Redox Metabolism During Aerial Exposure of the Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter: An Ecophysiological Perspective
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Collection
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes
2.4. Lipid Peroxidation Measurement
2.5. Statistics
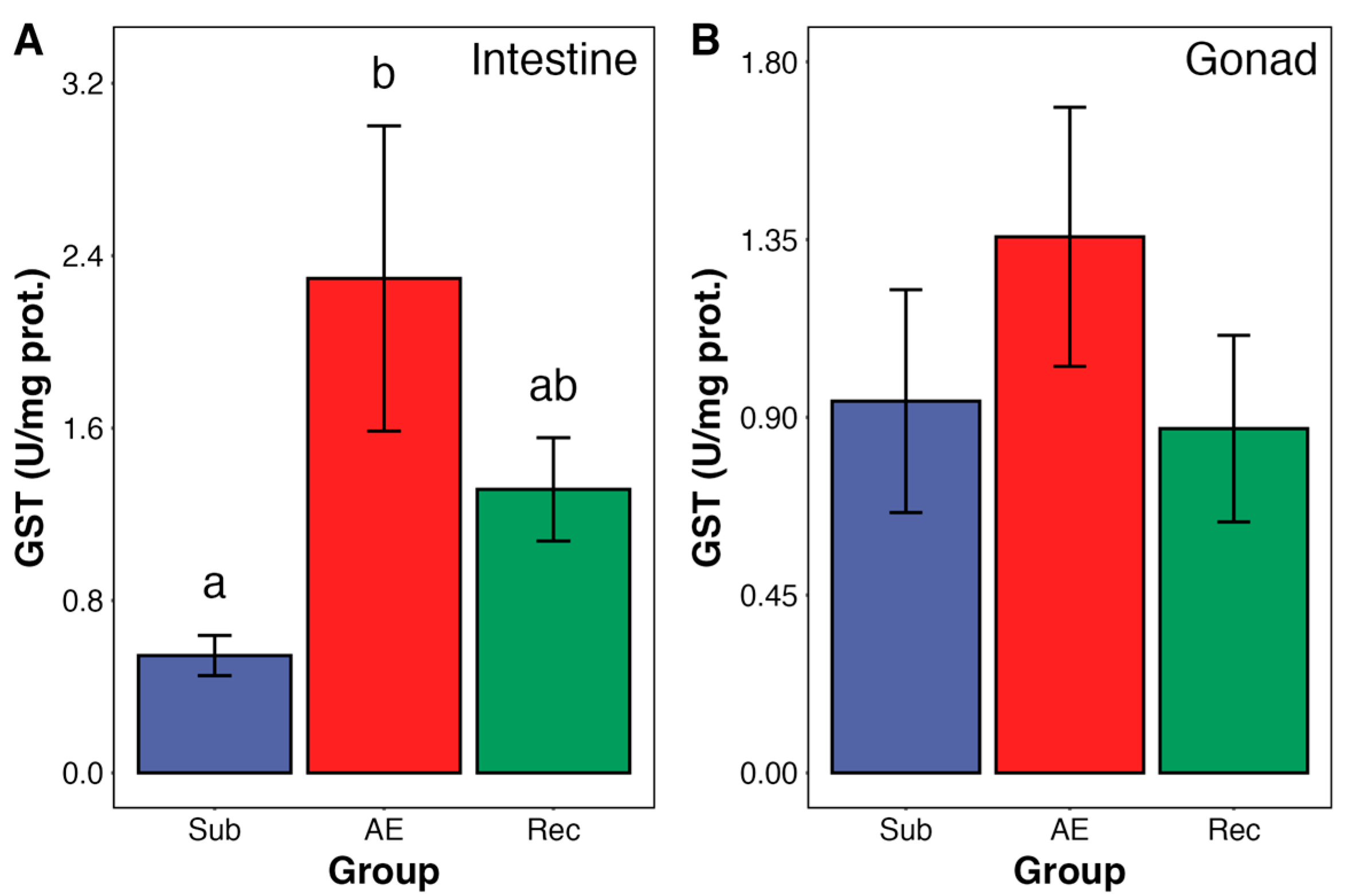
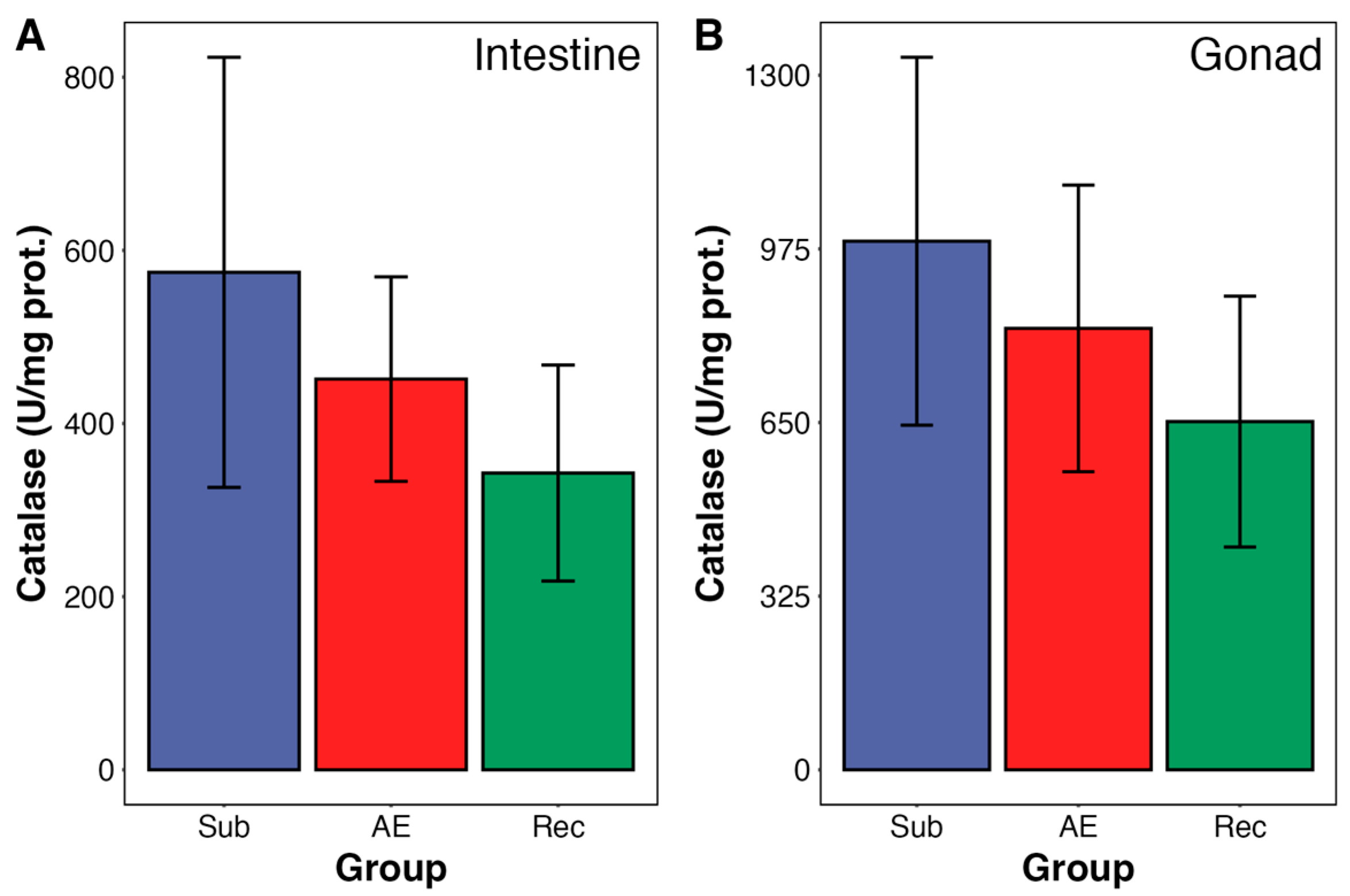
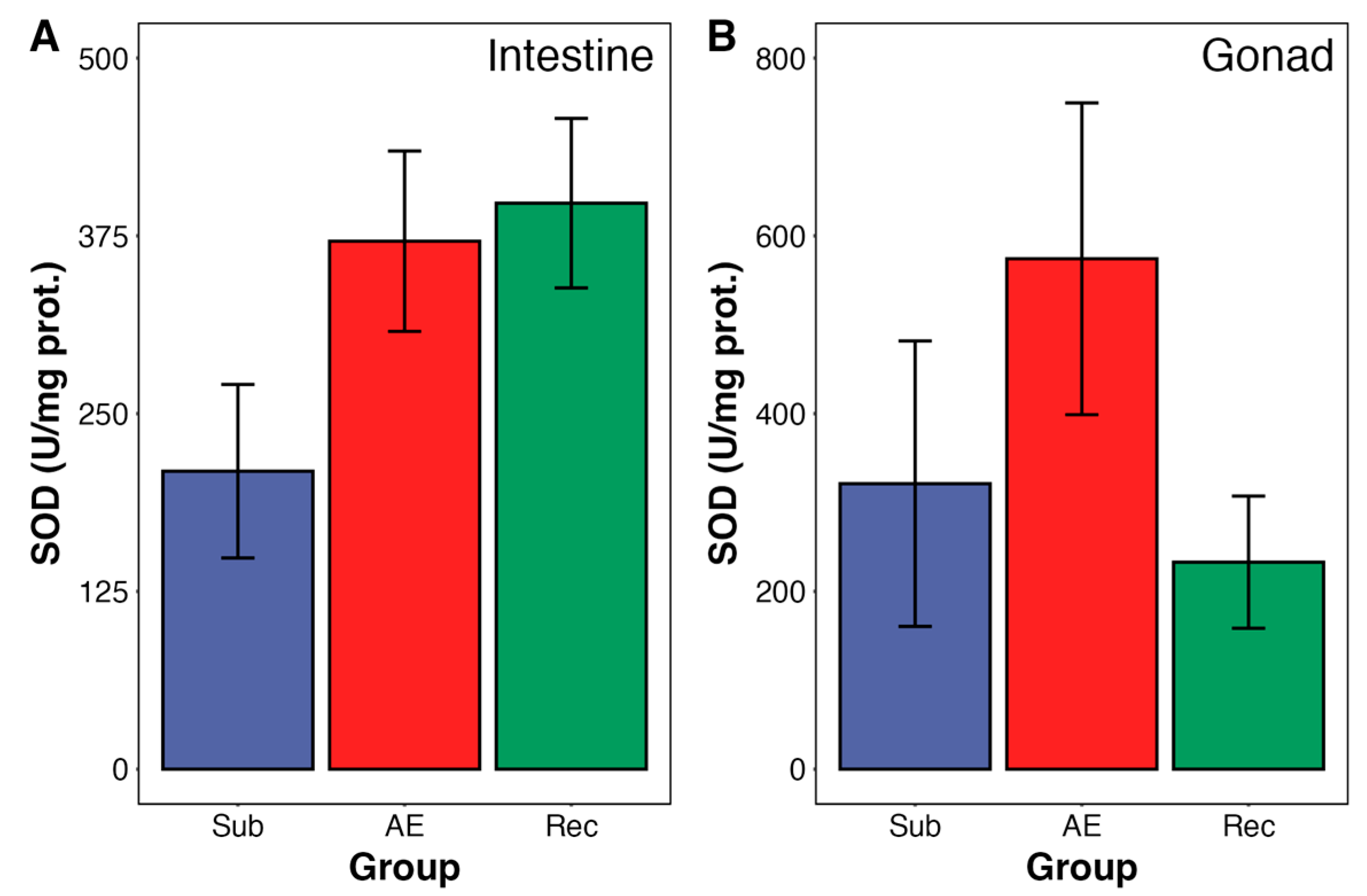
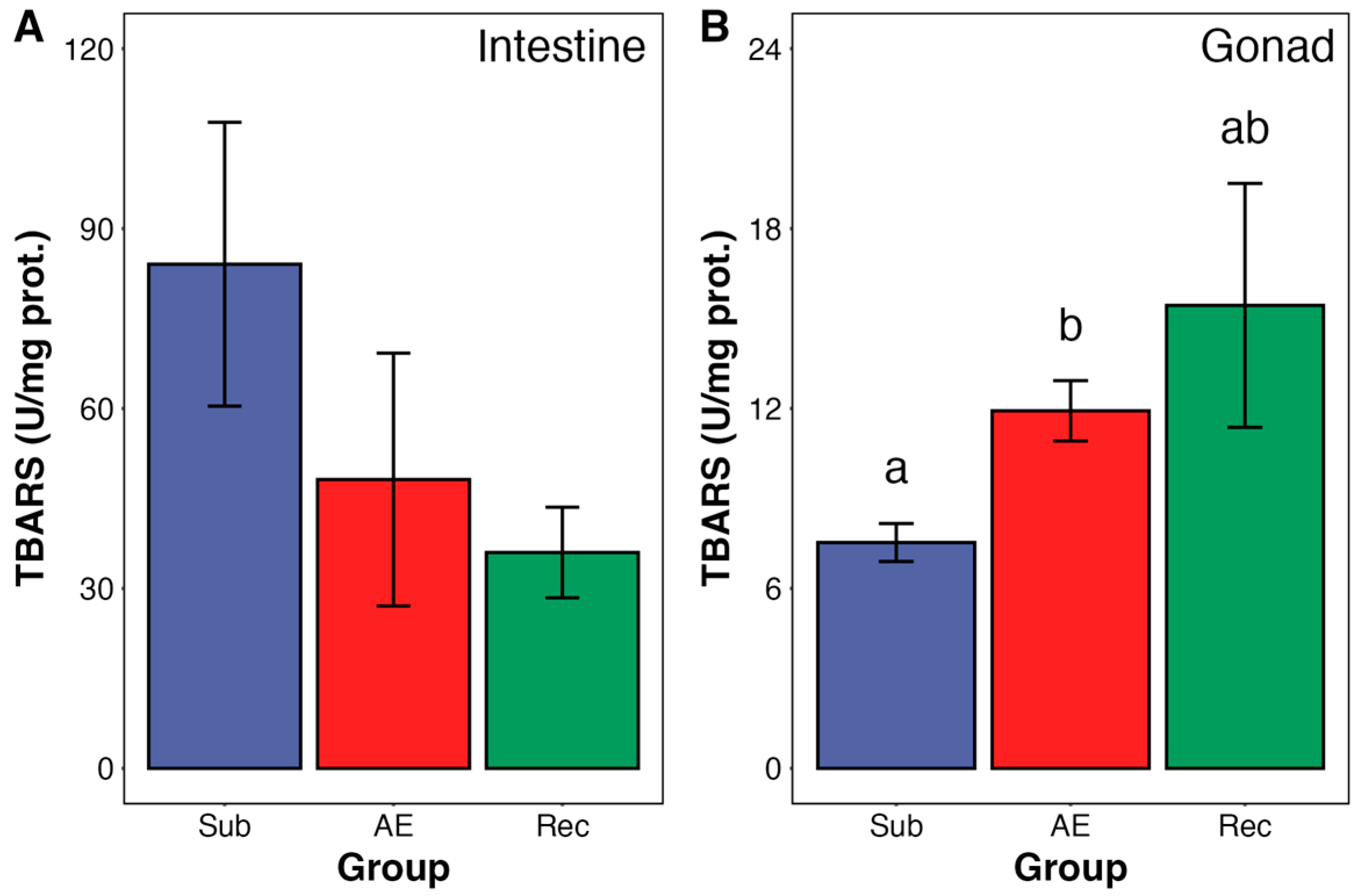
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Petraitis, P.S.; Fisher, J.A.D.; Dudgeon, S. Rocky Intertidal Zone. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 3107–3113. ISBN 978-0-08-045405-4. [Google Scholar]
- Giraud-Billoud, M.; Rivera-Ingraham, G.A.; Moreira, D.C.; Burmester, T.; Castro-Vazquez, A.; Carvajalino-Fernández, J.M.; Dafre, A.; Niu, C.; Tremblay, N.; Paital, B.; et al. Twenty Years of the ‘Preparation for Oxidative Stress’ (POS) Theory: Ecophysiological Advantages and Molecular Strategies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2019, 234, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, J.; Nash, S.; Hernandez, E.; Rahman, M.S. Effects of Elevated Temperature on Gonadal Functions, Cellular Apoptosis, and Oxidative Stress in Atlantic Sea Urchin Arbacia punctulata. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 149, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinagre, C.; Madeira, D.; Mendonça, V.; Dias, M.; Roma, J.; Diniz, M.S. Effect of Temperature in Multiple Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Coastal Shrimp. J. Therm. Biol. 2014, 41, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.C.; Sabino, M.A.C.T.; Minari, M.; Kuzniewski, F.T.B.; Angelini, R.; Hermes-Lima, M. The Role of Solar Radiation and Tidal Emersion on Oxidative Stress and Glutathione Synthesis in Mussels Exposed to Air. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos, V.M.; Lamare, M.D.; Peake, B.M.; Burritt, D.J. Cellular Changes Associated with the Acclimation of the Intertidal Sea Anemone Actinia tenebrosa to Ultraviolet Radiation. Photochem Photobiol. 2014, 90, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Malio, A.; Díaz, M.; Mella, M.; Montoya, M.J.; Miranda, A.; Landaeta, M.F.; Sánchez, G.; Hidalgo, M.E. Are the Intertidal Fish Highly Resistant to UV-B Radiation? A Study Based on Oxidative Stress in Girella laevifrons (Kyphosidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Environmentally Induced Oxidative Stress in Aquatic Animals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waypa, G.B.; Smith, K.A.; Schumacker, P.T. O2 Sensing, Mitochondria and ROS Signaling: The Fog Is Lifting. Mol. Asp. Med. 2016, 47–48, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geihs, M.A.; Moreira, D.C.; López-Martínez, G.; Minari, M.; Ferreira-Cravo, M.; Carvajalino-Fernández, J.M.; Hermes-Lima, M. Ultraviolet Radiation Triggers “Preparation for Oxidative Stress” Antioxidant Response in Animals: Similarities and Interplay With Other Stressors. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2020, 239, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, T.; Diniz, M.; Calado, R.; Rosa, R. Coral Physiological Adaptations to Air Exposure: Heat Shock and Oxidative Stress Responses in Veretillum cynomorium. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 439, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.C.; Sabino, M.A.C.T.; Kuzniewski, F.T.B.; Furtado-Filho, O.V.; Carvajalino-Fernández, J.M.; Angelini, R.; Freire, C.A.; Hermes-Lima, M. Redox Metabolism in Mussels (Brachidontes solisianus) Under the Influence of Tides in a Rocky Beach in Southern Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes-Lima, M.; Moreira, D.C.; Rivera-Ingraham, G.A.; Giraud-Billoud, M.; Genaro-Mattos, T.C.; Campos, É.G. Preparation for Oxidative Stress Under Hypoxia and Metabolic Depression: Revisiting the Proposal Two Decades Later. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 1122–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomina, A.; Belcheva, N.; Chelomin, V. Antioxidant System of the Intertidal Mollusk Littorina kurila in Its Natural Habitat. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. A 2013, 2, 713–718. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, J.M. Laboratory, Field and Natural Experiments. Nature 1983, 304, 586–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisi, R.M.; Bentley, G.E. Lab and Field Experiments: Are They the Same Animal? Horm. Behav. 2009, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, E.M.; Gomez Isaza, D.F. The Mechanistic Basis and Adaptive Significance of Cross-Tolerance: A ‘Pre-Adaptation’ to a Changing World? J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb245644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C.; Sokolova, I.; Sun, B.; Mao, Y.; Xiong, K.; Peng, J.; Fang, J.K.-H.; Hu, M.; et al. Antioxidant Response of the Oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis Exposed to Diel-Cycling Hypoxia under Different Salinities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 179, 105705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, B.; Li, D.; Yan, X. Modulated Expression and Activities of Ruditapes philippinarum Enzymes after Oxidative Stress Induced by Aerial Exposure and Reimmersion. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, J. Interactive Effects of Ocean Acidification, Ocean Warming, and Diurnal Temperature Cycling on Antioxidant Responses and Energy Budgets in Two Sea Urchins Strongylocentrotus intermedius and Tripneustes gratilla from Different Latitudes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud-Billoud, M.; Moreira, D.C.; Minari, M.; Andreyeva, A.; Campos, É.G.; Carvajalino-Fernández, J.M.; Istomina, A.; Michaelidis, B.; Niu, C.; Niu, Y.; et al. Evidence Supporting the ‘Preparation for Oxidative Stress’ (POS) Strategy in Animals in Their Natural Environment. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2024, 293, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M. (Ed.) Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 4th ed.; Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-0-12-819569-7. [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan, T.R.; Muthiga, N.A. Echinometra. In Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 43, pp. 497–517. ISBN 978-0-12-819570-3. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide Dismutase: Improved Assays and an Assay Applicable to Acrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes-Lima, M.; Storey, K.B. Antioxidant Defenses and Metabolic Depression in a Pulmonate Land Snail. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1995, 268, R1386–R1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, T.Y.; Dong, Y.; Han, G.; Lau, S.L.Y.; Cheng, M.C.F.; Meepoka, C.; Ganmanee, M.; Williams, G.A. Timing Metabolic Depression: Predicting Thermal Stress in Extreme Intertidal Environments. Am. Nat. 2020, 196, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, L.; Terwilliger, N.; Carroll, A.; Jorgensen, D.; Scholnick, D. Respiratory and Acid-Base Physiology of the Purple Sea Urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, During Air Exposure: Presence and Function of a Facultative Lung. Biol. Bull. 2002, 203, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Ingraham, G.A.; Lignot, J.-H. Osmoregulation, Bioenergetics and Oxidative Stress in Coastal Marine Invertebrates: Raising the Questions for Future Research. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niture, S.K.; Khatri, R.; Jaiswal, A.K. Regulation of Nrf2—An Update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Jian, S.; Hu, B.; Wen, C. GST-Mu of Cristaria plicata Is Regulated by Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway in Detoxification Microcystin and Has Antioxidant Function. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 263, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Quan, D.; Min, X.; Nie, X.; Huang, X.; Ge, J.; Ren, Q. Glutathione S-Transferase Gene Diversity and Their Regulation by Nrf2 in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) during Nitrite Stress. Gene 2023, 864, 147324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, P.G.; Menon, D. Glutathione Transferases, Regulators of Cellular Metabolism and Physiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta G 2013, 1830, 3267–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes-Lima, M. Oxygen in Biology and Biochemistry: Role of Free Radicals. In Functional Metabolism; Storey, K.B., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 319–368. ISBN 978-0-471-67558-7. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, D.C.; Paula, D.P.; Hermes-Lima, M. Changes in Metabolism and Antioxidant Systems During Tropical Diapause in the Sunflower Caterpillar Chlosyne lacinia (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 134, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Storey, K.B.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Aestivation in Nature: Physiological Strategies and Evolutionary Adaptations in Hypometabolic States. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, E.; Kühnhold, H.; Novais, S.C.; Alves, L.M.F.; Indriana, L.; Kunzmann, A.; Slater, M.; Lemos, M.F.L. Effects of Thermal Stress on the Immune and Oxidative Stress Responses of Juvenile Sea Cucumber Holothuria scabra. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2017, 187, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fangyu, W.; Yang, Y.H.; Xiaoyu, W.; Kun, X.; Fei, G. Antioxidant Enzymes in Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) during Aestivation. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2011, 91, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klanian, M.G. Physiological and Immunological Conditions of the Sea Cucumber Isostichopus badionotus (Selenka, 1867) during Dormancy. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 444, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, K.N.; Lamare, M.D.; Burritt, D.J. Oxidative Damage in Response to Natural Levels of UV-B Radiation in Larvae of the Tropical Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, M.S. Effects of Elevated Temperature on Prooxidant-Antioxidant Homeostasis and Redox Status in the American Oyster: Signaling Pathways of Cellular Apoptosis during Heat Stress. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidantsis, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Vratsistas, A.; Makri, S.; Pappa, A.-Z.; Drosopoulou, E.; Anestis, A.; Mavridou, E.; Exadactylos, A.; Vafidis, D.; et al. Correlation between Intermediary Metabolism, Hsp Gene Expression, and Oxidative Stress-Related Proteins in Long-Term Thermal-Stressed Mytilus galloprovincialis. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2020, 319, R264–R281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomble, P.; Nath, B.B. Differential Manifestation of RONS and Antioxidant Enzymes in Response to Singular versus Combinatorial Stress in Chironomus ramosus. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomble, P.; Nath, B.B. Impact of Singular versus Combinatorial Environmental Stress on RONS Generation in Drosophila melanogaster Larvae. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1426169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, J.; Sun, L.; Qin, X.; Fan, X.; Zheng, X. Combined Stress of Acute Cold Exposure and Waterless Duration at Low Temperature Induces Mortality of Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei through Injuring Antioxidative and Immunological Response in Hepatopancreas Tissue. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 100, 103080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, L.; Garcia, D.; Cortez, F.S.; Pereira, C.D.S.; De Almeida, E.A. Combined Effects of Diesel and Air Exposure on Oxidative Stress Parameters of Mussels Perna perna (Mytilidae, Bivalvia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 195, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucey, N.; Aube, C.; Herwig, A.; Collin, R. Compound Extreme Events Induce Rapid Mortality in a Tropical Sea Urchin. Biol. Bull. 2022, 243, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.M.; Gnocchi, K.G.; Merçon, J.; Mendes, B.; Lopes, B.M.; Passos, L.S.; Chippari Gomes, A.R. The Success of the Fertilization and Early Larval Development of the Tropical Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) Is Affected by the pH Decrease and Temperature Increase. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 161, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.C.; Borges, J.C.S.; Santos, M.F.; Jensch Junior, B.E.; Da Silva, J.R.M.C. The Impact of Rising Sea Temperature on Innate Immune Parameters in the Tropical Subtidal Sea Urchin Lytechinus variegatus and the Intertidal Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, M.A.; Young, C.M. Temperature Limits to Fertilization and Early Development in the Tropical Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 236, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, E. Can Sea Urchins Beat the Heat? Sea Urchins, Thermal Tolerance and Climate Change. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
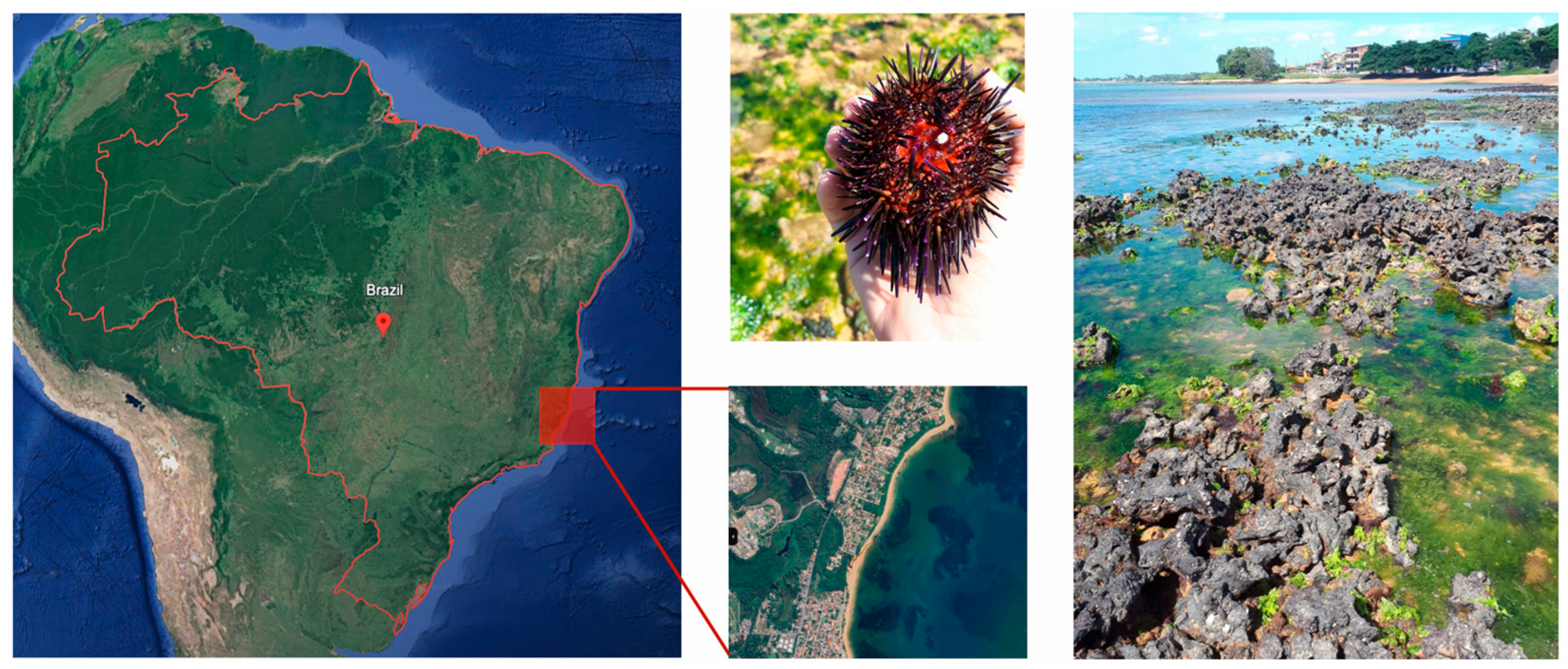

| Condition | Experimental Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S | AE | R | |
| Time (h) | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Tide (m) | 0.1 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| Solar radiation (kJ/m2) | 0.0 | 2302.2 | 15,210.9 |
| Air temperature (°C) | 25.5 | 27.9 | 30.8 |
| Water temperature (°C) | 23.5 | 24.0 | 26.0 |
| Dissolved oxygen (DO mg/L) | 7.8 | – | 6.1 |
| Relative DO (%) | 112 | – | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, T.M.; Minari, M.; Carvajalino-Fernández, J.M.; Moreira, D.C.; Hermes-Lima, M. Redox Metabolism During Aerial Exposure of the Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter: An Ecophysiological Perspective. Animals 2025, 15, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091251
Pereira TM, Minari M, Carvajalino-Fernández JM, Moreira DC, Hermes-Lima M. Redox Metabolism During Aerial Exposure of the Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter: An Ecophysiological Perspective. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091251
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Tatiana M., Marina Minari, Juan Manuel Carvajalino-Fernández, Daniel C. Moreira, and Marcelo Hermes-Lima. 2025. "Redox Metabolism During Aerial Exposure of the Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter: An Ecophysiological Perspective" Animals 15, no. 9: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091251
APA StylePereira, T. M., Minari, M., Carvajalino-Fernández, J. M., Moreira, D. C., & Hermes-Lima, M. (2025). Redox Metabolism During Aerial Exposure of the Sea Urchin Echinometra lucunter: An Ecophysiological Perspective. Animals, 15(9), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091251







