Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Management
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
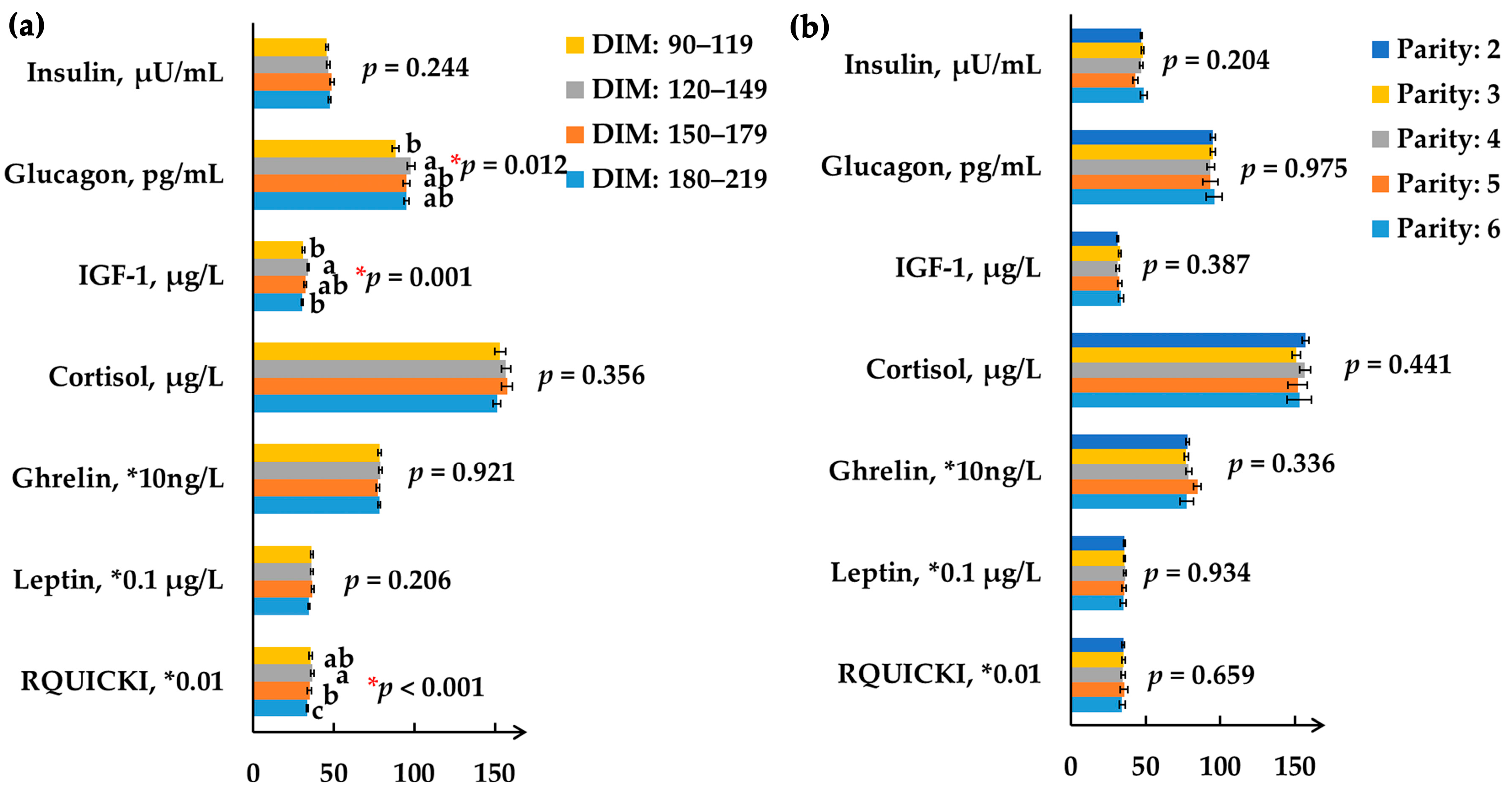
2.3. Grouping Based on Days-in-Milk and Parity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Information
3.2. Effects of Days-in-Milk on Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormones
3.3. Effects of Parity on Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormones
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowroozi-Asl, A.; Aarabi, N.; Rowshan-Ghasrodashti, A. Ghrelin and its correlation with leptin, energy related metabolites and thyroidal hormones in dairy cows in transitional period. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhtanen, P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Varvikko, T. Effects of abomasal infusions of histidine, glucose, and leucine on milk production and plasma metabolites of dairy cows fed grass silage diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.B.; Wall, E.H.; Mcfadden, T.B. Effects of increased milking frequency during early lactation on milk yield and udder health of primiparous Holstein heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Su, D.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ran, L.; Hu, R.; Cheng, J. Liver Metabolic Perturbations of Heat-Stressed Lactating Dairy Cows. Asian Austral J. Anim. 2018, 31, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.I.; Mayakrishnan, V.; Park, J.H.; Ki, K.S.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, S.B.; Park, S.M.; Jeong, H.Y.; Park, B.Y. The effect of lactation number, stage, length, and milking frequency on milk yield in Korean Holstein dairy cows using automatic milking system. Asian Austral J. Anim. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, S.; Frahm, J.; Tienken, R.; Kersten, S.; Meyer, U.; Huber, K.; Dänicke, S. Effects of energy supply and nicotinic acid supplementation on serum anti-oxidative capacity and on expression of oxidative stress-related genes in blood leucocytes of periparturient primi- and pluriparous dairy cows. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, e87–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Sun, H.; Wu, X.; Guan, L.L.; Liu, J. Assessment of rumen microbiota from a large cattle cohort reveals the pan and core bacteriome contributing to varied phenotypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbach, J.R.; Penner, G.B.; Stumpff, F.; Gabel, G. RUMINANT NUTRITION SYMPOSIUM: Role of fermentation acid absorption in the regulation of ruminal pH. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, H.; Xue, M.; Wang, D.; Guan, L.L.; Liu, J. Serum metabolome profiling revealed potential biomarkers for milk protein yield in dairy cows. J. Proteom. 2018, 184, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtenius, P.; Holtenius, K. A model to estimate insulin sensitivity in dairy cows. Acta Vet. Scand. 2007, 49, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, G.; Ravarotto, L.; Gottardo, F.; Stefani, A.L.; Contiero, B.; Moro, L.; Brscic, M.; Dalvit, P. Short communication: Reference values for blood parameters in Holstein dairy cows: Effects of parity, stage of lactation, and season of production. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3895–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.E.; Roussel, A.J. Evaluation of the Ruminant Serum Chemistry Profile. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2007, 23, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F. Serum chemistry profiles in dairy cows—A herd management tool? Vet. Med. 1997, 92, 986–991. [Google Scholar]
- Puppel, K.; Kuczyńska, B. Metabolic profiles of cow’s blood; a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowski, T.; Kuczyńska, B.; Puppel, K.; Metera, E.; Słoniewski, K.; Barszczewski, J. Relationships between physiological indicators in blood, and their yield, as well as chemical composition of milk obtained from organic dairy cows. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Qi, L.; Sheng, R.; Zhao, Y. Effects of beta-Hydroxybutyric Acid on Expressions of Genes Involved in Milk Protein Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 26, 3836–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobe, G.; Hippen, A.R.; She, P.; Lindberg, G.L.; Young, J.W.; Beitz, D.C. Effects of glucagon infusions on protein and amino acid composition of milk from dairy cows 1. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippen, A.R.; She, P.; Young, J.W.; Beitz, D.C.; Lindberg, G.L.; Richardson, L.F.; Tucker, R.W. Metabolic responses of dairy cows and heifers to various intravenous dosages of glucagon. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, C.G.; Davis, S.R.; Farr, V.C.; Moore, L.G.; Gluckman, P.D. Effects of close-arterial (external pudic) infusion of insulin-like growth factor-II on milk yield and mammary blood flow in lactating goats. J. Endocrinol. 1994, 142, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, S.A.; Cant, J.P. IGF-1 stimulates protein synthesis by enhanced signaling through mTORC1 in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2010, 38, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerestes, M.; Faigl, V.; Kulcsár, M.; Balogh, O.; Földi, J.; Fébel, H.; Chilliard, Y.; Huszenicza, G. Periparturient insulin secretion and whole-body insulin responsiveness in dairy cows showing various forms of ketone pattern with or without puerperal metritis. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2009, 37, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.W.; Kunz, P.L.; Leuenberger, H.; Gautschi, K.; Keller, M. Thyroid hormones, blood plasma metabolites and hematological parameters in relationship to milk yield in dairy cows. Anim. Prod. 1983, 36, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, H.; Ofer, L.; Elbaz, M.; Kaim, M.; Shinder, D.; Gershon, E. Seasonal and parity effects on ghrelin levels throughout the estrous cycle in dairy cows. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 235, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Days in Milk | SEM 1 | p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90–119 (n = 53) | 120–149 (n = 74) | 150–179 (n = 57) | 180–219 (n = 103) | |||
| Milk performance | ||||||
| Milk yield, kg/d | 36.0 a | 33.9 ab | 31.7 b | 32.4 b | 0.336 | <0.001 |
| Milk protein, % | 2.89 b | 3.08 a | 3.13 a | 3.14 a | 0.015 | <0.001 |
| Milk protein yield, kg/d | 1.04 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.009 | 0.351 |
| Milk urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 13.4 c | 13.8 bc | 14.5 ab | 14.8 a | 0.116 | <0.001 |
| Somatic cell counts, ×103/mL | 170 bc | 168 c | 284 a | 244 ab | 14.474 | <0.001 |
| Serum biochemical parameters | ||||||
| Blood urea nitrogen, mmol/L | 3.97 b | 3.70 c | 4.33 a | 4.47 a | 0.049 | <0.001 |
| Total protein, g/L | 66.6 a | 66.7 a | 62.7 b | 59.2 c | 0.440 | <0.001 |
| Albumin, g/L | 37.7 | 39.3 | 37.6 | 38.8 | 0.303 | 0.190 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 3.94 c | 4.28 b | 4.49 ab | 4.73 a | 0.046 | <0.001 |
| NEFA, mmol/L 2 | 0.22 b | 0.17 c | 0.21 b | 0.26 a | 0.005 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 6.01 | 6.09 | 5.71 | 6.18 | 0.067 | 0.090 |
| β-hydroxybutyrate, mmol/L | 0.55 a | 0.49 ab | 0.46 b | 0.49 b | 0.008 | 0.006 |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.005 | 0.354 |
| Creatinine, μmol/L | 56.4 b | 56.7 b | 62.2 a | 62.5 a | 0.685 | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin, μmol/L | 3.92 b | 4.08 b | 4.71 a | 4.93 a | 0.061 | <0.001 |
| Malonaldehyde, nmol/mL | 5.00 a | 4.72 a | 3.29 b | 3.64 b | 0.091 | <0.001 |
| Superoxide dismutase, U/mL | 136 | 135 | 136 | 136 | 0.796 | 0.833 |
| Glutathione peroxidase, U/mL | 128 ab | 131 ab | 134 a | 126 b | 1.098 | 0.038 |
| T-AOC, U/mL 3 | 4.01 a | 3.52 b | 3.42 b | 3.54 b | 0.050 | 0.001 |
| Parity | 2.92 | 3.16 | 3.00 | 3.01 | 0.066 | 0.619 |
| Item | Parity | SEM 1 | p-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 (n = 117) | 3 (n = 89) | 4 (n = 49) | 5 (n = 19) | 6 (n = 13) | |||
| Milk performance | |||||||
| Milk yield, kg/d | 34.0 a | 33.6 a | 32.9 ab | 31.9 ab | 28.9 b | 0.336 | 0.020 |
| Milk protein, % | 3.12 a | 3.09 ab | 3.02 abc | 2.98 bc | 2.94 c | 0.015 | 0.006 |
| Milk protein yield, kg/d | 1.06 a | 1.03 ab | 0.98 abc | 0.94 bc | 0.85 c | 0.009 | 0.020 |
| Milk urea nitrogen, mg/dL | 14.7 a | 14.0 ab | 14.1 ab | 14.1 ab | 13.0 b | 0.116 | 0.007 |
| Somatic cell counts, ×103/mL | 152 b | 234 ab | 289 a | 296 ab | 341 a | 14.474 | 0.002 |
| Serum biochemical parameters | |||||||
| Blood urea nitrogen, mmol/L | 4.13 | 4.11 | 4.32 | 4.02 | 4.03 | 0.049 | 0.544 |
| Total protein, g/L | 61.6 b | 63.8 ab | 63.4 ab | 67.5 a | 66.4 ab | 0.440 | 0.005 |
| Albumin, g/L | 38.9 | 38.5 | 38.7 | 36.4 | 36.8 | 0.303 | 0.251 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 4.30 | 4.51 | 4.54 | 4.36 | 4.50 | 0.046 | 0.237 |
| NEFA, mmol/L 2 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.005 | 0.837 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 6.35 a | 5.86 b | 5.87 ab | 5.81 ab | 5.24 b | 0.067 | 0.001 |
| β-hydroxybutyrate, mmol/L | 0.50 ab | 0.51 a | 0.49 ab | 0.47 ab | 0.40 b | 0.008 | 0.035 |
| Triglyceride, mmol/L | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.32 | 0.005 | 0.595 |
| Creatinine, μmol/L | 62.5 a | 59.1 ab | 57.2 ab | 54.3 b | 58.5 ab | 0.685 | 0.008 |
| Total bilirubin, μmol/L | 4.43 | 4.62 | 4.28 | 4.47 | 4.20 | 0.061 | 0.584 |
| Malonaldehyde, nmol/mL | 4.19 | 4.15 | 3.83 | 4.00 | 4.07 | 0.091 | 0.664 |
| Superoxide dismutase, U/mL | 138 a | 135 ab | 133 ab | 131 b | 131 b | 0.796 | 0.034 |
| Glutathione peroxidase, U/mL | 127 | 131 | 128 | 133 | 128 | 1.098 | 0.487 |
| T-AOC, U/mL 3 | 3.6 | 3.57 | 3.72 | 3.36 | 3.63 | 0.050 | 0.663 |
| Days in milk | 153 | 161 | 160 | 158 | 139 | 1.979 | 0.481 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Sun, H.-Z.; Xue, M.; Wang, D.; Guan, L.; Liu, J. Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows. Animals 2019, 9, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9050230
Wu X, Sun H-Z, Xue M, Wang D, Guan L, Liu J. Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows. Animals. 2019; 9(5):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9050230
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuehui, Hui-Zeng Sun, Mingyuan Xue, Diming Wang, Leluo Guan, and Jianxin Liu. 2019. "Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows" Animals 9, no. 5: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9050230
APA StyleWu, X., Sun, H.-Z., Xue, M., Wang, D., Guan, L., & Liu, J. (2019). Days-in-Milk and Parity Affected Serum Biochemical Parameters and Hormone Profiles in Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows. Animals, 9(5), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9050230





