Regional Analyses of Rainfall-Induced Landslide Initiation in Upper Gudbrandsdalen (South-Eastern Norway) Using TRIGRS Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Case Study
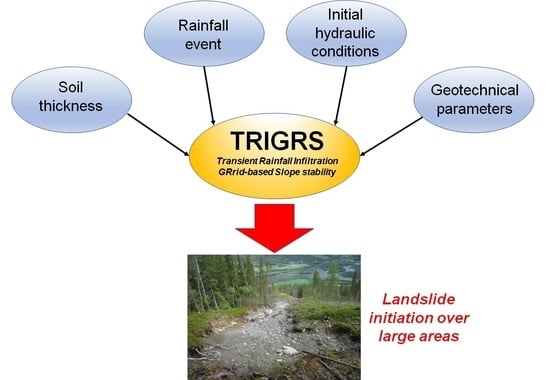
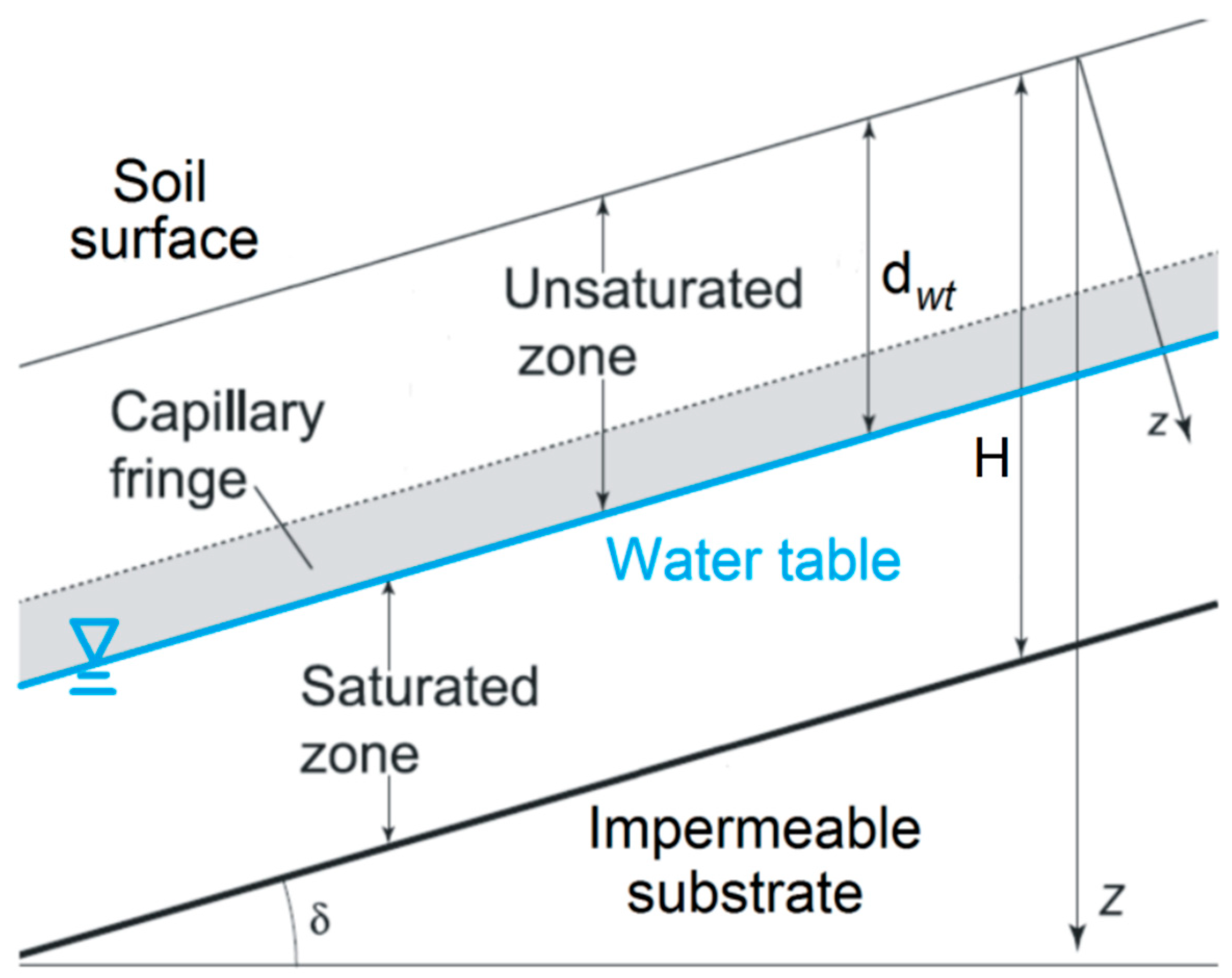
2.2. The TRIGRS Model
| Parameter | Unit | Attributed Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (δ) | (°) | Spatially variable | 5 × 5 m DEM |
| Soil thickness (H) | (m) | Spatially variable | Fitting equation |
| Friction angle (φ’) | (°) | 32 | [27] |
| Cohesion (c’) | (kN m−2) | 4 | [27] |
| Soil unit weight (γ) | (kN m−3) | 20 | [27] |
| Hydraulic conductivity (Ks) | (m s−1) | 1.0 × 10−5 | [27] |
| Hydraulic diffusivity (D0) | (m2 s−1) | 4.0 × 10−4 | [27] |
| Saturated water content (θs) | (-) | 0.45 | ROSETTA Lite module |
| Residual water content (θr) | (-) | 0.03 | ROSETTA Lite module |
| Pore-size parameter (αG) | (m−1) | 0.02 | ROSETTA Lite module + [28] |
| Initial water table depth (dwt) | (m) | Spatially variable | Varsom Xgeo |
| Background rainfall rate (IZLT) | (m s−1) | Spatially variable | Varsom Xgeo |
| Rainfall rate (IZ) | (m s−1) | Spatially variable | Norwegian Meteorological Institute |
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zêzere:, J.L.; Pereira, S.; Melo, R.; Oliveira, S.C.; Garcia, R.A.C. Mapping landslide susceptibility using data-driven methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, L.; Ciurleo, M.; Gullà, G. Shallow landslide susceptibility assessment in granitic rocks using GIS-based statistical methods: The contribution of the weathering grade map. Landslides 2018, 15, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Hong, H.; Akgun, A.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, S. Novel hybrid artificial intelligence approach of bivariate statistical-methods-based kernel logistic regression classifier for landslide susceptibility modeling. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 4397–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasang, S.; Kubíček, P. Landslide susceptibility mapping using statistical methods along the Asian Highway, Bhutan. Geosciences 2020, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, G.; Calvello, M.; Piciullo, L. Monitoring strategies for local landslide early warning systems. Landslides 2019, 16, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piciullo, L.; Calvello, M.; Cepeda, J.M. Territorial early warning systems for rainfall-induced landslides. Earth Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR) Developing Early Warning Systems: A Checklist. Available online: http://www.unisdr.org/2006/ppew/info-resources/ewc3/checklist/English.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Liao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Kirschbaum, D.; Liu, C. Assessment of shallow landslides from Hurricane Mitch in central America using a physically based model. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 66, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formetta, G.; Capparelli, G.; Versace, P. Evaluating performance of simplified physically based models for shallow landslide susceptibility. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4585–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Jang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-H. Physically based susceptibility assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslides using a Fuzzy Point Estimate Method. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, F.; De Vita, P.; Mirus, B.B.; Baum, R.L.; Allocca, V.; Tufano, R.; Di Clemente, E.; Calcaterra, D. Physically based estimation of rainfall thresholds triggering shallow landslides in volcanic slopes of Southern Italy. Water 2019, 11, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Savage, W.Z.; Godt, J.W. TRIGRS—A Fortran Program for Transient Rainfall Infiltration and Grid-Based Regional Slope-Stability Analysis; Version 2.0; Open-File Report 2008-1159; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; 75p.
- Devoli, G.; Tiranti, D.; Cremonini, R.; Sund, M.; Boje, S. Comparison of landslide forecasting services in Piedmont (Italy) and Norway, illustrated by events in late spring 2013. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 1351–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, A.; Nystuen, J.P.; Englund, J.O.; Hossack, J. Lillehammer-Berggrunnskart, 1:250.000; Norges Geologiske Undersøkelse: Trondheim, Norway, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sletten, K.; Blikra, L.H. Holocene colluvial (debris-flow and water-flow) processes in eastern Norway: Stratigraphy, chronology and palaeoenvironmental implications. J. Q. Sci. 2007, 22, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki, K.; Forssen, K.; Vangelsten, B.V. Factors Contributing to CI Vulnerability and Resilience, INTACT Deliverable D3.2. In Project Co-Funded by the European Commission under the 7th Frame-Work Programme; European Commission: Tampere, Finland, 2015; 103p. [Google Scholar]
- Viet, T.T.; Lee, G.; Thu, T.M.; An, H.U. Effect of Digital Elevation Model resolution on shallow landslide modeling using TRIGRS. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2017, 18, 04016011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilirò, L.; Cevasco, A.; Esposito, C.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. Shallow landslide initiation on terraced slopes: Inferences from a physically based approach. Geomat. Nat. Hazard Risk 2018, 9, 295–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.; Satyam, N.; Pradhan, B. Estimation of rainfall-induced landslides using the TRIGRS Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M. Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Yeh, T.-C.J. Analytical solutions for one dimensional, transient infiltration toward the water table in homogeneous and layered soils. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W.; Savage, W.Z. Estimating the timing and location of shallow rainfall-induced landslides using a model for transient, unsaturated infiltration. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, F03013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanapalli, S.K.; Fredlund, D.G. Comparison of different procedures to predict unsaturated soil shear strength. In Advances in Unsaturated Geotechnics; Shackelford, C.D., Houston, S.L., Chang, N.Y., Eds.; Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W. Infinite-slope stability under steady unsaturated conditions. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W11404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W.; Wu, D.T. A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W05515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, G.M.; Beven, K.; Obled, C. Including spatially variable effective soil depths in TOPMODEL. J. Hydrol. 1997, 202, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, C.; Frattini, P. Modelling probability of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in a changing climate, Otta, Central Norway. Clim. Chang. 2012, 113, 413–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzehei, T.A.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Su, G.W. Correspondence of the Gardner and van Genuchten-Mualem relative permeability function parameters. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, G. Case Study of Rainfall Induced Debris Flows in Veikledalen, Norway, 10th of June 2011. Master’s Thesis, Department of Geosciences, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haugen Edvardsen, D. Utløsningsårsaker og Utløsningsmekansimer til Flomskred I Moreneavsetninger—Feltstudie av Terrengtyper og Inngrep I Naturen som Potensielt kan føre til Skred inn mot Fremtidige Vegprosjekter. Eksempel fra Kvam, Norge. Master’s Thesis, Norges Teknisknaturvitenskapelige Universitet Institutt for Geologi og Bergteknikk, Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. ROSETTA: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; Huang, M.; Šejna, M.; van Genuchten, M.T. The HYDRUS-1D Software Package for Simulating the One Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media, Version 1.0; International Ground Water Modeling Center, Colorado School of Mines: Golden, CO, USA, 1998; 186p. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J.R. Unsaturated zone flow processes. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences: Part 13 Groundwater; Anderson, M.G., Bear, J., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2005; pp. 2299–2322. [Google Scholar]
- Anfinnsen, S. Characterization of shallow landslides, based on field observations and remote sensing. Developing and testing a field work form at four sites in Western and Eastern Norway. Master’s Thesis, Department of Geosciences, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W.R. Some steady-state solutions of the unsaturated moisture flow equation with application to evaporation from a water table. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.W. Correspondence of hydraulic functions for unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilirò, L.; Poueme Djueyep, G.; Esposito, C.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G. The role of initial soil conditions in shallow landslide triggering: Insights from physically based approaches. Geofluids 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krøgli, I.K.; Devoli, G.; Colleuille, H.; Boje, S.; Sund, M.; Engen, I.K. The Norwegian forecasting and warning service for rainfall- and snowmelt-induced landslides. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 1427–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beldring, S.; Engeland, K.; Roald, L.A.; Sælthun, N.R.; Voksø, A. Estimation of parameters in a distributed precipitation runoff model for Norway. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 7, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, S. Experience from applications of the HBV hydrological model from the perspective of prediction in ungauged basins. In Large Sample Basin Experiments for Hydrological Model Parameterization: Results of the Model Parameter Experiment-MOPEX; Andreassian, V., Hall, A., Chahinian, N., Schaake, J., Eds.; IAHS Publications: Wallingford, UK, 2006; Volume 307, pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Salciarini, D.; Godt, J.W.; Savage, W.Z.; Baum, R.L.; Conversini, P. Modeling landslide recurrence in Seattle, Washington, USA. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.N.; Wu, C.C. Mapping susceptibility of rainfall triggered shallow landslides using a probabilistic approach. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Im, S.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, Y.; Cha, K.S. Predicting the rainfall-triggered landslides in a forested mountain region using TRIGRS model. J. Mt. Sci. 2010, 7, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Nikhil, N.V.; Lee, S.R. Landslide and debris flow susceptibility zonation using TRIGRS for the 2011 Seoul landslide event. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
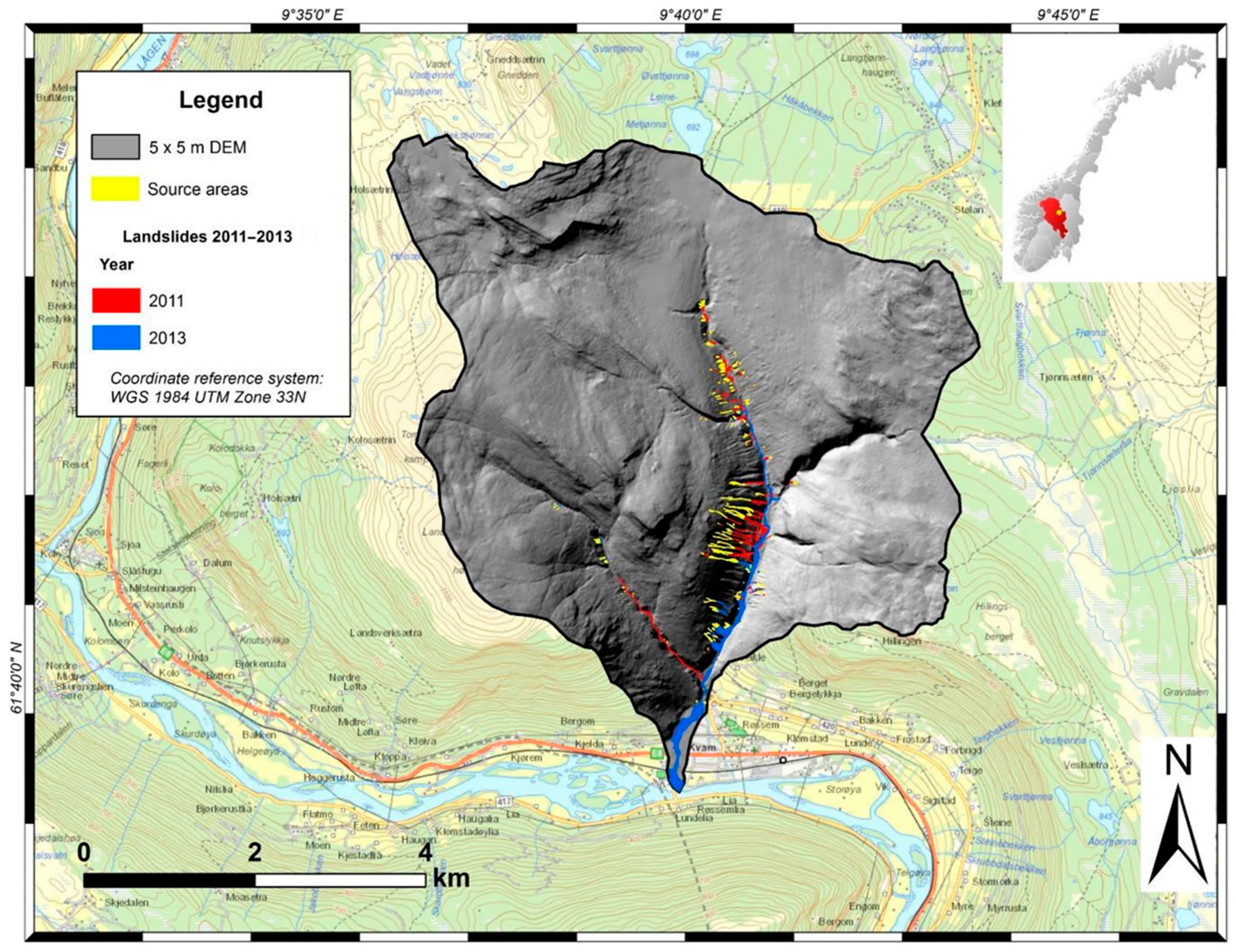
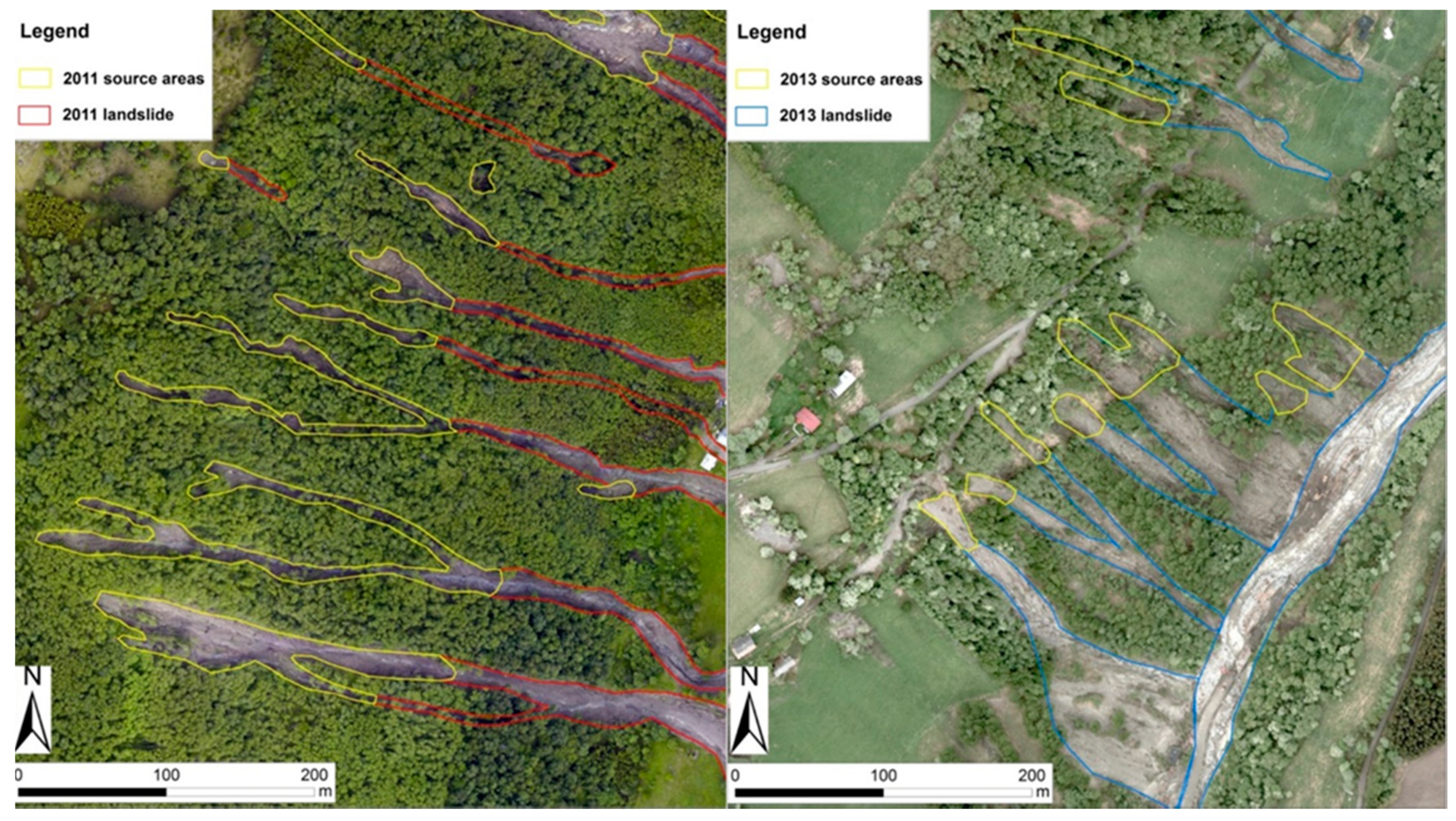
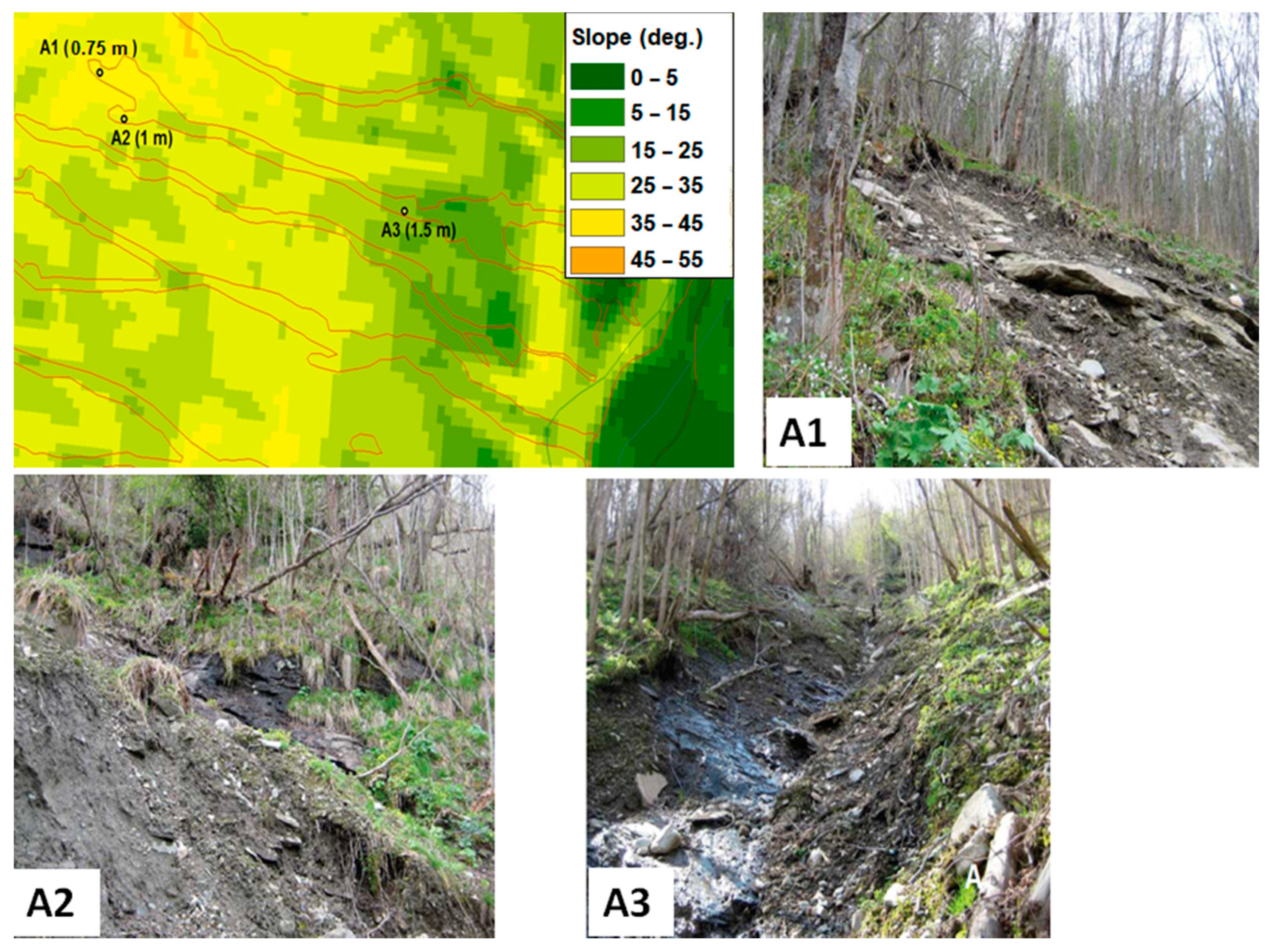
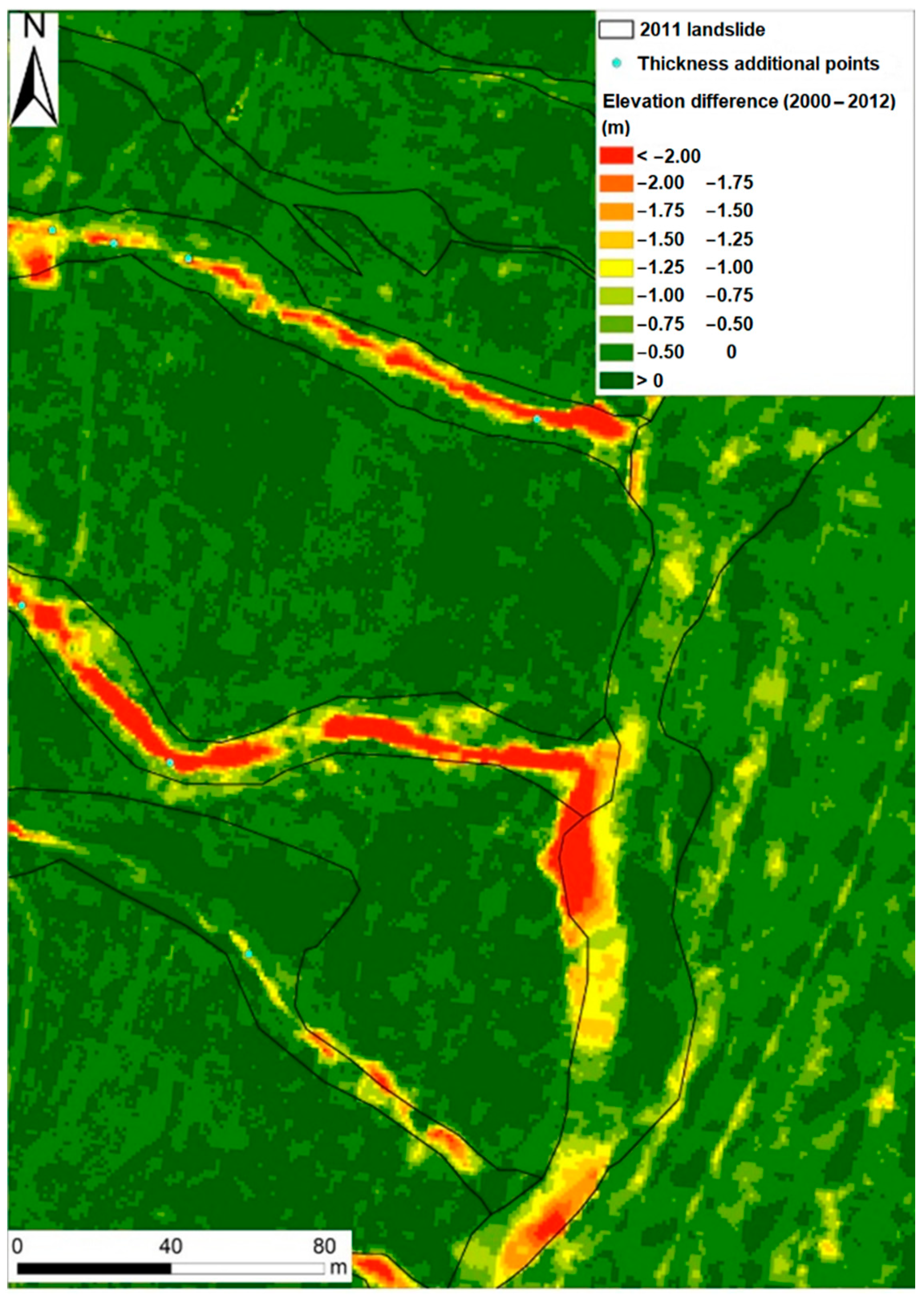
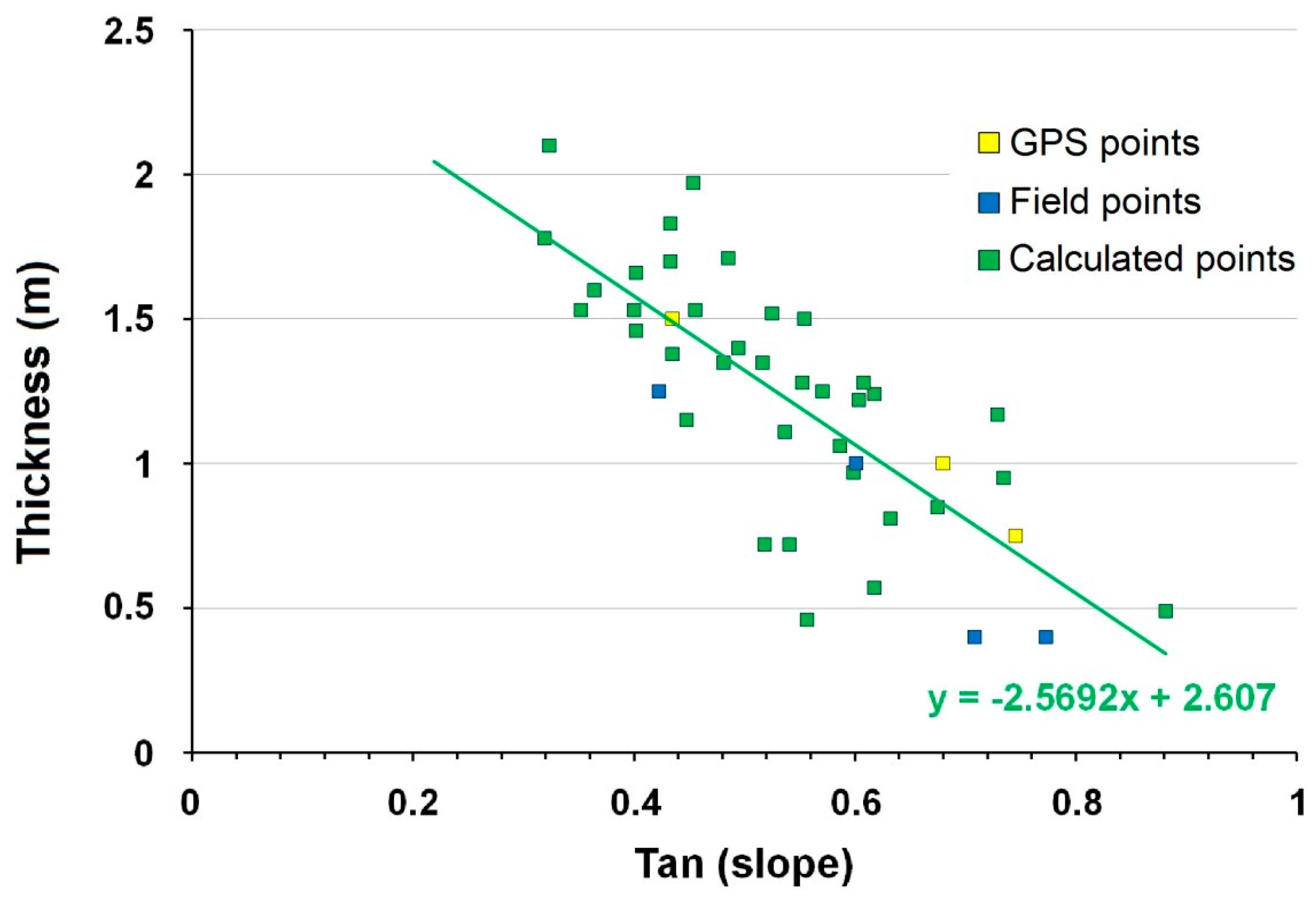
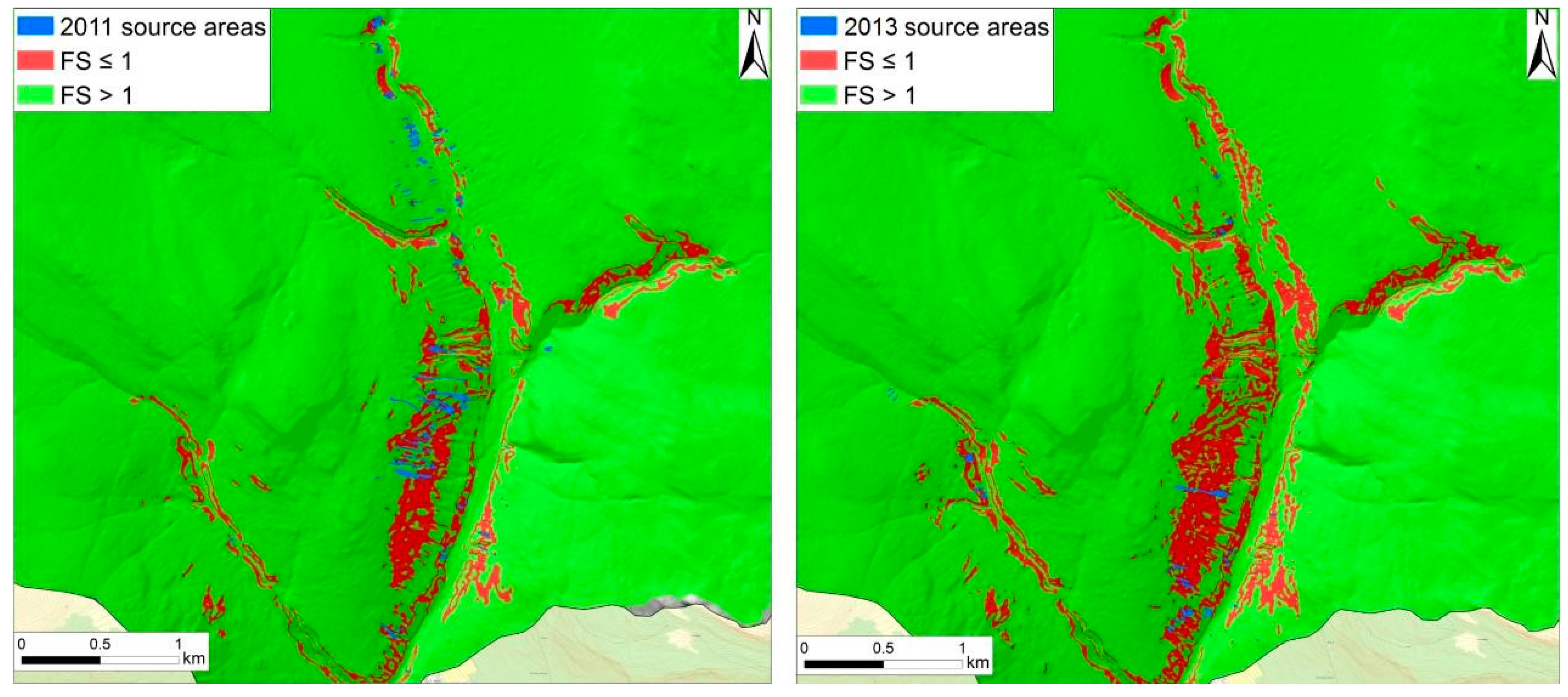
| Type of Data | Points | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Field data–GPS position | 3 | [29] |
| Field data | 4 | [30] |
| Calculated data | 36 | LIDAR-based 1 × 1 m2 DEMs |
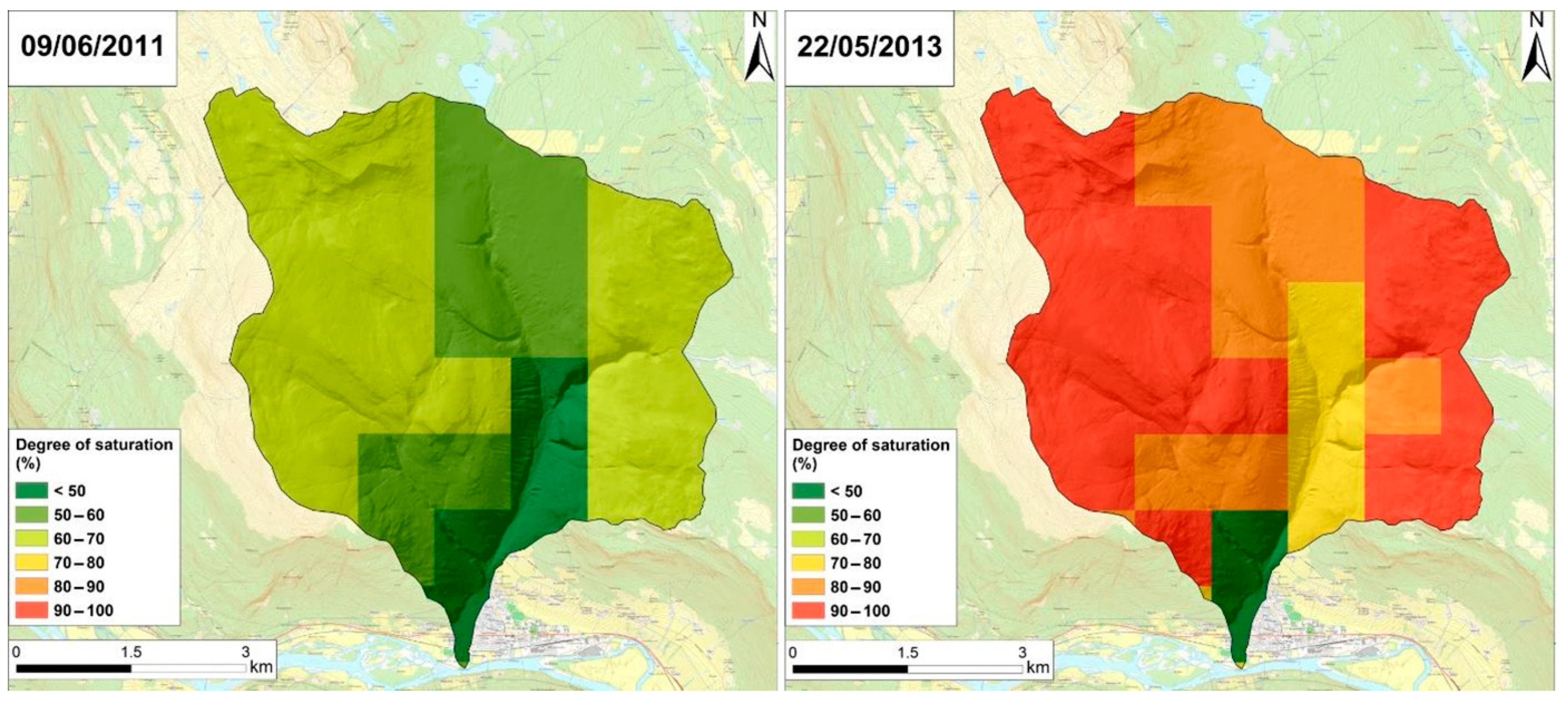
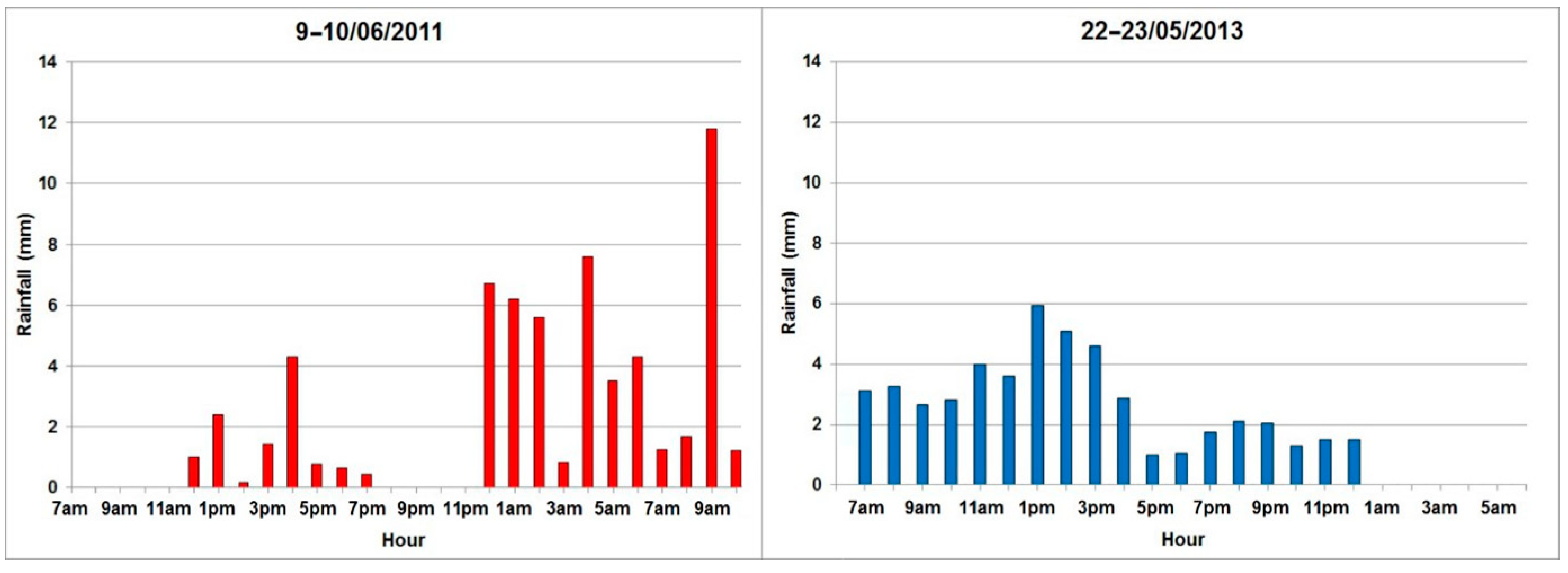
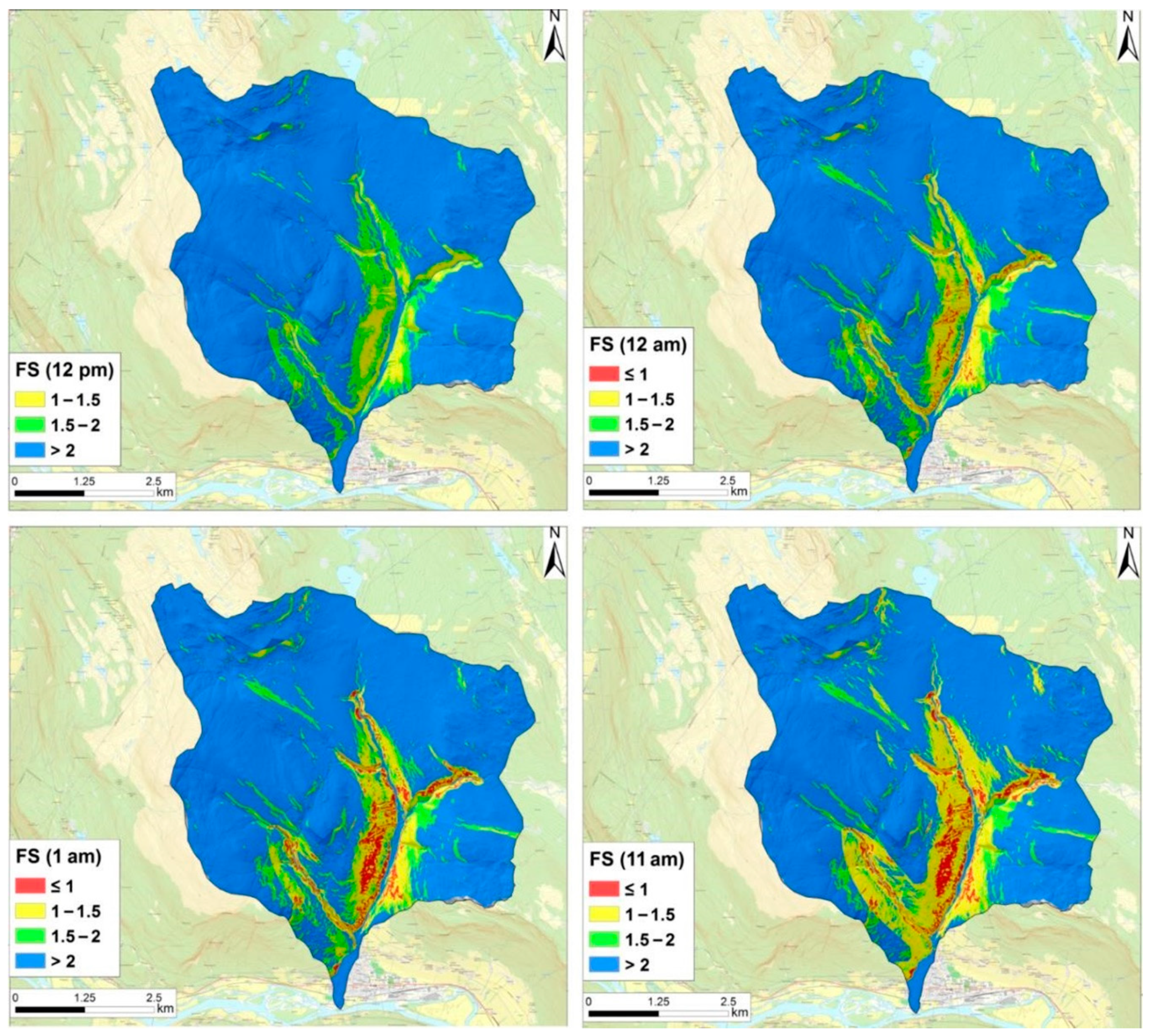
| Time (2011) | N. of Unstable Cells (2011) | Time (2013) | N. of Unstable Cells (2013) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 p.m. | 0 | 7 a.m. | 0 |
| 12 a.m. | 10,878 | 11 a.m. | 21,299 |
| 1 a.m. | 30,262 | 1 p.m. | 46,300 |
| 11 a.m. | 33,692 | 12 a.m. | 52,415 |
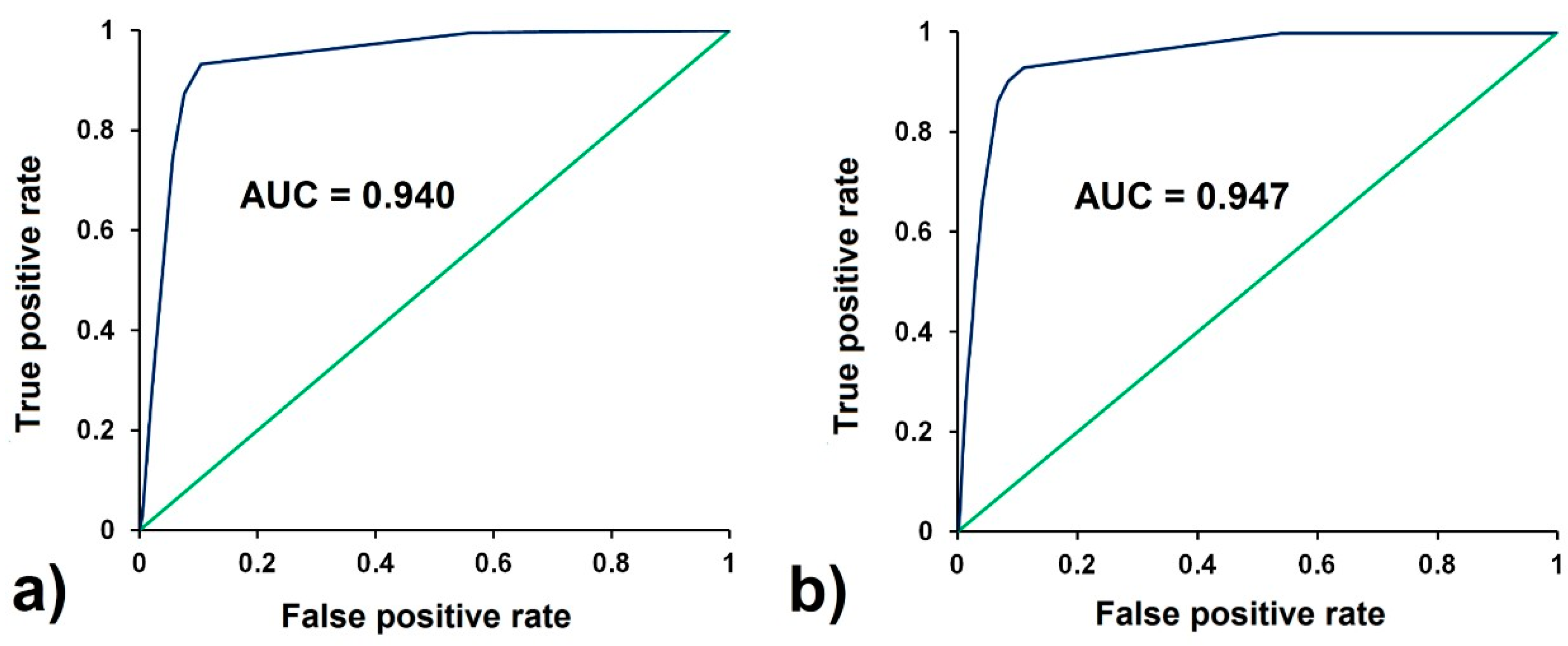
| 2011 | Predicted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—Stable | 1—Unstable | |||
| Observed | 0—Stable | TN | FP | N. of Stable Observations |
| 1,193,631 | 72,188 | 1,265,819 | ||
| 1—Unstable | FN | TP | N. of Unstable Observations | |
| 892 | 2620 | 3512 | ||
| N. of Stable Predictions | N. of Unstable Predictions | Total N. of Observations and Predictions | ||
| 1,194,523 | 74,808 | 1,269,331 | ||
| 2013 | Predicted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—Stable | 1—Unstable | |||
| Observed | 0—Stable | TN | FP | N. of Stable Observations |
| 1,186,063 | 84,603 | 1,270,666 | ||
| 1—Unstable | FN | TP | N. of Unstable Observations | |
| 170 | 1049 | 1219 | ||
| N. of Stable Predictions | N. of Unstable Predictions | Total N. of Observations and Predictions | ||
| 1,186,233 | 85,652 | 1,271,885 | ||
| Parameter | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Value for Sensitivity Analysis (±st. dev.) | Early n. Unstable Cells | Difference with Values Table 3 | Final n. Unstable Cells | Difference with Values in Table 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Friction angle (φ’) | 32 | 3.2 | 28.8 | 0 | 0 | 100,856 | +48,441 |
| 35.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −52,415 | |||
| Cohesion (c’) | 4 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 134,432 | +82,017 |
| 5.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −52,415 | |||
| Soil unit weight (γ) | 20 | 0.4 | 19.6 | 0 | 0 | 54,231 | +1816 |
| 20.4 | 0 | 0 | 50,693 | −1722 | |||
| Hydraulic conductivity (Ks) | 1 × 10−5 | 2.5 × 10−6 | 7.5 × 10−6 | 0 | 0 | 48,193 | −4222 |
| 1.25 × 10−5 | 0 | 0 | 54,681 | +2266 | |||
| Hydraulic diffusivity (D0) | 4 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−5 | 3.5 × 10−4 | 0 | 0 | 52,415 | 0 |
| 4.5 × 10−4 | 0 | 0 | 52,415 | 0 | |||
| Soil thickness (H) | 1.2 (thick) 0.8 (shallow) | 0.3 | 0.9 (thick) 0.5 (shallow) | 884 | +884 | 25,919 | −26,496 |
| 1.5 (thick) 1.1 (shallow) | 40,775 | +40,775 | 129,107 | +76,692 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schilirò, L.; Cepeda, J.; Devoli, G.; Piciullo, L. Regional Analyses of Rainfall-Induced Landslide Initiation in Upper Gudbrandsdalen (South-Eastern Norway) Using TRIGRS Model. Geosciences 2021, 11, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11010035
Schilirò L, Cepeda J, Devoli G, Piciullo L. Regional Analyses of Rainfall-Induced Landslide Initiation in Upper Gudbrandsdalen (South-Eastern Norway) Using TRIGRS Model. Geosciences. 2021; 11(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchilirò, Luca, José Cepeda, Graziella Devoli, and Luca Piciullo. 2021. "Regional Analyses of Rainfall-Induced Landslide Initiation in Upper Gudbrandsdalen (South-Eastern Norway) Using TRIGRS Model" Geosciences 11, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11010035
APA StyleSchilirò, L., Cepeda, J., Devoli, G., & Piciullo, L. (2021). Regional Analyses of Rainfall-Induced Landslide Initiation in Upper Gudbrandsdalen (South-Eastern Norway) Using TRIGRS Model. Geosciences, 11(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11010035