Simple Summary
In this study, the localization of the EHMT2/G9A gene in Sertoli cells was examined, the higher-level structures of the two splice variants of EHMT2 were predicted, two lentiviral vectors to infect Sertoli cells were constructed, proliferation and activity were evaluated, and the differential expression of sperm-related genes was measured.
Abstract
The epigenetic regulation of gene expression through the covalent modification of histones is crucial for developing germline cells. To study the regulatory role of alternative splicing (AS) of euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase 2 (EHMT2/G9A) in spermatogenesis in Mongolian horses, this study first examines the localization of the EHMT2 gene in testicular support cells and then predicts the higher-order structures of sequences with and without AS. Two types of lentiviral vectors for overexpression were subsequently constructed for the EHMT2 gene, one with AS and one without, to infect support cells. The proliferation and activity of infected cells were measured using CCK8, and the differential expression of spermatogenesis-related genes in the two types of support cells was analyzed via qRT–PCR. We analyzed the expression of EHMT2 by immunofluorescence staining. EHMT2 was expressed in the nuclei of Sertoli cells. The expression of spermatogenesis-related genes was measured in the two types of cells. The results reveal that the expression levels of the FSH, Stra8, CCNB2, CDC27, NRG1, PPP2R5C, CCNB2, and YWHAZ genes in the AS group were greater than those in the control group. These results indicate that AS events in EHMT2 affect gene expression and thus affect spermatogenesis.
1. Introduction
The Mongolian horse is a unique breed; it is one of the oldest breeds of domestic horse, serving as a significant genomic resource [1], with strong adaptability and resistance to harsh climates and challenging feeding conditions [2]. Currently, Mongolian horses are predominantly found in regions of northeastern and northern China, particularly Inner Mongolia and Mongolia, and certain eastern Russian areas. There has been extensive research on the athletic ability [3], genetic evolution [4], and gut microbiota [5] of Mongolian horses, as well as on male fertility [6] and female reproductive capabilities [7] in this breed.
Male fertility is crucial for the survival of the Mongolian horse species. Spermatogenesis is not only one of the most critical biological processes for male fertility, but also a definitive determinant of reproductive success, holding significant implications in the livestock industry. Spermatogenesis is a highly complex and coordinated process. The process is divided into the spermatogonia proliferation phase, spermatocyte meiotic phase, and spermiogenesis phase [8]. Sertoli cells are somatic cells of the testis and are essential for testicular formation and spermatogenesis. Sertoli cells promote the progression of germ cells to sperm by coming in contact with and controlling the environment within the seminiferous tubules [9]. Additionally, Sertoli cells play an essential role in testis development and normal spermatogenesis by providing support and nutrients.
Alternative splicing (AS) is critical for the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. Studies have shown that approximately 70% of human genes may undergo AS, and up to half of these alter the reading frame of the transcript [10]. AS notably expands the function and form of the genome of organisms with limited gene numbers and is especially important in highly complex tissues and organisms [11,12]. AS constitutes a crucial posttranscriptional regulatory mechanism for gene expression, enabling the generation of multiple mature messenger RNAs (mRNAs) from a single precursor mRNA through the process of selective splicing [13,14].
AS plays a key role in sperm production in male mammals. The progression of spermatogenesis along specific developmental trajectories depends on the coordinated regulation of AS at the post-transcriptional level. It ensures the normal production of sperm by regulating the expression of genes related to spermatogenesis, testicular development, or the development of germ cells. Given the consisting of diverse cell types and biological processes, spermatogenesis is an excellent model for studying gene regulation at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels [15]. For example, ESRP1, a specific RNA-binding protein found in epithelial cells, has been implicated in mouse oogenesis and female fertility through its role in regulating mRNA AS [16], and, as a key alternative splicing regulator, Ptbp2 plays an important role in male fertility and male germ cell survival by regulating the AS of germ cell mRNAs in the testis [17]. Studies have shown that AS of hormone receptor genes affects male infertility. Recently, research has demonstrated that the RNA helicase DDX5 plays crucial post-transcriptional roles in sustaining and facilitating the function of spermatogonia by regulating the splicing of functional genes within these cells [18].
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression by covalent modification of histones is critical for germline cell development. In mammals, histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9)-specific histone methyltransferases (HMTases), such as G9a/EHMT2, SETDB1, and SUV39H, play important roles [19]. It has been reported that male and female germline cells of G9a/EHMT2 mutant mice cannot undergo meiosis, indicating an essential role of G9a/EHMT2 during reproduction [20]. Importantly, in previous transcriptome sequencing studies, the EHMT2 gene in Mongolian horses was shown to undergo exon skipping events, and the expression level in the testicular tissue of mature Mongolian horses was significantly greater than that in immature testicular tissue [21]. This phenomenon suggests that AS of the EHMT2 gene may be related to spermatogenesis in Mongolian horses. However, the fundamental mechanism of as in spermatogenesis remains to be investigated. In this study, we explored the regulatory effect of AS events in the EHMT2 gene on spermatogenesis in Mongolian horses. These findings lay a theoretical foundation for the study of the role of AS in spermatogenesis and provide new ideas for genetic breeding improvements.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Testis Collection and Cell Culture
All animal work was performed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (NO.NND2022047). Testicular tissue samples were obtained from Mongolian horses sourced from the Equus Research Center at Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. The testicular Sertoli cells of Mongolian horses were provided by a laboratory [22,23,24].
2.2. Immunofluorescence
Sertoli cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Solarbio, Beijing, China) for 30 min at room temperature and then permeabilized in 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 30 min. After blocking at 37 °C for 1 h with 5% bovine serum albumin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), the Sertoli cells were incubated with G9a/EHMT2 Rabbit mAb (C6H3, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at 4 °C overnight. Then, the corresponding secondary antibody, Rabbit lgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody Donkey anti-Mouse Alexa FluorTM 488 (R37118, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), was added. The mixture was incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The cell nuclei were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) for 30 min.
2.3. Analysis of the Predicted Protein Sequence
The ExPASy translation module (https://web.expasy.org/translate/, accessed on 29 May 2024) was used to translate the non-AS and AS nucleotide sequences of EHMT2 to amino acid sequences. Protein secondary structures were predicted using SOPMA (https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html, accessed on 31 May 2024), and three-dimensional model prediction was conducted via the Swiss-Meier program on the basis of known homologous structures.
2.4. Construction of the Lentiviral Vector
The Mongolian horse EHMT2 gene sequence was obtained by sequencing. The lentiviral overexpression vectors with AS events and no AS of the EHMT2 gene, named EX24 and EX24-1, respectively, were synthesized by GENEWIZ, Inc., Suzhou, China.
2.5. Cell Transfection
Sertoli cells were cultured in a culture dish, and transfection was initiated when the cells reached 50–60% confluence. An appropriate amount of lentivirus and culture medium was added. The culture dish was placed in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C. After 24 h, the transfection efficiency was measured.
2.6. Cell Proliferation Detected Using the CCK8 Assay
Sertoli cells were seeded in 96-well plates. Three replicates were established for each lentivirus at each time point in an incubator for 24 h (37 °C, 5% CO2). An appropriate amount of lentivirus and culture medium was added. Ninety microliters of fresh culture medium and CCK-8 solution (Meilun Bio, Dalian, China) were added at 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h post infection. After 2 h, the absorbance at 450 nm was measured via a microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for three consecutive days. The data were analyzed and graphed using Excel software and GraphPad Prism 9 software.
2.7. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT–PCR Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from Sertoli cells by using TRIzol reagent (Takara, Kyoto, Japan) following the manufacturer’s procedure. cDNA synthesis was completed via the use of PrimeScriptTM RT Master Mix (Takara, Kyoto, Japan). Using Primer (5.0) software, primers were designed based on reference sequences from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 3 June 2024) and subsequently synthesized by Sangon Biotech iotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was selected as the internal reference gene for RT–PCR, RT–PCR was performed with TB Green TM Premix Ex TaqTM II (Tli RNaseH Plus) (Takara, Kyoto, Japan). Differences in gene expression levels between groups were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method. All experiments were performed with a minimum of three independent replicates, with the data presented as the means ± standard deviations. Intergroup differences were statistically evaluated using GraphPad Prism 9.0 software, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. The sequences of primers used are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
3. Results
3.1. EHMT2 Expression in Sertoli Cells
To precisely detect the localization and expression of EHMT2 in Sertoli cells, we examined EHMT2 expression in the testis by immunostaining with a G9A/EHMT2 rabbit mAb (C6H3). EHMT2 was found to be expressed in the nucleus of Sertoli cells (Figure 1A).
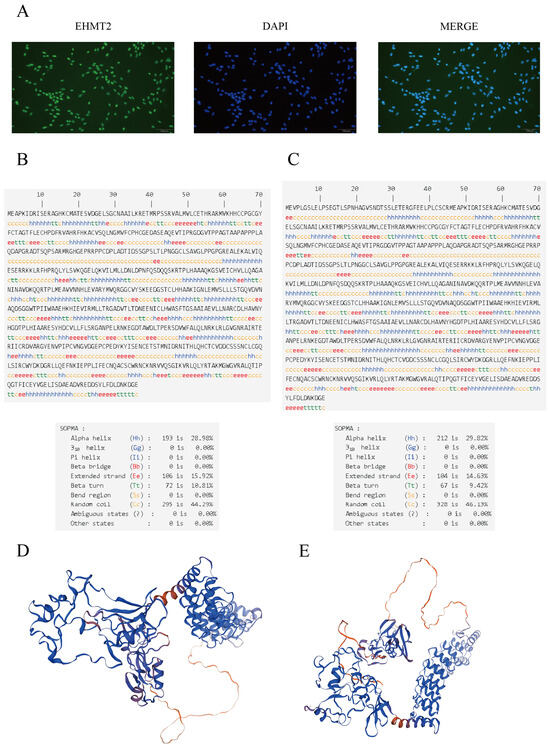
Figure 1.
Subcellular localization of EHMT2 and high-resolution structural predictions of alternative splicing events and no alternative splicing. The localization of EHMT2 in Sertoli cells was determined by immunofluorescence (A). Secondary structure of the protein encoded by the EHMT2 gene with and without AS ((B) and (C), respectively). Three-dimensional models for the proteins obtained with and without AS of the EHMT2 gene ((D) and (E), respectively).
3.2. Predicted Secondary Structure of the EHMT2 Protein
The predicted secondary structure of the protein encoded by the EHMT2 gene with AS included 28.98% alpha helix (Hh), 10.81% beta turn (Tt), 15.92% extended strand (Ee), and 44.29% random coil (Cc) structures, and that without AS included 29.82% alpha helix (Hh), 9.42% beta turn (Tt), 14.63% extended strand (Ee), and 46.13% random coil (Cc) structures (Figure 1B,C). Three-dimensional models of the proteins encoded by the EHMT2 gene with and without AS were constructed (Figure 1D,E).
3.3. Lentiviral Vector Construction
Maps of the two lentiviral vectors for overexpression are presented (Figure 2A,C). The EX24 and EX24-1 vectors encoded red and green fluorescent proteins and were 8790 bp and 8685 bp in length, respectively. The lengths of the predicted gene fragments and target bands obtained were consistent, which confirmed that the vectors were successfully constructed (Figure 2B,D).
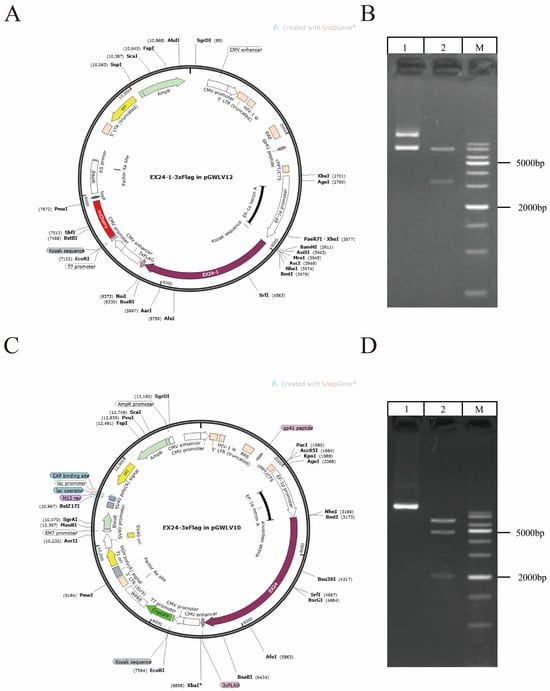
Figure 2.
Construction of the lentiviral vector. Map of the construction of the overexpression lentiviral vector EX24-1. (A) Map of the constructed EX24-overexpressing lentiviral vector (C). Electrophoretic map of the EX24-1-overexpressing lentiviral vector (B). Electrophoretic map of the EX24-overexpressing lentiviral vector (D).
3.4. Effects of the Two Lentiviruses on SERTOLI Cells
The Sertoli cells were infected with two lentiviral vectors at optimal doses, resulting in significant expression while maintaining the cells in their optimal state. Transfection was conducted for 24, 48, and 72 h, with the best transfection state observed at 72 h (Figure 3A,B). Photographs were taken to record the results. The infection efficiency was approximately 70%.
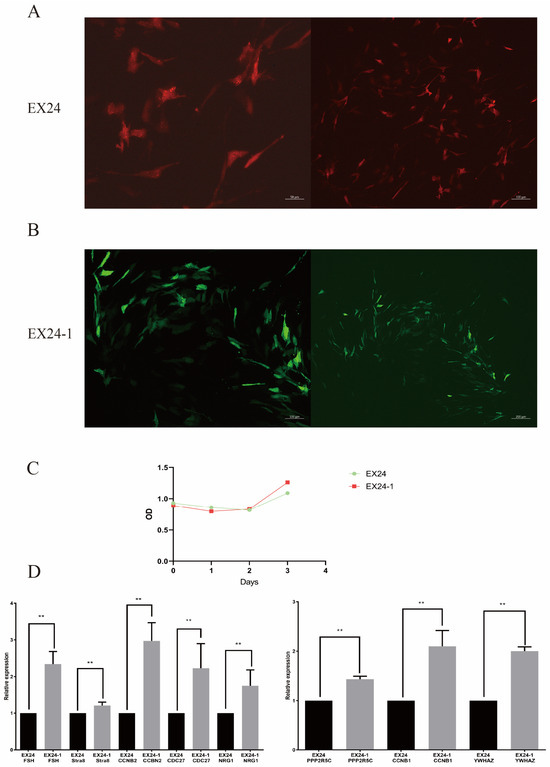
Figure 3.
Effects of the two lentiviruses on Sertoli cells. Fluorogram after lentiviral transduction of EX24-1 cells (A). Fluorogram after lentiviral transduction of EX24 cells (B). Cell proliferation of the two types of cells (C). RT–PCR was used to detect the expression of the spermatogenesis-related genes FSH, Stra8, CCNB2, CDC27, NRG1, PPP2R5C, CCNB2, and YWHAZ in the two types of cells (D). ** indicates p < 0.01.
3.5. Cell Proliferation Detected of Sertoli Cells by the CCK-8 Assay
The effect of AS of the EHMT2 gene on the proliferation of Sertoli cells was determined via the CCK8 method. The OD values measured within 3 days were plotted as a growth curve (Figure 2C), with EX24-1 exhibiting peaks on day 3.
3.6. qRT–PCR
The expression levels of spermatogenesis-related genes were measured in the two groups. The results revealed that the expression levels of the FSH, Stra8, CCNB2, CDC27, NRG1, PPP2R5C, CCNB2, and YWHAZ genes in the AS group were greater than those in the control group (Figure 3D). These results indicate that AS events in EHMT2 affect gene expression and thus affect spermatogenesis.
4. Discussion
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression by covalent modification of histones is important for germline cell development. In mammals, histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9)-specific histone methyltransferases (HMTases) play a critical role [19]. In addition, two kinds of proteins are encoded by EHMT2 genes in mammals: EHMT1 encodes GLP, and EHMT2 encodes G9a [25]. G9a plays critical roles in germline cell development in mammals. For example, it has been reported G9a knockout is embryonically lethal in mice [26]. Both male and female germline cells of G9a mutant mice cannot undergo meiosis [20], indicating an essential role of G9a during germ cell development. We found that EHMT2 was expressed in Sertoli cell nuclei, as shown by immunofluorescence. Therefore, Sertoli cells can be used to verify the function of the EHMT2 gene.
Sertoli cells, which envelop spermatogenic cells at distinct developmental stages, serve as the sole somatic cells maintaining direct contact with germ cells throughout their maturation. Sertoli cells regulate spermatogenesis by secreting proliferation- and differentiation-associated trophic factors to provide physiological and metabolic support for germ cells, while simultaneously establishing the blood–testis barrier (BTB) [27,28]. Studies demonstrate that Sertoli cells regulate androgen-binding protein (Androgen-Binding Protein, ABP) metabolism via highly active autophagic activity, thereby establishing a high-concentration androgen milieu essential for germ cell development and critically influencing spermatogenesis [29]. The number of Sertoli cells in the adult testis determines the population of germ cells supportable during spermatogenesis, modulates the progression of spermatogenesis, and ultimately governs daily sperm output [30,31].
According to the Human Genome Project (HGP), which released a draft of the human genome in 2001, the entire human genome is approximately 2.91 G bp, equivalent to more than 35,000 genes [32,33,34]. This is not what scientists had predicted [35,36]. The diversity of gene transcription plays a very important role in this phenomenon. The main mechanisms for increasing the diversity and quantity of gene transcripts and proteins include DNA recombination, RNA editing, and AS, with AS serving as the primary mechanism. AS is commonly observed in the testes of mammals and affects spermatogenesis by influencing genes related to sperm production. For example, the RNA binding protein 9 gene (RANBP9) regulates AS events in spermatogenic cells and is closely related to spermatogenesis [37]. Transcriptomic analysis of mouse spermatogenesis has revealed over 13,000 AS events, indicating that AS is a key driver of cell differentiation events during spermatogenesis [38].
In this study, we explored the regulatory effect of AS of the EHMT2 gene on spermatogenesis in Mongolian horses. These findings lay a theoretical foundation for the study of AS in spermatogenesis and provide new ideas for genetic breeding improvements. Many studies have shown that AS plays an important role in regulating the expression and function of related genes in germ cells. Spermatogenesis plays a very important role in the life process of male animals and is a prerequisite for the stable transmission of genetic information from parents to the next generation. The secondary structures of the proteins encoded by the EHMT2 gene with and without AS exhibit marked structural divergences, suggesting potential variations in the encoded protein isoforms. Further investigation is warranted to elucidate the functional implications of these structural differences.
In this study, we selected key genes involved in spermatogenesis and examined their differential expression in two types of cells. The results reveal that the expression levels of the target genes were significantly greater in the cells with AS. These findings indicate that AS of the PPP2R5C gene indeed upregulates the expression of meiosis-related genes, thereby affecting spermatogenesis. PPP2R5C is a subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and mutation if this gene can affect cell proliferation and accelerate apoptosis. Downregulation of PPP2R5C can cause cell cycle arrest, thereby promoting apoptosis [39]. The CCNB1 and CCNB2 genes are expressed at various stages of spermatogonial mitosis. When CCNB1 and CCNB2 are knocked out in the testes of experimental male mice, spermatogonia cannot proliferate normally, and apoptosis increases, resulting in male mouse infertility [40,41]. Male FSH-R knockout (FORKO) mice present fewer Sertoli cells and many that are structurally abnormal, and, as a consequence, fewer germ cells. Lower levels of serum testosterone (T) and androgen binding protein (ABP) also occur in these mice, along with reduced fertility. Successful spermatogenesis occurs through precise regulation of gene expression. Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 (Stra8) is a key molecule involved in meiosis initiation and plays an important role in spermatogenesis [42]. The major function of Stra8 in spermatogonial differentiation is also involved in meiotic initiation, the establishment and maintenance of SSCs, cell proliferation, self-renewal, undifferentiation, and other physiological processes [43]. The YWHA-binding proteins in sperm can be classified as those involved in fertilization, acrosome reactions, energy metabolism, protein folding, and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. A subset of these putative YWHA-binding proteins contains known amino acid consensus motifs, not only for YWHA binding, but also for PPP1C binding [44].
5. Conclusions
To study the regulatory role of AS events in the EHMT2 gene in spermatogenesis in Mongolian horses, this study first examined the localization of the EHMT2 gene in testicular support cells and then predicted the higher-order structures of sequences with and without AS. Two types of overexpressed lentiviral vectors were constructed for the EHMT2 gene, one with AS and one without AS, to infect support cells. The proliferation and activity of the infected cells were detected using CCK8, and the differential expression of spermatogenesis-related genes in the two types of support cells was analyzed via qRT–PCR. This study fills the knowledge gap regarding alternative splicing mechanisms in Mongolian horse spermatogenesis. The findings of this study could provide a theoretical foundation for advancing Mongolian horse breeding programs, thereby enabling a more comprehensive and in-depth investigation into the regulatory mechanisms of alternative splicing events in spermatogenesis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15081106/s1, Table S1. RT-qPCR primers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L., M.D. and TB.; investigation, T.B. and D.S.; formal analysis, T.B. and Y.W.; validation, T.B. and G.W.; software, T.B.; writing—original draft preparation, T.B. and G.W.; writing—review and editing, L.J.; visualization, T.B. and R.G.; supervision, T.B.; resources, B.L. and M.D.; project administration, B.L. and M.D.; funding acquisition, B.L. and M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Program for Improving the Scientific Research Ability of 286 Youth Teachers of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (BR230152), Inner Mongolia Education Department Special Research Project for First Class Disciplines (YLXKZX-NND-045) and Key Research Projects for Directly Affiliated Institutions of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (BR221018, BR251007).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All the sampling procedures were approved by the Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University and were conducted in accordance with the prescribed standards. All procedures involving animals were approved and authorized by the Key Laboratory of Equine Genetics, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. All the experiments and methods were carried out according to the guidelines and regulations of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Librado, P.; Khan, N.; Fages, A.; Kusliy, M.A.; Suchan, T.; Tonasso-Calvière, L.; Schiavinato, S.; Alioglu, D.; Fromentier, A.; Perdereau, A.; et al. The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes. Nature 2021, 598, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Du, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, N.; Dugarjaviin, M. Single-Cell Transcriptome Sequencing Reveals Molecular Expression Differences and Marker Genes in Testes during the Sexual Maturation of Mongolian Horses. Anim. Open Access J. 2024, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou, T.; Ding, W.; Liu, H.; Gong, W.; Jia, Z.; Dugarjaviin, M.; Bai, D. A genome-wide landscape of mRNAs, miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs of skeletal muscles during dietary restriction in Mongolian horses. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 46, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Randhawa, I.A.S.; MacHugh, D.E.; McGivney, B.A.; Katz, L.M.; Dugarjaviin, M.; Hill, E.W. Selection signatures for local and regional adaptation in Chinese Mongolian horse breeds reveal candidate genes for hoof health. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Du, M.; Wu, J.; Bai, D.; Li, B.; Bou, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Characterization and comparison of the bacterial microbiota in different gastrointestinal tract compartments of Mongolian horses. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, 1085–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, D.; Li, D.; Zhou, Z.; Manglai, D. Analysis of the miRNA transcriptome during testicular development and spermatogenesis of the Mongolian horse. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2020, 32, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Shen, Y.; Xing, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Bou, G.; Bai, D.; et al. Proteome and metabolomic profile of Mongolian horse follicular fluid during follicle development. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatley, J.M.; Brinster, R.L. Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal in mammals. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 24, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, M.D. The central role of Sertoli cells in spermatogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 9, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Castle, J.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Kan, Z.; Loerch, P.M.; Armour, C.D.; Santos, R.; Schadt, E.E.; Stoughton, R.; Shoemaker, D.D. Genome-wide survey of human alternative pre-mRNA splicing with exon junction microarrays. Science 2003, 302, 2141–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Irimia, M.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, H.Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Lee, L.J.; Slobodeniuc, V.; Kutter, C.; Watt, S.; Colak, R.; et al. The evolutionary landscape of alternative splicing in vertebrate species. Science 2012, 338, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen, T.W.; Graveley, B.R. Expansion of the eukaryotic proteome by alternative splicing. Nature 2010, 463, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, D.L. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 291–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, H.; Lev-Maor, G.; Ast, G. Alternative splicing and evolution: Diversification, exon definition and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.; Cai, T.; Lin, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Han, C. Integrative proteomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal multiple post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of mouse spermatogenesis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2013, 12, 1144–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Guan, X.; Qin, D.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X. Loss of ESRP1 blocks mouse oocyte development and leads to female infertility. Development 2021, 148, dev196931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagore, L.L.; Grabinski, S.E.; Sweet, T.J.; Hannigan, M.M.; Sramkoski, R.M.; Li, Q.; Licatalosi, D.D. RNA Binding Protein Ptbp2 Is Essential for Male Germ Cell Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 4030–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, J.M.D.; Chan, A.L.; La, H.M.; Rossello, F.J.; Änkö, M.L.; Fuller-Pace, F.V.; Hobbs, R.M. DDX5 plays essential transcriptional and post-transcriptional roles in the maintenance and function of spermatogonia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushijima, Y.; Inoue, Y.H.; Konishi, T.; Kitazawa, D.; Yoshida, H.; Shimaji, K.; Kimura, H.; Yamaguchi, M. Roles of histone H3K9 methyltransferases during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, M.; Nozaki, M.; Takeda, N.; Shinkai, Y. Functional dynamics of H3K9 methylation during meiotic prophase progression. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3346–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, D.; Du, M.; Song, L.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Manglai, D. Transcriptome profiling of developing testes and spermatogenesis in the Mongolian horse. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, D.; Ren, X.; Te, R.; Mang, L.; Li, B. Isolation, Culture and Identification of Testis Sertoli Cells in Mongolian Horses in vitro. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2020, 47, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ge, R.; Mang, L.; Du, M. Comparison of testicular tissue morphology and spermatogenic epithelial cells between Mongolian horses before and after sexual maturity. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2024, 1–5+116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Tseweendolmaa, U.; Davshilt, T.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Du, M.; Ren, H.; Mang, L.; Gerelchimeg, B. Research Progress on Function, Isolation, Purification and Identification of Sertoli Cells. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 48, 2947–2956. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, J.M.; Kochinke, K.; Oortveld, M.A.; Marks, H.; Kramer, D.; de Jong, E.K.; Asztalos, Z.; Westwood, J.T.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Sokolowski, M.B.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of learning and memory by Drosophila EHMT/G9a. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1000569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Nozaki, M.; Ueda, J.; Ohta, T.; Ohki, M.; Fukuda, M.; Takeda, N.; Niida, H.; Kato, H.; et al. G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1779–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, R.J.; Baker, M.A. Causes and consequences of apoptosis in spermatozoa; contributions to infertility and impacts on development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, E.; Villalon, R.; Ribeiro, S.; Berger, T. Role for endogenous estrogen in prepubertal Sertoli cell maturation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 135, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzuk, M.M.; Lamb, D.J. The biology of infertility: Research advances and clinical challenges. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, R.M.; McKinnell, C.; Kivlin, C.; Fisher, J.S. Proliferation and functional maturation of Sertoli cells, and their relevance to disorders of testis function in adulthood. Reproduction 2003, 125, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebourcet, D.; Darbey, A.; Monteiro, A.; Soffientini, U.; Tsai, Y.T.; Handel, I.; Pitetti, J.L.; Nef, S.; Smith, L.B.; O’Shaughnessy, P.J. Sertoli Cell Number Defines and Predicts Germ and Leydig Cell Population Sizes in the Adult Mouse Testis. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2955–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, B.; Green, P. Analysis of expressed sequence tags indicates 35,000 human genes. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Holt, I.; Pertea, G.; Karamycheva, S.; Salzberg, S.L.; Quackenbush, J. Gene index analysis of the human genome estimates approximately 120,000 genes. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. Human Genome Project. And the gene number is…? Science 2000, 288, 1146–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bhetwal, B.P.; Zheng, H.; Yan, W. RAN-binding protein 9 is involved in alternative splicing and is critical for male germ cell development and male fertility. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, G.; Khil, P.P.; Kim, J.; Bellani, M.A.; Camerini-Otero, R.D. Integrated transcriptome analysis of mouse spermatogenesis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, E. Protein phosphatase 2A: The Trojan Horse of cellular signaling. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandeis, M.; Rosewell, I.; Carrington, M.; Crompton, T.; Jacobs, M.A.; Kirk, J.; Gannon, J.; Hunt, T. Cyclin B2-null mice develop normally and are fertile whereas cyclin B1-null mice die in utero. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4344–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.M.; Hu, B.; Sun, T.C.; Li, X.Y.; Batool, A.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, X.X.; Deng, S.L.; et al. Requirement for CCNB1 in mouse spermatogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Romer, K.A.; Anderson, E.L.; Baltus, A.E.; de Rooij, D.G.; Page, D.C. Periodic retinoic acid-STRA8 signaling intersects with periodic germ-cell competencies to regulate spermatogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2347–E2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.T.; Niu, C.M.; Xia, J.; Shen, X.Y.; Xia, M.M.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y. Stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 (Stra8) plays important roles in many stages of spermatogenesis. Asian J. Androl. 2018, 20, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Myers, K.; Kline, D.; Vijayaraghavan, S. Proteomic analysis of bovine sperm YWHA binding partners identify proteins involved in signaling and metabolism. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 79, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).