Supplementation with Lentinan Improves the Colostrum Quality of Holstein Dairy Cows and the Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Newborn Calves
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Ethics
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Colostrum Composition Parameters
2.5. Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Colostrum Yield and Composition
3.2. Colostrum Immunoglobulin Concentration and Production
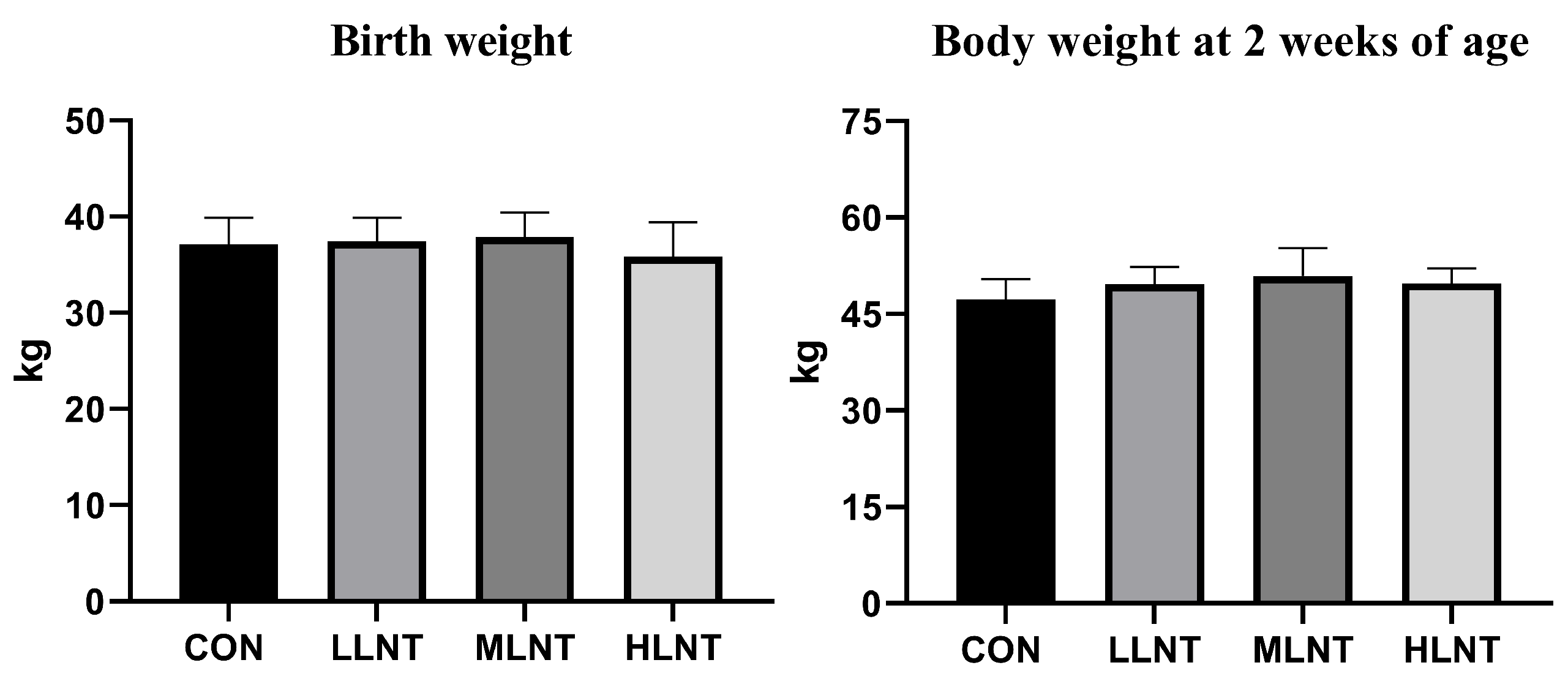
3.3. Weight of Calf
3.4. Serum Oxidative Stress Parameters in Calves
3.5. Serum Inflammatory Factors and Immune Globulin Parameters in Calves
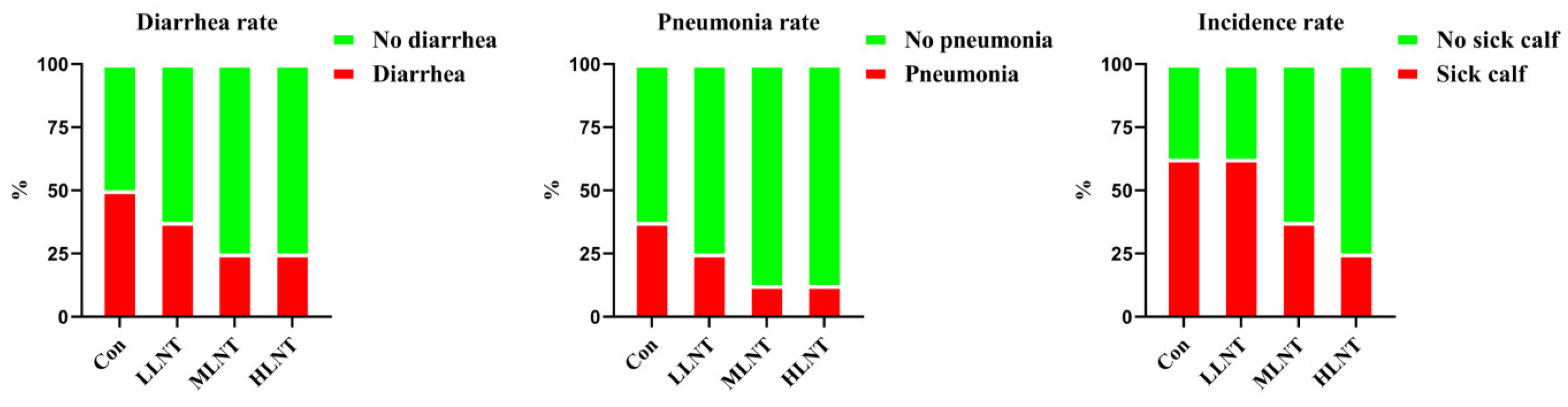
3.6. Incidence of Newborn Calves
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peter, A.T. Bovine placenta: A review on morphology, components, and defects from terminology and clinical perspectives. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer-Tlustos, A.J.; Lopez, A.; Hare, K.S.; Wood, K.M.; Steele, M.A. Effects of colostrum management on transfer of passive immunity and the potential role of colostral bioactive components on neonatal calf development and metabolism. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 101, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, J.D.; Cattell, M.B.; Quigley, J.D., 3rd; McCoy, G.C.; Hurley, W.L. Passive immunoglobin transfer in newborn calves fed colostrum or spray-dried serum protein alone or as a supplement to colostrum of varying quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2834–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, M.R.; Watson, D.L.; Lascelles, A.K. The mechanism of transfer of immunoglobulin into mammary secretion of cows. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 1971, 49, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdorf, H.T.; Kendall, S.J.; Ruh, K.E.; Caputo, M.J.; Combs, G.J.; Henisz, S.J.; Brown, W.E.; Bresolin, T.; Ferreira, R.E.P.; Dorea, J.R.R.; et al. Increasing the prepartum dose of rumen-protected choline: Effects on milk production and metabolism in high-producing Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 5988–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westland, A.; Martin, R.; White, R.; Martin, J.H. Mannan oligosaccharide prepartum supplementation: Effects on dairy cow colostrum quality and quantity. Animal 2017, 11, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragona, K.M.; Rice, E.M.; Engstrom, M.; Erickson, P.S. Supplementation of nicotinic acid to prepartum Holstein cows increases colostral immunoglobulin G, excretion of urinary purine derivatives, and feed efficiency in calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2287–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.H.; Wang, L.; Niu, X.D.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, Q.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Supplementation with beta-1,3-glucan improves productivity, immunity and antioxidative status in transition Holstein cows. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 134, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilu, R.; Yitong, D.; Xuejing, Z.; Keyong, T.; Jie, L. Extraction, purification, bioactivities and prospect of lentinan: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangyang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Xiaohua, W.; Lina, Z.; Peter, C.K.C. Advances in lentinan: Isolation, structure, chain conformation and bioactivities. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Cai, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Qiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; et al. Anti-Influenza Effect and Mechanisms of Lentinan in an ICR Mouse Model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 892864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, G.; Kuai, J.; Fan, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, Q.; et al. Lentinan inhibits tumor angiogenesis via interferon γ and in a T cell independent manner. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Jin, H.; Song, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, L.; Yu, R.; Wang, D.; Gao, Q.; Peng, S.; Sun, H.; et al. The effect of lentinan on dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources; Committee on Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle, 8th ed.; The National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Datsomor, O.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, Z.; Zhan, K.; Yang, T.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, G. Partial Substitution of Alfalfa Hay by Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) Hay Can Improve Lactation Performance, Rumen Fermentation, and Nitrogen Utilization of Dairy Cows. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 899148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, T.E.; Gay, C.C. The importance of colostrum to the health of the neonatal calf. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1994, 10, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrucker, C.R.; Gross, J.J.; Bruckmaier, R.M. The importance of colostrum in maternal care and its formation in mammalian species. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Zhuo, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, J. The Effects of Lentinan on the Hematological and Immune Indices of Dairy Cows. Animals 2024, 14, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Effect of Lentinan on Peyer’s patch structure and function in an immunosuppressed mouse model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Jeon, E.; Kim, J.C.; Kang, S.G.; Yoon, S.I.; Ko, H.J.; Kim, P.H.; Lee, G.S. Lentinan from shiitake selectively attenuates AIM2 and non-canonical inflammasome activation while inducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zou, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Anti-tumor effect of β-glucan from Lentinus edodes and the underlying mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opgenorth, J.; Sordillo, L.M.; VandeHaar, M.J. Colostrum supplementation with n-3 fatty acids and α-tocopherol alters plasma polyunsaturated fatty acid profile and decreases an indicator of oxidative stress in newborn calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Liu, G.; Duan, J.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Birth oxidative stress and the development of an antioxidant system in newborn piglets. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuervo, W.; Sordillo, L.M.; Abuelo, A. Oxidative Stress Compromises Lymphocyte Function in Neonatal Dairy Calves. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramah, A.; Kato, T.; Shinya, U.; Baakhtari, M.; Imatake, S.; Jadi, A.R.; Yasuda, M. Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves. Animals 2023, 13, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacometo, C.B.; Alharthi, A.S.; Zhou, Z.; Luchini, D.; Loor, J.J. Maternal supply of methionine during late pregnancy is associated with changes in immune function and abundance of microRNA and mRNA in Holstein calf polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8146–8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parraguez, V.H.; Sales, F.; Peralta, O.A.; De Los Reyes, M.; Campos, A.; González, J.; Peralta, W.; Cabezón, C.; González-Bulnes, A. Maternal Supplementation with Herbal Antioxidants during Pregnancy in Swine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachut, M.; Contreras, G.A. Symposium review: Mechanistic insights into adipose tissue inflammation and oxidative stress in periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 3670–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, J.; Jin, H. Mangiferin ameliorates gestational diabetes mellitus-induced placental oxidative stress, inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress and improves fetal outcomes in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 859, 172522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.C.; Reyes-Castro, L.A.; Rodríguez-González, G.L.; Bautista, C.J.; Vázquez-Martínez, M.; Larrea, F.; Chamorro-Cevallos, G.A.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Zambrano, E. Resveratrol partially prevents oxidative stress and metabolic dysfunction in pregnant rats fed a low protein diet and their offspring. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 1483–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Aldo, P.; Alvero, A.B. The unique immunological and microbial aspects of pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchieri-Ronchi, C.B.; Kim, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Correa, C.R.; Yeum, K.J.; Ferreira, A.L. Oxidative stress status of highly prolific sows during gestation and lactation. Animal 2011, 5, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.F.; Wu, D.; He, T.F.; Piao, X.S. Dietary supplementation with Forsythia suspensa extract during late gestation improves reproductive performance, colostrum composition, antioxidant status, immunoglobulin, and inflammatory cytokines in sows and newborn piglets. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 271, 114700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Sun, S.; Luo, Z.; Shi, B.; Shan, A.; Cheng, B. Maternal dietary resveratrol alleviates weaning-associated diarrhea and intestinal inflammation in pig offspring by changing intestinal gene expression and microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5626–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrill, K.M.; Conrad, E.; Lago, A.; Campbell, J.; Quigley, J.; Tyler, H. Nationwide evaluation of quality and composition of colostrum on dairy farms in the United States. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calloway, C.D.; Tyler, J.W.; Tessman, R.K.; Hostetler, D.; Holle, J. Comparison of refractometers and test endpoints in the measurement of serum protein concentration to assess passive transfer status in calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 1605–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infascelli, F.; Tudisco, R.; Mastellone, V.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Avallone, L. Diet aloe supplementation in pregnant buffalo cows improves colostrum immunoglobulin content. Rev. Vet. 2010, 21, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Furman-Fratczak, K.; Rzasa, A.; Stefaniak, T. The influence of colostral immunoglobulin concentration in heifer calves’ serum on their health and growth. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5536–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urie, N.J.; Lombard, J.E.; Shivley, C.B.; Adams, A.E.; Kopral, C.A.; Santin, M. Preweaned heifer management on US dairy operations: Part III. Factors associated with Cryptosporidium and Giardia in preweaned dairy heifer calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9199–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, I.; Gottardo, F.; Contiero, B.; Dall Ava, B.; Bonfanti, L.; Stefani, A.; Barberio, A. Association between passive immunity and health status of dairy calves under 30 days of age. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 152, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaura, R.; Dorbek-Kolin, E.; Loch, M.; Viidu, D.A.; Orro, T.; Mõtus, K. Association of clinical respiratory disease signs and lower respiratory tract bacterial pathogens with systemic inflammatory response in preweaning dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 5988–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, L.; Malmuthuge, N.; Guan, L.L.; Bu, D.P. Dynamics of oxidative stress and immune responses in neonatal calves during diarrhea. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad Riyadh, A.; Luma, W.K. Effect of Lentinan administration on some immunological and biochemical parameters in intact rabbits. Int. J. Health Sci. (IJHS) 2022, 6, 6362–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.D.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.M. The shiitake mushroom-derived immuno-stimulant lentinan protects against murine malaria blood-stage infection by evoking adaptive immune-responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Whole corn silage | 36 |
| DDGS 1 | 7 |
| Corn meal | 8 |
| Soybean meal | 11 |
| Flaked corn | 10 |
| Cottonseed | 4 |
| Oat hay | 22 |
| Prenatal Premix 2 | 2 |
| Total | 100 |
| Nutrient levels 3 | |
| CP | 12.66 |
| EE | 2.88 |
| NDF | 38.41 |
| ADF | 25.91 |
| Ash | 7.86 |
| Calcium | 0.52 |
| Phosphorus | 0.45 |
| NEL 4, Mcal/kg DM | 1.40 |
| Items | Treatment | SEM 1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | LLNT | MLNT | HLNT | |||
| Milk fat, % | 6.59 | 6.48 | 6.58 | 6.90 | 0.30 | 0.969 |
| Milk protein, % | 16.22 | 17.79 | 19.03 | 18.91 | 0.42 | 0.060 |
| Lactose, % | 3.05 | 3.07 | 3.17 | 3.12 | 0.10 | 0.979 |
| Total solids, % | 26.19 | 27.73 | 28.61 | 29.26 | 0.60 | 0.315 |
| Milk fat yield, kg | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.490 |
| Milk protein yield, kg | 1.41 b | 1.53 b | 2.22 a | 1.83 ab | 0.10 | 0.014 |
| Lactose yield, kg | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.074 |
| Milk yield, kg/d | 8.67 | 8.79 | 11.56 | 9.73 | 0.47 | 0.101 |
| 4% FMT, kg/d | 8.58 | 8.94 | 11.09 | 10.33 | 0.64 | 0.488 |
| Items | Treatment | SEM 1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | LLNT | MLNT | HLNT | |||
| IgA, g/L | 27.15 | 25.66 | 24.40 | 23.86 | 0.82 | 0.513 |
| IgG, g/L | 34.45 b | 37.46 ab | 43.59 a | 45.49 a | 2.58 | 0.037 |
| IgM, g/L | 10.93 | 10.37 | 9.69 | 9.82 | 0.62 | 0.902 |
| IgA yield, g | 234.83 | 227.80 | 281.68 | 235.73 | 14.82 | 0.576 |
| IgG yield, g | 290.63 c | 330.21 bc | 502.49 a | 434.85 ab | 24.23 | 0.003 |
| IgM yield, g | 93.67 | 90.94 | 111.61 | 96.04 | 7.76 | 0.801 |
| Items | Treatment | SEM 1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | LLNT | MLNT | HLNT | |||
| SOD, U/mL | 115.21 b | 124.53 ab | 135.26 a | 135.73 a | 2.69 | 0.012 |
| CAT, U/lmL | 33.89 b | 38.75 b | 63.47 a | 46.11 b | 3.31 | 0.004 |
| GSH-PX, U | 488.29 | 512.51 | 460.16 | 485.94 | 11.79 | 0.500 |
| TAOC, mM/L | 1.17 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 1.14 | 0.01 | 0.237 |
| MDA, umol/L | 20.00 a | 15.87 ab | 14.61 b | 13.96 b | 0.81 | 0.003 |
| Items | Treatment | SEM 1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | LLNT | MLNT | HLNT | |||
| TNF-α, ng/mL | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.04 | 0.138 |
| IL-1β, ng/mL | 3.82 a | 2.85 b | 2.46 b | 2.06 b | 0.19 | 0.003 |
| IL-6, ng/mL | 2.76 | 4.88 | 3.94 | 2.15 | 0.47 | 0.170 |
| Items | Treatment | SEM 1 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | LLNT | MLNT | HLNT | |||
| IgA, g/L | 1.09 | 1.08 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 0.02 | 0.737 |
| IgG, g/L | 15.51 b | 18.52 ab | 22.96 a | 21.16 a | 0.98 | 0.033 |
| IgM, g/L | 2.26 | 2.26 | 2.40 | 2.88 | 0.18 | 0.591 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lv, L.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, Z.; Fan, C.; Cheng, J. Supplementation with Lentinan Improves the Colostrum Quality of Holstein Dairy Cows and the Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Newborn Calves. Animals 2025, 15, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060835
Huang Y, Hu Y, Lv L, Wang D, Li X, Liu S, Zhuo Z, Fan C, Cheng J. Supplementation with Lentinan Improves the Colostrum Quality of Holstein Dairy Cows and the Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Newborn Calves. Animals. 2025; 15(6):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060835
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yinghao, Yapeng Hu, Longfei Lv, Dian Wang, Xiao Li, Sijia Liu, Zhao Zhuo, Caiyun Fan, and Jianbo Cheng. 2025. "Supplementation with Lentinan Improves the Colostrum Quality of Holstein Dairy Cows and the Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Newborn Calves" Animals 15, no. 6: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060835
APA StyleHuang, Y., Hu, Y., Lv, L., Wang, D., Li, X., Liu, S., Zhuo, Z., Fan, C., & Cheng, J. (2025). Supplementation with Lentinan Improves the Colostrum Quality of Holstein Dairy Cows and the Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity of Newborn Calves. Animals, 15(6), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060835





