Prediction of Mineral Composition in Commercial Extruded Dry Dog Food by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Mineral Reference Analyses
2.3. Near-Infrared Spectra Collection
2.4. Chemometric Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition
3.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Prediction Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemical Composition
4.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Prediction Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuchs, M.; Obernhuber, C. Hypercompetitive rivalries in the pet food industry. In Fallstudien zum Internationalen Management; Zentes, J., Swoboda, B., Morschett, D., Eds.; Gabler Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011; pp. 943–962. ISBN 9783834967930. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dell, B.L. Bioavailability of and interactions among trace elements. In Trace Elements in Nutrition of Children; Chandra, R.K., Ed.; Nestlé Nutrition; Vevey/Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 41–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kochanowski, B.A.; McMahan, C.L. Inhibition of iron absorption by calcium in rats and dogs: Effects of mineral separation by time and enteric coating. Nutr. Res. 1990, 10, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, B.L. Mineral interactions relevant to nutrient requirements. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedekind, K.J.; Titgemeyer, E.C.; Twardock, R.; Baker, H.D. Phosphorus but not calcium affects manganese absorption and turnover in chicks. J. Nutr. 1991, 121, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackelford, M.E.; Collins, T.F.X.; Black, T.N.; Ames, M.J.; Dolan, S.; Sheikh, N.S.; Chi, R.K.; O’Donnell, M.W. Mineral interactions in rats fed AIN-76A diets with excess calcium. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetke, L.M.; Chow-Johnson, H.S.; Chow, C.K. Copper: Toxicological relevance and mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B.T.; Burns, M.J. Zinc metabolism and the zinc-deficiency syndrome in the dog. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1963, 24, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanecki, R.K.; Corbin, J.E.; Forbes, R.M. Tissue changes in dogs fed a zinc-deficient ration. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1982, 43, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Sanecki, R.K.; Corbin, J.E.; Forbes, R.M. Extracutaneous histologic changes accompanying zinc deficiency in pups. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1985, 46, 2120–2123. [Google Scholar]
- Budis, H.; Kalisińska, E.; Łanocha, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. Concentrations of manganese, iron, and strontium in bones of the domestic dog (Canis lupus familiaris). Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2015, 39, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Loftus, J.; Gagne, J.W.; Rutzke, M.A.; Glahn, R.P.; Wakshlag, J.J. Evaluation of selected ultra-trace minerals in commercially available dry dog foods. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2018, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Chung, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Choi, E.-W.; Kim, M.-K.; Hwang, C.-Y.; Youn, H.-Y. Hypoglycemic effects of vanadium on alloxan monohydrate induced diabetic dogs. J. Vet. Sci. 2006, 7, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, N.L. Lithium toxicity in two dogs. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 1991, 62, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.H.; Noble, P.J.M.; Swift, S.T.; Higgins, B.M.; Sieniawska, C.E. Barium toxicosis in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 237, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.A.; Polzin, D.J.; Lulich, J.P.; Kruger, J.M.; Johnston, G.R.; O’Brien, T.D.; Felice, L.J. Relationship of nutritional factors to the cause, dissolution, and prevention of canine uroliths. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1989, 19, 583–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Polzin, D.J.; Osborne, C.A.; Allen, T.A.; Kirk, C.A.; Neaton, J.D.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Swanson, L.L. Clinical evaluation of dietary modification for treatment of spontaneous chronic kindney failure in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.J.; Osborne, C.A.; Kirk, C.A.; Lowry, S.R.; Koehler, L.A.; Polzin, D.J. Clinical evaluation of dietary modification for treatment of spontaneous chronic kidney disease in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulich, J.P.; Berent, A.C.; Adams, L.G.; Westropp, J.L.; Bartges, J.W.; Osborne, C.A. ACVIM Small animal consensus recommendations on the treatment and prevention of uroliths in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulich, J.P.; Osborne, C.A.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Allen, T.A.; Nakagawa, Y. Canine calcium oxalate urolithiasis: Case-based applications of therapeutic principles. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1999, 29, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, L.P.; Daristotle, L.; Hayek, M.G.; Raasch, M.F. Vitamin and mineral requirements. In Canine and Feline Nutrition A Resource for Companion Animal Professionals; Mosby Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1017 of 15 June 2017 amending Regulation (EU) No 68/2013 on the Catalogue of feed materials. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32017R1017 (accessed on 12 July 2019).
- Manley, M. Near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging: Non-destructive analysis of biological materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8200–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, M.; Manuelian, C.L.; Ton, S.; Cassandro, M.; Penasa, M. Feasibility of near infrared transmittance spectroscopy to predict fatty acid composition of commercial processed meat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büning-Pfaue, H. Analysis of water in food by near infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, C. Near infrared spectroscopy: Fundamentals, practical aspects and analytical applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.H.; Mayland, H.F.; Lamb, R.C. Mineral analysis of aorages with near anfrared aeflectance apectroscopy. Agron. J. 1987, 79, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T.H.; Lanza, E.; Norris, K.H.; Hruschka, W.R. Determination of aodium chloride in meat by near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuelian, C.L.; Currò, S.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M.; De Marchi, M. Prediction of minerals, fatty acid composition and cholesterol content of commercial cheeses by near infrared transmittance spectroscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 71, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, I.; Hernández-Hierro, J.M.; Revilla, I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.; Lobos Ortega, I. The mineral composition (Ca, P, Mg, K, Na) in cheeses (cow’s, ewe’s and goat’s) with different ripening times using near infrared spectroscopy with a fibre-optic probe. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Andueza, D.; Rock, E.; Martin, B. Prediction of dry matter, fat, pH, vitamins, minerals, carotenoids, total antioxidant capacity, and color in fresh and freeze-dried cheeses by visible-near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6801–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, M.; Manuelian, C.L.; Ton, S.; Manfrin, D.; Meneghesso, M.; Cassandro, M.; Penasa, M. Prediction of sodium content in commercial processed meat products using near infrared spectroscopy. Meat Sci. 2017, 125, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevolnik, M.; Škrlep, M.; Janeš, L.; Velikonja-Bolta, Š.; Škorjanc, D.; Čandek-Potokar, M. Accuracy of near infrared spectroscopy for prediction of chemical composition, salt content and free amino acids in dry-cured ham. J. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschetti, L.; Ottavian, M.; Facco, P.; Barolo, M.; Serva, L.; Balzan, S.; Novelli, E. A correlative study on data from pork carcass and processed meat (Bauernspeck) for automatic estimation of chemical parameters by means of near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, D.; Hodgkinson, S.; Abarzúa, D.; Fuchslocher, R.; Alvarado, C.; Rosales, E. Nutritional evaluation of commercial dry dog foods by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 90, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M.; Zidi, A.; Manuelian, C.L. Invited review: Use of infrared technologies for the assessment of dairy products—Applications and perspectives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10589–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenk, J.S.; Westerhaus, M.O.; Abrams, S. Protocol for NIR calibrations: Monitoring analysis results and recalibration. In Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS): Analysis of Forage Quality. USDA-ARS Agriculture Handbook, II; Martens, G., Shenk, J., Barton, F., Eds.; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Sobering, D. Comparison of commercial near infrared transmittance and reflectance instruments for analysis of whole grains and seeds. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 1993, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Mouazen, A.M.; Dufour, E.; Pillonel, L.; Picque, D.; Bosset, J.O.; De Baerdemaeker, J. Mid-infrared spectrometry: A tool for the determination of chemical parameters in Emmental cheeses produced during winter. Lait 2006, 86, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams The RPD Statistic: A Tutorial Note. NIR News 2014, 25, 22–26. [CrossRef]
- FEDIAF. Nutritional Guidelines for Complete and Complementary Pet Food for Cats and Dogs; FEDIAF: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M.; Alborough, R.; Jones, L.; Davis, C.; Williams, C.; Gardner, D.S. Mineral analysis of complete dog and cat foods in the UK and compliance with European guidelines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.M.; Pinto, E.; Matos, E.; Castanheira, F.; Almeida, A.A.; Baptista, C.S.; Segundo, M.A.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; Cabrita, A.R.J. Mineral composition of dry dog foods: Impact on nutrition and potential toxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7822–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, M.; Righi, F.; Meneghesso, M.; Manfrin, D.; Ricci, R. Prediction of chemical composition and peroxide value in unground pet foods by near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 102, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervera, M.; Castrillo, C.; Albanell, E.; Baucells, M.D. Use of near-infrared spectroscopy to predict energy content of commercial dog food. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4401–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Martín, I.; González-Pérez, C.; Hernández-Méndez, J.; Alvarez-García, N. Mineral analysis (Fe, Zn, Ca, Na, K) of fresh Iberian pork loin by near infrared reflectance spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 468, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, I.; Álvarez-García, N.; González-Pérez, C.; Villaescusa-García, V. Determination of inorganic elements in animal feeds by NIRS technology and a fibre-optic probe. Talanta 2006, 69, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Determination of the mineral composition of foods by infrared spectroscopy: A review of a green alternative. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 44, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuelian, C.L.; Currò, S.; Visentin, G.; Penasa, M.; Cassandro, M.; Dellea, C.; Bernardi, M.; De Marchi, M. Technical note: At-line prediction of mineral composition of fresh cheeses using near-infrared technologies. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6084–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
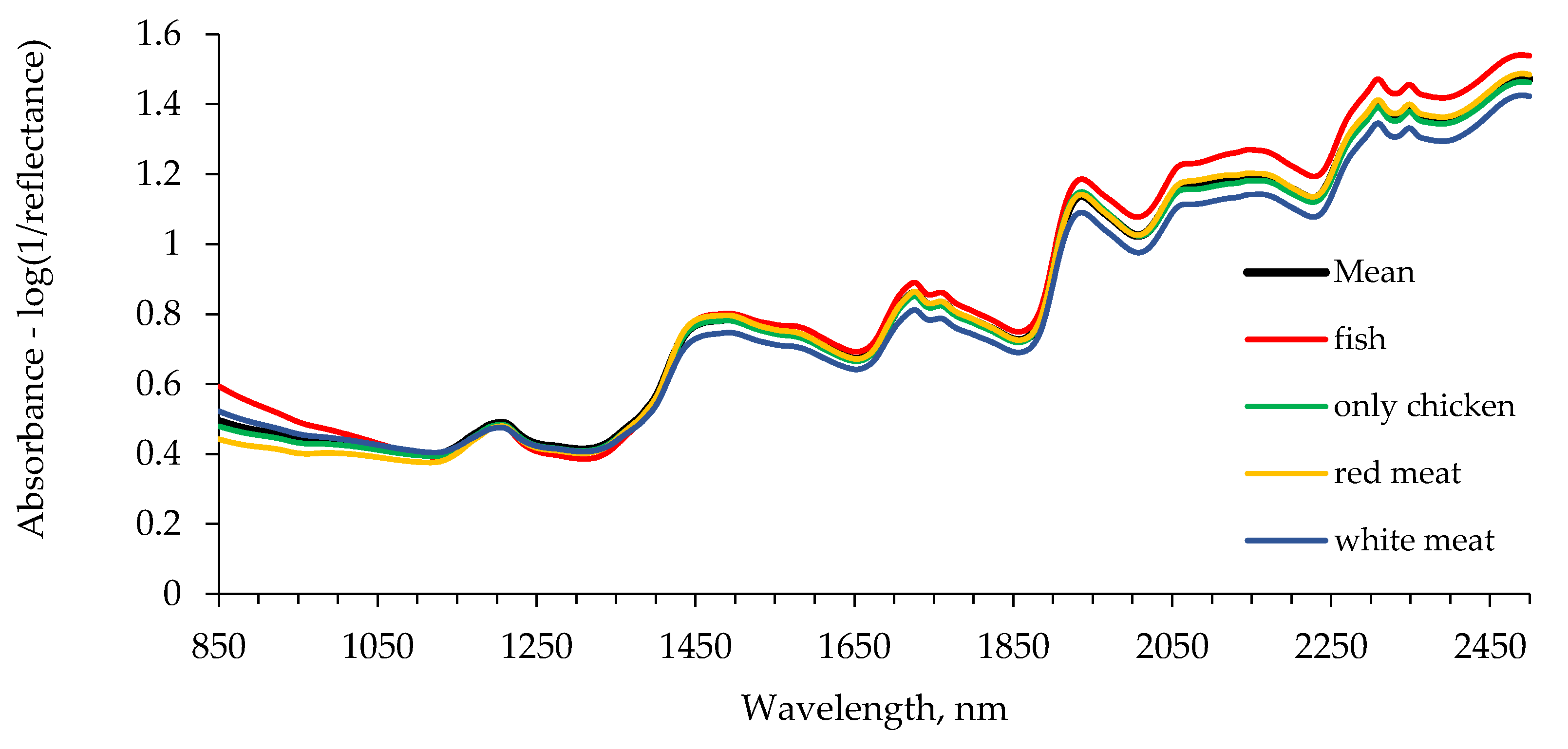
| Group | Main Protein Sources | Other Ingredients | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red meat | Pork, lamb, horse, venison | Eggs, pea, rice, potato | 37 |
| Fish | Only fish | Potato, rice | 13 |
| Mixed | Chicken, pork, fish | - | 15 |
| Chicken | Only chicken | Rice | 29 |
| White meat | Rabbit, chicken, duck | Eggs, potato | 21 |
| Other | Not specified on the label | - | 4 |
| Trait | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 5.56 | 1.22 | 2.50 | 8.00 |
| Crude protein | 28.14 | 3.95 | 21.26 | 43.09 |
| Ether extract | 13.71 | 2.20 | 8.12 | 17.86 |
| Crude fiber | 3.36 | 0.94 | 1.92 | 9.38 |
| Ash | 6.25 | 1.21 | 3.25 | 10.24 |
| Nitrogen-free extract 1 | 42.98 | 5.91 | 23.70 | 54.05 |
| Mineral | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major minerals, g/kg DM | |||||
| Ca | 13.57 | 4.89 | 4.34 | 37.69 | 36.1 |
| P | 9.94 | 3.24 | 3.68 | 19.41 | 32.6 |
| K | 7.19 | 2.88 | 3.77 | 16.02 | 40.0 |
| Na | 5.34 | 1.64 | 1.23 | 9.66 | 30.8 |
| S | 3.87 | 1.43 | 1.54 | 8.32 | 37.0 |
| Mg | 1.21 | 0.21 | 0.80 | 1.97 | 17.3 |
| Trace minerals, mg/kg DM | |||||
| Fe | 370.87 | 90.89 | 128.58 | 702.70 | 24.5 |
| Zn | 190.24 | 57.07 | 37.77 | 357.53 | 30.0 |
| Al | 152.83 | 54.99 | 65.54 | 307.38 | 36.0 |
| Mn | 74.66 | 18.39 | 19.48 | 122.16 | 24.6 |
| Cu | 25.58 | 8.02 | 11.08 | 55.34 | 31.3 |
| Sr | 18.77 | 11.45 | 5.94 | 72.25 | 61.0 |
| Ba | 5.60 | 2.47 | 1.47 | 18.63 | 44.1 |
| B | 5.08 | 1.73 | 2.36 | 11.65 | 34.1 |
| Cr | 1.74 | 0.89 | 0.54 | 5.26 | 50.9 |
| Ni | 1.28 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 3.81 | 34.8 |
| Mo | 0.86 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 2.70 | 45.9 |
| V1 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 1.18 | 49.8 |
| Li | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 47.3 |
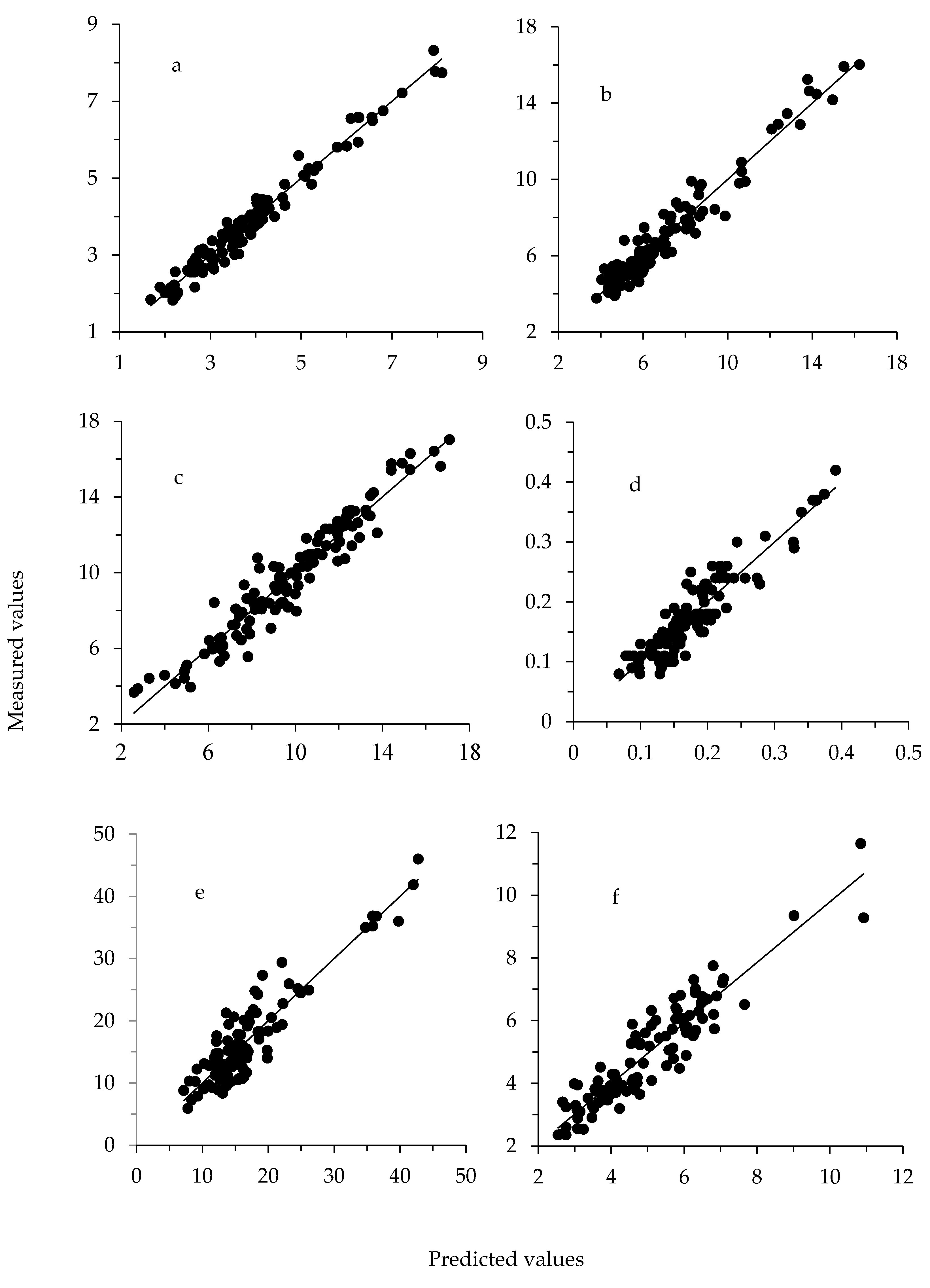
| Item | Outliers | n | Scatter Correction 2 | Math Treatment 3 | LF | Mean | SD | R2C | SEC | R2CrV | SECrV | RPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major minerals | ||||||||||||
| Ca | 7 | 112 | D | 1881 | 8 | 13.32 | 4.34 | 0.68 | 2.47 | 0.55 | 2.91 | 1.49 |
| P | 5 | 114 | D | 210101 | 10 | 9.80 | 3.14 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 1.66 | 1.89 |
| K | 6 | 113 | MSC | 210101 | 9 | 7.03 | 2.74 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 1.06 | 2.58 |
| Na | 6 | 113 | ISC | 210101 | 8 | 5.31 | 1.60 | 0.83 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 1.00 | 1.59 |
| S | 5 | 114 | D | 2551 | 9 | 3.82 | 1.36 | 0.96 | 0.26 | 0.89 | 0.45 | 3.04 |
| Mg | 10 | 109 | ISC | 1441 | 9 | 1.19 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.08 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 1.64 |
| Trace minerals | ||||||||||||
| Fe | 7 | 112 | WMSC | 210101 | 10 | 363.84 | 78.24 | 0.89 | 25.89 | 0.59 | 49.67 | 1.58 |
| Zn | 9 | 110 | NONE | 1441 | 7 | 189.46 | 50.20 | 0.65 | 29.89 | 0.49 | 35.78 | 1.40 |
| Al | 5 | 114 | SNV | 210101 | 4 | 149.25 | 52.70 | 0.66 | 30.76 | 0.52 | 36.47 | 1.44 |
| Mn | 9 | 110 | SNV | 1881 | 4 | 74.22 | 14.97 | 0.38 | 11.75 | 0.20 | 13.29 | 1.13 |
| Cu | 17 | 102 | WMSC | 2551 | 1 | 23.72 | 3.95 | 0.34 | 3.22 | 0.25 | 3.41 | 1.16 |
| Sr | 10 | 109 | SNV + D | 1441 | 9 | 16.65 | 7.44 | 0.83 | 3.08 | 0.72 | 3.92 | 1.90 |
| Ba | 6 | 113 | MSC | 2551 | 5 | 5.34 | 1.93 | 0.71 | 1.04 | 0.47 | 1.39 | 1.38 |
| B | 9 | 110 | ISC | 2551 | 6 | 5.06 | 1.72 | 0.86 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.91 | 1.90 |
| Cr | 11 | 108 | D | 0011 | 1 | 1.53 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.49 | 1.10 |
| Ni | 6 | 113 | WMSC | 1881 | 6 | 1.25 | 0.36 | 0.64 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.27 | 1.35 |
| Mo | 13 | 106 | NONE | 1881 | 6 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.50 | 0.17 | 1.43 |
| V | 5 | 103 | SNV + D | 2551 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 1.46 |
| Li | 10 | 109 | D | 1441 | 9 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.84 | 0.03 | 0.74 | 0.03 | 1.98 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goi, A.; Manuelian, C.L.; Currò, S.; De Marchi, M. Prediction of Mineral Composition in Commercial Extruded Dry Dog Food by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. Animals 2019, 9, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090640
Goi A, Manuelian CL, Currò S, De Marchi M. Prediction of Mineral Composition in Commercial Extruded Dry Dog Food by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. Animals. 2019; 9(9):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090640
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoi, Arianna, Carmen L. Manuelian, Sarah Currò, and Massimo De Marchi. 2019. "Prediction of Mineral Composition in Commercial Extruded Dry Dog Food by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy" Animals 9, no. 9: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090640
APA StyleGoi, A., Manuelian, C. L., Currò, S., & De Marchi, M. (2019). Prediction of Mineral Composition in Commercial Extruded Dry Dog Food by Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. Animals, 9(9), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9090640





