Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Galectin from Dirofilaria immitis Excretory/Secretory Antigens Activate Proangiogenic Pathway in In Vitro Vascular Endothelial Cell Model
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Endothelial Cell Stimulation, Citotoxity and Cell Viability
2.4. Angiogenic Factors Assays
2.5. Proliferation, Migration, and Endothelial Cell Tube Formation Assays
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
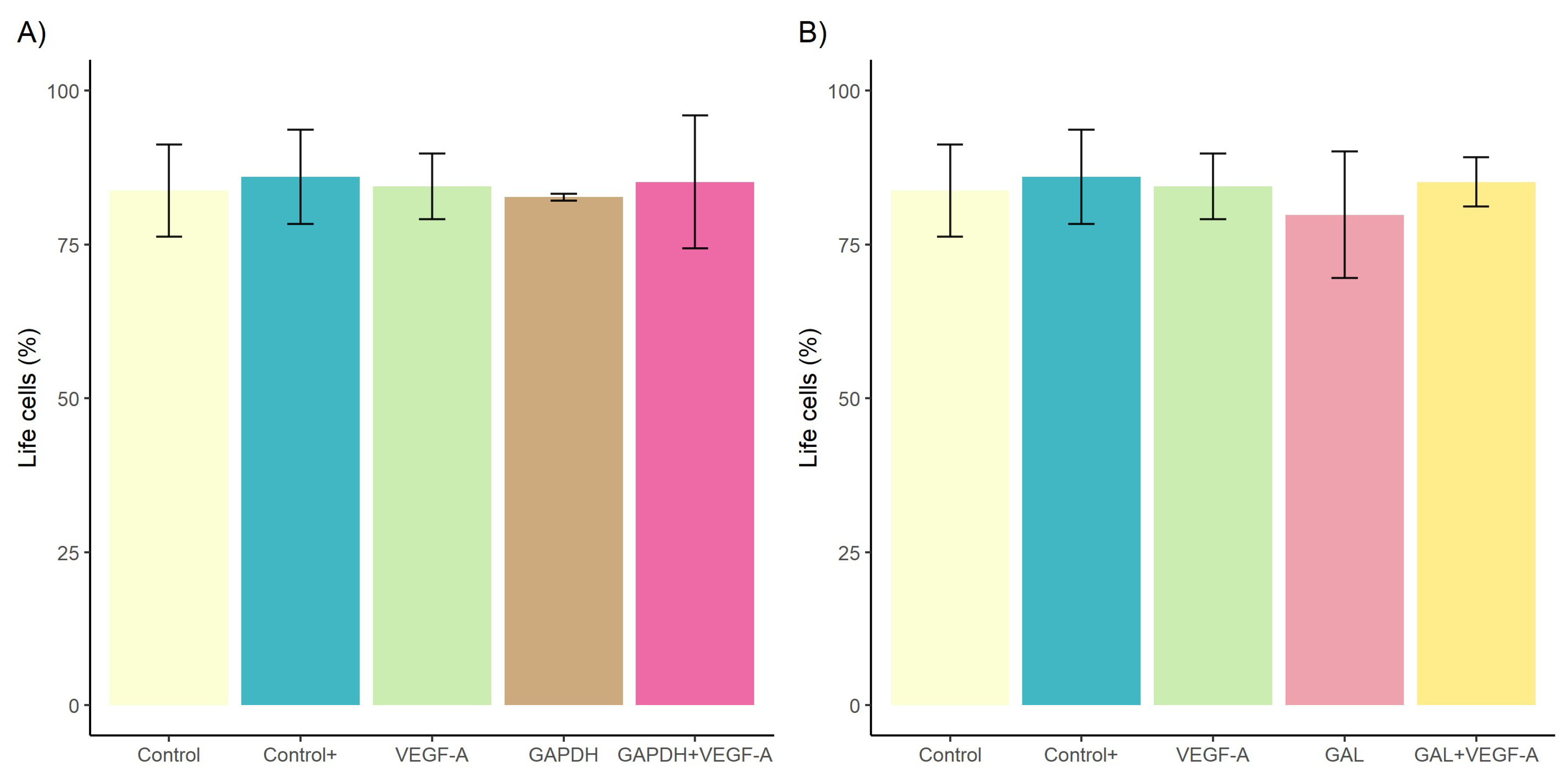
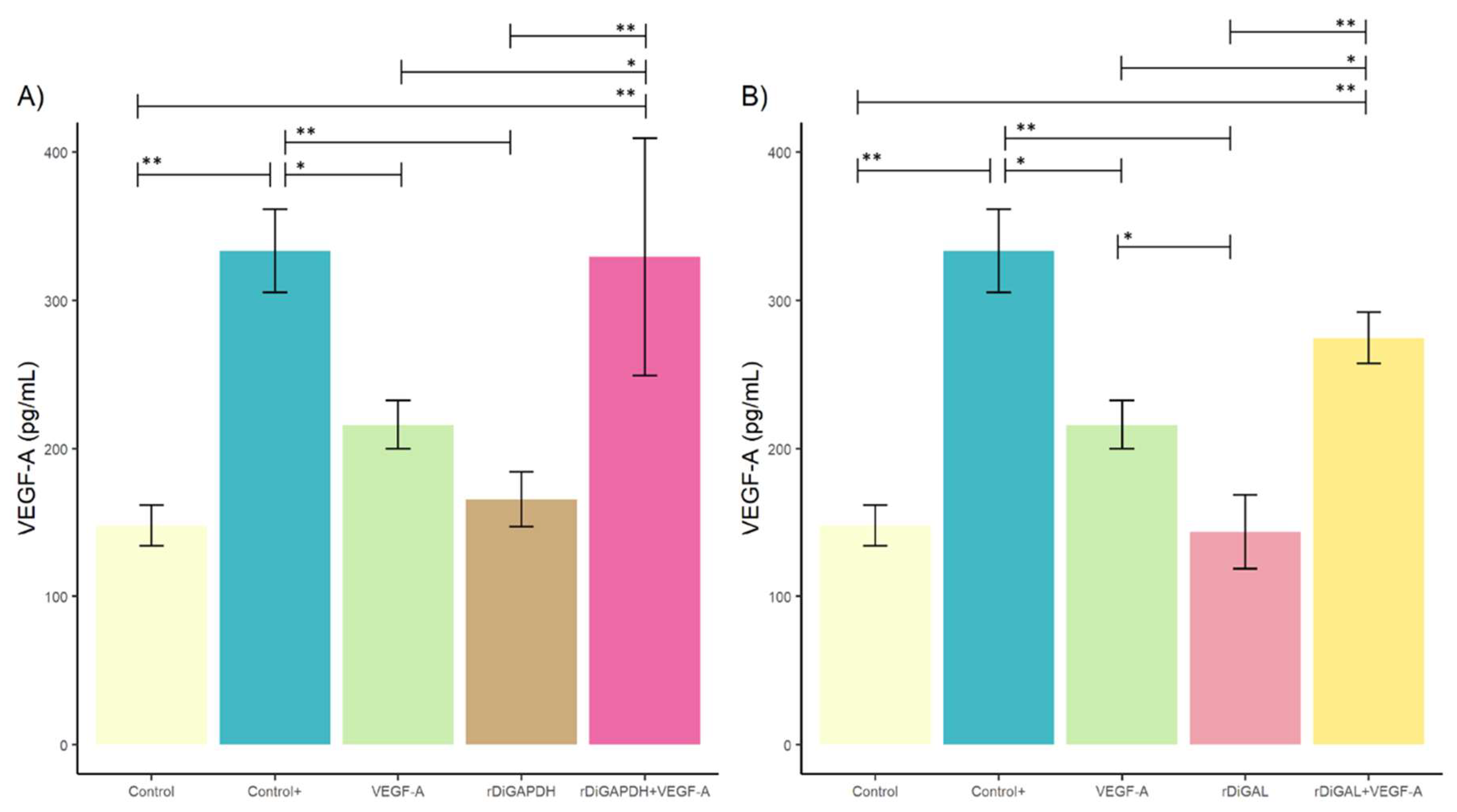
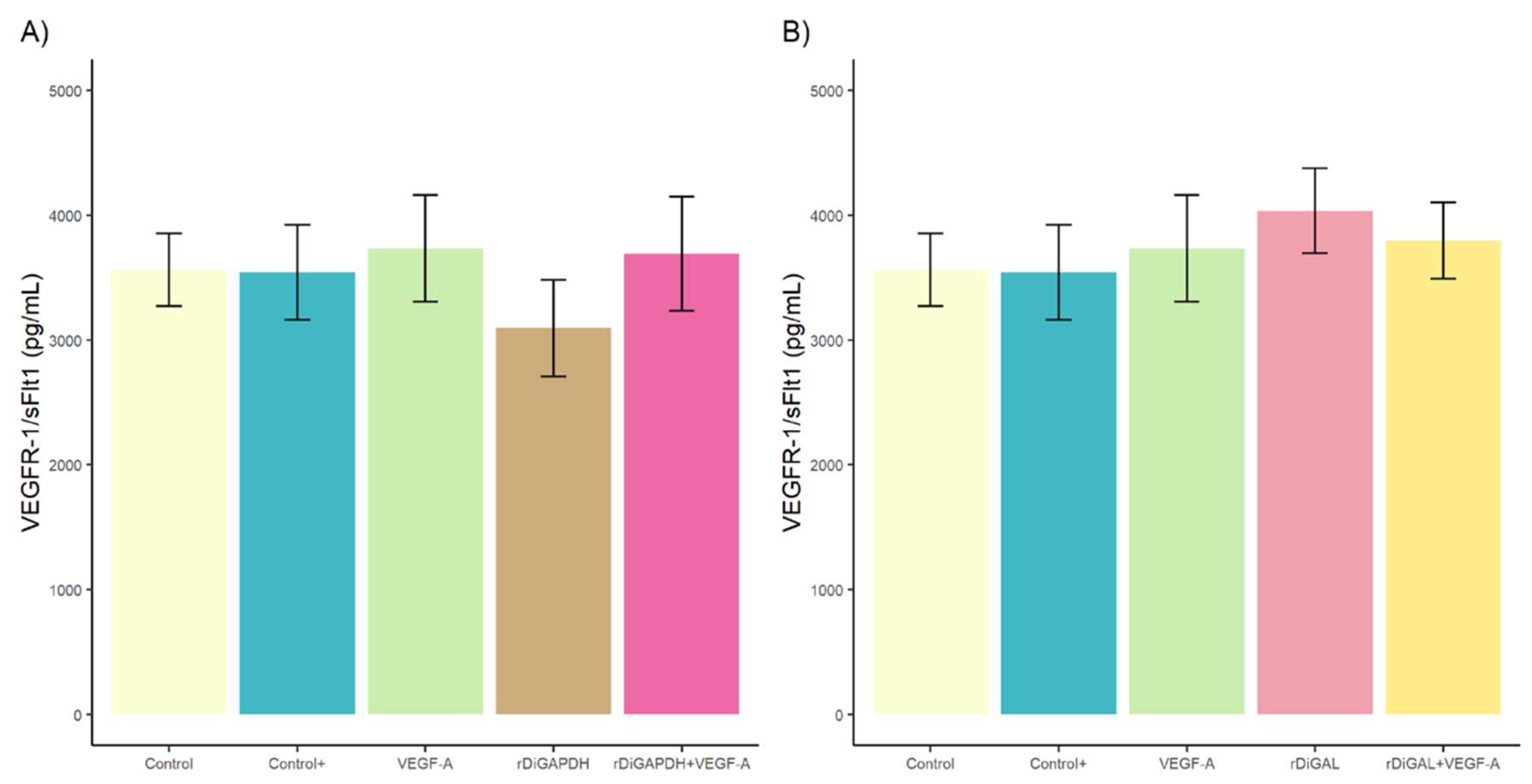
3.1. Effect of rDiGAPDH and rDiGAL on Cell Viability, Cytotoxicity, and Angiogenic Factors via VEGF-A
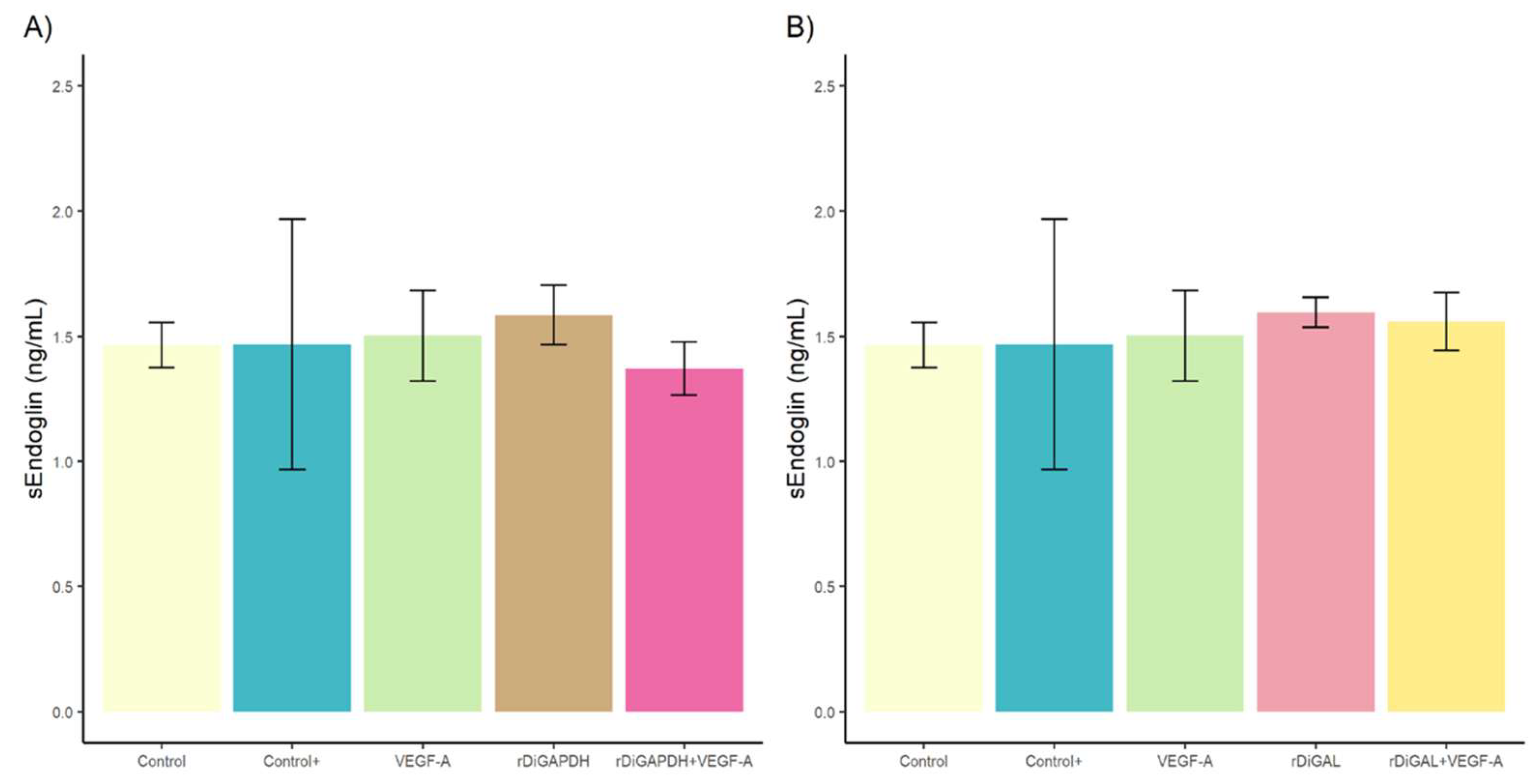
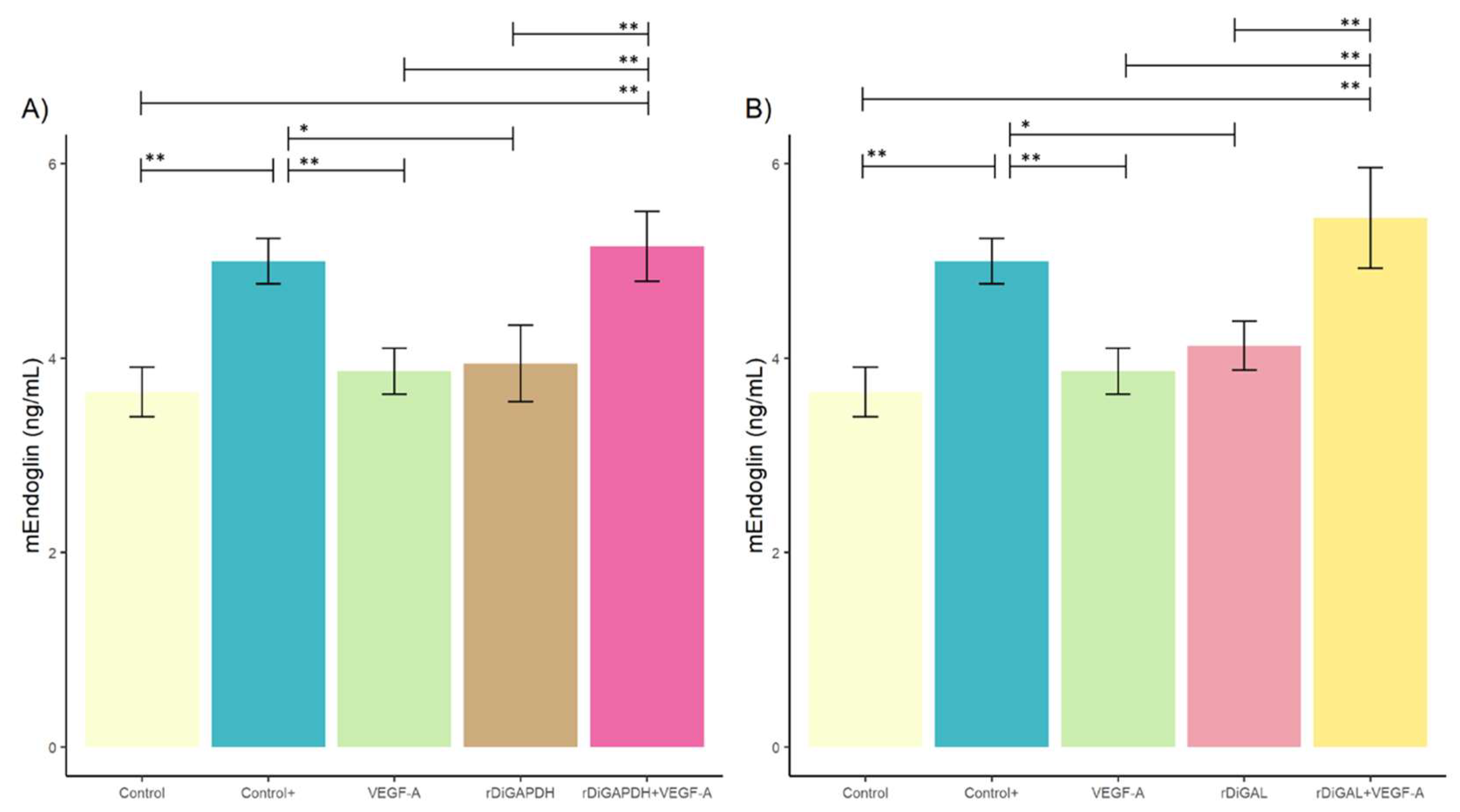
3.2. Effect of rDiGAPDH and rDiGAL on Endoglin Production
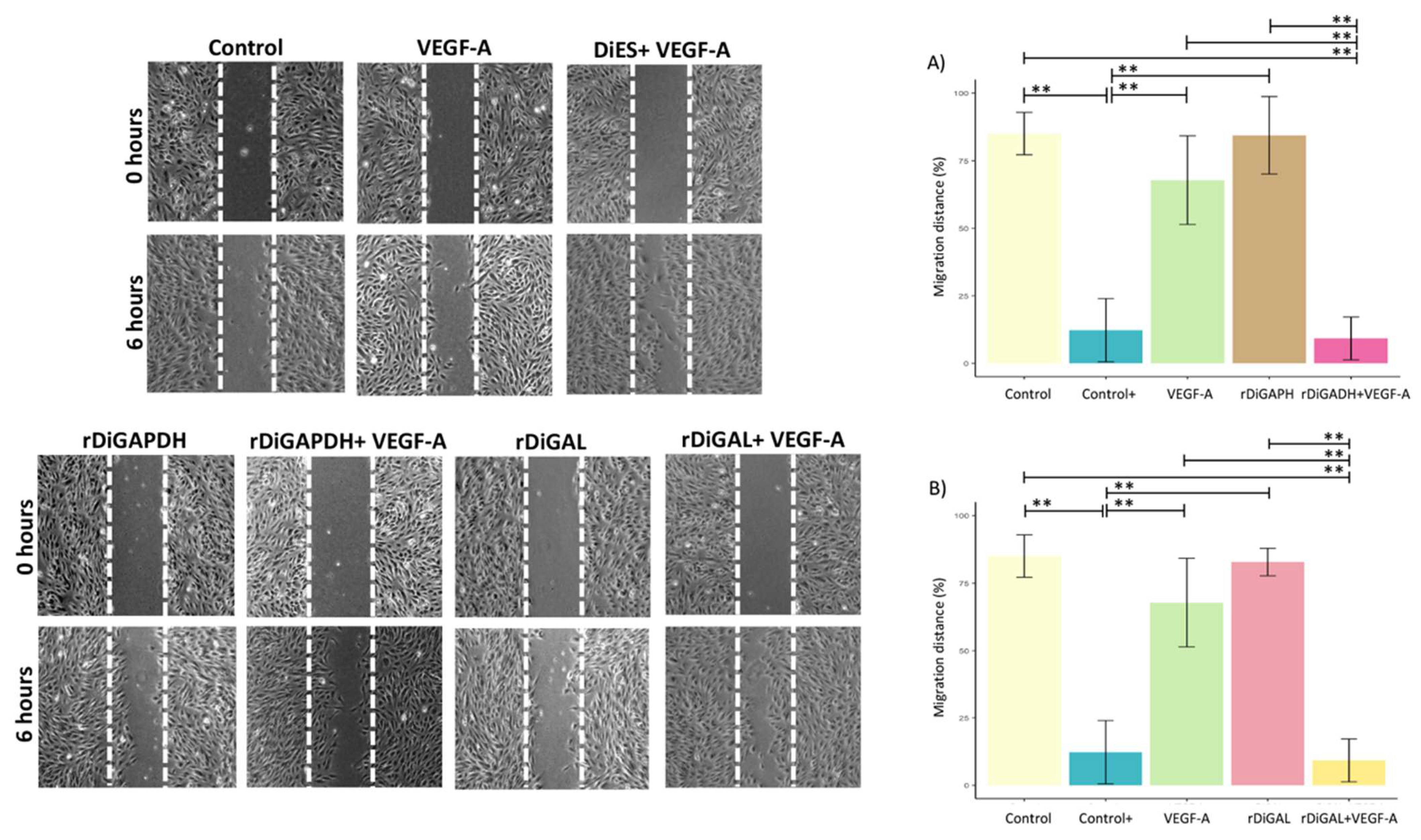
3.3. Effect of Antigens on Cell Proliferation and Migration
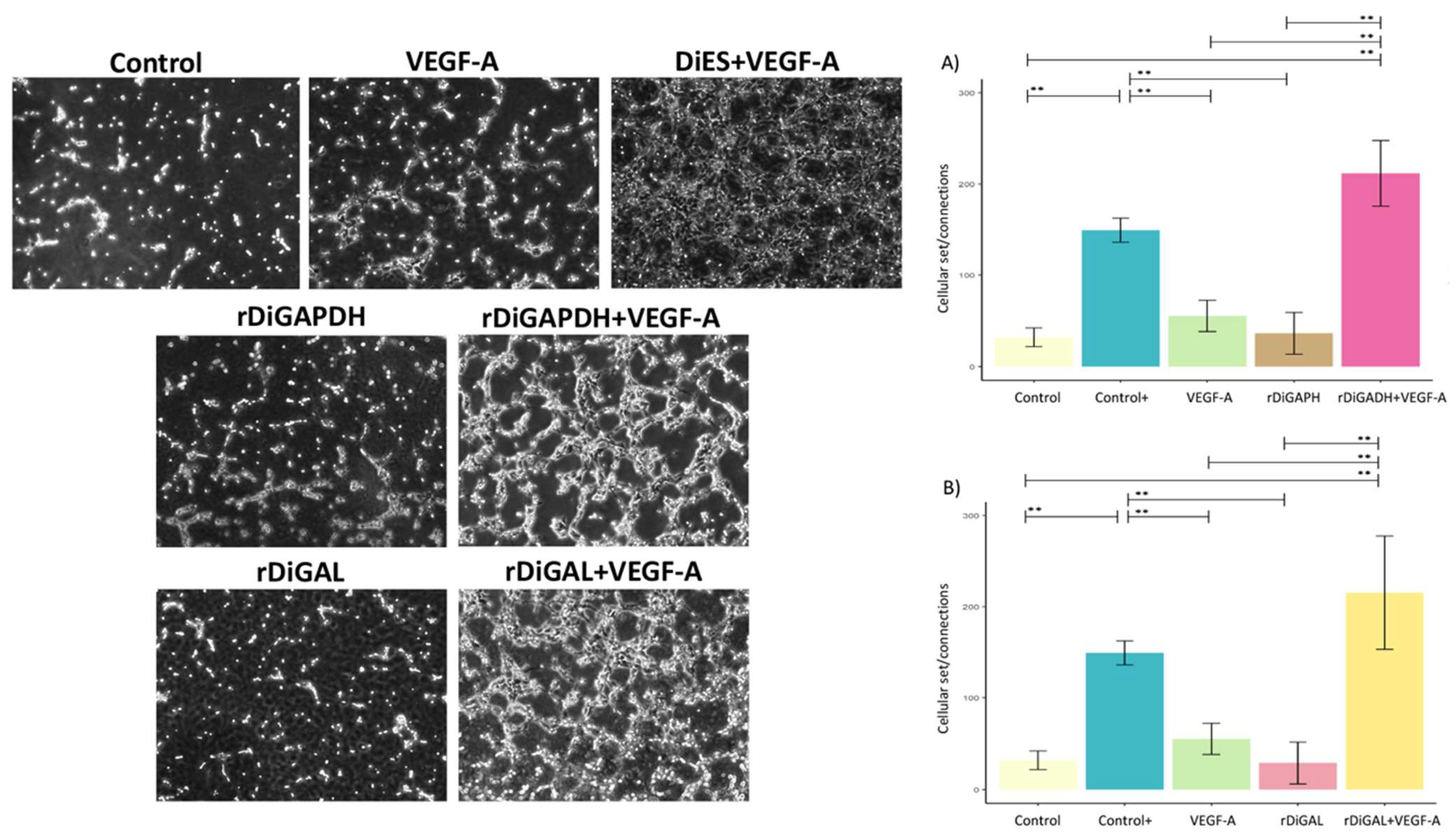
3.4. Effect of Antigens on Pseudocapillary Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richarz, N.A.; Boada, A.; Carrascosa, J.M. Angiogenesis in dermatology—Insights of molecular mechanisms and latest developments. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2017, 108, 515–523. [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo, K.; Carmeliet, P. Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell. 2022, 1, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Gómez, E.; Pericacho, M.; Ollauri-Ibáñez, C.; Bernabéu, C.; López-Novoa, J.M. The role of endoglin in post-ischemic revascularization. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ollauri-Ibáñez, C.; López-Novoa, J.M.; Pericacho, M. Endoglin-based biological therapy in the treatment of angiogenesis-dependent pathologies. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Nam, S.K.; Hoon Jun, Y. S-endoglin expression is induced in hyperoxia and contributes to altered pulmonary angiogenesis in bronchopulmonary dysplasia development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3043. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, A.P.; Levy, N.S.; Loscalzo, J.; Calderone, A.; Takahashi, N.; Yeo, K.T.; Koren, G.; Colucci, W.S.; Goldberg, M.A. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 1995, 76, 758–766. [Google Scholar]
- Shamloo, A.; Heilshorn, S.C. Matrix density mediates polarization and lumen formation of endothelial sprouts in VEGF gradients. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar]
- Peach, C.J.; Mignone, V.W.; Arruda, M.A.; Alcobia, D.C.; Hill, S.J.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Woolard, J. Molecular pharmacology of VEGF-A isoforms: Binding and signalling at VEGFR2. Intern. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1264. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, S.; Leppänen, V.M.; Alitalo, K. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in development and disease. Development 2018, 145, dev151019. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: Physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases. J. Biochem. 2013, 153, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Novoa, J.M.; Bernabeu, C. The physiological role of endoglin in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H959–H974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lebrin, F.; Maring, J.A.; van den Driesche, S.; van der Brink, S.; van Dinther, M.; Thorikay, M.; Martin, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Hawinkels, L.J.; et al. ENDOGLIN is dispensable for vasculogenesis, but required for vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoonderwoerd, M.J.A.; Goumans, M.T.H.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C. Endoglin: Beyond the endothelium. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Bernabeu, C. Novel vascular roles of human endoglin in pathophysiology. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Torres, J.; Espino-y-Sosa, S.; Martínez-Portilla, R.; Borboa-Olivares, H.; Estrada-Gutiérrez, G.; Acevedo-Gallegos, S.; Ruiz-Ramírez, E.; Velasco-Espin, M.; Cerda-Flores, P.; Ramírez-González, A.; et al. A Narrative review on the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado-Hernández, I. Heartworm disease (Dirofilaria immitis) and their vectors in Europe—New distribution trends. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 196. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, J.W.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Guerrero, J.; Venco, L. Heartworm disease in animals and humans. Adv. Parasitol. 2008, 66, 193–285. [Google Scholar]
- Venco, L.; Genchi, C.; Simón, F. La filariosis cardiopulmonar (Dirofilaria immitis) en el perro. In La Filariosis en las Especies Domésticas y en el Hombre; Merial Laboratorios Ed.: Barcelona, Spain, 2011; pp. 19–60. [Google Scholar]
- Basile, A.; Napoli, E.; Brianti, E.; Venco, L. Right Pulmonary Artery Distensibility Index in Heartworm Infected Dogs: Are the Different Methods Leading to Same Results? Animals 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.; Atkins, C.E. Understanding feline heartworm infection: Disease, diagnosis, and treatment. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2010, 25, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Selkirk, M.E.; Smith, V.P.; Thomas, G.R.; Gounaris, K. Resistance of filarial nematode parasites to oxidative stress. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1315–1332. [Google Scholar]
- European Society of Dirofilariosis and Angiostrongylosis. Available online: https://www.esda.vet/index.php/guidelines (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- American Heartworm Society. Available online: https://www.heartwormsociety.org/veterinary-resources/american-heartworm-society-guidelines (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Paes-de-Almeida, E.C.; Ferreira, A.M.; Labarthe, N.V.; Caldas, M.L.; McCall, J.W. Kidney ultrastructural lesions in dogs experimentally infected with Dirofilaria immitis (Leidy, 1856). Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 113, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Grandi, G.; González-Miguel, J.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Simón, F.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H. Anti-Wolbachia Surface Protein antibodies are present in the urine of dogs naturally infected with Dirofilaria immitis with circulating microfilariae but not in dogs with occult infections. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, L.; Spickard, R.C.; Sparks, H.V., Jr.; Williams, J.F. Dirofilaria immitis: Alteration of endothelium-dependent relaxation in the in vivo canine femoral artery. Exp. Parasitol. 1989, 69, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mupanomunda, M.; Williams, J.F.; Mackenzie, C.D.; Kaiser, L. Dirofilaria immitis: Heartworm infection alters pulmonary artery endothelial cell behavior. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.I.; Atwell, R.B. Immunohistological observations on pulmonary tissues from dogs infected with Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Res. Commun. 1993, 17, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Simón, F.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Morchón, R.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Human and animal dirofilariasis: The emergence of a zoonotic mosaic. Clin. Microiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 507–544. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, A.B.; Wesselowski, S.; Cusack, K. Transesophageal echocardiography-guided Dirofilaria immitis extraction from the right atrium in a dog. CASE 2020, 4, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bennuru, S.; Semnani, R.; Meng, Z.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Nutman, T.B. Brugia malayi excreted/secreted proteins at the host/parasite interface: Stage- and gender-specific proteomic profiling. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.; Geary, T.G. Stage- and gender-specific proteomic analysis of Brugia malayi excretory-secretory products. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e326. [Google Scholar]
- Morchón, R.; González-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Velasco, S.; Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; Simón, F. Adult Dirofilaria immitis excretory/secretory antigens upregulate the production of prostaglandin E2 and downregulate monocyte transmigration in an “in vitro” model of vascular endothelial cell cultures. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 170, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- González-Miguel, J.; Morchón, R.; Mellado, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Simón, F. Excretory/secretory antigens from Dirofilaria immitis adult worms interact with the host fibrinolytic system involving the vascular endothelium. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 181, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Miguel, J.; Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Simón, F. Surface associated antigens of Dirofilaria immitis adult worms activate the host fibrinolytic system. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Miguel, J.; Morchón, R.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Simón, F. Fibrinolysis and proliferative endarteritis: Two related processes in chronic infections? The model of the blood-borne pathogen Dirofilaria immitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124445. [Google Scholar]
- González-Miguel, J.; Larrazabal, C.; Loa-Mesón, D.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Simón, F.; Morchón, R. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and galectin from Dirofilaria immitis participate in heartworm disease endarteritis via plasminogen/plasmin system. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 223, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machado, C.D.C.; Alarcón-Torrecillas, C.; Pericacho, M.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Morchón, R. Involvement of the excretory/secretory and surface-associated antigens of Dirofilaria immitis adult worms in the angiogenic response in an in-vitro endothelial cell model. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 318, 109939. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, M.D.P.; Alarcón-Torrecillas, C.; Pericacho, M.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Carretón, E.; Morchón, R. Effect of somatic antigens of Dirofilaria repens adult worms on angiogenesis, cell proliferation and migration and pseudo-capillary formation in human endothelial cells. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Eilken, H.M.; Diéguez-Hurtado, R.; Schmidt, I.; Nakayama, M.; Jeong, H.W.; Arf, H.; Adams, S.; Ferrara, N.; Adams, R.H. Pericytes regulate VEGF-induced endothelial sprouting through VEGFR1. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1574. [Google Scholar]
- Hershey, J.C.; Baskin, E.P.; Glass, J.D.; Hartman, H.A.; Gilberto, D.B.; Rogers, I.T.; Cook, J.J. Revascularization in the rabbit hindlimb: Dissociation between capillary sprouting and arteriogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 618–625. [Google Scholar]
- Zueva, T.; Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Ollauri-Ibáñez, C.; Pericacho, M.; Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; Simón, F. Angiogenesis in cardiopulmonary dirofilariosis: Does the Wolbachia surface protein have a pro- or anti-angiogenic effect? J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e162. [Google Scholar]
- Simón, F.; Morchón, R.; Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; López-Belmonte, J.; Grandi, G.; Genchi, C. Dirofilaria immitis and Wolbachia-derived antigens: Its effect on endothelial mammal cells. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado-Cuadrado, M.; Alarcón-Torrecillas, C.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Balmori-de la Puente, A.; Infante González-Mohino, E.; Pericacho, M.; Morchón, R. Wolbachia promotes an anti-angiogenic response using an in vitro model of vascular endothelial cells in relation to heartworm disease. Pathogens 2024, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysmołek, M.E.; Długosz, E.; Wiśniewski, M. The immunological role of vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells in filarial infections. Animals 2022, 12, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennuru, S.; Maldarelli, G.; Kumaraswami, V.; Klion, A.D.; Nutman, T.B. Elevated levels of plasma angiogenic factors are associated with human lymphatic filarial infections. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 884–890. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, R.D.; Schubert, U.; Bauer, C. Angiogenesis and parasitic helminth-associated neovascularization. Parasitology 2011, 138, 426–439. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan, P.B.; Akabas, L.; Tariq, S.; Huda, N.; Bennuru, S.; Sabzevari, H.; Hofmeister, R.; Nutman, T.B.; Tolouei Semnani, R. Similarities and differences between helminth parasites and cancer cell lines in shaping human monocytes: Insights into parallel mechanisms of immune evasion. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, T.; Morchón, R.; Carretón, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A.; Santana, A.; Bargues, M.D.; Mas-Coma, S.; Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; Simón, F. Angiogenic response in an in vitro model of dog microvascular endothelial cells stimulated with antigenic extracts from Dirofilaria immitis adult worms. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 315. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collado-Cuadrado, M.; Balmori-de la Puente, A.; Rodríguez-Escolar, I.; Infante González-Mohino, E.; Alarcón-Torrecillas, C.; Pericacho, M.; Morchón, R. Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Galectin from Dirofilaria immitis Excretory/Secretory Antigens Activate Proangiogenic Pathway in In Vitro Vascular Endothelial Cell Model. Animals 2025, 15, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070964
Collado-Cuadrado M, Balmori-de la Puente A, Rodríguez-Escolar I, Infante González-Mohino E, Alarcón-Torrecillas C, Pericacho M, Morchón R. Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Galectin from Dirofilaria immitis Excretory/Secretory Antigens Activate Proangiogenic Pathway in In Vitro Vascular Endothelial Cell Model. Animals. 2025; 15(7):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070964
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollado-Cuadrado, Manuel, Alfonso Balmori-de la Puente, Iván Rodríguez-Escolar, Elena Infante González-Mohino, Claudia Alarcón-Torrecillas, Miguel Pericacho, and Rodrigo Morchón. 2025. "Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Galectin from Dirofilaria immitis Excretory/Secretory Antigens Activate Proangiogenic Pathway in In Vitro Vascular Endothelial Cell Model" Animals 15, no. 7: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070964
APA StyleCollado-Cuadrado, M., Balmori-de la Puente, A., Rodríguez-Escolar, I., Infante González-Mohino, E., Alarcón-Torrecillas, C., Pericacho, M., & Morchón, R. (2025). Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Galectin from Dirofilaria immitis Excretory/Secretory Antigens Activate Proangiogenic Pathway in In Vitro Vascular Endothelial Cell Model. Animals, 15(7), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070964






