Impact of the Hydrogeological Conditions on the Calculated Surface Uplift above Abandoned and Flooded Coal Mines
Abstract
1. Introduction
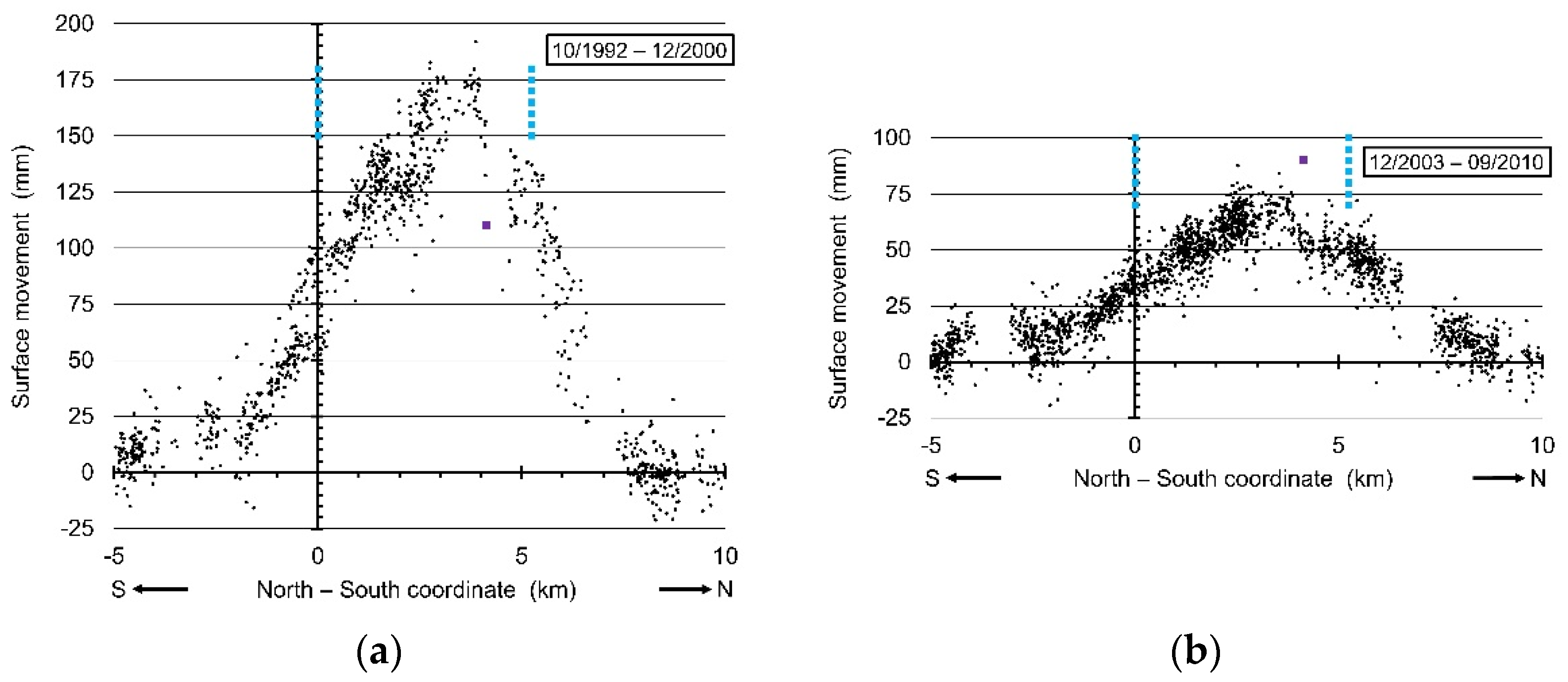
2. Overview of Past Studies on the Surface Uplift in the Campine Coal District, Belgium
3. Framework for Different Hydrogeological Conditions
3.1. Original Applied Framework
3.2. Alternative Hydrogeological Conditions
4. Comparison of Impact of Hydrogeological Conditions and Their Variation as a Function of Time
4.1. Results for Framework Developed by Vervoort [17]
4.2. Impact of Filling up Open Reservoir, Starting from Zero Water Pressure in Reservoir
4.3. Relation between Increase Water Pressure and Uplift
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vervoort, A. Uplift of the surface of the earth above abandoned coal mines. Part A: Analysis of satellite data related to the movement of the surface. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 148, 104896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglikow, V. Damage-relevant effects of mine water recovery—Conclusions from the Erkelenz hard coal district. Markscheidewesen 2011, 118, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Caro Cuenca, M.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Surface deformation induced by water influx in the abandoned coal mines in Limburg, the Netherlands observed by satellite radar interferometry. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devleeschouwer, X.; Declercq, P.Y.; Flamion, B.; Brixko, J.; Timmermans, A.; Vanneste, J. Uplift revealed by radar interferometry around Liège (Belgium): A relation with rising mining groundwater. In Proceedings of the Symposium Post-Mining 2008, Nancy, France, 6–8 February 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, D.; Bateson, L.; Sowter, A.; Grebby, S.; Novellino, A.; Cigna, F.; Marsh, S.; Banton, C.; Wyatt, L. Ground Motion in Areas of Abandoned Mining: Application of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) to the Northumberland and Durham Coalfield, UK. Geosciences 2017, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, C.; Muñoz, A.; Catalina, J.C.; Hadj-Hassen, F.; Kuchenbecker, R.; Spreckels, V.; Juzwa, J.; Bennett, S.; Purvis, M.; Bigby, D.; et al. Prediction and Monitoring of Subsidence Hazards Above Coal Mines (Presidence); RFCS Final Report RFCR-CT-2007-00004, EUR 25057 EN; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Samsonov, S.; d’Oreye, N.; Smets, B. Ground deformation associated with post-mining activity at the French–German border revealed by novel InSAR time series method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirankova, E.; Konicek, P. Ground surface uplift during hardcoal longwall mining. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 153, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, A.; Derakhshani, R.; Nilfouroushan, F.; Rahnamarad, J.; Azarafza, M. Spatiotemporal subsidence over Pabdana coal mine Kerman Province, central Iran using time-series of Sentinel-1 remote sensing imagery. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2022, 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A. The Time Duration of the Effects of Total Extraction Mining Methods on Surface Movement. Energies 2020, 13, 4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A. Long-term impact of coal mining on surface movement: Residual subsidence versus uplift. Min. Rep. Glückauf. 2020, 156, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Vervoort, A. Impact of the closure of a coal district on the environmental issue of long-term surface movements. AIMS Geosci. 2022, 8, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanieh, A.; Macciotta, R. Updated Understanding of the Ripley Landslide Kinematics Using Satellite InSAR. Geosciences 2022, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Zhan, H.Z.; Ni, W.K.; Liu, Y.; Gan, Z.H.; Liu, S.H. Surface Environmental Evolution Monitoring in Coal Mining Subsidence Area Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 790737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatza, S.; Papoutsis, I.; Paradissis, D.; Kontoes, C.; Papadopoulos, G.A.; Raptakis, C. InSAR Time-Series Analysis for Monitoring Ground Displacement Trends in the Western Hellenic Arc: The Kythira Island, Greece. Geosciences 2020, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Characteristics of Surface Deformation in Lanzhou with Sentinel-1A TOPS. Geosciences 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A. Uplift of the surface of the earth above abandoned coal mines. Part B: Framework to understand and explain uplift. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 148, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A. Surface movement above an underground coal longwall mine after closure. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2107–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A. Upward surface movement above deep coal mines after closure and flooding: Analytical modeling results. In Proceedings of the SME 2022 International Conference on Ground Control in Mining, Canonsburg, PA, USA, 26–28 July 2022. Paper 0601. [Google Scholar]
- Vervoort, A. Challenge to explain the upward surface movement above abandoned coal mines. In Proceedings of the Geotechnical Challenges in Mining, Tunneling and Underground Infrastructures, ICGMTU 2021, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, Virtual, 20 December 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.; Timms, W.A.; Barbour, S.L.; Mitra, R. Tracking changes in the specific storage of overburden rock during longwall coal mining. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammetta, P. Estimation of the height of complete groundwater drainage above mined longwall panels. Groundwater (NGWA) 2013, 51, 723–734, and comments by author on discussion, Groundwater (NGWA) 2014, 52, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Konietzky, H. An overview on flooding induced uplift for abandoned coal mines. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 148, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Konietzky, H.; Herbst, M.; Morgenstern, R. Numerical simulation of flooding induced uplift for abandoned coal mines: Simulation schemes and parameter sensitivity. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnichon, J.D.; Volckaert, G. Observations and predictions of hydromechanical coupling effects in the Boom clay, Mol Underground Research Laboratory, Belgium. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, F.; Li, X.L.; Bastiaens, W. Twenty-five years’ geotechnical observation and testing in the Tertiary Boom Clay formation. Géotechnique 2007, 57, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A.; Declercq, P.Y. Surface movement above old coal longwalls after mine closure. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, A.; Declercq, P.Y. Upward surface movement above deep coal mines after closure and flooding of underground workings. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vervoort, A. Impact of the Hydrogeological Conditions on the Calculated Surface Uplift above Abandoned and Flooded Coal Mines. Geosciences 2022, 12, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120454
Vervoort A. Impact of the Hydrogeological Conditions on the Calculated Surface Uplift above Abandoned and Flooded Coal Mines. Geosciences. 2022; 12(12):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120454
Chicago/Turabian StyleVervoort, Andre. 2022. "Impact of the Hydrogeological Conditions on the Calculated Surface Uplift above Abandoned and Flooded Coal Mines" Geosciences 12, no. 12: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120454
APA StyleVervoort, A. (2022). Impact of the Hydrogeological Conditions on the Calculated Surface Uplift above Abandoned and Flooded Coal Mines. Geosciences, 12(12), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences12120454






