Combined Use of Indirect ELISA and Western Blotting with Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Antigen 59 Is a Potential Immunodiagnostic Tool for the Detection of Prepatent Haemonchus contortus Infection in Goat
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Recombinant Protein Purification
2.2. Study Populations
2.3. Western Blotting Assay
2.4. Development of Indirect ELISA
2.5. Determination of Cut-Off Value
2.6. Calculation of Sensitivity and Specificity
2.7. Development of the Western blot-rHc-HCA59
2.8. Repeatability of ELISA-rHc-HCA59
3. Results
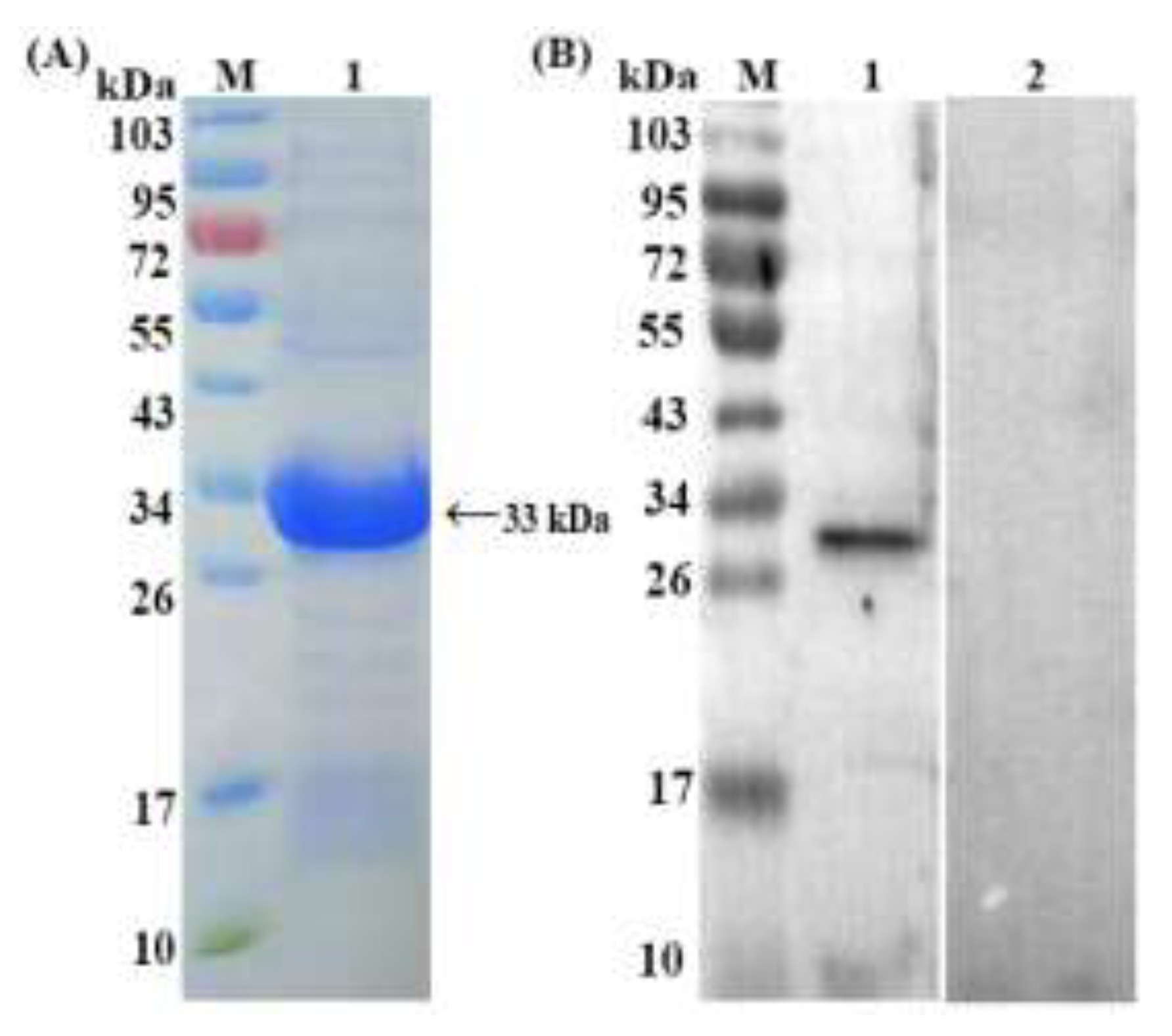
3.1. Purification and Western Blotting
3.2. Microscopic Examination
3.3. Cut-Off Value of Indirect ELISA
3.4. Development and Serodiagnostic Potential of Indirect ELISA
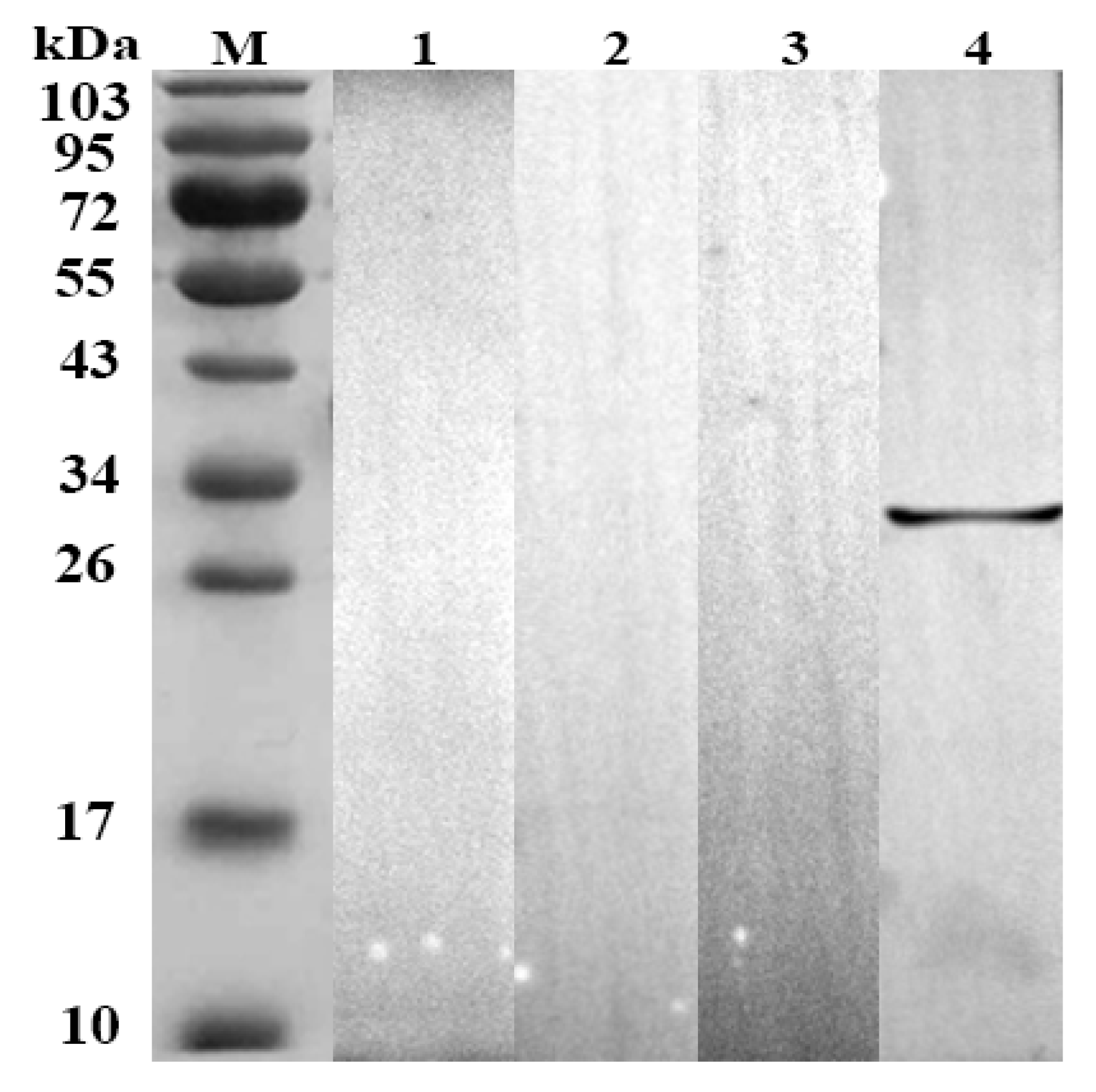
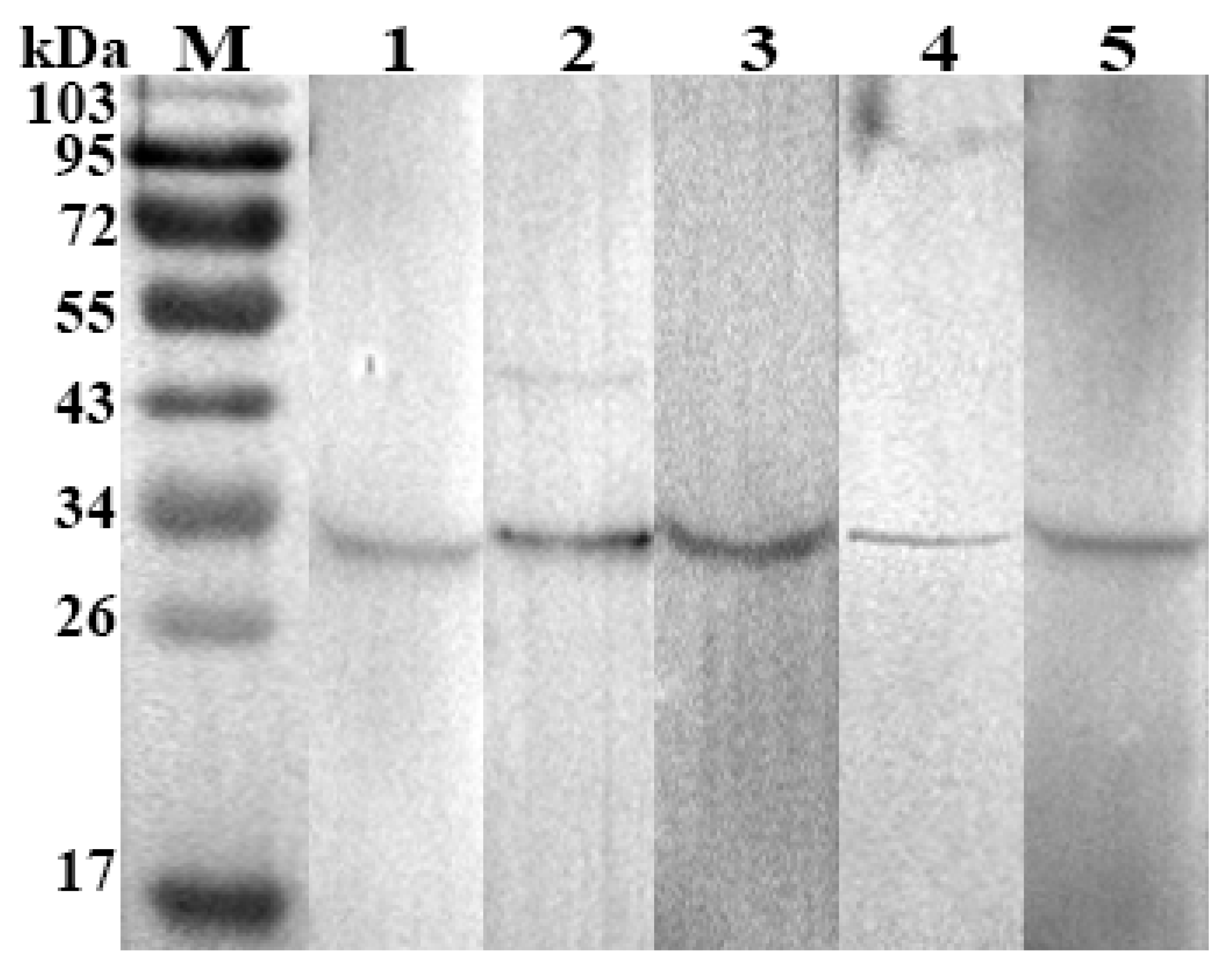
3.5. Western Blotting for Ratification of Indirect ELISA Results
3.6. Test Repeatability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| rHc-HCA59 | Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-associated antigen 59 |
| PI | Post infection |
| HcESPs | Excretory and secretory products of Haemonchus contortus |
| NAU | Nanjing Agricultural University |
| LB | Luria Bertini |
| AEC | Animal Ethics Committee |
| IPTG | Isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactopyranoside |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF | Polyvinyl difluoride membrane |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| TMB | Tetramethylbenzidine |
| OD | Optical density |
| P/N | Positive to negative |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| TBS-T | Tris-Buffered Saline containing 0.05% Tween 20 |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| kDa | Kilodalton |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
References
- Alam, M.B.B.; Omar, A.I.; Faruque, M.O.; Notter, D.R.; Periasamy, K.; Mondal, M.M.H.; Sarder, M.J.U.; Shamsuddin, M.; Cao, J.; Du, X.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes are significantly associated with resistance to Haemonchus contortus infection in goats. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, A.; Notter, D.R.; Soudre, A.; Kaboré, A.; Álvarez, I.; Fernández, I.; Sanou, M.; Shamshuddin, M.; Periasamy, K.; Tamboura, H.H.; et al. Resistance to gastrointestinal parasite infection in Djallonké sheep. Animal 2017, 11, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, M.F.; Maqbool, A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, N.; Muneer, M.A. Epidemiology of haemonchosis in sheep and goats under different managemental conditions. Vet. World 2009, 2, 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, A.V.; Goldberg, V.; Viotti, H.; Ciappesoni, G. Early detection of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep using three different faecal occult blood tests. Open Vet. J. 2015, 5, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kandil, O.M.; Eid, N.A.; Elakabawy, L.M.; Abdelrahman, K.A.; Helal, M.A. Immunodiagnostic Potency of Different Haemonchus contortus Antigens for Diagnosis of Experimentally and Naturally Haemonchosis in Egyptian Sheep. APG 2015, 6, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, J.M.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Zajac, A.M. Effects of artemisinin and Artemisia extracts on Haemonchus contortus in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, R.B.; Bott, N.J.; Chilton, N.B.; Hunt, P.; Beveridge, I. Toward practical, DNA-based diagnostic methods for parasitic nematodes of livestock - Bionomic and biotechnological implications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovskaya, N.N.; Scherbakov, A.V.; Yakovleva, A.S.; Tsyvanyuk, M.A.; Mudrak, N.S.; Drygin, V.V.; Borisov, A.V. Detection of antibodies to avian infectious bronchitis virus by a recombinant nucleocapsid protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 135, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuda, A.P.; Krijgsveld, J.; Cornelissen, A.W.C.A.; Heck, A.J.R.; De Vries, E. Comprehensive analysis of the secreted proteins of the parasite Haemonchus contortus reveals extensive sequence variation and differential immune recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16941–16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Yongqian, B.; Ehsan, M.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Xu, L.X.; Li, X.R. Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins (HcESPs) suppress functions of goat PBMCs in vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35,670–35,679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallig, H.D.F.H.; Leeuwen, M.A.W.V.; Hendrikx, W.M.L. Immune responses of Texel sheep to excretory/secretory products of adult Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology 1994, 108, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Wang, S.; Bo, G.; Ehsan, M.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Xu, L.X.; Li, X.R. Proteomic Analysis of the Excretory and Secretory Proteins of Haemonchus contortus (HcESP) Binding to Goat PBMCs In Vivo Revealed Stage-Specific Binding Profiles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, K.-J.; Pang, X.-W.; Vaughan, H.A.; Qu, W.; Dong, X.Y.; Peng, J.R.; Zhao, H.T.; Rui, J.A.; Leng, X.S.; et al. Large scale identification of human hepatocellular carcinoma-associated antigens by autoantibodies. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Wu, L.Y.; Hasan, M.W.; Lu, M.M.; Wang, W.J.; Yan, R.F.; Xu, L.X.; Song, X.K.; Li, X.R. Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated antigen 59 of Haemonchus contortus modulates the functions of PBMCs and the differentiation and maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells of goats in vitro. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Li, X. Cloning, expression and characterization of NAD+-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase of adult Haemonchus contortus. J. Helminthol. 2011, 85, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungström, S.; Melville, L.; Skuce, P.J.; Höglund, J. Comparison of Four Diagnostic Methods for Detection and Relative Quantification of Haemonchus contortus Eggs in Feces Samples. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 4, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hassan, E.M.; El-Bahr, S.M. Antigenic and immunogenic components of Haemonchus longistipes identified by western Immunobloting. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 8, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankaew, P.; Srisawat, W.; Singhla, T.; Tragoolpua, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Sawada, T.; Sthitmatee, N. Comparison of two indirect ELISA coating antigens for the detection of dairy cow antibodies against Pasteurella multocida. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 145, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuracpreeda, P.; Chawengkirtikul, R.; Tinikul, Y.; Poljaroen, J.; Chotwiwatthanakun, C.; Sobhon, P. Diagnosis of Fasciola gigantica infection using a monoclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for detection of circulating cathepsin B3 protease. Acta Trop. 2013, 127, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akao, T.; Kakehi, Y.; Wu, X.; Kinoshita, H.; Takahashi, T.; Ogawa, O.; Kato, T.; Yoshida, O. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Telomerase Activity of Exfoliated Cells in Urine of Patients with Urothelial Cancers. Urol. Oncol. 1997, 3, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Banerjee, P.S.; Kumar, S.; Garg, R.; Ram, H.; Kundu, K.; Raina, O.K. Development and evaluation of serodiagnostic assays with recombinant BgSA1 of Babesia gibsoni. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankaew, P.; Singh-La, T.; Titaram, C.; Punyapornwittaya, V.; Vongchan, P.; Sawada, T.; Sthitmatee, N. Evaluation of an In-house indirect ELISA for detection of antibody against haemorrhagic septicemia in Asian elephants. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 134, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.; Nasir, A.; Singh, N. Detection of anti-Haemonchus contortus antibodies in sheep by dot- ELISA with immunoaffinity purified fraction of ES antigen during prepatency. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 46, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.M.; Martín, S.; Hernández, Y.I.; González, J.F.; Ferrer, O.; Ruiz, A. Immunoprotective effect of cysteine proteinase fractions from two Haemonchus contortus strains adapted to sheep and goats. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Li, X. Vaccination of goats with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase DNA vaccine induced partial protection against Haemonchus contortus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 149, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Xu, L.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Li, X. Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of enolase from adult Haemonchus contortus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Li, B.; Ehsan, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hasan, M.W.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Recombinant Haemonchus contortus 24 kDa excretory/secretory protein (rHcES-24) modulate the immune functions of goat PBMCs in vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83926–83937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, A.K.J. Sero-prevalence of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep by Indirect-ELISA using somatic antigen. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 40, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmad, A.; Chandra, D.; Saravanan, B.C.; Manjunathchar, H.V.; Vinodh, K.O.R.; Fular, A.; Chigure, G.; Kaur, N.; Ghosh, S. Development of a recombinant TaSP-based Dot-ELISA for detection of Theileria annulata infection in cattle. Ticks Tick. Borne. Dis. 2018, 9, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, A.; Cai, W.; Hou, Y.; Pang, L.; Gao, X. Evaluation of a recombinant excretory secretory Haemonchus contortus protein for use in a diagnostic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 115, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, B.A.; Chishti, M.Z.; Ahmad, F.; Tak, H.; Hassan, J. Immunodiagnosis of Haemonchus contortus infection in sheep by indirect enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Ir J. Vet. Res. 2012, 13, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kooyman, F.N.J.; Van Kooten, P.J.S.; Huntley, J.F.; MacKellar, A.; Cornelissen, A.W.C.A.; Schallig, H.D.F.H. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for ovine immunoglobulin E and its application to monitor serum IgE responses to Haemonchus contortus infection. Parasitology 1997, 114, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.T.; Leite, O.M.; Arruda, R.S.; Ferreira, A.W. Combined use of Western blot/ELISA to improve the serological diagnosis of human tuberculosis. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 9, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waritani, T.; Chang, J.; McKinney, B.; Terato, K. An ELISA protocol to improve the accuracy and reliability of serological antibody assays. MethodsX 2017, 4, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

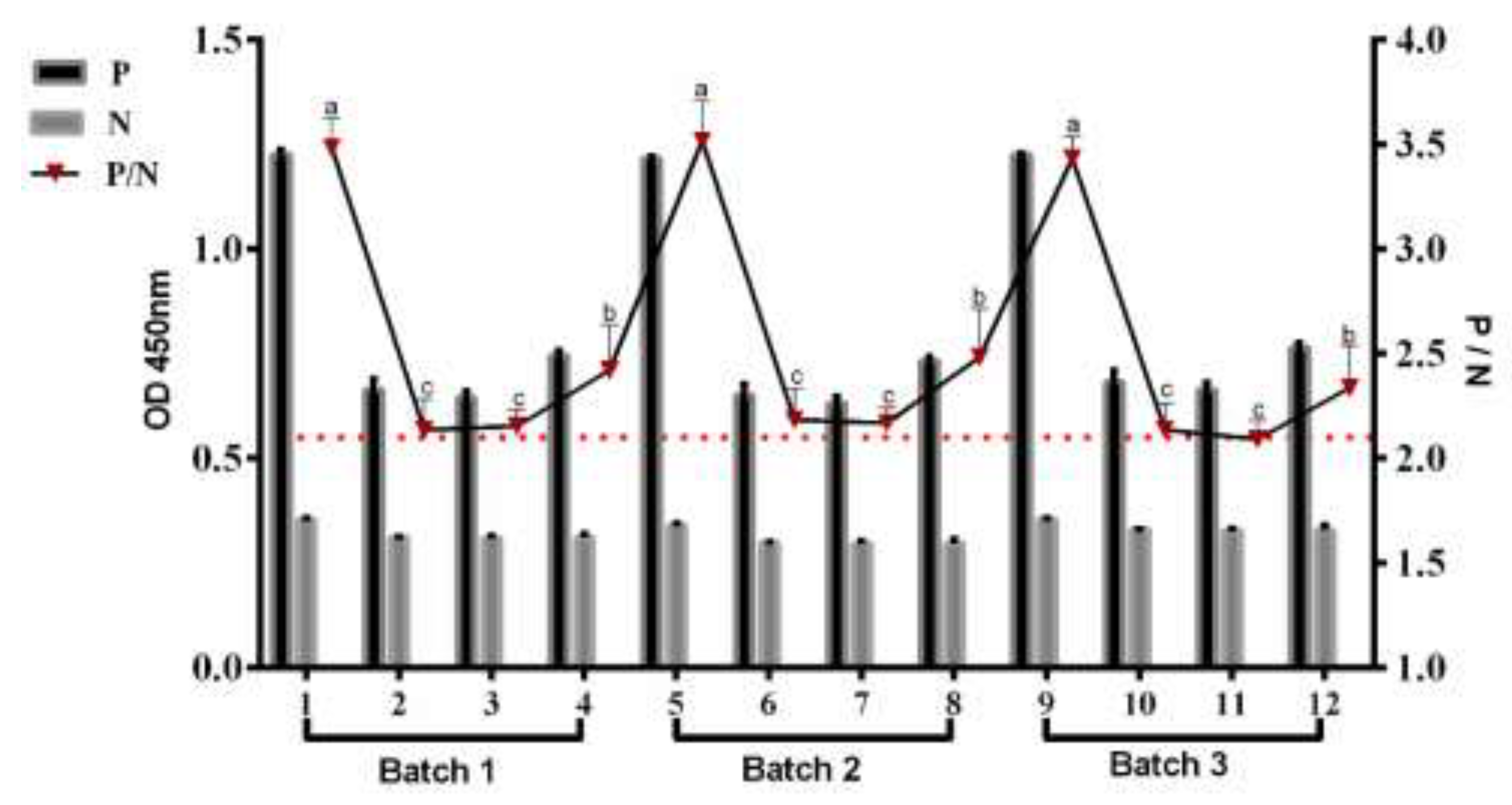
| Antigen Dilution | OD450 | Antibody Dilution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/well | 1:25 | 1:50 | 1:100 | 1:200 | |
| 6.5 | (P) | 1.631 | 1.517 | 0.738 | 0.528 |
| (N) | 1.428 | 1.204 | 0.541 | 0.273 | |
| P/N | 1.142 | 1.26 | 1.364 | 1.934 | |
| 3.25 | (P) | 1.467 | 1.291 | 0.679 | 0.623 |
| (N) | 0.673 | 0.584 | 0.379 | 0.321 | |
| P/N | 2.180 | 2.211 | 1.792 | 1.941 | |
| 1.62 | (P) | 1.248 | 1.074 | 0.685 | 0.595 |
| (N) | 0.536 | 0.456 | 0.304 | 0.251 | |
| P/N | 2.328 | 2.355 | 2.253 | 2.371 | |
| 0.81 | (P) | 1.256 | 1.102 | 0.613 | 0.465 |
| (N) | 0.393 | 0.269 | 0.211 | 0.201 | |
| P/N | 3.196 | 4.097 | 2.905 | 2.313 | |
| 0.40 | (P) | 1.022 | 0.853 | 0.538 | 0.407 |
| (N) | 0.359 | 0.235 | 0.199 | 0.187 | |
| P/N | 2.847 | 3.63 | 2.704 | 2.176 | |
| 0.2 | (P) | 0.919 | 0.738 | 0.427 | 0.371 |
| (N) | 0.335 | 0.221 | 0.194 | 0.178 | |
| P/N | 2.743 | 3.339 | 2.201 | 2.084 | |
| 0.1 | (P) | 0.611 | 0.432 | 0.338 | 0.301 |
| (N) | 0.312 | 0.204 | 0.196 | 0.188 | |
| P/N | 1.958 | 2.118 | 1.724 | 1.601 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naqvi, M.A.-u.-H.; Naqvi, S.Z.; Memon, M.A.; Aimulajiang, K.; Haseeb, M.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Yan, R. Combined Use of Indirect ELISA and Western Blotting with Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Antigen 59 Is a Potential Immunodiagnostic Tool for the Detection of Prepatent Haemonchus contortus Infection in Goat. Animals 2019, 9, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080548
Naqvi MA-u-H, Naqvi SZ, Memon MA, Aimulajiang K, Haseeb M, Xu L, Song X, Li X, Yan R. Combined Use of Indirect ELISA and Western Blotting with Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Antigen 59 Is a Potential Immunodiagnostic Tool for the Detection of Prepatent Haemonchus contortus Infection in Goat. Animals. 2019; 9(8):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080548
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaqvi, Muhammad Ali-ul-Husnain, Sana Zahra Naqvi, Muhammad Ali Memon, Kalibixiati Aimulajiang, Muhammad Haseeb, Lixin Xu, Xiaokai Song, Xiangrui Li, and Ruofeng Yan. 2019. "Combined Use of Indirect ELISA and Western Blotting with Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Antigen 59 Is a Potential Immunodiagnostic Tool for the Detection of Prepatent Haemonchus contortus Infection in Goat" Animals 9, no. 8: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080548
APA StyleNaqvi, M. A.-u.-H., Naqvi, S. Z., Memon, M. A., Aimulajiang, K., Haseeb, M., Xu, L., Song, X., Li, X., & Yan, R. (2019). Combined Use of Indirect ELISA and Western Blotting with Recombinant Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Associated Antigen 59 Is a Potential Immunodiagnostic Tool for the Detection of Prepatent Haemonchus contortus Infection in Goat. Animals, 9(8), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080548








