Abstract
Over the last few centuries, mapping the ocean seabed has been a major challenge for marine geoscientists. Knowledge of seabed bathymetry and morphology has significantly impacted our understanding of our planet dynamics. The history and scientific trends of seabed mapping can be assessed by data mining prior studies. Here, we have mined the scientific literature using the keyword “seabed mapping” to investigate and provide the evolution of mapping methods and emphasize the main trends and challenges over the last 90 years. An increase in related scientific production was observed in the beginning of the 1970s, together with an increased interest in new mapping technologies. The last two decades have revealed major shift in ocean mapping. Besides the range of applications for seabed mapping, terms like habitat mapping and concepts of seabed classification and backscatter began to appear. This follows the trend of investments in research, science, and technology but is mainly related to national and international demands regarding defining that country’s exclusive economic zone, the interest in marine mineral and renewable energy resources, the need for spatial planning, and the scientific challenge of understanding climate variability. The future of seabed mapping brings high expectations, considering that this is one of the main research and development themes for the United Nations Decade of the Oceans. We may expect a new higher resolution ocean seafloor map that might be as influential as The Floor of the Oceans map.
1. Introduction
Although the first documentation of studies concerning the sea date back to Aristotle’s time—384–322 AD, the beginning of marine sciences is generally considered to be the 17th century with Boyle’s “The Saltness of the Sea” (1674). One of the first bathymetric maps, if not the first, long before geophysical methods, was based on plumb measurements (fathoms units) and was published in an 1855 textbook by Matthew Fontaine Maury [1], who is considered to the father of modern oceanography. The HMS Challenger expedition (1873–1876) can be considered a striking fact of the seabed mapping history; much of the information preceding the 20th century presented herein were recovered from the “Report of The Voyage of HMS Challenger” [2]. More than 500 plumb measurements were acquired in the Challenger Expedition, revealing the depth of the Mariana Trench and the Dolphin, Connecting, and Challenge Ridges, known today as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. At the beginning of the 20th century, an important theory regarding the ocean basins was put forth: the Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift and seafloor spreading. In 1977, another milestone of seafloor mapping elaborated by Bruce Heezen and Marie Tharp [3] helped to consolidate the Wegener hypothesis and also illustrated submarine morphology in a reliable and similar way to what we know today [4,5].
Prior to the 19th century, the methods for depth measurements were archaic. The “lead and line” system is a classical example, in which a plumb attached to a cable sank through the water column until it reached the seafloor. Such measurements were greatly influenced by vessel drift and marine currents. There had been a few attempts to improve the method, e.g., by Hooke during the 18th century and Brooke in the 19th century. In parallel, the lack of knowledge about the seafloor allowed hypotheses to emerge that were sometimes eccentric, such as a perpetual ice cover over the seabed (French naturalist Péron, 1805—mentioned in Thompson and Murray, 1885, Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. “Challenger” [2] p. 37). The operation to lay down the first telegraph cable across the Atlantic was an event of great importance, around 1850. This spawned and drove a need to produce better knowledge about the ocean depths and encouraged technological advances.
By 1920, the development of acoustic technology changed the course of seabed mapping, and then “lead and line” measurements were gradually replaced by echo sounders. The German Meteor Expedition (1925–1927) surveyed the South Atlantic Ocean using echo sounding equipment and other oceanographic tools. During this expedition, among other findings, the continuity of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge was observed, now known as being by far the largest geological formation on Earth. Seismic methods also came into use during this period, with the first records in water-covered areas in 1926 (historical events can be found in [6]), and the first important marine survey with this technique conducted in 1938 [7]. Between the decades of 1950 and 1960, substantial progress and development was made on electronic stabilization, interferometric modulation and positioning improvement [8]. In the 1970s, new perspectives for seabed acoustic mapping were driven by a revolutionary multibeam bathymetry system [9]. In 1977, during the Jean Charcot Expedition, the first non-military versions of multibeam systems were employed—Seabeam and Hydrochart, for deep and shallow waters, respectively. These systems have greatly enriched the future of the seabed mapping and the quality of bathymetric surveys [10,11], already enabling the inference of seafloor characteristics from backscatter data [12]. After these enhancements to acoustic systems, the science related to seabed classification leveraged major developments and innovations, e.g., geomorphological and habitat classification using geophysical data such as bathymetry and side scan sonar. In recent years, the use of correlations between acoustic properties and biological and/or geological parameters has been successful, but this type of transformation of acoustic properties into physical properties has been used in submarine acoustics for substantially longer [13].
Over time, seabed mapping gained further importance due to technological developments, providing substantive contributions to a better understanding of tectonics and ocean spreading. In addition to the unquestionable scientific importance and essential relationship with other oceanographic fields, the role of seabed mapping has been paramount for national and international limit jurisdiction issues, first established in 1982 (Law of the Sea). This subject is closely related to fields such as economic zoning, natural resources management and the exploration of marine mineral and oil and gas resources. The main points and implications of Article 76 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea were reviewed [14,15], identifying, among other issues, the importance of geophysical methods. Even today, one often hears or reads—with a degree of frustration or regret—that we know more about the moon’s surface and even some other planets than about our own oceans, and that around 82% of the ocean floor is as yet unmapped [16]. A notorious example is the southeastern Indian Ocean mapping that was conducted to search for a Malaysian Airlines flight that disappeared. As a byproduct, that dataset revealed interesting geomorphological findings that improved the understanding of that ocean floor region [17]. As well as the “The Nippon Foundation—GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project” efforts to map the oceans’ floor by 2030, the importance of seabed mapping for several fields is also corroborated by the United Nations with the declaration of the Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–2030), including the map of the oceans as one of the research and development priorities.
Here, the goal is not to be an audacious and challenging historical review of marine sciences [18,19], nor an ocean mapping review [20,21], as it would demand a large historiographical effort and a study of the cartography aspects. The purpose here is to provide a consistent picture of seabed mapping supported by scientific studies, visualize the evolution of mapping methods (from the 1930s until now), and emphasize the main trends and challenges. In this context, the analyses performed were based on a set of scientific manuscripts (dated between 1930 and 2019) retrieved from the Brazilian virtual library “Portal de Periódicos da CAPES”. The web search was conducted using the keyword “seabed mapping”. The assessments comprised primarily a vocabulary analysis, presenting statistical results according to the main and frequent words from sets of manuscripts from each decade. The logic was to implement an important outcome from “machine learning” and “data science”, in which an algorithm previously scans a dataset and shows results and connections somewhat difficult to be noted by a single individual, instead of using the usual order of a hypothesis that arises and then is subsequently tested for validity through data [22].
Nevertheless, it is important to recognize that there are very relevant book references that are not considered in this analysis as they are not necessarily included in citation libraries. These are mainly old scientific books such as the seminal Submarine Geology (1948) by Francis Shepard and The Floors of the Ocean-North Atlantic (1959) by Bruce Heezen, Marie Tharp, and Maurice Ewing. Also, there are important publications associated with geological/hydrographic surveys that were not included in the analysis. The importance of these agencies is unquestionable and difficult to measure. Among other functions, in most nations these agencies played a lead role in data collection, interpretation and publication of contributions to geosciences (e.g., natural resource sustainability and fundamental geology mapping) [23]. An important goal of these geological/hydrographic surveys is to produce information required by governments to map the limits of economic zoning and provide a basic seafloor knowledge for national or multilateral marine spatial planning.
2. Materials and Methods
The applied methodology is summarized in the following main steps (Figure 1): (i) search for scientific literature; (ii) elaboration and processing of the input data (text files); (iii) performance of statistical analyses. During the literature searches, some inclusion criteria were adopted to make this step more transparent and replicable [24], such as definition of the search term used, databases searched, dates included, that only studies written in English were considered, and type of reports. These elements are detailed further below.
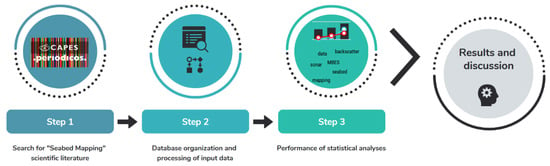
Figure 1.
Methodological flow.
Reference data mining was conducted using the Brazilian virtual library “Portal de Periódicos da CAPES/” This library provides access to several database, including Scopus (Elsevier), Science Citation Index Expanded (Web of Science), OneFile (GALE), Aquatic Sciences and Fisheries Abstracts (ASFA), Elsevier (CrossRef), Technology Research Database, Oceanic Abstracts, Engineering Research Database, Materials Science & Engineering Database, Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), Advanced Technologies & Aerospace Database, Springer (CrossRef), SpringerLink, Civil Engineering Abstracts, Advanced Technologies Database with Aerospace, GeoRef, Mechanical & Transportation Engineering Abstracts, Aerospace Database, Taylor & Francis Online Journals, and Wiley Online Library. It is important to point out that books and grey literature (such as publications from geological/hydrographic surveys) were excluded from the scope proposed for this overview. As mentioned before, we do acknowledge the importance of technical reports, atlas, and books produced by government agencies and geological surveys around the globe, but in order to follow a procedure, we could only consider the scientific literature found in international citation libraries.
The term “seabed mapping” was adopted as the keyword for the search. Our choice of this keyword combination instead of “seafloor mapping” was based on the assumption that this term is widely used; overall, the conceptual definition of seabed and seafloor is very similar. By way of example, considering the papers mined in this work, the terms of both “seabed” and “seafloor” did not appear between 1930 and 1940, but rather the term “bottom”; in the 1960s, “ocean floor”, “seabed”, and “seafloor” were each identified three times; between 2000 and 2010, “seabed” appeared 114 times and “seafloor” 86 times. The selected term also makes reference to the global project name “Seabed 2030”. A wider search contemplating more keywords would provide a more complete overview, but such additional methodological effort is not suitable herein.
The scientific papers found were considered only when available in English and were carefully evaluated considering the thematic. This screening process can be seen as a bit subjective or uncertain, but nevertheless it is necessary due to the mismatch between “seabed mapping” and the results provided at times, and also the presence of some inappropriate publications for the approach proposed here (e.g., conference abstracts). It was internally defined as a cut-off point to use only the first 300 references per decade during the searches; after the 300th, we found the manuscripts were no longer closely related to “seabed mapping”.
The lexical analysis is based on the reading and transformation of the manuscript text into factors or numbers through computational language. Thus, based on textual corpora, the algorithm can calculate the occurrence of words and obtain syntactic relations, aiming to distinguish classes of words or even content analysis. Therefore, this type of analysis involves statistical and computational procedures providing comparable and quantitative results.
The lexical analyses (word frequency and word co-occurrence) were performed in a graphical interface within the R environment. It was the Iramuteq (Interface de R pour les analyses multidimensionnelles de textes et de questionnaires) [25]. With this software, it is possible to perform calculations of word frequency or even more complex multivariate analysis. Herein, we will present
- word clouds—graphically interesting by enabling the quick identification of more frequent words (more frequent word is larger in size). The words were only analyzed in active forms, i.e., supplementary forms (such as pronouns, articles and prepositions) were not included in the results;
- similarity graphs, which are based on graph theory used to observe and describe the connection among the words [26]. The analysis performed considered the relations and co-occurrence (similar to Euclidean Distance) among the 100 most frequent words, and the graphic chosen for this result was “Fruchterman Reingold (force-directed layout algorithm—the default for Iramuteq—which considers the connection thickness between the words to define the dispersion of the main vertices) [27], Score Co-occurrence with Halo Communities”. From this configuration, the higher the frequency that two words appear close, the thicker the grey connections become.
The preparation and processing of linguistic corpora must be undertaken so that the script can read the input data (UTF-8 format). The main processing steps involved the removal of special characters and syntagma reconstitution, i.e., joining one or more words with a unique meaning. In this case, each space between the words is replaced by “_” (underline)—e.g., “continental shelf” becomes “continental_shelf”. In addition, the words “seabed” and “mapping” were excluded to preserve statistical independence. One further step applied (by Iramuteq) was lemmatization, which reduced different forms of a word to a core root (e.g., datum/data, sampling/samples/sample). Although lemmatization was successfully implemented, there are some acronyms and abbreviations (such as MBES, BS, kHz, km) that were linguistically neglected by the lemmatization tool. The occurrence of an acronym did not change the overall result or the five most frequent terms for each year. It must be highlighted that only the title, abstract and keywords from each paper were considered for the analyses. This was a settlement defined by the authors due to the large volume of textual content, and by the internal perception that a large amount of “textual noise” could arise if the entire paper was considered that would disturb interpretation of the results.
3. Results and Discussions
Scientific manuscript mining using “seabed mapping” as the keyword successfully collected a total of 454 papers dated between 1930s and 2019. Supplementary Material (S1) provides the complete reference list.
In the following subsections, we will present and discuss the obtained results qualitatively and quantitatively. The results were divided into three major topics. For the first topic, a temporal analysis was conducted over the decades using primarily word clouds and attempted to separate them between deep- and shallow-water contexts. The second topic addresses the similarity analysis for the two last decades, a timeframe chosen because of the coexistence of numerous technologies for mapping, as well as different approaches and classification techniques [28]. In addition, due to the large number of papers analyzed for the 2011–2019 period (280 papers), word clouds for each year were created to obtain a better visualization with more details. The third topic discusses the importance, applicability and future directions of seabed mapping.
3.1. Seabed Mapping Temporal Evolution
All of the papers were evaluated in such a way as to rate them as shallow-water (depth < 200 m), deep-water (>200 m), or not applicable (e.g., bibliographic review and methodological development). The graph (Figure 2) presents it in terms of percentages.
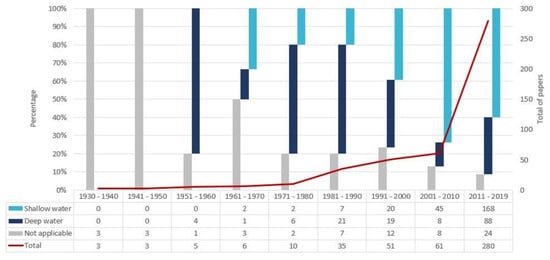
Figure 2.
Deep/shallow water context in the manuscripts with the keyword “seabed mapping” by decade.
Overall, the growth of scientific production over the decades is notable, with an increase that was more considerable in 1980s and more remarkable in number for the current decade. This fact follows the trend of investments in research, science and technology, as well as the increase in research in the seabed mapping science field. Recently, UNESCO published a world map based on ocean science publications in each country [29]. Scientific production was highlighted in countries such as USA, China, Canada, Europe, and Australia. The remarkable presence of China was not observed for the database analyzed here. This may represent a large volume of work in ocean science fields unrelated to “seabed mapping” and/or the limited availability of Chinese papers in the library.
Still regarding the growth of scientific production, it is important to emphasize the very important role played by extensive mapping programs. Several of them appeared in the word clouds. Amongst these, specific mention can be made of the General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) [5], the Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance (AORA), the European Marine Observation and Data Network (EDMODnet) [30], the Marine Area Database for Norwergian Waters (MAREANO) [31], the Integrated Mapping Survey for the Sustainable Developments of Ireland’s Marine Resource (INFOMAR) [32], and Australian programs such as Seamap Australia [33]. More information on some of these programs and other repositories can be found in [34].
Another interesting result that can be extracted from the graph (Figure 2) is the predominance of deep-water studies until the decade of 1980. This deep-water dominance did not remain unbalanced in 1990s, and shallow-water studies became dominant after that time. The direct comparison between decades is a complex exercise, since changes over time occurred in variables such as the development stage of computational technology, activities that had economic influence (e.g., mineral exploration and port trades), and the knowledge and concern about the sea environment.
Currently, studies on shallow-water still hold a majority, but a greater number of papers in deep-waters were published at the end of 2010–2019 [17,35,36]. Recently, the Frontiers in Marine Sciences Journal has published a research topic edition (seafloor mapping of the Atlantic Ocean) with deep-sea studies. However, due to the advances and availability of new technologies (e.g., multibeam bathymetry and autonomous underwater vehicles), these newer studies have achieved a much better resolution than older works. It is also worth to mentioning the approach of deep-water seafloor mapping from crowd-sourced bathymetry [37], an idea already present in 1956 [38]. This would certainly contribute toward one the goals of the Seabed 2030 Project—mapping unknown regions (#mapthegap) and the improvement of data resolution [16].
The current large number of papers associated with shallow waters shows us efforts and priorities related to the coastal region/continental shelf in several subjects ranging from coastal processes and morphological studies to seabed spatial planning. Furthermore, there is still difficulty with financial means to access suitable technologies for deep-water studies; we must also consider that using autonomous underwater vehicles in the deep sea for seabed mapping purposes is still novel and the response in terms of scientific publication may increase in the next decade.
The lexical analysis provided us with the word cloud for each decade, indicating the more frequent words and the scientific context in each group of papers. Figure 3 and Figure 4 present the word clouds in a timeline.
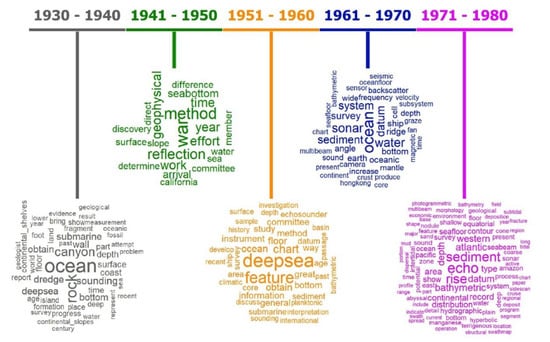
Figure 3.
Word cloud for each decade (1930–1980).
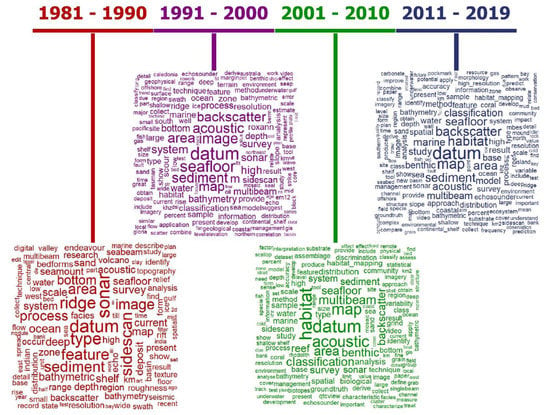
Figure 4.
Word cloud for each decade (1981–2019).
For the 1931–1940 decade, the most frequent words were “ocean”, “rock”, and “canyon”, and only two scientific works were found (and both are exploratory reviews). In the 1940s, the result was only different due to the historical background. The more recurrent words were “war”, “method”, and “reflection”. During the searches for this decade, it became evident that a scientific publication blackout had been present (e.g., library destruction due to battles and fanaticism), although numerous inventions and scientific principles emerged during the war. This was not exclusive to the marine sciences.
In the 1951–1960 decade, the highlights were “deepsea”, “feature”, and “chart”. The term “chart” already addressed seabed mapping more clearly. The presence of words such as “interpretation” referenced warnings about methodologies employed. The strong presence of the “deepsea” term in the 1950s word cloud is in line with the context presented on the graph in Figure 2. The 1961–1970 decade showed the most frequent terms were “ocean”, “sonar”, and “water”. Although a low number of manuscripts were found, the presence of terms in the word cloud such as “seismic”, “frequency”, “sound”, “bathymetry”, “multibeam”, and “backscatter” are a demonstration of the importance of submarine geophysics. The vocabulary suggests study development that was more complex than before, involving acoustic backscatter as a proxy of sediment properties [13,39]. Besides this, prominent terms indicate the research subject of importance is the revolutionary multibeam charting system [9].
For the decade of 1971–1980, the most recurrent terms were “echo”, “rise”, and “sediment”. The highlight of “echo” was driven by an echo character study of the Atlantic floor [40]. The occurrence of words such “deep” and “abyssal” support the predominance of works in deep-water shown in Figure 2. Furthermore, the term “Seabeam” is from the first multibeam system used for non-military purposes, during the N.O. Jean Charcot expedition.
In the 1980s, the most frequent terms were “sonar” and “datum” (same frequency), “ridge” and “type” (same frequency), and “sidescan”. As indicated in Figure 2, there is an increase in scientific production, which explains the greater number of terms in the word cloud. Scientific development can be inferred based on the presence of technical terms (“analysis”, “technique”, “measurement”, “process”), besides words related with methods and equipment (“sidescan”, “backscatter”, “multibeam”, “classification”). A number of words related to deep-water appeared (“deep”, “ridge”, “polymetallic”), but also starting to emerge were more terms concerning shallow-waters (“shallow”, “continental_shelf”, “exclusive_economic_zone”).
In the following decade, between 1991–2000, shallow-water papers stood out (“shallow”, “shelf”, “continental_shelf”). The most frequent words were “datum”, “seafloor” and “image”. The term “multibeam” rather than “sidescan” became higher occurrence, and “backscatter” increased in importance. Terms such as “resolution”, “accuracy”, “ground truth”, “classification”, “Roxan”, and “QTC_view” demonstrate how the scientific literature had progressed. During the 2001–2010 period, the terms occurrence was dominated by “datum”, “habitat”, “map”, and “acoustic” (same frequency), with shallow-water papers making up the majority. The marine conservation approach became more common (“reef”, “habitat_mapping”, “marine_protected_area”, “ecosystem_based_management”). It is interesting to note that the GeoHab Conference (Marine Geological and Biological Habitat Mapping) began in this decade.
Finally, considering the decade of 2011–2019, the most frequent terms were “datum”, “map”, and “habitat”. Words such as “backscatter” and “classification” also show great importance. In the particular case of “classification”, the development is outstanding, exemplified by terms such as “algorithm” (53 times), “machine_learning” (34 times), “angular_response” (37 times), “geomorphometry” (23 times), “unsupervised” (21 times), and “multispectral” (31 times). This decade also shows a greater frequency of the term “marine_protected_area” than the 2000s, which is consistent with the use of marine protected area (MPA) growth maps as a restoration intervention for rebuilding marine life [41].
Figure 5 summarizes the most frequent words in each decade. The word “datum” positioning itself as the most important term over the last several decades, consistent with an increase in data availability and quality. This demonstrates how laborious the challenge of building data repositories will be, besides the difficulties associated with compiling and harmonizing datasets across surveys (as approached with backscatter data in Misiuk et al., 2020 [42]).
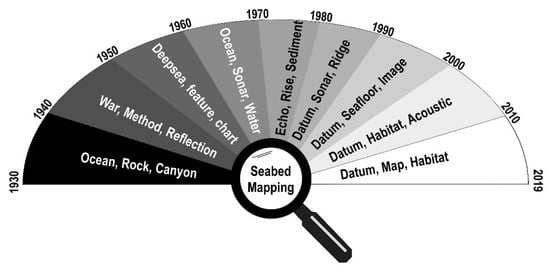
Figure 5.
Illustrative scheme summarizing the most frequent words by decade.
3.2. The Seabed Mapping Science of the Two Last Decades in Focus
For the last two decades, a large number of publications were analyzed and, as a result, a greater number of terms appeared in the word cloud showing technological and methodological advances. During these decades, side scan sonar and multibeam were the main seabed mapping technologies [43]. The progress of benthic habitat mapping was reviewed [28] based on the three most widely used techniques (single beam, side scan sonar, and multibeam) in more than 140 publications. In Lecours et al. (2016) [44], a broad range of techniques for geomorphometric classifications were discussed, in different spatial domains with different approaches, along with the data quality influence on the classifications. In addition, the authors mention the importance of combining techniques to understand deep-sea environments during the last 20 years of research.
In an attempt to better visualize and understand the last two decades in more detail, this section presents the similarity graphs for both these decades, and the word cloud for each year of the last decade. Figure 6 presents the similarity graph for the 2001–2010 decade. From it, is possible to identify word clusters. Geophysical data and sediment data appear, along with several other types of data (e.g., ground truth and video), and serve as the input for classifications. “Classification”, in turn, appear strongly connected to “habitat”. The importance of “multibeam” and “backscatter” is clear. “Remote_sensing” appears with a thin connection within a group that is insufficiently defined, perhaps due the limited applicability.
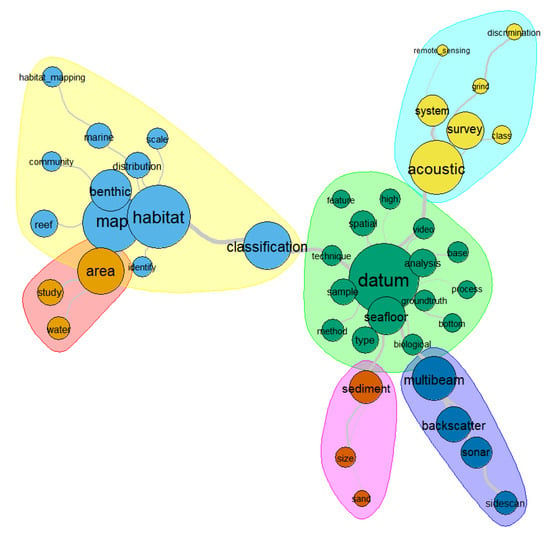
Figure 6.
Graph of the similarity among the more frequent terms in the decade of 2000–2010. Note that colors do not represent a specific similarity value. Colors are used to clearly represent the word clustering. The bigger the word font and the associated circle, the higher is the frequency of appearance of that word. The thickness of the grey roots connecting the words represents the frequency that two words appear close to each other, i.e., the co-occurrence among the words. Thicker roots mean higher frequency.
For the current decade, the similarity graph presented some changes (Figure 7). Based on this clustering, it is possible to observe “datum” playing a central role, which is coherent with technological advances and the increasing availability of data. In such a context, it is also possible to infer an even greater importance of multibeam and backscatter data. In addition, an interesting outcome appeared with a branch cluster including terms such as “model”, “accuracy”, and “percent”.
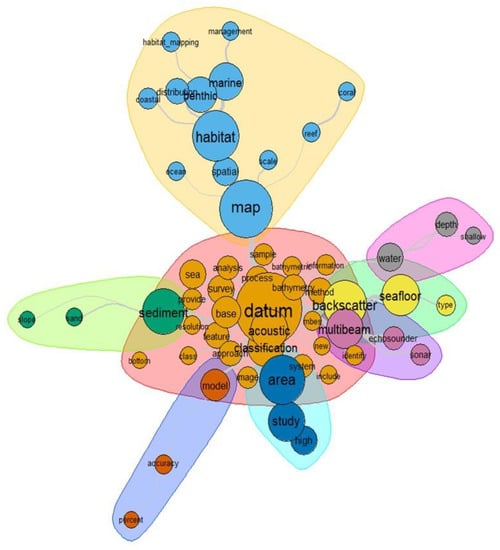
Figure 7.
Graph of the similarity among the more frequent terms in the decade of 2011–2019. Note that colors do not represent a specific similarity value. Colors are used to clearly represent the word clustering. The bigger the word font and the associated circle, the higher is the frequency of appearance of that word. The thickness of the grey roots connecting the words represents the frequency that two words appear close to each other, i.e., the co-occurrence among the words. Thicker roots mean higher frequency.
The following image (Figure 8) shows the word cloud for each year during the last decade. Seeking to optimize the graphic presentation, these word clouds were set to exhibit fewer words.

Figure 8.
Word cloud composition for each year over the last decade.
As expected, the term “datum” was always very present. Based on these word clouds for the last decade, it is also possible to note the almost ever-present word “classification” (exception in 2012). Indeed, the development of classification schemes, which are also related to the word “model”, is strongly associated with the development of classification and segmentation tools (several publications in a special edition of the Geosciences journal in 2017 were dedicated to a geomorphometric theme), such as BTM (Benthic Terrain Modeler), BRESS and RSobia, among other supervised and unsupervised methods. For the last several years, an increase occurred for “accuracy” (2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019), “repeatable” (2017, 2018, and 2019), “multispectral” (2017, 2018, and 2019) and “machine_learning” (2018 and 2019). Once again, “multibeam” and “backscatter”, as well the acronyms “mbes” and “bs”, are important terms and have been consolidated as the most useful data for classification and mapping the seabed [45,46]. Evidence of this is the special edition of the Marine Geophysical Research journal (2018) that was entirely dedicated to seafloor backscatter data.
Furthermore, considering that we are dealing with scientific publication as a metric to understand the evolution of seabed mapping science, it is very important to highlight how academic or professional initiatives may have influenced the number of publications in specific topics. We mention above the GeoHab meetings, which started in 2001 and is associated with a number of journal special issues (e.g., Continental Shelf Research, 2014, Volume 83) [47,48]. It is also worth mentioning the Special Sessions on Seafloor Mapping at the Fall Meeting of the American Geophysics Union and the work of the Submarine Geomorphology Working Group of the International Association of Geomorphologists [21].
In the last two decades, the words “habitat”, “acoustic”, and “map” became the most frequent, together with “datum” (Figure 5). Considering that we have not included conference abstracts in the analysis, it means that these meetings, among others, have highly influenced the seabed mapping scientific community by fomenting a great number of publications. While national seabed mapping programs have also driven this production, these scientific meetings were one of the main forums to discuss future scientific collaborations and progress. Thus, it is crucial to mention that these special meetings and forums shed a light on the importance of global initiatives, to bring together the scientific community; gather young scientists, industry, and governments; and promote scientific publications that can lead to a better understanding of the seabed, providing countless applications.
3.3. Importance, Applicability, and Future Directions of Seabed Mapping
The results and discussions presented above have successfully provided an overview of research concerning seabed mapping. In addition, the importance and the worldwide embracement becomes clear for several fields: hydrography, mineral resource exploration [49], renewable energy, planning and management of MPAs [50], issues related to exclusive economic zones [51,52], marine pollution [53,54], technological research and development [10,55,56,57], oceanographic and multidisciplinary studies [58], fishery resources management [59,60], environmental impact [61], climate changes, and several others applications.
In both editions of Harris and Baker [62,63], authoritative volumes in marine habitat mapping, the importance of seabed mapping for multiple applications and approaches is also clear (mainly for marine spatial planning and marine protected area design in both editions). In addition, the variables/data most often reported on both editions were acoustic backscatter and water depth. Geographically, the concentration of studies observed in western Europe and North America is similar to the UNESCO ocean science metrics [29].
Gathering together some future directions observed in several overviews, it is possible to recognize concordances. Since 2006, mentions occurred of the ability to provide thematic information about the seabed, broad-band sonar, monitoring of water column structure, improvement in autonomous underwater vehicles, data resolution and data visualization issues [64]. It is suitable to emphasize the review of acoustic seabed classification (ASC) [65], which provided some future directions for the ASC field in that year, such as the “statistical × interpretation” issue, sampling resolution and the use of multiple frequencies to improve ASC. Resolution has been a recurrent theme since 1954 [66]—when accuracy was better than 1 in 3000 fathoms—and today has reached the centimetric resolution of synthetic aperture sonar [67]. Both “resolution” and “accuracy” have appeared in the word cloud since 1990 until now, in a way fully concordant with the technological advances.
We believe that future directions for seabed mapping will probably engage increasingly integrated investigations, i.e., we expect further advances based on the great volume of data available and sophisticated classifications (unsupervised approaches, random forest and machine learning) [68]. Moreover, the terms such as “multispectral” and “water column” will probably become more accessible and will contribute to enhance seabed classification. As seabed mapping progresses, terms such as “resolution” and “accuracy” will remain present, as well as the challenge to create a suitable spatial and multiple layers representation, perhaps using virtual reality. In parallel, the technological development of better batteries, as well as the progress on data transfer techniques have potential to contribute with improvements to autonomous data acquisition and data repositories. Also, the use of non-acoustic systems to map shallow waters, such as Lidar in drones, should be widespread in this new decade.
The 2020s decade begins with a major step forward for seabed mapping and the recognition of a major knowledge gap for our planet—a global seabed map with “enough” resolution. All the affirmations previously mentioned in this study underline the need for better global ocean mapping, whilst slightly distorting the history of seabed mapping considering the available technologies. Indeed, there are several technical restrictions when considering gravimetry and satellite methodologies for global seabed mapping, mainly in terms of resolution. The resolution of topographic maps of the moon and other planets, when compared to the ocean seafloor, brings into focus some issues for achieving a seabed map with better resolution: spatial representation of a global map with suitable resolution, technical limitations of remote sensing—electromagnetic methods—due to properties of seawater and high operational cost (financial, temporal, and computational). In Mayer et al. (2018) and Jakobsson et al. (2017) [16,69], perspectives on ocean mapping and a number of challenges for the ambitious target of a full seabed mapping can be found. Considering some assumptions, 967 years were calculated to be necessary for a single survey ship to cover the GEBCO grid area, most of this time—64%—would be required for the shallow areas (0–200 m) [16]. The fact is that less than 20% of our ocean’s floor has been measured so far. The beautiful satellite-derived seafloor global map is biased, inferior to real knowledge of directly (even acoustically) measured ocean depths. The United Nations declaration of the Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–2030) stated that A Map of the Ocean (Digital Atlas) is a research and technology development priority area (R&D Priority Area 1) [70]. In partnership with the UN Decade of the Oceans, the Nippon Foundation—GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project is also crowdfunding for seabed mapping and improving an open source data set of seafloor measurements. The expectation is that this will provide a profound impact on our knowledge of the oceans, our ability to produce better circulation and climate models, to predict habitat distribution, discover new marine landscapes and among others, to improve our planning and management, which is the main goal to achieve a sustainable development of the oceans. We expect that at the end of the decade all of these expectations will also be recorded in the world’s scientific production, and that another major global impact on our knowledge about the ocean seafloor, as happened with the seminal work The Floor of the Oceans by Bruce Heezen and Marie Tharp, strikes the marine geosciences once again.
4. Conclusions
Overall, the use of lexical analysis based on an extensive reference data mining allowed us to determine the evolution of the state of the art in seabed mapping through the scientific literature over almost a century. Seabed mapping started with words indicating exploratory investigations (“ocean”, “interpretation”, “investigation”) and changed to the significant influence of technology in scientific outcomes (echo, side scan, and multibeam) and started to incorporate a more integrated approach, by using terms such as habitat mapping and concepts of seabed classification and backscatter, involving statistical analysis trying to predict biological distributions. The growth of scientific production related to seabed mapping is observed over the decades. It may follow the trend of investments in research, science, and technology but is also related to national and international demands regarding defining the countries’ exclusive economic zones, the interest in marine mineral resource and oil and gas exploitation, marine sites for renewable energy, the need for spatial planning, the scientific challenge of understanding climate variability and tectonics processes, etc.
The range of applications is clear for seabed mapping. The perspective for the 2020 decade is that the scientific production in seabed mapping will follow the new trends, such as technological advances in autonomous or unmanned surface vessels for hydrographic surveys; the application of even more highly advanced statistical modelling and artificial intelligence to predict and automate seabed mapping and the prediction of biodiversity distribution; the use of even higher resolution maps, both in shallow and deep waters to improve spatial marine planning; and, possibly, the most important outcome during this decade would be a high resolution global map of the ocean floor, with an open source data set that will flood the scientific community with data to produce a better understanding of our oceans.
The well-known seafloor map produced by Marie Tharp and Bruce Heezen in the late 1960s influenced generations of marine geoscientists, and the expectations for this decade is to produce a map that will similarly generate a new vision of our ocean seabed morphology, influencing future generations. Based on the set of publications, it was possible to note some methodological trends through the word’s frequency and similarity graphs. The currently observed trend, with repeatable and quantitative methodologies is coherent with that proposed in this review, in which statistical calculations were employed to assess a variable that was essentially qualitative—the words.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3263/10/7/273/s1, S1 is available with the references used for the analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.S.M. and A.C.B.; methodology, P.S.M.; writing—review and editing, P.S.M. and A.C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
A.C.B. is a CNPq Fellow, with a PQ1D scholarship covering the costs of this publication.
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to the Editor and three anonymous reviewers that provided important comments and suggestion to the original manuscript. This is work is a contribution to the Brazilian Marine Geology and Geophysics Program—PGGM, and its importance for the implementation of this scientific realm in Brazil during the past 50 years.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Maury, M.F. The Physical Geography of the Sea; Sampson, Low, Son & Co.: London, UK, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thompson, C.W.; Murray, J. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. “Challenger” during the Years 1873–76 under the Command of Capt. George S. Nares, R.N., F.R.S., and Capt. F.T. Thomson, R.N. Nature 1884, 31, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heezen, B.; Tharp, M. World Ocean Floor. 1977; Library of Congress Geography and Map Division Washington. Available online: http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.gmd/g9096c.ct003148 (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Smith, W.H.F.; Sandwell, D.T. Global sea floor topography from satellite altimetry and ship depth soundings. Science 1997, 277, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherall, P.; Marks, K.M.; Jakobsson, M.; Schmitt, T.; Tani, S.; Arndt, J.E.; Rovere, M.; Chayes, D.; Ferrini, V.; Wigley, R. A new digital bathymetric model of the world’s oceans: New digital bathymetric model. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, R.E.; Geldart, L.P. Exploration Seismology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, M.; Vine, A. Deep-sea measurements without wires or cables. Trans. AGU 1938, 19, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moustier, C. State of the art in swath bathymetry survey systems. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1988, 65, 25–54. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, M.F. Introducing an operational multi-beam array sonar. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1970, 47, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, V.; Allenou, J.-P. SEA BEAM, multi-beam echo-sounding in “Jean Charcot”: Description, evaluation and first results. Int. Hydrogr. Rev. 1979, 1, 35–67. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, H.K. Multibeam bathymetric sonar: Sea beam and hydro chart. Mar. Geod. 1980, 4, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moustier, C. Beyond bathymetry: Mapping acoustic backscattering from the deep seafloor with sea beam. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafe, J.E.; Drake, C.L. Physical properties of marine sediments. Tech. Rep. 1961, 3, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Verlaan, P.A. New seafloor mapping technology and article 76 of the 1982 United Nations convention on the law of the sea. Mar. Policy 1997, 21, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persand, S. A Practical Overview of Article 76 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. 2005, pp. 1–37. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/A-Practical-Overview-of-Article-76-of-the-United-on-Persand/3e7c93ed3ae5216972ab4d303cd10676660cb274 (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Mayer, L.; Jakobsson, M.; Allen, G.; Dorschel, B.; Falconer, R.; Ferrini, V.; Lamarche, G.; Snaith, H.; Weatherall, P. The Nippon Foundation—GEBCO seabed 2030 project: The quest to see the world’s oceans completely mapped by 2030. Geosciences 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, K.; Brooke, B.P.; Harris, P.T.; Siwabessy, P.J.W.; Coffin, M.F.; Tran, M.; Spinoccia, M.; Weales, J.; Macmillan-Lawler, M.; Sullivan, J. Malaysia airlines flight MH370 search data reveal geomorphology and seafloor processes in the Remote Southeast Indian Ocean. Mar. Geol. 2018, 395, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, F.P. Submarine Geology, 3rd ed.; Harper & Raw Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Seibold, E.; Berger, W. The Sea Floor; Springer Textbooks in Earth Sciences, Geography and Environment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, M. Scientists and the Sea, 1650–1900: A Study of Marine Science, 2nd ed.; Ashgate: Aldershot, Hampshire, UK; Brookfield, VT, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Micallef, A.; Krastel, S.; Savini, A. (Eds.) Submarine Geomorphology; Springer Geology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, V. Data science and prediction. Commun. ACM 2013, 56, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, J.M. National geological surveys policies and practice. Resour. Policy 1995, 21, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, K.M.; Koenka, A.C.; Sanchez, C.E.; Moshontz, H.; Cooper, H. Reporting standards for literature searches and report inclusion criteria: Making research syntheses more transparent and easy to replicate: Reporting standards for literature searches. Res. Syn. Meth. 2015, 6, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratinaud, P. IRAMUTEQ: Interface de R Pour Les Analyses Multidimensionnelles de Textes et de Questionnaires. 2009. Available online: http://www.iramuteq.org/ (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Marchand, P.; Ratinaud, P. L’analyse de similitude appliqueé aux corpus textueles: Les primaires socialistes pour l’election présidentielle française. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on the Statistical Analysis of Textual Data (JADT 2012), Liége, Belgium, 13 June 2012; pp. 687–699. [Google Scholar]
- Fruchterman, T.M.J.; Reingold, E.M. Graph drawing by force-directed placement. Softw. Pract. Exper. 1991, 21, 1129–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic habitat mapping: A review of progress towards improved understanding of the spatial ecology of the seafloor using acoustic techniques. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOC/Unesco. The Science We Need for the Ocean We Want: The United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development (2021–2030). 2019. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000261962 (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Kaskela, A.; Kotilainen, A.; Alanen, U.; Cooper, R.; Green, S.; Guinan, J.; van Heteren, S.; Kihlman, S.; Van Lancker, V.; Stevenson, A.; et al. Picking up the pieces—Harmonising and collating seabed substrate data for European Maritime Areas. Geosciences 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl-Mortensen, L.; Buhl-Mortensen, P.; Dolan, M.F.J.; Holte, B. The MAREANO Prog$$ramme—A full coverage mapping of the norwegian off-shore benthic environment and fauna. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetti, F.; Benetti, S.; Fitzpatrick, F. The Irish Seabed Mapping Programme: INFOMAR—Integrated Mapping Survey for the Sustainable Developments of Ireland’s Marine Resources. 2006. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006AGUFMOS31B1634S/abstract (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Lucieer, V.; Barrett, N.; Butler, C.; Flukes, E.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Ingleton, T.; Jordan, A.; Monk, J.; Meeuwig, J.; Porter-Smith, R.; et al. A seafloor habitat map for the Australian continental shelf. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfl, A.-C.; Snaith, H.; Amirebrahimi, S.; Devey, C.W.; Dorschel, B.; Ferrini, V.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Jakobsson, M.; Jencks, J.; Johnston, G.; et al. Seafloor mapping—The challenge of a truly global ocean bathymetry. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, T.; Gillet, H.; Hanquiez, V.; Reijmer, J.J.G.; Droxler, A.W.; Recouvreur, A.; Fabregas, N.; Cavailhes, T.; Fauquembergue, K.; Blank, D.G.; et al. Into the deep: A coarse-grained carbonate turbidite valley and canyon in ultra-deep carbonate setting. Mar. Geol. 2019, 407, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, H.A.; Jamieson, A.J. The five deeps: The location and depth of the deepest place in each of the world’s oceans. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaczek, E.; Devillers, R.; Edinger, E. Generating higher resolution regional seafloor maps from crowd-sourced bathymetry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paisley, J.T.K. Survey of a seapeak in the mozambique channel. Deep Sea Res. 1956, 3, 145–149. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, C.M.; Anderson, C.D. Measurements of backscattering of sound from the ocean bottom. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1964, 36, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damuth, J.E. Echo character of the western equatorial atlantic floor and its relationship to the dispersal and distribution of terrigenous sediments. Mar. Geol. 1975, 18, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Agusti, S.; Barbier, E.; Britten, G.L.; Castilla, J.C.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Hughes, T.P.; Knowlton, N.; Lovelock, C.E.; et al. Rebuilding marine life. Nature 2020, 580, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiuk, B.; Brown, C.J.; Robert, K.; Lacharité, M. Harmonizing multi-source sonar backscatter datasets for seabed mapping using bulk shift approaches. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.J.; Cato, I.; Desprez, M.; Fader, G.; Schüttenhelm, R.T.E.; Side, J. An overview of seabed-mapping technologies in the context of marine habitat classification. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecours, V.; Dolan, M.F.J.; Micallef, A.; Lucieer, V.L. A review of marine geomorphometry, the quantitative study of the seafloor. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3207–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldens, P.; Schulze, I.; Papenmeier, S.; Schönke, M.; Schneider von Deimling, J. Improved interpretation of marine sedimentary environments using multi-frequency multibeam backscatter data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellen, M.; Gaida, T.C.; Koop, L.; Alevizos, E.; Simons, D.G. Performance of multibeam echosounder backscatter-based classification for monitoring sediment distributions using multitemporal large-scale ocean data sets. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 44, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, B.J.; Greene, H.G. Mapping the Seafloor for Habitat Characterization; Geological Association of Canada: Newfoundland, NF, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lurton, X.; Lamarche, G. Backscatter Measurements by Seafloor-Mapping Sonars. Guidelines and Recommendations. 2015. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Backscatter-measurements-by-seafloor-mapping-and-Lurton-Lamarche/792763b9321fe1c0408fc260e8a3e57fd3d0192f (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Wadhawan, S.K. Marine geology and coastal surveys for seabed mapping and mineral resource evaluation in India—An overview. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2016, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, S.; Tonielli, R.; Romagnoli, C.; Budillon, F.; Di Martino, G.; Innangi, M.; Laterza, R.; Le Bas, T.; Lo Iacono, C. Seabed mapping in the Pelagie Islands marine protected area (Sicily Channel, Southern Mediterranean) using Remote Sensing Object Based Image Analysis (RSOBIA). Mar. Geophys. Res. 2019, 40, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, M.; Hill, G.W. Developing a 10-year EEZ seafloor mapping and research program. Mar. Geod. 1988, 12, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.; de Araújo, T.C.M. Survey and assessment of seabed resources from the Brazilian continental shelf by the law of the sea: From national to international jurisdictions. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 178, 104858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, H.A.; Schwab, W.C.; Wright, A.S.C.; Drake, D.E.; Chin, J.L.; Danforth, W.W.; Ueber, E. Acoustic mapping as an environmental management tool: I. detection of barrels of low-level radioactive waste, gulf of the farallones national marine sanctuary, California. Ocean Coast. Manag. 1994, 22, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.J.; Walker, T.R.; Brown, C.J.; Wilson, B.R.; Gazzola, V.; Sameoto, J.A. Benthic marine debris in the bay of fundy, Eastern Canada: Spatial distribution and categorization using seafloor video footage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 150, 110722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H.D.; Rafik, T.A.; Meng, Z.; Cowan, C.F.N.; Shafeeu, H.; Anthony, D.K. Interferometric synthetic aperture sonar for high-resolution 3-D mapping of the seabed. IEEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1997, 144, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglini, F.; Grande, V.; Marchese, F.; Bracchi, V.A.; Prampolini, M.; Angeletti, L.; Castellan, G.; Chimienti, G.; Hansen, I.M.; Gudmundsen, M.; et al. Application of hyperspectral imaging to underwater habitat mapping, Southern Adriatic Sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaida, T.; Tengku Ali, T.; Snellen, M.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.; van Dijk, T.; Simons, D. A multispectral bayesian classification method for increased acoustic discrimination of seabed sediments using multi-frequency multibeam backscatter data. Geosciences 2018, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovane, L.; Hein, J.R.; Yeo, I.A.; Benites, M.; Bergo, N.M.; Corrêa, P.V.F.; Couto, D.M.; Guimarães, A.D.; Howarth, S.A.; Miguel, H.R.; et al. Multidisciplinary scientific cruise to the Rio Grande Rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, F.; Matte, G.; Lerda, O.; Naud, F.; Charlot, D.; Rioblanc, M.; Corbières, C. Scientific potential of a new 3D multibeam echosounder in Fisheries and Ecosystem research. Fish. Res. 2016, 178, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, S.; Bonanno, A.; Tonielli, R.; Innangi, M.; Mazzola, S. High resolution 3-D shapes of fish schools: A new method to use the water column backscatter from hydrographic multibeam echo sounders. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 111, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.; Burnside, N.G. Identification of marine management priority areas using a GIS-based multi-criteria approach. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 172, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.T.; Baker, E.K. GeoHab atlas of seafloor geomorphic features and benthic habitats. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.T.; Baker, E.K. Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat: GeoHAB Atlas of Seafloor Geomorphic Features and Benthic Habitats; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, L.A. Frontiers in seafloor mapping and visualization. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2006, 27, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.T.; Van Holliday, D.; Kloser, R.; Reid, D.G.; Simard, Y. Acoustic seabed classification: Current practice and future directions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luskin, B.; Heezen, B.C.; Ewing, M.; Landisman, M. Precision measurement of ocean depth. Deep Sea Res. (1953) 1954, 1, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegård, Ø.; Hansen, R.E.; Singh, H.; Maarleveld, T.J. Archaeological use of synthetic aperture sonar on deepwater wreck sites in Skagerrak. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2018, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelada Leon, A.; Huvenne, V.A.; Benoist, N.M.; Ferguson, M.; Bett, B.J.; Wynn, R.B. Assessing the repeatability of automated seafloor classification algorithms, with application in marine protected area monitoring. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Allen, G.; Carbotte, S.M.; Falconer, R.; Ferrini, V.; Marks, K. The Nippon Foundation—GEBCO—Seabed 2030: Roadmap for Future Ocean Floor Mapping. 2017. Available online: https://seabed2030.gebco.net/documents/seabed2030 (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Ryabinin, V.; Barbière, J.; Haugan, P.; Kullenberg, G.; Smith, N.; McLean, C.; Troisi, A.; Fischer, A.; Aricò, S.; Aarup, T.; et al. The UN decade of ocean science for sustainable development. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).