Ground-Penetrating Radar Survey for the Study of the Church of Saint Cosma in Helerito (Tagliacozzo, L’Aquila, Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Site, Material, and Methods
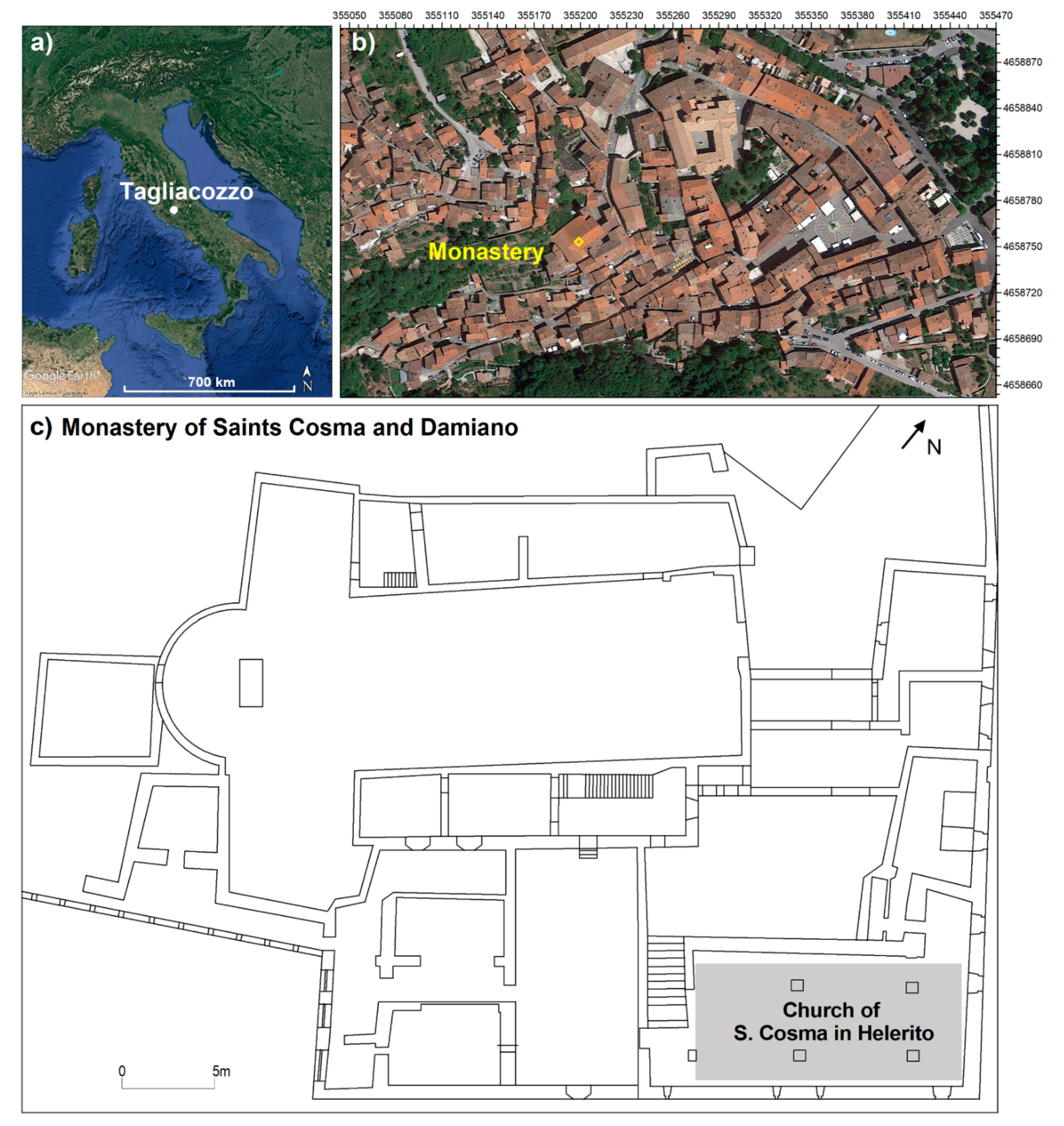
2.1. Test Site
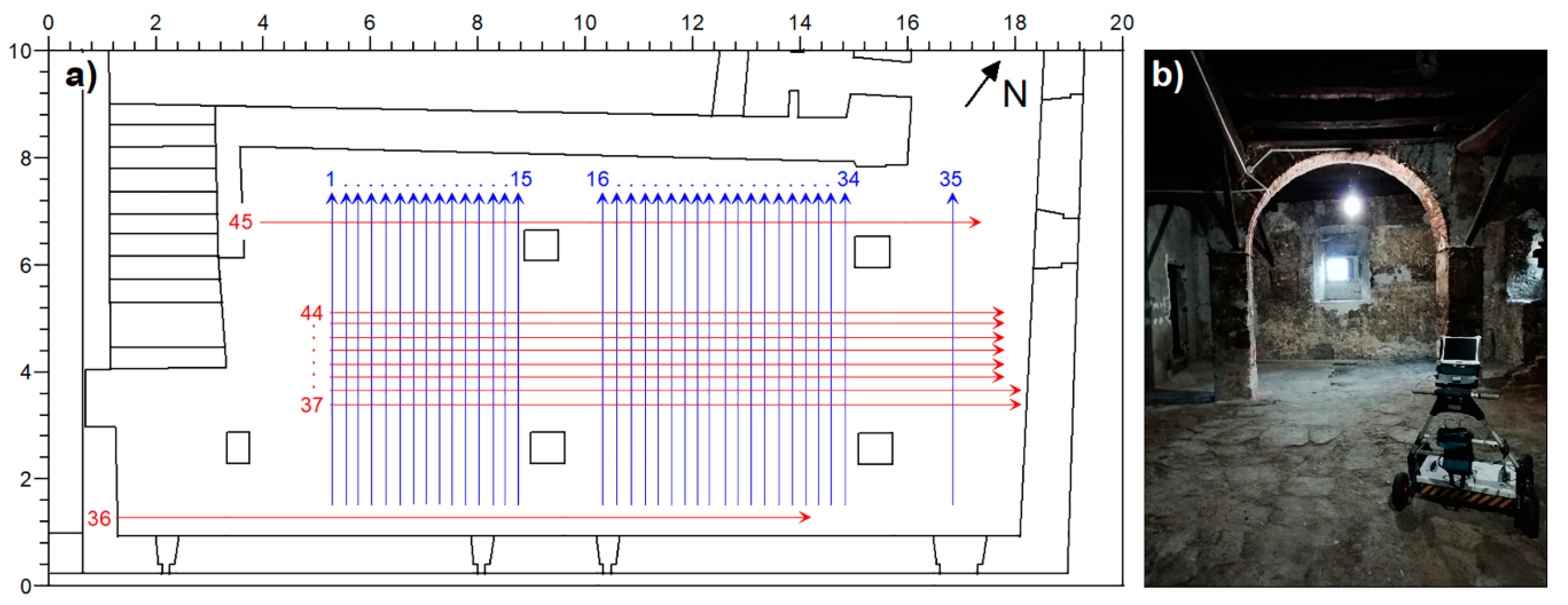
2.2. Materials and Methods
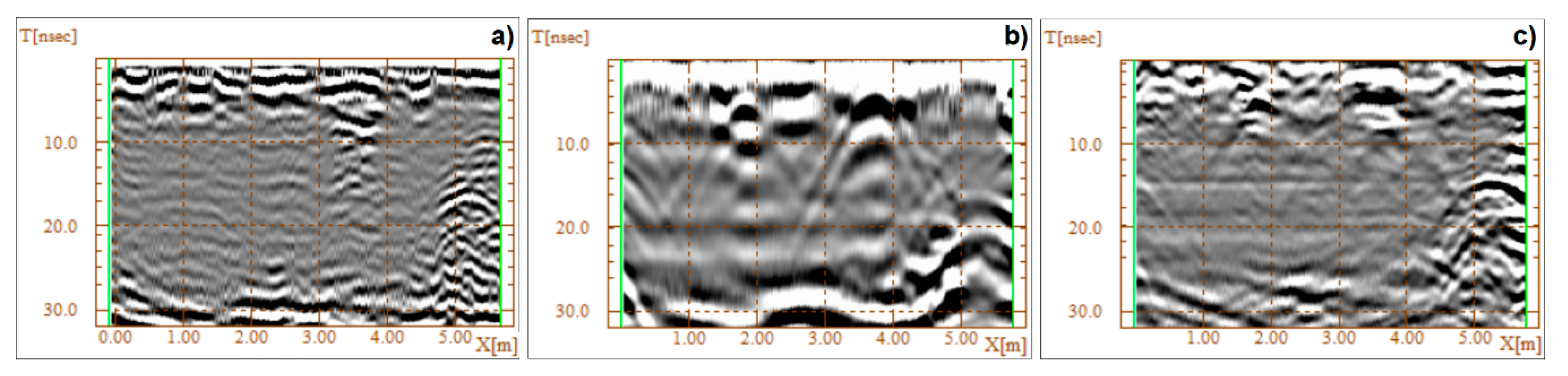
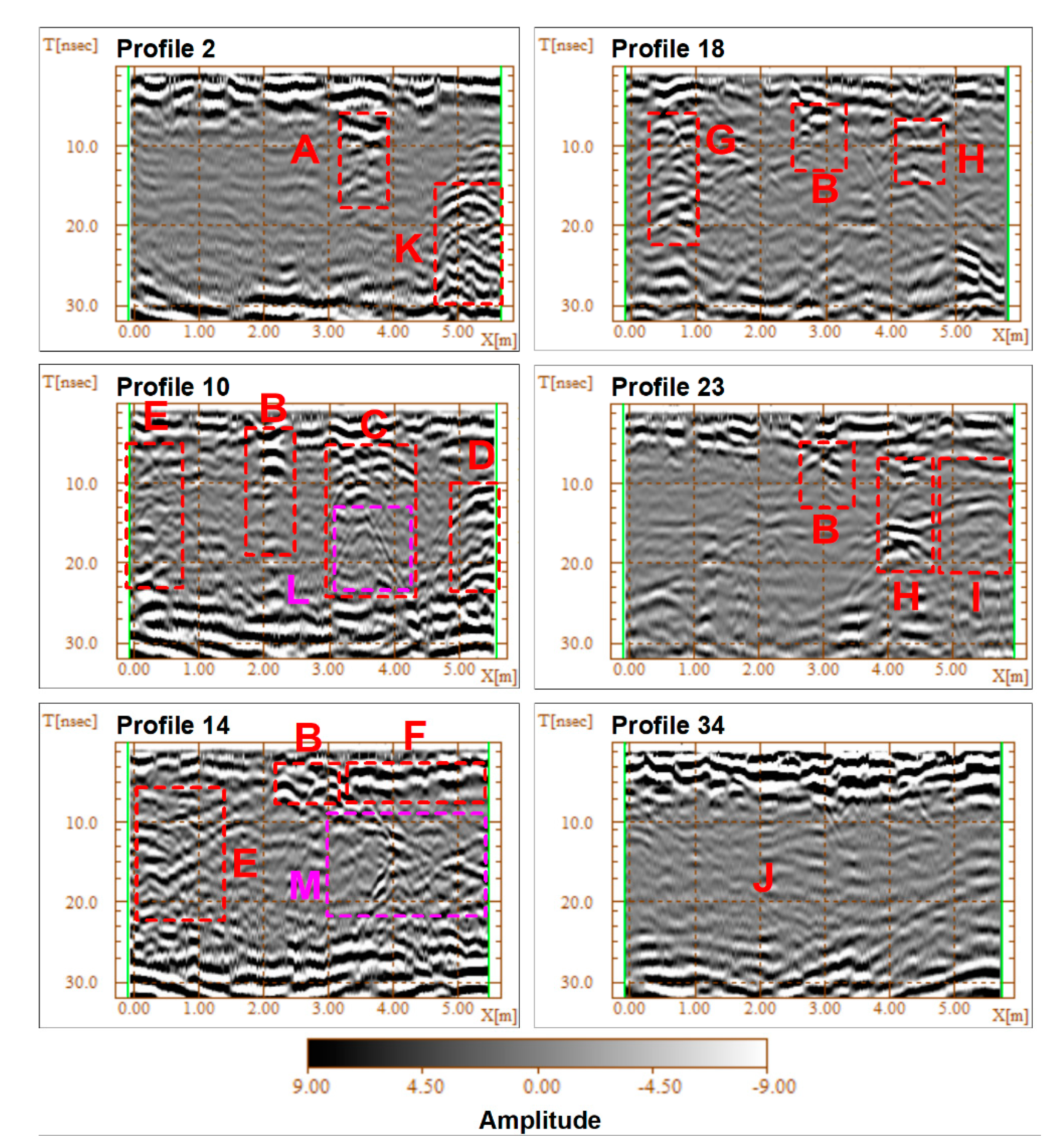
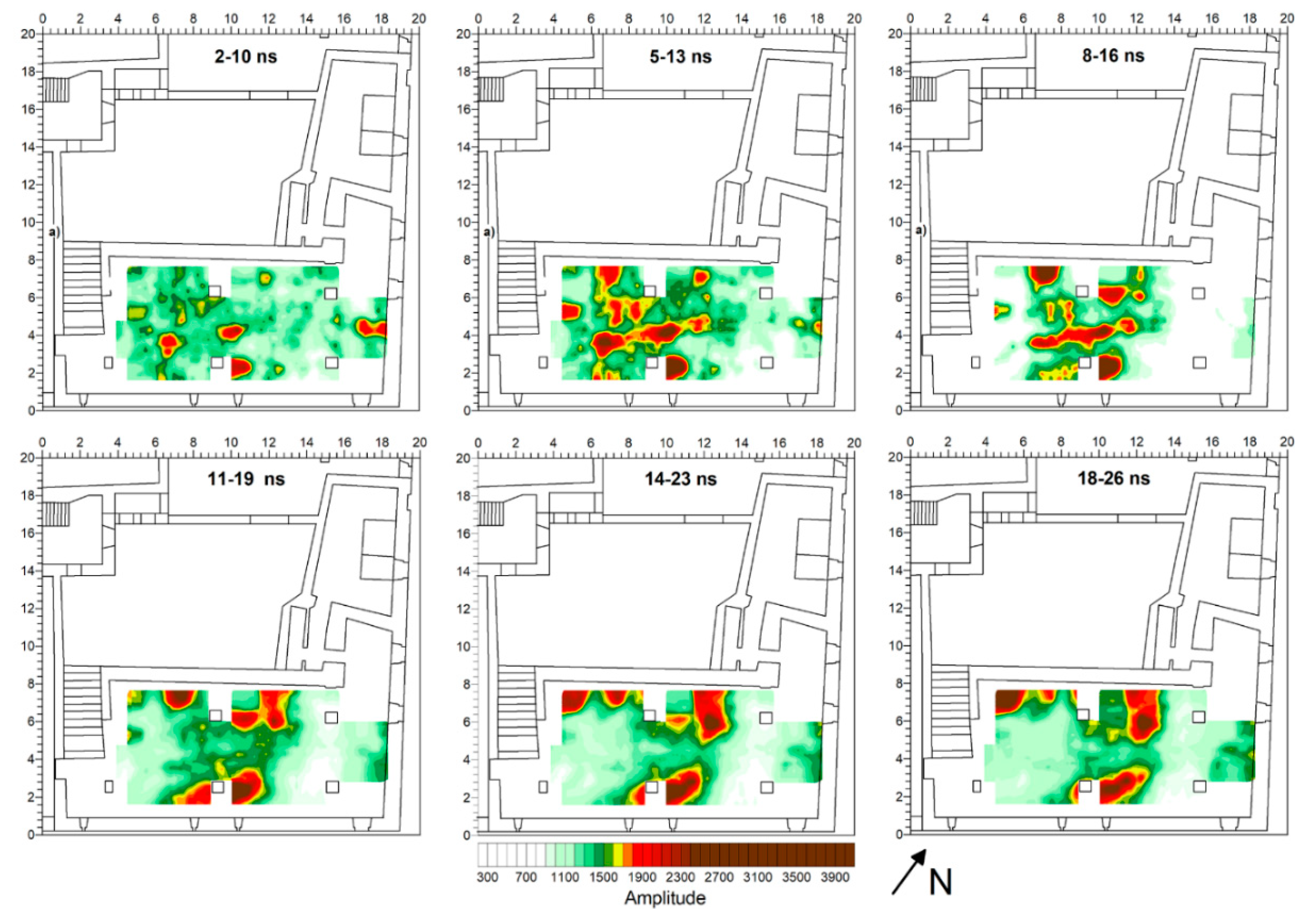
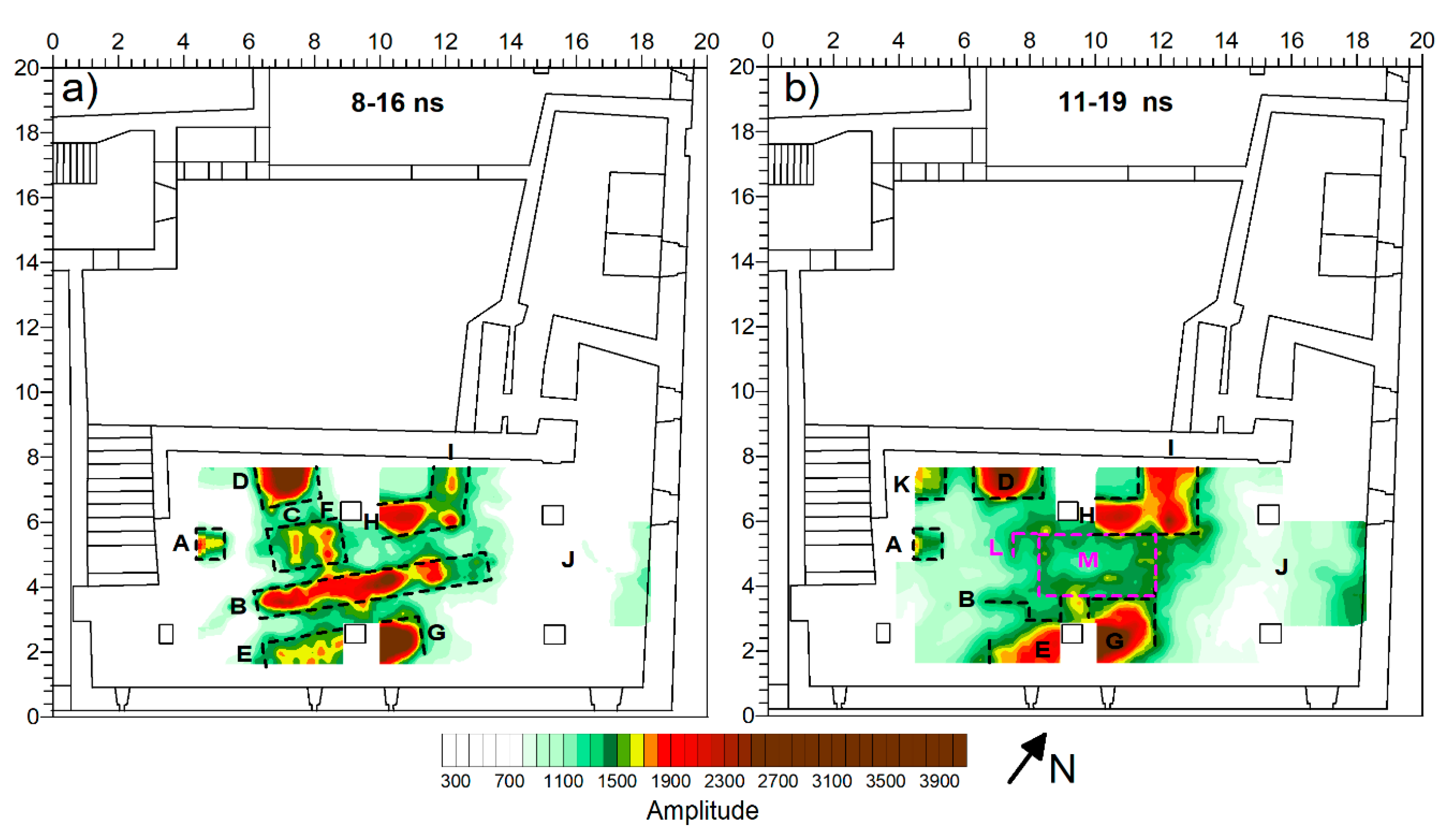
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cozzolino, M.; Di Giovanni, E.; Mauriello, P.; Piro, S.; Zamuner, D. Geophysical Methods for Cultural Heritage Management; Springer Geophysics Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.; Linford, P.; Lindford, N.; Gaffney, C.; David, A. (Eds.) EAC Guidelines for the Use of Geophysics in Archaeology; Archaeolingua Press: Budapest, Hungary, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Compare, V.; Cozzolino, M.; Di Giovanni, E.; Mauriello, P. Examples of resistivity tomography for cultural heritage management. In Near Surface 2010—16th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics; European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, EAGE: Houten, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Di Giovanni, E.; Mauriello, P.; Vanni Desideri, A.; Patella, D. Resistivity tomography in the Park of Pratolino at Vaglia (Florence, Italy). Archaeol. Prospect. 2012, 19, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, A.; Cozzolino, M.; Di Nucci, A.; Guglielmi, S.; Giannantonio, M.; D’Amore, D.; Pittoni, E.; Groot, A.M. The prehistory of the Colombian territory: The results of the Italian archaeological investigation on the Checua site (Municipality of Nemocòn, Cundinamarca Department). J. Biol. Res. 2012, 85, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osella, A.; Grunhut, V.; Martinelli, H.P.; de la Vega, M.; Bonomo, N. ERT for localizing 17th century tunnels at a Jesuit Mission in Buenos Aires, Argentina. In Near Surface Geoscience 2013—19th EAGE European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics; European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers, EAGE: Houten, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mauriello, P.; Patella, D. Resistivity tomography imaging of the substratum of the bedestan monumental complex at Nicosia, Cyprus. Archaeometry 2014, 56, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Saadi, O.S.; Schmidt, V.; Becken, M.; Fritsch, T. Very-high-resolution electrical resistivity imaging of buried foundations of a Roman villa near Nonnweiler, Germany. Archaeol. Prospect. 2018, 25, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero-Andrade, A.; Argote-Espino, D.L.; Cifuentes-Nava, G.; Hernández-Quintero, E.; Chávez, R.E.; García-Serrano, A. ‘Illuminating’ the interior of Kukulkan’s Pyramid, Chichén Itzá, Mexico, by means of a non-conventional ERT geophysical survey. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2018, 90, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrocki, L.; Eder, B.; Gehrke, H.J.; Lang, F.; Vött, A.; Willershäuser, T.; Rusch, K.; Wilken, D.; Hatzi-Spiliopoulou, G.; Kolia, E.-I.; et al. Detection and localization of chamber tombs in the environs of ancient Olympia (Peloponnese, Greece) based on a combination of archaeological survey and geophysical prospection. Geoarchaeology 2019, 34, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischanger, F.; Catanzariti, G.; Comina, C.; Sambuelli, L.; Morelli, G.; Barsuglia, F.; Ellaithy, A.; Porcelli, F. Geophysical anomalies detected by electrical resistivity tomography in the area surrounding Tutankhamun’s tomb. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 36, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Caliò, L.M.; Gentile, V.; Mauriello, P.; Di Meo, A. The Discovery of the Theater of Akragas (Valley of Temples, Agrigento, Italy): An archaeological confirmation of the supposed buried structures from a geophysical survey. Geosciences 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smedt, P.; Saey, T.; Lehouck, A.; Stichelbaut, B.; Meerschman, E.; Islam, M.M.; van DeVijver, E.; van Meirvenne, M. Exploring the potential of multi-receiver EMI survey for geoarchaeological prospection: A 90 ha dataset. Geoderma 2013, 199, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.X.; Tabbach, A.; Sarris, A. Practical assessment of a multi-frequency slingram EMI for archaeological prospection. In CAA2014: 21st Century Archaeology-Concepts, Methods and Tools; Archaeopress Archaeology: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lascano, E.; Martinelli, P.; Osella, A. EMI data from an archaeological resistive target revisited. Near Surf. Geophys. 2006, 4, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, L.I.; Dekayir, A.; Bokbot, Y.; Festuccia, S.; Cozzolino, M.; Gentile, V.; Merola, P.; Repola, L.; Cecalupo, C.; Seghir, M. Integrated multi scale archaeological analysis in Béni Mellal-Khenifra district (Morocco). The case of the fortress of Ighram Aousser. Archeol. Calc. 2020, 31, forthcoming. [Google Scholar]
- Mekkawi, M.; Arafa-Hamed, T.; Abdellatif, T. Detailed magnetic survey at Dahshour archeological sites Southwest Cairo, Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2013, 2, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fröhlich, N.; Posselt, M.; Schleifer, N. Excavating in a “blind mode”. Magnetometer survey, excavation and magnetic susceptibility measurements of a multiperiod site at Bad Homburg, Germany. Archaeol. Pol. 2003, 41, 167–169. [Google Scholar]
- Aspinall, A.; Gaffney, C.F.; Schmidt, A. Magnetometry for Archaeologists; Altamira Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H. Caesium magnetometry for landscape-archaeology. In Seeing the Unseen–Geophysics and Landscape Archaeology; Campana, S., Piro, S., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor &Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 129–165. [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer, W.; Eder-Hinterleitner, A. 3D-interpretation of post-processed archaeological magnetic prospection data. Archaeol. Prospect. 1997, 4, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, P.; Armesto, J.; Di-Capua, D.; González-Drigo, R.; Lorenzo, H.; Pérez-Gracia, V. Digital photogrammetry, GPR and computational analysis of structural damages in a mediaeval bridge. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludeno, G.; Cavalagli, N.; Ubertini, F.; Soldovieri, F.; Catapano, I. On the combined use of ground penetrating radar and crack meter sensors for structural monitoring: Application to the historical consoli palace in Gubbio, Italy. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 41, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Gabrielli, R.; Galatà, P.; Gentile, V.; Greco, G.; Scopinaro, E. Combined use of 3D metric surveys and non-invasive geophysical surveys for the determination of the state of conservation of the Stylite Tower (Umm ar-Rasas, Jordan). Ann. Geophys. Italy 2019, 62, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Di Meo, A.; Gentile, V. The contribution of indirect topographic surveys (photogrammetry and the laser scanner) and GPR investigations in the study of the vulnerability of the Abbey of Santa Maria a Mare, Tremiti Islands (Italy). Ann. Geophys. Italy 2019, 62, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscarini, C.; Catapano, I.; Cavalagli, N.; Ludeno, G.; Pepe, F.A.; Ubertini, F. UAV photogrammetry, infrared thermography and GPR for enhancing structural and material degradation evaluation of the Roman masonry bridge of Ponte Lucano in Italy. NDT E Int. 2020, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavusi, M.; Soldovieri, F.; Piscitelli, S.; Loperte, A.; Vallianatos, F.; Soupios, P. Ground penetrating radar and microwave tomography to evaluate the crack and joint geometry in historical buildings: Some examples from Chania, Crete, Greece. Near Surf. Geophys. 2010, 8, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuelli, L.; Bhom, G.; Capizzi, P.; Cardarelli, E.; Cosentino, P. Comparison between GPR measurements and ultrasonic tomography with different inversion algorithms: An application to the base of an ancient Egyptian sculpture. J. Geophys. Eng. 2011, 8, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, V.; Cozzolino, M.; De Benedittis, G.; Di Paola, G.; Gentile, V.; Giordano, C.; Marino, P.; Rosskopf, C.M.; Valente, E. An integrated quantitative approach to assess the archaeological heritage in highly anthropized areas: The case study of Aesernia (southern Italy). Acta IMECO 2016, 5, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gracia, V.; Canas, J.A.; Pujades, L.G.; Clapés, J.; Caselles, O.; Garcıa, F.; Osorio, R. GPR survey to confirm the location of ancient structures under the Valencian Cathedral (Spain). J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinks, I.; Karlsson, P.; Biwall, A.; Hinterleitner, A. Mapping the urban subsoil using ground penetrating radar—Challenges and potentials for archaeological prospection. ArcheoSciences 2009, 33, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinks, I.; Hinterleitner, A.; Neubauer, W.; Nau, E.; Löcker, K.; Wallner, M.; Gabler, M.; Filzwieser, R.; Wilding, J.; Schiel, H.; et al. Large-area high-resolution ground-penetrating radar measurements for archaeological prospection. Archaeol. Prospect. 2018, 25, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Longo, F.; Pizzano, N.; Rizzo, M.L.; Voza, O.; Amato, V.A. Multidisciplinary approach to the study of the temple of Athena in Poseidonia-Paestum (Southern Italy): New geomorphological, geophysical and archaeological data. Geosciences 2019, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspari, G.; Sadykov, T.; Blochin, J.; Buess, M.; Nieberle, M.; Balz, T. Integrating remote sensing and geophysics for exploring early nomadic funerary architecture in the Siberian Valley of the Kings. Sensors 2019, 19, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conyers, L.B.; Sutton, M.J.; St. Pierre, E. Dissecting and interpreting a three-dimensional ground-penetrating radar dataset: An example from Northern Australia. Sensors 2019, 19, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Baković, M.; Borovinić, N.; Galli, G.; Gentile, V.; Jabučanin, M.; Mauriello, P.; Merola, P.; Živanović, M. The contribution of geophysics to the knowledge of the hidden archaeological heritage of Montenegro. Geoscience 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, C.; De Giorgi, L.; Giannotta, M.T.; Leucci, G.; Meo, F.; Persico, R. The Messapic Site of Muro Leccese: New Results from Integrated Geophysical and Archaeological Surveys. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Gentile, V.; Giordano, C.; Mauriello, P. Imaging buried archaeological features through Ground Penetrating Radar: The case of the ancient Saepinum (Campobasso, Italy). Geoscience 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, M. Edilizia Storica della Marsica Occidentale; Dedalo, R., Ed.; Editrice Dedalo Roma: Roma, Italy, 2011; pp. 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chronica Monasterii Casinensis, Die Chronik von Montecassino; Hoffmann, H., Ed.; MGH.SS 34; Hahnsche Buchhandlung: Hannover, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Gattola, E. Historia Abbatiae Cassinensis per Saeculorum Seriem Distribuita; Nabu Press: Charleston, SC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra, A. Tagliacozzo: Momenti di archeologia medieval. In Proceedings of the Tagliacozzo e la Marsica tra XII e XIII secolo. Aspetti di vita Artistica, Civile e Religiosa. Atti del Convegno, Tagliacozzo, Italy, 19 May 2001; pp. 23–44. [Google Scholar]
- Colasante, D. Il Taglio nella Roccia. Tagliacozzo e il suo Territorio dal Medioevo al Novecento. Storia di una Comunità dell’Appennino Abruzzese; Villamagna: Tinari, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ground Penetrating Radar, Products. Available online: www.idsgeoradar.com (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Goodman, D. GPR-SLICE. Ground Penetrating Radar Imaging Software, User’s Manual; Geophysical Archaeometry Laboratory: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Catapano, I.; Gennarelli, G.; Ludeno, G.; Soldovieri, F. Applying ground-penetrating radar and microwave tomography data processing in cultural heritage: State of the art and future trends. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catapano, I.; Gennarelli, G.; Ludeno, G.; Soldovieri, F.; Persico, R. Ground-penetrating radar: Operation principle and data processing. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering; Webster, J.G., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cozzolino, M.; Di Giovanni, E.; Gentile, V.; Mauriello, P.; Pizzano, N. Ground-Penetrating Radar Survey for the Study of the Church of Saint Cosma in Helerito (Tagliacozzo, L’Aquila, Italy). Geosciences 2020, 10, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060244
Cozzolino M, Di Giovanni E, Gentile V, Mauriello P, Pizzano N. Ground-Penetrating Radar Survey for the Study of the Church of Saint Cosma in Helerito (Tagliacozzo, L’Aquila, Italy). Geosciences. 2020; 10(6):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060244
Chicago/Turabian StyleCozzolino, Marilena, Elisa Di Giovanni, Vincenzo Gentile, Paolo Mauriello, and Natascia Pizzano. 2020. "Ground-Penetrating Radar Survey for the Study of the Church of Saint Cosma in Helerito (Tagliacozzo, L’Aquila, Italy)" Geosciences 10, no. 6: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060244
APA StyleCozzolino, M., Di Giovanni, E., Gentile, V., Mauriello, P., & Pizzano, N. (2020). Ground-Penetrating Radar Survey for the Study of the Church of Saint Cosma in Helerito (Tagliacozzo, L’Aquila, Italy). Geosciences, 10(6), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10060244





