Abstract
This study employed electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) in characterising the shallow groundwater aquifers of Eastern Dahomey basin in southwestern Nigeria to assess the possible occurrence and distribution of saltwater within the aquifers. Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), induced polarization (IP) and borehole logging were carried in locations with relatively enhanced electrical conductivity (EC) within the coastal zone of the basin through 97 groundwater samples from shallow wells and boreholes; 500 m-length ERT and IP sections were carried out along three traverses A–B, C–D and E–F in directions perpendicular and parallel to the coastline. Three geoelectrical layers were identified along traverse line A–B which comprises cross-sections 1, 2, 3 and 4 located around Ugbonla, Aboto and Igbokoda with layers’ resistivity and chargeability values ranging from (1–1000, 33–200 and 1–1700 Ωm), and (−50–200 Ωm, −30–200 Ωm and −50–120 Ωm, respectively, from the top to the bottom layer. These values indicated unconsolidated sand/lateritic silty clay, underlain by a sandy/silty clay layer with underlying fine-grained sand with disseminated clay lenses. The average thickness of the first two layers was 16 and 53 m while that of the third layer was undetermined. Resistivity and chargeability results from ERT and IP cross-sections along profile C–D exhibited characteristics similar to that of profile A–B with unconsolidated sands which were underlain by intercalation of sandy/silty clay and fine-grained sands with suspected clay lenses saturated with saline water. Profile E–F revealed a geoelectrical layer with low resistivity which ranged from 1–30 Ωm with the corresponding chargeability between −150–400 ms. This indicated a saline water-saturated layer of fine-grained sand and silty clay which is overlaid by the unconsolidated unconfined freshwater aquifer. Correlation of selected ERT results with borehole logs further affirmed the suspected lithology from the sections. Two scenarios of saltwater intrusions into coastal freshwater aquifer were suggested which include the presence of trapped salt-saturated clay lenses within aquifer lithology and seawater incursion induced by over-drafting of groundwater in this basin.Therefore, it identified the need for further investigation which will involve a combination of hydrochemical and isotopes to further understand the paleowater hypothesis.
1. Introduction
Seawater intrusion is gradually becoming an inevitable problem of the coastal aquifer, especially in coastal zones of the world [1]. Coastal regions have been described as the area of the world that is fast becoming home to high and growing populations which are consequently undergoing environmental degradation [1,2]. High population contributes significantly to this environmental decline. As at the year 2003, approximately three billion people, about half of the world’s population, lived within 200 km of the coastline, a figure which will likely double by the year 2025 [2]. Coastal areas account for approximately 40% and 45% of the world’s and Nigeria’s population, respectively [3,4].
Rural–urban migration associated with economic, industrial and agricultural opportunities among other factors leads to this rapid population growth. In most of the developing countries around the world, there is associated infrastructural deficiency which includes erratic pipe-borne water supply among others. This, therefore, puts significant pressure on coastal freshwater aquifers which remain the only alternative source of water, to meet water required for domestic, agricultural, industrial and recreational purposes.
Eastern Dahomey Basin in Nigeria comprises two major inland river basins which include the Ogun-Osun and Benin-Owena river basin, with the addition of the coastal aquifer. This basin contributes significantly to the water resources of Nigeria and is also the major source of freshwater supply to various households. There are several reports from different sectors, ranging from government agencies, non-governmental organisations, research and academic institutions to “ad-hoc” and uncoordinated individuals and private companies, on the alarming degradation and the threat to groundwater quality, especially in the coastal area. Here, the groundwater level is generally higher, which permits constant interaction with the polluted surface water. The daily water demand in Lagos, the most populous city in Subsaharan Africa underlain by this basin is about 724 million gallons with production standing at 317 million gallons, this leaves a gap of about 407 million gallons which is complemented through the groundwater from shallow hand-dug wells and boreholes. Worse still, some of the pipe-borne water never reached households due to constant defects from burst transmission pipes and old trunk lines [5]. This further emphasises the importance of this invaluable resource to the economic and health status of inhabitants of the country’s southwest coast. Indiscriminate waste disposal and management also pollute surface water which recharges the groundwater. This direct interaction of contaminated and polluted surface water with groundwater degrades the quality of groundwater in the unconfined top aquifer in this coastal area as observed in the work of [6,7,8]. In the search for potable freshwater, most wells and boreholes in this area are drilled to the second aquifer, which is a confined aquifer (Figure 1) underlying the coastal area of the basin which is most densely populated, in order to meet their daily water demand. This development has put pressure on groundwater and led to saltwater intrusion in the freshwater aquifer through up conning wedge shift resulting from over-abstraction of groundwater [3,9,10,11,12]. Proximity to the sea also encourages saltwater intrusion into the freshwater of the coastal aquifer due to sea-level rise (SLR) [13]. Another school of thought has also suggested possible dissolution of evaporite minerals trapped within the basin lithology during a past event of ocean transgression and regression into groundwater causing their enhanced salinity and electrical conductivity [14,15]. The work of [3,7,9,10,16,17,18,19,20,21] have employed different methods such as electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), induced polarization (IP) and hydrochemistry on groundwater in some selected and specific locations within this basin. Some of these studies which have identified saltwater intrusion in the upper aquifers mainly in the eastern coast of Lagos, such as Lekki, Ajjah, Victoria Island, Sagontedo. The deterioration of water quality in parts of Lekki phase 1 and Oniru environs of Lagos metropolis due to saltwater infiltration in the freshwater aquifer has become a significant concern [10]. Despite all this, the report still shows that systematic and detailed groundwater quality assessment and monitoring are insufficient for sustainable management of groundwater in the face of the menace of salty water. This challenge results from a combination of factors, such as costs associated with water-quality monitoring, the relatively low levels of funding for research in Sub-Sahara Africa over the past decade and limited national regulation of high-intensity rainfall events which pose a risk to shallow and poorly protected groundwater sources [9,22]. Also, groundwater is a dynamic resource whose quality requires constant regimented monitoring for early detection of contamination and pollution to ensure a sustainability and health safety measure of life, and possibly plant and animals which depends on it for survival. Moreover, there is a vital need to monitor the possible risk of saline water intrusion of the coastal aquifers because, once saline intrusion into coastal aquifer has occurred, it is challenging to overcome and to improve the management of the water resources based on long-term strategy. Within this location, several boreholes have had to be abandoned, and other water sources sought, often at a high cost. Furthermore, subsurface data are generally scarce because invasive methods such as borehole drilling and associated aquifer tests are expensive and time-consuming. The current lack of hydrogeological information of the existing commercial boreholes is also a factor. Therefore, non-invasive hydrogeophysical methods of subsurface data acquisition provide an alternative, or a complement to, direct observations. Protection of groundwater resources in coastal areas and their sustainable management, in conjunction with other water resources (e.g., surface water, seawater), require an understanding of the coastal aquifer hydrogeology.
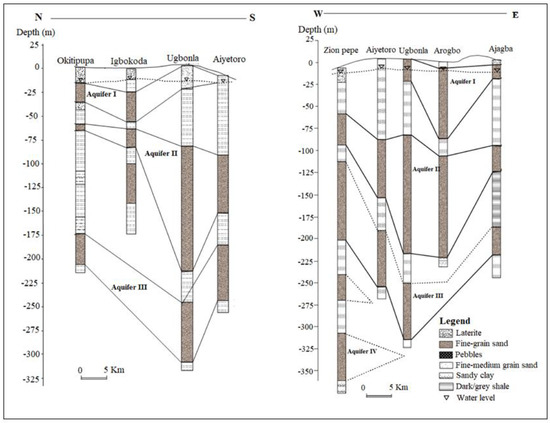
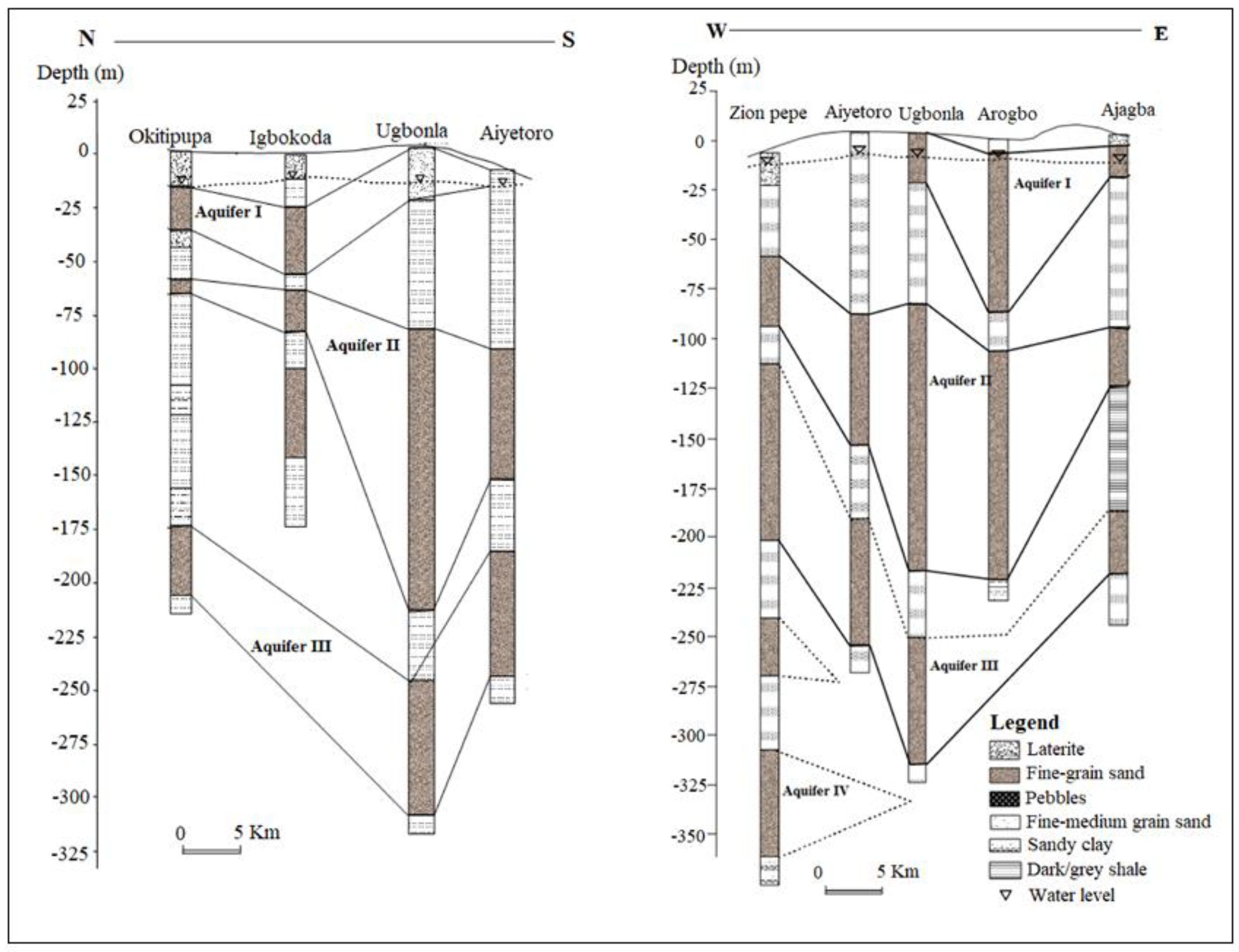
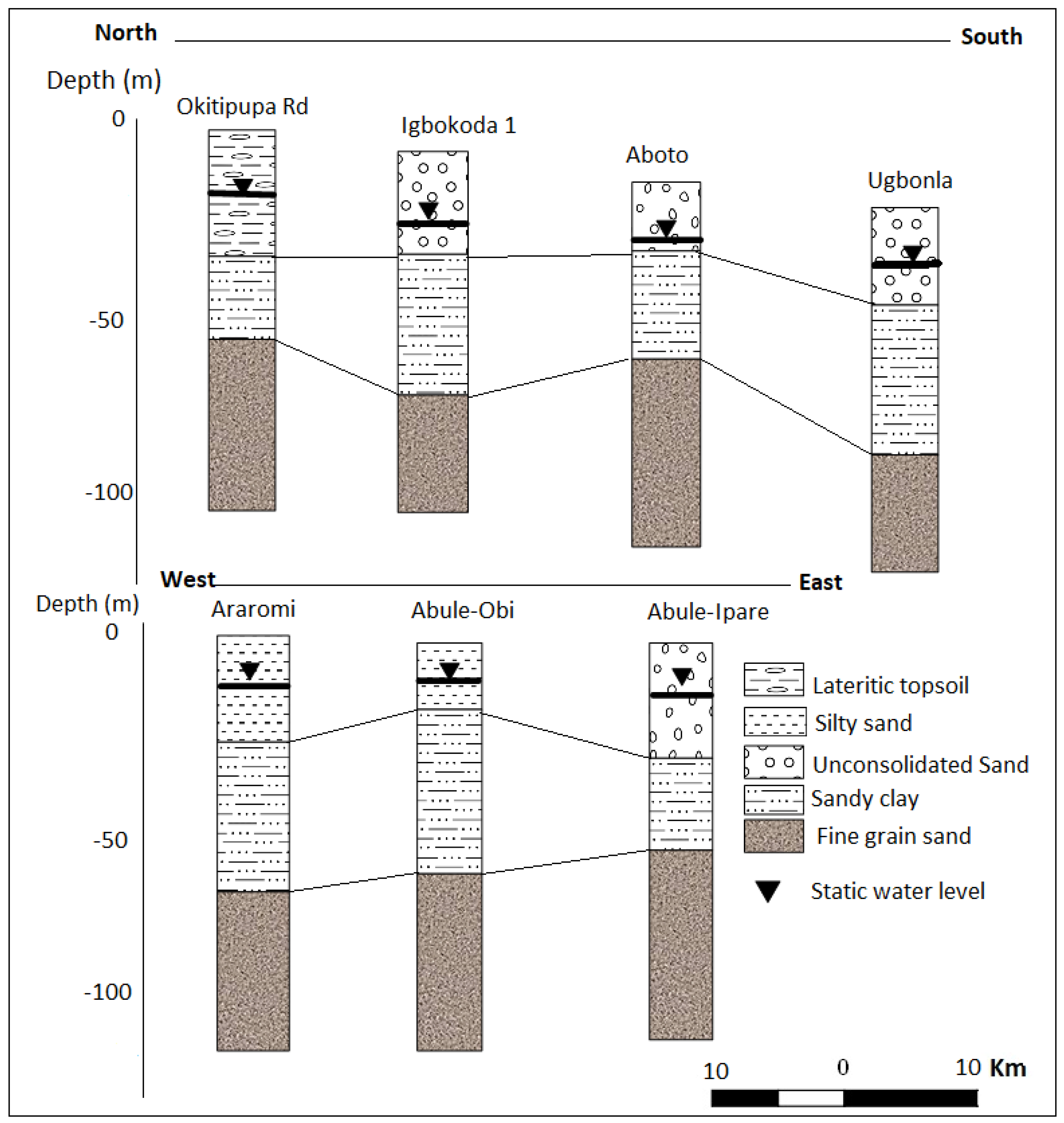
Figure 1.
Generalised aquifer description in parts of Eastern Dahomey basin, modified from [28].
This study, therefore, focuses on the delineation of origin and distribution of saltwater intrusion in the coastal freshwater aquifer of Eastern Dahomey Basin using a physicochemical approach through the electrical conductivity (EC) and geophysical method of ERT and IP complemented with borehole logs with the objective of identify saltwater bearing lithological units that are responsible for salinisation of freshwater. Complementary use of these methods improves the extensive coverage of hydrogeological investigations due to the difference between their characteristics and capability.
1.1. Study Area and Geomorphology
The Eastern Dahomey Basin lies in the southwestern part of Nigeria, which is the eastern part of Dahomey Basin (also called Benin or Keta Basin in Nigerian literature). It is a transboundary basin that extends from Ghana through Togo and Benin to Nigeria. This basin is bounded by Okitipupa Ridge, which is the boundary it shares with Niger Delta basin [23]. It lies between latitudes 2°41′10.00″ and 4°59′5900″ N and longitudes 6°21′1300″ and 7°52′42.00″ E along the coast of the Gulf of Guinea (see Figure 2). The basin is bounded in the south by the Atlantic Ocean, west by the Republic of Benin, and thins out at the north by the Precambrian basement rocks. The area of investigation towards the south is low lying with several points virtually at sea level which are prone to flooding. The highest elevation is found around the city of Abeokuta in the northern parts of the study basin. Two major climatic seasons can be recognised, a dry one from November to March and a wet one which starts in April and ends in October with a short break in mid-August. Major rivers such as the Ogun, Ose, and Oluwa drain the basin into the delta and the Atlantic Ocean. The basin hosts two major administrative water basins authorities in Nigeria which include Ogun-Osun and Benin-Owena river basins, and accommodates about 40% population of the country’s residents including the metropolitan city of Lagos, which signifies it is essential to the economy of Nigeria and West Africa.
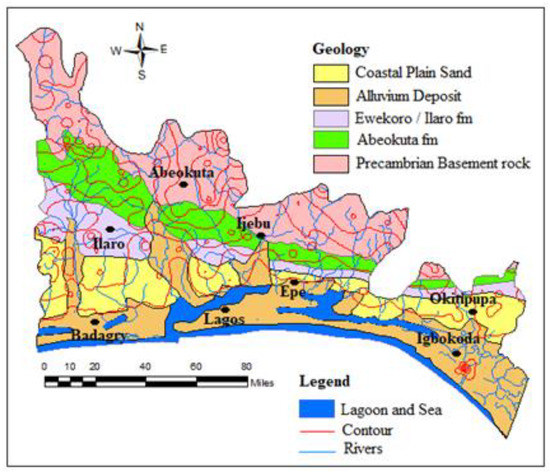
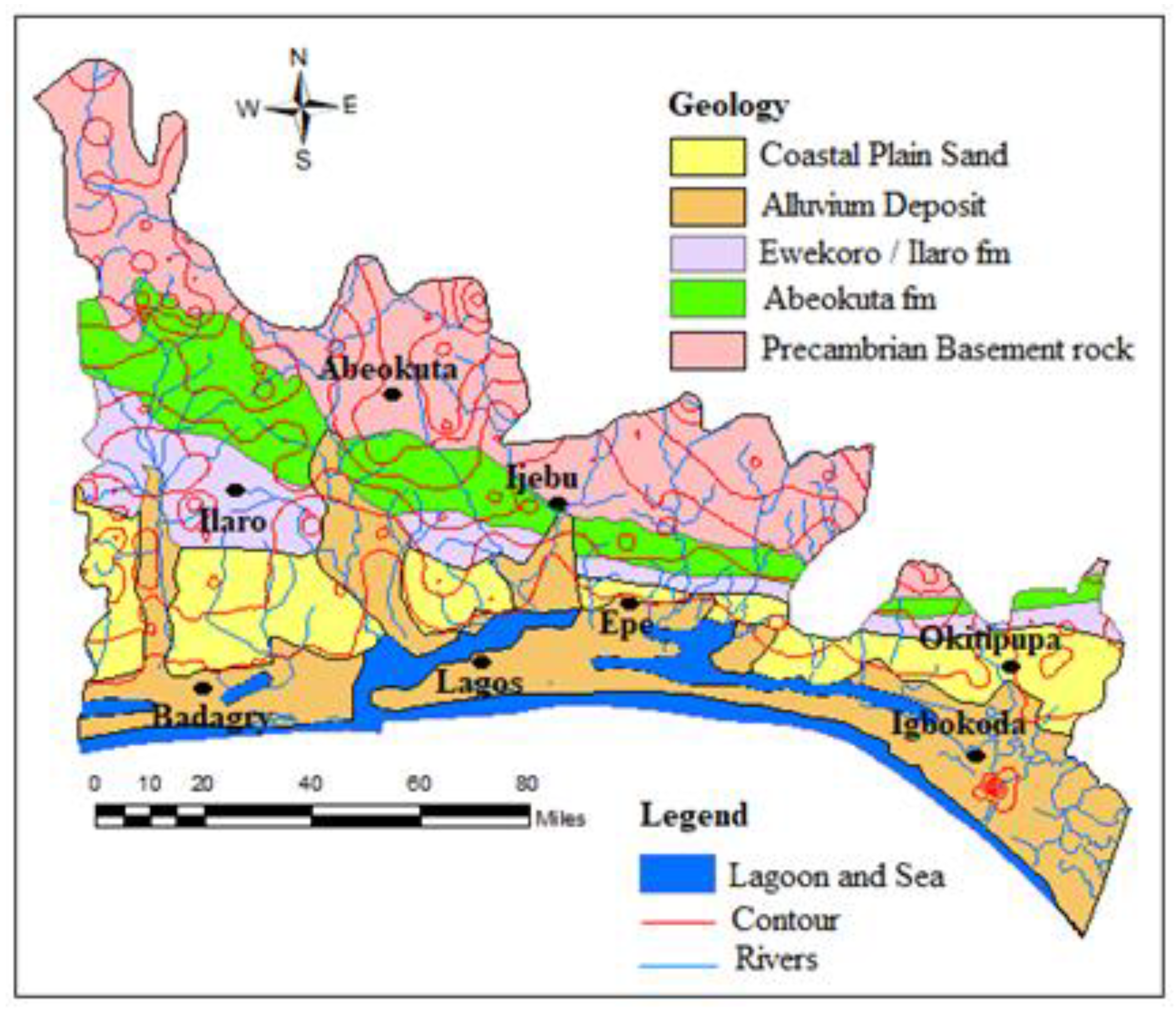
Figure 2.
Geological map of Eastern Dahomey Basin.
1.2. Geology and Hydrogeology of Eastern Dahomey Basin
The lithological character of the sediments was dictated by the regime of transgressions and regressions of the sea since the Cretaceous age, and the transgressions are found to have been coming from the south. The stratigraphic description of the sediments has been provided by various authors, including [23,24,25,26], as presented in Table 1. Some of these authors have proven the area to be composed of the following stratigraphic units from youngest to the oldest. The Alluvium Deposits and coastal plain sands consist of soft, very poorly sorted clayey sands, pebbly sands, sandy clays and rare thin lignite of Oligocene to the recent age. This is underlain by Ilaro formation which consists of massive, yellowish, poorly consolidated, cross-bedded sandstones, which are fine to medium-grained and poorly sorted [23]. This is followed by the Ewekoro formation which consists of predominantly Paleocene fossiliferous limestone which becomes arenaceous towards the base [26] and the Abeokuta formation which consists of lower Cretaceous sandstone and grits with interbedded mudstone unconformity overlain the basement complex fine detrital sandstone, siltstone and shale overlying the formation in the upper parts. The youngest sets of strata are marginal to fully marine sand and shale of the Maastrichtian Age.

Table 1.
Stratigraphic sequence in the Eastern Dahomey Basin (modified from Adelana et al., 2004).
The Coastal Plains Sands represents the main aquifer in the southern parts of the basin which most of the well and boreholes exploit. This has resulted in a multi-aquifer system consisting of three aquifer horizons separated by silty or clayey layers [16]. The aquifer shows high thickness at the northern part of Abeokuta, through Ewekoro, Ilaro, and thins out into the coastal plain sands, in locations closer to the coast in the south. The percentage of sands in lithology also increases towards the south [16]. The geological map of the basin is presented in Figure 2, showing the distribution of rock units within the basin.
The coastal plain and alluvium deposits of the Eastern Dahomey Basin are characterised by a multi-layer aquifer, which is classified into three types [16]. The first aquifer is a water table aquifer which is prone to pollution because of its nearness to the ground surface. The second and third are confined aquifers composed of an alternating sequence of sand and clay. They are harnessed through boreholes and are the basis of mini water-works in the Lagos area and other parts of the Basin. These aquifers belong to the continental Ilaro Formation. The third aquifer seems to be the most productive and faces the highest level of groundwater exploitation within which most boreholes terminated. Within it, groundwater exists confined to the semi-confined condition [16,19,27]. Generally, the water-table ranges from 2.0 to 15.0 m below ground level (b.g.l) in the area. Also, the study area is well drained by rivers and streams that flows southerly into the lagoon and the Atlantic Ocean. The average annual precipitation is above 1700 mm and serves as a primary source of groundwater replenishment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Physico-Chemical Measurement
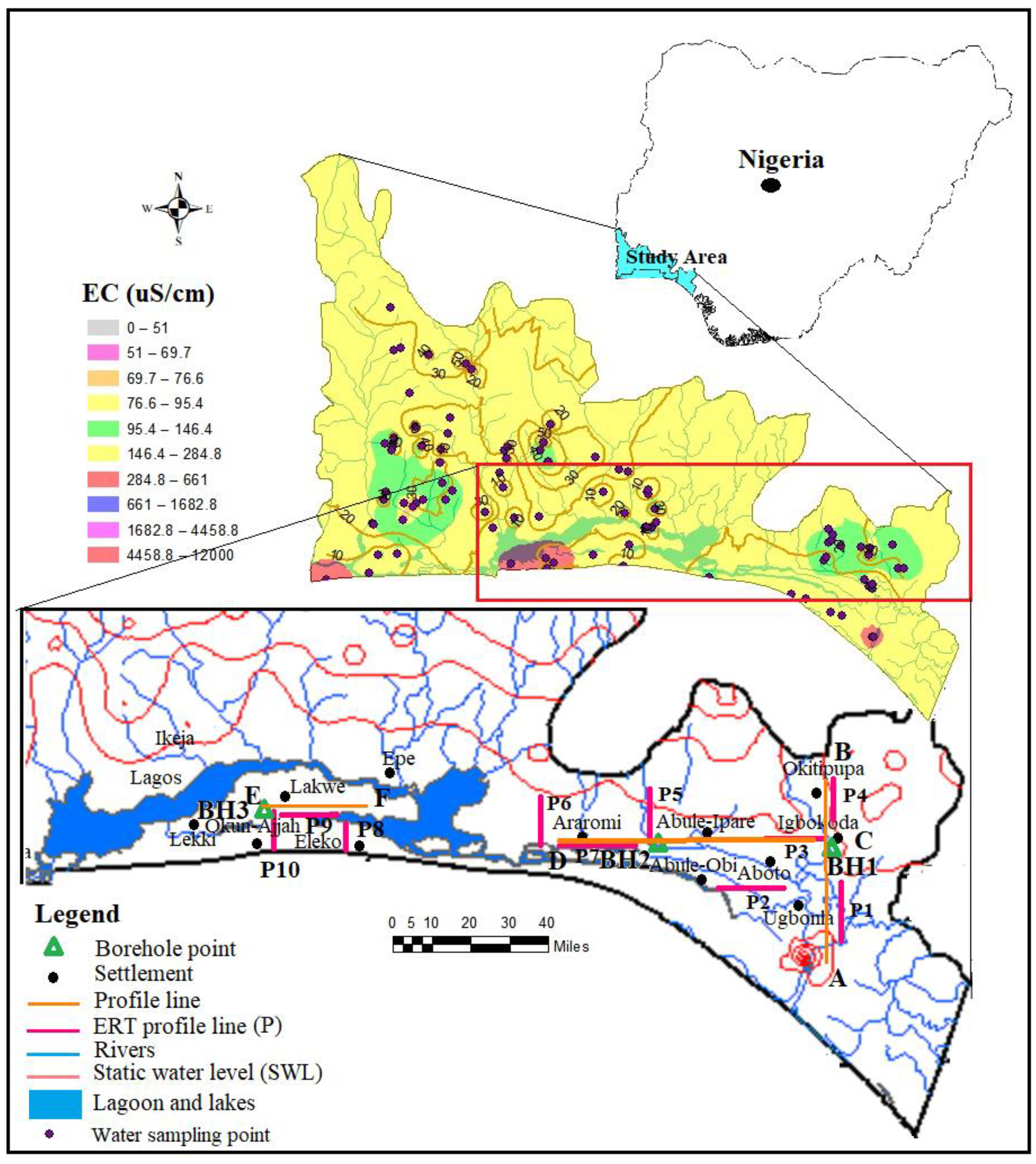
The physicochemical field measurement of electrical conductivity, salinity and water level are groundwater parameters that are critical to water quality regarding the saltwater intrusion. Monitoring a change in conductivity could provide a clue to the early stage of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer [12,16]. This was employed as a preliminary approach to the selection of locations for geophysical investigation. This was also necessary to save time and cost. The physicochemical parameters were measured in the field using a Model 99,720 microprocessor pH/conductivity meter capable of measuring total dissolved solids (TDS), salinity, temperature and oxidation and reduction potential (Eh/ORP). The depth of the wells and static water level were measured with the aid of a water depth meter while the coordinates of each sampled well were recorded using a global positioning system (GPS). Conductivity from 6.7 to 12,000 µS/cm. were found in water samples from wells in locations around Igbokoda, Ungbonla, Ibeju-Lekki and Okun-Ajjah. (Figure 3 and Table 2). It was challenging to select a continuous length of resistivity profile due to the marshy nature of the coastal area. Also, the isolated and drained sandbars which could have served as the survey are built-up for residential use, especially in part of the coast near to the metropolitan city of Lagos. Hence, the selection of the profile lines is mainly controlled by the available space (Figure 3).
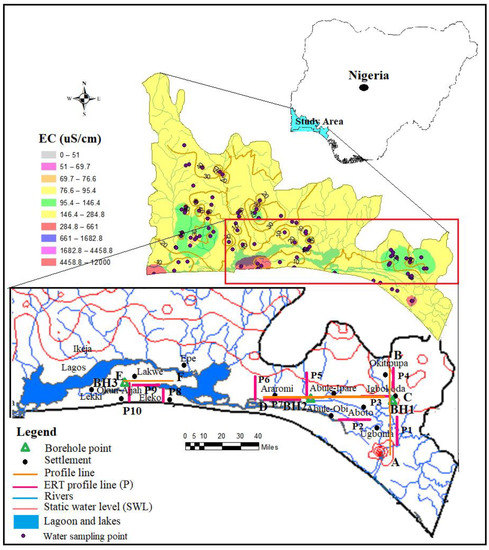
Figure 3.
Map of the Eastern Dahomey Basin showing well sampling points, borehole points and geoelectrical profile and spatial distribution map of electrical conductivity (EC).

Table 2.
Regional electrical conductivity.
2.2. Hydro-Geophysical Approach
Electrical near-surface-geophysical methods used in this study, such as ERT and IP, have been employed in various areas in the field of Hydrogeology for groundwater studies [29]. This method was chosen over vertical electrical sounding (VES) because, the latter only presented a limited vertical overview of resistivity distribution below the survey point which does not capture the lateral stratigraphic relationship of the different layers [30]. The IP and ERT are integrated in this study because of the common ambiguities and challenges posed when lithology such as clay and sand units or other factors such as contaminants and saltwater which are characterized with low resistivity values are faced during the interpretation of electrical resistivity data. IP method is very important since it measured chargeability of lithology which is a key parameter that differentiates clayey and sandy units within similar resistivity range.
The principle of the ERT method is based on the measurement of the soil apparent resistivity, using a large number of electrodes placed along the profile or in the area. The electrodes are interconnected by a special cable that enables connection to the electrodes as current and potential electrode step by step. This allows measurement of a large number of variants of a 4-electrode array with differing geometry and penetration depth. The measurement proceeds automatically and is controlled by a computer/laptop. Details of this method can be found in the work of [31,32,33,34].
The IP method targets electrical resistivity and chargeability of the subsurface lithology, which applies to delineate the zones of freshwater and saltwater contact, permeable sands aquifers and impermeable clayey aquitard and their overall geometry. Groundwater applications of this method include delineating aquifer depth and thickness, mapping aquitards or confining units, identifying fluid migration paths such as fractures and fault zones, and mapping contamination of the groundwater such as saltwater intrusion [3,17,35,36,37].
2.3. Geophysical Field Data Acquisition
Ten geoelectrical profiles (L1–L10), each of 500 m length with electrode spacing of 6 m, were carried out for both ERT and IP using an Advance Geophysical Instrument (AGI) SuperSting R8/IP8 Earth Resistivity meter, an eight-channel Memory Resistivity and IP Meter with inbuilt processor for 84 multi-electrodes systems. Resistivity profiles were carried out around Igbokoda, Ungbonla, Araromi Eleko, Lakowe and Okun-Ajjah within the coastal area of the Basin. The selection of the location of the profile was based on both enhanced EC results (Figure 3) and accessibility, as observed during the groundwater well inventory. The sections were conducted along two directions, North–South and West–East respectively A–B, C–D and E–F as shown in Figure 3. Traverse A-B, which consists of ERT and IP profiles sections 1 and 4, were carried out around Ugbonla, Aboto, and Igbokoda, and perpendicular to the shoreline. Traverse C–D consisted of profile sections 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 with 2, 3 and 7 ran parallel to the shoreline profile sections while 5 and 7 ran at an angle almost perpendicular to the shoreline around Abule-Ipare, Abule-Obi and Araromi Figure 3). The third traverse is E–F which consists of profile section 8 and 10 ran at an at almost perpendicular to the shoreline while profile section 9 ran parallel to the shoreline in location between 8 and 10. The traverse E–F which ran parallel to the shoreline was carried out around the Eleko, Lakowe and Oku-Ajjah area of the metropolitan city of Lagos. There was constrained to the length of the traverse line due to the high water level which is above the ground surface in most of the area. Details of the profiles and coordinates are shown in Figure 3.
2.4. Geophysical Data Processing
The ERT and IP data acquired were processed and analysed using the AGI EarthImager 2D software. The results presented were inverted using the standard method of inversion (L2-norm approach) after the 5th iteration. For all sections’ results, a root mean squre (RMS) model error below 96.7% was obtained. On the IP, the resistivity and chargeability variations as contoured pseudo-sections that give rough visual impressions of the variability of resistivity and chargeability with depth below the profiles. The acquired ERT and IP data were inverted to produce sections with vertical scales in depth, which give significantly improved pictures of actual resistivity and chargeabilities variations.
In addition to ERT and IP measurements, data from borehole drilling and geophysical well loggings were correlated with information from ERT and IP results for validation. These borehole logging points were selected in locations along or sufficiently close to the ERT sections. The respective sections were, therefore, interpreted using resistivity classifications of groundwater types as shown in Table 3 below.

Table 3.
Classification of aquifer based on resistivity value after [11].
3. Results
3.1. Results of Well and Borehole Field Inventories
Results of some physicochemical parameters such as electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS) salinity static water level, well depth and others parameters which could serve as a fingerprint to saltwater intrusion were carried out on 93 shallow boreholes, and hand-dug wells across the Eastern Dahomey basin are presented in Table 2. The respective ranges of EC, TDS, salinity, static water level and well depth are 6.7–12,000 µS/cm, 3.2–8500 mg/L, 2–5000 mg/L, 0.2–67 m and 2.10–125 m (Table 2). EC, TDS and salinity increase from the north towards the shoreline, which shows the influence of seawater. These two parameters also decrease with the depth of the well and static water level (SWL) which could increase the influence of surface and groundwater interaction causing pollution and contamination of groundwater and positively altering these values [12,38,39,40]. Enhanced EC showed by the value of standard deviation and variance (Table 2) were observed in some wells around Igbokoda, Ode-Mahin, Ugbonla, Ogombo, Okun-Ajjah and Lekki.
3.2. Results of Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) and Induced Polarisation (IP)
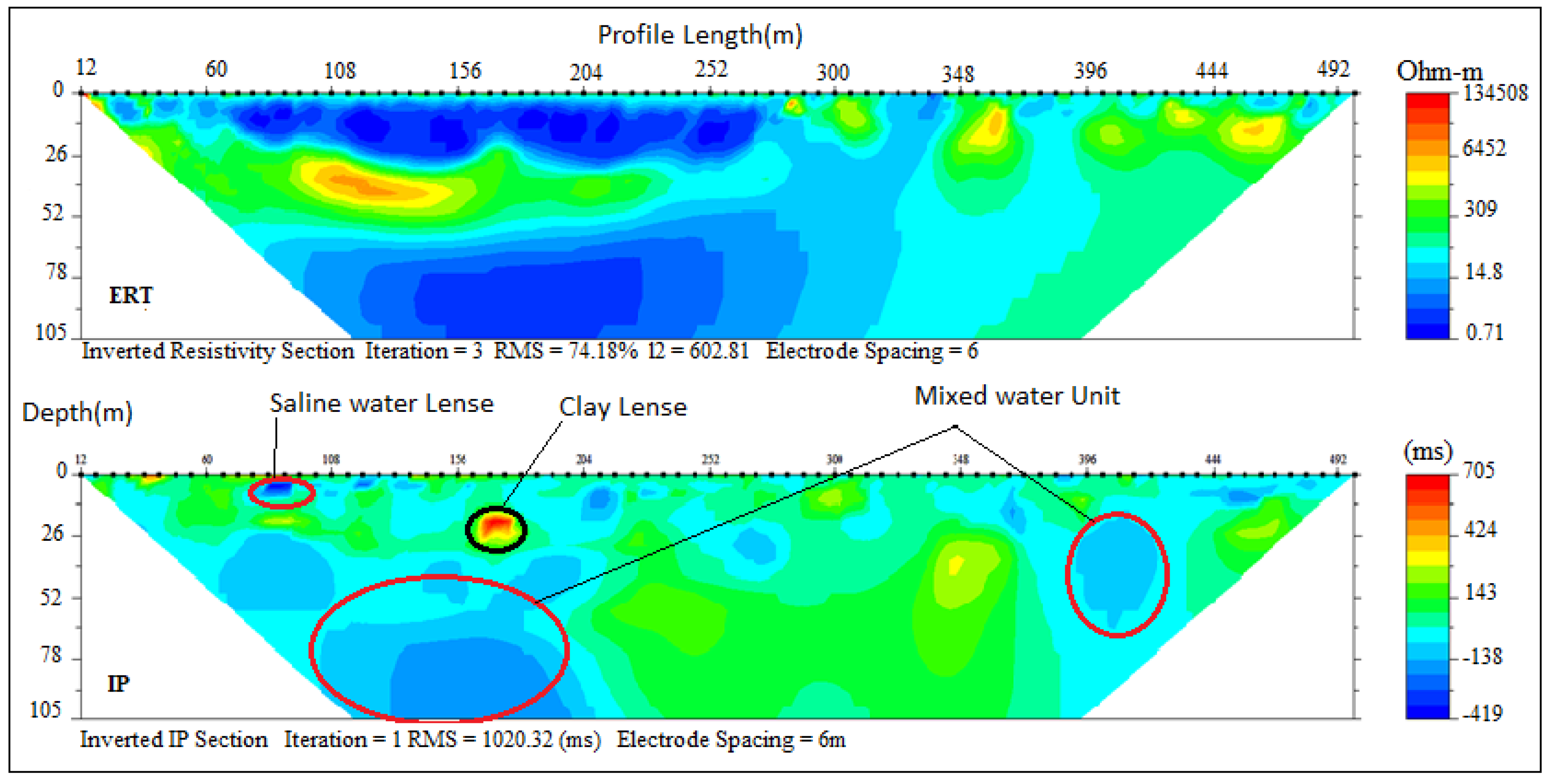
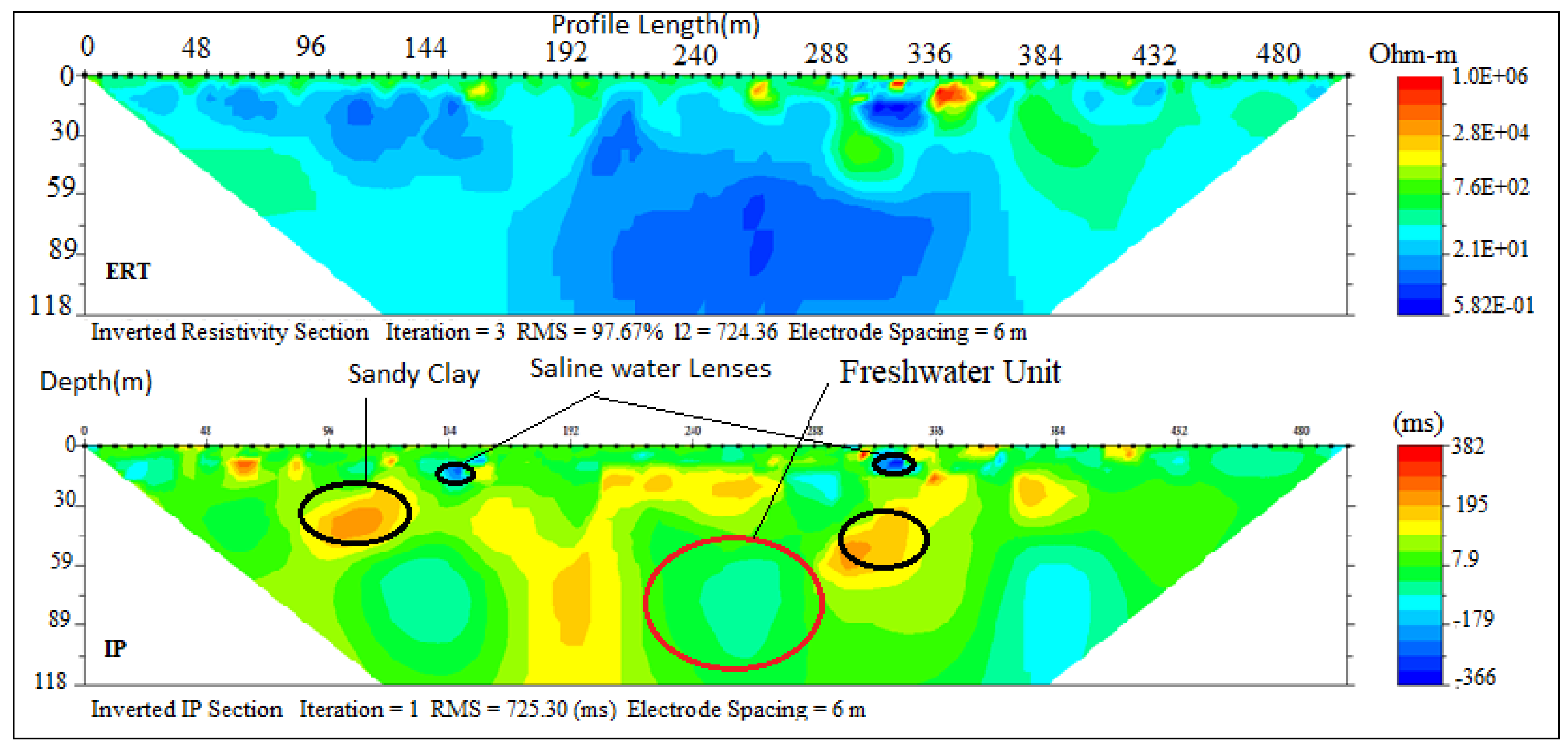
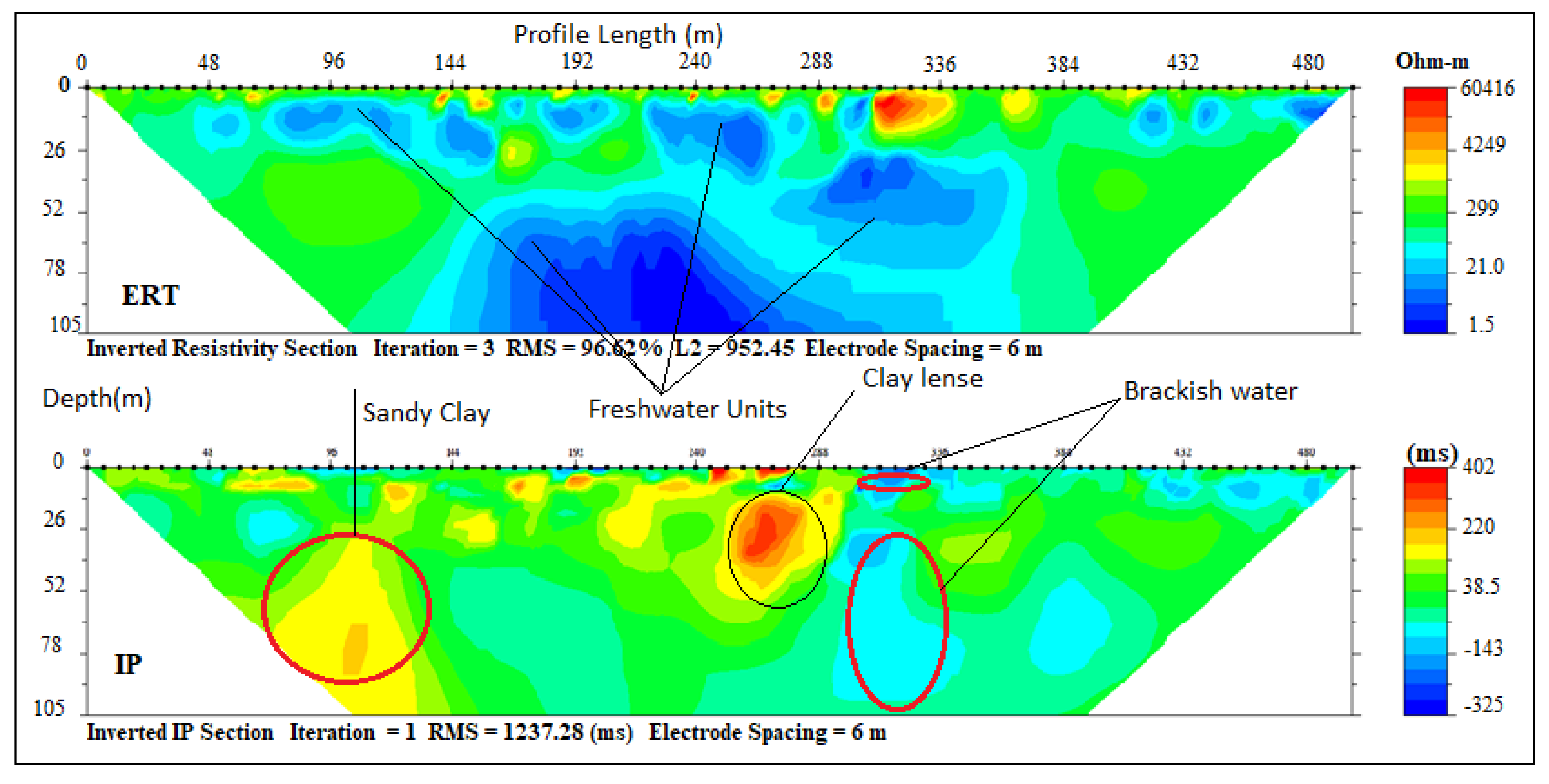
The 500 m long ERT-IP sections from some selected locations based on enhanced EC revealed different geoelectrical layers across the profile sections with maximum depth probed ranging between 105 and 118 m. Traverse A–B consists of 1, 2, 3 and 4 ERT and IP profile sections which out of P1 and P4 are perpendicular while P2 and P3 are parallel to the coastline. On the ERT and IP section P1 (Figure 4), located at the front of the palace of the Olugbo of the Ugbo Kingdom in Ode-Ugbo, three geoelectric layers were delineated with resistivity values /chargeability range between (1–30 Ωm /−50–45 Ms), (70–200 Ωm/−30–20 Ms) and (1–30 Ωm /−50–70 Ms) Figure 4, with respective average depth of 23, 47 and 70 m (Table 4).
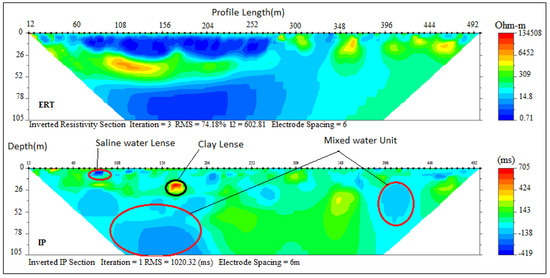
Figure 4.
Inverted resistivity and induced polarisation (IP) cross-sections Ugbonla (Profile section P1).

Table 4.
Lithological interpretation of geoelectrical sections from Profile A–B.
These ERT and IP section P1 (Figure 4), values are delineated to be silty sand and clay which represent the topsoil, sandy clay and underlain by fine-grain sands which have the impression of saltwater saturated clay lenses. This could be attributed to low resistivity within this unit, hence the saline water that characterised abandoned deep boreholes in this area.
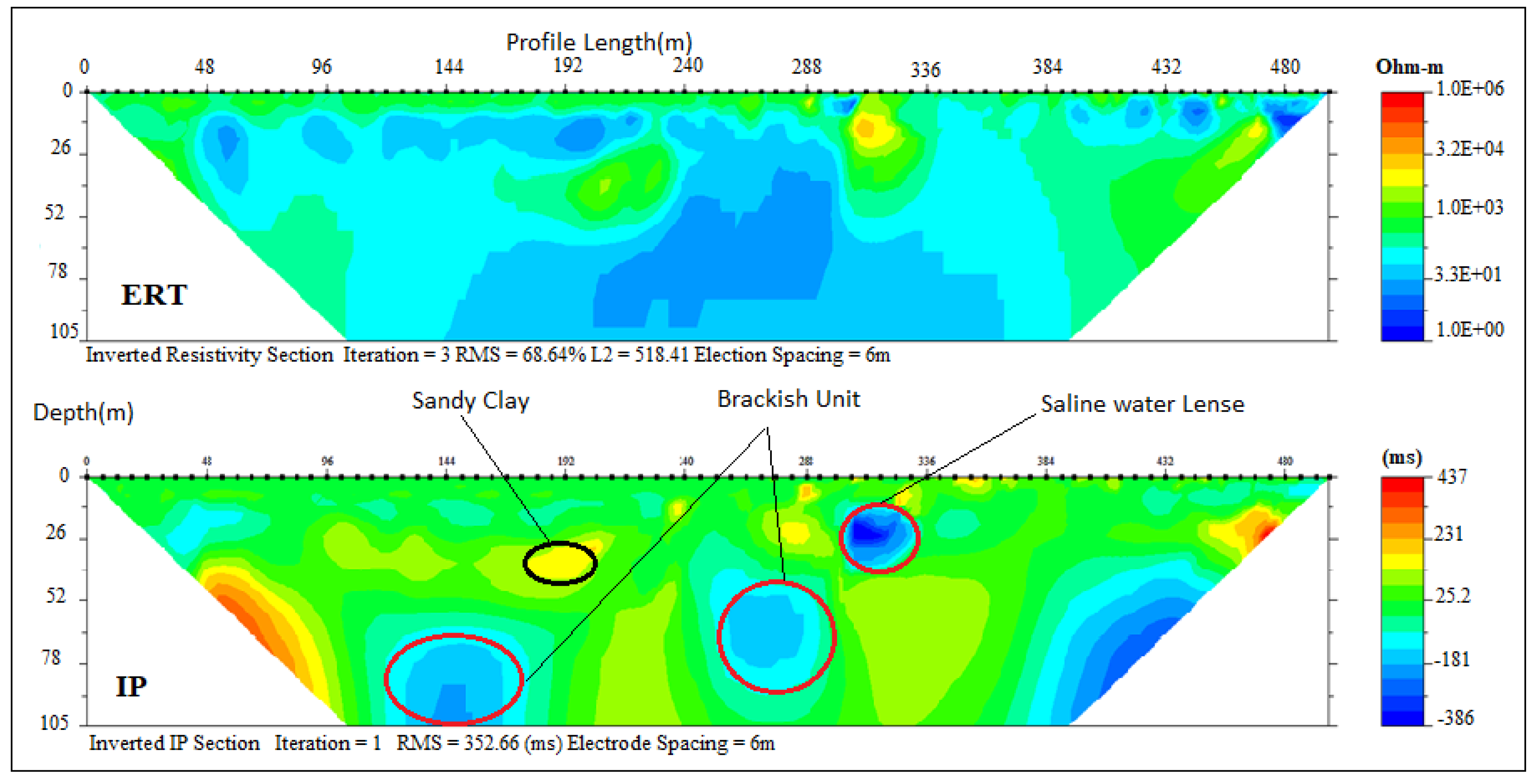
The ERT and IP section P2 (Figure 5), located at Aboto village, revealed two geoelectric layers with resistivity/chargeability values between (300–700 Ωm/10–40 ms) and (5–75 Ωm /−5–100 ms). These values indicated silty sand topsoil and fine-grain sand with clay lenses saturated with saline water with respective depths of 14 m and above 104 m. The presence of clay lenses is responsible for low resistivity values within the layers. Three geoelectric layers were delineated along ERT and IP section P3 (Figure 6), located at the south-eastern part of Igbokoda along Aboto Road. Resistivity/chargeability of the layers from top to bottom ranged between (700–1000 Ωm/15–30 ms), (33–50 Ωm/1–128 ms) and (10–20 Ωm and −12–100 ms) which were indications of silty sand topsoil, clayey sand/sandy clay and fine-grain sands with respective average thicknesses of 25 m, 42 m and more than 25 m. The low resistivity with corresponding high chargeability within the layers indicated clay lenses saturated with saline water which characterised the second and third layers.
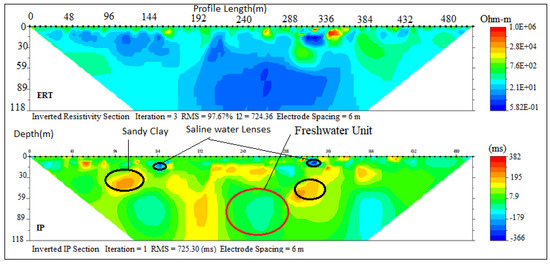
Figure 5.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Aboto (Profile section P2).
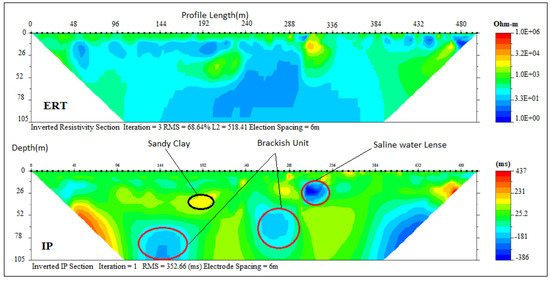
Figure 6.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections of Igbokoda (Profile section P3).
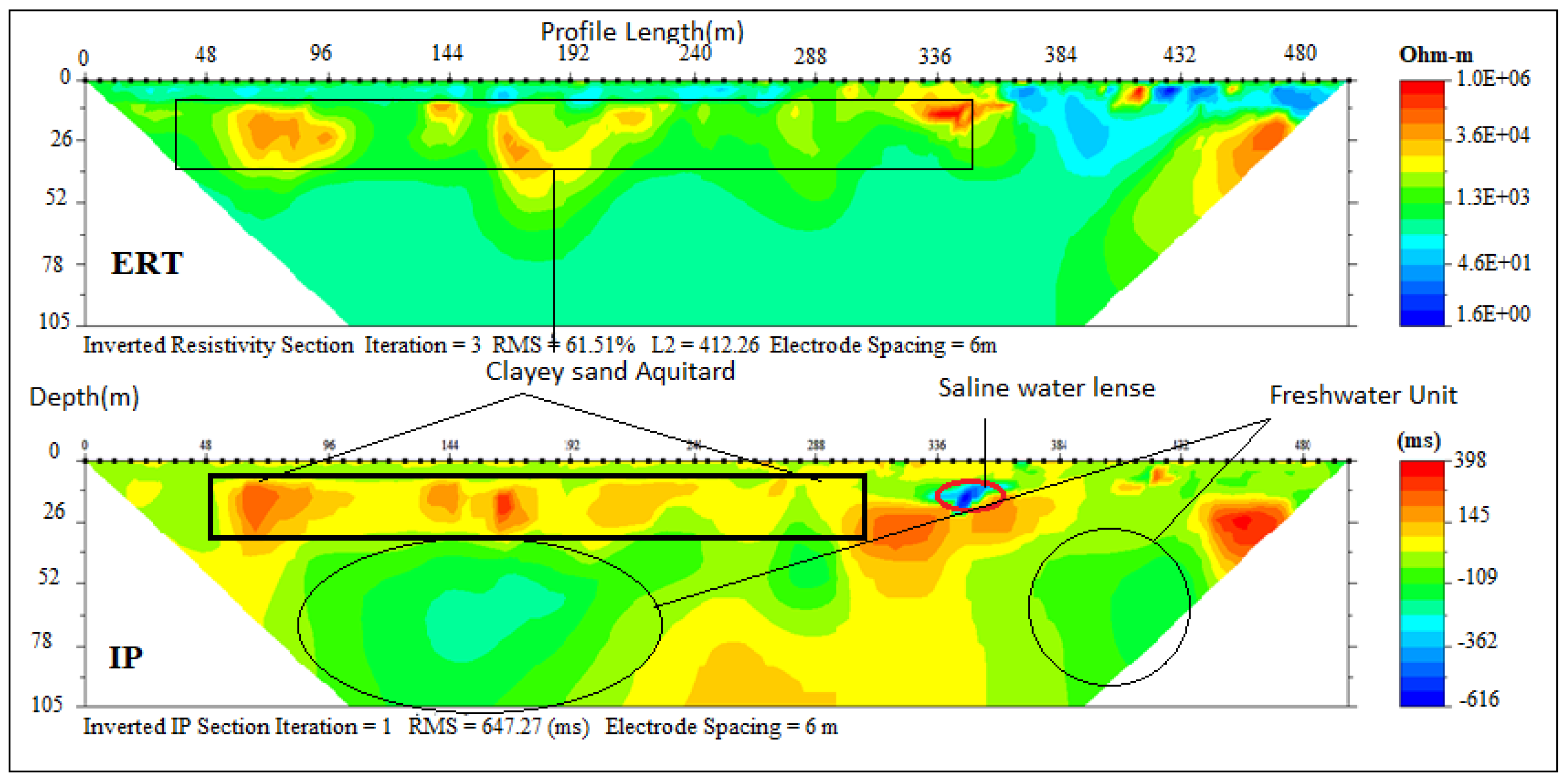
Table 4 (Figure 7) at the northern end for profile A–B were carried out along the Igbokoda Okitipupa road. These sections revealed three geoelectrical layers with resistivity/chargeability values ranging between (60–300Ωm/100–200 ms), (300–1700 Ωm/80–150 ms) and (200–700 Ωm /30–120 ms) suspected to be lateritic topsoil, sandy clay and fine grain sand with clay lenses. The resistivity values indicated a freshwater aquifer with depth ranges between 13m to 36 m underlying the lateritic clay topsoil which serve as a protective layer for the aquifer. Hence the relatively good groundwater quality observed in wells around this area. The overall results on this profile showed an improved water quality along the northern part of the study area away from the coast, which is due to hydraulic properties of the lithology.
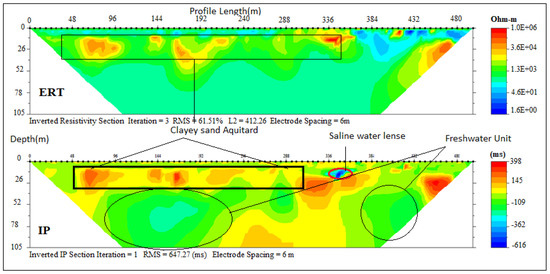
Figure 7.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections of Okitipupa road (Profile section P4).
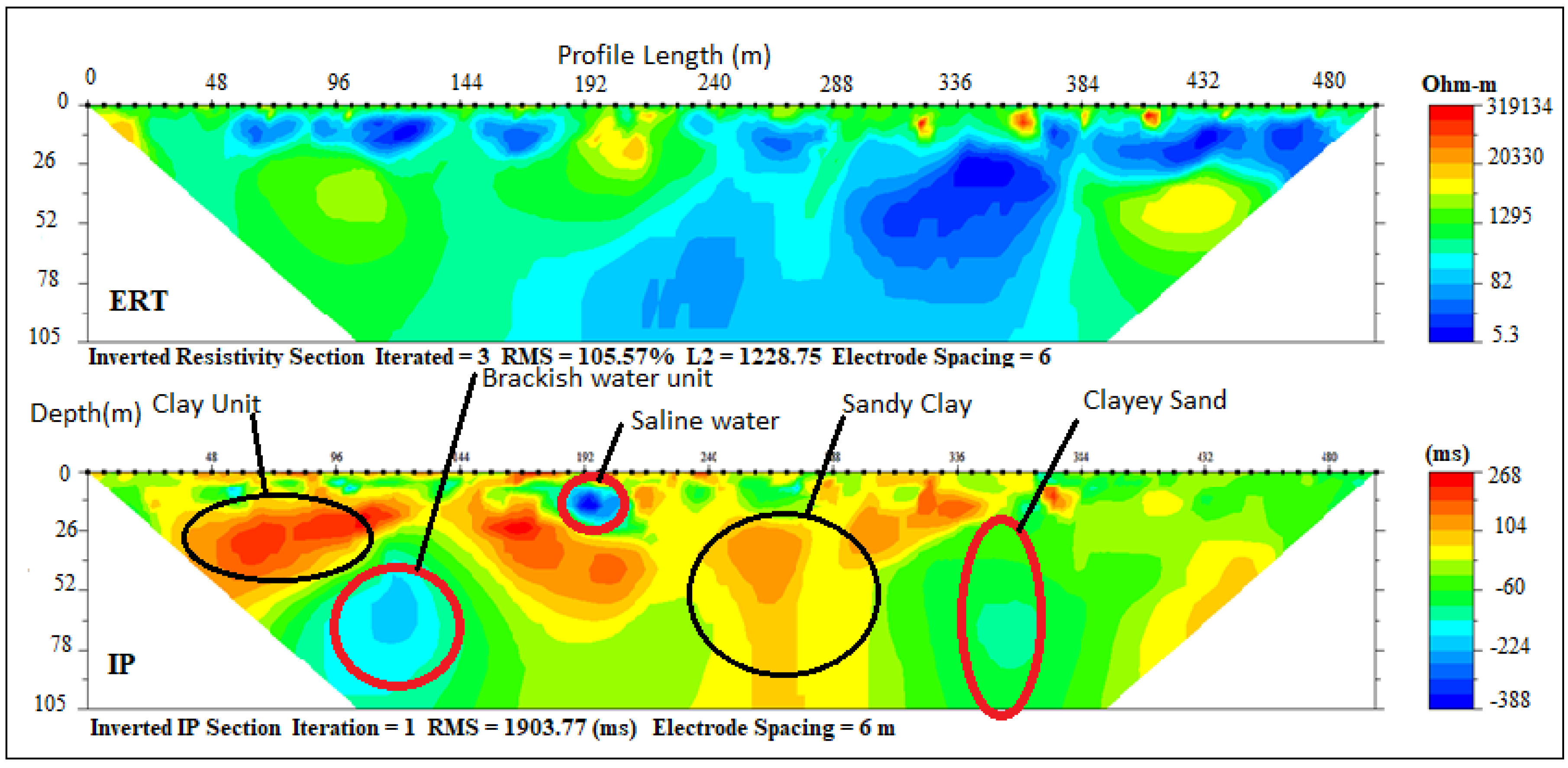
Profile C–D (Figure 1) is parallel to the coastline and consists of three ERT, with their respective IP sections (2, 3, 5, 6 and 7) carried out at Aboto, Abule-Ipare, Abule-Obi and Araromi towns, respectively. ERT and IP section P5 (Figure 8) revealed three geoelectrical layers with resistivity/chargeability values ranges between (50–496 Ωm/−100–40 ms), (32–300 Ωm/0–100 ms) and (40–180 Ωm/−40–20 ms). These results revealed unconsolidated wet sand, sandy clay and fine-grain sand with clay lenses. The average thickness of the first and second layers are 25 m and 35 m, respectively, while the second layer has thickness beyond 58 m. Saline water intrusion was observed around some lensoid shape clay with low resistivity, and high chargeability observed within the layers. Sandy clay with an average thickness of 35 m formed a semi-aquitard layer. A lensoid shape area within the geoelectric section with a resistivity of about 4200 Ωm and chargeability of 400 ms was suspected to be buried hardpan of ferruginised clay or mudstone found at a very shallow depth.
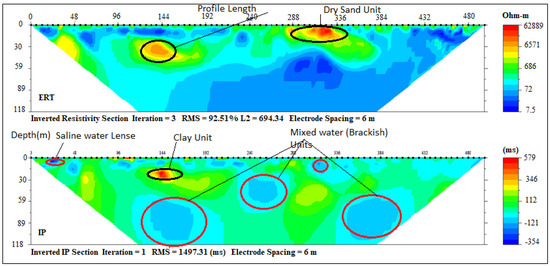
Figure 8.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Ebute Ipare (Profile section P5).
At Abule-Obi, integrated ERT and IP sections P7 (Figure 9) also delineated three geoelectrical layers with resistivity and chargeability value ranges between (10–130 Ωm/80–300 ms), (1–70 Ωm/20–120 ms) and (1–50 Ωm/10–60 ms) which were indications of silty clay topsoil, sandy clay and fine-grain sand with clay lenses similar to Abule-Ipare section. The average thickness of these layers was 15, 27, and 63 m. Low resistivity and chargeability of the third layer indicated saline water intrusion.
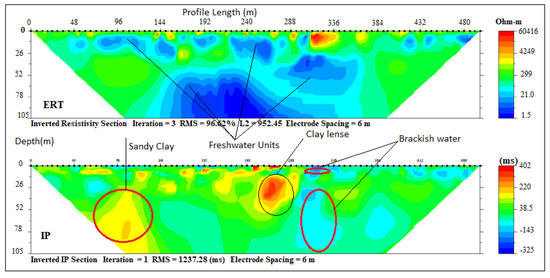
Figure 9.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Abule-Obi (Profile section P7).
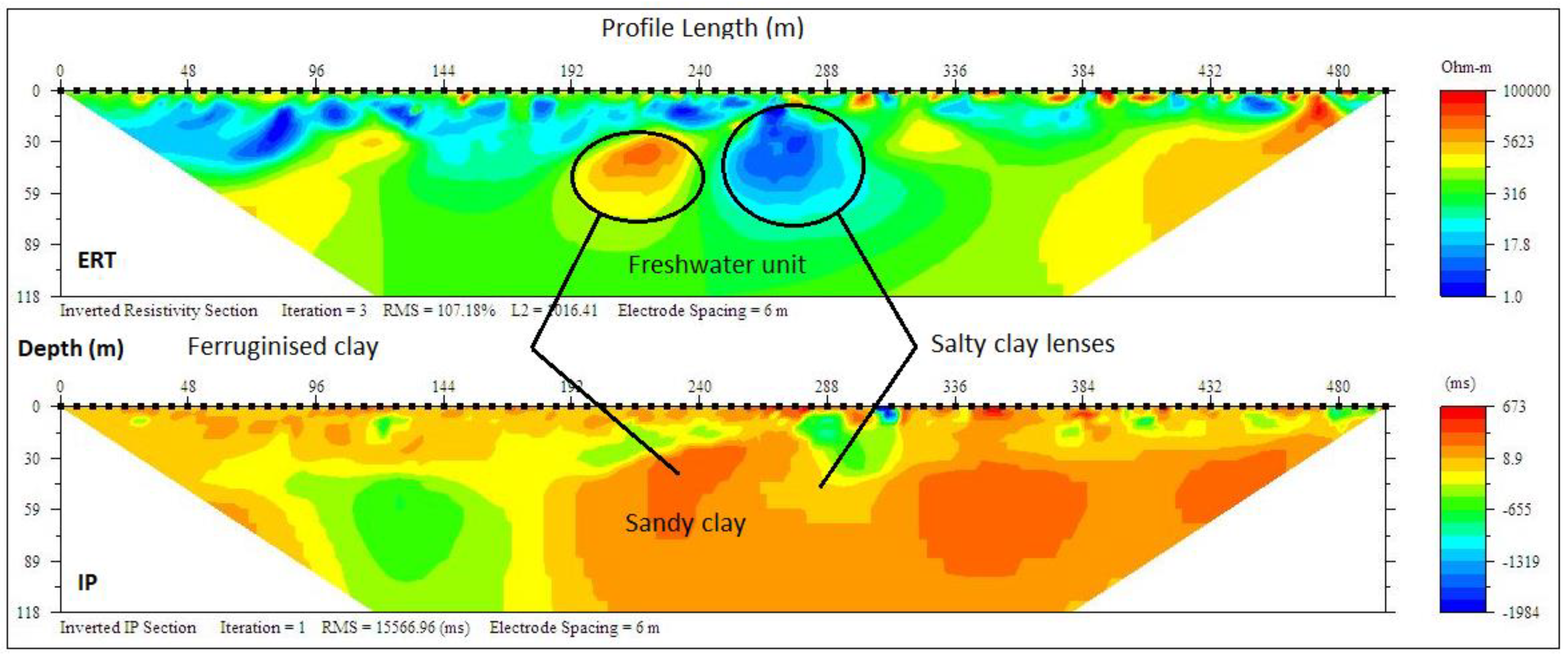
ERT and IP Section P6 (Figure 10) carried out around Araromi village delineated only two distinct geoelectrical layers with resistivity values range between (1–20/-200 Ωm–10 ms) and (5–150 Ωm/80–20 ms) which was an indication of a silty sand topsoil and fine-grain sand with silty/clay lenses with 23 m and >76 m thick respectively. The second layer, though predominantly clay, had a portion of sandy clay which can be classified as the freshwater aquifer in the area which was well protected by the first layer of sandy clay, thus responsible for the relatively improved water quality in this zone compared to Ugbonla and Igbokoda salt lenses trapped within the clayey layers (Figure 11). The general low resistivity observed in the form of salt lenses in most of the sections could be due to the effect of the ocean transgression and regression which occurred along this coast in past ages (Cretaceous to Tertiary), responsible for the deposition of the sediments that formed the strata [41,42,43]. Both resistivity and chargeability interpretations of these section with depths are presented in Table 5.
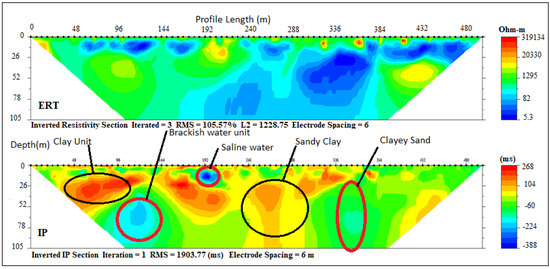
Figure 10.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Araromi (Profile section P6).
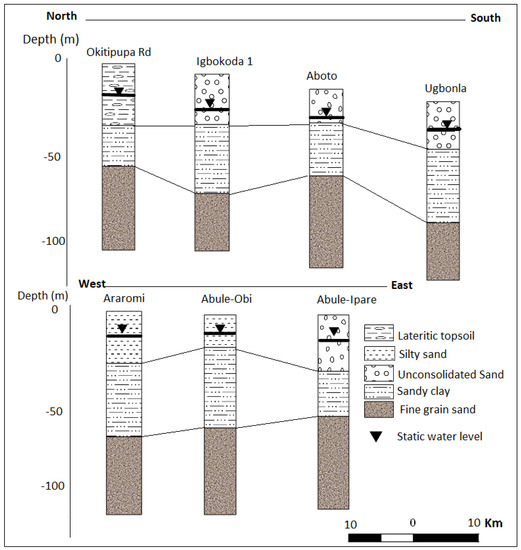
Figure 11.
Lithological description of profiles A–B and C–D.

Table 5.
Lithological interpretation of geoelectrical sections from Profile B–C.
Profile E–F (Figure 1) is located parallel to the coastline of Lagos and very close to areas with wells with enhanced electrical conductivity (EC) values suspected to be a fingerprint of saltwater intrusions as presented earlier in Figure 1. Locations such as Eleko, Lakowe and Okun-Ajjah were selected along profile line E–F.
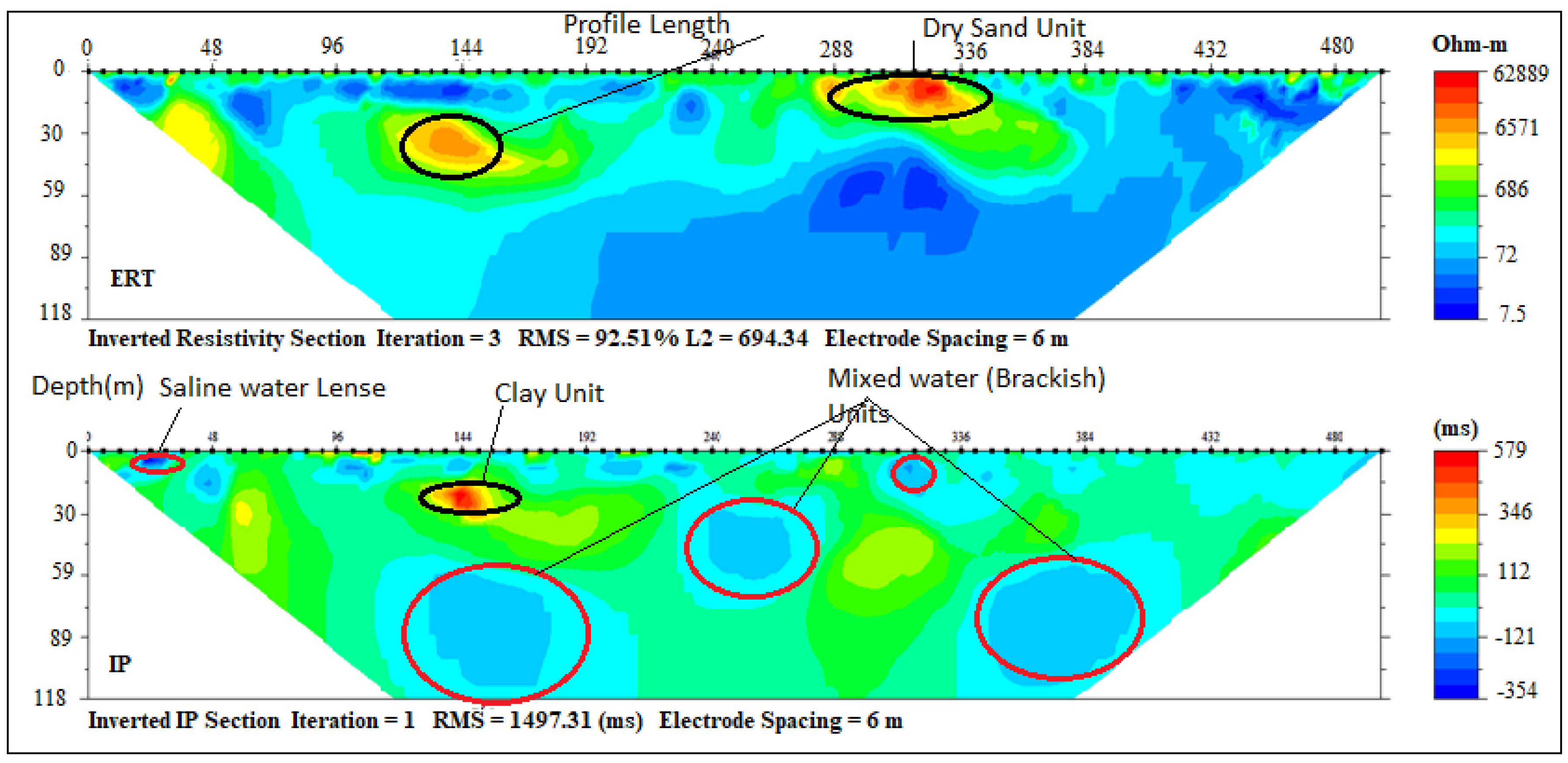
Three (3) geoelectrical layers delineated under ERT and IP section P8 (Figure 12) with resistivity/chargeability ranging from (300–6000 Ωm/−100–301 ms) −300 and 300–400 Ωm/, 1–20 and 10–400 ms respectively. These lithological units were suspected to be dry loose sand, ferruginised clayey sand and sandy clay with the depth ranging 0–6, 6–45, and 45–118 m, respectively.
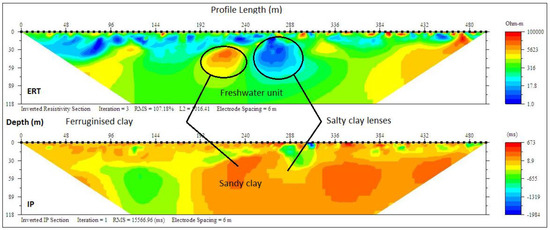
Figure 12.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Eleko Profile E–F (Profile section P8).
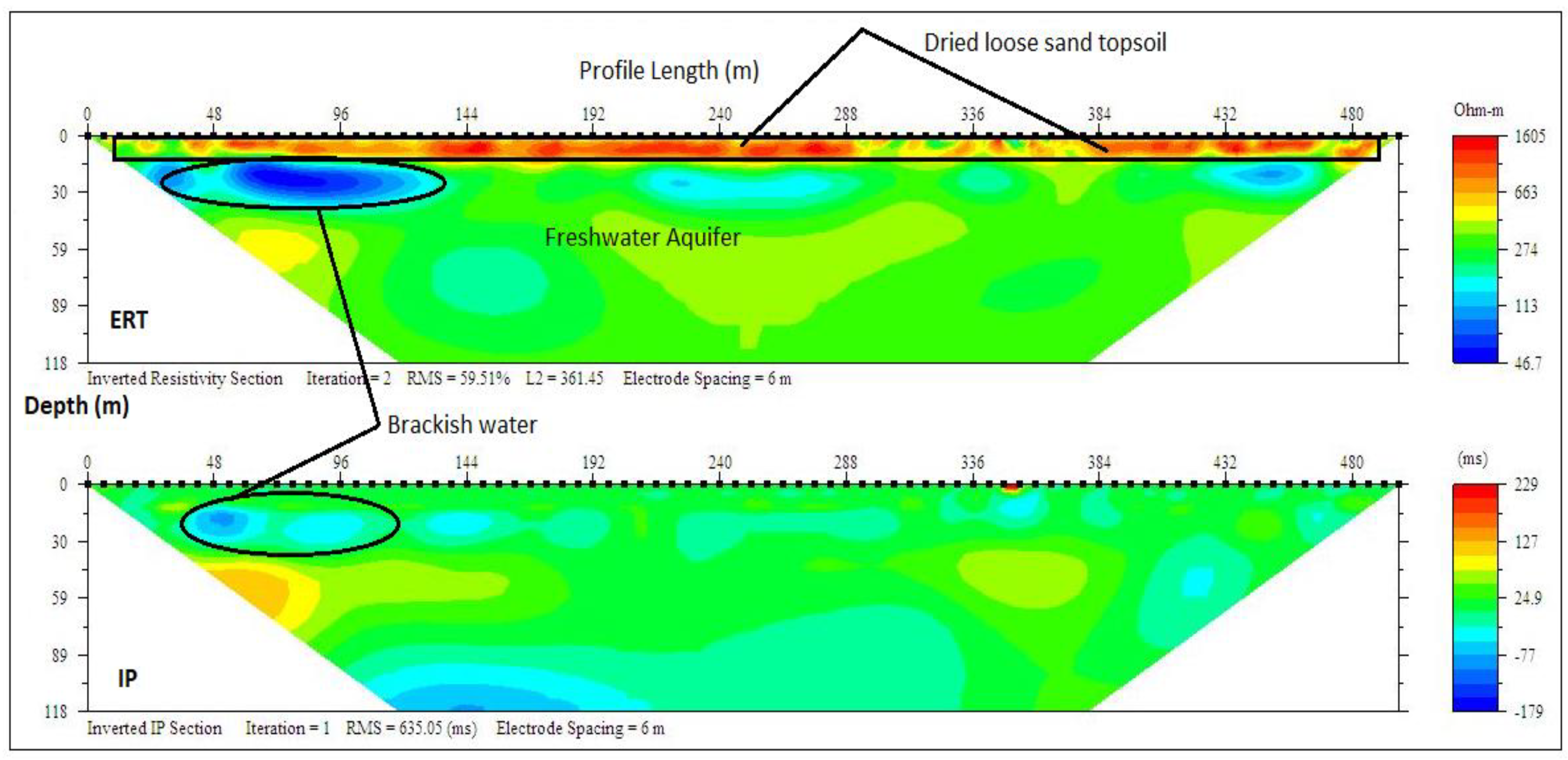
The ERT and IP profile section P9 (Figure 13) at Lakwe revealed three layers with resistivity and chargeability (470–1605 Ωm/10–30 ms), (100–200 Ωm/−80–10 ms) and (200–500 Ωm/−100–110 ms) respectively. These layers were suspected to be dry loose sand topsoil, sandy clay with lenses of brackish water and fine grain sands saturated with freshwater with a respective average depth of 8, 23 and 79 m.
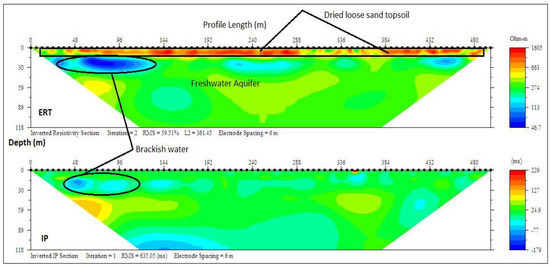
Figure 13.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Lakowe (Profile section P9).
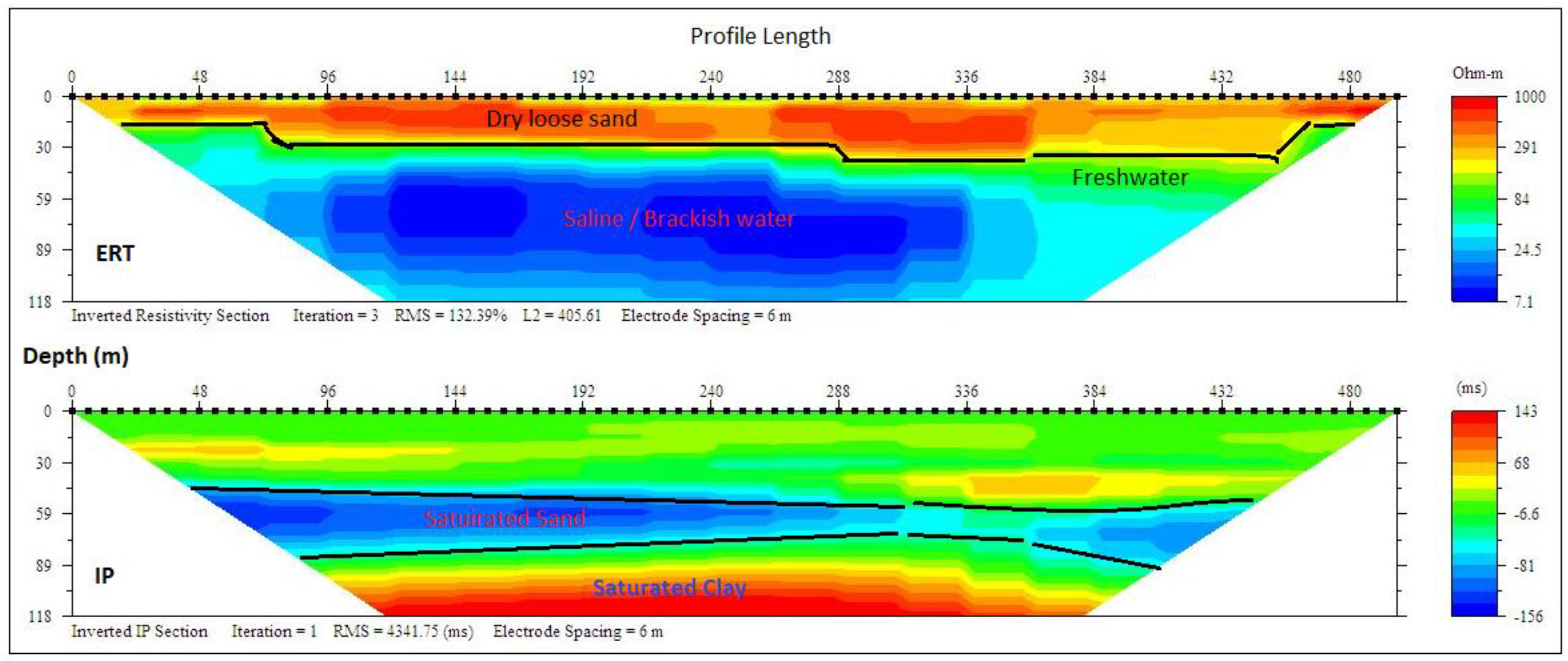
ERT and IP profile section P10 at Okun-Ajjah (Figure 14), like the previous ones, delineated three layers with resistivity/chargeability values ranging between (100–1000 Ωm/−10–60 ms), (50–200 Ωm/−150–1 ms) and (7–30 Ωm/50–143 ms) from the top to the third layer. These values indicated loose dry sand and fine-medium grain sand and clay/sandy clay, with an average thickness of 15, 28 and 79 m. The first layers contained freshwater, while the underlining layers were saturated with saline water which could be attributed to the enhanced conductivity observed in water sampled from wells which were below 15 m at Okun Ajjah and Ogumbo. However, most of the wells in this zone are shallow wells which are generally below 20 m which were vulnerable to contamination and pollution from the surface water, while deeper wells are around Lekki, Victoria Island and Okun-Ajjah were tapping saline water. The interpretations of the three sections along this profile line is presented in Table 6 with lithostratigraphical sections presented in Figure 15.
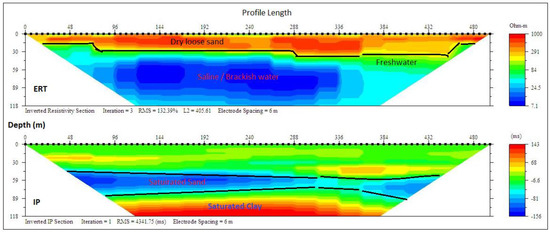
Figure 14.
Inverted resistivity and IP cross-sections Okun-Ajjah (Profile section P10).

Table 6.
Lithological interpretation of geoelectrical sections from Profile E–F.
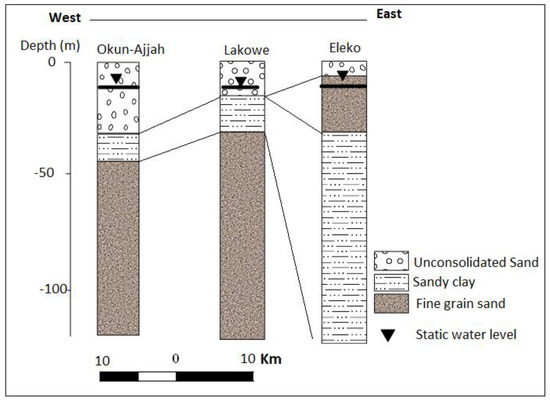
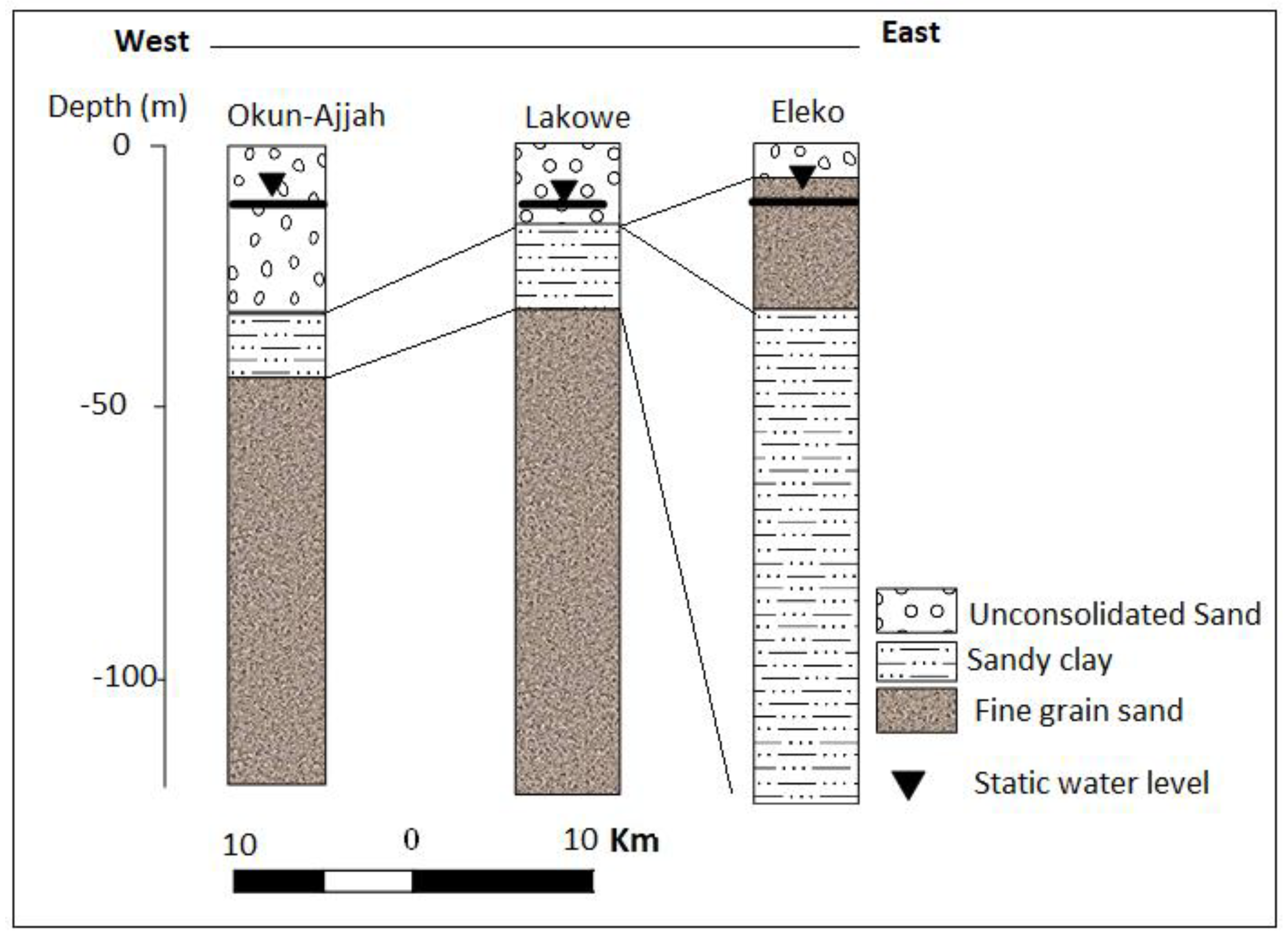
Figure 15.
Litho-log from electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and IP from Profile E–F.
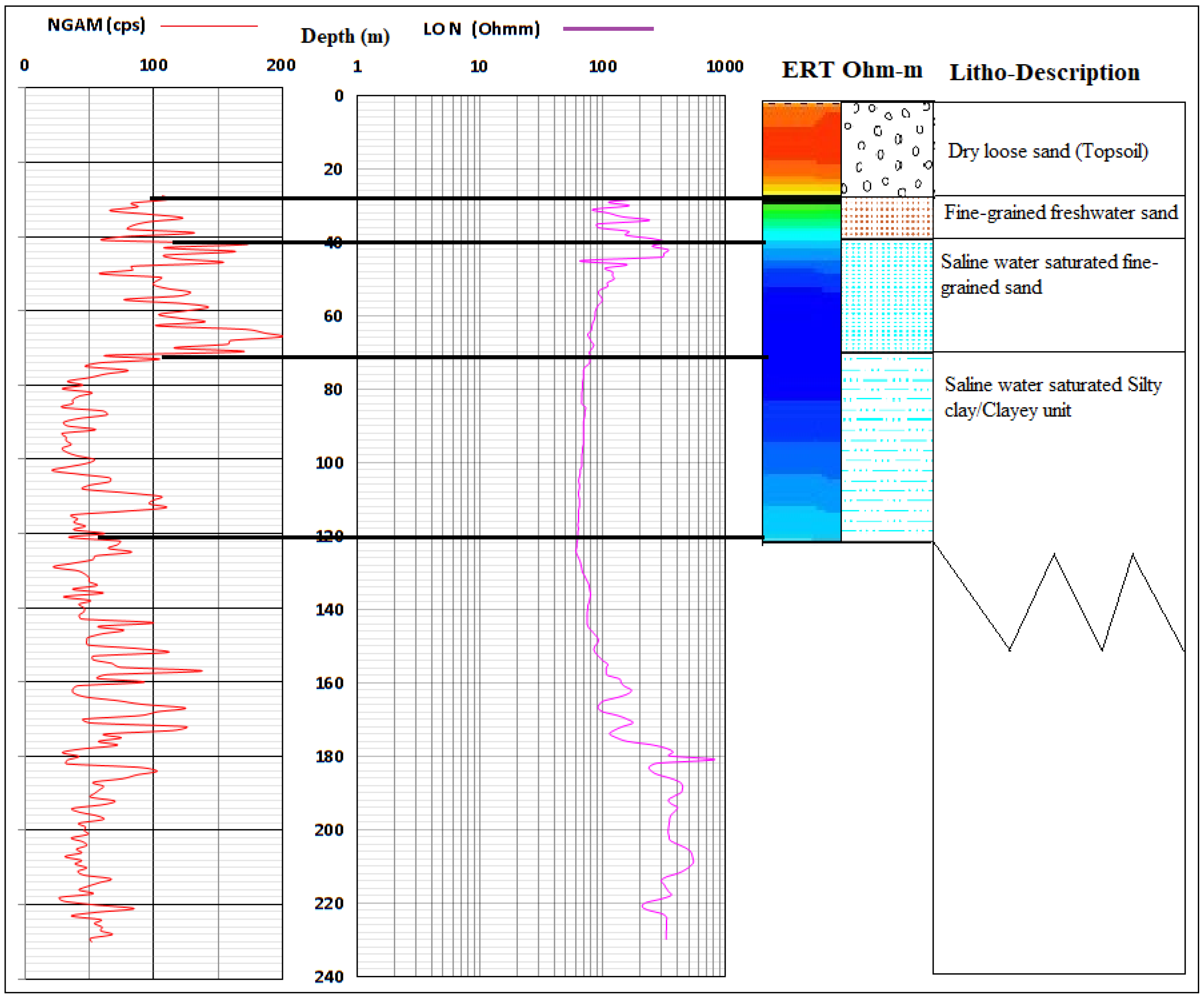
3.3. Correlation of the Geoelectrical Sections with Borehole Logs
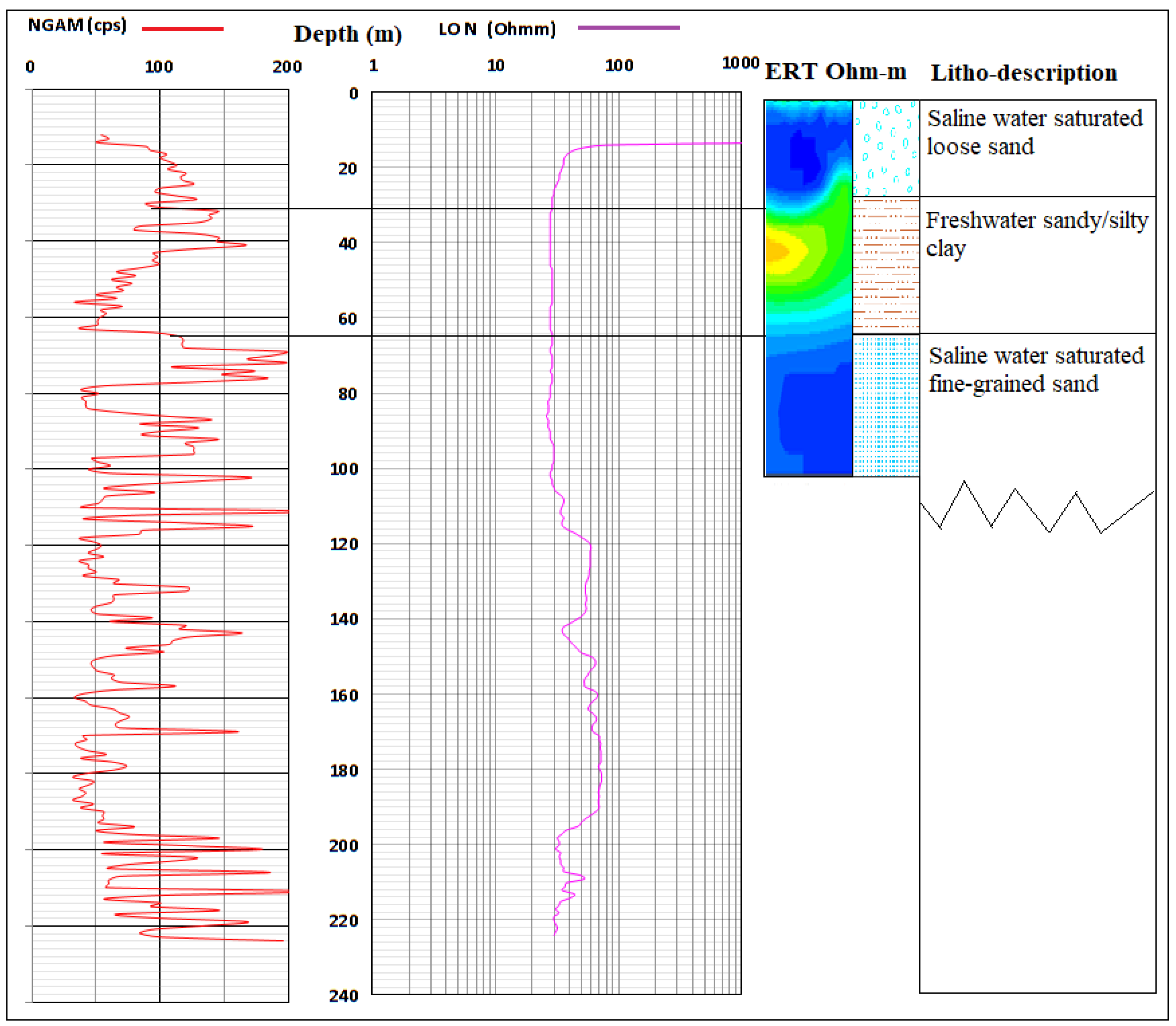
Challenges result from complex geo-electrical and hydrogeological characteristics such as electrical conductivity/resistivity and porosity/hydraulic conductivity of coastal lithology. This is commonly attributed to cumulative error from data acquisition and processing; it is necessary to apply this method together with other direct tools such as borehole logging for the subsurface investigation to increase confidence in results and outcome. The result of the ERT was, therefore, correlated with two borehole logs from both ends of the basin along profiles A–B and E–F in a bid to confirm the lithological surface boundary as established from ERT and IP. Gamma and ERT profiles alongside lithological log description are presented in Figure 16 and Figure 17. The results confirm the presence of lower hydraulic conductivity in the second layer of sandy/silty clay which separated it from the top unconsolidated sandy to the silty sand unconfined aquifer and the third layer of confined fine-grained sands with clay lenses aquifer around Igbokoda and Ugbonla which experience enhanced conductivity in a few of the sampled boreholes. Also, correlation of sections with a borehole log (Figure 17) along with profile/traverse line E–F revealed a thick layer of saltwater saturated fine-grained sands, and silty clay around the Okun-Ajjah area of Lekki. The layers are overlain by unconsolidated loose sand which is common to entire Cretaceous to the recent coastal plain sand of the basin.
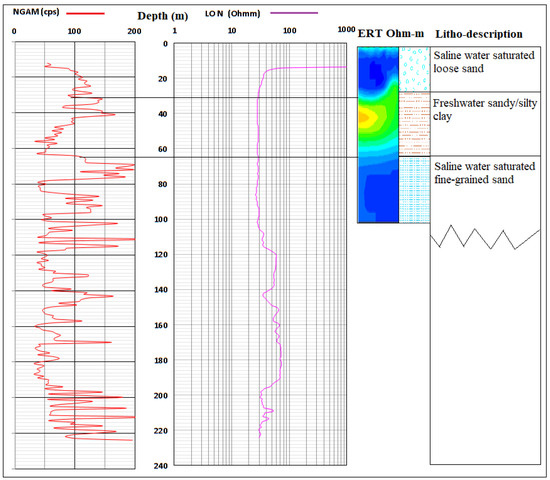
Figure 16.
Correlation of borehole log (BH-1) with ERT along Profile A–B.
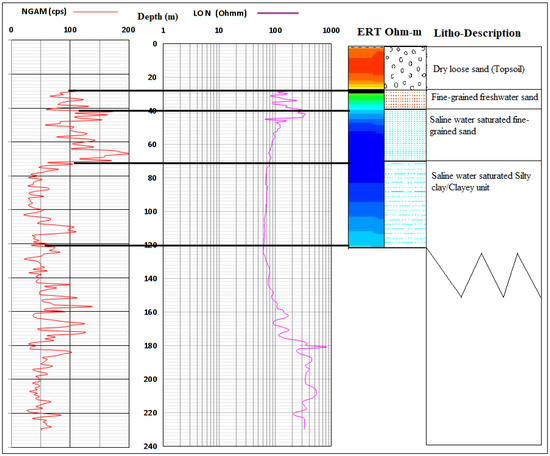
Figure 17.
Correlation of borehole log (BH-3) with ERT along Profile E–F.
4. Conclusions
This study has conducted investigations to characterise the hydrostratigraphy of the shallow coastal aquifer of the Eastern Dahomey Basin, Southwestern Nigeria. Enhanced electrical conductivity revealed from field physicochemical measurements across the basin, the geophysical method of ERT and IP and a few borehole loggings were carried out in locations around Igbokoda, Aboto, Ugbonla, Abule-Ipare, Abule Obi and Araromi, Okun-Ajjah, Lakowe and Eleko across the coastal communities of the basin.
These approaches have demonstrated a high level of efficiency and effectiveness in delineating lithological layers underlying the coaster aquifers and detected clay lenses which are possible sources of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer in the area. The results of the ERT and IP revealed intercalation of sand and clay underlying the coastal area. However, the maximum depth delineated along the traverses were 105 m and 118 m from which 3 to 4 geoelectrical layers were mapped and from which the resistivity and chargeability values indicated lateritic topsoil, unconsolidated sand, sandy clay/clayey sandy, fine grain sand with clay lenses.
Unconsolidated sands at the top constitute the unconfined aquifer which is underlain in most areas by sandy clay /clayey sand, which serves as a semi-aquifer unit with depth ranges between 13 m and 45 m, while the third layer represents the fine-grained sands with clay lenses in some areas which characterised the Ondo-State axis of the coast. The results reveal the clay lenses in the second and third layers, which could be the trap of saltwater attributed to evaporite deposited within the basin during the ancient transgression and regression that produced deposition sediments. Some clay lenses suspected to contain saltwater also were delineated under the sections in Lakowe while a thick sandy aquifer with an average thickness of 25 m saturated with saline water was observed in the Okun-Ajjah profile sections. There is a thin layer of freshwater overlying this unit which is the source of freshwater recharging the shallow wells less than 20 m deep. This layer is highly vulnerable and sensitive to saline water intrusion if groundwater exploitation exceeds the current state. This type of intrusion is responsible for the enhanced electrical conductivity in most wells in the area which are drilled beyond 25 m. This situation is wholly unsustainable since most of the freshwater units in this area generally reside within the unconfined or semi-confined aquifer which is vulnerable to contamination from polluted surface water and leachates from industrial and municipal waste that characterise this densely populated coastal zone.
Finally, the methods used have identified two possible sources of saltwater intrusion into the coastal freshwater aquifer of Eastern Dahomey Basin; namely, dissolution of evaporite/salt lenses within the clay layer and direct (flow boundary) connection between the sea and the coastal aquifer in areas very close to the sea due to lack of a hydraulic boundary. For a further understanding of the saltwater within the coastal areas of this basin, it is, therefore, necessary to use another method such as hydrochemical and isotope analysis. Finally, a detailed saltwater vulnerability map of the area is necessary to develop a sustainable groundwater management strategy to protect this fragile resource from further deterioration.
Author Contributions
J.A.A. and R.M.K. designed the research; J.A.A. wrote the original draft; R.M.K., P.S. and I.H. reviewed and edited the manuscript; R.M.K. gave critical views on the manuscript for further improvement. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Nigeria Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND and supported by the Scottish Government under the Climate Justice Fund Water Futures Programme, awarded to the University of Strathclyde (R.M. Kalin).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge Ismail Babatunde, Sanni Babatunde and Damilola Bolaji Ajibola for field assistance during data acquisition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mulrennan, M.E.; Woodroffe, C.D. Saltwater intrusion into the coastal plains of the Lower Mary River, Northern Territory, Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 1998, 54, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creel, L. Ripple Effects: Population and Coastal Regions. Available online: https://www.prb.org/rippleeffectspopulationandcoastalregions (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Oteri, A.U.; Atolagbe, F.P. Saltwater Intrusion into Coastal Aquifers in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers—Monitoring, Modeling, and Management, Mérida, Mexico, 30 March–2 April; pp. 1–15.
- Wu, M.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, C.C.; Wang, H.; Dong, J.-D.; Yin, J.P.; Han, S.H. Identification of coastal water quality by statistical analysis methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwafemi, A.; Jakpor, P.; Bohme, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Lobina, E. Lagos Water Crisis Alternative Roadmap for Water Sector. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/nigeria/lagos-water-crisis-alternative-roadmap-public-water-sector (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Ayolabi, E.A.; Oyelayo, F.J. Geophysical and hydrochemical assessment of groundwater pollution due to a dumpsite in Lagos State, Nigeria. J. Geol. Soc. India 2005, 66, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Ayolabi, E.A.; Folorunso, A.F.; Odukoya, A.M.; Adeniran, A.E. Mapping saline water intrusion into the coastal aquifer with geophysical and geochemical techniques: The University of Lagos Campus Case (Nigeria). SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayolabi, E.A.; Epelle, E.S.; Lucas, O.B.; Ojo, A. Geophysical and geochemical site investigation of eastern part of Lagos Metropolis, Southwestern Nigeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 8, 7445–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, A.U.; Rasheed, A.A. The Lagos Megacity Project. Available online: http://eaumega.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/EN-Lagos-Monograph.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Adepelumi, A.A.; Ako, B.D.; Ajayi, T.R.; Afolabi, O.; Omotoso, E.J. Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, K.D.; Aizebeokhai, A.P.; Oladunjoye, M.A. Integrated geophysical and geochemical investigations of saline water intrusion in a Coastal Alluvial Terrain, Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2015, 10, 973–6077. [Google Scholar]
- Edet, A. Hydrogeology and groundwater evaluation of a shallow coastal aquifer, southern Akwa Ibom State (Nigeria). Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 7, 2397–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, J.A. Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal California Aquifer; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Tran, L.T.; Larsen, F.; Pham, N.Q.; Christiansen, A.V.; Tran, N.; Vu, H.V.; Tran, L.V.; Hoang, H.V.; Hinsby, K. Origin and extent of fresh groundwater, salty paleowaters and recent saltwater intrusions in Red River flood plain aquifers, Vietnam. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1295–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Bertrand, G.; Kloppmann, W.; Aquilina, L.; Martins, V.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Pauwels, H.; Chatton, E.; et al. Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 530, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longe, E.O.; Malomo, S.; Olorunniwo, M.A. Hydrogeology of Lagos metropolis. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1987, 6, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, A.U. Geophysical investigations of sea water intrusion into the Cainozoic aquifers of South Coast Kenya—A review. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1991, 13, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoti, L.; Alile, O.M.; Uchegbulam, O. Geophysical investigation of saline water intrusion into freshwater aquifers: A case study of Oniru, Lagos State. Sci. Res. Essays 2010, 5, 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Longe, E.O. Groundwater Resources Potential in the Coastal Plain Sands Aquifers, Lagos, Nigeria. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ayolabi, E.A.; Folorunso, A.F.; Kayode, O.T. Integrated geophysical and geochemical methods for environmental assessment of municipal dumpsite system. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odukoya, A.M.; Folorunso, A.F.; Ayolabi, E.A.; Adeniran, E.A. Groundwater quality and identification of hydrogeochemical processes within University of Lagos, Nigeria. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Krishan, G.; Macdonald, A.M.; Rao, M.S. Groundwater quality in the alluvial aquifer system of northwest India: New evidence of the extent of anthropogenic and geogenic contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, O.S.; Omatsola, M.E. Tectonic evolution and cretaceous stratigraphy of the dahomey Basin. J. Min. Geol. 1981, 18, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Okunlola, O.A.; Adeigbe, O.C.; Oluwatoke, O.O. Compositional and petrogenetic features of schistose rocks of Ibadan Area, Southwestern Nigeria. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2009, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar]
- Offodile, M.E. The Hydrogeology of coastal areas of southeastern states of Nigeria. J. Min. Geol. 1971, 14, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.A.; Hockey, R. The geology of part of southwestern Nigeria. GSN Bull. 1964, 31, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Adelana, S.M.A.; Olasehinde, P.I.; Bale, R.B.; Vrbka, P.; Edet, A.E.; Goni, I.B. An overview of the geology and hydrogeology of Nigeria. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1996, 29, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omosuyi, G.O.; Ojo, J.S.; Olorunfemi, M.O. Geoelectric sounding to delineate shallow aquifers in the coastal plain sands of Okitipupa Area, Southwestern Nigeria. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 62–77. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.H. Geoelectric resistivity sounding for delineating salt water intrusion in the Abu Zenima area, west Sinai, Egypt. J. Geophys. Eng. 2006, 3, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, K.O.; Raji, W.O.; Ayolabi, E.A. Application of 2-D resistivity survey to groundwater aquifer delineation in a sedimentary terrain: A case study of south-western Nigeria. Water Util. J. 2017, 17, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Buselli, G.; Lu, K. Groundwater contamination monitoring with multichannel electrical and electromagnetic methods. J. Appl. Geophys. 2001, 48, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, T.; Dlugosch, R.; Holland, R.; Yaramanci, U. Aquifer characterization using coupled inversion of DC/IP and Mrs Data on a hydrogeophysical test-site. Symp. Appl. Geophys. Eng. Environ. Probl. 2010, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayolabi, E.A.; Enoh, I.J.E.; Folorunso, A.F. Engineering site characterisation using 2-D and 3-D electrical resistivity tomography. Earth Sci. Res. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.; Nawawi, M.; Saad, R.; Abu-Rizaiza, A.S.; Yusoff, M.S.; Khalil, A.E.; Ishola, K.S. Characterization of active and closed landfill sites using 2D resistivity/IP imaging: Case studies in Penang, Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteri, A.U. Geoelectric investigation of saline contamination of a chalk aquifer by mine drainage water at Tilmanstone, England. Geoexploration 1981, 19, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franco, R.; Biella, G.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Lozej, A.; Chiozzotto, B.; Giada, M.; Rizzetto, F.; Claude, C.; Mayer, A.; et al. Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, D.; Silliman, S.; Boukari, M.; Yalo, N.; Orou-Pete, S.; Fertenbaugh, C.; Sarre, K.; Fayomi, H. Combined application of electrical resistivity and shallow groundwater sampling to assess salinity in a shallow coastal aquifer in Benin, West Africa. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, A.E.; Merkel, B.J.; Offiong, O.E. Trace element hydrochemical assessment of the Calabar Coastal Plain Aquifer, southeastern Nigeria using statistical methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2003, 44, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, A. An aquifer vulnerability assessment of the Benin formation aquifer, Calabar, Southeastern Nigeria, using DRASTIC and GIS approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1747–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyelami, A.C.; Ojo, O.A.; Aladejana., J.A.; Agbede, O.O. Assessing the effect of a dumpsite on groundwater quality: A case study of Aduramigba Estate within Osogbo Metropolis. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 3, 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Francés, A.P.; Ramalho, E.C.; Fernandes, J.; Groen, M.; Hugman, R.; Khalil, M.A.; De Plaen, J.; Santos, F.A.M. Contributions of hydrogeophysics to the hydrogeological conceptual model of the Albufeira-Ribeira de Quarteira coastal aquifer in Algarve, Portugal. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiora, D.N.; Onwuka, O.S. Groundwater exploration in Ikorodu, Lagos-Nigeria: A surface geophysical survey contribution. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2005, 6, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Igel, J.; Günther, T.; Kuntzer, M. Ground-penetrating radar insight into a coastal aquifer: The freshwater lens of Borkum Island. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).