Abstract
Soil erosion represents one of the most important global issues with serious effects on agriculture and water quality, especially in developing countries, such as Ethiopia, where rapid population growth and climatic changes affect widely mountainous areas. The Meskay catchment is a head catchment of the Jemma Basin draining into the Blue Nile (Central Ethiopia) and is characterized by high relief energy. Thus, it is exposed to high degradation dynamics, especially in the lower parts of the catchment. In this study, we aim at the geomorphological assessment of soil erosion susceptibilities. First, a geomorphological map was generated based on remote sensing observations. In particular, we mapped three categories of landforms related to (i) sheet erosion, (ii) gully erosion, and (iii) badlands using a high-resolution digital elevation model (DEM). The map was validated by a detailed field survey. Subsequently, we used the three categories as dependent variables in a probabilistic modelling approach to derive the spatial distribution of the specific process susceptibilities. In this study we applied the maximum entropy model (MaxEnt). The independent variables were derived from a set of spatial attributes describing the lithology, terrain, and land cover based on remote sensing data and DEMs. As a result, we produced three separate susceptibility maps for sheet and gully erosion as well as badlands. The resulting susceptibility maps showed good to excellent prediction performance. Moreover, to explore the mutual overlap of the three susceptibility maps, we generated a combined map as a color composite where each color represents one component of water erosion. The latter map yields useful information for land-use managers and planning purposes.
1. Introduction
Erosion is a natural process levelling the relief of the landscape. Its intensity is influenced by weather extremes and environmental conditions. In areas exposed to weather extremes, such as heavy rainfall events followed by dry periods, sheet and gully erosion, as well as Badland formation, could appear. These forms develop due to a complex interplay of driving forces, such as tectonics, the nature of soils, slope characteristics, land cover, and land use, as well as the aforementioned climatic conditions [1]. Ethiopian highlands, in particular, are subjected to huge soil losses with over 1.5 billion tons of topsoil lost yearly [2,3]. The region has been formed by a combination of tectonic uplift and episodic volcanism related to the rift valley formation. Hence the actual landscape shows deeply incised gorges characterized by over-steepened unstable slopes [4,5].
Soil erosion modeling is a promising tool for the identification of erosion-prone areas. Among the available techniques, empirical relationships are considered a good solution to identify the source areas of soil erosion, especially in cases of low data availability [6,7,8].
Physically-based models rely on the solution of fundamental physical equations describing streamflow, sediment fluxes, and associated nutrient fluxes in a catchment [6]. Generally, the large number of parameters involved can only be measured with appropriate quality at the small scale, while, at the catchment or regional scales, they are estimated through best-fit solutions. Therefore, at a large scale, the calibration procedure introduces a bias that depends on the lack of data and on the non-uniqueness of best-fit solutions [6,9,10]. Conceptual models lie somewhere between physically-based and empirical models. They are based on general descriptions of catchment processes. Their calibration is site-specific, and soil mechanical properties and rainfall characteristics are only taken indirectly into account [11]. Many useful insights related to the choice of the most appropriate model can be found in Beven [12] and Sight [13] and references therein.
On the other hand, stochastic approaches proved to be successful for a susceptibility assessment at the catchment and regional scale for water erosion and landslide hazards. Such methods are commonly applied to investigate and model the response of a binary outcome (presence/absence) in relation to a set of independent variables (predictors). Different multivariate statistical approaches have been tested to predict the occurrence of landforms and analyze their relationships with respect to environmental variables [14]. In particular, the most commonly employed approaches are binary logistic regression [15,16,17,18,19], multiple adaptive regression splines [20,21], classification and regression trees [22,23,24], stochastic gradient boosting [25,26,27], and maximum entropy distribution—MaxEnt [28,29,30], which also proved to be successful in transferability studies [31].
Concerning the Ethiopian Highlands, there are several approaches reported in the literature to model soil erosion. Among others, Tilahun et al. (2013) performed a detailed study on the Anjeni catchment (~1.3 km2), which is located at the center of the Blue Nile basin [32]. In particular, they combined a hydrological model with an erosion model to improve sediment concentration distribution; Steenhuis et al. (2009) [33] predicted discharge and sediment for the Abay (Blue Nile). Haregeweyn et al. (2013) predicted the absolute sediment yield and assessed the spatial distribution of erosion in 12 catchments located in Northern Ethiopia [34]. Nyssen et al. (2008) analyzed the evolution of geomorphic processes identifying natural and anthropogenic driving factors, as well as elaborating a sediment budget for the May Zegzeg catchment [35]. Sima et al. (2009) evaluated the mass wasting susceptibility at the regional scale (Jemma river basin) in an area, which includes the northern Meskay catchment by using a scoring system [36].
Photogrammetric approaches were also used to map the gully erosion in southern and northern Ethiopia [37,38]. However, the advantages of stochastic models in assessing the probability of geomorphic processes and their spatial distribution have already been explored for the lower Jemma basin by [39]. Therefore, in this study, we selected the maximum entropy distribution [40] because it is a presence-only (PO) approach and does not suffer from the bias in selecting absence of data at certain locations where they may not be evident [40,41]. Inventories of the geomorphological processes and related forms and features are generally carried out by field works and high-resolution remote sensing [42].
Water erosion, as well as landslide susceptibility studies, mainly apply statistical approaches to predict binary responses. The study cases show that the resulting erosion maps only represent the probability of occurrence of one phenomenon, either gully erosion, sheet erosion, Badlands, or landslides. Since water erosion produces different landforms, the evaluation of single susceptibility maps does not give information on the spatial relationships among the different phenomena. In this regard, a multi-label classification might help to illustrate compound water erosion mechanisms. Multi-label classification approaches are especially used in remote sensing for the identification of, e.g., land-use classes [43], geological or geomorphological mapping. It may be applied following two different approaches: (i) the problem transformation and (ii) the algorithm adaptation. The first transforms the problem into a single-label classification task, while the second extends specific learning algorithms to handle multi-label data [44]. Previous attempts in evaluating the susceptibility of more than one phenomenon have been tested by applying a multi-label classification method with a problem transformation approach [25,28,45]. In particular, the susceptibility was calculated for single classes, and the combined water erosion susceptibility maps are based on a heuristic combination of the binarized susceptibility maps without any information on their relative importance. Other approaches for multi-classification usually employ regression trees or Random forest methods. In particular, Random forest proved to be successful for landform classification [24] and soil erosion [22]. However, regression trees are presence/absence methods that might not be suitable for superficial erosion processes. Differently from the traditional approaches, in this study we assessed soil erosion process susceptibilities applying a presence only algorithm (MaxEnt). Moreover, we propose a combined water erosion map showing the prevalence of each landform in probabilistic terms. Thus, the map might be used as a tool for landscape investigations and geomorphological risk control.
Particularly, we addressed the following three main objectives: (i) the prediction of the spatial occurrence of sheet and gully erosion, as well as Badlands, by integrating remotely sensed data and terrain attributes derived from digital elevation models; (ii) the analysis of the relationships between soil erosion processes and controlling factors; (iii) the prognosis of erosion susceptibilities in a synoptic map.
2. Regional Setting
The Meskay watershed is located in the central part of Ethiopa, in the North of Shewa province (Amhara Region) ca. 130 km Northeast of Addis Ababa close to Debre Sina town (Figure 1). It is situated at 39°43′East and 9°48′North (Figure 1a), 130 km ENE from Addis Ababa. The area covers a surface of about 45 km2, belonging to the bigger Jemma River Basin, one of the main tributaries of the Abay River (Blue Nile) (Figure 1a, b). The Meskay catchment is an important area for agricultural production, and hence, soil conservation is a key issue in the region. In particular, the steep slopes are extensively terraced but exposed to persistent erosion processes due to a strong seasonality of precipitation and frequent heavy rainfall events. Consequently, sophisticated agricultural management is required to maintain agricultural production levels. The Meskay watershed is located in the central part of Ethiopia, in the North of Shewa province (Amhara Region).
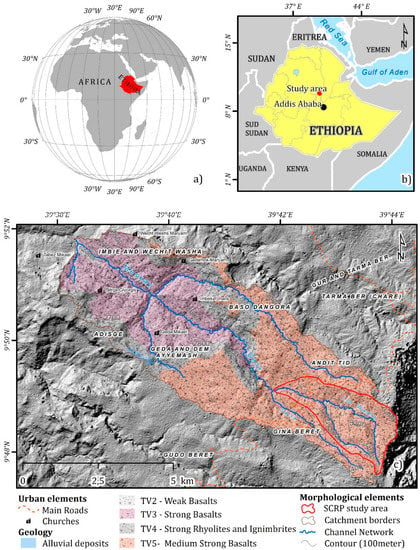
Figure 1.
Location of the study area: (a) Location of the study area in the African continent; (b) Location of the study area in the Ethiopian territory; (c) Andit-Tid bedrock lithotypes and main elements of the study area.
The precipitation regime is characterized by three distinct seasons: the first is a dry season from October to January, the second from February to May is responsible for variable rainfall conditions, while the third is a long rainy season peaking in August. The mean annual rainfall ranges between 1350 and 1800 mm. Single precipitation events exceeding 100 mm are causing intense erosion. The rainfall is influenced by topography and ESE winds [36,46,47]
The geology of the area is represented by a sequence of tertiary volcanic deposits characterized by different geomechanical properties (Figure 1c). The tertiary volcanic (TV) units represent the final product of the second fissure eruption, which took place from the end of Oligocene until the Upper-middle Miocene (25–15 Ma). The sequence starts with basaltic magmas, continues with silica magmas, and ends again with basaltic magmas. The results of such magmatic activity and magma differentiation [48] correspond to differences in mineralogy and geo-mechanical properties, which have been documented by Sima et al. (2009). In particular, the TV2 formation (Middle basalts) is an alternation of highly fractured and weathered lava beds, classified as weak basalts; the TV3 formation (Upper Basalts) is classified as medium–strong, and the TV4 formation is characterized by an alternation of rhyolites and ignimbrites classified as strong. The TV5 formation is the result of a central type of volcanism and is characterized by medium–strong basalts.
The distribution of soils is closely related to the relief forms and characterized by a high variability on the small scale due to strong management (terracing) and lithological heterogeneities [49]. The following dominant soil types occur: humic andosols, fluvisols, regosols, and lithosols. According to the World Reference Base for Soils (WRB)classification, fluvisols and cambisols are highly erodible soils, attributing an erodibility class equal to 5 (in the range from 1 to 6). Stony humic andosols are considered as having very low erodibility. Lithosols and regosols show, instead, a medium erodibility.
Land use is characterized by annual crop production, such as wheat, barley, and tef [49]. The cropping period coincides with the rainy seasons, the Belg and the Kiremt [36,50]. The agricultural activity mainly consists of rain-fed subsistence farming, based on cereals and legumes. Some small patches are covered by eucalyptus plantations periodically harvested to satisfy the wood demand [51]. Apart from the highest eastern part, grasslands are present and scattered within the catchment. During the year, grassland and cropland are often alternated, respectively. The vegetation cover of the area includes sparse patches of bushes. In the last decades, the Ethiopian Highlands have been characterized by intense population growth leading to an increase in agricultural production on an already fragile rural ecosystem. As a consequence, intensified erosion processes caused productivity declines and often result in a population–poverty–land degradation cycle [2,46]. In this regard, the eastern part of the Meskay catchment, known in the literature as Andit Tid, was introduced in the Soil Conservation Research Program of the Ethiopian Government (SCRP) [52] (Figure 1c derived from the SCRP report).
The aforementioned program started with a series of experiments, which included the implementation of soil and water conservation measures (SWC) in 1981–1998. Following this program, several studies have been published dealing with runoff and soil loss estimations in the test area (Figure 1c). It was documented that on the one hand, mechanical SWC produced a reduction in soil loss and runoff, and on the other hand, they caused a reduction in soil productivity. Liu et al. (2008) performed a rainfall discharge analysis and discovered that for rainfall events larger than 500 mm, 50% of the catchment area contributes to the runoff [53]. Engda (2009) analyzed a dataset collected in the framework of the SCRP to investigate runoff sources and to parametrize hydrologic and empirical erosion models. His results clearly show that runoff processes and soil loss are related, and their interplay should be considered when implementing management activities. Guzman et al. (2013) estimated the mean suspended sediment concentration (SSC) with 5.2 t ha−1yr−1 [54]. The SSC shows a seasonal increase until June and a decrease in the rest of the monsoon season. This relatively low mean SSC value a result of the implementation of mechanical SWC measures [49,54]. Tezera et al. (2016) performed a detailed study on land cover change and demonstrated that the area experienced an increase of 11.3% of agricultural land from 1994 to 2014 with a reduction in shrubland of about 7% [55]
Although a decrease in runoff value and soil loss due to the implementation of SWC measures is registered, mass wasting processes are still an important problem in the area. In fact, mechanical SWC cause waterlogging, but these measures have to be accompanied by efficient drainage systems. However, the maintenance of the agricultural terraces and drainage systems is mandatory to reduce soil loss.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geomorphological Mapping
Accurate mapping and quantitative assessment of landforms are a prerequisite to assess the impact of erosion in an area [56]. According to Guzzetti et al. (2012), inventory maps can be produced both using conventional and innovative methods [57]. The first includes field mapping and photointerpretation, and the second refers to mapping operations supported by new methods and technologies, such as multispectral images and high resolution digital elevation model (DEM) analysis [56].
In this study, we mapped and modeled three forms of erosion: (i) sheet erosion, (ii) gully erosion, as well as (iii) Badlands. The term sheet erosion is defined as areal rill and interrill erosion following [58]. This type of erosion especially affects overgrazed and cultivated soils where there is only scarce vegetation protecting the soils. It is generated by a gradual process, which removes the fine soil aggregates and particles containing most of the available nutrients and organic matter because of raindrop impact. When running water flows on the soil surface, at a certain point, the laminar flow becomes turbulent and starts incising in the substrates forming deeper rills. These features are discontinuous and can be removed by tillage actions [59].
Gully erosion occurs when the concentrated flow is large enough to form large channels that cannot be removed by normal tillage operations. Ephemeral gullies appear at the same position on the landscape each year, but they are small enough to be filled in by tillage [60]. Gullies are characterized by periodic runoff and interflow, especially after storm events [59,61].
The term Badlands refers to intensely dissected areas that are difficult to cross and are useless for agriculture [62]. Badlands’ landscapes are characterized by sparse or no vegetation cover, steep slopes, shallow to not-existing regolith mantle, and intensive erosion processes [63].
The difference between the above-mentioned landforms is related to the inconstant morphodynamic conditions on the slopes. In fact, not all landscape positions are equally sensitive to erosion, and when dealing with soil erosion susceptibility, it is important to identify the different sources of sediments within the catchment [64]
Among the innovative methods, automatic and semi-automatic mapping are more and more employed, especially due to the availability of high resolution multispectral remote sensing data [65,66,67,68,69]. However, by now, such methods still suffer from biases. Since this study aims to evaluate the susceptibility to different erosion processes, the inventory has to be as reliable as possible. Therefore, we used conventional consolidated methods, such as field mapping and photointerpretation supported by visual analysis of DEM derived attributes and multispectral images. To produce a complete and reliable soil erosion inventory, the mapping was performed in three phases as proposed and described by Otto and Smith (2013): (i) pre-mapping; (ii) the fieldwork, and (iii) post-mapping [70]. In the pre-mapping phase, information about the study area was collected through the consultation of a topographical map at 1:50.000 scale (Sela Dingay 0939 B1 Ethiopian Mapping agency 1986), geological maps at 1:50,000 scale, remote sensing data from ASTER, Kompsat-2, and RapidEye imagery and high-resolution DEM derived from ALOS/PRISM stereoscopic images. Due to the fact, that the vegetation cover substantially changes between the dry and wet seasons, we acquired two satellite scenes for photointerpretation (01-11-2013 for the dry period and 11-01-2010 regarding the wet period; ©Google Earth). As a first result, a preliminary version of the geomorphological map containing drainage network, lithology, and water erosion landforms was obtained. In this first stage, two types of water erosion processes were distinguished: linear forms (gullies) and areal forms (sheet erosion and Badlands). We wanted to highlight that some of the Badlands close to the riverbanks lie on pre-existing landslides. In this case, we adhered to the Badlands definition of Alexander (1982) keeping in the inventory only the part of landslides characterized by bare soil and high erosion rate [71]
The second phase was based on fieldwork, which was conducted in March 2015. We validated the previously identified landforms in the field, and we identified and mapped other cartographic information, such as geologic limits and land-use changes (Figure 2). In the last step, we produced the final geomorphological map of the Meskay catchment by digitizing and coding the field information.

Figure 2.
Examples of mapped erosional landforms: (a) Gully erosion; (b) Sheet erosion; (c) Badland erosion.
3.2. Explanatory Variables
3.2.1. Remotely Sensed Data
We applied a remote sensing approach to gain further predictors for the stochastic modeling based on the physical properties of the land surface related to lithology, vegetation, and land cover. For a general characterization of land cover and vegetation, we used multispectral satellite data from RapidEye, which is a German satellite system comprising 5 identical sun-synchronous satellites with the first launched in 2008. It has 6.5 m resolution, and it operates at the visible and near-infrared wavelength. We transformed the original dataset of five spectral bands covering visible and near-infrared into three non-correlated principal components (PCA1, PCA2, PCA3). The three components contain most of the variation inherent in the original dataset, which leads to a reduction in input to the stochastic model. Furthermore, we derived the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) using RapidEye red and near-infrared spectral bands.
To characterize lithology from remote sensing data, a sensor also covering the short-wave infrared (SWIR) spectra is required. We used data provided by the Japanese ASTER instrument carried onboard Terra satellite, which is a component of NASA’s Earth Observation program since its launch in 2000. The instrument acquires image data in 14 spectral bands from visible to thermal infrared with spatial resolution ranging from 15 to 90 m. We calculated the ferrous iron index as an arithmetic band ratio of two SWIR bands denoted commonly as B5 and B4 following Cudahy (2012) [72]. This index is useful, especially for the mapping of mafic and ultramafic lithologies rich in ferrous silicates and/or ferrous carbonates.
Additionally, we derived land cover by applying an unsupervised image classification and change detection approach using RapidEye cloud-free multispectral imagery dated 18.01.2010 and 29.11.2013 [73,74]. More in detail, a K-means algorithm was used to group the pixels in clusters on a layer stack of the 2010 RapidEye scene. Subsequently, the land cover clusters were validated through comparison with a second set of images acquired in 2013 and validations during the field campaign in 2015. The final map is representative of the land use for the period 2010/2013 and presents a satisfying accuracy [75,76]. The five land-use classes are described in Table 1. The most important observed feature was the presence of agricultural terraces characterizing the landscape of the northern part of the Meskay catchment. Harvested eucalyptus plantations were detected through the use of the second set of satellite images.

Table 1.
Remote sensing derived attributes.
To facilitate terrain analysis on a sufficiently detailed spatial scale, an image triplet from ALOS/PRISM was processed. ALOS-1 was a Japanese remote sensing satellite for the exploration of natural resources operating from 2006–2011. PRISM is an optical instrument consisting of three panchromatic cameras allowing along-track stereo-scanning of the Earth’s surface in panchromatic mode with a spatial resolution of 1.25 m. An image triplet of the study area acquired by the PRISM instrument in 2008 was processed using stereo-photogrammetric software packages. The resulting DEM contained noisy areas due to low contrast or a lack of homologous features amongst the triplet scenes essential for feature matching. Median filtering was applied to smooth the model surface. The resulting DEM has a pixel size of 10 m and contains detailed morphological features.
3.2.2. Topographic Indices
The effects of water erosion depend on slope position, energy of the relief, and water distribution along the slope. To define the morphological properties of the catchment, a set of 13 topographic predictors were applied in the model, such as elevation (ELEV) together with northness (NORTH) and eastness (EAST). Components of the slope aspect were chosen as indicators of topographic position in turn. They are often used in water erosion or landslide modeling because they are correlated with vegetation and rainfall as well as temperature [20]. The slope steepness (SLO) is related to the relief energy, and together with the catchment area (CAREA), they can be used to discriminate areas susceptible to water erosion ([77], and references therein). Plan curvature (C_CROSS) and longitudinal curvature (C_LONG) indicate the distribution of concavity and convexities, which regulates the overland flow distribution. The topographic wetness index (WETNESS) is a proxy variable directly related to the soil moisture [78]. The topographical indices were calculated using the 10 m DEM using SAGA GIS 2.1.1 [79]. Further details are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
List of digital elevation model (DEM) derived attributes.
3.3. Predictive Modeling Approach
Presence-only methods were developed to model phenomena when the knowledge of their absence is inadequate or unavailable [80]. This is normally the case in soil erosion susceptibility modeling. In fact, depending on the temporary conditions, such as seasonal changes in vegetation cover or agricultural practices, areas exposed to soil erosion can be masked and hence, are hardly recognizable.
The method applied in this research was a presence-only (PO) algorithm called maximum entropy [40,41,80]. The maximum entropy (MaxEnt) is a very popular tool for studies on habitat suitability and environmental modeling, and recently it also has been successfully applied to assess landslides and gully erosion susceptibility [29,30,81]. Its popularity is likely for two reasons: (i) MaxEnt typically outperforms other methods based on predictive accuracy and performance [80,82], (ii) the software is particularly easy to use and is implemented in a statistical software package (dismo).
The MaxEnt algorithm calculates the relative occurrence rate (ROR), which is the relative probability that a cell in the study area belongs to a sample of presence cases as a function of environmental variables ROR and is expressed as:
where z is the vector of the predictors at the location xi, λ is the vector of regression coefficients. Therefore, the above formula can be rewritten as:
where J is the number of predictors at the position xi. Since the denominator is the sum of the RORs values across the dataset, the calculated occurrence rates are normalized, and their sum over the dataset is equal to 1. The probability of presence is then calculated, transforming the ROR in susceptibility by means of a function called logistic output.
The validation process in MaxEnt is performed contrasting the presences with the background locations where the value of presence/absence is unknown. These cases are called pseudo-absences, and they are only selected to sample the set of conditions available in the region under study [82]. Every modification in the pseudo-absence sample size affects the results of the model in terms of the probability distribution, variable selection, and prediction skills.
In this study, the pixels containing, respectively, sheet erosion (11.692), Badlands (11.087), and gullies (22.486) were chosen as samples of presences. Phillips and Dudík (2008) demonstrated that the number of 10,000 background points is enough to ensure the good performance of the models [83]. However, more samples can be requested in case of big presence data samples. In this case, the presence dataset consists of 10.000 samples, so we decided to choose a pseudo-absence sample that is around 5 times larger (35.076 for sheet erosion, 33.261 for Badlands, and 67.458 for gullies) to ensure an efficient calibration of the model. Each dataset was replicated 100 times to evaluate the robustness of the resulting models. We calculated the three final susceptibility models for gullies, sheet erosion, and Badlands as averages of the 100 replicates.
3.4. Model Evaluation
A usual statistical approach for erosion and landslide susceptibility models is to evaluate the models’ results in terms of the predictors’ contribution and prediction skills. The predictors’ contribution refers to the importance and the role of each covariate in the resulting model. It is here evaluated by means of percent contribution (PC), permutation importance (PI), and response curves (RC). The first represents the increase in regularized gain added by each new variable, the second represent the drop in gain due to the permutation of the variables, and the third represents the partial relation between the predictors and the probability of occurrence. The predictors’ contribution analysis is often used to evaluate the geomorphological consistency of the models [27,30,84]. Since the different modeled landforms are driven by different predisposing factors in the present study, it is expected that such difference is highlighted by the predictor contribution analysis.
We validated the accuracy of the predictive performance of the three susceptibility models using two indexes: (i) the receiver operative curves and the corresponding area under the curve (ROC-AUC) as independent threshold indices, and (ii) the sensitivity (TPR) as threshold dependent index.
Since MaxEnt is a presence only (PO) method, the ROC-AUC test indicates how the model separates between presence and background samples containing both presence and absence. Therefore, the ROC-AUC value, in this case, was lower than the one calculated for presence–absence (PA) models. Moreover, its estimation depends on the number of background points chosen for the validation, and, for this reason, the AUC should only be compared in models resulting from the same dataset and comparable sample size [40,41,80,83]. The ROC/AUC test was here calculated 100 times for each model through a cross folded validation procedure in which 80% of the dataset was chosen as calibration and 20% as validation data. For a full interpretation of the resulting susceptibility maps, it is necessary to introduce a probability threshold. Therefore, the 100 ROC-AUC tests were used to calculate the same number of Youden Indices [85], whose average value was used to derive probability thresholds for “Low” and “High” classes of susceptibility. The three contingency tables resulting from the binarization of the susceptibility maps were used to calculate the true positive rate (TPR). The other indexes based on specificity were not used because the background points did not correspond to absence, and their use was not recommended [80].
The three susceptibility maps were finally combined in a layer stack and visualized as an RGB composite. We generated this further map because the visualization of the separate susceptibility maps did not give enough importance to the coalescence of different erosion landforms. Moreover, when two or more landforms were present in the same place, the individual susceptibility maps did not give any information on the prevalence of one phenomenon on the others. This visualization allows for proper identification of areas where a phenomenon prevails on the others and/or where two or more landforms are contemporarily existing.
4. Results
The analysis of erosional forms (Figure 3) revealed that an area of about 11% of the watershed shows erosional processes (~4.5 km2). Among this percentage, gully erosion prevails on the other two landforms covering a total of ~2.25 km2, while the remaining part was almost equally covered by sheet erosion and Badlands.
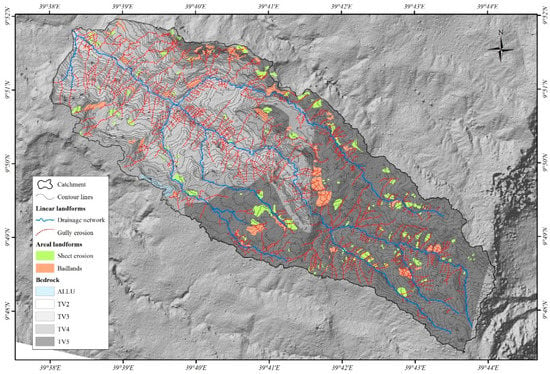
Figure 3.
Water erosion inventory map.
Figure 4 shows the PC and the PI for the three classes of erosion models: Badlands, gully, and sheet erosion. The results show that ELEV highly influences the three models presenting a PC > 20% and a PI > 25%. It is the most important variable for Badlands and sheet erosion models. Gully erosion models are mainly influenced by CAREA (PC = 48%, PC = 42%), which had a low influence in the Badlands models and nearly no influence in sheet erosion models. SLO was the second most influencing variable for Badlands models, and it also had a high influence on gully and sheet erosion models. Land-use (LUSE), NORTH, PCA1, and mineralogic index (FERRSIL) (PI and PC = ~10%) were important for Badlands and sheet erosion models while they did not influence the gully erosion models particularly. The remaining predictors did not contribute significantly to the model.
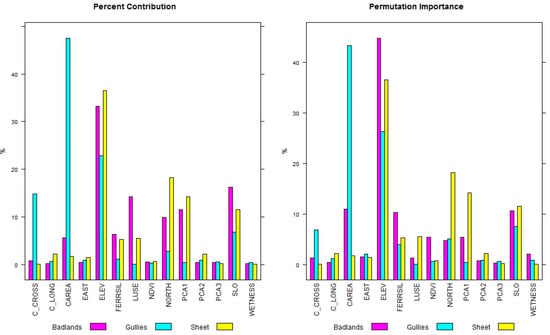
Figure 4.
Variable importance for the three models.
Figure 5 shows the response curves calculated between the predictors and the mean value of the susceptibility for gullies, Badlands, and sheet erosion. In general, the most important predictive variable ELEV had different influences on the three models: it presented a general positive influence for Badlands and sheet erosion and a negative influence for gully erosion. The predictor C_AREA had a different behavior for the three sets of models: a negative influence for sheet erosion models with a positive influence for lower values, which turns into negative ones for gully erosion. It had no relevant response for Badlands. The predictor SLO had a positive influence on Badlands and gully erosion models, while its influence changed from positive to negative in the sheet erosion model for values higher than 0.5 Rad. The predictor FERRSIL had the same positive trend for the three models up to a threshold value of 83. Thereafter, its influence became negative for Badlands, slightly negative for sheet erosion, and slightly positive for gully erosion. The predictor C_CROSS was the variable that showed a higher variability among the three landforms. It had a marked negative influence for gully erosion in the range of −0.03–0 Rad/m, while its distribution did not show an important response for the other two models.
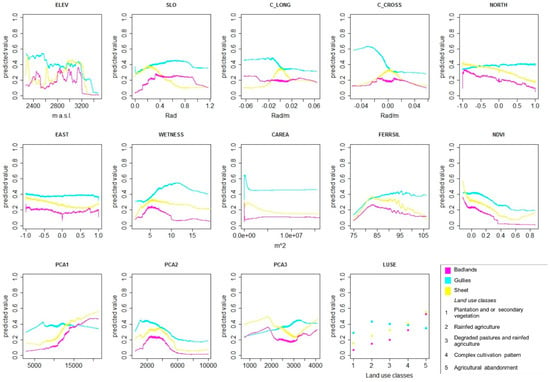
Figure 5.
Response curves for the predictive models for Badlands, gullies, and sheeting.
The distribution of the three susceptibilities in the area reflects the different contributions of the predictors. Figure 6 shows the mean susceptibility values over 100 replicates (Figure 6a, c, e) together with the corresponding ROC/AUC tests calculated in a cross-folded validation procedure. The susceptibility distribution of the gully erosion model reflects a strong influence of the predictor C_AREA: it was higher in the drainage lines and lower in the remaining parts of the slope. It shows good performances both in calibration and validation. The sheet erosion susceptibility distribution was higher on the open slope areas, while the drainage lines showed values close to zero. The results of the cross-folded validation showed AUC > 0.8 for both calibration and validation. The high susceptibility classes for Badland were mainly situated on the highest part of the slopes and in correspondence to the steep river banks. This model presents the best accuracy and prediction skills with AUC = 0.88 in calibration and AUC = 0.87.
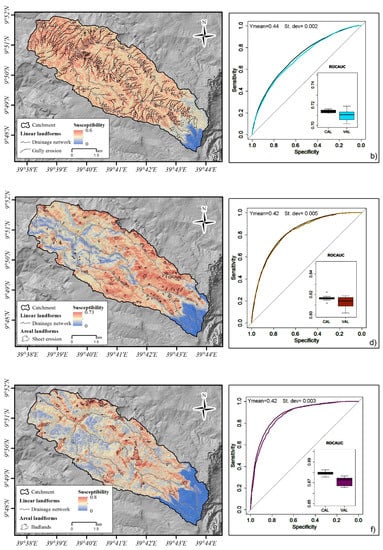
Figure 6.
Susceptibility map and corresponding results of cross folded validation: (a) Mean susceptibility of 100 gully erosion models; (b) receiver operative curves and area under the curve (ROC-AUC) distribution over 100 replicates for gully erosion models; (c) Mean susceptibility of 100 sheet erosion models; (d) ROC-AUC distribution over 100 replicates for sheet erosion models; (e) Mean susceptibility of 100 Badland models; (f) ROC-AUC distribution over 100 replicates for Badlands models.
Figure 7 shows the results of prediction skills evaluated by means of threshold-based indices. In particular, as already mentioned in the previous section, the three susceptibility maps (Figure 6) were binarized using the mean Youden index calculated over the 100 replicates, as represented in Figure 6. In addition, Figure 7 shows the contingency table and three indices: prevalence, sensitivity, and percentage of presence introduced in the model in the first place. Among the three models, the one with the best prediction skill was the Badland susceptibility model presenting a TPR of 0.83, followed by the sheet erosion model with a TPR of 0.76, and the gully erosion model with a TPR of 0.55. In all the cases, the prevalence was remarkably higher than the number of presences introduced in the model. In particular, the presences against the prevalence were from 9% to 27% for the gully erosion model, from 3% to 29% for the sheet erosion model, and from 3% to 24% for the Badlands model.
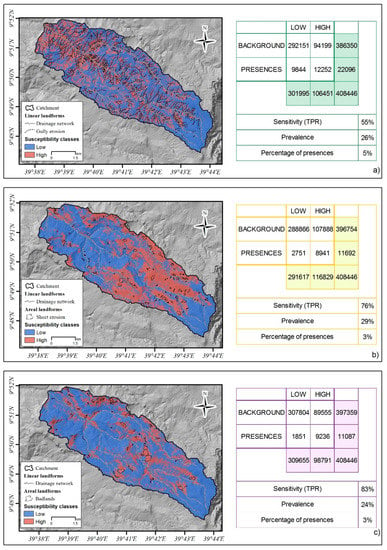
Figure 7.
Binarized susceptibility maps, contingency tables, and threshold dependent indexes of performances: (a) Gully erosion; (b) Sheet erosion; (c) Badlands.
To understand the spatial variability of different erosion phenomena and their mutual overlap, we visualized all three susceptibilities as components of an RGB composite. We followed the approach of Kropacek et al. (2010), who proposed RGB synthesis as an effective visualization tool for the analysis of snow cover distribution [86]. The susceptibility values exceeding the Youden index threshold were visualized in an RGB image without any contrast manipulation to preserve the true relations among the three susceptibility values. An inversion of susceptibility values was applied to improve an intuitive perception, where black represents a susceptibility of 100% in all three components. Areas with low susceptibilities in the range of 0% to 40% are regarded as areas not susceptible to water erosion and are shown in white. As a result of the inversion, the three components are represented in complementary colors (CMY) and combinations of two components in RGB colors (see the legend in Figure 8). A decrease in susceptibility is then represented by a higher brightness and saturation of a certain hue, which is given by a combination of the two components, whereas high susceptibilities are shown in dark colors. The advantage of this visualization approach is an integrated representation of all three components of water erosion in a single image allowing the study of their spatial relationships and distribution.
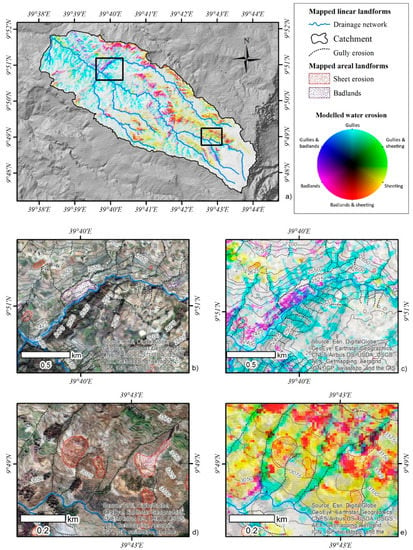
Figure 8.
Water erosion model: (a) combined water erosion susceptibility map; (b) Zoom of the water erosion inventory in area A; (c) Zoom of the combined susceptibility model in area A; (d) Zoom of water erosion inventory in area B; (e) Zoom of the combined susceptibility model in area B.
Figure 8 illustrates that gullying, when present, was the principal water erosion mechanism in the study area. It was only associated with Badlands in correspondence with riverbanks in the north-eastern part of the catchment (Figure 8b, c). The prevalence of red color in the image shows that areal phenomena (Badlands and sheet erosion) were mostly coalescent, and discrimination was barely possible (Figure 8d, e). The remaining combinations, gullies and Badlands or gullies and sheet erosion, were rare, which corresponds well to the fact that different terrain, substrate, and vegetation settings were predisposing these phenomena. The white color close to the water divide (southeast part of the study area) shows a large area of no susceptibility. This is likely due to a combination of lower slope inclination, the presence of grassland as vegetation cover, as well as small contribution areas.
5. Discussion
Most predictors used in this study describing terrain or surface properties rely on high-resolution remote sensing data. Apart from the land cover based on the clustering of a multispectral dataset, we used non-categorized data, which limits the bias introduced by an arbitrary setting of thresholds or the selection of a limited number of abstract classes. This approach is also less laborious and benefits from the use of continuous ranges rather than discrete variables [87].
The present study demonstrates that MaxEnt is suitable for the evaluation of water erosion susceptibility and produced models with satisfying accuracy and predictive performances. The differences among the three susceptibility models reflected the different dynamics and evolution stages of gullying, sheet erosion, and Badlands. The differences were analyzed based on the relationships between variables and susceptibilities and were related to predictive performances.
The analysis of the PC and PI showed that the main controlling factors change by modeling different phenomena. In particular, gully erosion was mainly controlled by topographic variables (C_AREA, ELEV, C_CROSS, and SLO). Differently, the Badlands and sheet erosion models were primarily influenced by ELEV and SLO, but also by anthropogenic activities (LUSE), type of soil (whose proxy is represented by PCA1), and lithology (FERRSIL).
The response curves also highlighted differences in the structure of the three models. The trends of morphologic variables (ELEV, SLO, CAREA, C_CROSS) were very different among the three models. On the other hand, Badlands and sheet erosion models shared some similarities in the LUSE, FERRSIL, and PCA1 responses, which were not relevant for gully erosion. The geomorphological interpretation of such behavior is that the gully erosion develops in very specific morphological contexts, which can be mainly identified with catchment area, elevation, and slope curvature. Sheet erosion and Badlands are similarly related to land-use conditions, type of soil, and lithology, but they develop in different morphological contexts.
The prediction skills of the three models were evaluated using ROC-AUC and sensitivities. The results showed that sheet erosion and Badlands susceptibility models are characterized by excellent AUC both in calibration and validation. On the other hand, the ROC/AUC of the gully erosion model is limited to good predictive performances and is able to predict only 55% of the positive cases. These results seem to be anomalous if we consider that the predictor importance gives geomorphological interpretable results. In the opinion of the authors, the drop in prediction skills of the gully model is related to different evolution mechanisms of this landform: one is mainly connected to a natural geomorphological evolution, while the other evolves as a consequence of dynamic anthropogenic activity [88], such as changes in land-use and animals’ passage. Although proxy variables of land-use were used, no proxies of animal migration or land-use changes were introduced into the models, and, therefore, the results were affected by a drawback in predictive performances. This interpretation also agrees with the findings of Nyssen et al. (2008), who identified human-induced environmental changes as the main cause of gully development in the Ethiopian Highlands [35].
Another important point regards the possible use of the susceptibility maps for the prediction of landscape evolution. In Figure 7, the percentage of the area affected by water erosion was compared to the prevalence (percentage of the susceptible area). In particular, according to our inventory, the areas mapped as water erosion features (gullies and sheet erosion as well as Badlands) represent ~15% of the total catchment area. The calculated highly susceptible areas were 27%, 29%, and 24%, respectively, for gullies, sheet erosion, and Badlands. This result cannot be considered intrinsically as predictive scenarios for landscape evolution. However, they should be taken into consideration when planning SWC measures and their respective maintenance.
The final integrative water erosion susceptibility map illustrates a combination of the three different susceptibility maps. To the knowledge of the authors, it is the first time this visualization method has been applied for a susceptibility map of water erosion. In fact, the combination of binarized maps proposed by Lombardo et al. (2018) and Angileri et al. (2016) offers the main advantage of being clearly legible because it shows only a limited number of susceptibility classes [25,81]. On the other hand, classifying susceptibility maps introduces biases because the threshold method might be arbitrary. Moreover, when combining high susceptible classes, it is not possible to identify which erosion mechanism prevails on the other. The map attached here overcomes these problems. In fact, no bias due to thresholds are introduced, and complex situations with coalescent and overlapping phenomena are shown in a range of continuous values corresponding to the prevalent mechanism.
6. Conclusions
The present study demonstrates that MaxEnt is a suitable model to assess water erosion susceptibilities. Moreover, it allowed the production of models with satisfying accuracy and predictive performances. The differences among the three susceptibility models reflected the different dynamics and evolution stages of gully erosion, sheet erosion, and Badlands. These differences were analyzed concerning the relationships between variables and susceptibility as well as concerning the predictive performances. The Maximum Entropy model was successfully applied to evaluate single susceptibility maps for gullies, sheet erosion, and Badlands using a set of predictors derived from high-resolution remotely sensed data. The three single susceptibility maps were integrated into a combined map, illustrating the spatial probability of occurrence of the three phenomena using a continuous scale.
We show that the true color composite of the water erosion models is a suitable tool to identify target areas to apply and focus soil conservation measures. Moreover, it constitutes a possible landscape evolution scenario, which can be useful in further studies aimed at evaluating soil erosion hazard and risk, especially in the light of climate change.
Most predictors used in this study, whether those describing terrain or surface properties, rely on high-resolution remote sensing data. Apart from the land cover based on the clustering of multispectral datasets, we used non-categorized data, which limits the bias introduced by the arbitrary setting of thresholds or selection of a limited number of abstract classes. This approach is also less laborious and benefits from the use of continuous ranges rather than discrete variables. Our results demonstrate that the utilization of predictors derived from high-resolution satellite data, such as ALOS/PRISM and RapidEye, allows for proper modeling of water erosion susceptibilities at a detailed scale, such as small drainage basins. Susceptibility maps at such scale may be helpful for planning concerted erosion prevention measures, which might result in a higher effectivity and lower costs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C., C.S., and M.M.; methodology, M.C., C.S., and M.M.; software, M.C., C.S., and J.K.; validation, M.C., C.S. and M.M.; formal analysis, M.C. and C.S.; Field investigation, C.S., J.K., and M.M.; resources, C.S., M.M., and V.H.; data curation, C.S., M.C., and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and C.S.; writing—review and editing, C.S., M.C., V.H., J.K., M.M.; project administration, V.H, M.M.; funding acquisition, M.M., C.S. and V.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We would like to thank the Germany Research Foundation (DFG) for financing the project entitled: “Integrated assessment of geomorphological process dynamics on different spatio-temporal scales in the Ethiopian Highlands using remote sensing and advanced modelling approaches” (Project No HO 1840/11-1). Moreover, we would like to thank the ROCEEH project financed by the Heidelberg Academy of Sciences and Humanities for traveling support. The University of Tübingen provided lab and computing facilities.
Acknowledgments
RapidEye imagery was obtained by the grant RESA-ID 131 Title: Integrated assessment of geomorphological process dynamics on different spatio-temporal scales in the Ethiopian Highlands using remote sensing and advanced modelling approaches. Finally, we would like to thank also the FLUMEN project (EU Marie Curie Programme; PIRSES-GA-2012-318969) for supporting researcher exchanges.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bosino, A.; Omran, A.; Märker, M. Identification, characterisation and analysis of the Oltrepo Pavese calanchi in the Northern Apennines (Italy). Geomorphology 2019, 340, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamene, L.; Vlek, P.L.G. Soil Erosion Studies in Northern Ethiopia. In Land Use and Soil Resources; Braimoh, A.K., Vlek, P.L.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 73–100. ISBN 978-1-4020-6778-5. [Google Scholar]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Haregeweyn, N.; Parsons, T. Environmental change, geomorphic processes and land degradation in tropical highlands. Catena 2008, 75, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusák, M.; Kropáček, J.; Vilímek, V.; Scillaci, C. Analysis of the influence of tectonics on the evolution of valley networks based on SRTM DEM, Jemma River basin, Ethiopia. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2016, 1, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropacek, J.; Vařilová, Z.; Baroň, I.; Bhattacharya, A.; Eberle, J.; Hochschild, V. Remote Sensing for Characterisation and Kinematic Analysis of Large Slope Failures: Debre Sina Landslide, Main Ethiopian Rift Escarpment. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16183–16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, W.; Letcher, R.; Jakeman, A.J. A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 761–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Dietrich, W.E.; Bonfini, L.; Karlovich, C.; Dasgupta, C.; Banerjee, U. Channel Initiation and the Problem of Landscape Scale. Science 1992, 255, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, A.N.; Ahmadi, H.; Jafari, M.; Boggs, G.; Ghoddousi, J.; Malekian, A. Geomorphic threshold conditions for gully erosion in Southwestern Iran (Boushehr-Samal watershed). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.B. Water quality modeling: A review of the analysis of uncertainty. Water Resour. Res. 1987, 23, 1393–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, H.S.; Jakeman, A.J.; Beven, K.J. Progress and directions in rainfall-runoff modelling. In Modelling Change in Environmental Systems; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1993; pp. 101–132. ISBN 0-471-94263-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sorooshian, S. Parameter Estimation, Model Identification, and Model Validation: Conceptual-Type Models. In Recent Advances in the Modeling of Hydrologic Systems; Bowles, D.S., O’Connell, P.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 443–467. ISBN 978-94-011-3480-4. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, K. How to make advances in hydrological modelling. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Hydrologic modeling: Progress and future directions. Geosci. Lett. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Acosta, A.; Chu, M.L.; Guzman, J.A.; Starks, P.J.; Moriasi, D.N. Riparian erosion vulnerability model based on environmental features. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Massari, R. Generalised linear modelling of susceptibility to landsliding in the central Apennines, Italy. Comput. Geosci. 1998, 24, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, M.; Lombardo, L.; Conoscenti, C.; Agnesi, V.; Rotigliano, E. Predicting storm-triggered debris flow events: Application to the 2009 Ionian Peloritan disaster (Sicily, Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1785–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, M.; Conoscenti, C.; Lombardo, L.; Rotigliano, E. Exploring relationships between grid cell size and accuracy for debris-flow susceptibility models: A test in the Giampilieri catchment (Sicily, Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, J.; Brenning, A.; Petschko, H.; Leopold, P. Evaluating machine learning and statistical prediction techniques for landslide susceptibility modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Mondini, A.C.; Peruccacci, S. Optimal landslide susceptibility zonation based on multiple forecasts. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conoscenti, C.; Rotigliano, E.; Cama, M.; Arias, N.A.C.; Lombardo, L.; Agnesi, V. Exploring the effect of absence selection on landslide susceptibility models: A case study in Sicily, Italy. Geomorphology 2016, 261, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.G.; Conoscenti, C.; Angileri, S.E.; Rotigliano, E.; Schnabel, S. Using topographical attributes to evaluate gully erosion proneness (susceptibility) in two mediterranean basins: Advantages and limitations. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märker, M.; Pelacani, S.; Schröder, B.; Märker, M. A functional entity approach to predict soil erosion processes in a small Plio-Pleistocene Mediterranean catchment in Northern Chianti, Italy. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.G.; Schnabel, S.; Contador, F.L. Using and comparing two nonparametric methods (CART and MARS) to model the potential distribution of gullies. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3630–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Hurni, L. Random Forest with semantic tie points for classifying landforms and creating rigorous shaded relief representations. Geomorphology 2014, 224, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angileri, S.E.; Conoscenti, C.; Hochschild, V.; Märker, M.; Rotigliano, E.; Agnesi, V.; Märker, M. Water erosion susceptibility mapping by applying Stochastic Gradient Treeboost to the Imera Meridionale River Basin (Sicily, Italy). Geomorphology 2016, 262, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, C.; Lombardo, L.; Saia, S.; Fantappiè, M.; Märker, M.; Acutis, M. Modelling the topsoil carbon stock of agricultural lands with the Stochastic Gradient Treeboost in a semi-arid Mediterranean region. Geoderma 2017, 286, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Cama, M.; Conoscenti, C.; Marker, M.; Rotigliano, E. Binary logistic regression versus stochastic gradient boosted decision trees in assessing landslide susceptibility for multiple-occurring landslide events: Application to the 2009 storm event in Messina (Sicily, southern Italy). Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1621–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Bachofer, F.; Cama, M.; Märker, M.; Rotigliano, E. Exploiting Maximum Entropy method and ASTER data for assessing debris flow and debris slide susceptibility for the Giampilieri catchment (north-eastern Sicily, Italy). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 1776–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakerinejad, R.; Märker, M. Prediction of gully erosion susceptibility using detailed terrain analysis and Maximum Entropy Modeling: A case study in the Mazayejan plain, Southwest Iran. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2014, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerker, M.; Bosino, A.; Scopesi, C.; Giordani, P.; Firpo, M.; Rellini, I. Assessment of calanchi and rill-interrill erosion susceptibility in northern Liguria, Italy: A case study using a probabilistic modelling framework. Geoderma 2020, 371, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, J.; Ujanen, J.; Parviainen, M.; Tolgensbakk, J.; Etzelmüller, B. Transferability of geomorphological distribution models: Evaluation using solifluction features in subarctic and Arctic regions. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.A.; Guzman, C.D.; Zegeye, A.D.; Engda, T.A.; Collick, A.S.; Rimmer, A.; Steenhuis, T.S. An efficient semi-distributed hillslope erosion model for the subhumid Ethiopian Highlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhuis, T.S.; Collick, A.S.; Easton, Z.M.; Leggesse, E.S.; Bayabil, H.K.; White, E.; Awulachew, S.B.; Adgo, E.; Ahmed, A.A. Predicting discharge and sediment for the Abay (Blue Nile) with a simple model. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Poesen, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Govers, G.; De Vente, J.; Nyssen, J.; Deckers, J.; Moeyersons, J. Assessing the performance of a spatially distributed soil erosion and sediment delivery model (watem/sedem) in northern ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 24, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Moeyersons, J.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J. Dynamics of soil erosion rates and controlling factors in the Northern Ethiopian Highlands—Towards a sediment budget. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, J. Water Resources Management and Nvironmental Protection Studies of the Jemma Basin River for Improved Food Security; AcquaTest: White Lake, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kropáček, J.; Schillaci, C.; Salvini, R.; Märker, M. GFDQ—Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria 039_2_06_2016. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat. 2016, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Stal, C.; Abraha, A.; Nyssen, J.; Rieke-Zapp, D.; De Wulf, A.; Jean, P. Detailed recording of gully morphology in 3D through image-based modelling. Catena 2015, 127, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märker, M.; Hochschild, V.; Maca, V.; Vilímek, V. Stochastic assessment of landslides and debris flows in the Jemma Basin, Blue Nile, Central Ethiopia. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2016, 39, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Graham, C.H.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Ferrier, S.; Guisan, A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Huettmann, F.; Leathwick, J.R.; Lehmann, A.; et al. Novel methods improve prediction of species’ distributions from occurrence data. Ecography 2006, 29, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerker, M.; Schillaci, C.; Melis, R.T.; Kropáček, J.; Bosino, A.; Vilímek, V.; Hochschild, V.; Sommer, C.; Altamura, F.; Mussi, M. Geomorphological processes, forms and features in the surroundings of the Melka Kunture Palaeolithic site, Ethiopia. J. Maps 2019, 15, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachofer, F.; Quénéhervé, G.; Hochschild, V.; Maerker, M. Multisensoral Topsoil Mapping in the Semiarid Lake Manyara Region, Northern Tanzania. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9563–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyromitros-Xioufis, E.; Groves, W. Multi-Label Classification Methods for Multi-Target Regression. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1211.6581. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, L.; Fubelli, G.; Amato, G.; Bonasera, M. Presence-only approach to assess landslide triggering-thickness susceptibility: A test for the Mili catchment (north-eastern Sicily, Italy). Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 565–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, G. Land Degradation, Famines and Resource Scenarios in Ethiopia. In. World Soil Erosion and Conservation; Pimentel, D., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 27–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw, B. Resource degradation and adoption of land conservation technologies in the Ethiopian Highlands: A case study in Andit Tid, North Shewa. Agric. Econ. 1998, 18, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanettine, B.; Justine-Visentine, E.; Piccirillo, E.M. Volcanic Succession, Tectonics and Magmatologyin Central Ethiopia; Istituto di Mineralogia e Petrologia, Universitá degli Studi di Padova: Padua, Italy, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Meshesha, D.T.; Schütt, B.; Adgo, E.; Tegegne, F. Soil erosion and conservation in Ethiopia. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2015, 39, 750–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engda, T.A. Modeling Rainfall, Runoff and Soil Loss Relationships in the Northeastern Highlands of Ethiopia, Andit Tid Watershed. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yitaferu, B.; Abewa, A.; Amare, T. Expansion of Eucalyptus Woodlots in the Fertile Soils of the Highlands of Ethiopia: Could It Be a Treat on Future Cropland Use? J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, H. Area of Andit Tid, Shewa, Ethiopia: Long-Term Monitoring of the Agricultural Environment 1982–1994; SCRP (Soil Conservation Research Programme): Shewa, Ethiopia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.M.; Collick, A.S.; Zeleke, G.; Adgo, E.; Easton, M.Z.; Steenhuis, T.S. Rainfall-discharge relationships for a monsoonal climate in the Ethiopian highlands. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 2274, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweg, K.; Ludi, E. The performance of selected soil and water conservation measures—case studies from Ethiopia and Eritrea. Catena 1999, 36, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezera, A.; Chanie, T.; Feyisa, T.; Jemal, A. Impact Assessment of Land Use/ Land Cover Change on Soil Erosion and Rural Livelihood in Andit Tid Watershed, North Shewa, Ethiopia. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2016, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, F.; Ardizzone, F.; Rossi, M.; Torri, D. The use of stereoscopic satellite images to map rills and ephemeral gullies. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14151–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Cardinali, M.; Fiorucci, F.; Santangelo, M.; Chang, K.T. Landslide inventory maps: New tools for an old problem. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 112, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerswald, K.; Schmidt, F. Atlas der Erosionsgefährdung in Bayern--Karten zum flächenhaften Bodenabtrag durch Regen.--GLA-Fachberichte 1; Bayer. Geol. Landesamt (Hrsg.): München, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, M.J. Hillslope Materials and Processes, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; ISBN 9780198741831. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, D.E.; Pritchard, H.W. Resource conservation glossary. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1976, 31, 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, C.G.; Coates, D.R. (Eds.) Groundwater Geomorphology: The Role of Subsurface Water in Earth-surface Processes and Landforms; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1990; Volume 252. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbridge, R.W. The Encyclopedia of Geomorphology. Rhodes W. Fairbridge, Ed. Reinhold, New York, 1968. xvi + 1296 pp.,. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series, vol. 3. Science (80-. ) 1969, 165, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.D. Badland Morphology and Evolution: Interpretation Using a Simulation Model. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 1997, 22, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A.; Collins, R. Predicting erosion and sediment yield at the catchment scale. In Soil Erosion at Multiple Scales: Principles and Methods for Assessing Causes and Impacts; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1998; pp. 317–342. [Google Scholar]
- Mondini, A.C.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P.; Rossi, M.; Cardinali, M.; Ardizzone, F. Remote Sensing of Environment Semi-automatic recognition and mapping of rainfall induced shallow landslides using optical satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; Jetten, V.; Van Westen, C.J.; Kumar, K.V. Geomorphology Characterising spectral, spatial and morphometric properties of landslides for semi-automatic detection using object-oriented methods. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curzio, S.L.; Magliulo, P. Soil erosion assessment using geomorphological remote sensing techniques: An example from Southern Italy. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatorre, L.C.; Beguería, S. Identification of eroded areas using remote sensing in a badlands landscape on marls in the central Spanish Pyrenees. Catena 2009, 76, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desprats, J.F.; Raclot, D.; Rousseau, M.; Cerdan, O.; Garcin, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Ben Slimane, A.; Fouche, J.; Monfort-Climent, D. Mapping Linear Erosion Features Using High And Very High Resolution Satellite Imagery. L. Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, J.-C.; Smith, M.J. Geomorphological mapping. Geomorphol. Tech. 2013, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Difference between ‘Calachi’ and ‘Biancane’ Badlands in Italy. In Badland Geomorphology and Piping; Geo Abstracts: Norwich, UK, 1982; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cudahy, T. Satellite ASTER Geoscience Product Notes for Australia; Report Number EP-30-07-12-44. 2012. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.700.1754&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Tapsall, B.; Milenov, P.; Tasdemir, K. Analysis of Rapideye Imagery for Annual Landcover Mapping As an Aid To European Union ( Eu ) Common Agricultural Policy. 100 Years ISPRS - Adv. Remote Sens. Sci. 2010, XXXVIII, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Landa, A.; Algeet-Abarquero, N.; Fernández-Moya, J.; Guillén-Climent, M.; Pedroni, L.; García, F.; Espejo, A.; Villegas, J.F.; Marchamalo, M.; Bonatti, J.; et al. An Operational Framework for Land Cover Classification in the Context of REDD+ Mechanisms. A Case Study from Costa Rica. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruki, H.M.; Zanden, E.H.; Malek, Ž.; Verburg, P.H. Land Cover Change and Woodland Degradation in a Charcoal Producing Semi-Arid Area in Kenya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, D.; Poesen, J. A review of topographic threshold conditions for gully head development in different environments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 130, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, C.; Braun, A.; Kropáček, J. 2.4.2. Terrain Analysis and Landform Recognition; Geomorphological Techniques (Online Edition); British Society for Geomorphology: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 2047-0371. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merow, C.; Smith, M.J.; Silander, J.A. A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: What it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography (Cop.) 2013, 36, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Mai, P.M. Presenting logistic regression-based landslide susceptibility results. Eng. Geol. 2018, 244, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, J. Article Sample selection bias and presence-only distribution models: Implications for background and pseudo-absence data Reference Sample selection bias and presence-only distribution models: Implications for background and pseudo-absence data. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M. Modeling of species distribution with Maxent: New extensions and a comprehensive evalutation. Ecograpy 2008, 31, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorpahl, P.; Elsenbeer, H.; Märker, M.; Schröder, B. How can statistical models help to determine driving factors of landslides? Ecol. Modell. 2012, 239, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropacek, J.; Feng, C.; Alle, M.; Kang, S.; Hochschild, V. Temporal and spatial aspects of snow distribution in the Nam Co Basin on the Tibetan Plateau from MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2700–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, N.; Foresti, L.; Robert, S.; Leuenberger, M.; Pedrazzini, A.; Jaboyedoff, M.; Kanevski, M. Machine Learning Feature Selection Methods for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping. Math. Geosci. 2014, 46, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnia, A.; Darabi, H.; Choubin, B.; Omidvar, E.; Onyutha, C.; Haghighi, A.T. Contribution of climatic variability and human activities to stream flow changes in the Haraz River basin, northern Iran. J. Hydro-environment Res. 2019, 25, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).