A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Microbial Amplicon Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.3. Metagenome Sequencing and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
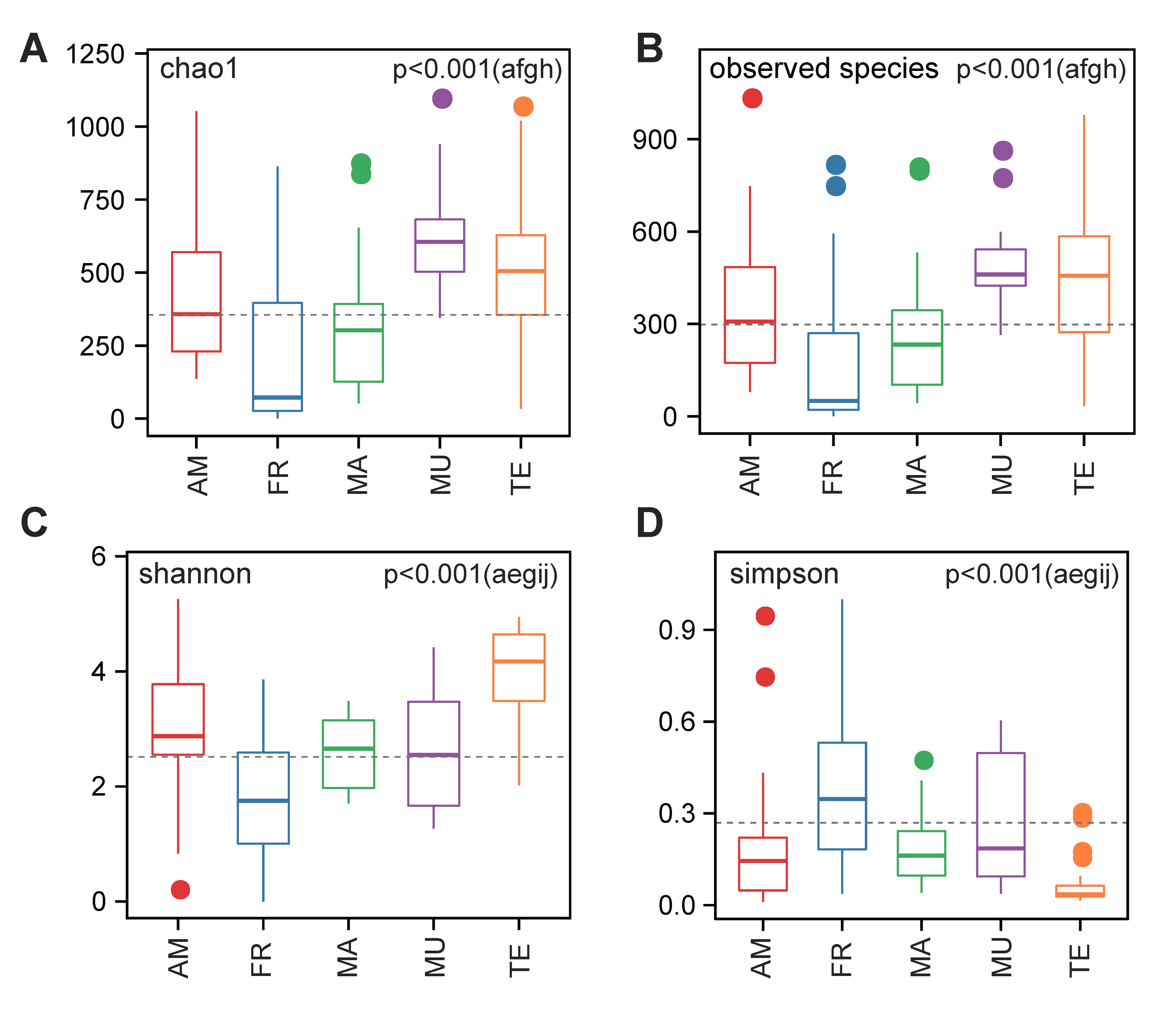
3.1. Summary of the Achieved 16S Amplicon Data
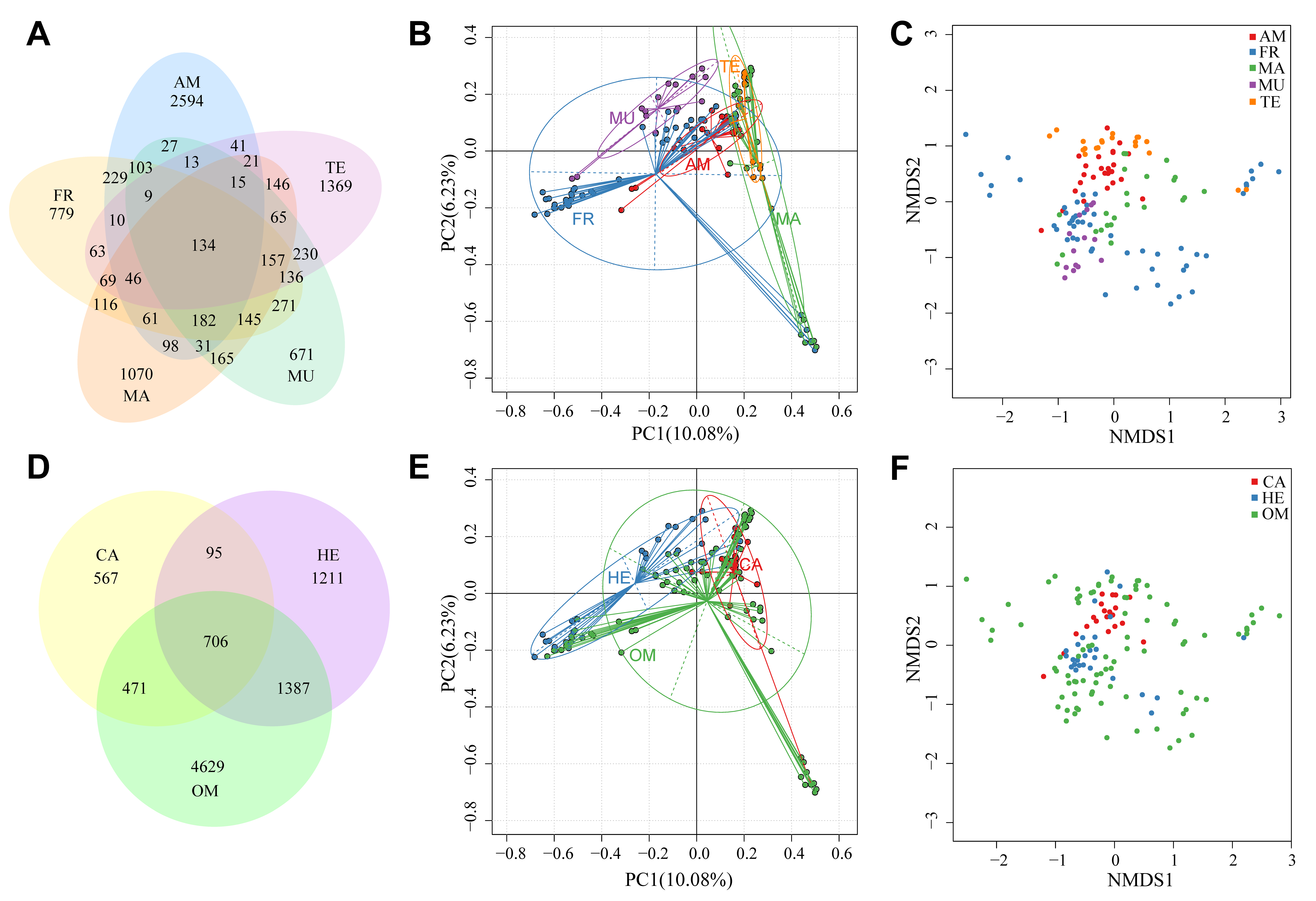
3.2. Differential OTUs among the Five Examined Groups
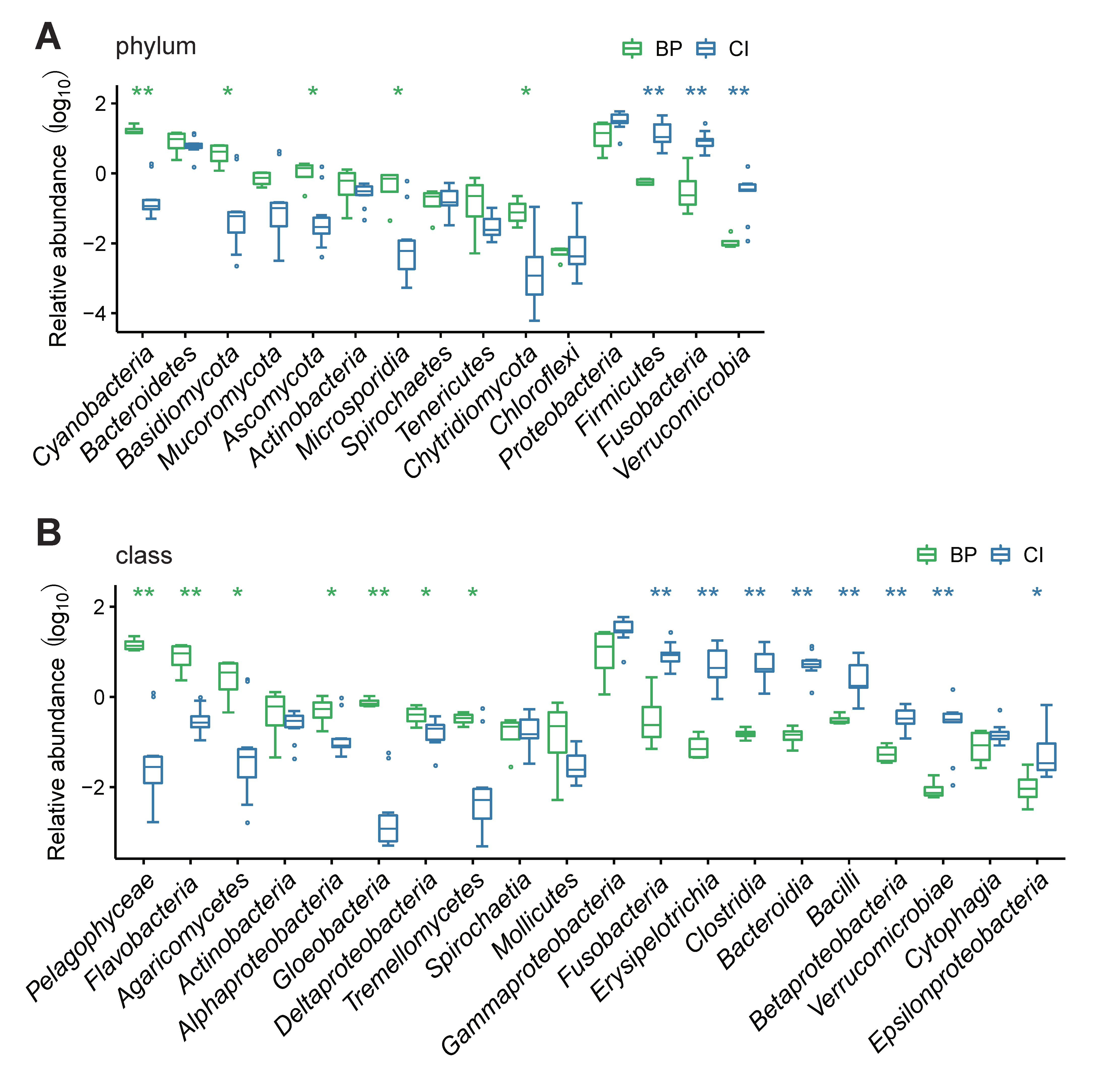
3.3. Results of a Taxonomic Composition Analysis
3.4. Metagenomic Analysis of Five Common Fish Species
3.5. Functional Classifications
4. Discussion
4.1. GI Bacterial Taxa in Different Vertebrates
4.2. Factors for Shaping the GI Microbiome
4.3. Functional Potentiality of Metagenomes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clements, K.D.; Angert, E.R.; Montgomery, W.L.; Choat, J.H. Howard Intestinal microbiota in fishes: What’s known and what’s not. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost microbiomes: The state of the art in their characterization, manipulation and importance in aquaculture and fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, J.F.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4596–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruijn, I.; Liu, Y.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Exploring fish microbial communities to mitigate emerging diseases in aquaculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 94, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Bian, C.; Zan, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Mudskipper genomes provide insights into the terrestrial adaptation of amphibious fishes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayer, M.D.J. Adaptations of amphibious fish for surviving life out of water. Fish Fish. 2005, 6, 186–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, C.E.; Ransom, B.; Bano, N.; Hollibaugh, J.T. Comparison of the gut microbiomes of 12 bony fish and 3 shark species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 518, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Magoč, T. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2012, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Meinicke, P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.; Yue, Z.; He, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, G.; Xie, M.; Zhan, D.; Baxter, S.W.; Vasseur, L.; Gurr, G.M.; et al. A heterozygous moth genome provides insights into herbivory and detoxification. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomsadze, A.; Zhu, W.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar]
- Godzik, A.; Li, W. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, O.E.; Bendall, M.; Manimaran, S.; Hong, C.; Clement, N.L.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Snell, Q.; Schaalje, G.B.; Clement, M.J.; Crandall, K.A.; et al. Pathoscope: Species identification and strain attribution with unassembled sequencing data. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorsson-Norheim, E. Kruskal-Wallis test: BASIC computer program to perform nonparametric one-way analysis of variance and multiple comparisons on ranks of several independent samples. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 1986, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.C.; Longnecker, M.T. A modified Wilcoxon rank sum test for paired data. Biometrika 1983, 70, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, T.P.; Faisal, M. Emerging flavobacterial infections in fish: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Burgos, F.A.; Ray, C.L.; Arias, C.R. Fish intestinal microbiome: Diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’Connor, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: A meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, T.J.; Jackson, C.R. Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3776–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.A.; Stone, R.P.; McLaughlin, M.R.; Kellogg, C.A. Microbial consortia of gorgonian corals from the aleutian islands. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; McGinnity, P.; Dionne, M.; Letourneau, J.; Thonier, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Derome, N. The biogeography of the atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) gut microbiome. ISME J. 2015, 10, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Takanami, K.; Takei, Y. The amphibious mudskipper: A unique model bridging the gap of central actions of osmoregulatory hormones between terrestrial and aquatic vertebrates. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichmiller, J.J.; Hamilton, M.J.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Environment shapes the fecal microbiome of invasive carp species. Microbiome 2016, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Amberg, J.; Chapman, D.; Gaikowski, M.; Liu, W.-T. Fish gut microbiota analysis differentiates physiology and behavior of invasive Asian carp and indigenous American fish. ISME J. 2013, 8, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeselers, G.; Mittge, E.K.; Stephens, W.Z.; Parichy, D.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Guillemin, K.; Rawls, J.F. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahli, T.; Madsen, L. Flavobacteria, a never ending threat for fish: A review. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.; LeCleir, G.R.; Gulvik, C.A.; González, J.M. Master recyclers: Features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, J.-F.; Pollet, T.; Misson, B.; Garnier, C.; Le Poupon, C.; Durrieu, G.; Berdjeb, L. Prokaryotic community successions and interactions in marine biofilms: The key role of Flavobacteriia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 083. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, S.; Hatosy, S.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Huse, S.M.; Mark Welch, D.B.; Sogin, M.L.; Martiny, A.C. Global distribution and diversity of marine Verrucomicrobia. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.H.; Farooqui, S.M.; White, A.R.; Greene, A.C. Production of manganese oxide nanoparticles by Shewanella species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5402–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikow, R.B. Genome-level homology and phylogeny of Shewanella (Gammaproteobacteria: Lteromonadales: Shewanellaceae). BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumoto, I.I.; Iwata, H.; Sawabe, T.; Ueno, K.; Ichise, N.; Matsuyama, H.; Okuyama, H.; Kawasaki, K. Characterization of a facultatively psychrophilic bacterium, vibrio rumoiensis sp. nov., that exhibits high catalase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rivas, A.; Lemos, M.; Osorio, C. Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae, a bacterium pathogenic for marine animals and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The gut microbiota of marine fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiike, T.; Otsuka, O.; Tanaka, Y.; Terahara, T.; Imada, C.; Yamashita, M. Diversity of salt-tolerant tellurate-reducing bacteria in a marine environment. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreeland, R.H.; Litchfield, C.D.; Martin, E.L.; Elliot, E. Halomonas elongata, a new genus and species of extremely salt-tolerant bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1980, 30, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astudillo-García, C.; Bell, J.J.; Webster, N.S.; Glasl, B.; Jompa, J.; Montoya, J.M.; Taylor, M.W. Evaluating the core microbiota in complex communities: A systematic investigation. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A. Marine animal microbiomes: Toward understanding host–microbiome interactions in a changing ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, Q.; Xie, S.; Hu, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, Z. Gut microbiota contributes to the growth of fast-growing transgenic common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parris, D.J.; Brooker, R.M.; Morgan, M.A.; Dixson, D.L.; Stewart, F.J. Whole gut microbiome composition of damselfish and cardinalfish before and after reef settlement. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stephens, W.Z.; Burns, A.R.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J.M. The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetlock, A.; Yost, C.K.; Stavrinides, J.; Manzon, R.G. Changes in the gut microbiome of the sea lamprey during metamorphosis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrill-Mix, S.; McCormick, K.; Lauder, A.; Bailey, A.; Zimmerman, L.; Li, Y.; Django, J.-B.N.; Bertolani, P.; Colin, C.; Hart, J.A.; et al. Allometry and ecology of the Bilaterian gut microbiome. mBio 2018, 9, e00319-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.; Amaral-Zettler, L.; Davidson, J.; Summerfelt, S.; Good, C. Influence of fishmeal-free diets on microbial communities in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) recirculation aquaculture systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4470–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.R.; Snowberg, L.K.; Gregory Caporaso, J.; Knight, R.; Bolnick, D.I. Dietary input of microbes and host genetic variation shape among-population differences in stickleback gut microbiota. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas-García, P.; Pajares, S.; Sosa-Jiménez, V.M.; Rétaux, S.; Miranda-Gamboa, R.A. Microbiome differences between river-dwelling and cave-adapted populations of the fish Astyanax mexicanus (De Filippi, 1853). PeerJ 2018, 6, e5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Xu, C.; Ji, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, P. Comparative study on intestinal bacterial communities of Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus with different sexes and feeding strategies. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.R.; Sanders, J.G.; Song, S.J.; Nute, M.; Metcalf, J.L.; Thompson, L.R.; Morton, J.T.; Amir, A.; McKenzie, V.J.; Humphrey, G.; et al. Evolutionary trends in host physiology outweigh dietary niche in structuring primate gut microbiomes. ISME J. 2018, 13, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvallet, C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Irizarry, R.A.; Alm, E.J. Meta-analysis of gut microbiome studies identifies disease-specific and shared responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A new genomic blueprint of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, S.; van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E.; Oosting, M.; et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crits-Christoph, A.; Diamond, S.; Butterfield, C.N.; Thomas, B.C.; Banfield, J.F. Novel soil bacteria possess diverse genes for secondary metabolite biosynthesis. Nature 2018, 558, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Ghosh, K.; Doan, H.V.; Beck, B.R.; Song, S.K. Lactic acid bacteria in finfish—An update. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A.; Gil-Campos, M. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S49–S66. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, O.A.; Shashidhar, R.; Rath, D.; Bandekar, J.R.; Rath, A. Characterization of multiple antibiotic resistance of culturable microorganisms and metagenomic analysis of total microbial diversity of marine fish sold in retail shops in Mumbai, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6228–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.H.; Lin, G.; Fu, G.H.; Wan, Z.Y.; Lee, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.J.; Yue, G.H. The intestinal microbiome of fish under starvation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, J.S.; Marques, T.V.; Barone, R.S.C.; Cyrino, J.E.P.; Kublik, S.; Nesme, J.; Schloter, M.; Rath, S.; Vestergaard, G. Oral administration of antibiotics increased the potential mobility of bacterial resistance genes in the gut of the fish Piaractus mesopotamicus. Microbiome 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, C.; Amaro, C.; Biosca, E.G.; Garay, E. Biochemical and toxigenic properties of Vibrio furnissii isolated from a European eel farm. Aquaculture 1995, 132, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.-H.; Li, H.-C.; Tsai, F.-M.; Ting, Y.-Y.; Chao, W.-L. Changes in the composition of Vibrio communities in pond water during tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) cultivation and in the hepatopancreas of healthy and diseased shrimp. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 236, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman-Brenner, F.W.; MacDonald, K.L.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Fanning, G.R.; Brenner, D.J.; Farmer, J.J. Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 900–906. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.; Colque-Navarro, P.; Kühn, I.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; Möllby, R. Identification and characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria associated with epizootic ulcerative syndrome in fish in Bangladesh. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J. Aeromonas spp. whole genomes and virulence factors implicated in fish disease. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozińska, A. Dominant pathogenic species of mesophilic aeromonads isolated from diseased and healthy fish cultured in Poland. J. Fish Dis. 2007, 30, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Bera, A.K.; Paria, P.; Das, A.; Parida, P.K.; Kumari, S.; Bhowmick, S.; Das, B.K. Identification and pathogenicity of Plesiomonas shigelloides in Silver Carp. Aquaculture 2018, 493, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, I. Plesiomonas shigelloides: An emerging pathogen with unusual properties. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 15, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovico, M.S.; Martins, L.M.; Bianco, J.E.R.; Andrade, C.G.T.; Falcon, R.; Joazeiro, P.P.; Gatti, M.S.V.; Yano, T. Plesiomonas shigelloides exports a lethal cytotoxic-enterotoxin (LCE) by membrane vesicles. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumithra, T.G.; Reshma, K.J.; Anusree, V.N.; Sayooj, P.; Sharma, S.R.K.; Suja, G.; Amala, P.V.; Joseph, S.; Sanil, N.K. Pathological investigations of Vibrio vulnificus infection in Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) cultured at a floating cage farm of India. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, H.; Pi, D.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X. Virulence properties of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from diseased zoea of freshness shrimp Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 127, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, L.-I.; Chen, C.-L. Cytotoxins of Vibrio vulnificus: Functions and roles in pathogenesis. BioMedicine 2013, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.M.; Mohammed, H.H.; Arias, C.R. Characterization of the gut microbiota of three commercially valuable warmwater fish species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Y.; Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ai, P.; You, X.; Bian, C.; Shi, Q.; Dong, B. A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals. Animals 2019, 9, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090660
Yi Y, Liang L, Wang Z, Ai P, You X, Bian C, Shi Q, Dong B. A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals. Animals. 2019; 9(9):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090660
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Yunhai, Lifeng Liang, Zhilin Wang, Peng Ai, Xinxin You, Chao Bian, Qiong Shi, and Bo Dong. 2019. "A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals" Animals 9, no. 9: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090660
APA StyleYi, Y., Liang, L., Wang, Z., Ai, P., You, X., Bian, C., Shi, Q., & Dong, B. (2019). A Comparative Metagenomics Study on Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Amphibious Mudskippers and Other Vertebrate Animals. Animals, 9(9), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090660




