A Novel SNP in EIF2AK4 Gene Is Associated with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
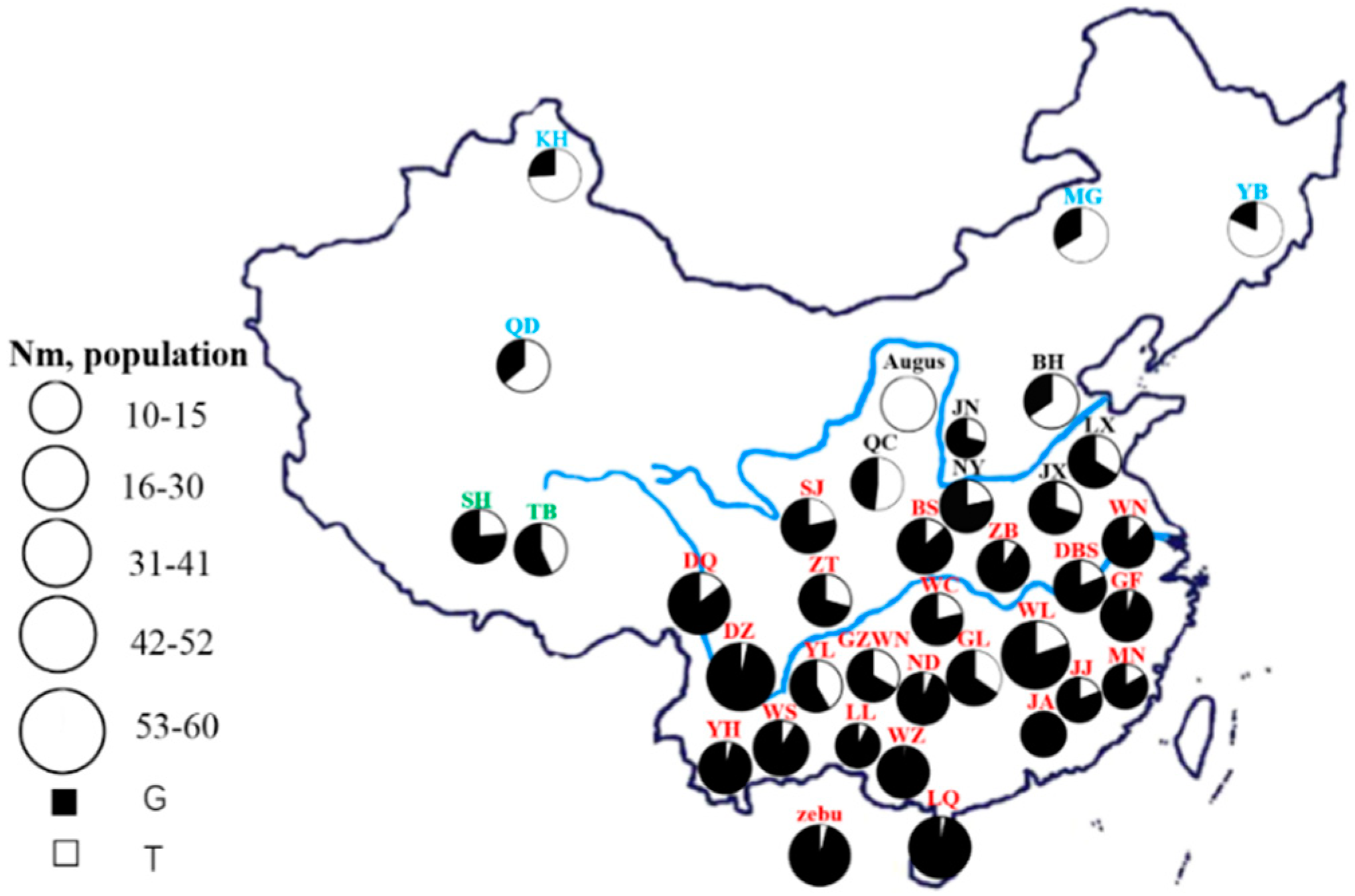
2.2. Animals, DNA Extraction, and Data Collection
2.3. PCR Analysis of the EIF2AK4 Gene in Chinese Cattle
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity Analysis
3.2. Analysis of Genotypic and Allelic Frequencies
3.3. Associations of EIF2AK4 Variation with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle Breeds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonna, L.A.; Fujita, J.; Gaffin, S.L.; Lilly, C.M. Invited review: Effects of heat and cold stress on mammalian gene expression. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanks, K.W. Modulators of the eukaryotic heat shock response. Exp. Cell Res. 1986, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, S. The heat-shock response. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1986, 55, 1151–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Park, K.; Hwang, D.S.; Rhee, K. Importance of eIF2α phosphorylation as a protective mechanism against heat stress in mouse male germ cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniuchi, S.; Miyake, M.; Tsugawa, K.; Oyadomari, M.; Oyadomari, S. Integrated stress response of vertebrates is regulated by four eIF2α kinases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga, J.J.; Ventoso, I.; Harding, H.P.; Deng, J.; Ron, D.; Sonenberg, N.; Carrasco, L.; de Haro, C. Antiviral effect of the mammalian translation initiation factor 2α kinase GCN2 against RNA viruses. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dever, T.E.; Feng, L.; Wek, R.C.; Cigan, A.M.; Donahue, T.F.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell 1992, 68, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Harding, H.P.; Raught, B.; Gingras, A.C.; Berlanga, J.J.; Scheuner, D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Ron, D.; Sonenberg, N. Activation of GCN2 in UV-irradiated cells inhibits translation. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grousl, T.; Ivanov, P.; Frýdlová, I.; Vasicová, P.; Janda, F.; Vojtová, J.; Malínská, K.; Malcová, I.; Nováková, L.; Janosková, D.; et al. Robust heat shock induces eIF2alpha-phosphorylation-independent assembly of stress granules containing eIF3 and 40S ribosomal subunits in budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edea, Z.; Dadi, H.; Dessie, T.; Uzzaman, M.R.; Rothschild, M.F.; Kim, E.S.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Kim, K.S. Genome-wide scan reveals divergent selection among taurine and zebu cattle populations from different regions. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Ju, Z.; Zhang, Z. A survey of cattle production in China. World Anim. Rev. 1993, 76, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; et al. Genome-wide assessment of genetic diversity and population structure insights into admixture and introgression in Chinese indigenous cattle. BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Lei, C.; Wang, S.; Xue, K.; Zhang, B. mtDNA diversity and genetic lineages of eighteen cattle breeds from Bos taurus and Bos indicus in China. Genetica 2007, 131, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H. Studies on Sex Chromosome Polymorphism of Four Local Cattle (Bos taurus) Breeds in China. Hereditas 1993, 52, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, F.C. POPGENE (version 1.3. 1). Microsoft Window-Bases Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis. 1999. Available online: http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/ (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Nei, M.; Roychoudhury, A.K. Sampling variances of heterozygosity and genetic distance. Genetics 1974, 76, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohmanova, J.; Misztal, I.; Cole, J.B. Temperature–Humidity Indices as Indicators of Milk Production Losses due to Heat Stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farny, N.G.; Kedersha, N.L.; Silver, P.A. Metazoan stress granule assembly is mediated by P-eIF2α-dependent and-independent mechanisms. RNA 2009, 15, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Narasimhan, J.; Wek, R.C. Differential activation of eIF2 kinases in response to cellular stresses in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics 2004, 168, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga, J.J.; Rivero, D.; Martín, R.; Herrero, S.; Moreno, S.; de Haro, C. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase Sty1 in regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinases in response to environmental stress in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, N.; Ning, Q.; Yao, Y.; Chen, H.; Dang, R.; Zhang, H.; Lei, C. PRLH and SOD 1 gene variations associated with heat tolerance in Chinese cattle. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Lin, B.Z.; Baig, M.; Mitra, B.; Lopes, R.J.; Santos, A.M.; Magee, D.A.; Azevedo, M.; Tarroso, P.; Sasazaki, S.; et al. Zebu cattle are an exclusive legacy of the South Asia neolithic. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangkumhang, P.; Wilantho, A.; Shaw, P.J.; Flori, L.; Moazami-Goudarzi, K.; Gautier, M.; Duangjinda, M.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. Genetic analysis of Thai cattle reveals a Southeast Asian indicine ancestry. PeerJ 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, X.M.; Campana, M.G.; Huang, J.P.; Chang, Z.H.; Qi, X.B.; Shi, H.; Su, B.; Zhang, R.F.; Lan, X.Y.; et al. Paternal origins of Chinese cattle. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolberg, F. Progress in the utilization of urea-ammonia treated crop residues: biological and socio-economic aspects of animal production and application of the technology on small farms. Livestock Res. Rural Dev. 1992, 4, 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dolberg, F.; Finlayson, P. Treated straw for beef production in China. World Anim. Rev. 1995, 82, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; He, H.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J.W.; Lei, C.Z.; Zhang, G.M.; Dang, R.H.; Niu, H.; Qi, X.L.; Chen, H.; et al. Detection of 19-bp deletion within PLAG1 gene and its effect on growth traits in cattle. Gene 2018, 675, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.J.; Swain, D.L.; Kadarmideen, H.N. Evolutionary process of Bos taurus cattle in favourable versus unfavourable environments and its implications for genetic selection. Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cai, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals world-wide ancestry and adaptive introgression events of domesticated cattle in East Asia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.D.; Ding, X.D.; Wang, S.; Wójcik, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Tokarska, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.S.; Faruque, O.; Nielsen, R.; et al. Pervasive introgression facilitated domestication and adaptation in the Bos species complex. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Qing, Z.R.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, A.D. Bovine Breeds in China; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1988; pp. 31–117. [Google Scholar]
- Berlanga, J.J.; Santoyo, J.; De Haro, C. Characterization of a mammalian homolog of the GCN2 eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2010, 265, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SNP | Genotype (n) | Temperature | Relative Humidity | Temperature–Humidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) (LSM ± SE) | (%) (LSM ± SE) | Index (LSM ± SE) | ||
| EIF2AK4: NC_037337.1: g.35615224 T > G | TT (121) | 9.016A ± 0.3487 | 62.16A ± 1.094 | 50.4976A ± 0.47930 |
| GT (310) | 11.113B ± 0.2914 | 65.64B ± 0.706 | 53.4225B ± 0.40590 | |
| GG (591) | 15.072C ± 0.2471 | 73.68C ± 0.392 | 58.8280C ± 0.35644 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Cao, Y.; Rong, Y.; Ning, Q.; Jia, P.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Dang, R.; Chen, H.; Lei, C. A Novel SNP in EIF2AK4 Gene Is Associated with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle. Animals 2019, 9, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9060375
Wang K, Cao Y, Rong Y, Ning Q, Jia P, Huang Y, Lan X, Dang R, Chen H, Lei C. A Novel SNP in EIF2AK4 Gene Is Associated with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle. Animals. 2019; 9(6):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9060375
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kaiyue, Yanhong Cao, Yu Rong, Qingqing Ning, Peng Jia, Yongzhen Huang, Xianyong Lan, Ruihua Dang, Hong Chen, and Chuzhao Lei. 2019. "A Novel SNP in EIF2AK4 Gene Is Associated with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle" Animals 9, no. 6: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9060375
APA StyleWang, K., Cao, Y., Rong, Y., Ning, Q., Jia, P., Huang, Y., Lan, X., Dang, R., Chen, H., & Lei, C. (2019). A Novel SNP in EIF2AK4 Gene Is Associated with Thermal Tolerance Traits in Chinese Cattle. Animals, 9(6), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9060375





