Elevated CO2 Emissions during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Degassing at Awu Volcano, Sangihe Arc, Indonesia
Abstract
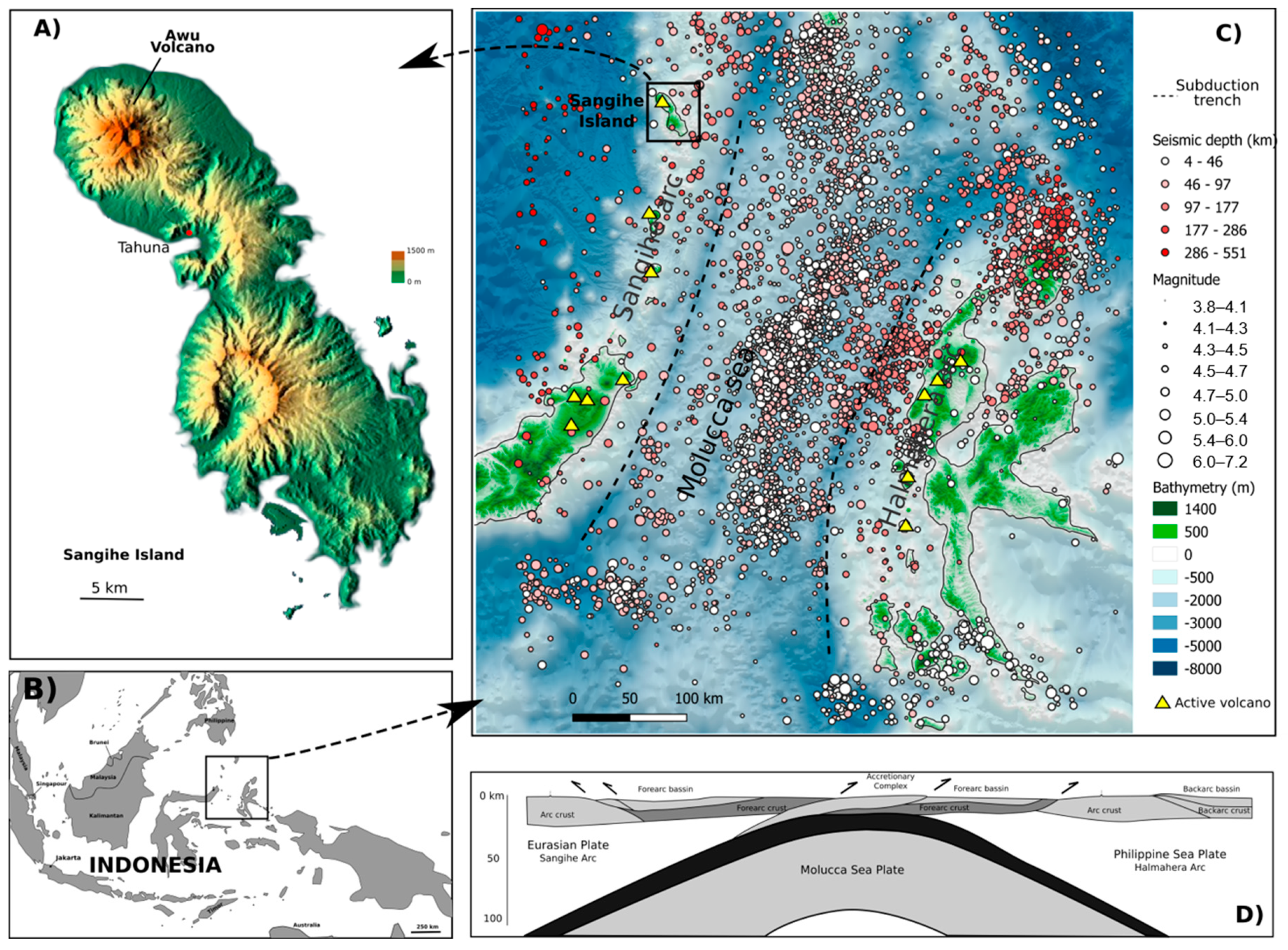
1. Introduction
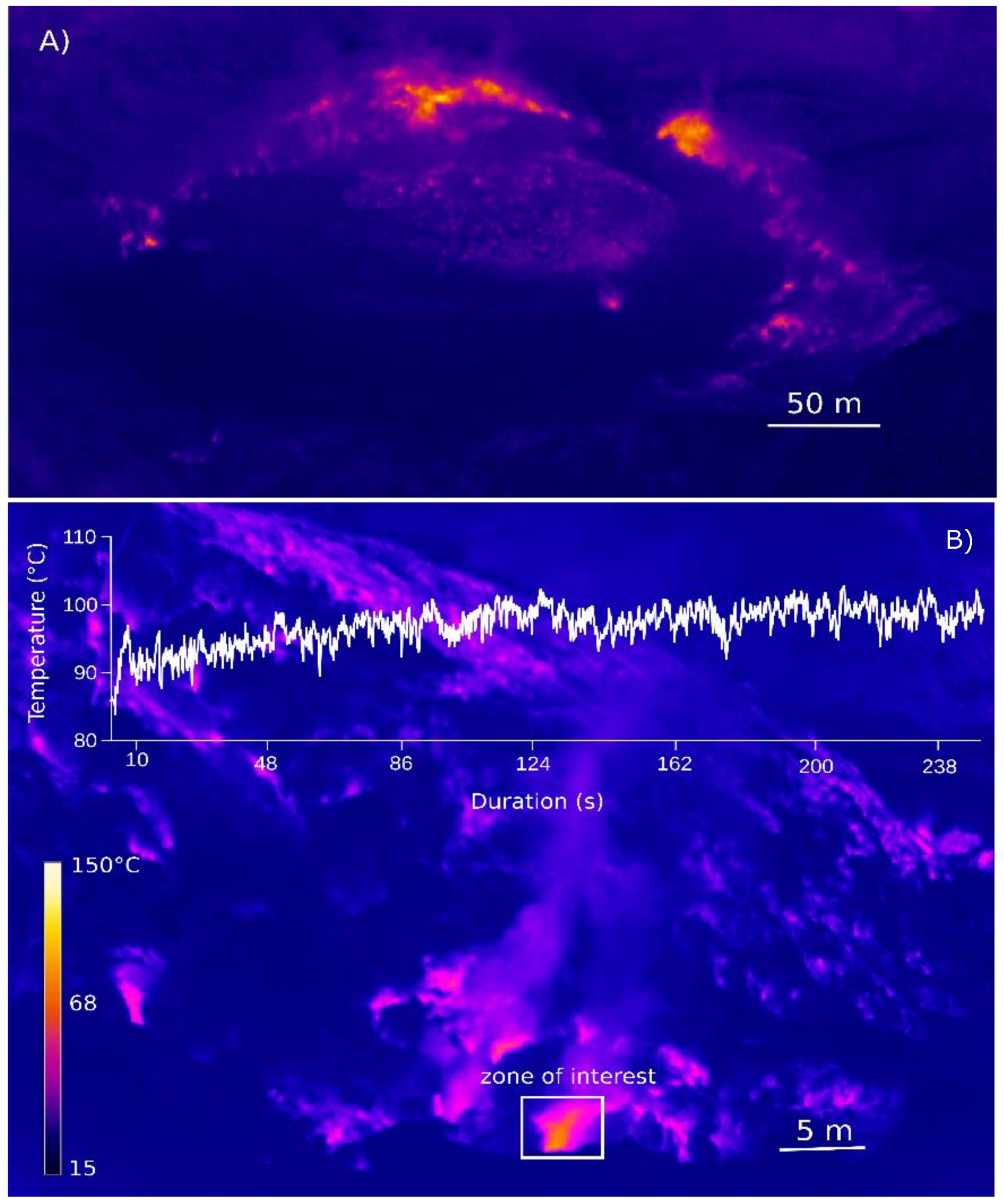
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. SO2 Emission Rate
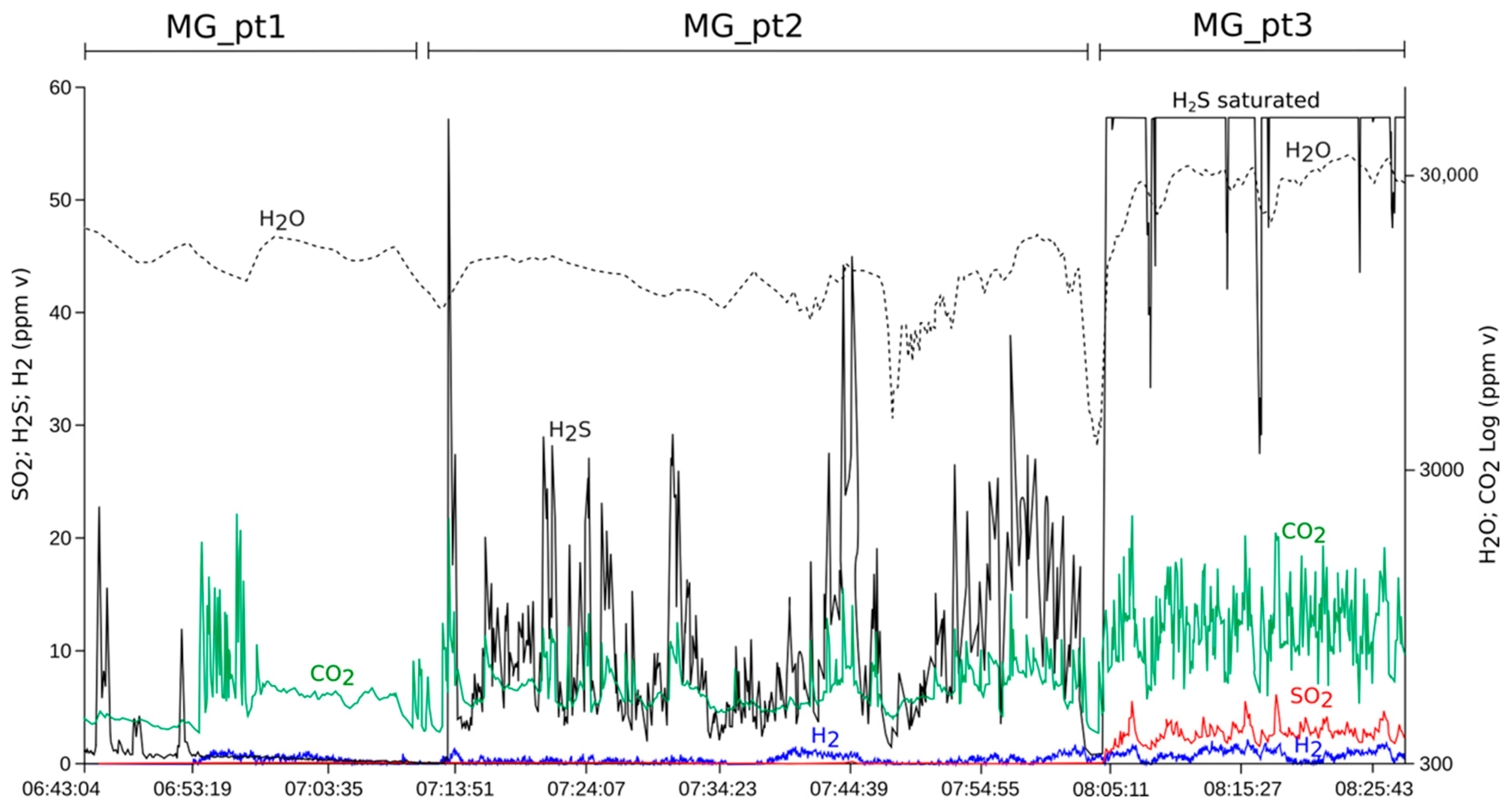
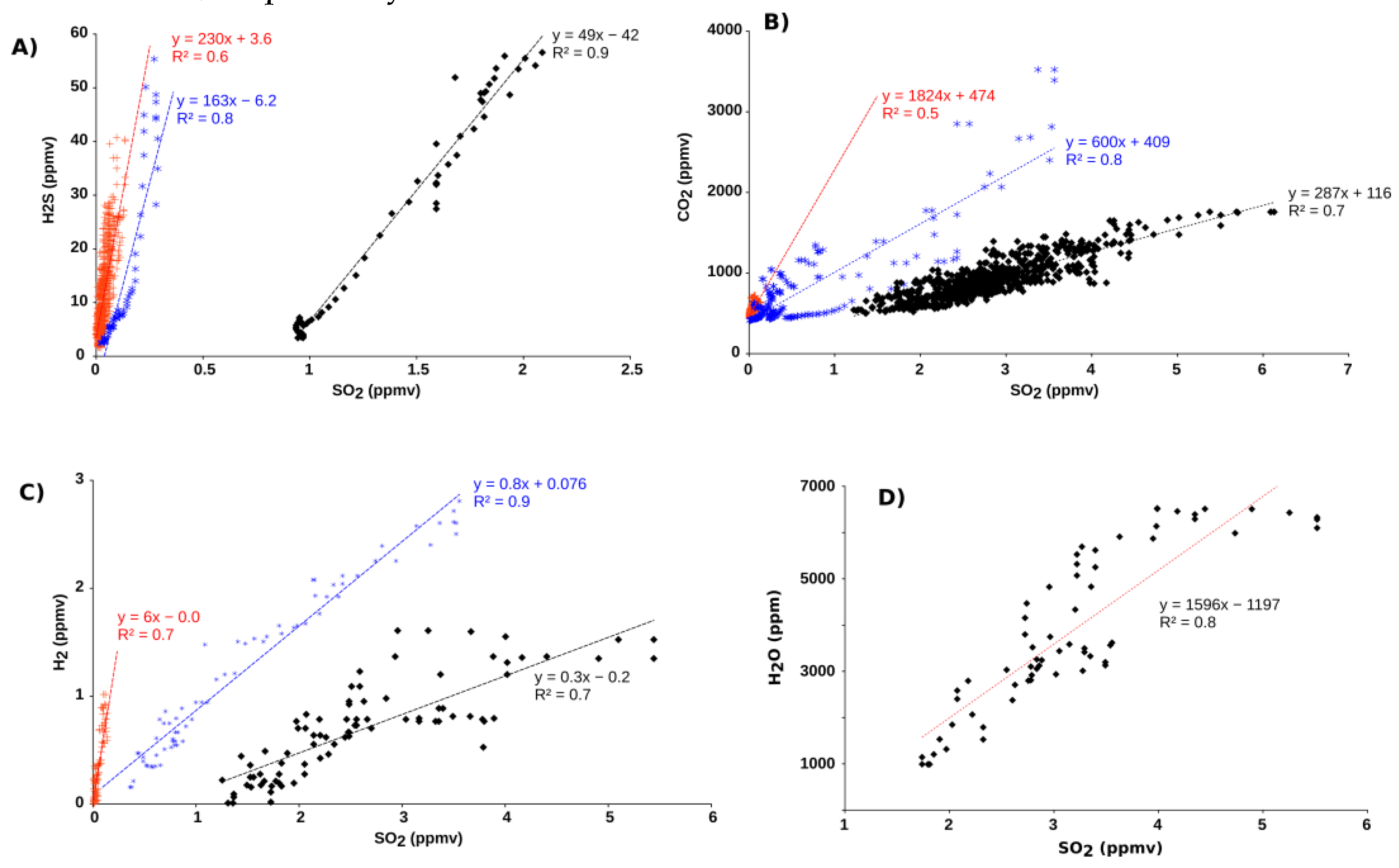
3.2. Gas Composition
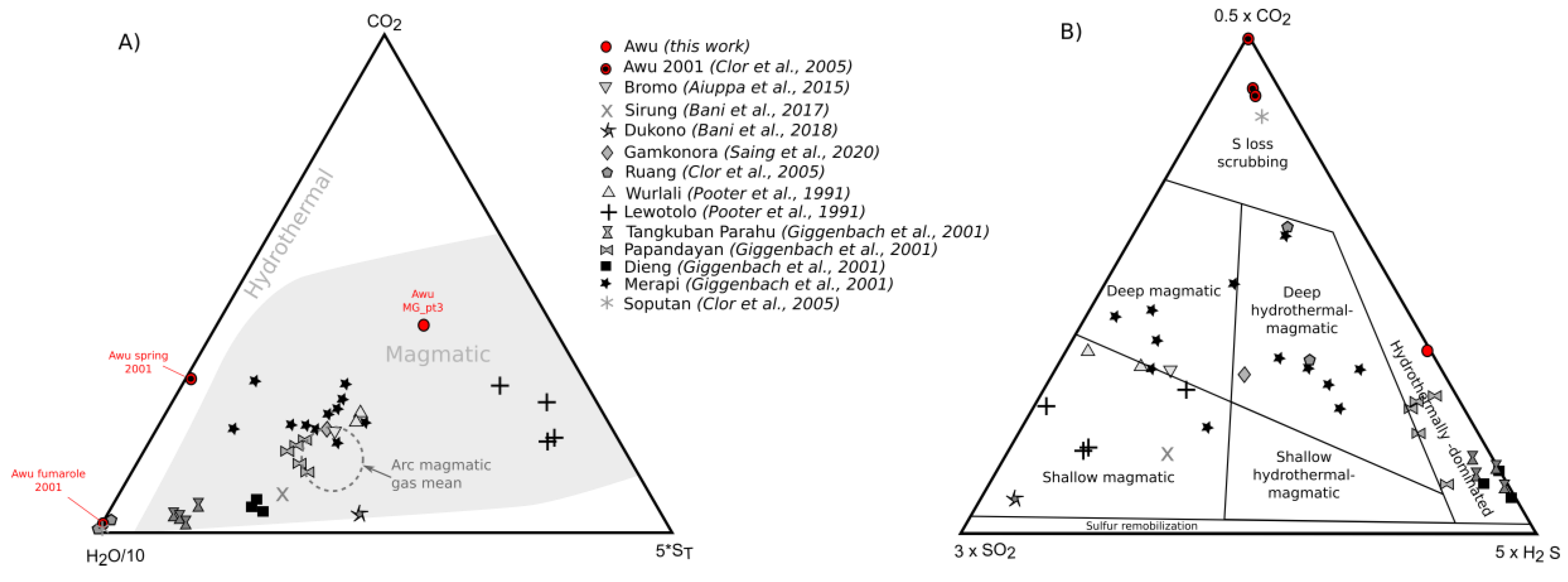
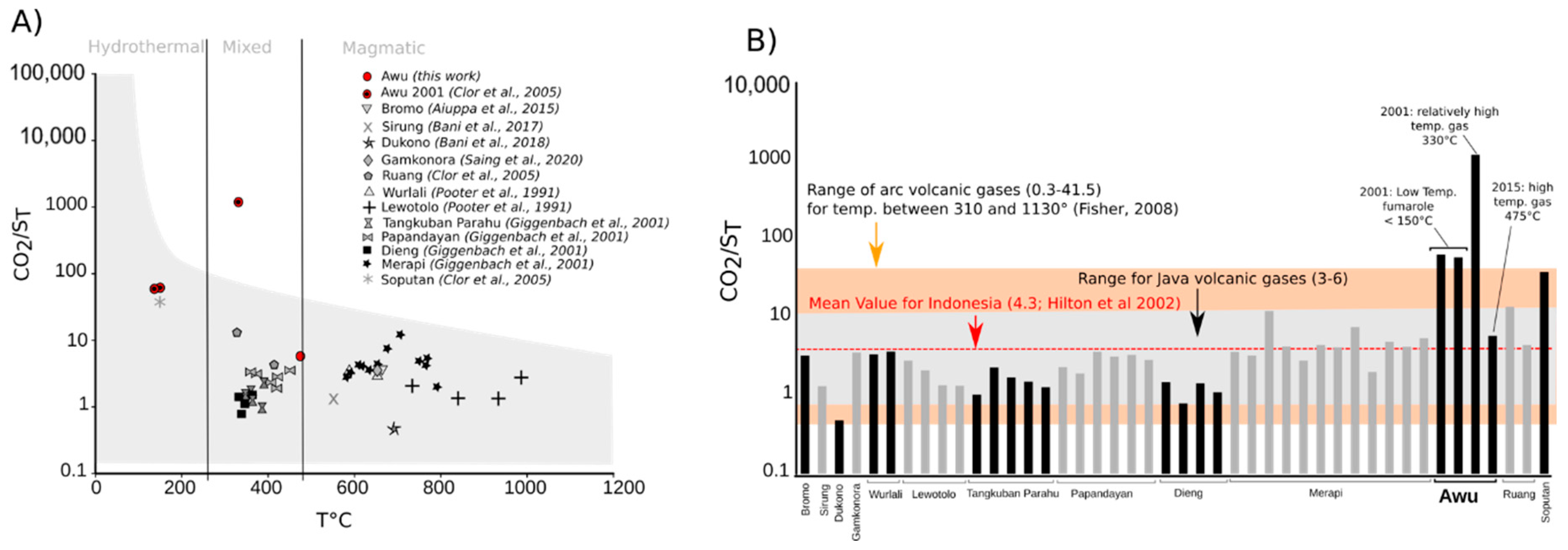
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poorter, R.; Varekamp, J.; Poreda, R.; Van Bergen, M.; Kreulen, R. Chemical and isotopic compositions of volcanic gases from the east Sunda and Banda arcs, Indonesia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Kasgnoc, A.D. A time-averaged inventory of subaerial volcanic sulfur emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1998, 103, 25251–25261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giggenbach, W.; Tedesco, D.; Sulistiyo, Y.; Caprai, A.; Cioni, R.; Favara, R.; Fischer, T.; Hirabayashi, J.-I.; Korzhinsky, M.; Martini, M.; et al. Evaluation of results from the fourth and fifth IAVCEI field workshops on volcanic gases, Vulcano island, Italy and Java, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2001, 108, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, D.; Fischer, T.P.; Marty, B. Noble Gases and Volatile Recycling at Subduction Zones. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2002, 47, 319–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, B.; Oppenheimer, C.; Geyer, A.; Mcgonigle, A.J.S.; Edmonds, M.; Horrocks, L. A miniaturised ultraviolet spectrometer for remote sensing of SO2 fluxes: A new tool for volcano surveillance. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2003, 119, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Burton, M. The SO2 camera: A simple, fast and cheap method for ground-based imaging of SO2 in volcanic plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 24804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Federico, C.; Giudice, G.; Gurrieri, S. Chemical mapping of a fumarolic field: La Fossa Crater, Vulcano Island (Aeolian Islands, Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, H. A new technique to estimate volcanic gas composition: Plume measurements with a portable multi-sensor system. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2005, 143, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smekens, J.-F.; Clarke, A.B.; Burton, M.R.; Harijoko, A.; Wibowo, H.E. SO2 emissions at Semeru volcano, Indonesia: Characterization and quantification of persistent and periodic explosive activity. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 300, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Normier, A.; Bacri, C.; Allard, P.; Gunawan, H.; Hendrasto, M.; Surono; Tsanev, V. First measurement of the volcanic gas output from Anak Krakatau, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 302, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, H.; Caudron, C.; Pallister, J.; Primulyana, S.; Christenson, B.; McCausland, W.; Van Hinsberg, V.; Lewicki, J.; Rouwet, D.; Kelly, P.; et al. New insights into Kawah Ijen’s volcanic system from the wet volcano workshop experiment. Geol. Soc. London Speéc. Publ. 2016, 437, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Alfianti, H.; Aiuppa, A.; Oppenheimer, C.; Sitinjak, P.; Tsanev, V.; Saing, U.B. First study of the heat and gas budget for Sirung volcano, Indonesia. Bull. Volcanol. 2017, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Tamburello, G.; Rose-Koga, E.F.; Liuzzo, M.; Aiuppa, A.; Cluzel, N.; Amat, I.; Syahbana, D.K.; Gunawan, H.; Bitetto, M. Dukono, the predominant source of volcanic degassing in Indonesia, sustained by a depleted Indian-MORB. Bull. Volcanol. 2018, 80, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primulyana, S.; Kern, C.; LerneriD, A.; Saing, U.B.; Kunrat, S.L.; Alfianti, H.; Marlia, M.; Marlia, M. Gas and ash emissions associated with the 2010–present activity of Sinabung Volcano, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2019, 382, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saing, U.B.; Bani, P.; Haerani, N.; Aiuppa, A.; Primulyana, S.; Alfianti, H.; Syahbana, D.K. Kristianto First characterization of Gamkonora gas emission, North Maluku, East Indonesia. Bull. Volcanol. 2020, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guern, F. Les débits de CO2 et de SO2 volcaniques dans l’atmosphère. Bull. Volcanol. 1982, 45, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, P.A.; Jacob, D.J.; Logan, J.A. Global inventory of sulfur emissions with 1°×1° resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1992, 97, 6023–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmer, M.M.; Schmincke, H.-U.; Graf, H.-F. The annual volcanic gas input into the atmosphere, in particular into the stratosphere: A global data set for the past 100 years. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2002, 115, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carn, S.A.; Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Krotkov, N.A. A decade of global volcanic SO2 emissions measured from space. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Fischer, T.P.; Plank, T.; Bani, P. CO2 flux emissions from the Earth’s most actively degassing volcanoes, 2005–2015. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.P.; Arellano, S.; Carn, S.; Aiuppa, A.; Galle, B.; Allard, P.; Lopez, T.; Shinohara, H.; Kelly, P.; Werner, C.; et al. The emissions of CO2 and other volatiles from the world’s subaerial volcanoes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrice, M.; Jezek, P.; Gill, J.; Whitford, D.; Monoarfa, M. An introduction to the Sangihe arc: Volcanism accompanying arc—Arc collision in the Molucca Sea, Indonesia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1983, 19, 135–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyu, T.; Gill, J.; Tatsumi, Y.; Kimura, J.-I.; Sato, K.; Chang, Q.; Senda, R.; Miyazaki, T.; Hirahara, Y.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Across- and along-arc geochemical variations of lava chemistry in the Sangihe arc: Various fluid and melt slab fluxes in response to slab temperature. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Kunrat, S.; Syahbana, D.K. Kristianto Insights into the recurrent energetic eruptions that drive Awu, among the deadliest volcanoes on Earth. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2119–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J. Compilation of Whole Rock Geochemistry and Petrography of Samples from the Sangihe Arc, Northern Sulawesi, Indonesia, Version 1.0. Interdisciplinary Earth Data Alliance (IEDA). Available online: https://doi.org/10.26022/IEDA/111503 (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Hall, R.; Wilson, M. Neogene sutures in eastern Indonesia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 781–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardwell, R.K.; Isacks, B.L.; Karig, D.E. The spatial distribution of earthquakes, focal mechanism solutions and subducted lithosphere in the Philippine and northeast Indonesian islands. Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr. 1980, 23, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Newhall, C.G.; Self, S. The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) an estimate of explosive magnitude for historical volcanism. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1982, 87, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Volcanism Program. Awu (267040), in Volcanoes of the World, v.4.9.1 (17 Sep 2020). Smithsonian Institution. Available online: https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=267040 (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Badan-Geologi. Data Dasar Gunung Api, Wilaya Timur, 2nd ed.; Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2011; pp. 1–450. [Google Scholar]
- Robock, A. A latitudinally dependent volcanic dust veil index, and its effect on climate simulations. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1981, 11, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A. Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handler, P. Possible association of stratospheric aerosols and El Nino type events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1984, 11, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, G.A.; Fiacco, R.J.; Whitlow, S.; Twickler, M.S.; Germani, M.S.; Endo, K.; Yasui, M. Climatic impact of the AD 1783 eruption of Asama (Japan) was minimal: Evidence from the GISP2 ice core. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Briffa, K.R.; Schweingruber, F.H. Tree-ring evidence of the widespread effects of explosive volcanic eruptions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.S.; Van Ommen, T.; Curran, M.A.J.; Morgan, V.; Souney, J.M.; Mayewski, P.A. High-precision dating of volcanic events (A.D. 1301-1995) using ice cores from Law Dome, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 28089–28095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donarummo, J.; Ram, M.; Stolz, M.R. Sun/dust correlations and volcanic interference. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Murua, A.; Hendy, E.J.; Rust, A.C.; Cashman, K.V. Consistent decrease in North Atlantic Tropical Cyclone frequency following major volcanic eruptions in the last three centuries. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 9425–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latter, J.H. Tsunamis of volcanic origin: Summary of causes, with particular reference to Krakatoa, 1883. Bull. Volcanol. 1981, 44, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Switzer, A.D.; Belousova, M.; Belousov, A.; Ontowirjo, B.; Whelley, P.L.; Ulvrova, M. Volcanic tsunami: A review of source mechanisms, past events and hazards in Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Philippines, Papua New Guinea). Nat. Hazards 2013, 70, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Padang, N. History of volcanology in the former Netherlands East Indies. Scripta Geol. 1983, 71, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tanguy, J.-C.; Ribière, C.; Scarth, A.; Tjetjep, W.S. Victims from volcanic eruptions: A revised database. Bull. Volcanol. 1998, 60, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witham, C.S. Volcanic disasters and incidents: A new database. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2005, 148, 191–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagmay, A.M.F.; Rodolfo, K.S.; Siringan, F.P.; Uy, H.; Remotigue, C.; Zamora, P.; Lapus, M.; Rodolfo, R.; Ong, J. Geology and hazard implications of the Maraunot notch in the Pinatubo Caldera, Philippines. Bull. Volcanol. 2007, 69, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Bani, P.; Moussallam, Y.; Di Napoli, R.; Allard, P.; Gunawan, H.; Hendrasto, M.; Tamburello, G. First determination of magma-derived gas emissions from Bromo volcano, eastern Java (Indonesia). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 304, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.L. New equations for computing vapor pressure and enhancement factor. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburello, G. Ratiocalc: Software for processing data from multicomponent volcanic gas analyzers. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 82, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 597. [Google Scholar]
- Bogumil, K.; Orphal, J.; Homann, T.; Voigt, S.; Spietz, P.; Fleischmann, O.C.; Vogel, A.; Harmann, M.; Kromminga, H.; Bovensmann, H.; et al. Measurements of molecular absorption spectra with SCIAMACHY preflight model: Instrument characterization and reference data for atmospheric remote sensing in the 230–2380 nm region. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2003, 157, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, S.; Orphal, J.; Bogumil, K.; Burrows, J.P. The temperature dependence (203–293 K) of the absorption cross-sections of O3 in the 230–850 nm region measured by Fourier-transform spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, P.; Hendrasto, M.; Gunawan, H.; Primulyana, S.; Surono, M. Sulfur dioxide emissions from Papandayan and Bromo, two Indonesian volcanoes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Fischer, T.P.; Aiuppa, A.; Edmonds, M.; Cardellini, C.; Carn, S.; Chiodini, G.; Cottrell, E.; Burton, M.; Shinohara, H.; et al. Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Subaerial Volcanic Regions. In Deep Carbon; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 188–236. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, H.D. Some applications of thermochemical data to problems of ore deposits II. Mineral assemblages and the composition of ore-forming fluids. Econ. Geol. 1965, 60, 1101–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, R.; Gerlach, T.; Reed, M. Magmatic gas scrubbing: Implications for volcano monitoring. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2001, 108, 303–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Fischer, T.P.; Plank, T.; Robidoux, P.; Di Napoli, R. Along arc, inter-arc and arc-to-arc variations in volcanic gas SO2/ST ratios reveal dual source of carbon in arc volcanism. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 168, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiuppa, A.; Shinohara, H.; Tamburello, G.; Giudice, G.; Liuzzo, M.; Moretti, R. Hydrogen in the gas plume of an open-vent volcano, Mount Etna, Italy. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clor, L.E.; Fischer, T.; Hilton, D.R.; Sharp, Z.D.; Hartono, U. Volatile and N isotope chemistry of the Molucca Sea collision zone: Tracing source components along the Sangihe Arc, Indonesia. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stix, J.; De Moor, J.M. Understanding and forecasting phreatic eruptions driven by magmatic degassing. Earth Plan. Space 2018, 70, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenson, B.; Németh, K.; Rouwet, D.; Tassi, F.; Vandemeulebrouck, J.; Varekamp, J.C. Volcanic Lakes. In Advances in Volcanology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Primulyana, S.; Bani, P.; Harris, A. The effusive-explosive transitions at Rokatenda 2012–2013: Unloading by extrusion of degassed magma with lateral gas flow. Bull. Volcanol. 2017, 79, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.J.; Gardeweg, M.C.; Sparks, R.S.J. The 1984 to 1996 cyclic activity of Lascar Volcano, northern Chile: Cycles of dome growth, dome subsidence, degassing and explosive eruptions. Bull. Volcanol. 1997, 59, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.S.J. Dynamics of magma degassing. Geol. Soc. London Speéc. Publ. 2003, 213, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, T.; Manning, C.E. Subducting carbon. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 574, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.P. Fluxes of volatiles (H2O, CO2, N2, Cl, F) from arc volcanoes. Geochem. J. 2008, 42, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, L.; Hilton, D.; Fischer, T.; Hartono, U. Tracing magma sources in an arc-arc collision zone: Helium and carbon isotope and relative abundance systematics of the Sangihe Arc, Indonesia. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.D.; Jezek, P.A.; Hart, S.R.; Hill, J.B.; Hayes, D.E. The Halmahera Island Arc, Molucca Sea collision zone, Indonesia: A geochemical survey. In Sea Ice; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 1983; Volume 27, pp. 373–387. [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey, R. Seismic wave propagation beneath the Molucca Sea arc-arc collision zone, Indonesia. Tectonophysics 1983, 96, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pubellier, M.; Quebral, R.; Rangin, C.; Deffontaines, B.; Muller, C.; Butterlin, J.; Manzano, J. The Mindanao collision zone: A soft collision event within a continuous Neogene strike-slip setting. J. Asian Earth Sci. 1991, 6, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, S.M.; Rushmer, T.; Thompson, A.B. Partial melting of subducting oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1994, 121, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, F.M.; Troll, V.R.; Freda, C.; Misiti, V.; Chadwick, J.P.; McLeod, C.L.; Davidson, J.P. Magma–Carbonate Interaction Processes and Associated CO2 Release at Merapi Volcano, Indonesia: Insights from Experimental Petrology. J. Pet. 2010, 51, 1027–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco, T.; Freda, C.; Gaeta, M.; Mollo, S.; Dallai, L. Magma chamber emplacement in carbonate substrate: Petrologenesis of skarn and cumulate rocks and implication fpr CO2 degassing in volcanic areas. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 2307–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, S.; Gertisser, R.; Halama, R.; Preece, K.; Troll, V.R.; Deegan, F.M. Crustal CO2 contribution to subduction zone degassing recorded through calc-silicate xenoliths in arc lavas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K.; Hori, M.E.; Yukimoto, S.; Sigmond, M. Solar modulation of the Northern Hemisphere winter trends and its implications with increasing CO2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.M.; Jones, A.; Bellouin, N.; Stephenson, D.B. Asymmetric forcing from stratospheric aerosols impacts Sahelian rainfall. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
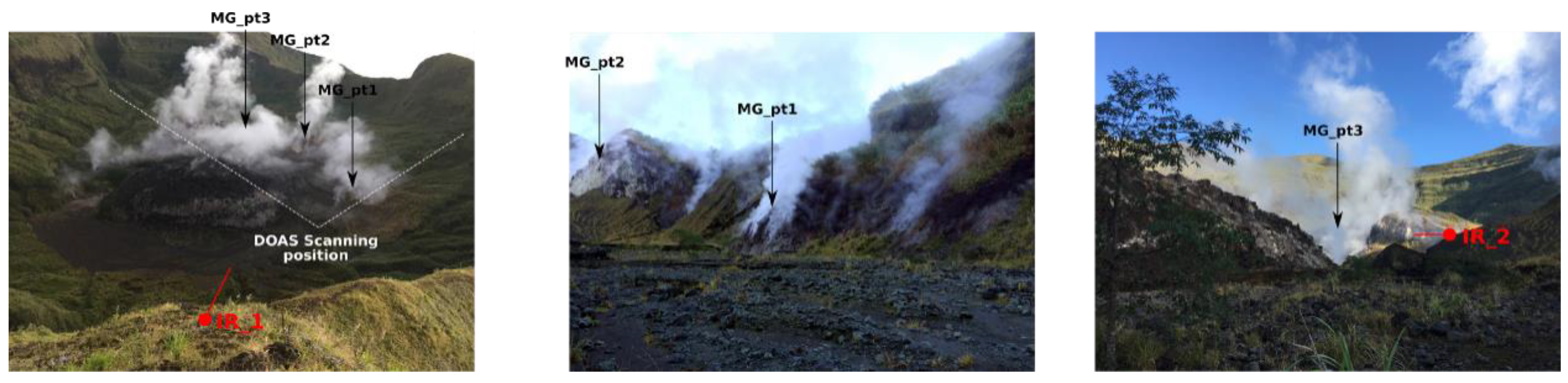

| Year | Eruptive Events |
|---|---|
| 1640 | Magmatic eruption. |
| 1641 | Phreatic eruption, lahar event. |
| 1677 | Phreatic eruption. |
| 1711 | Violent eruption (VEI 3) triggered a pyroclastic flow and hot lahar claiming about 3000 victims. |
| 1812 | Large phreatomagmatic eruption (VEI 4). Lahar and pyroclastic events. Villages destroyed, 963 victims. |
| 1856 | Large phreatomagmatic eruption (VEI 3). Pyroclastic and lahar flows killed 2806 inhabitants. |
| 1875 | Phreatic eruption (VEI 2) was reported with no further detail. |
| 1883 | Possible phreatic eruption (VEI 2) was reported with no further detail. |
| 1885 | Phreatic eruption (VEI 2) was reported with no further detail. |
| 1892 | Large phreatomagmatic eruption (VEI 3) with lahar events claiming 1532 victims. |
| 1893 | Phreatic eruption (VEI 2). |
| 1913 | Phreatic eruption (VEI 2). |
| 1921 | Phreatic eruption—crater lake activity. |
| 1922 | Phreatic eruption—crater lake activity. |
| 1931 | Lava dome developed through a crater lake. |
| 1966 | Large VEI 4 eruption. Violent blast, heavy ashfall, pyroclastic flow, lahars events. 39 victims and 11,000 inhabitants evacuated. |
| 1992 | Phreatic eruption (VEI 1). |
| 2004 | Magmatic eruption (VEI 2), 18,648 inhabitants evacuated. |
| Start Time (LT) | Scan Step (m) | Nber of Spectra | Mean CA (mg/m2) | SO2 Flux | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg/s | t/d | |||||
| Scan 1 | 08:38 | 15 | 33 | 62 | 0.04 | 4 |
| Scan 2 | 08:44 | 47 | 24 | 74 | 0.11 | 9 ± 4 |
| Scan 3 | 08:52 | 47 | 24 | 189 | 0.27 | 23 ± 10 |
| Scan 4 | 09:00 | 47 | 24 | 80 | 0.11 | 10 ± 4 |
| Scan 5 | 09:08 | 47 | 24 | 89 | 0.13 | 11 ± 5 |
| Scan 6 | 09:12 | 47 | 24 | 48 | 0.05 | 6 |
| Scan 7 | 09:16 | 47 | 24 | 96 | 0.14 | 12 ± 5 |
| Scan 8 | 09:19 | 47 | 24 | 118 | 0.17 | 15 ± 7 |
| Scan 9 | 09:25 | 47 | 24 | 102 | 0.15 | 13 ± 6 |
| Scan 10 | 09:33 | 47 | 24 | 104 | 0.15 | 13 ± 5 |
| Scan 11 | 09:41 | 47 | 24 | 24 | 0.03 | 3 |
| Scan 12 | 09:53 | 47 | 9 | 170 | 0.03 | 3 |
| Scan 13 | 09:59 | 15 | 23 | 23 | 0.01 | 1 |
| Scan 14 | 10:02 | 15 | 23 | 30 | 0.01 | 1 |
| Scan 15 | 10:05 | 15 | 23 | 63 | 0.03 | 2 |
| Scan 16 | 10:07 | 15 | 23 | 48 | 0.02 | 2 |
| Scan 17 | 10:10 | 15 | 23 | 46 | 0.02 | 2 |
| Scan 18 | 10:14 | 15 | 23 | 54 | 0.02 | 2 |
| Scan 19 | 10:18 | 15 | 23 | 88 | 0.05 | 4 |
| Scan 20 | 10:23 | 15 | 23 | 58 | 0.03 | 3 |
| Scan 21 | 10:24 | 15 | 23 | 52 | 0.03 | 3 |
| Scan 22 | 10:27 | 15 | 23 | 64 | 0.04 | 3 |
| Scan 23 | 10:30 | 15 | 23 | 66 | 0.04 | 3 |
| Scan 24 | 10:33 | 15 | 23 | 53 | 0.03 | 2 |
| Mean SO2 emission rate: 13 ± 6 t/day | ||||||
| Sampling Date | 28 July 2015 | 3 August 2001 * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample. ID | MG_Pt1 | MG_Pt2 | MG_Pt3 | IND-15 | IND-16 | IND-17 | ||
| Vent type | Fumarole | Fumarole | Fumarole | Fumarole | Fumarole | Spring | ||
| H2O (ppm v) | 10,000–20,000 mean val. 16091 | 5000–18,000 mean val. 13395 | 20,000–30,000 mean val. 27080 | |||||
| CO2 (ppm v) | 400–2100 mean val. 510 | 450–2050 mean val. 549 | 400–2050 mean val. 867 | |||||
| SO2 (ppm v) | <0.1 mean val. 0.017 | <0.1–1.5 mean val. 0.027 | 1–6 mean val. 2.43 | |||||
| H2S (ppm v) | 0.5–22 mean val. 1.03 | 2–57 mean val. 10.34 | 27–57 (saturation) mean val. 51.21 | |||||
| H2 (ppm v) | 0.1–1.2 mean val. 0.27 | 0.1–1.5 mean val. 0.31 | 0.1–2.2 mean val. 0.84 | |||||
| H2S/SO2 | 230 ± 110 | 163 ± 62 | 49 ± 20 | H2S/SO2 | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.81 | |
| CO2/SO2 | 1824 ± 850 | 600 ± 230 | 287 ± 164 | CO2/SO2 | 115 | 113 | 2175 | |
| H2/SO2 | 6 ± 4 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | H2/SO2 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.91 | |
| H2O/SO2 | - | - | 1596 ± 670 | H2O/SO2 | 62349 | 62356 | 2175 | |
| CO2/ST | 7.9 ± 3.7 | 3.6 ± 1.4 | 5.7 ± 3.2 | CO2/ST | 63 | 58 | 1199 | |
| Composition (mol %) | Flux (t/d) * | Composition (mol %) | ||||||
| H2O | 82.5 ± 34.1 | 5800 ± 2400 | H2O | 99.80 | 99.81 | 95.55 | ||
| CO2 | 14.8 ± 6.8 | 2600 ± 1200 | CO2 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 4.44 | ||
| SO2 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 13 ± 6 | SO2 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | ||
| H2S | 2.5 ± 1.1 | 340 ± 150 | H2S | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | ||
| H2 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.1 ± 0.04 | H2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | ||
| HCl | 0.018 | 0.009 | 0.002 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bani, P.; Le Glas, E.; Kristianto; Aiuppa, A.; Bitetto, M.; Syahbana, D.K. Elevated CO2 Emissions during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Degassing at Awu Volcano, Sangihe Arc, Indonesia. Geosciences 2020, 10, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110470
Bani P, Le Glas E, Kristianto, Aiuppa A, Bitetto M, Syahbana DK. Elevated CO2 Emissions during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Degassing at Awu Volcano, Sangihe Arc, Indonesia. Geosciences. 2020; 10(11):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110470
Chicago/Turabian StyleBani, Philipson, Etienne Le Glas, Kristianto, Alessandro Aiuppa, Marcello Bitetto, and Devy Kamil Syahbana. 2020. "Elevated CO2 Emissions during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Degassing at Awu Volcano, Sangihe Arc, Indonesia" Geosciences 10, no. 11: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110470
APA StyleBani, P., Le Glas, E., Kristianto, Aiuppa, A., Bitetto, M., & Syahbana, D. K. (2020). Elevated CO2 Emissions during Magmatic-Hydrothermal Degassing at Awu Volcano, Sangihe Arc, Indonesia. Geosciences, 10(11), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10110470





