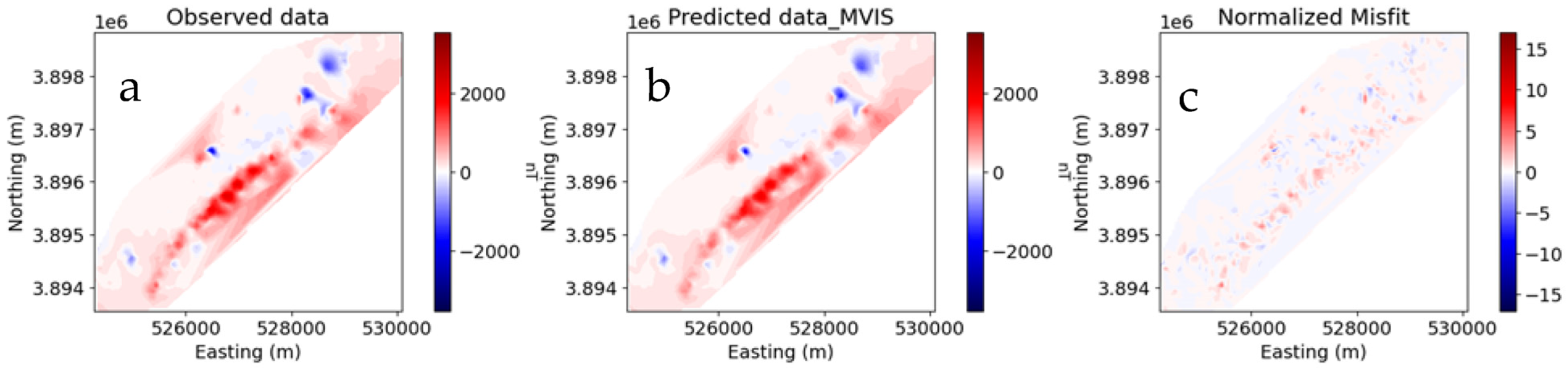
6. Magnetic Vector Inversion (in Cartesian and Spherical Formula)
7. Model Setup and Inversion
8. Magnetic Susceptibility Model
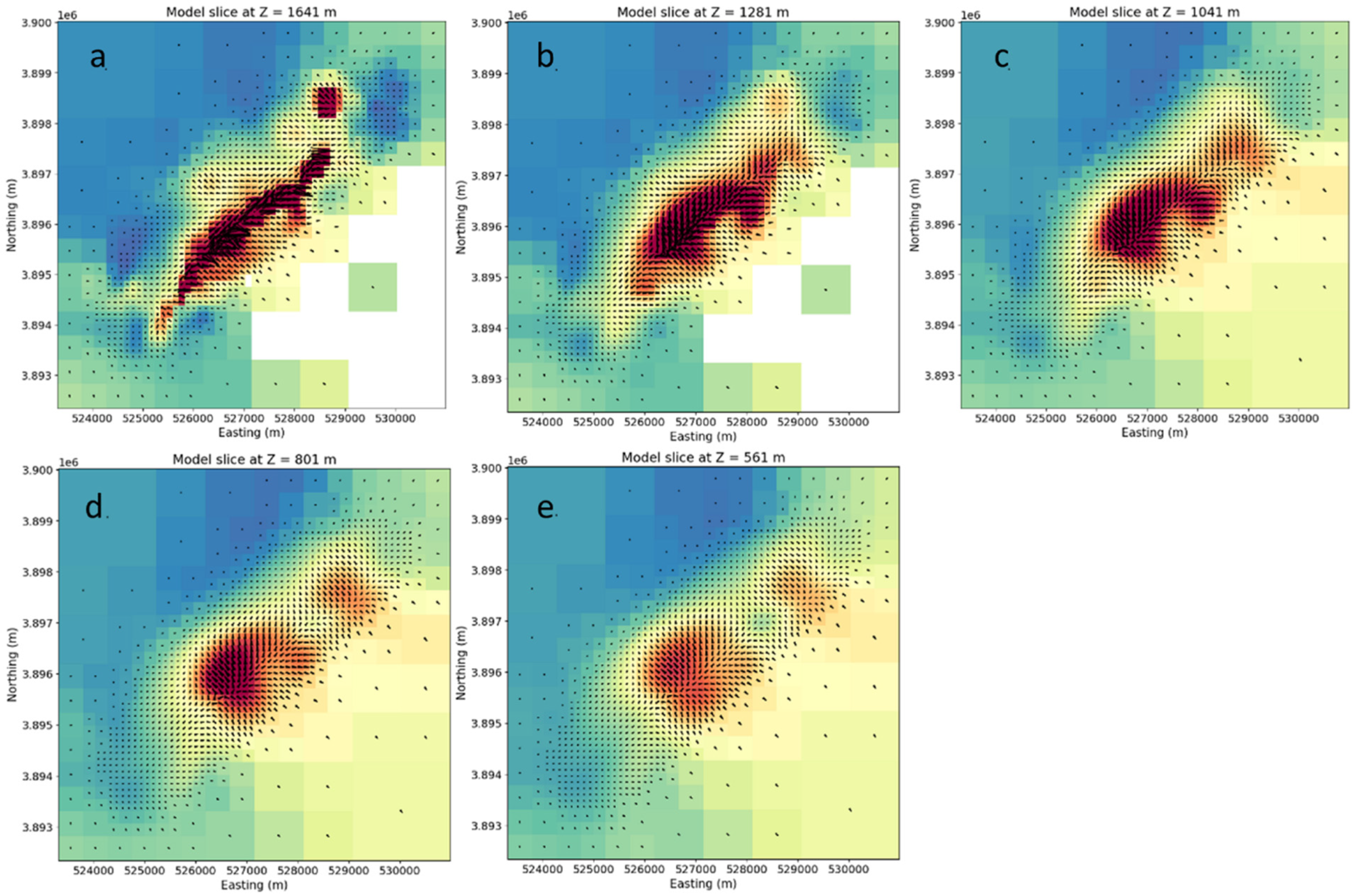
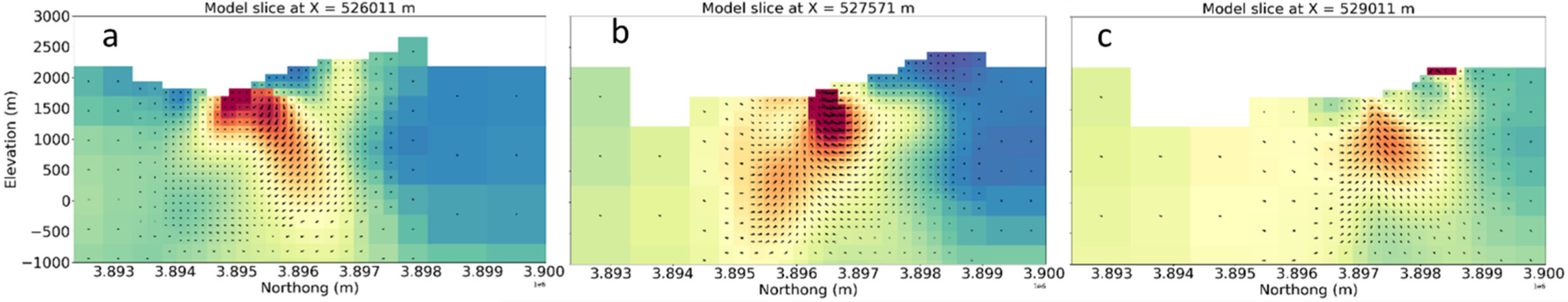
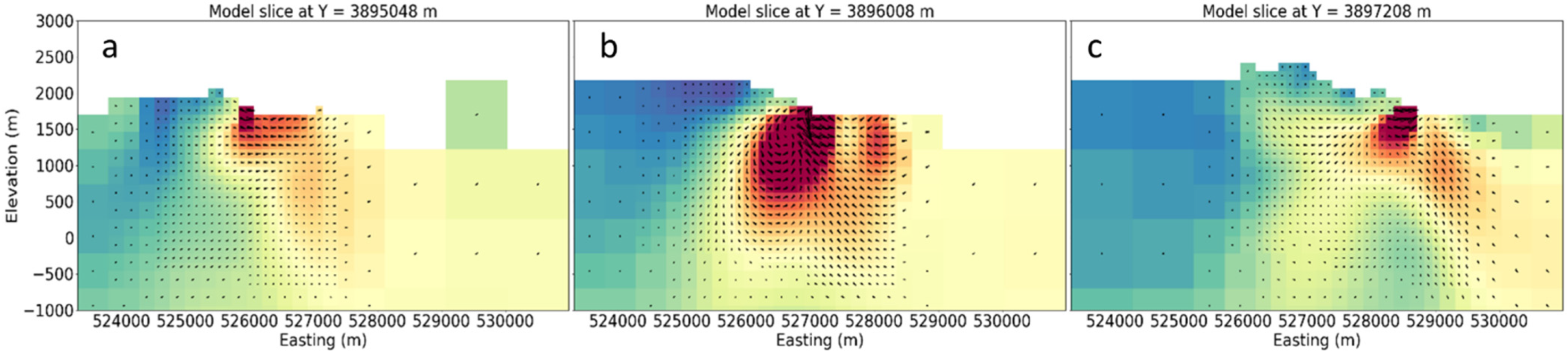
9. Magnetization Vector Model
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, W.C.; Piper, D.Z. Rapidly-formed ferromanganese deposit from the eastern Pacific Hess Deep. Nature 1977, 265, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, E.; González, F.; Somoza, L.; Lunar, R.; Ortega, L.; Vázquez, J.; Reyes, J.; Bellido, E. Strategic and rare elements in Cretaceous-Cenozoic cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from seamounts in the Canary Island Seamount Province (northeastern tropical Atlantic). Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 87, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusty, P.A.J.; Murton, B.J. Deep-Ocean Mineral Deposits: Metal Resources and Windows into Earth Processes. Elements 2018, 14, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q. An eco-friendly and efficient process of low potential thiosulfate leaching-resin adsorption recovery for extracting gold from a roasted gold concentrate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive recoveries of selenium, copper, gold, silver and lead from a copper anode slime with a clean and economical hydrometallurgical process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, B.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, F.; Jiang, T.; Xu, B. Selective Flotation of Elemental Sulfur from Pressure Acid Leaching Residue of Zinc Sulfide. Minerals 2021, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Duan, S.; Zhu, Y. Application of Integrated Geophysical Technologies to the Exploration of Polymetal Deposits: Case study in Fufang, Jiangxi, China. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2019, 12, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharef, M.H.; Eldosouky, A.M.; Zamzam, S.; Boubaya, D. Polymetallic mineralization prospectivity modelling using mul-ti-geospatial data in logistic regression: The Diapiric Zone, Northeastern Algeria. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 15392–15427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zuo, R. Mapping geochemical anomalies related to Fe–polymetallic mineralization using the maximum margin metric learning method. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, B.; Yu, H.; Burnett, W.C.; Li, S.; Lian, E.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Chen, G.; Duan, X.; et al. Exploration of Deep Ocean Ferromanganese Nodule Fields Using Radon as a Tracer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.-W.; Li, T.-D.; Lü, Q.-T.; Gao, R.; Yang, J.-S.; Chen, X.-H.; Wei, W.-B.; Zhou, Q. Progress in deep lithospheric exploration of the continental China: A review of the SinoProbe. Tectonophysics 2013, 606, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, S.; Wei, W.; Ye, G.; Jing, J.; Dong, H.; Xie, C. Lithospheric electrical structure of South China imaged by magnetotelluric data and its tectonic implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 98, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Gao, R. Potential-field evidence for the tectonic boundaries of the central and western Jiangnan belt in South China. Precambrian Res. 2018, 309, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Cai, X.; Liang, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B. Application of 2D magnetotelluric methods in a geological complex area, Xinjiang, China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. The Study on Application of the Audio Frequency Magnetotelluric Method in Azelik Area of Niger. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2014, 88, 1428–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdows, M.S.; Ramazi, H.R. Application of the singularity mapping technique to identify local anomalies by polarization data (a case study: Hamyj Copper Deposit, Iran). Acta Geod. Geophys. 2015, 50, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Waheidi, M.M.; Ghrefat, H.A.; Batayneh, A.; Nazzal, Y.H.; Zumlot, T. Integrated application of geoelectrical techniques for structural investigations: Case study of Wadi Marsad Graben. Jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, R.J. Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, B.; Purucker, M.E.; Mandea, M. Crustal magnetic field of Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2004, 109, E02008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.M.; Bloxham, J. The construction of sparse models of Mars’s crustal magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2017, 122, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, N.; Ebbing, J. Basement characterization and crustal structure beneath the Arabia–Eurasia collision (Iran): A combined gravity and magnetic study. Tectonophysics 2018, 731–732, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouligand, C.; Tivey, M.A.; Finn, C.A.; Morgan, L.A.; Shanks, W.C.P.; Sohn, R.A. Geological and Thermal Control of the Hydrothermal System in Northern Yellowstone Lake: Inferences from High-Resolution Magnetic Surveys. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2020JB019743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão-Santos, M.; Li, Y.; Moraes, R. Application of 3D magnetic amplitude inversion to iron oxide-copper-gold deposits at low magnetic latitudes: A case study from Carajás Mineral Province, Brazil. Geophysics 2015, 80, B13–B22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, S.M.; Pedersen, L.B.; Kamm, J.; Kalscheuer, T. A new reference model for 3D inversion of airborne magnetic data in hilly terrain—A case study from northern Sweden. Geophysics 2018, 83, B1–B12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Pratt, D.A. Geophysical Inversion for Mineral Exploration: A Decade of Progress in Theory and Practice. Proc. Explor. 2007, 7, 61–95. [Google Scholar]
- Rezayee, M.H.; Khalaj, M.; Mizunaga, H. Structural analysis and susceptibility inversion based on ground magnetic data to map the chromite mineral resources: A case study of the Koh Safi Chromite Ore Deposit, Parwan, Afghanistan. Geosci. Lett. 2023, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmyriov, V.M.; Kafarskiy, A.K.; Abdullah, D.; Dronov, V.I.; Stazhilo-Alekseev, K.F. Tectonic Zoning of Afghanistan; Geological Survey of India: Calcutta, India, 1982; Volume 41, pp. 317–329. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=9419101 (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Shadchinev, A.S.; Khandozhko, N.V.; Drannikov, V.S.; Matin, S.J.; Salikhi, Z.; Gemat, A.K. Geological Structure and Minerals of the Basins of the Ghorband, Salang, and Panjsher Rivers. Unpublished Map for the Afghan Ministry of Mines and Industries, Technoexport, USSR, Contract No. 18455/17500, 2 Maps, Scale 1:100,000 and 1:2,000. 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Samarin, Y.S.; Akkermantsev, S.M. R1208: Report on the Results of Prospecting Exploration Activities at the Panjsher Emerald Deposit in 1975–1976; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.H.; Chmyriov, V.M.; Stazhilo-Alekseev, K.F.; Dronov, V.I.; Gannon, P.J.; Lubemov, B.K.; Kafarskiy, A.K.; Mal-yarov, E.P. Mineral Resources of Afghanistan, 2nd ed.; Afghanistan Geological Survey: Kabul, Afghanistan, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Snee, L.W.; Lindsay, C.R.; Bohannon, R.G.; Turner, K.J.; Wasay, A.; Omar, M.; Seal, R.R.I.I.; Wilds, S.R.; Wilsono, E.M. Emerald Deposits of the Panjsher Valley, Afghanistan—Preliminary Assessment of Geologic Setting and Origin of the Deposits. 2005. Available online: https://afghanistan.cr.usgs.gov/information-package- (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Stettner, W.R.; Koroleva, N.E.; Masonic, L.M.; Shields, D.A. Geologic and Mineral Map (Modified from the 1975 Original Map Compilation by A.S. Shadchinev and Others) and Hyperspectral Surface Materials Maps of the Ghorband, Salang, and Panjsher River Basins; Kapisa, Panjsher, Parwan, and Baghlan Provinces, Afghanistan; Open-File Report 2020–1101, 2 Sheets, Scale 1:100,000; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A. Detection of forests using mid-infrared reflectance: An application to the Amazon basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2785–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, R.K. Aster perspective on volcanic eruption. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, M.J. Remote sensing of urban heat islands by day and night. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 977–984. [Google Scholar]
- King, T.V.V.; Hoefen, T.M.; Kokaly, R.F.; Livo, K.E.; Giles, S.A.; Johnson, M.R. Hyperspectral Surface Materials Map of Quadrangle 3770, Faizabad (217) and Parkhaw (218) Quadrangles, Afghanistan, Showing Iron-Bearing Minerals and Other Materials; Open-File Report 2013–1219–B, 1 Sheet, Scale 1:250,000; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, V.; Naudy, H. Numerical calculation of the formula of reduction to the magnetic pole. Geophysics 1964, 29, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedi, M.; Rapolla, A.; Russo, G. Upward continuation of scattered potential field data. Geophysics 1999, 64, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, H.; Alemu, A.; Fisseha, S. Upward continuation and polynomial trend analysis as a gravity data decomposition, case study at Ziway-Shala basin, central Main Ethiopian rift. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roest, W.R.; Verhoef, J.; Pilkington, M. Magnetic interpretation using the 3-D analytic signal. Geophysics 1992, 57, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S. An analytic signal approach to the interpretation of total field magnetic anomalies. Geophys. Prospect. 1994, 42, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Li, L. Edge detection in potential fields with the normalized total horizontal derivative. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 41, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockett, R.; Kang, S.; Heagy, L.J.; Pidlisecky, A.; Oldenburg, D.W. SimPEG: An open-source framework for simulation and gradient based parameter estimation in geophysical applications. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 85, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Oldenburg, D.W. 3-D inversion of magnetic data. Geophysics 1996, 61, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.J. Iteratively Reweighted Least Squares for Maximum Likelihood Estimation, and Some Robust and Resistant Alternatives. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1984, 46, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I.; DeVore, R.; Fornasier, M.; Güntürk, C.S. Iteratively reweighted least squares minimization for sparse recovery. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2009, 63, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, D.; Heagy, L.J.; Oldenburg, D.W. Sparse magnetic vector inversion in spherical coordinates. Geophysics 2020, 85, J33–J49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelièvre, P.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. A 3D total magnetization inversion applicable when significant, complicated remanence is present. Geophysics 2009, 74, L21–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezayee, M.H.; Akbar, A.Q.; Poyesh, T.; Rawnaq, E.; Samim, K.M.; Mizunaga, H. 3D Geophysical Modeling Based on Multi-Scale Edge Detection, Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion, and Magnetization Vector Inversion in Panjshir, Afghanistan to Detect Probabilistic Fe-Polymetallic Bearing Zone. Geosciences 2023, 13, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13120376
Rezayee MH, Akbar AQ, Poyesh T, Rawnaq E, Samim KM, Mizunaga H. 3D Geophysical Modeling Based on Multi-Scale Edge Detection, Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion, and Magnetization Vector Inversion in Panjshir, Afghanistan to Detect Probabilistic Fe-Polymetallic Bearing Zone. Geosciences. 2023; 13(12):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13120376
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezayee, Mohammad Hakim, Ahamd Qasim Akbar, Torabaz Poyesh, Ezatullah Rawnaq, Khair Mohammad Samim, and Hideki Mizunaga. 2023. "3D Geophysical Modeling Based on Multi-Scale Edge Detection, Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion, and Magnetization Vector Inversion in Panjshir, Afghanistan to Detect Probabilistic Fe-Polymetallic Bearing Zone" Geosciences 13, no. 12: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13120376
APA StyleRezayee, M. H., Akbar, A. Q., Poyesh, T., Rawnaq, E., Samim, K. M., & Mizunaga, H. (2023). 3D Geophysical Modeling Based on Multi-Scale Edge Detection, Magnetic Susceptibility Inversion, and Magnetization Vector Inversion in Panjshir, Afghanistan to Detect Probabilistic Fe-Polymetallic Bearing Zone. Geosciences, 13(12), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences13120376







