Age Structure of Water Frogs of the Genus Pelophylax in the Middle Volga River Region (European Russia)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Description of the Area and Object of Research
2.2. Study of Age Structure in Water Frogs
3. Results
Determination of the Age of Start of Sexual Maturity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terent’ev, P.V. The influence of climatic temperature on the size of snakes and tailless amphibians. Bull. Mosc. Soc. Nat. Biol. Ser. 1951, 56, 14–23. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Garanin, V.I. Life expectancy of amphibians in nature. Nature 1969, 10, 105. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Goncharenko, A.E. Age Dependence of Size in Cer-tain Amphibia. Vestn. Zool. 1979, 4, 46–50. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kleinenberg, S.E.; Smirina, E.M. A contribution to the method of age determination in amphibians. Zool. Zh. 1969, 48, 1090–1094. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Smirina, E.M. On the Methodology of Determining the Age of Amphibians. Zool. J. 1969, 48, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Smirina, E.M. Age determination and longevity in amphibians. Gerontology 1994, 40, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, T.R.; Verrell, P.A. Body size and age in amphibians and reptiles. J. Herpetol. 1988, 22, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanet, J.; Francillon-Vieillot, H.; Meunier, F.J.; De Ricqlès, A. Bone and individual aging. In Bone Growth; Hall, B.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; Volume 7, pp. 245–283. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsch, U. Review: Skeletochronological assessment of demographic life-history traits in amphibians. Herpetol. J. 2015, 25, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Borkin, L.J.; Tikhenko, N.D. Some aspects of morphological variability, color polymorphism, growth, population structure and activity of the pool frog, Rana lessonae, at the northern border of its range. Tr. Zool. Inst. 1979, 89, 18–54. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Socha, M.; Ogielska, M. Age structure, size and growth rate of water frogs from central European natural P. ridibundus-P. esculentus mixed populations estimated by skeletochronology. Amphibia-Reptilia 2010, 31, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, S.; Dursun, C.; Tabak, C.; Büyüksofuoğlu, S.; Özdemir, N. Age Structure, Body Size, and Sexual Dimorphism in a High-Altitude Population of P. ridibundus (Pallas, 1771). Animals 2024, 14, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garanin, V.I. Amphibians and Reptiles of Volga-Kama Region; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1983; p. 175. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zamaletdinov, R.I. Ecology of Amphibians in a Big City (on Example of Kazan). Ph.D. Thesis, Kazan State University, Kazan, Russia, 4 November 2003. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Fayzulin, A.I.; Zamaletdinov, R.I. Analysis of the age and sex structure of marsh frog (Rana ridibunda) and green toad (Bufo viridis) populations in the city of Tolyatti. Relev. Probl. Herpetol. Toxinol. 2007, 10, 160–165. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Fayzulin, A.I.; Mikhailova, R.I.; Kuzovenko, A.E. Materiais to monitoring of amphibians populations age structure in the urbanized territories of the Volga basin. Sci. Notes Kazan State Acad. Vet. Med. Named After N.E. Bauman 2013, 213, 85–90. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Svinin, A.O.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Mikhaylova, R.I. Age structure of mixed population systems of green frogs from the north-eastern part of the area. In Problems of Population Biology; STRING: Yoshkar-Ola, Russia, 2017. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Smirina, E.M. About the layered structure of some bones of the common toads in connection with the possibility of determining the age. Proc. Mordovia State Nat. Reserve 1972, 6, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Fayzulin, A.I.; Lada, G.A.; Litvinchuk, S.N.; Korzikov, V.A.; Svinin, A.O.; Zaks, M.M.; Rosanov, Y.M.; Kuzovenko, A.E.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Ermakov, O.A. On distribution of the edible frog Pelophylax esculentus (Linnaeus, 1758) on the territory of the Volga river basin. Tambov Univ. Rep. Ser. Nat. Tech. Sci. 2017, 22, 809–817. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plötner, J. Die Westpaläarktische Wasserfrösche; Laurenti: Bielefeld, Germany, 2005; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov-Leonov, S.Y. Evolutionary Potential of the Hybrid Form Pelophylax esculen-tus-ridibundus (Amphibia, Ranidae) within Dnieper and Desna Drainages: Its Loss Caused by the Hemiclonal Inheritance and the Compensatory Role of Parental Genomes’ Re-combination. Cytol. Genet. 2021, 55, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Plötner, J.; Pruvost, N.; Christiansen, D.G.; Röthlisberger, S.; Choleva, L.; Mikulíček, P.; Cogălniceanu, D.; Sas-Kovács, I.; Shabanov, D.; et al. Genetic diversity and distribution patterns of diploid and polyploid hybrid water frog populations (Pelophylax esculentus complex) across Europe. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 4371–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaune, I.A.; Borkin, L.J. New variant of uni-bisexual population systems in European green frogs (Rana esculenta complex). Hybridization and species problem in vertebrates. Arch. Zool. Mus. Mosc. State Univ. 1993, 30, 34–52. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ruchin, A.B.; Lada, G.A.; Borkin, L.J.; Litvinchuk, S.N.; Rosanov, J.M.; Ryzhov, M.K.; Zamaletdinov, R.I. On habitat distribution of three green frog species of the Rana esculenta complex in the Volga river basin. Povolzhskiy J. Ecol. 2009, 2, 137–147. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Akın, C.; Bilgin, C.C.; Beerli, P.; Westaway, R.; Ohst, T.; Litvinchuk, S.N.; Uzzell, T.; Bilgin, M.; Hotz, H.; Guex, G.-D.; et al. Phylogeographic patterns of genetic diversity in eastern Mediterranean water frogs were determined by geological processes and climate change in the Late Cenozoic. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, O.A.; Zaks, M.M.; Titov, S.V. Diagnostics and distribution of «western» and «eastern» forms of the marsh frog Pelophylax ridibundus s. l. in the Penza Province (on data of analysis of mtDNA cytochrome oxidase gene). Tambov Univ. Rep. Ser. Nat. Tech. Sci. 2013, 18, 2999–3002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ermakov, O.A.; Fayzulin, A.I.; Zaks, M.M.; Kaybeleva, E.I.; Zaripova, F.F. Distribution of «western» and «eastern» forms of the marsh frog Pelophylax ridibundus s. l. in the Samara and Saratov regions (on data of analysis of mtDNA and nDNA). Proc. Samara Sci. Cent. RAS 2014, 16, 409–412. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Pavlov, A.V.; Zaks, M.M.; Ivanov, A.Y.; Ermakov, O.A. Molecular-genetic characteristic of Pelophylax esculentus complex from the eastern range of distribution (Volga region, Tatarstan Republic). Tomsk. State Univ. J. Biol. 2015, 3, 54–66. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayzulin, A.I.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Litvinchuk, S.N.; Rosanov, J.M.; Borkin, L.J.; Ermakov, O.A.; Ruchin, A.B.; Lada, G.A.; Svinin, A.O.; Bashinsky, I.V.; et al. Species composition and distributional peculiarities of green frogs (Pelophylax esculentus complex) in Protected Areas of the Middle Volga Region (Russia). Nat. Conserv. Res. 2018, 3, 1–16. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinin, A.O.; Dedukh, D.V.; Borkin, L.J.; Ermakov, O.A.; Ivanov, A.Y.; Litvinchuk, J.S.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Mikhaylova, R.I.; Trubyanov, A.B.; Skorinov, D.V.; et al. Genetic structure, morphological variation, and gametogenic peculiarities in water frogs (Pelophylax) from northeastern European Russia. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2021, 59, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinchuk, S.N.; Skorinov, D.V.; Ivanov, A.Y.; Ermakov, O.A. Detection of glacial refugia and post-glacial colonization routes of morphologically cryptic Marsh frog species (Anura: Ranidae: Pelophylax) Using Environmental Niche Modeling. Diversity 2024, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usova, E.E. Age and growth rate of green frogs (Pelophylax esculentus complex) of the Lower Dobritsky pond (Zmiyiv district, Kharkiv region). J. V. N. Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Biol. 2014, 20, 204–212. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, A.E.; Borkin, L.J.; Günther, R.; Rosanov, J.M. Genome elimination in diploid and triploid Rana esculenta males: Cytological evidence from DNA flow cytometry. Genome 1990, 33, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, O.; Ivanov, A.; Titov, S.; Svinin, A.; Litvinchuk, S.N. New multiplex PCR method for identification of East European green frog species and their hybrids. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2019, 26, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenblut, B.; Ogielska, M. Development and growth of long bones in European water frogs (Amphibia: Anura: Ranidae), with remarks on age determination. J. Morphol. 2005, 265, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumyantsev, A.V. Experimental Investigation of Evolution of Cartilage and Bone Tissues; Izdatel’stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR: Moscow, Russia, 1958; p. 376. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, F.M.; Garcia, G.; Andreone, F. Huge but moderately long-lived: Age structure in the mountain chicken, Leptodactylus fallax, from Montserrat, West Indies. Herpetol. J. 2014, 24, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, M.; Garcia-Paris, M.; Buckley, D.; Castane, T.J. Bone growth and age in Rana saharica, a water frog living in a desert environment. Ann. Zool Fenn. 1999, 36, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Belyavsky, V.I.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Anisina, O.S.; Mikhailova, R.I. Application of a Microtome-Cryostat in Animal Ecology Research; Tutorial: Kazan, Russia, 2024; p. 104. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Smirina, E.M.; Makarov, A.N. On establishing the correspondence of the number of layers in the tubular bones of amphibians to the age of individuals. Zool. Zh. 1987, 66, 599–604. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Belyavsky, V.I.; Mikhailova, R.I. Features of the size-age structure of the population and the rate of puberty in the pond frog Rana lessonae. In Actual Problems of Ecological Physiology, Biochemistry and Genetics of Animals; Ordovian University: Saransk, Russia, 2005. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Antonyuk, E.V.; Panchenko, I.M. Amphibians and Reptiles of Ryazan Region. Proc. Oka Nat. Reserve 2014, 32, 1–168. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Garanin, V.I. On the study of amphibian migrations. Proc. Zool. Inst. USSR Acad. Sci. 1977, 74, 39–49. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shaldybin, S.L. Age and sex structure of populations of anurans. Prirod. Zapoved. Volgo-Kamskogo Bass. 1976, 4, 112–117. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Kuzmina, E.I.; Pavlov, A.V.; Faizulin, D.A.; Mikhajlova, R.I. Comparative analysis of growth rate in pond green frogs in native and urbanization conditions. In Proceedings of the 4th Meeting of the Nikolsky Herpetological Society, 12–17 October 2009; Ananjeva, N.B., Borkin, L.J., Eds.; Russian collection: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2011. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Lazareva, O.A. Comparative skeletochronological analysis of demography of four amphibian species (Anura, Ranidae) from Ivanovo oblast’, European Russia. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2005, 12, 176–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lazareva, O.G. A comparative analysis of age characteristics of four frog species In Populyatsionnaya ekologiya zhivotnykh. Materialy Mezhdunar. konf. “Problemy populyatsionnoi ekologii zhivotnykh” (Population Ecology of Animals: Proc. Int. Conf. “The Problems of Population Ecology of Animals”); Tomsk. Gos. Univ.: Tomsk, Russia, 2006. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Okulova, N.M.; Borkin, L.Y.; Bogdanov, A.S.; Guseva, A.Y. The green frogs in Ivanovo province. Adv. Amphib. Res. Former Sov. Union 1997, 2, 71–94. [Google Scholar]
- Okulova, N.M.; Bogdanov, A.S. Age and Allometric Variability of Body Dimensions in the Green Frogs Rana ridibunda and Rana lessonae. Adv. Amphib. Res. Former Sov. Union 2002, 7, 181–193. [Google Scholar]
- Savchuk, G.G. Dimensionally age structure and sex structure of the reproductive part of the Рelophylax esculenta complex population under the anthropogenic influence. Sci. Bull. Nat. Sci. Biol. Sci. 2009, 12, 212–218. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Reminnyi, V.Y. Amphibians of the Dniester-Dnieper Forest Province: Species Composition, Distribution, Age Structure of Populations. Ph.D. Thesis, I.I. Schmalhausen Institute of Zoology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine, 2010. (In Ukrainian). [Google Scholar]
- Usova, E.E. Determining the level of mature water frogs (Pelophylax esculentus complex; Amphibia, Ranidae) natural mortality by use of skeletochronology. J. V. N. Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Biol. 2010, 12, 104–110. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Čavlović, K.; Buj, I.; Karaica, D.; Jelić, D.; Choleva, L. Composition and age structure of the P. esculentus complex (Anura; Ranidae) population in inland Croatia. Salamandra 2018, 54, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Skierska, K.; Lagner, A.; Rozenblut-Kościsty, B.; Kosiba, P.; Kolenda, K.; Ogielska, M. Population structure, mate choice, and genome transmission in naturally formed pairs in a Pelophylax lessonae–Pelophylax esculentus hybridogenetic system. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2023, 77, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, E.B.; Ryabinina, E.S.; Lyapkov, S.M. Body size, age, phenetic, morphophysiological, and cytogenetic characteristics of P. ridibundus (Amphibia, Ranidae) populations inhabiting polluted thermal reservoirs of Kamchatka. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2021, 48, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.L.; Zhigalski, O.A. Demographic features of populations of the marsh frog (Rana ridibunda Pall.) introduced into water bodies of the Middle Urals. Russ. J. Ecol. 2011, 42, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporkova, L.Y. Formation of Rana ridibunda population. In Problems of Herpetology; Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles: Leningrad, Russia, 1985. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.L. Marsh frog (Rana redibunda Pall) in cooling ponds in the Middle Urals. Rus. J. Ecol. 2002, 33, 125–128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.L. Growth characteristics and rates of the Mash frog Pelophylax ridibundus Pall. Introd. Into Water Bodies Middle Ural. Biol. Bull. 2017, 44, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Fominykh, A.S.; Lyapkov, S.M. Formation of new features of the life cycle of the marsh frog (Rana ridibunda) in the conditions of a heated reservoir. Zh. Obshch. Biol. 2011, 72, 403–421. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Savchuk, G.G. Structure of the Reproductive Part of the Pelophylax Ridibundus Pallas (Ranidae, Amphibia) in Povedenie, Ekologiya i Evolyutsiya Zhivotnykh (Animal Behavior, Ecology, and Evolution); Golos Gubernii: Ryazan, Russia, 2012; pp. 235–241. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Mykhailova, O.V.; Usova, O.E.; Shabanov, D.A. How to assess the population load, related with hemiclonal hybridization inPelophylax esculentus complex population systems? Proc. H. S. Skovoroda Kharkiv Natl. Pedagog. Univ. Biol. Val. 2011, 13, 44–50. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Misyura, A.N.; Marchenkovskaya, A.A. Ecologico-biochemical characteristic of marsh frog in urbanization conditions. Visnyk of Dnipropetrovsk University. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 9, 137–141. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gokhelashvili, R.K.; Tarkhnishvili, D.N. Age structure of six Georgian anuran populations and its dynamics during two consecutive years. Herpetozoa 1994, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrovskaya, T.O.; Kotova, E.L. Preliminary data on the age characteristics of marsh frogs (Rana ridibunda Pall.) from three points in Armenia. Proc. Zool. Inst. USSR Acad. Sci. 1986, 157, 177–180. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gül, S.; Olgun, K.; Kutrup, B. Body size and age structure of P. ridibundus populations from two different altitudes in Turkey. Amphibia-Reptilia 2011, 32, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, N.; Kutrup, B.; Çobanoğlu, Ü.; Özoran, Y. Age determination and some growth parameters of a Rana ridibunda population in Turkey. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2005, 51, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Altun, C.; Altunışık, A. Comparison of the Marsh Frog (P. ridibundus) populations living in different altitudes in terms of age, size, and some growth parameters. Biol. Bull. 2023, 50, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaya, A.; Şereflişan, H.A. Study on Age Determination and Life Cycle of Pelophylax ridibundus (Pallas, 1771) by skeletochronology method. Osman. Korkut Ata Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 2024, 7, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, Z.; Arnaudov, A.T.; Boyadzhiev, P. Colour polymorphism, sex ratio and age structure in the populations of P. ridibundus and Pseudepidalea viridis (Amphibia: Anura) from anthropogenically polluted biotopes in southern Bulgaria and their usage as bioindicators. Trakia J. Sci. 2014, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, P.; Stylianou, P.; Tsiora, A. A skeletochronological study of age, growth and longevity in a population of the frog Rana ridibunda from southern Europe. Zoology 2008, 111, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, A.; Saberi, F.; Mohammadi, T. First study of age structure, growth pattern and reproductive age in populations of marsh frog (P. ridibundus) species in the northern and southern habitats of Khuzestan province. Exp. Anim. Biol. 2019, 8, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkavandi, S.; Gharzi, A.; Abbassi, M. Age determination by skeletochronology in Rana ridibunda (Anuran: Amphibia). Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2012, 3, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Embrechts, E.; Reyer, H.U. Age and size of hybrid water frogs: The role of genotype and ecology. Herpetologica 2012, 68, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogalniceanu, D.; Miaud, C. Population age structure and growth in four syntopic amphibian species inhabiting a large river floodplain. Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkale, E.; Ulubeli, S.A.; Kaska, Y. Age structures and growth parameters of the Levantine frog, P. bedriagae, at different localities in Denizli, Turkey. Acta Herpetol. 2018, 13, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Erişmiş, U.C.; Chinsamy, A. Ontogenetic changes in the epiphyseal cartilage of Rana (P.) caralitana (Anura: Ranidae). Anat. Rec. 2010, 293, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikan, H. On a new form Rana ridibunda (Anura: Ranidae) from Turkey. Istanb. Üniversitesi Fen Fak. Mecmuası İstanbul 1988, 53, 81–87. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Arısoy, A.G.; Baskale, E. Body size, age structure and survival rates in two populations of the Beysehir frog Pelophylax caralitanus. Herpetozoa 2019, 32, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oromi, N.; Brunet, P.; Taibi, K.; Aït Hammou, M.; Sanuy, D. Life-history traits in P. saharicus from Tiaret semiarid lands (northwestern Algeria). Herpetol. J. 2011, 21, 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kidov, A.A.; Ivolga, R.A.; Kondratova, T.E.; Ivanov, A.A. Age, Growth, and fertility in Terentiev’s Frog (P. terentievi, Amphibia, Ranidae). Biol. Bull. 2023, 50, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Sofianidou, T.S.; Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, P. Bioacoustic and morphometric studies in water frogs (genus Rana) of Lake Ioannina in Greece, and description of a new species (Anura, Amphibia). Z. Zool. SYST. Evolut.-Forsch 1984, 22, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiora, A.; Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, P. A skeletochronological study of age and growth in relation to adult size in the water frog Rana epeirotica. Zoology 2002, 105, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; García-París, M.; Castanet, J. Use of bone histology in estimating the age of frogs (Rana perezi) from a warm temperate climate area. Can. J. Zool. 1996, 74, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patón, D.; Juarranz, A.; Sequeros, E.; Perez-Campo, R.; Lopez-Torres, M.; De Quiroga, G.B. Seasonal age and sex structure of Rana perezi assessed by skeletochronology. J. Herpetol. 1991, 25, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Zhou, C.Q.; Yang, Z.S.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, X. Age, size and growth in two populations of the dark-spotted frog Rana nigromaculata at different altitudes in southwestern China. Herpetol. J. 2010, 20, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, S.; Yoo, J.H.; Park, S.R.; Sung, H.C. Age estimation by skeletochronology and advertisement call variation in the black-spotted pond frog (Rana nigromaculata). Anim. Cells Syst. 2013, 17, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonsue, W.; Matsui, M.; Hirai, T.; Misawa, Y. A comparison of age structures in two populations of a pond frog Rana nigromaculata (Amphibia: Anura). Zool. Sci. 2001, 18, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, G.; Reyer, H.-U. Mate choice and fitness in a hybrid frog: Rana esculenta females prefer Rana lessonae males over their own. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1993, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lada, G.A. Dynamics of population systems of Green frogs (Pelophylax esculentus complex) on the territory of the Russian Plain. Field Biol. J. 2021, 3, 53–63. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kolenda, K.; Kaczmarski, M.; Żurawska, J.; Ogielska, M. Decline of Pelophylax lessonae in mixed populations of water frogs over the last 50 years. Eur. Zool. J. 2024, 91, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisachova, L.S.; Lisachov, A.P.; Ermakov, O.A.; Svinin, A.O.; Chernigova, P.I.; Lyapkov, S.M.; Zamaletdinov, R.I.; Pavlov, A.V.; Zaks, S.S.; Fayzulin, A.I.; et al. Continent-Wide Distribution of CMTV-Like Ranavirus, from the Urals to the Atlantic Ocean. Ecohealth 2025, 263, e5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapkov, S.M.; Ermakov, O.A.; Titov, S.V. Distribution and origin of two forms of the marsh frog Pelophylax ridibundus complex (Anura, Ranidae) from Kamchatka, based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA data. Zool. Zh. 2017, 96, 1384–1391. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, T.I.; Shirokova, V.B. Analysis of marsh frog reproductive cycle in the Northern Caucasus based on the degree of gonad maturity. In Herpetology; (In Russian). Kuban. Gos. Univ.: Krasnodar, Russia, 1979; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakopoulou-Sklavounou, P.; Loumbourdis, N. Annual Ovarian Cycle in Frog, Rana ridibunda in Northern Greece. J. Herpetol. 1990, 24, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapkov, S.M.; Bryakova, M.A. Variation of age composition and postmetamorphic growth rates in Pelophylax ridibundus (Ranidae, Anura): Comparison populations from Moscow region and Kamchatka. Curr. Stud. Herpetol. 2024, 24, 74–79. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizulin, A.I. The diet of the common grass snake Natrix natrix (Colubridae) in the Middle Volga region Samara Luka. Probl. Reg. Glob. Ecol. 2025, 34, 76–80. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Faizulin, A.I.; Svinin, A.O. Ecological analysis of the community helminths of the marsh frog Pelophylax ridibundus (PALLAS, 1771) (Anura: Amphibia) in the Mari El Republic. Proc. Samara Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2024, 26, 46–56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Fayzulin, A.I. Materials for the helminth fauna of the edible frog Pelophylax esculentus (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Volga basin. Bull. St. Petersburg Univ. Ser. 3 Biol. 2016, 175–180. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaripova, F.F.; Fayzulin, A.I.; Kuzovenko, A.E. Nutritional features of the lake frog in conditions of anthropogenic pollution with heavy metals (Republic of Bashkortostan). Bull. Tambov Univ. Ser. Nat. Tech. Sci. 2013, 18, 1279–1282. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Fayzulin, A.I. Materials to the helminth fauna of the pool frog Pelophylax lessonae (Camerano, 1882) in Togliatti (Samara region). Proc. Samara Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2018, 20, 549–554. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzovenko, A.E.; Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Zaripova, F.F.; Fayzulin, A.I. Characteristics of the stability of trophic bonds of the lake frog Pelophylax ridibundus (Pallas, 1771) (Amphibia, Anura) under conditions of anthropogenic habitat transformation. Proc. Samara Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2017, 19, 37–44. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Fayzulin, A.I.; Kuzovenko, A.E. Materials For The Helminth Fauna of the Marsh Frog Pelophylax ridibundus (Pallas, 1771) in Samara. Proc. Samara Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2017, 19, 80–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Ruchin, A.B.; Fayzulin, A.I. Short communication: An overview of the trematodes fauna of pool frog Pelophylax lessonae (Camerano, 1882) In the Volga basin, Russia: 1. Adult stages. Nusant. Biosci. 2018, 10, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Zaripova, F.F.; Yumagulova, G.R.; Fayzulin, A.I. Helminthofauna of the marsh frog Rana ribunda Pallas, 1771 on the urbanized areas of the Republic of Bashkortostan. Mod. Herpetol. 2012, 12, 134–142. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Burakova, A.V.; Vershinin, V.L.; Vershinina, S.D. Comparative Analysis of the Parasitofauna of Rana arvalis in Environmental Gradients of the Urals. Inland Water Biol. 2022, 15, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
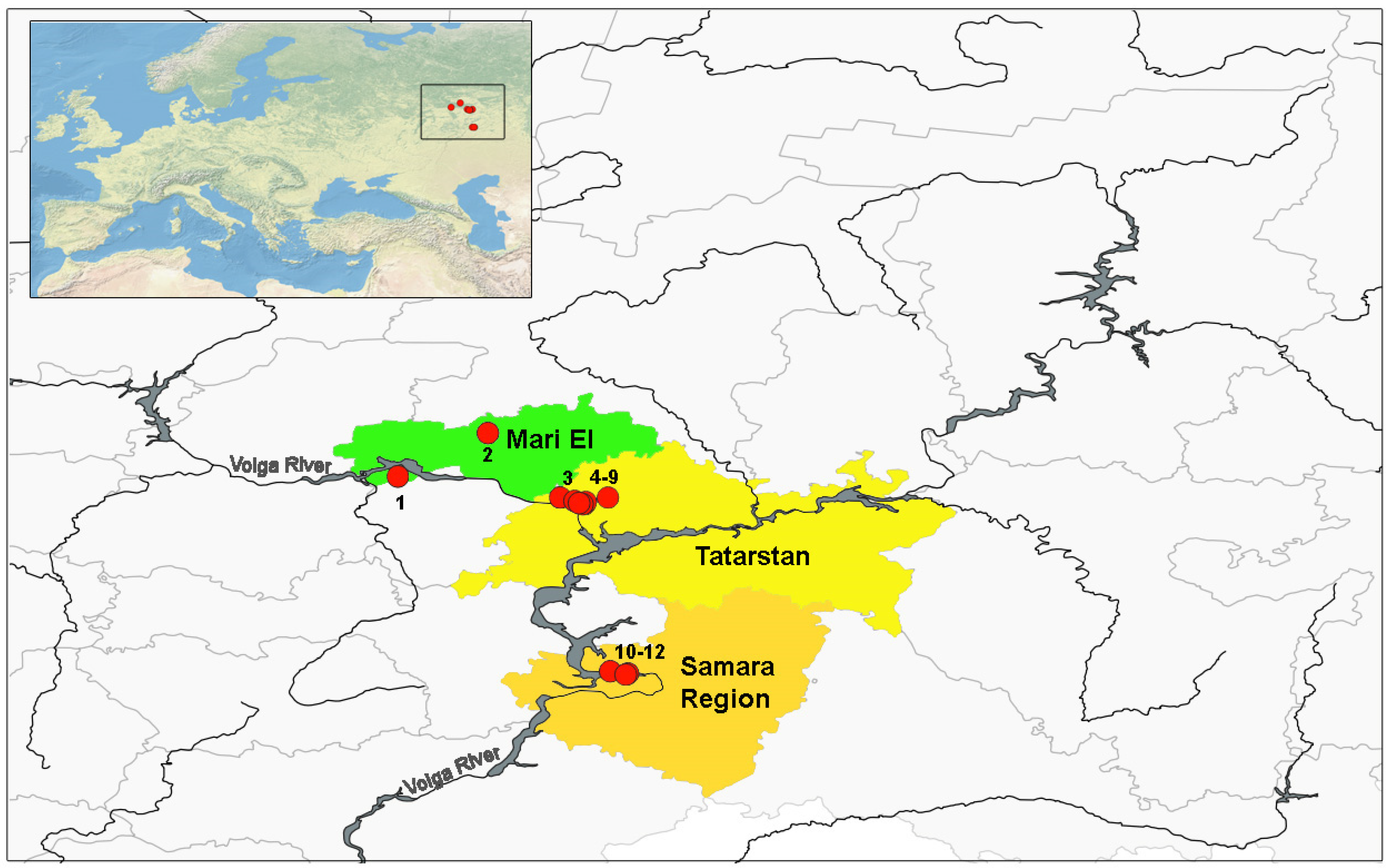

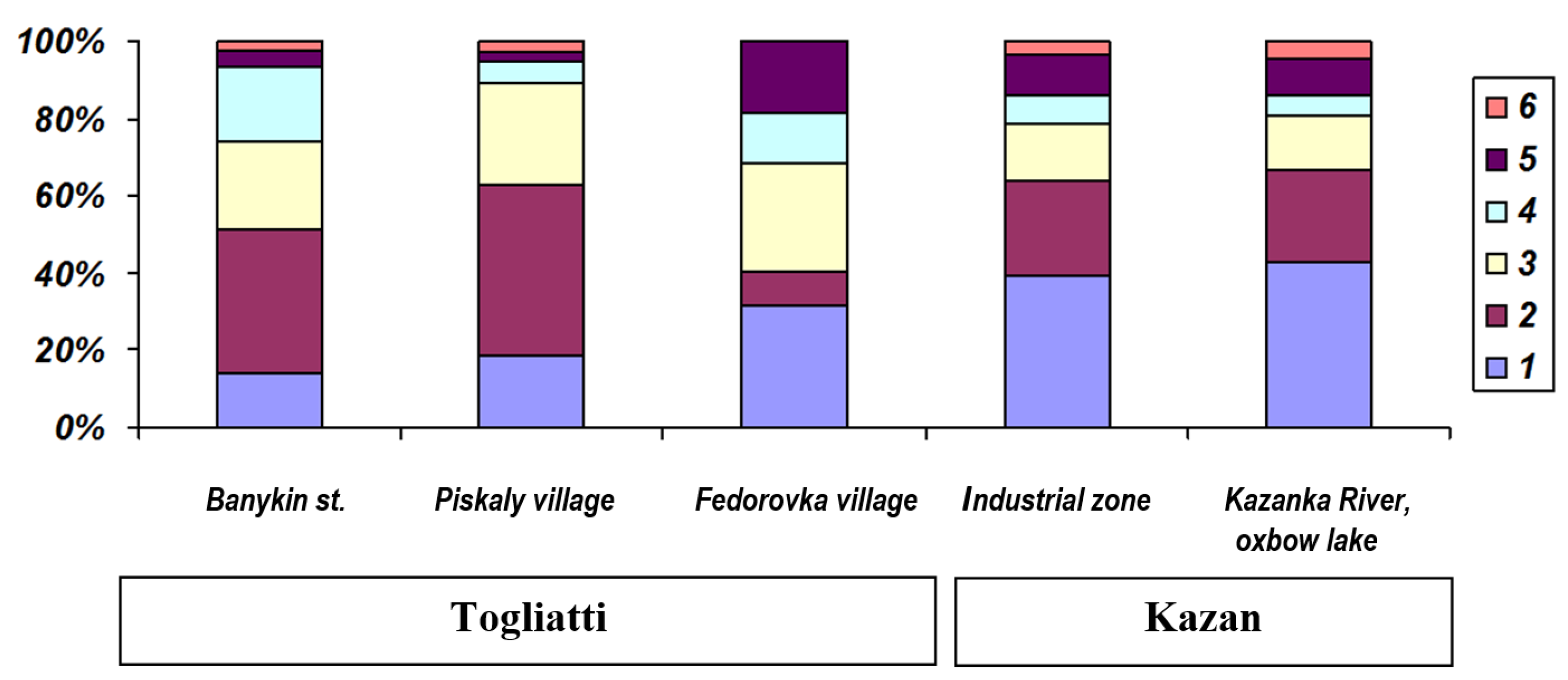
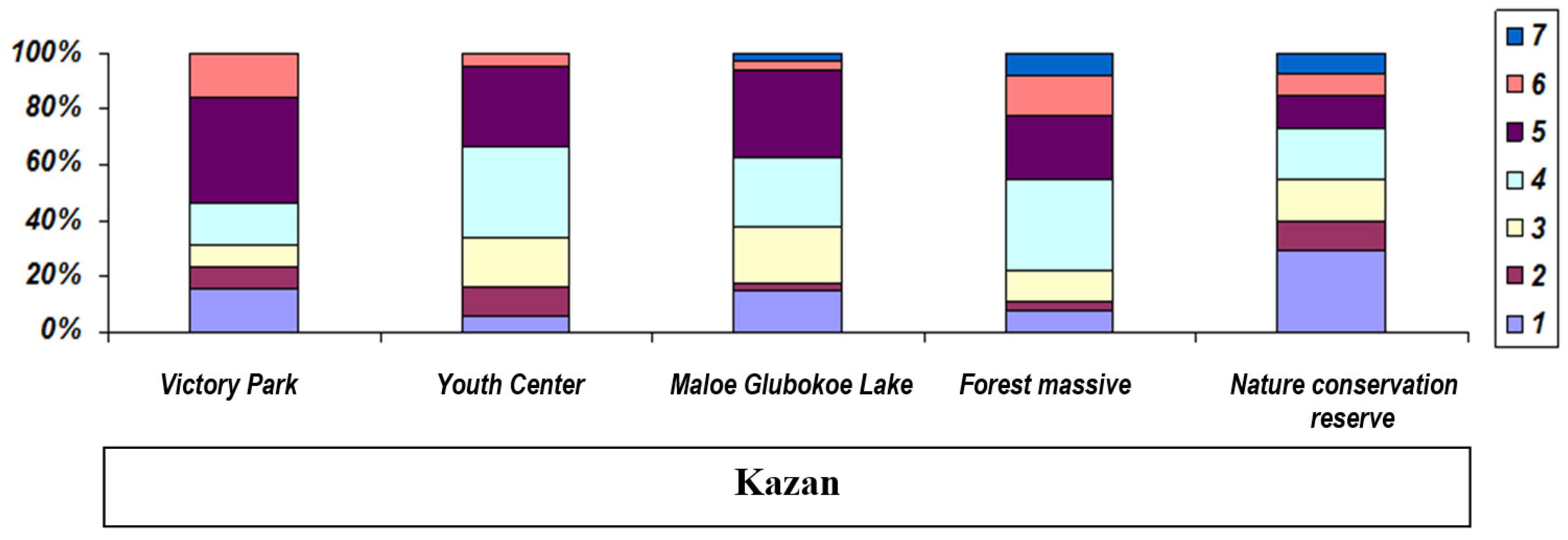
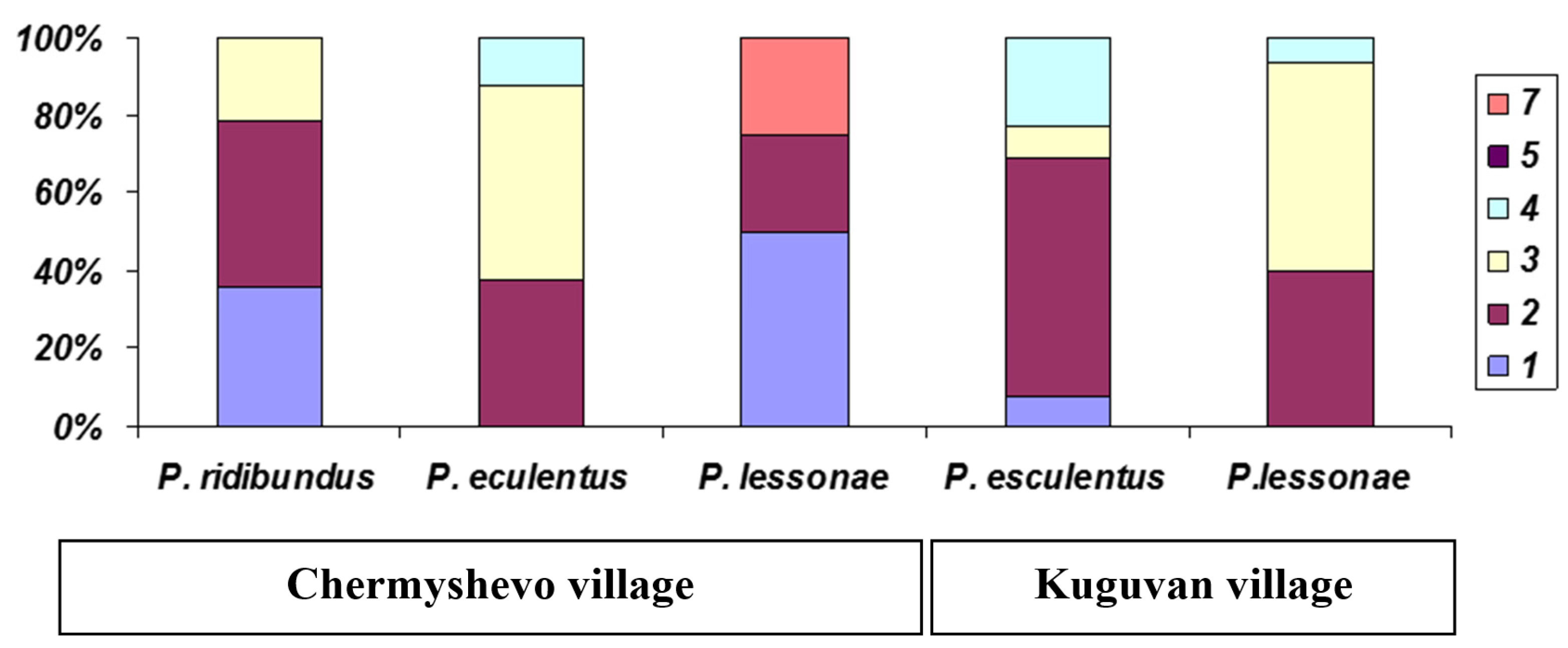


| Locality | Coordinates | Species | n | Sex | Average Age | Maximum Lifespan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nu | Name | Zone | N | E | |||||
| Republic of Mari El | |||||||||
| 1 | Chermyshevo village | ZC5 | 56.183 | 46.516 | P. ridibundus ** | 14 | ♀ | 1.8 | 3 |
| 5 | ♂ | 1.9 | 3 | ||||||
| P. esculentus * | 3 | ♀ | 2.3 | 3 | |||||
| 8 | ♂ | 2.8 | 4 | ||||||
| P. lessonae | 3 | ♀ | 2.0 | 3 | |||||
| 4 | ♂ | 1.3 | 2 | ||||||
| 2 | Kuguvan village | ZC5 | 56.783 | 47.766 | P. esculentus * | 3 | ♀ | 3.3 | 4 |
| 1 | ♂ | - | 4 | ||||||
| P. lessonae | 8 | ♀ | 3.3 | 7 | |||||
| 15 | ♂ | 2.7 | 4 | ||||||
| Kazan City, Republic of Tatarstan | |||||||||
| 3 | Nature conservation reserve | ZC5 | 55.900 | 48.752 | P. lessonae | 20 | ♀ | 3.6 | 7 |
| 34 | ♂ | 3.3 | 7 | ||||||
| 4 | Forest massive | ZC5 | 55.900 | 49.414 | P. lessonae | 14 | ♀ | 4.1 | 7 |
| 13 | ♂ | 3.6 | 7 | ||||||
| 5 | Maloe Glubokoe Lake | Z4 | 55.847 | 48.962 | P. lessonae | 41 | ♀ | 3.7 | 7 |
| 40 | ♂ | 3.3 | 7 | ||||||
| 6 | Youth Center | Z2 | 55.809 | 49.100 | P. lessonae | 29 | ♀ | 3.4 | 6 |
| 19 | ♂ | 3.2 | 6 | ||||||
| 7 | Victory Park | Z2 | 55.833 | 49.111 | P. lessonae | 11 | ♀ | 3.3 | 6 |
| 15 | ♂ | 3.1 | 6 | ||||||
| 8 | Kazanka River oxbow lake | Z1 | 55.804 | 49.068 | P. ridibundus ** | 9 | ♀ | 2.9 | 5 |
| 12 | ♂ | 2.3 | 5 | ||||||
| 9 | Industrial zone | Z1 | 55.824 | 49.015 | P. ridibundus ** | 13 | ♀ | 2.7 | 6 |
| 15 | ♂ | 2.1 | 5 | ||||||
| Togliatti City, Samarskaya oblast’ | |||||||||
| 10 | Banykino st. | Z4 | 53.500 | 49.439 | P. ridibundus ** | 25 | ♀ | 2.9 | 5 |
| 18 | ♂ | 2.7 | 6 | ||||||
| 11 | Piskaly village | Z3 | 53.470 | 49.690 | P. ridibundus ** | 18 | ♀ | 2.1 | 6 |
| 20 | ♂ | 2.6 | 4 | ||||||
| 12 | Fedorovka village | ZC5 | 53.466 | 49.665 | P. ridibundus ** | 19 | ♀ | 2.9 | 5 |
| 19 | ♂ | 2.4 | 5 | ||||||
| N | SAI-1 | COI | n | Sex | Average Age | Maximum Lifespan | Maximum SVL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RR | R | 2 | ♂ | 2.5 | 3 | 62.89 |
| 2 | ♀ | 4.0 | 5 | 82.79 | |||
| 2 | RR | B | 6 | ♂ | 2.3 | 5 | 71.99 |
| 4 | ♀ | 3.0 | 5 | 108.90 | |||
| 3 | RB | B | 2 | ♂ | 2.0 | 4 | 91.60 |
| 2 | ♀ | 2.5 | 5 | 98.70 | |||
| 4 | RB | R | 1 | ♀ | 0+ | 0+ | 34.58 |
| 5 | BB | R | 1 | ♀ | 0+ | 0+ | 33.37 |
| Country, Province | Maximum Lifespan | Average Age (Adults) | Method | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | Males | Females | |||
| P. lessonae | ||||||
| Russia, Ryazanskaya Oblast’ | 9 | 12 | - | M | [42] | |
| Russia, Republic of Tatarstan (near Kazan) | 9 | - | M | [43] | ||
| 12 | - | S | [44] | |||
| 5 | - | S | [45] | |||
| Russia, Republic of Tatarstan (Krugloe Lake) | 4 | - | S | [45] | ||
| Russia, Leningradskaya oblast’ (Luga) | 6 | 6 | - | S | [10] | |
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 7 | - | S | [46] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 7 | - | S | [47] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 4 * | 1.93 * | S | [48] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 8 | - | S | [49] | ||
| Forest-steppe zone of Ukraine | 6 | - | M | [3] | ||
| Ukraine, Chernovitskaya oblast’ | 7 | 8 | 3.15 | 3.56 | S | [50] |
| Ukraine, Vinnitskaya oblast’ | 4 | 4 | 2.56 | 3.17 | S | [51] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 5 | 7 | 3.78 | 5.00 | S | [52] |
| Croatia, Lova River | 8 | 4.80 | S | [53] | ||
| Poland, Wrocław (Raków) | 7 | 8 | - | S | [54] | |
| P. ridibundus (including southern lineages) | ||||||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 11 (12) | - | S | [46] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 5 * | 2.57 * | S | [48] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 7 * | - | S | [48] | ||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 11 | - | S | [47] | ||
| Russia, Republic of Tatarstan (near Kazan) | 11 | - | S | [44] | ||
| Russia, Kamchatskaya oblast’ | 6 | 9 | 3.30 | 3.49 | S | [55] |
| Russia, the Middle Urals | 9 | - | 4.90 | - | S | [56] |
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Verkhniy Tagil) | 6 | - | S | [57] | ||
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Refta) | - | 8 | - | S | [58] | |
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Verkhniy Tagil) | - | 9 | - | S | [58] | |
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Verkhniy Tagil) | 10 | 10 | - | S | [59] | |
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Refta) | 11 | - | S | [59] | ||
| Russia, Sverdlovskaya oblast’ (Nizhniy Tagil) | 5 | 5 | - | S | [60] | |
| Forest-steppe zone of Ukraine | 7 | - | M | [3] | ||
| Ukraine, Chernovitskaya oblast’ | 6 | 8 | 4.59 | 4.06 | S | [50] |
| Ukraine, Chernovitskaya oblast’ | 7 | 8 | 4.57 | 4.47 | S | [61] |
| Ukraine, Vinnitskaya oblast’ | 6 | 6 | 4.66 | 5.42 | S | [51] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 7 | 9 | 5.42 | 4.30 | S | [52] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 7 | 10 | 5.75 | 4.36 | S | [32] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 9 | 4.15 | S | [62] | ||
| Ukraine, Dnepropetrovskaya oblast’ | 7 | - | S | [63] | ||
| Georgia | 7 | 4.03 | 2.78 | S | [64] | |
| Armenia, Sevan Lake | 10 | 9 | 5.80 | 5.87 | S | [65] |
| Armenia, Khosrov Nature Reserve | 8 | 9 | 6.54 | 8.40 | S | [65] |
| Armenia, Razdan River | 5 | 6 | 3.67 | 4.63 | S | [65] |
| Turkey | 7 | 11 | 4.89 | 5.32 | S | [66] |
| Turkey (Artvin) | 6 | 6 | - | - | S | [12] |
| Turkey | 6 | 7 | 3.72 | 3.90 | S | [67] |
| Turkey | 11 | 13 | 5.42 | 6.19 | S | [68] |
| Turkey | 7 | 6 | 3.72 | 3.77 | S | [69] |
| Poland | 7 | 6 | 4.40 | 3.70 | S | [11] |
| Bulgaria, Rozov Kladenets | 3 | 5 | 2.16 | 3.25 | S | [70] |
| Bulgaria, Topolnitsa reservoir | 3 | 4 | 2.28 | 2.63 | S | [70] |
| Greece | 5 | 5 | 3.73 | 2.96 | S | [71] |
| Iran | 12 | 7 | 5.40 | 3.00 | S | [72] |
| Iran | 11 | 7 | 4.50 | 6.43 | S | [73] |
| Croatia | 13 | 8.00 | S | [53] | ||
| P. esculentus | ||||||
| Russia, Ivanovskaya oblast’ | 4 * | 1.22 * | S | [48] | ||
| Ukraine, Chernovitskaya oblast’ | 7 | 8 | 4.47 | 5.19 | S | [50] |
| Ukraine, Vinnitskaya oblast’ | 4 | 4 | 3.47 | 3.16 | S | [51] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 10 | 3.63 | S | [62] | ||
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 7 | 10 | 5.04 | 4.04 | S | [52] |
| Ukraine, Khar’kovskaya oblast’ | 8 | 9 | 4.83 | 4.46 | S | [32] |
| Sweden | 6 | 6 | - | - | S | [74] |
| Romania | 10 | 10 | 6.70 | 5.00 | S | [75] |
| Croatia | 10 | 5.10 | S | [53] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamaletdinov, R.; Svinin, A.; Fayzulin, A.; Ermakov, O.; Mikhaylova, R.; Litvinchuk, S. Age Structure of Water Frogs of the Genus Pelophylax in the Middle Volga River Region (European Russia). Animals 2025, 15, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091273
Zamaletdinov R, Svinin A, Fayzulin A, Ermakov O, Mikhaylova R, Litvinchuk S. Age Structure of Water Frogs of the Genus Pelophylax in the Middle Volga River Region (European Russia). Animals. 2025; 15(9):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091273
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamaletdinov, Renat, Anton Svinin, Alexander Fayzulin, Oleg Ermakov, Regina Mikhaylova, and Spartak Litvinchuk. 2025. "Age Structure of Water Frogs of the Genus Pelophylax in the Middle Volga River Region (European Russia)" Animals 15, no. 9: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091273
APA StyleZamaletdinov, R., Svinin, A., Fayzulin, A., Ermakov, O., Mikhaylova, R., & Litvinchuk, S. (2025). Age Structure of Water Frogs of the Genus Pelophylax in the Middle Volga River Region (European Russia). Animals, 15(9), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091273







