Aggressiveness, Mating Behaviour and Lifespan of Group Housed Rabbit Does
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Video Recording
- IA = number of initiated aggression events;
- PIA = number of attacked partners;
- SA = number of suffered aggression events;
- PSA = number of partners which initiated attack;
- n = group size.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
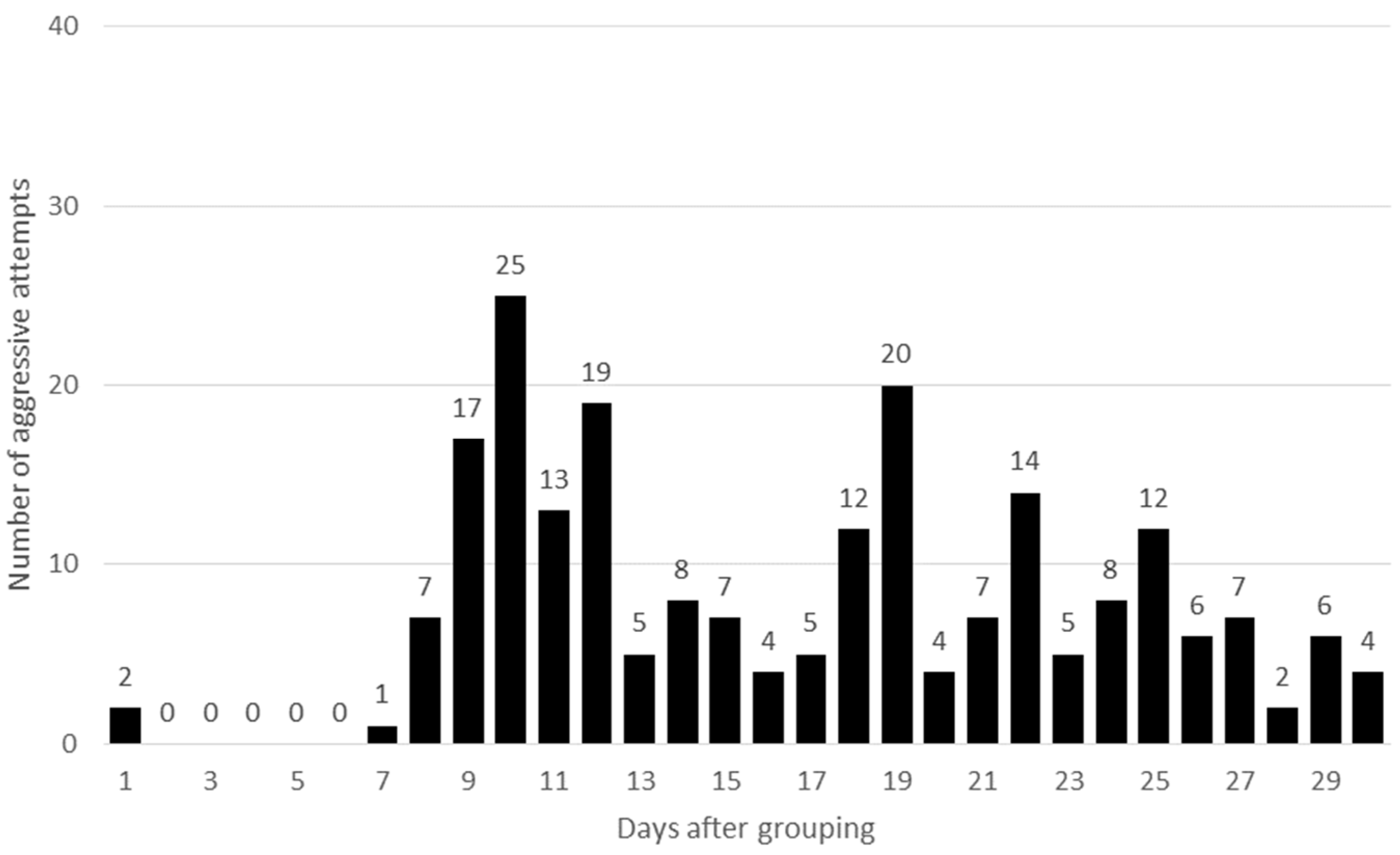
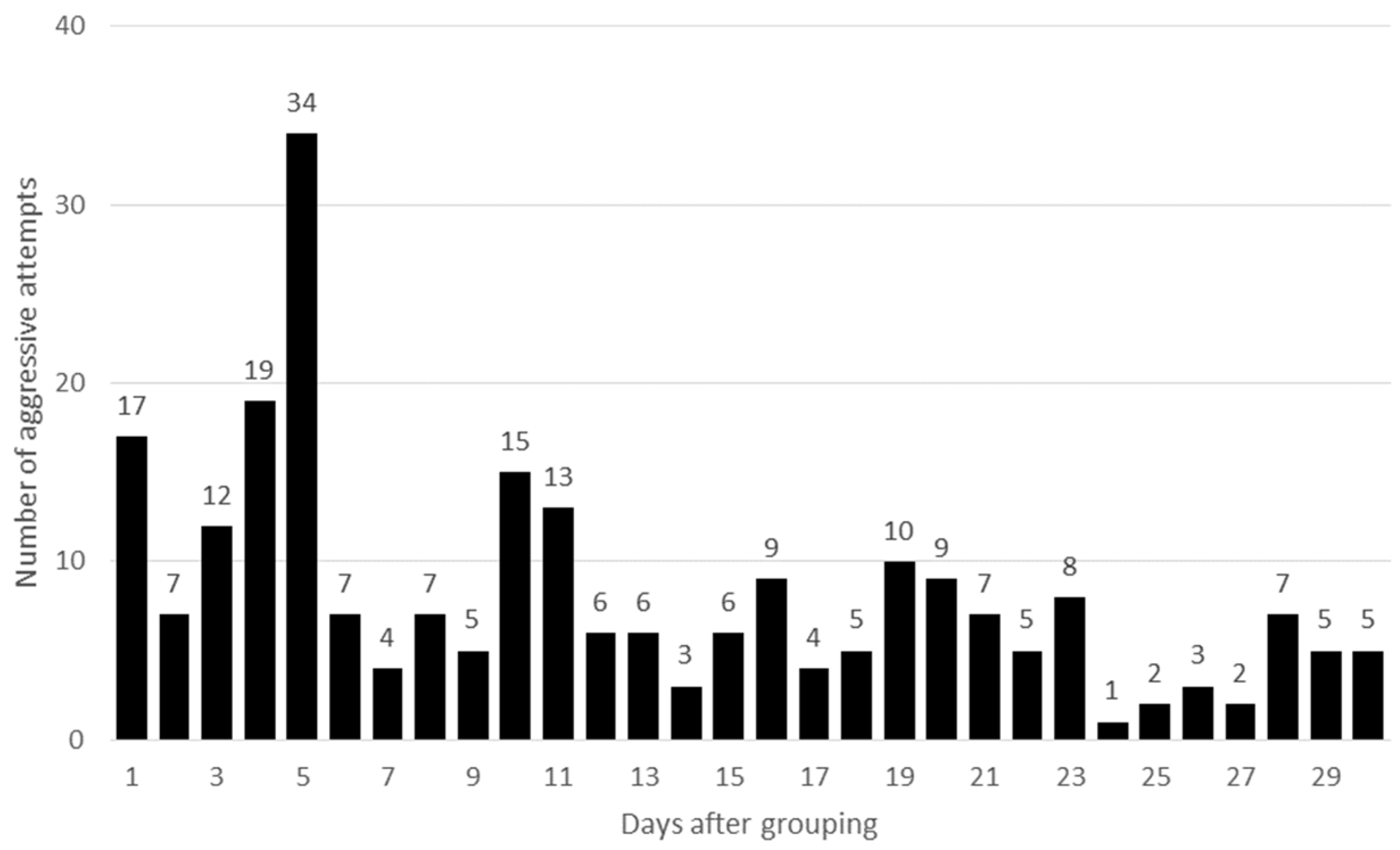
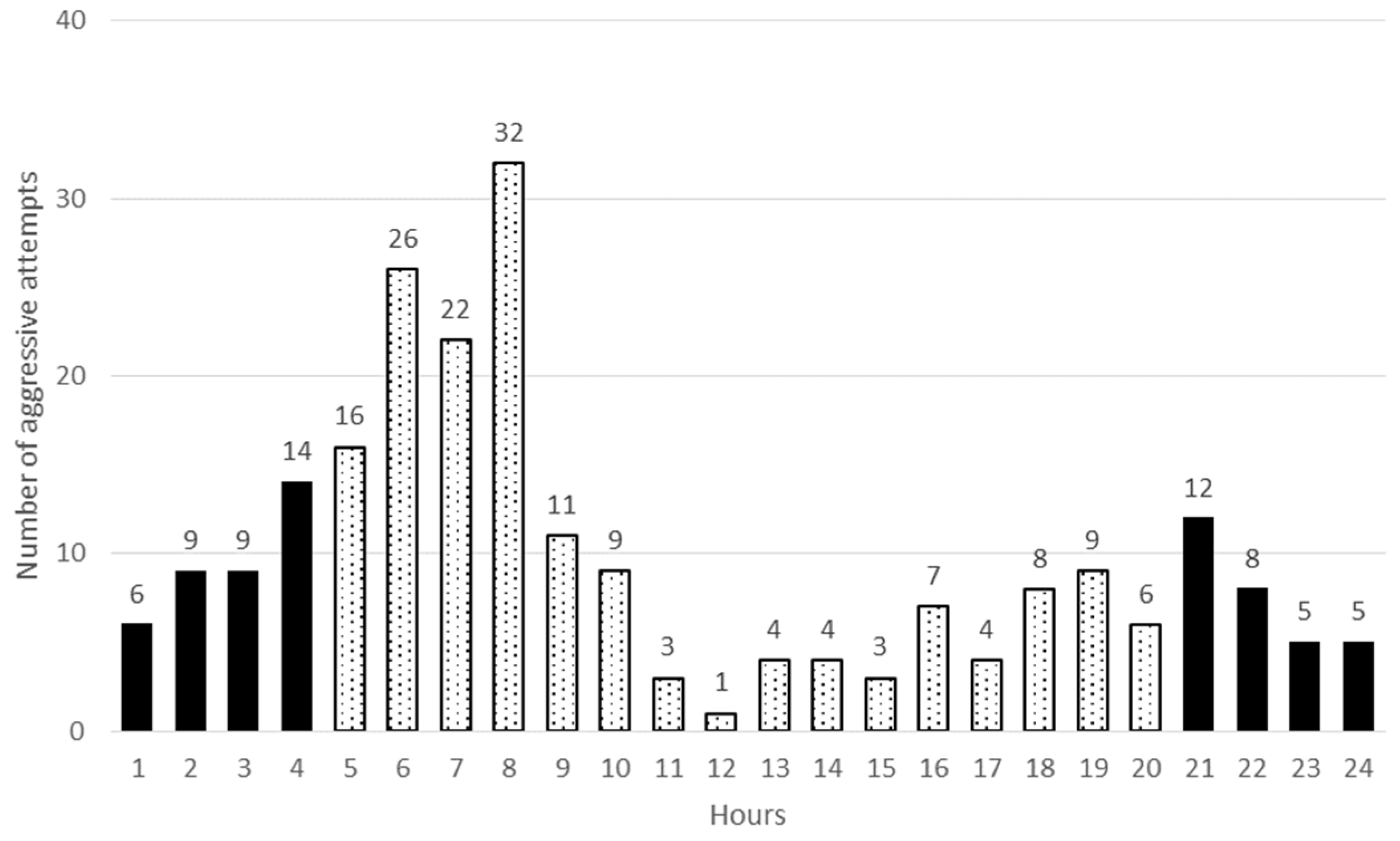
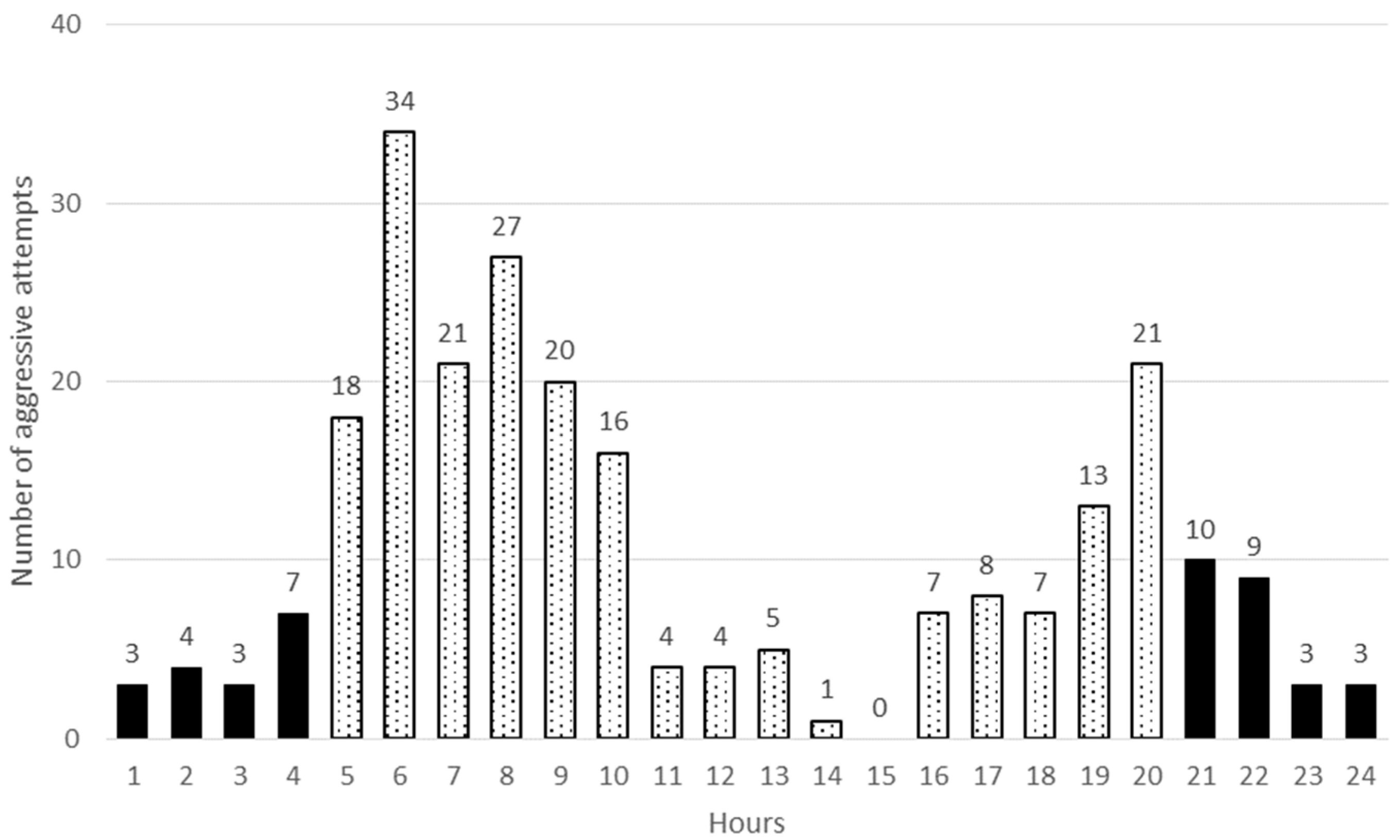
3.1. Aggressive Behaviour, Dominance Rank Order
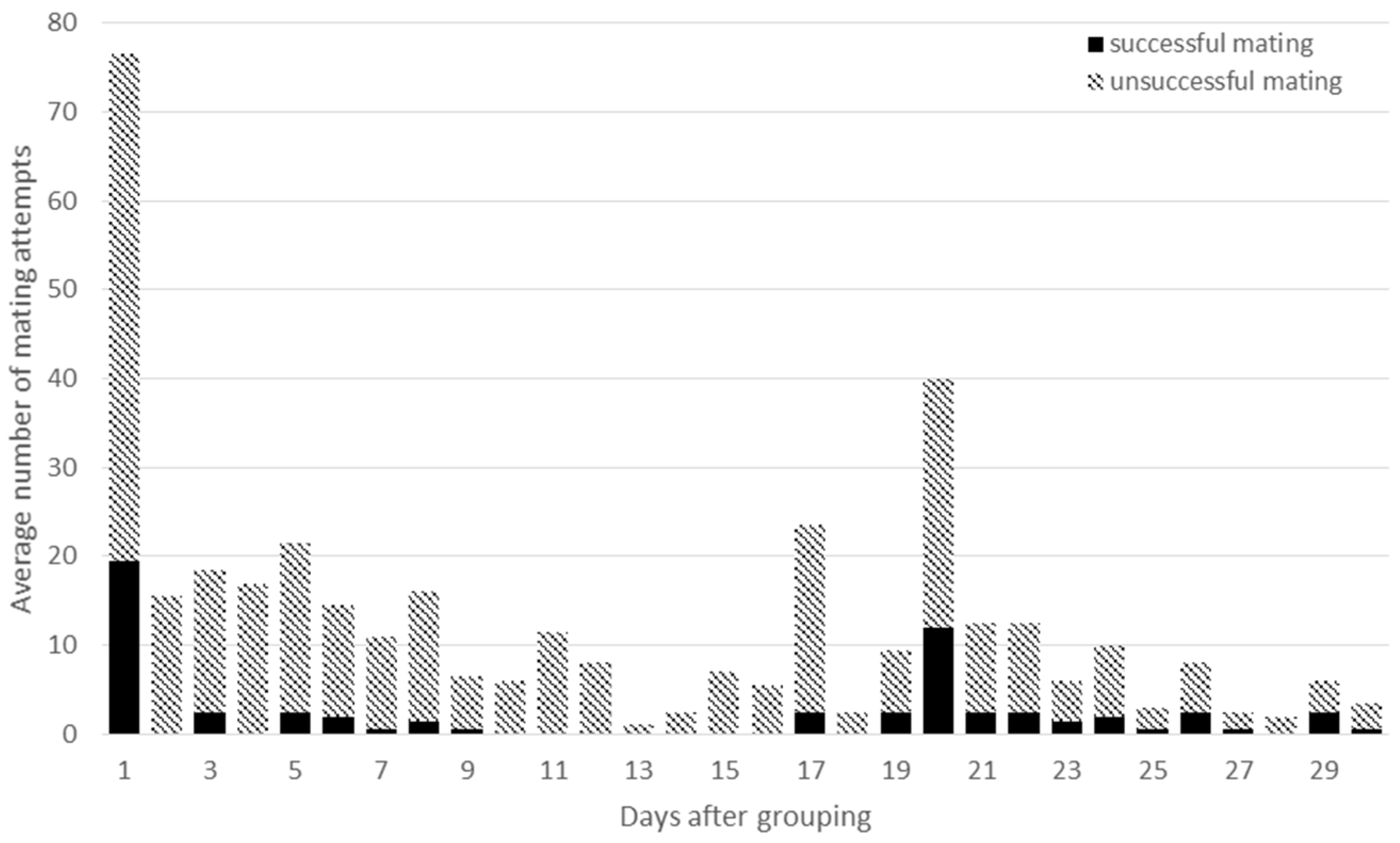
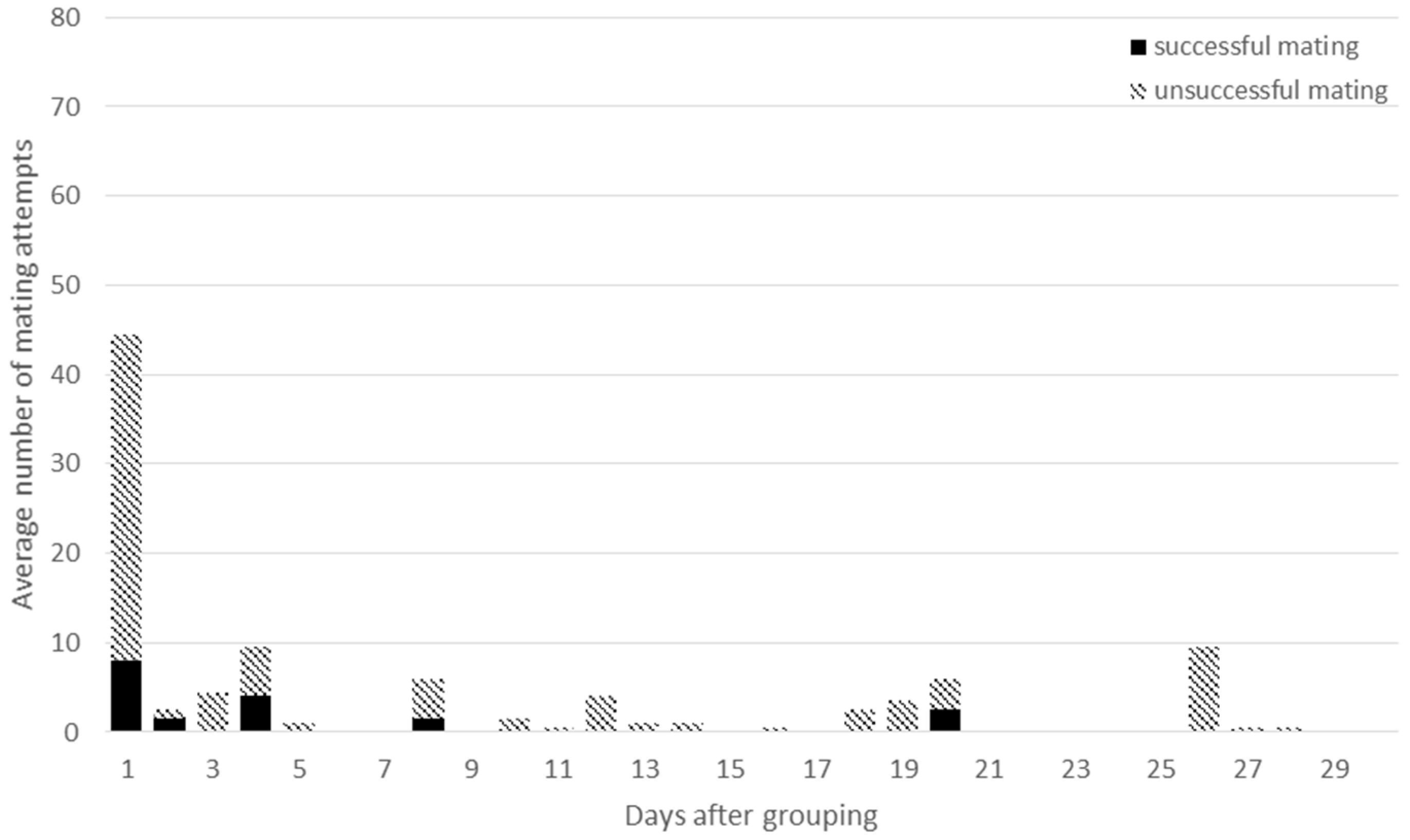
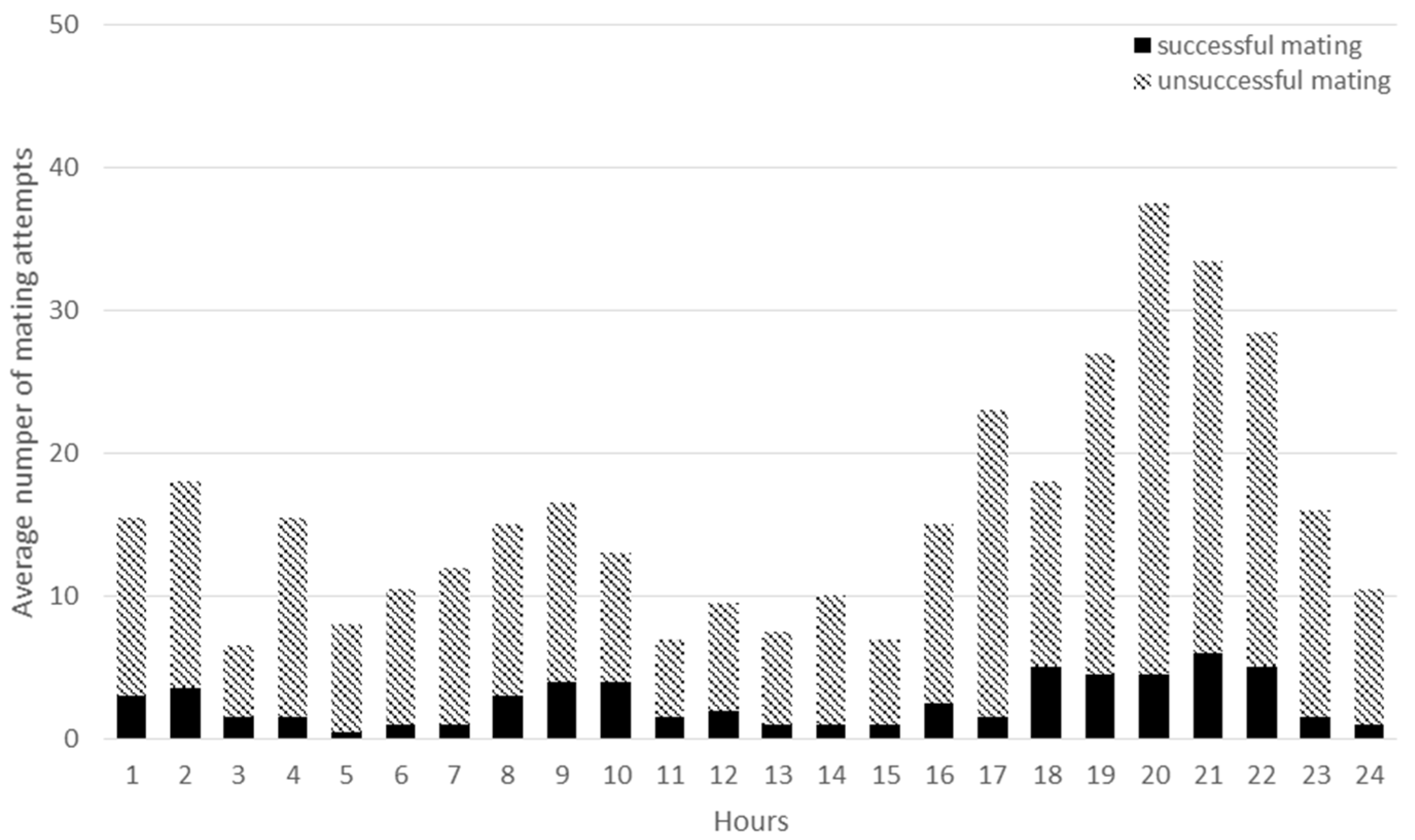
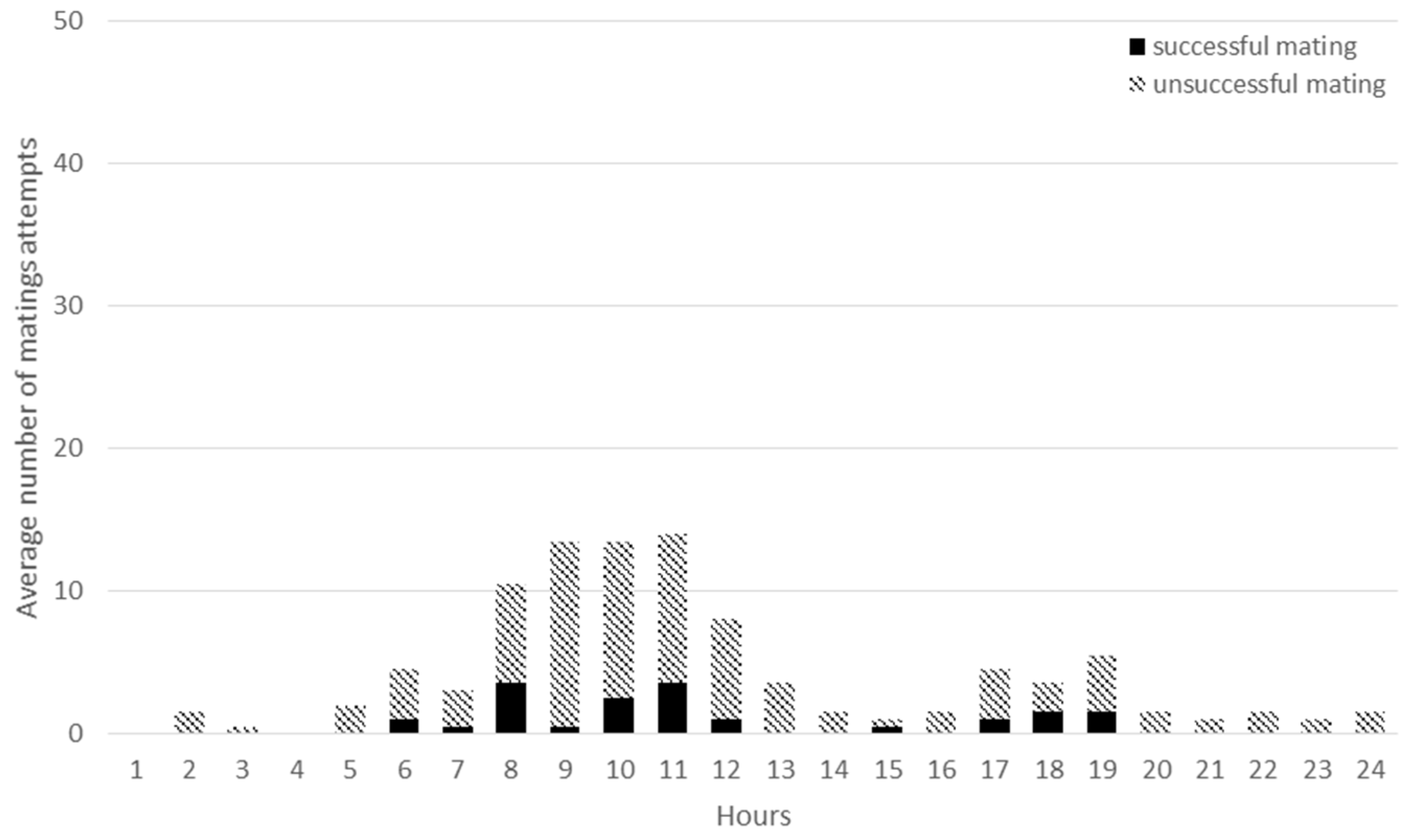
3.2. Mating
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szendrő, Z.; McNitt, I.J. Housing of rabbit does: Group and individual systems: A review. Livest. Sci. 2012, 150, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szendrő, Z.; McNitt, J.I.; Matics, Z.; Mikó, A.; Gerencsér, Z. Alternative housing systems for breeding does: A review. World Rabbit. Sci. 2016, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szendrő, Z.; Trocino, A.; Hoy, S.; Xiccato, G.; Villagrá, A.; Maertens, L. A review of recent research outcomes on the housing of farmed domestic rabbits: Reproducing does. World Rabbit. Sci. 2019, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrist, C.A.; van den Borne, B.H.P.; Bigler, L.M.; Buchwalder, T.; Roth, B.A. Epidemiologic survey in Swiss group-housed breeding rabbits: Extent of lesions and potential risk factors. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommers, J.M.; Boiti, C.; de Jong, I.; Brecchia, G. Performance and behaviour of rabbit does in a group-housing system with natural mating or artificial insemination. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2006, 46, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonetti, M.E.; Dessi-Fulgherl, F.; Farabollini, F. Intrafemale agonistic interactions in the domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus Cuniculus, L.). Aggress. Behav. 1990, 16, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szendrő, Z.; Mikó, A.; Odermatt, M.; Gerencsér, Z.; Radnai, I.; Dezséry, B.; Garai, É.; Nagy, I.; Szendrő, K.; Matics, Z. Comparison of performance and welfare of single-caged and group-housed rabbit does. Animal 2013, 7, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monclús, R.; Saavedra, I.; de Miguel, J. Context-dependent responses to neighbours and strangersin wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Behav. Process. 2014, 106, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykytowycz, R.; Hesterman, R.E. An experimental study of aggression in captive european rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus (L.). Behaviour 1975, 110, 104–123. [Google Scholar]
- Surridge, A.K.; Bell, D.J.; Hewitt, G.M. From population studies to individual behaviour: Genetic analysis of social structure in the European wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1999, 68, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, H.N. Sexual and aggressive behaviour in the wild rabbit. Behaviour 1948, 1, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holst, D.; Hutzelmeyer, H.; Kaetzke, P.; Khaschei, M.; Rödel, H.G.; Schrutka, H. Social rank, fecundity and lifetime reproductive success in wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2002, 51, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykytowycz, R. Social behaviour of an experimental colony of wild rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus (L.). I: Establishment of the colony. CSIRO Wildl. Res. 1958, 3, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meas, D.; Pluym, L.; Peltoniemi, O. Impact of group housing of pregnant soes on health. Porcine Health Manag. 2016, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrist, C.A.; Bigler, L.M.; Würbel, H.; Roth, B.A. Effects of group stability on aggression, stress and injuries in breeding rabbits. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 142, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabito, L.; Galliot, P.; Souchet, C.; Dumont, F.; Thomeret, F. Logement collectif des lapines reproductrices: Conséquences zootechniques. 11émes Journées de la Recherche Cunicole 2005, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rommers, J.M.; Reuvekamp, B.J.F.; Gunnink, H.; de Jong, J.C. Effect of hiding places, straw and territory on aggression in group-housed rabbit does. Appl. Anim. Beav. Sci. 2014, 157, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.; Bauer, J.; Borberg, C.; Chonsch, L.; Weirich, C. Impact of rank position on fertility of sows. Livest. Sci. 2009, 126, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, G.H.; Starkloff, A.; Seltmann, W.M.; Prager, G.; von Holst, D. Causes and predictors of nest mortality in a European rabbit population. Mamm. Biol. 2009, 74, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, G.H.; Bora, A.; Kaiser, J.; Kaetzke, P.; Khaschei, M.; von Holst, D. Density-dependent reproduction in the European rabbit: A consequence of individual response and age-dependent reproductive performance. OIKOS 2004, 104, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matics, Z.; Nagy, I.; Gerencsér, Z.; Radnai, I.; Gyovai, P.; Donkó, T.; Dalle Zotte, A.; Curik, I.; Szendrő, Z. Pannon Breeding Program in rabbit at Kaposvár University. World Rabbit Sci. 2014, 22, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holst, D. The concept of stress and its relevance for animal behaviour. Adv. Stud. Behav. 1998, 27, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zomeño, C.; Birolo, M.; Zuffellato, A.; Xiccato, G.; Trocino, A. Aggressiveness in group-housed rabbit does: Influence of group size and pen characteristics. Appl. Animal Behav. Sci. 2018, 194, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, H.N. The ecology and population dynamics of the wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Ann. Appl. Biol. 1940, 27, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, D.; Pérez, A.J.; Prieto, R.; Alonso, E.M.; Olmedo, A.J. Activity patterns of wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus, L.1758), under semi-freedom conditions, during autumn and winter. Wildl. Biol. Pract. 2005, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Díez, C.; Sanchez-García, C.; Pérez, J.A.; Bartolomé, D.J.; González, V.; Wheatley, C.J.; Alonso, N.E.; Gaudiosov, V.R. Behaviour activity of wild rabbit (Oryctolagus Cuniculus) under semi-natural rearing systems: Establishing a seasonal pattern. World Rabbit Sci. 2013, 21, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, K.; Poole, W. A study of the biology of the wild rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus (L.), in confined populations. II. The effects of season and population increase on behaviour. CSIRO Wildl. Res. 1961, 6, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, P.D. Aspects of the Social Organisation of the European Wild Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Ethology 1987, 75, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrist, C.A.; Bigler, L.M.; Würbel, H.; Roth, B.A. Masking odour when regrouping rabbit does: Effect on aggression, stress and lesions. Livest. Sci. 2014, 170, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeke, P.R.; Patton, N.M.; Lukefahr, S.D.; McNitt, J.I. Rabbit Production; The Interstate Printers and Publishers, Inc.: Danville, IL, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Caillol, M.; Dauphin-Villemant, C.; Martine, L. Oestrous behaviour and circulating progesterone and oestrogen levels during pseudopregnancy in the domestic rabbit. J. Reprod. Fert. 1983, 69, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.H.; Azrin, H.N. Temporal patterns of sexual behavior in rabbits as determined by an automatic recording technique. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1967, 10, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, P.; Serrano-Meneses, M.A.; Cuamatzi, E.; Gonzalez-Mariscal, G. Analysis of sexual behaviour in male rabbits across successive tests leading to sexual exhaustion. World Rabbit Sci. 2012, 20, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, C.; Rivaud, N. Sexual behaviour in pregnant and lactating domestic rabbits. Physiol. Behav. 1969, 4, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillol, M.; Solari, A.; Lefebvre, J. Changes in steroid concentrations in follicular fluid and sexual behavior during pseudopregnancy in the rabbit. Reprod. Nutr. Develop. 1984, 24, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonetti, M.E.; Fmbollini, F.; Dessi-Fulgheri, F. The acquisition of social dominance in female rabbits. Monit. Zoöl. Ital. 1988, 22, 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Jilge, B.; Hudson, R. Diversity and development of circadian rhythms in the European rabbit. Chronobiol. Int. 2001, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafuerte, R.; Kufner, B.M.; Delibes, M.; Moreno, S. Environmental factors influencing the seasonal daily activity of the European rabbit (Oryctolagm cuniculus) in a Mediterranean area. Mammalia 1993, 57, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilge, B. The Rabbit: A Diurnal or a Nocturnal Animal. J. Exp. Anim. Sci. 1991, 34, 170–183. [Google Scholar]
| Attacked | Attacker | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doe1 | Doe 2 | Doe 3 | Doe 4 | Total | |
| Doe1 | - | 3 | 7 | 6 | 16 |
| Doe2 | 18 | - | 28 | 25 | 71 |
| Doe3 | 51 | 2 | - | 4 | 57 |
| Doe4 | 8 | 0 | 2 | - | 10 |
| Total | 77 | 5 | 37 | 35 | 154 |
| Rank Index | 0.66 | −0.89 | −0.29 | 0.63 | |
| Rank order | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | |
| Attacked | Attacker | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doe1 | Doe 2 | Doe 3 | Doe 4 | Total | |
| Doe1 | - | 1 | 18 | 5 | 24 |
| Doe2 | 0 | - | 5 | 2 | 7 |
| Doe3 | 6 | 5 | - | 1 | 12 |
| Doe4 | 13 | 0 | 5 | - | 18 |
| Total | 19 | 6 | 28 | 8 | 61 |
| Rank Index | −0.26 | −0.05 | 0.40 | −0.15 | |
| Rank order | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| Attacked | Attacker | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doe1 | Doe 2 | Doe 3 | Doe 4 | Total | |
| Doe1 | - | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Doe2 | 3 | - | 0 | 2 | 5 |
| Doe3 | 30 | 2 | - | 0 | 32 |
| Doe4 | 59 | 5 | 3 | - | 67 |
| Total | 92 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 108 |
| Rank Index | 0.93 | 0.11 | −0.52 | −0.88 | |
| Rank order | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Attacked | Attacker | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doe1 | Doe 2 | Doe 3 | Doe 4 | Total | |
| Doe1 | - | 1 | 33 | 0 | 34 |
| Doe2 | 17 | - | 9 | 12 | 38 |
| Doe3 | 12 | 2 | - | 2 | 16 |
| Doe4 | 13 | 1 | 21 | - | 35 |
| Total | 42 | 4 | 63 | 14 | 123 |
| Rank Index | 0.25 | −0.81 | 0.59 | −0.52 | |
| Rank order | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerencsér, Z.; Matics, Z.; Szabó, R.T.; Kustos, K.; Mikó, A.; Nagy, I.; Odermatt, M.; Atkári, T.; Szendrő, Z. Aggressiveness, Mating Behaviour and Lifespan of Group Housed Rabbit Does. Animals 2019, 9, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100708
Gerencsér Z, Matics Z, Szabó RT, Kustos K, Mikó A, Nagy I, Odermatt M, Atkári T, Szendrő Z. Aggressiveness, Mating Behaviour and Lifespan of Group Housed Rabbit Does. Animals. 2019; 9(10):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100708
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerencsér, Zsolt, Zsolt Matics, Rubina T. Szabó, Károly Kustos, Annamária Mikó, István Nagy, Meinrad Odermatt, Tamás Atkári, and Zsolt Szendrő. 2019. "Aggressiveness, Mating Behaviour and Lifespan of Group Housed Rabbit Does" Animals 9, no. 10: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100708
APA StyleGerencsér, Z., Matics, Z., Szabó, R. T., Kustos, K., Mikó, A., Nagy, I., Odermatt, M., Atkári, T., & Szendrő, Z. (2019). Aggressiveness, Mating Behaviour and Lifespan of Group Housed Rabbit Does. Animals, 9(10), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9100708




