Abstract
The estimation of urban irrigation water requirements has often been approached from an agricultural perspective. This approach is flawed, as the intention of estimating agricultural water is to optimize yield. Recent studies have reported that urban irrigation systems waste about 34% of water, an alarming number for arid cities. The intention for urban irrigation is complex and dependent on the microclimates created by the development of the landscape. In this paper, we investigate the role of the urban landscape on the irrigation water requirements in arid cities. The role of the landscape in determining the irrigation water requirements is examined through the changes in surface-heat energy exchanges. The effects of landscapes are examined through land use change, buildings’ geometry and orientation, and vegetation types. The irrigation water requirement is assessed as the function of urban evapotranspiration and irrigation efficiency. The development of land use characteristics includes the transition from undeveloped (natural) surfaces to residential, commercial, road surfaces, or vegetated surfaces. The orientation and geometry of the streets are assessed by changes in sky view factor values due to building geometry. Three landscapes varying in vegetation type and water use are investigated. The study focuses on understanding the heat exchanges and their effects on irrigation water requirements in arid climates. Two major cities were studied: Las Vegas Valley and Phoenix metropolitan. The study concludes that the development of hardscapes, including commercial and road infrastructures, increases the overall surface temperature by 2 °C per unit change in albedo, thereby increasing evapotranspiration and urban irrigation water requirement. In addition, landscape diversity also plays a crucial role in changing the irrigation water requirement. This study highlights the importance of making development decisions in urban settings and their effects on water resources. It also contributes by providing the major factors changing the urban irrigation requirement. The study can help urban water managers and climatologists to develop improved urban irrigation models.
1. Introduction
Water is a scarce commodity in large cities in the Western United States [1,2]. With the recently increasing influx of new residents, new ways are needed to meet the demand for water across drought-affected states [3,4]. For example, while the majority of indoor water used in the Las Vegas Valley is already being recycled, most consumptive water losses in arid cities are actually from water uses outside the house, namely, the irrigation of lawns and public green spaces [5]. Local authorities have no choice but to remove lawns and high-water-use plant species. Plants and lawns play a vital role as natural drainage water filters and natural buffers to trap erosion. Replacing vegetated areas with impervious surfaces can increase flash flood impacts and urban heat-trapping, potentially causing devastating effects on outdoor activities and mental health in adults and children [6].
The Southwestern US is facing extreme drought mainly because of dwindling water resources. Since 2010, the Colorado River has been experiencing a prolonged drought, the most severe in recorded history, with the reservoir’s water storage being the lowest in over half a century. Recently, major metropolitan arid cities have been forced to reduce their water consumption in response to the drought emergency plan. Outdoor residential water consumption is unpredictable and contributes to significant water wastage [7]. In response, the water managers have decided to reduce water use by replacing high-water-use landscapes with low-water-use plants in residential lawns. The decision is helping reduce outdoor residential water consumption and is widely known as a rebate program [8].
Replacing high-water-use landscapes with desert landscapes might benefit water consumption, but the tradeoff and long-term effects on sustainability are inconclusive [9]. Additionally, recent studies have been skeptical about low-water-use landscapes mainly because of the low contribution to outdoor thermal comfort. This is primarily because of the low evapotranspiration (ET) rates induced by the low-water-use plants, resulting in high air temperatures [10]. Researchers predict that in the absence of vegetation, the urban heat island effects in arid cities will be exacerbated, adversely affecting socioeconomic conditions by discouraging outdoor activities in summer [11]. In turn, these unintended consequences may affect residents’ excessive heat-related illnesses, mental health, and future migration rates to sunbelt cities. These factors call into question the long-term sustainability of decisions regarding the rebate program.
Another sustainable solution to reducing urban outdoor water consumption is to optimize the irrigation water used for vegetated landscapes. The optimization of irrigation water use requires a deeper understanding of urban irrigation models, which must be added to the literature, mainly because the science of the irrigation water requirements leading to irrigation schedules has been borrowed from the agricultural field, creating biases in modeling approaches. The agricultural models are designed with the assumption that the vegetated surfaces would have an open sky. Therefore, the thermal effects of the surrounding features, often addressed as spatial heterogeneity, are missing. The spatial heterogeneity emerges from the types of structures, their orientations, and their net effects on both heat and water footprints. The lack of access to high-resolution data hampers further progress in optimizing water use in the US’s southwest urban areas, such as the Las Vegas Valley (LVV) [10,12]. Spatial heterogeneity plays a major role in urban energy balance. It specifically changes the longwave emission of an urban area that increases the surface temperature, causing an urban heat island effect and increased ET rates [13,14]. This effect is essentially the opposite in arid and semiarid regions where the urban surfaces reduce the surface temperature and irrigation demand [6]. However, a study by Shashua-Bar and Hoffman (2002) [15] reports that a city’s cooling effect is offset by heating the walls and pavements in case they are closely packed. Consequently, more research is required to understand the role of urban surfaces in changing thermal comfort (cooling effect) and evaporative demand.
This study addresses these limitations by illustrating the effects of urban landscapes on urban irrigation water requirements. Urban landscapes include, but are not limited to, residential, commercial, road infrastructure, and vegetation land use. The residential land use includes front and back yards, living space, swimming pools, and driveways. The commercial land use includes airports, high-rise buildings, and parking lots. The road infrastructure connects commercial and residential land use through asphalt (mostly main streets) and concrete (in the case of highways with high-speed vehicles). The vegetated land use involves public spaces and golf courses.
The study’s objective is to investigate the role of urban landscapes on irrigation water requirements. The study hypothesizes that the development and diversity of the landscape change the irrigation water rates. Consequently, it addresses three main questions:
- How does the land use change affect the urban irrigation water requirement?
- What is the role of urban geometry in altering the urban irrigation water requirement?
- How much does the type of landscape affect the urban irrigation water requirement?
The urban landscapes are analyzed regarding land use change, building geometry, and vegetation type. The study assumes that the irrigation water requirement is a function of evapotranspiration (ET) rates. The ET rates are assessed by understanding the changes in the surface energy budget due to the presence of different landscapes in an urban area.
2. Methodology
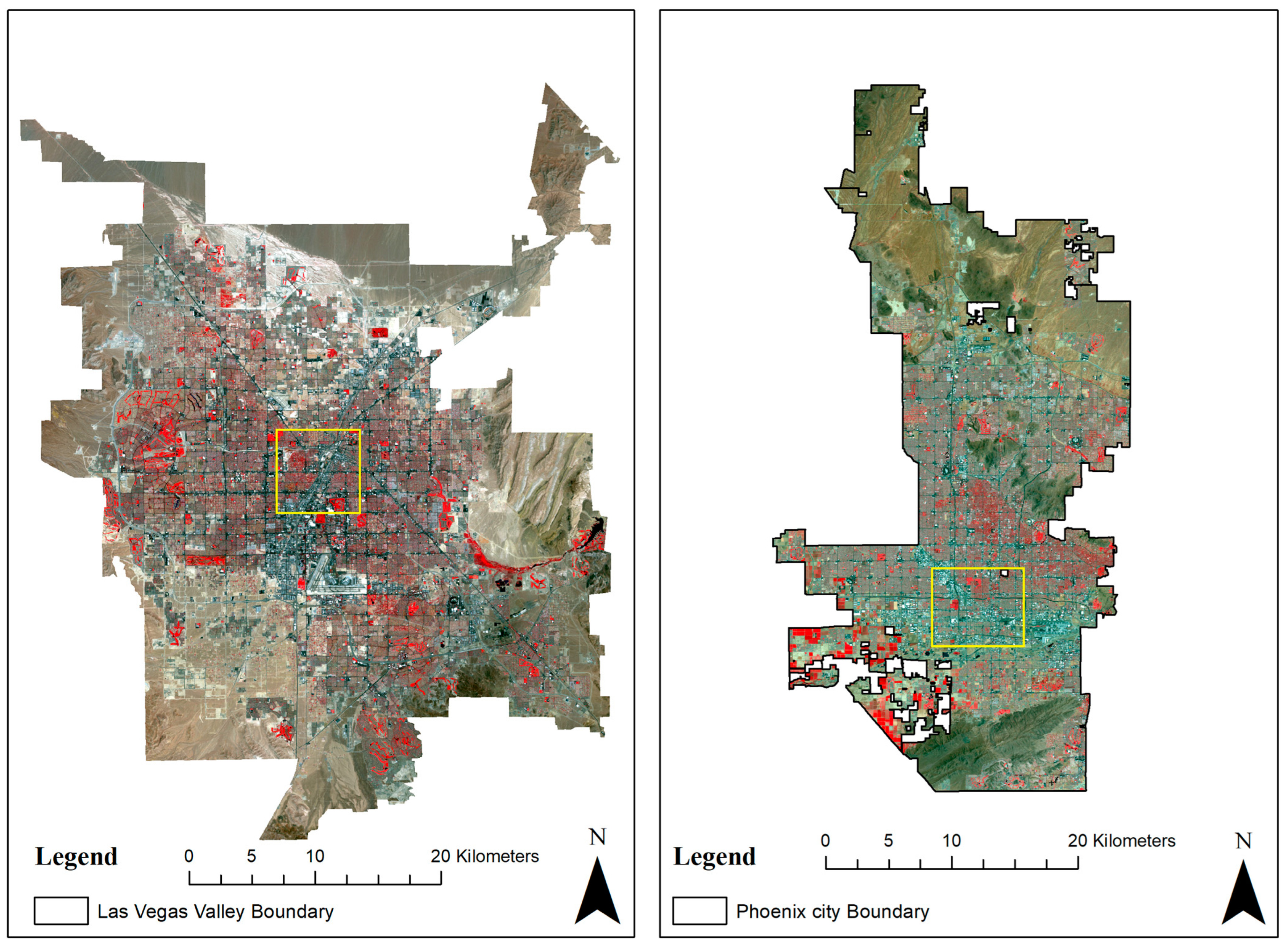
A variety of datasets has been used in this study, including the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and Thematic Mapper (TM) derived datasets with less than 5% cloud cover, National Aerial Imagery Program (NAIP) imagery, and the LiDAR dataset. The NAIP, TM, and OLI datasets were used to analyze the land cover change. In contrast, the LiDAR dataset was used to understand the shade dynamics and building geometry and their effects on the surface energy budget. The dataset was used to estimate the surface energy budget. Two arid urban regions, Las Vegas Valley and a patch of Phoenix, are used as study areas, as shown in Figure 1. Downtown Phoenix and the Las Vegas Valley residential neighborhood were considered for further analysis; the yellow boxes in Figure 1 highlight the downtown area. The two study areas were chosen because of their arid climate. In addition, the rainfall rates are low, making the irrigation water requirement a function of evapotranspiration and irrigation efficiency.
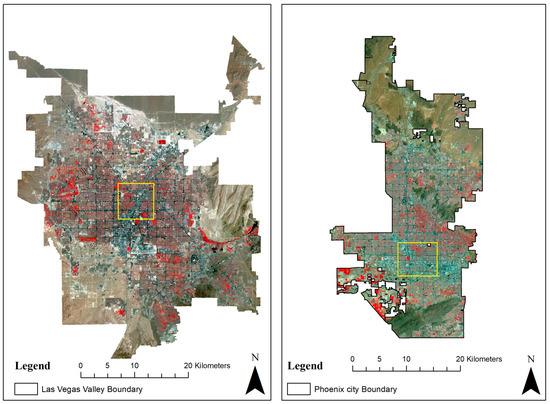
Figure 1.
Study area map retrieved from the OLI-sensor dataset (July 2017) of Las Vegas Valley, NV, and Phoenix, AZ; yellow squares show the focused area for the analysis considered.
The key variables investigated are the surface albedo, land surface temperature (LST), sky view factor (SVF), building height, and available energy (difference of net radiation (Rn) and soil heat flux (G)). The surface albedo illustrates the absorption capacity of the surface, while the LST predicts the outdoor thermal comforts. The SVF variable illustrates the amount of incident radiation being covered due to built structures inducing shade, while the building height demonstrates the height of the building inducing the shade. The available energy is the residual energy of net radiation and soil heat flux density, and it contributes to warming the atmosphere and increasing the evaporative demand and irrigation water requirement.
The study employed 27 (1993–2017) years of OLI- and TM-derived datasets to observe the land use change and estimate the difference in land use change. The OLI-derived dataset was retrieved at 5% cloud cover. The preprocessing of the dataset involved dark pixel subtraction and atmospheric attenuation. The surface albedo was calculated using the visible and shortwave bands, including red, green, blue, near-infrared (NIR), and shortwave infrared (SWIR1-2) bands in the OLI dataset. The algorithm used is given as follows:
where α is the surface albedo; p denotes the weight of each spectral band and is calculated as the function of solar constant and radiance associated with each band; r shows the reflectance of each band.
The surface temperature was estimated using the red, NIR, and thermal infrared (TIR) bands in the OLI dataset. The major computational steps involved in the LST estimation are as follows:
where ToA is the top of atmosphere and is calculated using the calibration constants in OLI sensor’s metadata file; K1 and K2 are the brightness constants of TIR; L(6,10) is the radiance of the TIR sensor; λ is the central thermal band wavelength, i.e., 11.45 mm; rc and ε are the surface emissivity estimated using the Giannini et al. (2015) [16] algorithm. A detailed methodology for calculating the surface albedo and LST is available [17].
The change detection was conducted by considering the initial (1993–1995) and final (2013–2017) 5-year datasets and taking the average of the LST and surface albedo for the summer (May–August) season. The reason for averaging the scenes was to avoid any atmospheric attenuation. In addition, the study calculated the surface albedo and LST for each scene and computed the change in the LST and surface albedo. To understand the changes in temperature because of urbanization, the imagery depicting the change in LST was divided by the surface albedo change imagery. This provided the changes in the temperature per unit albedo change.
To understand the effects of building geometry, the study analyzed 5-year (2013–2018) data of OLI-derived data for the LST and albedo of Phoenix. It used LiDAR data to calculate building geometry. LiDAR delivers densely spaced georeferenced point data based on the returns of the pulses per second. The LiDAR data were used to estimate the sky view factor (SVF), a function of the digital surface model (DSM). The DSM was retrieved by extracting a digital terrain model and a digital elevation model based on the returns of the pulses and merging the two models. SVF was estimated using the Bohner and Antonic model, a function of DSM and view factors [18]. The detailed computational steps for the estimation are present in Saher et al. (2021) [19]. The images were averaged over and acquired for the summer period. They were then cropped to show the different urban landscapes.
The effects of vegetation type on irrigation water requirement were assessed by comparing the two types of lawns typically used in arid regions, including mesic and xeric landscapes. The mesic landscape refers to tree-turf landscape and requires a sprinkler system for irrigation. The xeric landscape is a desert-friendly landscape; a drip system is used for the irrigation. The assessment was conducted using the water meter data provided by the Las Vegas Valley District. The meter data were aggregated; therefore, the study used the minimum average month method to segregate the indoor and outdoor water data. The details of the method are present in Mini et al. (2014) [7]. The irrigation water requirement was estimated by deducting the swimming pool water from the outdoor water use.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Land Use Change and Its Impacts on Irrigation Water Requirements
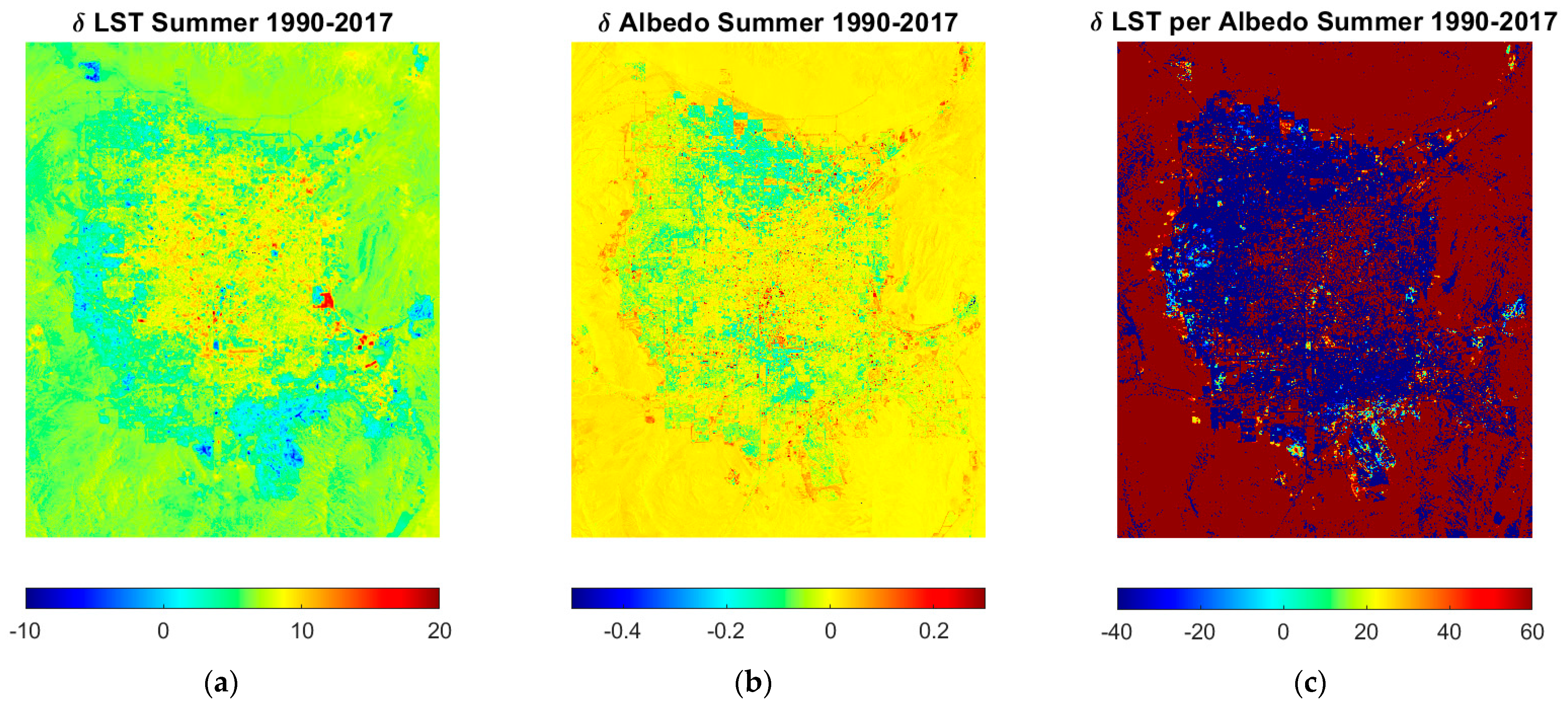
The land cover type is an essential factor that changes the relationship between surface temperature and surface albedo (Vahmani and Hogue, 2015) [20]. Figure 2 shows the summer season’s changes in LST (0–10 °C) and albedo between 1990 and 2017 for the summer season. An increased LST was observed at the city’s outskirts, while albedo increased from the downtown’s value (0–0.2). This phenomenon is possible because of the development of new houses and commercial areas, which reduced the temperature to 10 °C. The temperature changes are magnified at places with vegetated surfaces. The LST per unit change, as shown in Figure 2c, varied between 40 and 60 °C; the positive number indicates an increase in the temperature per unit change in albedo, while the negative values show a decrease in the temperature per unit albedo. The development in the valley shows a decrease in the LST ranging between 20 and 40 °C, while the city’s center, with the development of asphalt pavements, shows an increased temperature of 10–20 °C.
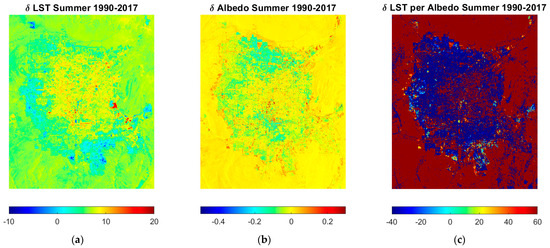
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of (a) LST and (b) albedo change acquired through OLI-derived dataset in Las Vegas Valley; the change was estimated by subtracting a 5-year underdeveloped (1990–1995) average summer image from a developed (2012–2017) summer image; (c) the changes in LST per unit albedo is acquired by dividing (a) by (b).
The interaction of residential surfaces with the atmosphere changes the surfaces’ microclimate effects. For instance, a single-story residential building made of stucco has an albedo of 0.5, with an average daytime LST value of 35 °C. In contrast, the same building with a brick roof has an albedo of 0.4, with an average LST value of 32 °C. In addition, the proximity of the surface to the vegetation patch, such as the front and back lawns, also changes the surface temperature because of the humidity and ET rates from the vegetation. Similarly, the pavements and walkways surrounded by the residential building add to the surface temperature, while the swimming pools or fountains reduce the surface temperature. The overall effects create discrepancies in the available and sensible heat flux, resulting in changes in ET rates since, in arid regions, the effective precipitation is minimal. Therefore, the ET rates are directly proportional to the irrigation water requirements of the landscapes.
In addition, the commercial surfaces near the vegetation also induce a similar effect. In arid regions, the distinct footprint of a concrete roof, asphalt-coated roof, and white-coated roof creates various temperature profiles. For instance, the white roof has an average surface albedo of 0.7–0.9, depending on the aging period; a fresh coat of white color has an albedo of 0.9, while approximately a year-old white coating has a similar albedo of natural soil, i.e., 0.7. This changes the absorption capacity of the surface. Typically, the relationship between surface albedo and surface temperature is inverse; the higher the albedo, the lower the surface temperature. Therefore, the increased surface temperature can be attributed to the decreased surface albedo due to asphalt and concrete roofs and aged white roofs. This contributes positively to sensible heat flux and the latent heat of evaporation, increasing the overall evaporative demand of the landscape.
The asphalt surfaces have long been the main contributor to increasing surface temperature, mainly due to the fact that their low albedo values inducing a high heat absorption capacity. The absorption of heat increases the surface temperature. The relationship between the surface and air temperature in arid regions is linear, with an average of 5–10 degrees difference. Air temperature plays a crucial role in ET rates. Air temperature and ET have a strong relationship in arid and semiarid regions, especially in summer (Salvador et al., 2011) [21]. In subtropical areas, the relationship weakens due to air advection. Vahmani and Hogue (2015) [20] determined the urban ET rates in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The study reported that the ET rates vary by 23 to 50% due to variations in air temperature. The climate of the regions played a key role in the air temperature variations. Inland areas, such as Solano, San Joaquin, and Stanislaus, with high wind speeds, showed a weak relationship between air temperature and ET rates. Lowry et al. (2011) [22] investigated the current and future irrigation water demand of Salt Lake County. The study reported that the climate factors, mainly air temperature and wind speed, were the main contributor to increasing the evaporative water demand [23]. Litvak et al. (2012) [24] determined the ET rates of trees and ground cover in the Los Angeles Metropolitan area. The study reported that the ET rates of lawns under trees were less than those without trees because of changes in air temperature.
The vegetated surface as an urban landscape varies from the front and backyard lawns in residential areas and open green spaces in commercial buildings to the green median in road infrastructures and long stretches of grass as golf courses. In urban areas, the vegetation is often connected with hardscapes, including walkways, pavements, and buildings. These hardscapes contribute to either shade (in the case of a building) or heated surfaces, as pavement changes the evaporative demand.
The study hypothesized that the land use change affects the urban irrigation water requirement. The development of surface, often known as land use change, alters the percentage of reflection being absorbed and reflected, causing variation in the surface albedo and surface temperature. The physical process of evapotranspiration has a strong linear relationship with surface temperature [25]. Since the commercial and road infrastructures are the main contributors to increased temperature, the vegetated surfaces in the proximity may cause high irrigation rates.
3.2. Building Geometry and Its Effects on Irrigation Water Requirements
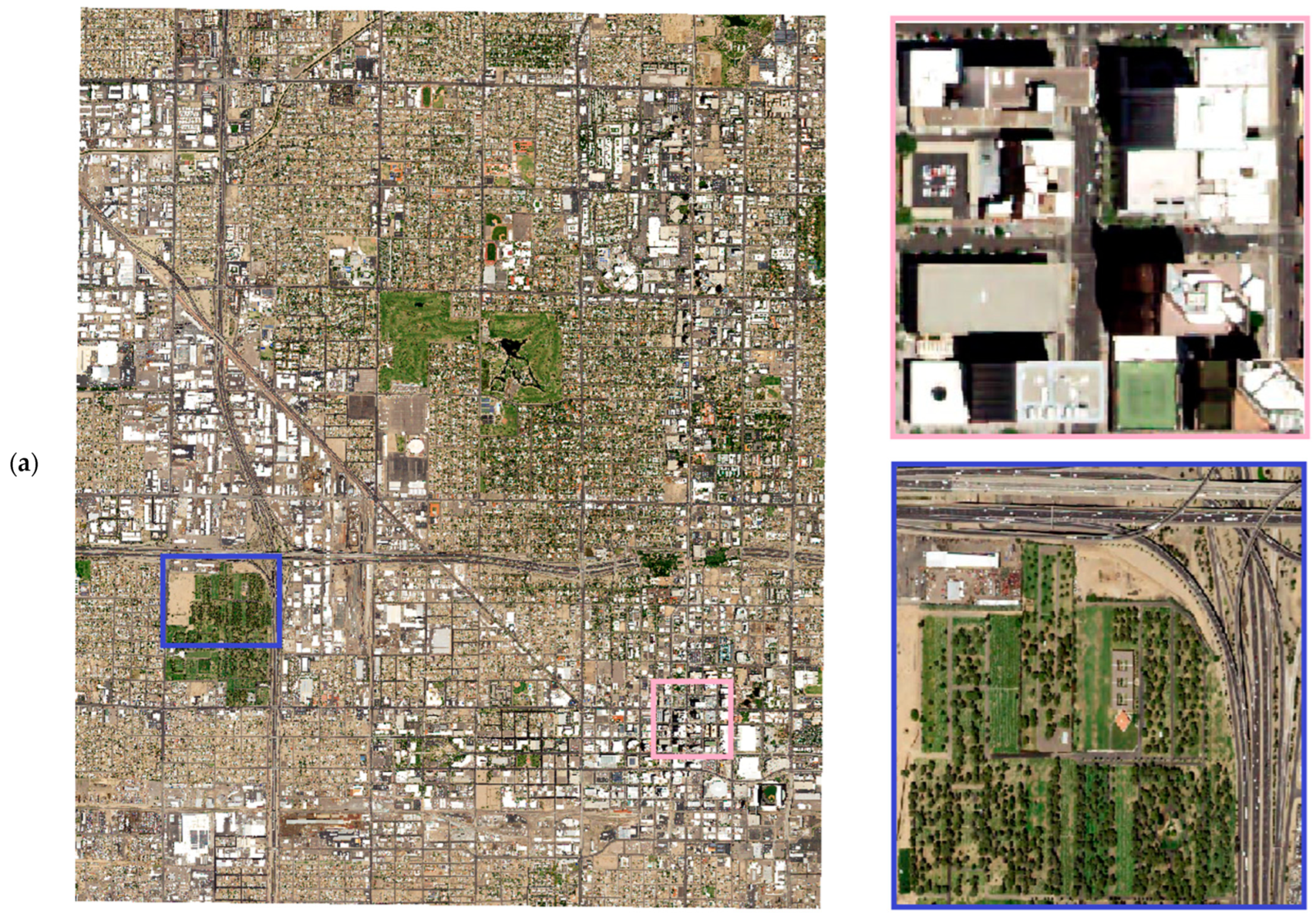
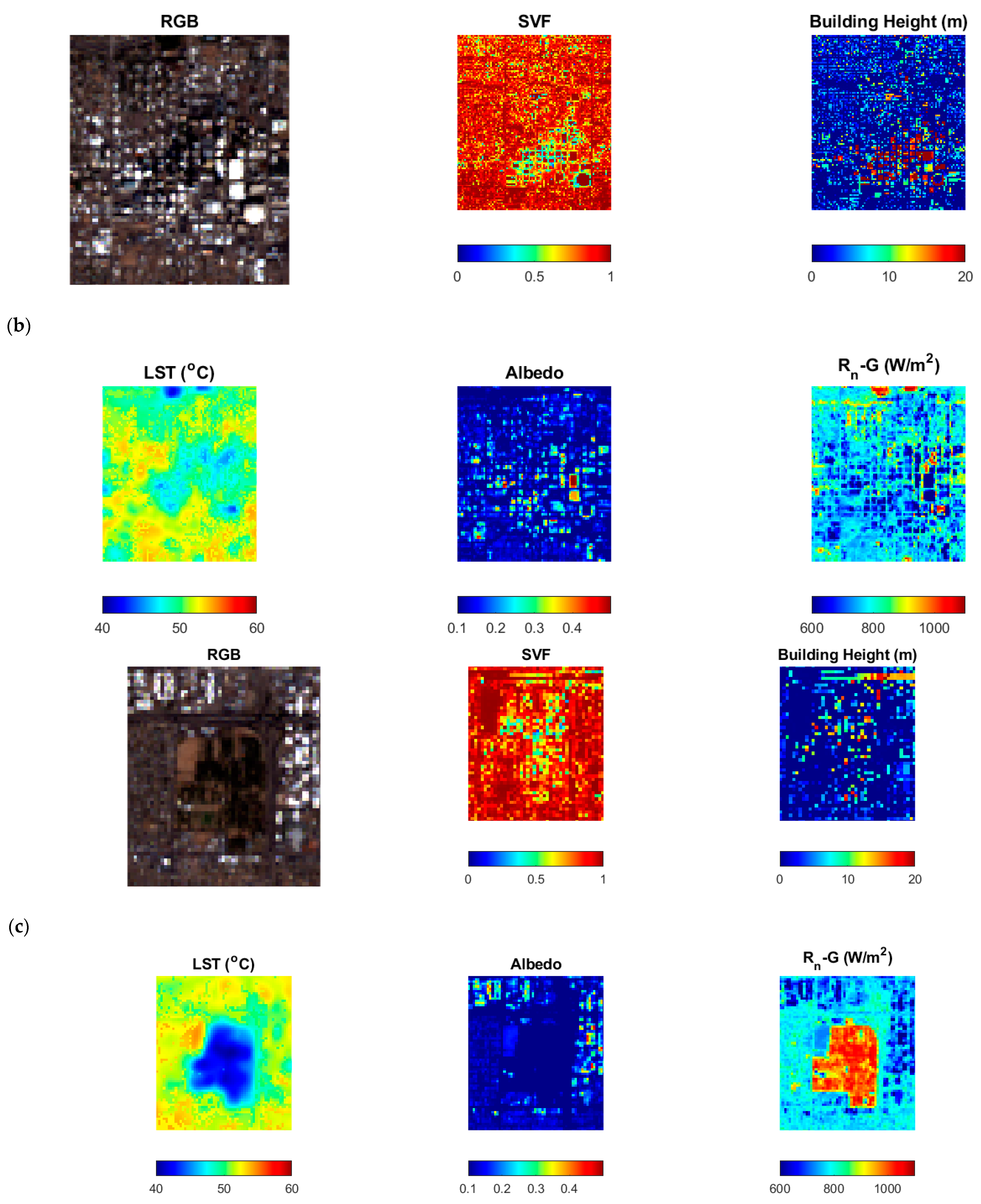
The interaction and placement of buildings create a complex land use pattern that changes the LST and ET rates. For instance, a vegetated surface close to road infrastructure has different available energy and LST profile than the vegetation around the building. Figure 3b,c show the differences in the surface energy budget of two distinct landscapes to understand the discrepancies created by landscapes. Figure 3a shows the surface energy budget of a downtown in an arid city during the daytime. The site has a mix of white roofs (surface albedo of 0.5) and brown surfaces (look for values of 0.3) with heights of buildings ranging between 5 to 20 m and an SVF value between 0.2 and 1. The areas with high SVF values are between the buildings and are also 10 °C cooler than the surrounding areas, with available energy ranging between 600–1000 watts/m2. A similar amount of cooling was noticed with a vegetated surface a few miles away from the downtown surface, as shown in Figure 3c, with trees groves scattered around the field having a height of 5–10 m and with SVF values ranging between 0.4 and 0.6; the LST was 15 °C less than the surrounding surfaces (red pixels). The surface albedo of the green surfaces is lower than the built surfaces; hence, the value ranges between 0.2–0.3 for vegetated landscapes. The available energy ranged between 900–1100 Watts/m2, relatively higher than the Figure 3b surfaces, which have a higher evaporative demand.
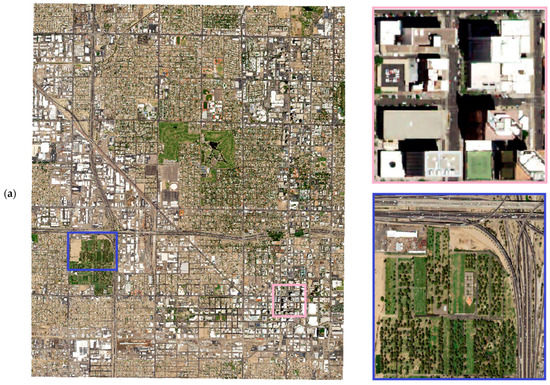
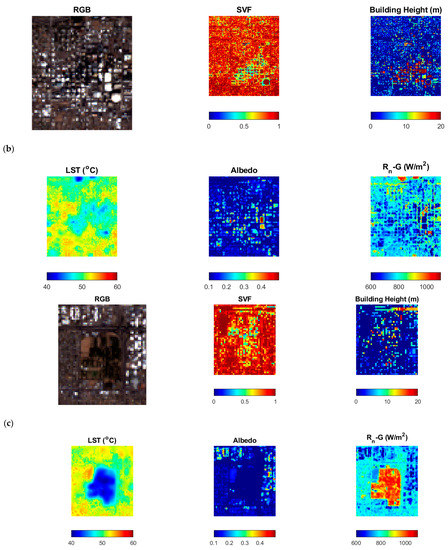
Figure 3.
(a) Aerial imagery of downtown Phoenix acquired through NAIP imagery; site delineated with blue box shows a lush tree turf landscape, and pink box shows downtown with high-rise buildings; (b) downtown site shown in (a) with a pink box with red, green, and blue image (RGB), sky view factor (SVF), heights of the buildings, LST, surface albedo, and available energy (Rn-G) values; (c) lush vegetated surface zoomed-in blue box with RGB image, SVF, heights of the buildings, LST, surface albedo, and available energy (Rn-G) values.
These discrepancies in the urban surface energy budget are one of the major causes of the biases in urban irrigation modeling. In regions where the relationship between surface temperature and ET rates is highly correlated, street orientation plays a crucial role in irrigation-water saving. Street orientation prolongs or decreases shade that changes the air and surface temperature. The orientation of streets, along with the aspect ratio of surrounding buildings, changes the surface and air temperature of the city, changing the ET rates. In broad streets, with an aspect ratio of 0.5, the increase in LST is negligible. However, in the case of narrow streets with an aspect ratio of 2 to 4, a significant change in surface temperature has been reported [26]. In subtropical latitudes, wide streets with an aspect ratio of 0.5 have high land surface temperatures. In summer, the N-S street orientation, with a high aspect ratio, has a low surface temperature compared to the E-W orientation. Similarly, the NE-SW or NW-SE orientations, with the same aspect ratio, have a relatively lower surface temperature than the N-S street orientation due to the longer shade of the walls. In the case of a hot desert climate, the N-S-oriented street increases the LST, while E-W-oriented street canyons have a negligible effect on surface temperature [27]. However, this varies based on the spatial location; a study conducted in Ghardaia, Algeria (hot and dry Saharan climate), reported that N-S-oriented streets reduce the surface temperature, while E-W street canyons increased the surface temperature [28,29].
An abundant amount of tree shade (from now on addressed as radiative shading) and turf grass changes the latent heat of a building, thus increasing ET rates. Typically, tree shade contributes to reducing the surface temperature of urban characteristics and air temperature, as shown in Figure 3c. However, these benefits have unintended consequences, including increased irrigation-water demand. In tropical regions, ET rates are susceptible to solar radiation. Qiu et al. (2017) [25] investigated the effects of urban characteristics on urban ET [29]. The study reported a strong relationship between ET rates and radiative fluxes, while a weak relationship was reported between air humidity, wind velocity, air temperature, and ET rates. Zou et al. (2019) [30] investigated the ET rates of urban hedges and their cooling effects. The study reported that the urban hedges, in summer, consume 61–70% of solar radiation, thus reducing air temperature by 1.3 °C min−1 m−2 [30]. Litvak et al. (2014) [23] estimated the ET of urban landscapes across Los Angeles and reported a value of 40% of excess irrigation rate compared to municipal recommendations on unshaded lawns [17]. The study measured and modeled the effect of tree shade on the wall surfaces of the building and reported that tree shade reduces the surface temperature of the wall by up to 9 °C and the air temperature by 1 °C. The contribution of turf grass in decreasing the wall-surface temperature is inconsiderable. An experimental study in a moderately humid climate to determine the changes between the wall surface and surface energy balance of turf grass reported a negligible effect between the wall surface temperature change in the presence of turf grass [31].
To answer the question posed earlier in Section 1 about the role of urban geometry in changing the irrigation rates, the proximity and the orientation of the buildings inducing the shade is the key driver in reducing the irrigation rates, especially for arid cities. The height of the building geometry and its orientation define the amount and frequency of the shade. These factors change the surface and air temperature of the landscape between the canyons by providing prolonged shade or increasing the temperature and irrigation rates. The shade on the landscape often reduces the temperature. The increased temperature between the canyon is often due to higher anthropogenic activities and narrower canyons with few or no trees to compensate for carbon emissions.
3.3. Landscape Diversity and Its Impacts on Irrigation Water Requirements
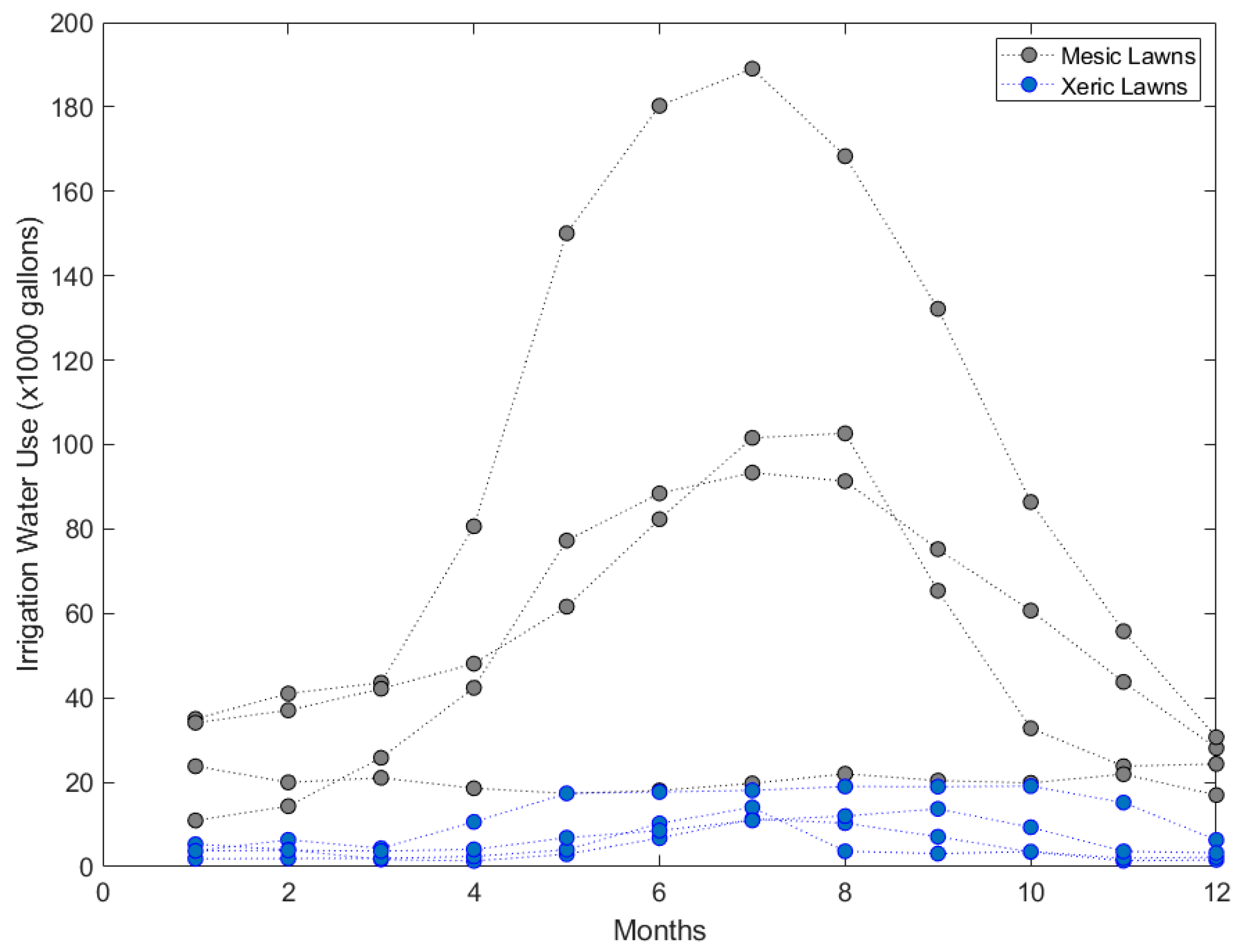
Figure 4 shows the two types of landscapes considered for the study. The mesic landscape has C3 and C4 group plants along with turf grass, while the xeric landscape includes shrubs and drought-tolerant trees. The ET rates are dependent on the leaf area of the landscape. Since the mesic landscape has a higher leaf area, the irrigation water requirement will be more than a xeric landscape. This explains the difference in irrigation water use of mesic and xeric landscapes, as shown in Figure 5. The data points are the three-year (2018–2020) averages of each house. The study involved a total of four houses with mesic and xeric landscapes. The sites were selected based on the average size of the houses, which was ~2000 sq.ft. In addition, the houses with a bell-curve pattern of water consumption were selected for the study for simplicity’s sake. The average irrigation water use of the mesic landscape was 57,090 gallons per year, while the xeric landscape average was 7272 gallons per year, which is a considerable decrease in irrigation water use. The study’s results corroborate well with the previous research. Studies have reported that native-species landscapes reduce the ET rates by half compared to turf tree landscapes, from now on addressed as mesic landscapes [32]. Al-ajlouni and Vanleeuwen (2014) [33] determined the irrigation water demand of xeriscape and mesic landscapes. The study reported that the landscapes with small crown cover and mulch had lower ET rates. Therefore, the landscape consumed 47% less irrigation water than the turf tree landscapes. In the desert environment of Las Vegas, Sovocool (2005) [8] reported that converting the traditional landscape to a xeric landscape could save up to 76% of irrigation water. In Florida, a humid subtropical climate zone (Koppen climate classification: Cfa and Cwa), Haley et al. (2005) [34] reported that the conversion of a mesic landscape to a xeric landscape saved 39% of irrigation water [8]. In Phoenix, Arizona, Volo et al. (2014) and Volo et al. (2015) [35,36] determined the response of seasonal irrigation and ET rates of xeric and mesic landscapes. The study reported that the xeric landscapes were able to withstand moisture deficiency under small, frequent irrigation events. This ultimately reduced ET rates and saved irrigation water by one-fifth of annual irrigation. However, in mesic landscapes, small water stress in plants induced a high risk of plant mortality. Consequently, seasonal irrigation as a conservation strategy was ineffective in mesic landscapes.

Figure 4.
Aerial map of the houses considered in the study area; yellow boxes show the houses considered for the analysis; the letters M and X represent mesic and xeric lawns, respectively.
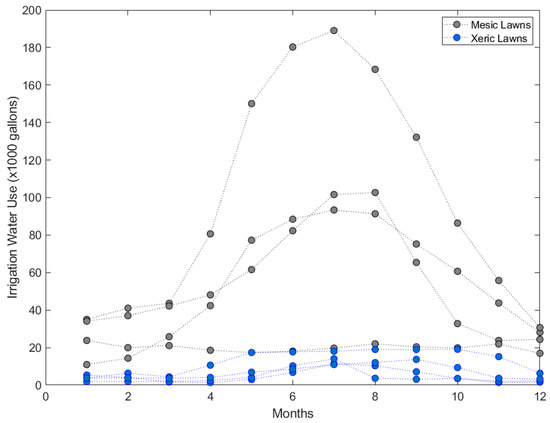
Figure 5.
Scatter plot of irrigation water use of four mesic and xeric lawns of the houses in Las Vegas Valley; each data point is a three-year average of irrigation water use provided by LVVWD.
A counter-intuitive result was reported by Manea and Leishman (2014) [37] which conducted an experiment to understand the change in the stomatal conductance of exotic and native species under elevated levels of CO2. Under elevated CO2 limits, the stomatal conductance of native grass was relatively higher than that of the exotic plants. This suggests that the exotic plants are less-influenced by extreme droughts than the C4 and native grasses under high CO2 limits.
Irrigation water use also depends on the choice of landscape and aesthetics. The two factors are highly controlled by end-users (homeowners). Figure 5 shows eight different irrigation water-use patterns through a bell-curve depicting the behavior of eight different homeowners. A few patterns (xeric landscape) show no irrigation in the winter months and early spring, while other patterns, mostly mesic landscapes, show a significant amount of irrigation. In addition, according to the Figure 5, a few houses have not followed the summer-high-winter-low pattern, which is highly dependent on the end-users. ET rates are highly correlated with irrigation rate and water availability. In addition, average household income also plays a key role in irrigating the landscape. Mini et al. (2014) [7] reported that in Los Angeles, medium-income households saved 6% of landscape irrigation water by adopting water conservation strategies voluntarily [7]. The same group saved 45% of landscape irrigation water when the mandatory water conservations were complied with. High-income households were less-responsive to water conservation practices.
Additionally, the percentage of unemployed or retired household members, education level, and personal interest in gardening also affect the water conservation strategies [38]. Hurd and White (2006) [32] conducted a survey to investigate the effects of homeowners’ awareness on landscape preference in New Mexico [33]. The study reported that 76% of homeowners in New Mexico were aware of local water issues, and 84% felt that homeowners play a crucial role in water conservation, yet 34% selected xeriscaping over a mesic landscape. The reason for low preference for xeriscaping is the shape and color of trees. Many water-conserving plants are greyish-green and columnar shaped. The investigation of homeowners’ responses to the plants’ colors and shapes has shown that homeowners preferred deep-green-colored trees over yellow-green, red, or blue trees and are more relaxed around the trees with green canopies with wide crowns [39,40,41]. This might explain the reluctance of homeowners to adopt the water-conserving plants.
The study posed the question regarding the effect of landscape type on urban irrigation water requirement. Based on the findings and the literature, the high-water-use of the landscape (typically grass) does not translate into higher cooling effects. The type of species in the landscape warrants the cooling effects. In this case, a mix of trees and shrubs warranted higher cooling effects than grass and was much more water efficient.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the effects of urban landscapes on irrigation water requirements. The study used various remote sensing datasets, including OLI, ETM+, and TM sensors; LiDAR; and NAIP imagery. The role of the landscape was investigated through the geometry and orientation of buildings, land use changes, and vegetation type.
One of the major findings is that the development of hardscapes increased the surface temperature by 2 °C per unit albedo. The study also reports that the narrow canyons induce the radiative shades, reducing the surface temperature by 5 °C. Another major finding includes that the low-water-use landscape with a mix of trees and shrubs warranted low irrigation rate and daytime cooling.
The study concludes that both LST and ET rates are sensitive to land use changes. Hence, land use change is key in defining the irrigation water requirement. The development of road and commercial infrastructure contributed to increased available energy, thereby increasing ET rates in the surroundings. In arid regions, residential development has had a dual effect; newer houses, located on the outskirts, created cooling (10 °C per unit change in albedo), while older houses contributed to 5 °C per unit change in albedo warming. The vegetation surfaces showed net-zero change in the LST with linear effects on the ET rates, and hence, on the irrigation water requirements.
The study also concluded that the building geometry and placement creates various aspect ratios and street orientations, which changes the shade profile, resulting in changes in irrigation water requirements. The shade profile was inferred using the SVF. The vegetated surfaces showed higher cooling (15 °C lower surface temperature), while the high-rise buildings induced with high values of SVF showed an LST decrease of 10 °C. In addition, the available energy of the high-albedo (white) built surfaces was relatively lower than the vegetated surface but higher than the brown roof areas; an average difference of 300 Watts/m2 was observed.
The landscape type was another key driver showing increased ET rates with an increase in leaf area index and the type of species. The mesic landscape consumed 87% more water than the xeric landscape. The study found water use to be a multivariate model dependent on water availability, end-users’ awareness and willingness to irrigate, and the type of species (drought-tolerant or high-water use). The study did not consider the homeowners’ economic status and overall inflation contributing to the decisions. Those arenas should be researched to understand the decisions of considering one landscape over another from a socioeconomic standpoint.
The status quo of urban irrigation modeling is still in its infancy. This study advances the knowledge of urban irrigation water requirement by understanding the major key drivers and its potential impacts on modeling. The study is useful to urban scientists and water managers in optimizing irrigation water requirement by placing the vegetated surfaces away from asphalt surfaces, in proximity of shade inducing structures, and in water-efficient landscapes instead of ones with traditionally high-water use.
Author Contributions
R.S. contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, and writing. H.S. contributed to conceptualization and review. S.A. contributed to conceptualization and review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Maki Endowment Funding, Division of Hydrologic Sciences, Desert Research Institute; grant # 17462.
Data Availability Statement
The data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Maki Endowment Funding, Division of Hydrologic Sciences, Desert Research Institute. We thank Southern Nevada Water Authority and Las Vegas Valley District for providing the water meter data in a timely manner.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dawadi, S.; Ahmad, S. Changing climatic conditions in the Colorado River Basin: Implications for water resources management. J. Hydrol. 2012, 430–431, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawadi, S.; Ahmad, S. Evaluating the impact of demand-side management on water resources under changing climatic conditions and increasing population. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaiser, K.; Ahmad, S.; Johnson, W.; Batista, J.R. Evaluating Water Conservation and Reuse Policies Using a Dynamic Water Balance Model. Environ. Manag. 2012, 51, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaiser, K.; Ahmad, S.; Johnson, W.; Batista, J. Evaluating the impact of water conservation on fate of outdoor water use: A study in an arid region. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stave, K.A. A system dynamics model to facilitate public understanding of water management options in Las Vegas, Nevada. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 67, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saher, R. Kaleidoscope of Urban Evapotranspiration: Exploring the Science and Modeling Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mini, C.; Hogue, T.; Pincetl, S. Estimation of residential outdoor water use in Los Angeles, California. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 127, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovocool, K.A. Xeriscape Conversion Study Final Report By. Area, 93. 2005. Available online: http://www.allianceforwaterefficiency.org/Xeriscape_Water_Savings.aspx (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Saher, R.; Middel, A.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Assessing the Microclimate Effects and Irrigation Water Requirements of Mesic, Oasis, and Xeric Landscapes. Hydrology 2022, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, R.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Urban evapotranspiration of green spaces in arid regions through two established approaches: A review of key drivers, advancements, limitations, and potential opportunities. Urban Water J. 2020, 18, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilaire, R.S.; Arnold, M.A.; Wilkerson, D.C.; Devitt, D.A.; Hurd, B.H.; Lesikar, B.J.; Lohr, V.I.; Martin, C.A.; McDonald, G.V.; Morris, R.L.; et al. Efficient Water Use in Residential Urban Landscapes. Hortscience 2008, 43, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Beecham, S.; Hassanli, A.M.; Kazemi, F. Water requirements of urban landscape plants: A comparison of three factor-based approaches. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 57, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middel, A.; Häb, K.; Brazel, A.J.; Martin, C.A.; Guhathakurta, S. Impact of urban form and design on mid-afternoon microclimate in Phoenix Local Climate Zones. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. Canyon Geometry and the Nocturnal Urban Heat Island: Comparison of Scale Model. J. Climatol. 1981, 1, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashua-Bar, L.; E Hoffman, M. The Green CTTC model for predicting the air temperature in small urban wooded sites. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, M.B.; Belfiore, O.R.; Parente, C.; Santamaria, R. Land Surface Temperature from Landsat 5 TM images: Comparison of different methods using airborne thermal data. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2015, 8, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, R.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Effect of land use change on summertime surface temperature, albedo, and evapotranspiration in Las Vegas Valley. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, J.; Bocher, E.; Petit, G.; Palominos, S. Sky View Factor Calculation in Urban Context: Computational Performance and Accuracy Analysis of Two Open and Free GIS Tools. Climate 2018, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, R.; Stephen, H.; Ahmad, S. Understanding the summertime warming in canyon and non-canyon surfaces. Urban Clim. 2021, 38, 100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahmani, P.; Hogue, T.S. Urban irrigation effects on WRF-UCM summertime forecast skill over the Los Angeles metropolitan area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9869–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.; Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Playán, E. Irrigation performance in private urban landscapes: A study case in Zaragoza (Spain). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, J.H.; Ramsey, R.D.; Kjelgren, R.K. Predicting urban forest growth and its impact on residential landscape water demand in a semiarid urban environment. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, E.; McCarthy, H.R.; Pataki, D.E. Transpiration sensitivity of urban trees in a semi-arid climate is constrained by xylem vulnerability to cavitation. Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvak, E.; Bijoor, N.S.; Pataki, D.E. Adding trees to irrigated turfgrass lawns may be a water-saving measure in semi-arid environments. Ecohydrology 2013, 7, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Tan, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yan, C. Characteristics of Evapotranspiration of Urban Lawns in a Sub-Tropical Megacity and Its Measurement by the ‘Three Temperature Model + Infrared Remote Sensing’ Method. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Toudert, F.; Mayer, H. Numerical study on the effects of aspect ratio and orientation of an urban street canyon on outdoor thermal comfort in hot and dry climate. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlmutter, D.; Berliner, P.; Shaviv, E. Integrated modeling of pedestrian energy exchange and thermal comfort in urban street canyons. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2396–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Toudert, F.; Mayer, H. Planning-oriented assessment of street thermal comfort in arid regions. In Proceedings of the 21th Conference on Passive and Low Energy Architecture, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 19–22 September 2004; Volume 41, pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shishegar, N. Street Design and Urban Microclimate: Analyzing the Effects of Street Geometry and Orientation on Airflowand Solar Access in Urban Canyons. J. Clean Energy Technol. 2013, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, G.Y. Quantifying the Evapotranspiration Rate and Its Cooling Effects of Urban Hedges Based on Three-Temperature Model and Infrared Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, J.L.; Gesch, R.W. Effects of turfgrass evaporation on external temperatures of buildings. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 1991, 43, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, B.H.; Hilaire, R.S.; White, J.M. Residential landscapes, homeowner attitudes, and water-wise choices in New Mexico. HortTechnology 2006, 16, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajlouni, M.G.; VanLeeuwen, D.M.; Hilaire, R.S. Linking Urban Residential Landscape Types in a Desert Environment to Landscape Water Budgets. HortTechnology 2014, 24, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, M.B.; Dukes, M.D.; Miller, G.L.; Haman, D.Z. Home Irrigation and Landscape Combinations for Water Conservation in Florida. EDIS 2005, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volo, T.J.; Vivoni, E.R.; Martin, C.A.; Earl, S.; Ruddell, B.L. Modelling soil moisture, water partitioning, and plant water stress under irrigated conditions in desert urban areas. Ecohydrology 2013, 7, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volo, T.J.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ruddell, B.L. An ecohydrological approach to conserving urban water through optimized landscape irrigation schedules. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 133, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, A.; Leishman, M. Leaf Area Index Drives Soil Water Availability and Extreme Drought-Related Mortality under Elevated CO2 in a Temperate Grassland Model System. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Garcia, X.; Llausàs, A.; Ribas, A.; Saurí, D. Watering the garden: Preferences for alternative sources in suburban areas of the Mediterranean coast. Local Environ. 2014, 20, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.; Rajagopalan, P.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Jamei, Y. Review on the impact of urban geometry and pedestrian level greening on outdoor thermal comfort. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelgren, R.; Rupp, L.; Kilgren, D. Water conservation in urban landscapes. HortScience 2000, 35, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinti, J.E.; Hilaire, R.S.; VanLeeuwen, D. Balancing Landscape Preferences and Water Conservation in a Desert Community. HortTechnology 2004, 14, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).